1. Introduction
Exosomes are the smallest material in extracellular vehicles which have a diameter of 30 – 150 nm and are produced by cells and released into the extra-cellular environment. This type of material is found in all biofluids including blood, urine, saliva, synovial fluid, and cerebrospinal fluid[
1,
2]. Recent reports state that an exosome can contain 4563 proteins, 194 lipids, 1639 messenger ribonucleic acids (mRNAs), and 764 micro RNAs (miRNAs) [
3]. Due to their abundant presence, exosomes have recently been considered as promising biomarkers in the early diagnosis of diseases because exosomes released by cells directly reflect the pathological condition of the host cells[
2].
Due to the above-mentioned advantages, analysis and quantification of exosomes has become one of the widely explored topics for the purpose of early detection of diseases. Several methods have been developed for this purpose such as nanoparticle tracking analysis[
4], flow cytometry[
5], dynamic light scattering[
6], and western blot[
7]. However, because the process is time consuming and the operation requires skilled operators, mass sample testing is difficult to realize. Recently, the use of biosensors, especially nanolasmonic biosensors, has become a very reliable alternative method because it is easy, label-free and offers real-time detection. The label-free characteristic of biosensors can reduce the experimental complexity that comes from using labels. To date, various configurations have been explored in nano-plasmonic biosensors and some of them are based on SPR, LSPR, and extraordinary optical transmission (EOT).
Apart from configuration, another aspect that is widely researched in nanoplasmonic biosensors is transducer engineering to obtain more sensitive analytical devices. The two most popular approaches for this purpose are to increase the molecular loading capacity of the biosensor chip[
8] or to enhance the plasmonic effect[
9]. Increasing the molecular loading capacity is carried out by coating the sensor surface with materials that have a high surface area to volume ratio such as graphene and MoS
2[
10,
11]. Based on research conducted by Chiu et al in 2017, the presence of graphene oxide on the surface of the SPR chip can increase the sensitivity of the biosensor up to 16 times higher[
12].
This paper summarizes recent developments in nanoplasmonic biosensors and their utilization for exosome detection. The types of nanoplasmonic biosensors discussed will focus on the development of SPR and LSPR biosensors. The theoretical background and working principles of these two types of biosensors will be discussed in the next section. In addition to introducing the latest results and detection mechanisms that have been developed in exosome detection, we will also introduce several methods that can be used for exosome isolation.
2. Theoretical Background and Working Principles of Nanoplasmonic Biosensors
2.1. SPR Based Biosensor
Surface Plasmons are the collective oscillations of free electrons at the interface between a conductive material, such as a metal, and a dielectric or insulating material. Resonance in surface plasmon waves occurs when the frequency of the incident light matches the vibration frequency of the electrons. In this situation, there is a transfer of energy from the incident light to the surface plasmon wave and this causes the intensity of the reflected light which is measured by the photodetector to decrease until it finally becomes zero after reaching the optimum resonance condition[
13].
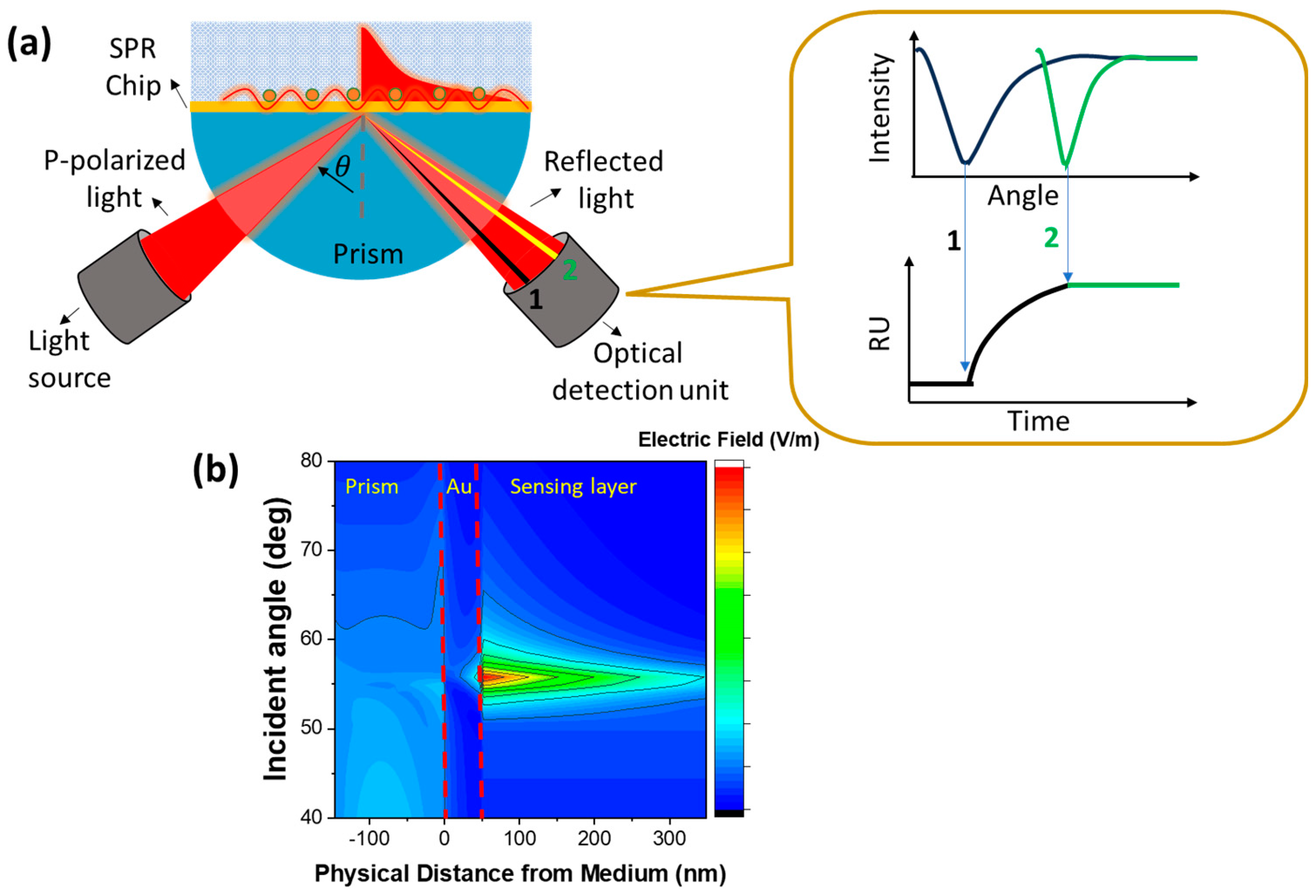
Figure 1a below shows one type of SPR biosensor based on prism coupling with an incident angle-based investigation mode. The binding and releasing phenomena on the sensing surface will cause a shift in the resonance angle and this shift is monitored in real time in the form of an SPR sensorgram. In resonance condition, the electric field produced is very high and this zone is a very sensitive area to changes in the refractive index[
14] as shown in the electric field contour in
Figure 1b. The resonance angle of the SPR chip which is composed of SF10 prism and Au film with a dielectric layer of water is at an incidence angle of ~56
0. There is a very significant difference regarding the electric field around the resonance angle and other incidence angles.
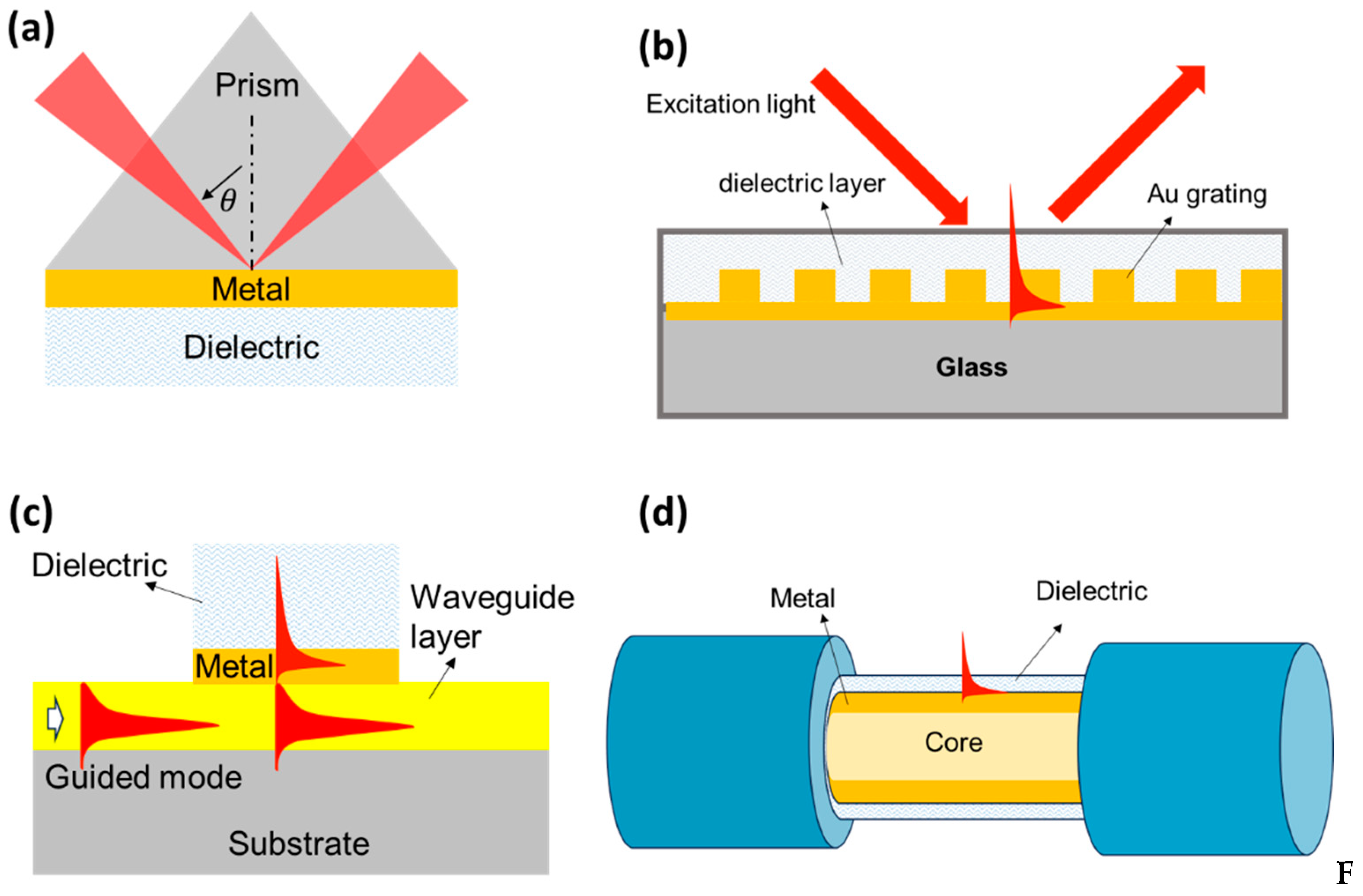
To obtain suitable conditions between the incident light frequency and the surface plasmon vibration frequency, a coupling medium is needed to implement the SPR biosensor. Coupling media that have been developed to date include using high refractive index prisms, gratings, waveguides, or optical fibers. The basic differences between these four types of biosensors are shown in
Figure 2. Of the several methods mentioned, prism coupling media with the Kretschmann configuration is an approach that has been widely explored. Light incident on one of the Au film interfaces passes through the high-index prism and facilitates total internal reflection at the prism-metal interface. In the resonance condition, most of the light is transferred to the metal-dielectric interface as surface waves causing a sharp decrease in the reflection spectrum. The resonance conditions to achieve SPR can be determined based on the following relationship[
14]:
where
,
, and
represent the dielectric constant of the prism, plasmonic material (metal), and dielectric layer (analyte medium), respectively, while
represents the resonance angle.
SPR biosensor development is still being carried out to obtain sensors with better performance. One of them is by utilizing nanomaterials to increase the sensitivity and resolution of biosensors. Chiu et al modified the SPR chip by utilizing the functional groups in graphene oxide. When compared with conventional SPR chips, the sensitivity of the biosensor can be increased up to 16 times[
11]. Another development direction of SPR biosensors is in miniaturization and integration. Miniaturization and integration are carried out by creating tools that are smaller, portable, and can be integrated with other devices to obtain more complete information during experiments. Chiu et al utilized electrochemical surface plasmon resonance (EC-SPR) signals to quantitatively detect real-time changes in the removal of oxygen functional groups in electrochemically-reduced graphene oxide (ERGO)[
15]. Miniaturization can also be done by integrating it with microfluidic technology. This integration offers the advantages of automation, small volumes, fast processing, and can also increase the sensing efficiency of the sensor[
16].
2.2. LSPR Based Biosensor
In the previous section we discussed types of biosensors that utilize the propagation of surface plasmon wave in their work. In this section we will discuss plasmonic phenomena in a nanometal structure with a size much smaller than the wavelength of the incident light. When light interacts with this type of nanometal, the collective oscillations of electrons will be localized around the nanoparticle. This occurs because the surface of the nanostructure is shorter than the propagating plasmon decay length, causing plasmon oscillations to tend to produce standing waves rather than propagating waves. The electromagnetic field brought by the incident light causes charge separation between the free electrons and the ionic metal nucleus. Furthermore, the repulsive force of coulomb repulsion between free electrons will act as a restoring force that causes collective oscillations of these electrons[
17].
Materials that can be used as transducers in LSPR biosensors must meet the Frohlich conditions, namely[
18]:
In this context, denotes the real part of the complex dielectric function of the nanoparticle while denotes the permittivity of the medium around the nanoparticle. From this equation it can be concluded that to implement an LSPR-based biosensor, we must use a material with negative and the imaginary part of the dielectric constant () is expected to be positive or perhaps ignored. For this reason, Au and Ag are the types of metals that are widely used in LSPR biosensor applications due to their small imaginary dielectric values.
The LSPR phenomenon is characterized by very strong absorption bands at certain frequencies[
19]. The LSPR signal can be tuned from the UV-Visible to the infrared region by controlling the size, shape, refractive index around the nanoparticle and its composition[
20].
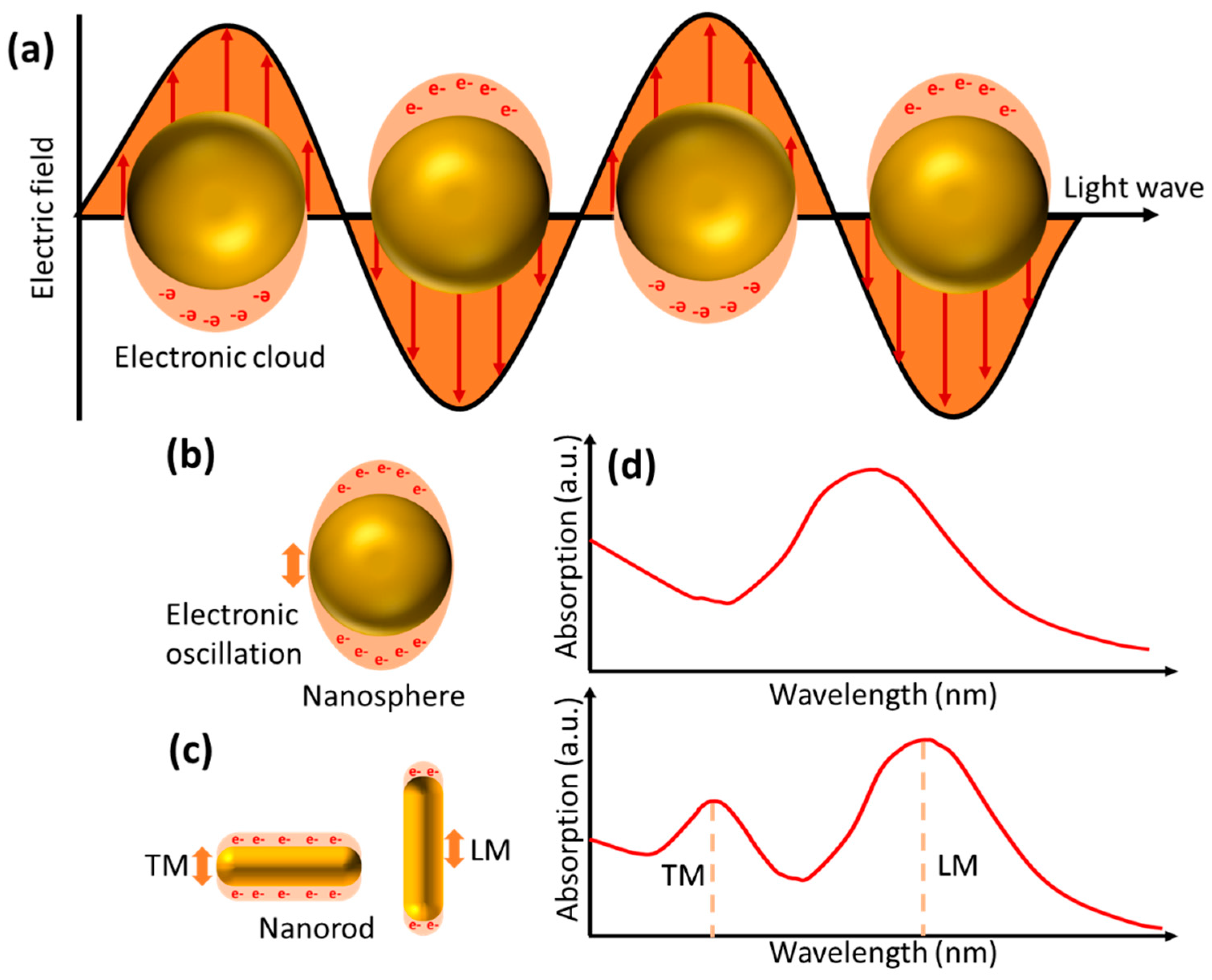
Figure 3 depicts oscillations in nanoparticles in the form of nanospheres and nanorods. Two different oscillation directions in the nanorod give rise to new absorption bands called transverse and longitudinal modes. When the analyte binds to the nanoparticle surface, it will cause a change in the refractive index on the nanoparticle surface, which further shifts the LSPR peak frequency. The LPSR peak shift is also influenced by the arrangement and shape of the nanoparticles. Materials with greater negative real dielectric constants will produce sensors that are more sensitive to changes in local refractive index[
21]. In addition, nanoparticles with asymmetric shapes are more sensitive than spherical shapes. Nurrohman and Chiu detected BSA with gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) with a diameter of 15 nm, the resulting detection limit was only 1 ng/mL[
17]. Prajna et al utilize nanomaterials with a more complex shape, namely Au nanostars, to detect difficult infections. In this research, the sensor detection limit can be reduced to 8.6 pM[
22].
3. Exosomes Isolation Methods
Exosomes have become a promising biomarker for early detection of cancer. However, the heterogeneity and complexity of biological fluids as well as the presence of nanoscale contaminants make the isolation of exosomes still a major challenge [
23]. There are at least five types of isolation techniques that have been developed, namely differential ultracentrifugation-based techniques, size-based techniques, immunoaffinity exosome capture-based precipitation, and microfluidics-based techniques[
24]. These techniques utilize the properties of exosomes in the isolation stage, such as density, shape, size, and proteins on the surface of exosomes. All of this will be explained in the following section.
The first method is called differential ultracentrifugation. The working principle of differential ultracentrifugation method utilizes differences in volume and physical properties of the material present in human tissue samples[
26].
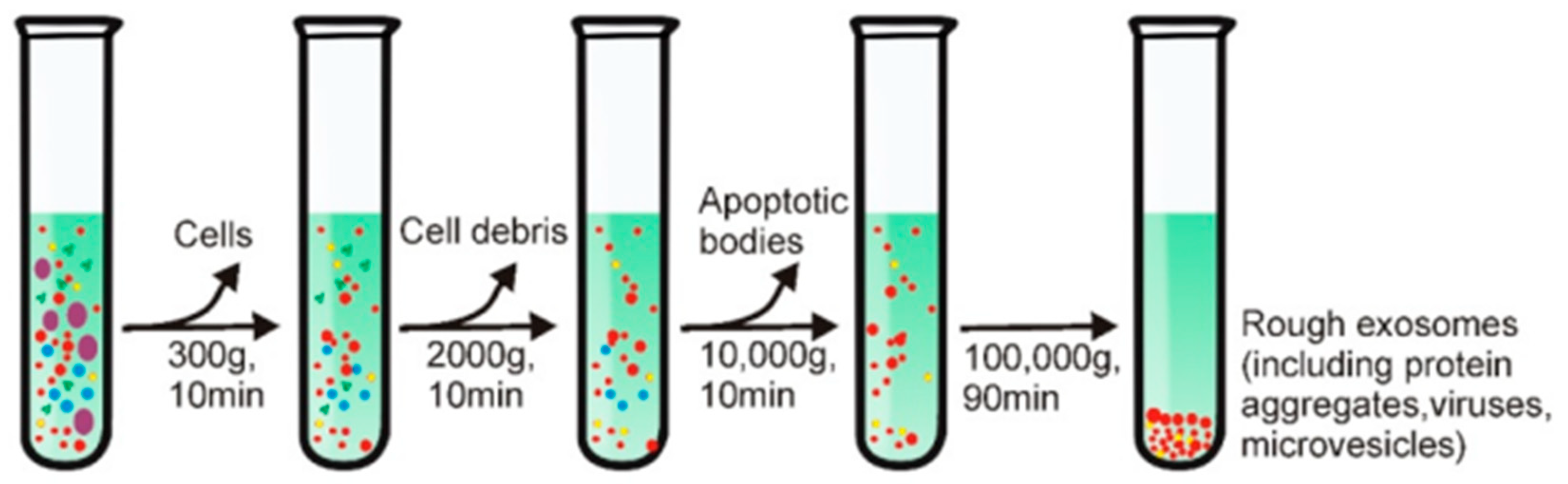
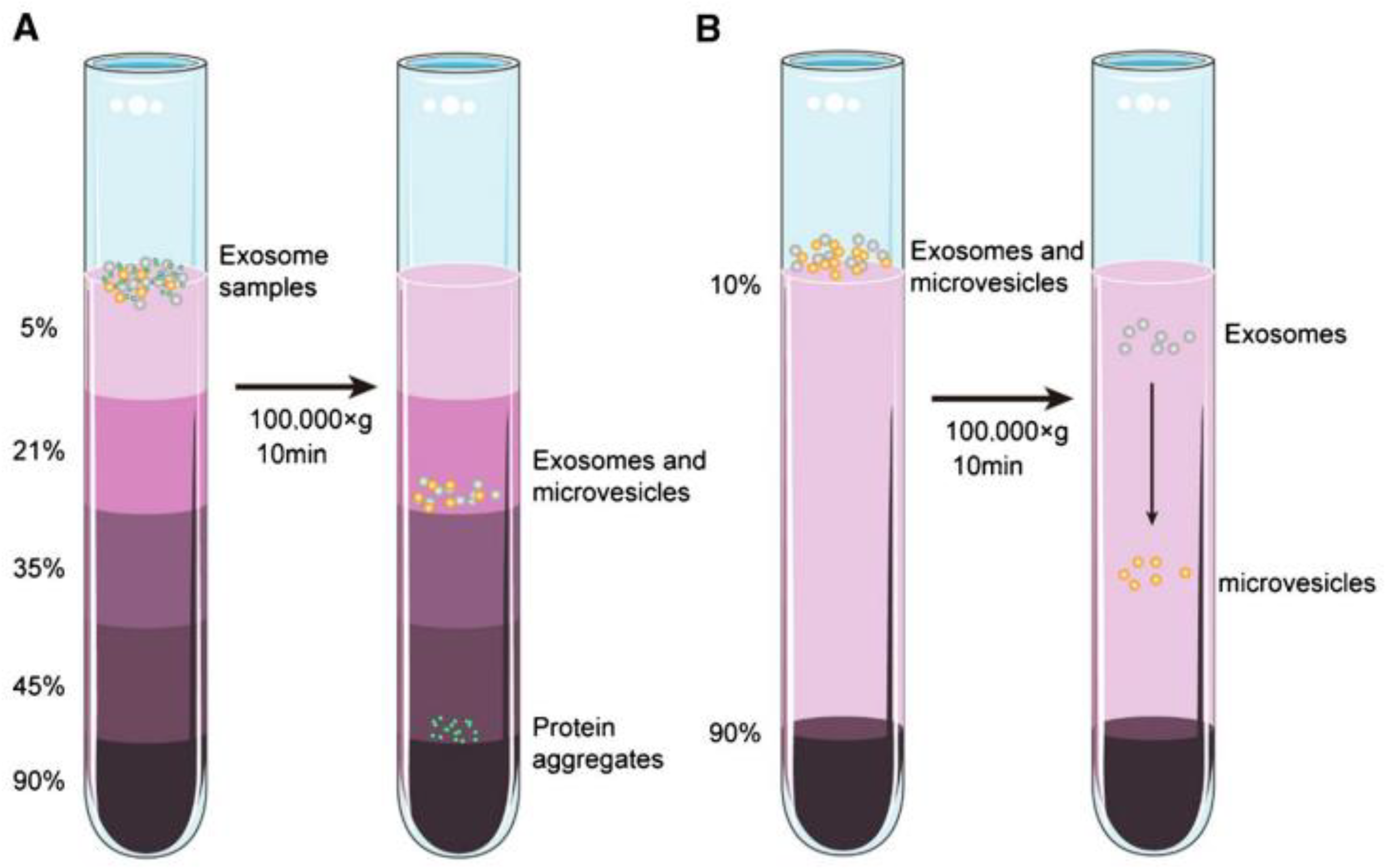
Figure 4 illustrates the exosome isolation steps using the density ultracentrifugation method[
25]. The step in this method begins with low-speed centrifugation (e.g., 300 g) to eliminate large particles such as cells. The centrifugation speed was then increased gradually to remove other contaminants in the sample such as cell debris and apoptotic bodies. The exosomes that have been cleaned are then precipitated by centrifuging the sample at a speed of 100,000 g for 90 minutes. All these steps are carried out in an environment with a temperature of 4
.
The second method for exosome separation is the density gradient method. The working principle of this method is carried out by utilizing centrifugation force where at a certain speed the materials in the sample will settle in the isodensity zone. As shown in
Figure 5, initially the exosome sample is placed at the top of an inert gradient medium such as a linear sucrose gradient (2.0-0.25M sucrose)[
25]. The gradient is then centrifuged at a certain speed and time at a temperature of 4
so that zones with different densities are produced in the sample. For exosomes, the density zone is in the range 1.10 – 1.18 g/mL. Because this method utilizes isodensity zones in exosome isolation, in several papers this method is also called the zone centrifugation method[
26].
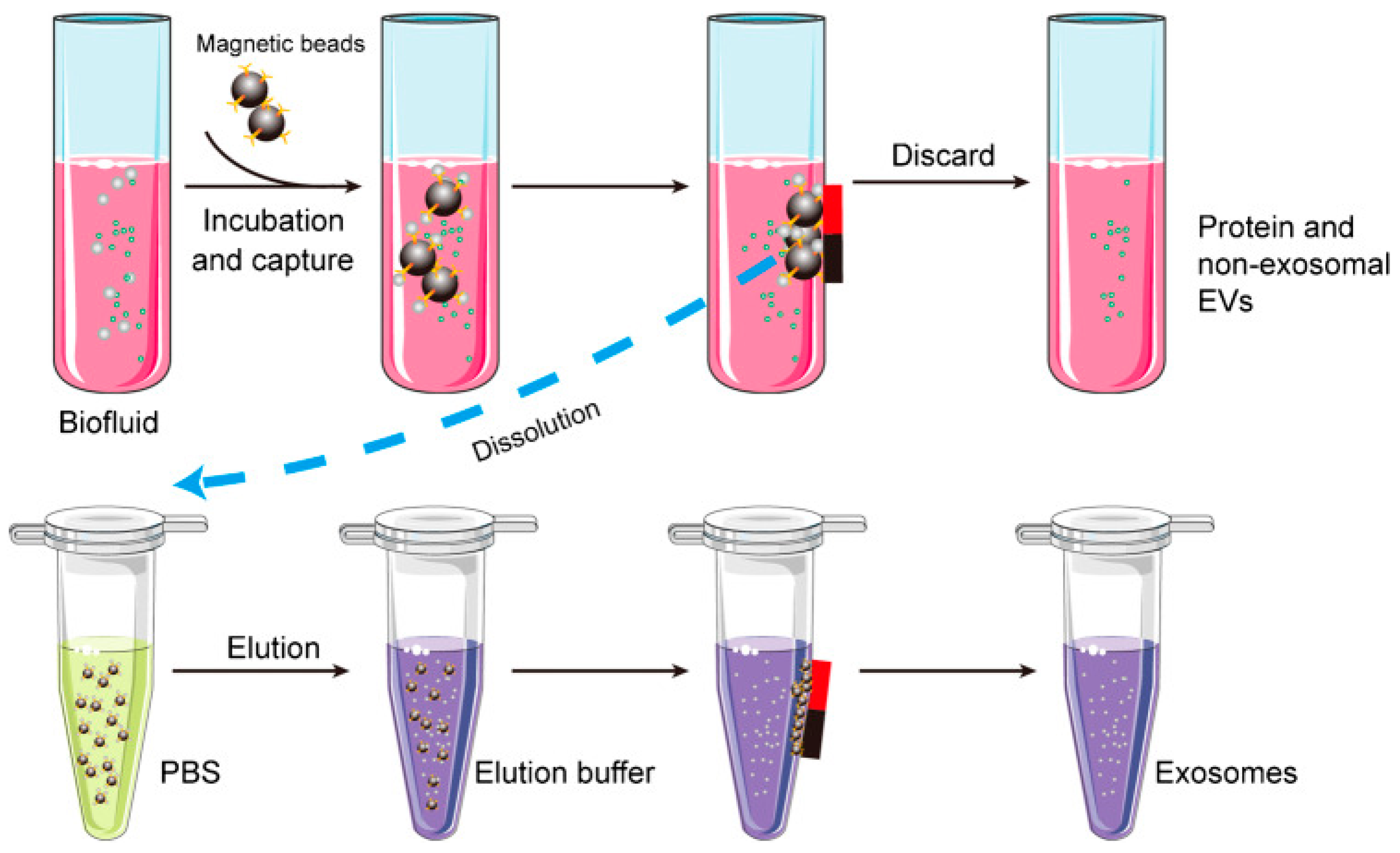
Exosomes are composed of proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides. Therefore, exosome isolation can be carried out by utilizing the bond between antigen and antibody. This technique is called the immunoaffinity technique, which is an approach that uses the affinity between antibodies and antigens to capture, purify, or detect certain compounds in a sample. As shown in
Figure 6, antibodies on the surface of magnetic beads can be used to capture specific proteins such as CD9, CD63, or CD81 on the surface of exosomes[
27]. As a result, the exosomes obtained will have high purity. Apart from that, the use of magnetic material in this method can simplify the separation process and speed up the exosome isolation time. Three methods of exosome isolation have been described. Other exosome isolation methods are summarized in
Table 1 below:
4. Development of Nanoplasmonic Biosensor for Exosome Detection
4.1. SPR Based Biosensor
There are at least two main problems that remain challenges in exosome detection using SPR biosensors[
28]. The first is due to the physical properties of the exosome itself. The small size of the exosome and its low mass make the measured SPR signal very small. Clear signal differences in exosomes with different concentrations were not visible. In this context, signal amplification becomes an unavoidable necessity. The second challenge arises because the collected exosomes are always mixed with serum-free target proteins. This makes the measurement results inaccurate because they are influenced by the presence of false positive signals. Engineering of SPR transducers and the biosensing mechanisms of SPR biosensors is still a topic that is being extensively investigated by many research groups in the world.
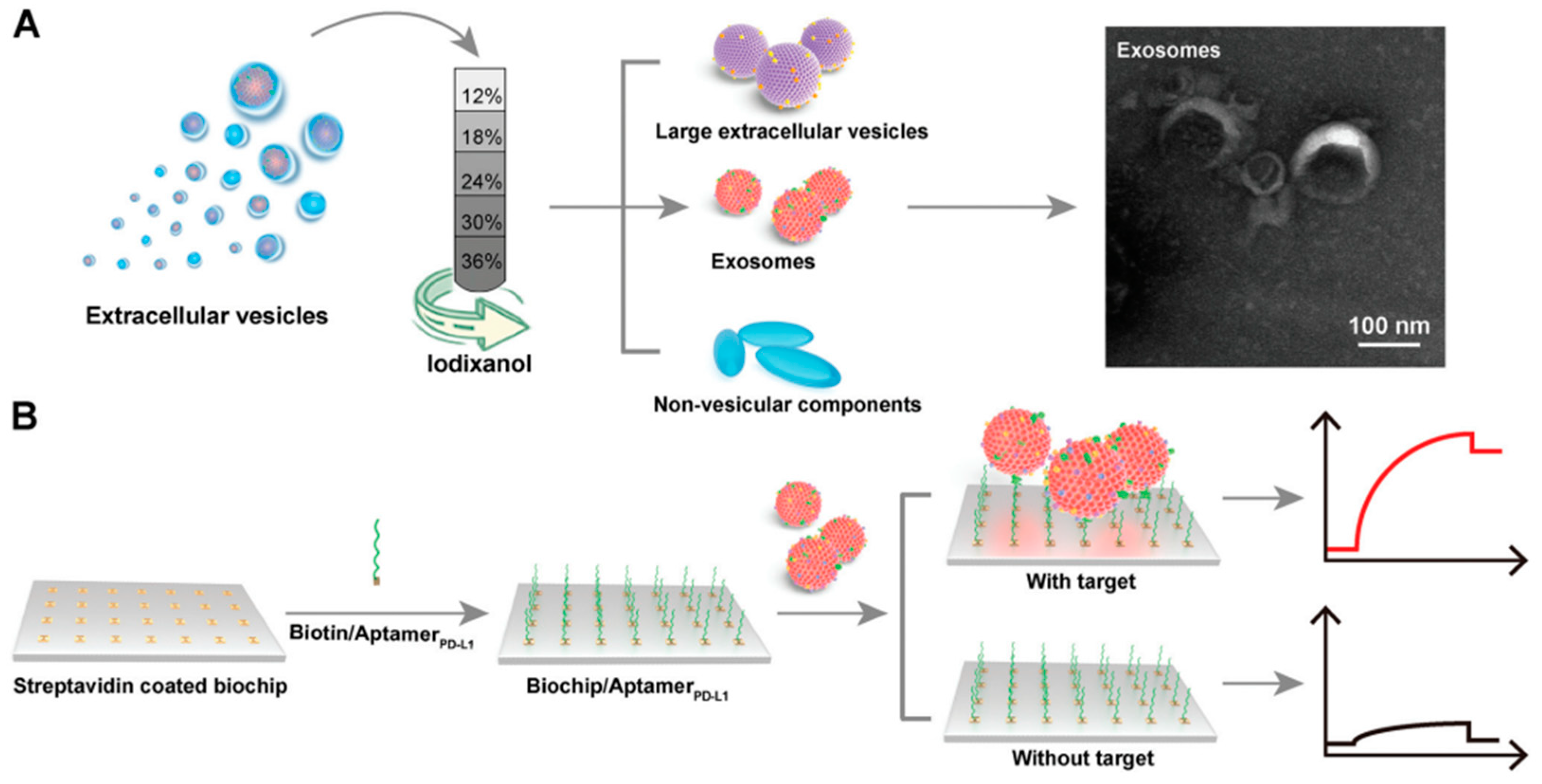
Zhang et al in 2022 detected exosomal PD-L1 using an SPR biosensor. The investigated exosomal PD-L1 was purified using the density gradient method. As shown in
Figure 7, crude exosomes were added to iodixanol dissolved in PBS with different concentrations. After the sample was centrifuged at 120 000 g at 4
overnight, the exosomes obtained were spherical or cup-shaped with a size of 50-150 nm based on the results of TEM characterization. Furthermore, to be able to specifically detect exosomal PD-L1, the SPR chip was immobilized with PD-L1 aptamer by utilizing the bond between streptavidin and biotin. In this study, the detection limit of the SPR sensor was 44.5 pM with a linear range ranging from 0.63 nM to 7.5 nM[
29]. Mao et al have also detected PD-L1 exosomes with an SPR chip that expanded its loading capacity by depositing graphene on a Au surface. Multifunctional peptide (M-Pep, SS-IMVTESSDYSSY-KK-FHYQRDTPKSYN) was chosen to increase the selectivity of the biosensor. In this sensor structure, the SPR biosensor is able to detect PD-L1 exosomes in the linear range from 10
4 -10
8 particles/mL with a detection limit of 20 particles/mL[
30].
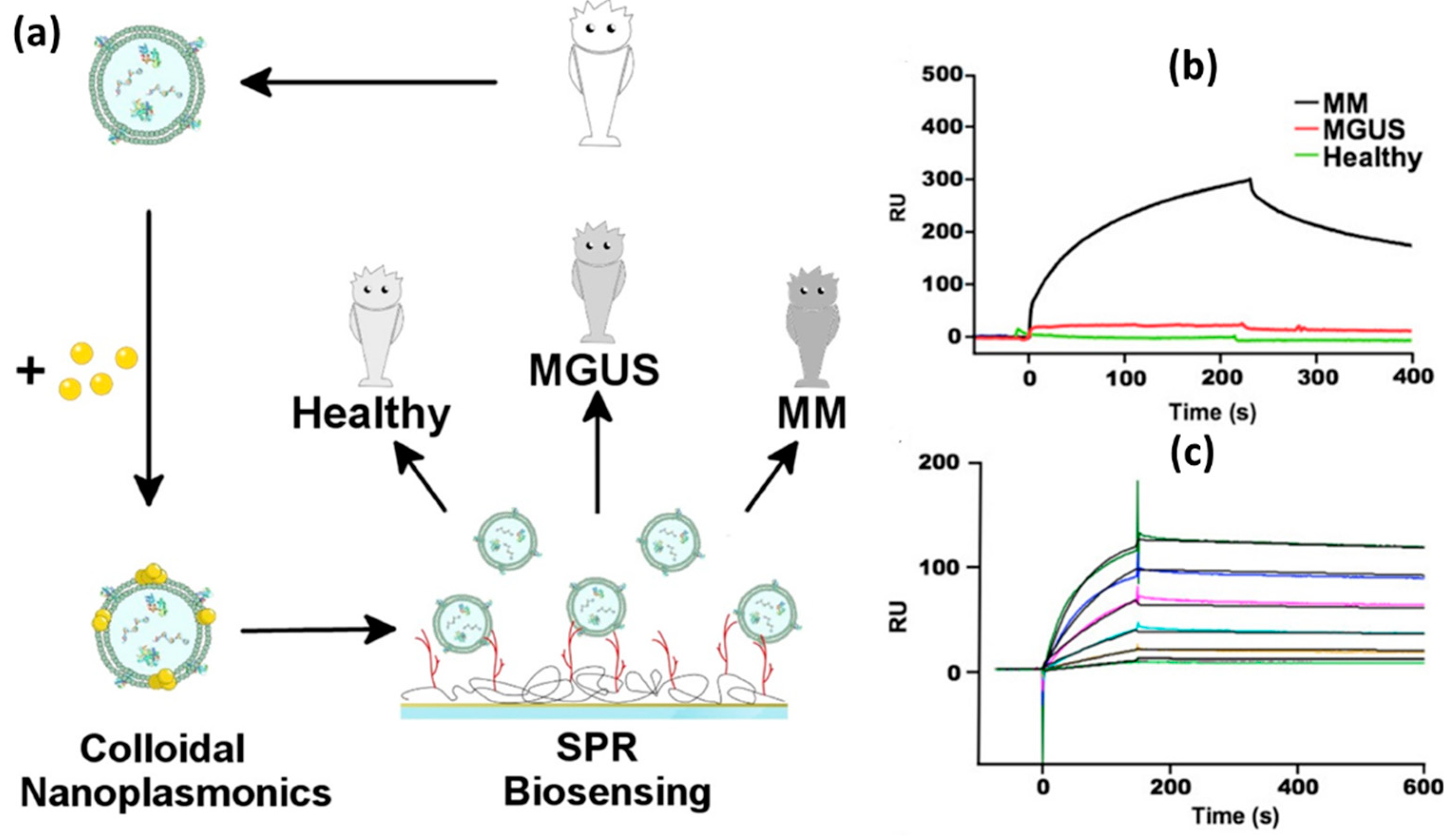
A different type of exosomes, namely multiple myeloma (MM), was also successfully investigated by Noto et al in 2016[
31]. In this study, the SPR signal was amplified using Au NPs with a diameter of 14 nm. The investigation began with purification of exosomes using a sucrose-based density gradient method. The pure exosomes were then incubated in an Au NPs solution with a concentration of 6 nM so that Au NPs clusters would form on the exosome membrane. Success at this stage is marked by a red shift in the LSPR signal obtained from UV-Vis characterization. Three different exosome samples were compared, namely exosomes from healthy, MGUS and MM patients. MGUS is a Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance and is an early phase of MM. In this condition, clonal plasma cells grow without causing clear and significant clinical symptoms.
Figure 8 shows the differences in the SPR signals of the three samples mentioned. From the sensorgram displayed, the MM sample shows a much higher signal than the other two samples. This indicates that the developed sensor system can be utilized for profiling exosomes derived from MM. At different MM concentrations, MM exosome samples were detected up to a concentration of 0.06 nM with the detection limit being on the order of approximately 10 pM.
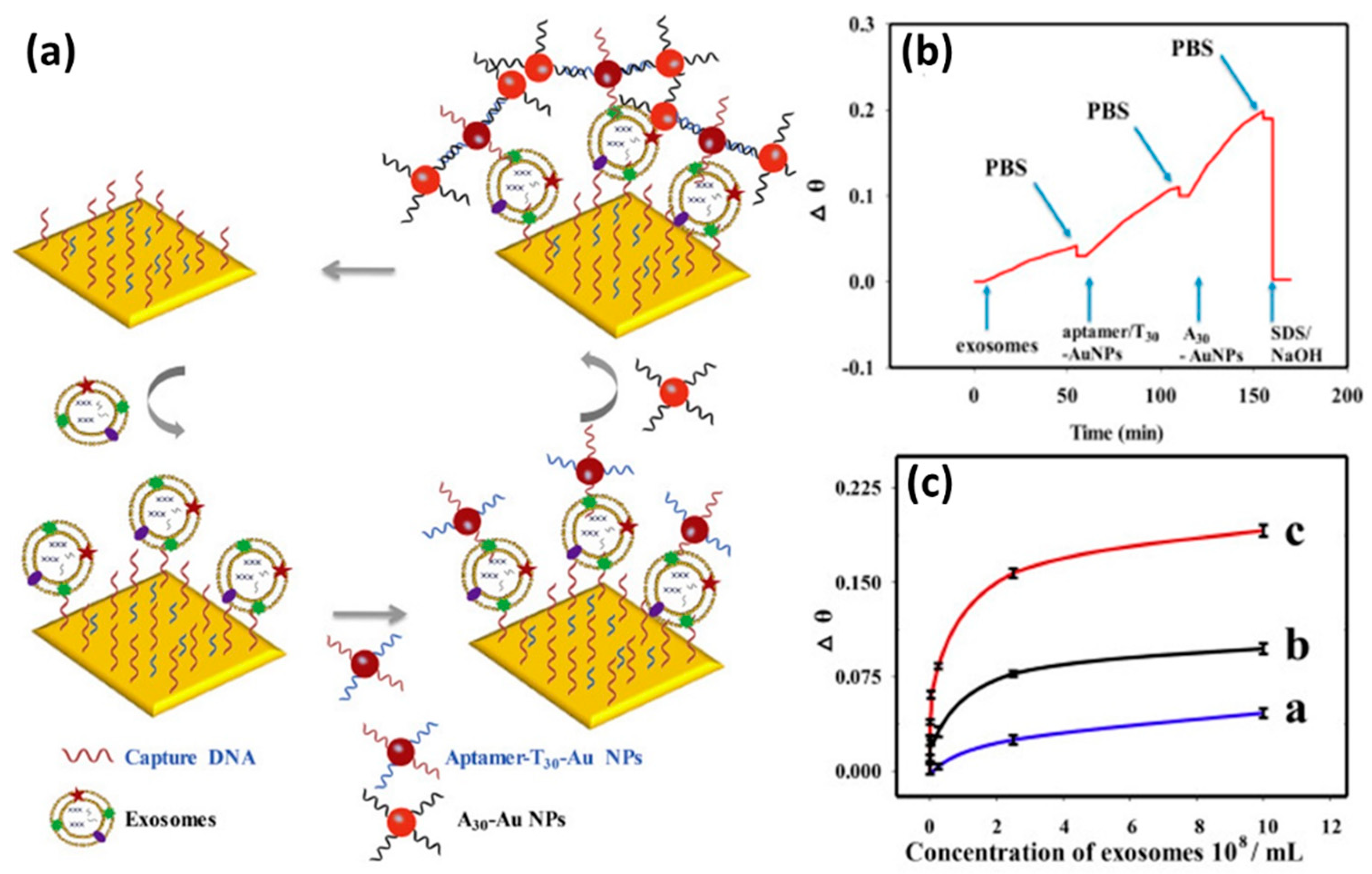
Signal amplification using Au NPs was also carried out by Wang et al[
32]. In this study they compared the performance of the SPR biosensor in the case of detecting cancer cell exosomes using different detection strategies, namely direct measurement, and single and dual amplification using Au NPs. Based on the SPR sensorgram shown in
Figure 9b, sample injection is carried out sequentially for the dual-amplified sensor system. Starting with injection of cancer cell exosome samples and continued with injection of Au NPs that have been functionalized with aptamer/T30 and A30. The signal differences of the three types of detection mechanisms at different exosome concentrations are shown in
Figure 9c. It is clear that the SPR signal for the dual-amplified sensor system (red line) has a higher response compared to the other two sensing strategies. They justified that the SPR biosensor with dual amplification had a detection limit which was 20 times lower than that of the SPR biosensor with single amplification. The detection limits of the SPR biosensor with direct detection, single amplification and dual amplification are 6.5×10
7 exosomes/mL, 1.0×10
5 exosomes/mL and 5.0×10
3 exosomes/mL, respectively.
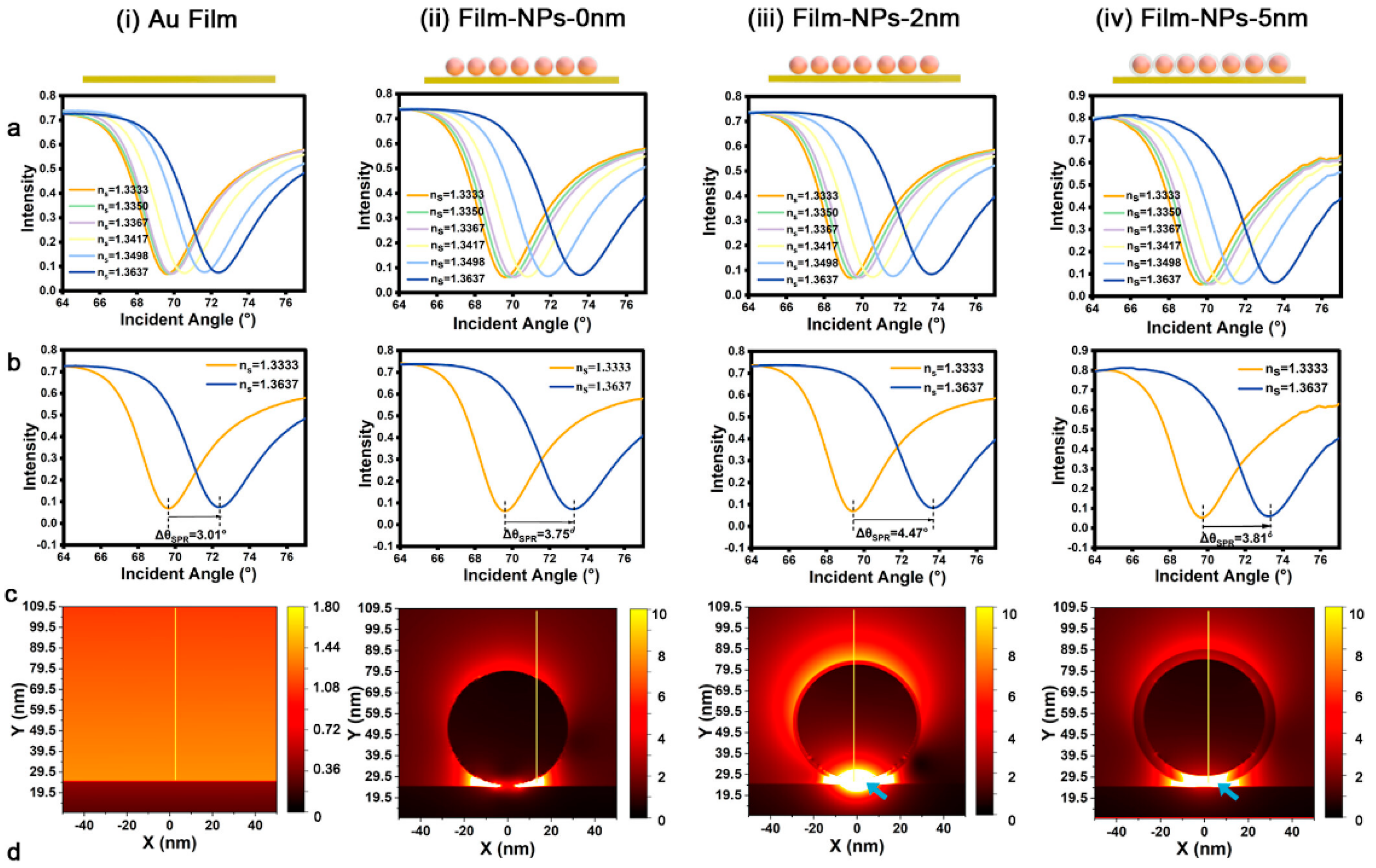
The effect of gap distance on enhancing sensitivity has been investigated by Zhou et al[
33]. As shown in
Figure 10a, there are four structures investigated in this study, namely bare Au film and Au NPs on the Au film surface with different gap distances (0 nm, 2 nm, and 5 nm). Gap distances of 2 and 5 nm were achieved by coating the AuNPs surface with SiO
2. As shown by the SPR curve in
Figure 10b, the presence of a gap greatly influences the SPR signal response. The higher the gap distance, the higher the SPR angle shift occurs. However, when the gap distance is increased to 5 nm, the SPR signal response decreases from 4.47
to 3.81
. However, this shift is still higher than that of bare Au film and SPR chips with a gap distance of 0 nm. To understand the mechanism behind the SPR enhancement, FDTD simulations are used to investigate the electric field at various designed interfaces. The result is that the electric field intensity at the 2 nm gap is 100 times greater than that of the bare Au film (
Figure 10c). Even with a gap of 5 nm, the electric field intensity remains greater than that of the bare Au film, this result agrees with the results shown in
Figure 10b. This biosensor system has been applied to detect programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) exosomes and the resulting detection limit is 0.14 particles/mL.
Several approaches, modifications and integrations have been carried out to obtain more sensitive SPR biosensors. The pyramid-shaped nanohole metastructure has been developed by Liang et al to detect prostate cancer[
34]. Other researchers, namely Zhang et al., have also integrated an SPR system coupled with a prism with microscopy techniques[
35]. This technology is called plasmonic scattering microscopy and it can be used to quantify exosomes and obtain their images at the same time. A summary of the SPR technology that has been developed and the resulting performance is shown in
Table 2.
4.2. LSPR Based Biosensor
In the previous section, we explained biosensors which utilize surface plasmon wave propagation for exosome quantification. In this section, we will focus on discussing a different type of plasmonic biosensor, namely LSPR-based biosensors. In simple terms, the structures used in LSPR biosensors can be classified into 3 different categories, namely solution phase-based colloidal nanoparticles, flat substrate-based platforms, and nanoparticle-coated optical fiber platforms[
41]. The signals analyzed are also obtained from various methods. Some of them are carried out using a UV-Vis spectrometer, fiber optics or dark field microscopy.
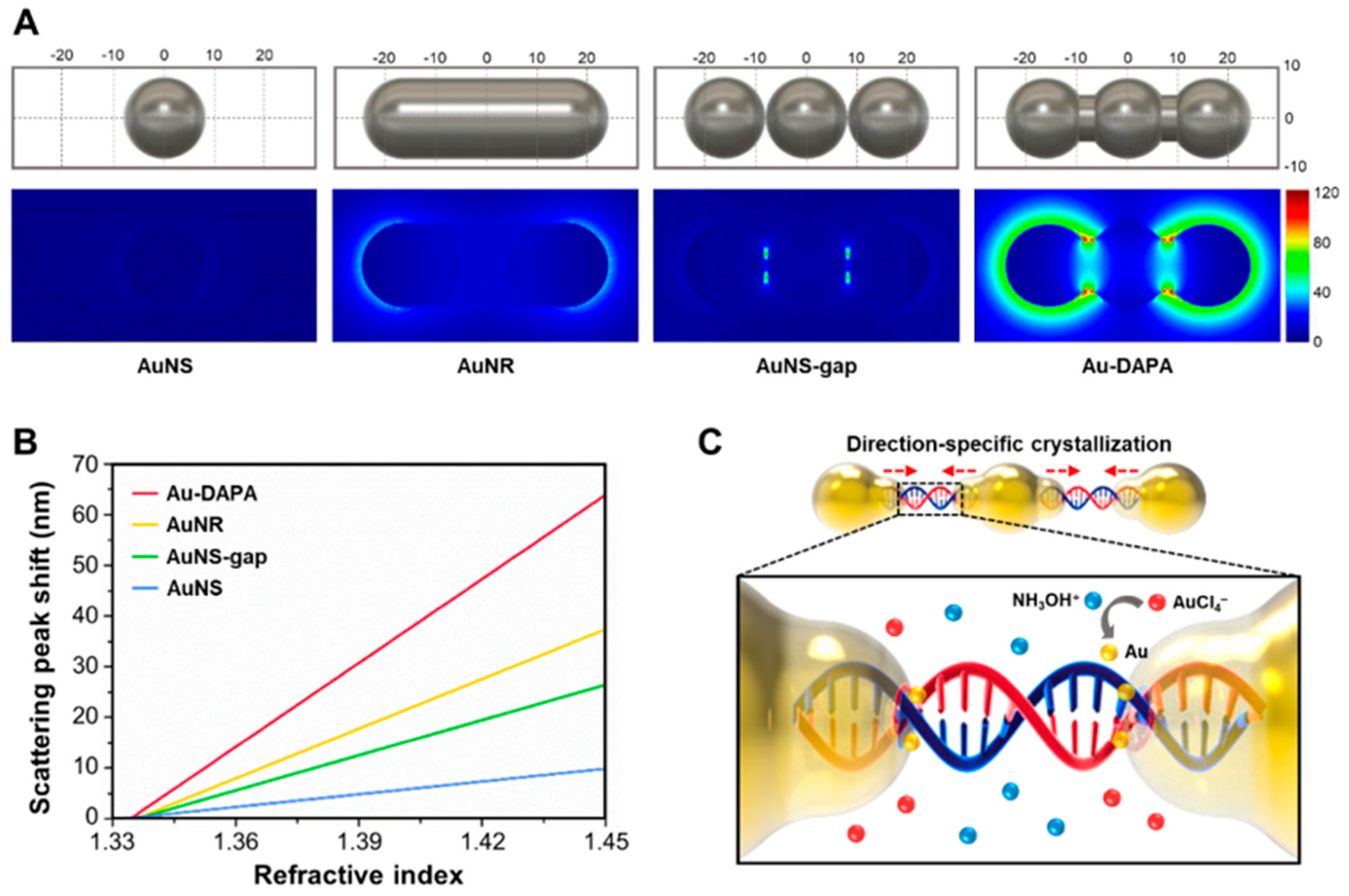
In the previous section, we stated that nanoparticles with an asymmetric shape have better sensitivity than nanosphere shapes. Using the Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) method, Song et al compared the electric field and sensitivity of 4 different structures and geometries of Au nanoparticles as shown in
Figure 11. We can see how the electric field profiles of LSPR biosensors with spherical gold-shaped (AuNS), rod-shaped (AuNR), rod-shaped with gaps (AuNS-Gap), and DNA-assembled advanced plasmonic architecture (DAPA) structures differ. A very strong electric field distribution is generated throughout the Au-DAPA surface which is due to the presence of nanogaps which have produced "hot-spots" which amplify the electromagnetic field energy with a higher enhancement factor. The sensitivity of the Au-DAPA based LSPR biosensor is 1.66 times higher than that of AuNR. These results have been successfully verified experimentally to detect exosomal miRNAs. The detection method used is based on changes in Rayleigh light scattering from single DAPA obtained from dark field microscope images. Of the three types of exo-miRNA, the detection limit of the sensor was 10.54 aM for exo-miR-125b, 13.53 aM for exo-miR-15a, and 11.10 aM for exo-miR-361.
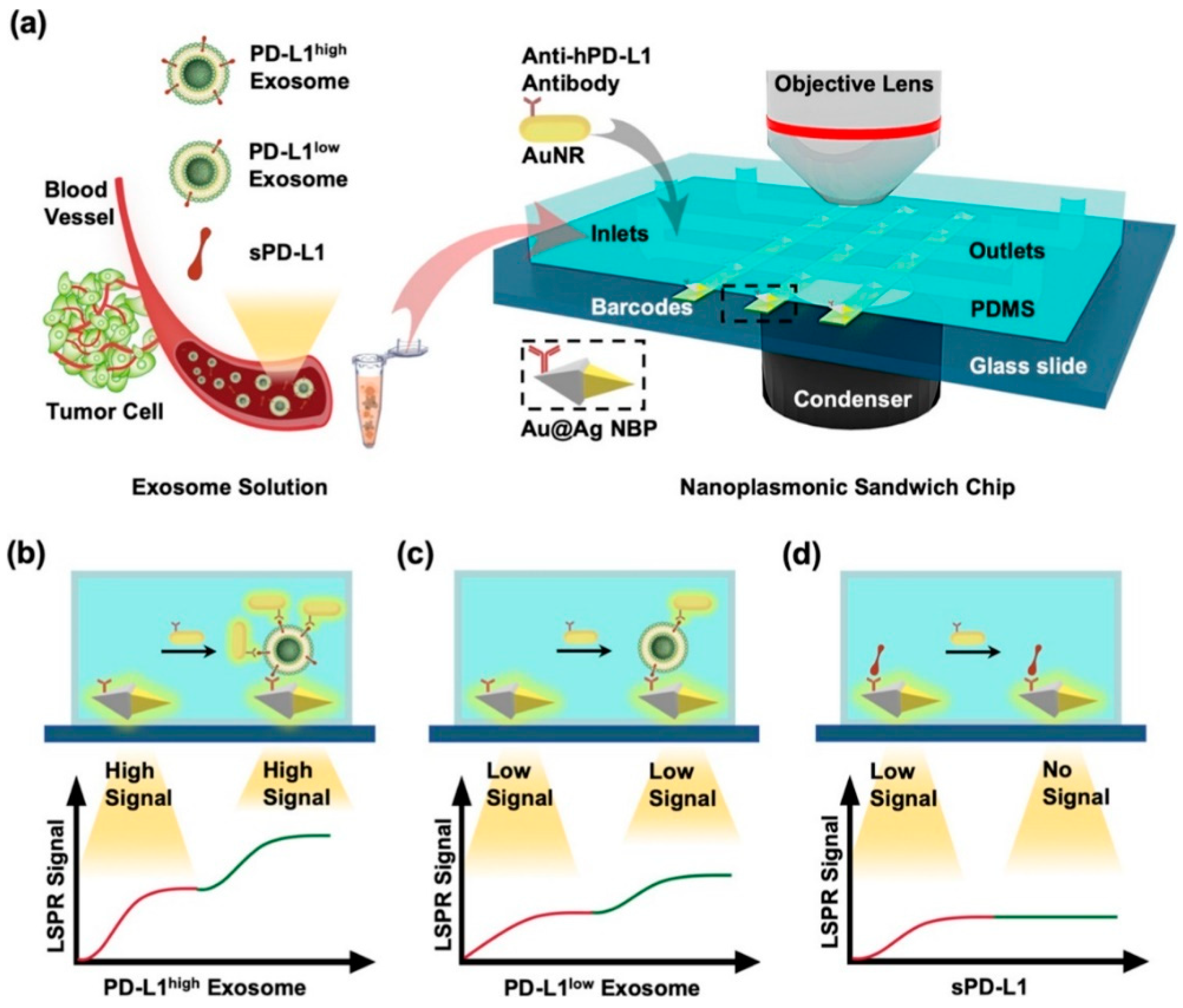
Using the same technique, namely by analyzing dark field images, Wang et al developed an LSPR biosensor based on a nanoplasmonic sandwich composed of Au@Ag core shell nanobipyramid (NBP) and AuNR[
43]. In this research, the LSPR biosensor has also been integrated with microfluidics and used for exosome detection. The exosome detection mechanism in this study is summarized in
Figure 12. The glass slide was deposited and patterned with Au@Ag NBP to obtain a barcode based on Au@Ag NBP. This barcode is then functionalized with anti-hPD-L1 to specifically capture exosomal PD-L1 or sPD-L1 present in samples injected via the microfluidic inlet. The bond that occurs between exosomes/sPD-L1 on the Au@Ag surface will result in a shift in the resonance wavelength and the scattering intensity will increase due to changes in the local refractive index. Changes in this optical signal are monitored in real time via dark field image. After that, the secondary labeling agent, namely AuNR, was functionalized as well as anti-hPD-L1 antibody (anti-hPD-L1−AuNR). This sample is then injected and will be bound by PD-L1 exosomes so that a sandwich structure will be formed. AuNRs show strong LSPR scattering under dark field imaging with a different resonance wavelength (∼660 nm) than NBPs (∼720 nm). Therefore, identification and quantification of exosomal PD-L1 can be performed based on secondary LSPR signal intensity. With this detection mechanism, the LSPR biosensor is able to detect PD-L1 exosomes up to a concentration of 1.2 × 10
3 particles/μL.
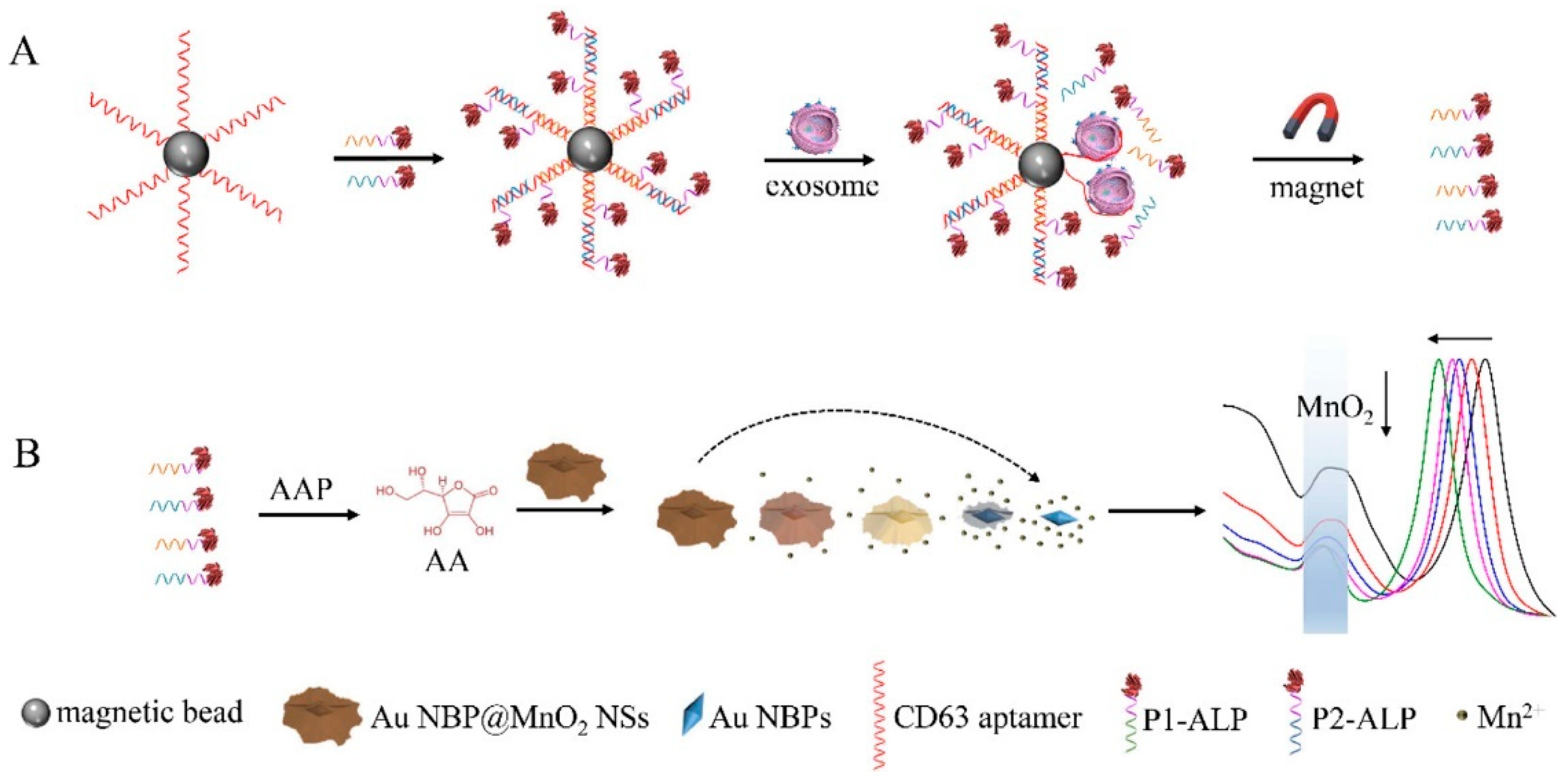
Previous research utilized dark field images in exosome detection. Zhang et al in 2022 developed a biosensor with a different approach, namely colorimetric based on Au NBP@MnO
2 nanostructures[
44]. The exosome detection mechanism in this study is shown in
Figure 13. Initially the magnetic beads were functionalized with CD63 aptamers, P1-ALP, and P2-ALP. Furthermore, the presence of detected exosomes will break down the hybridization complex (CD63 aptamer/P1-ALP/P2-ALP) because the binding energy of CD63 aptamer with CD63 has a stronger bond compared to CD63 aptamer with P1-ALP and P2-ALP. The released P1-ALP and P2-ALP will catalyze the dephosphorylation of AAP to produce ascorbic acid (AA). The resulting AA as a reductant etched MnO
2 nanosheets to produce Mn
2+ and was oxidized to dehydrogenated ascorbic acid (DHA). The etching-induced change in Au morphology contributes to the blue shift in the LSPR band of Au NBP. Therefore, exosomes can be measured based on ALP-triggered etching of Au NBP@MnO
2 NS. With this approach, they justified being able to detect exosomes up to a concentration of 1.35×10
2 particles/μL.
Apart from those discussed above, several researchers have developed LSPR biosensors based on optical microfiber. Specifically for exosome detection, this system has been used by Li et al to detect Clear Cell Renal Cancer Exosomes. We summarize the results of this study and other studies related to LSPR biosensors for exosome detection in
Table 3.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we have summarized recent developments in exosome detection using nanoplasmonic biosensors. Various sensor systems and detection mechanisms have been discussed in this paper, both SPR and LSPR based biosensors. If we consider the detection limit of sensors, nanoplasmonic biosensors have presented a highly sensitive and specific technology for detecting exosomes. Currently, this sensor has also been integrated with other technologies such as microfluidics. This opens up opportunities for the development of more complex and versatile exosome detection systems.
Although various results have been achieved in nanoplasmonic biosensors, several challenges need to be overcome to implement nanoplasmonic biosensors on a large scale. The production costs of sensors and reproducibility issues, especially in more real and complex samples, are still aspects that must be studied in the next few years. Apart from that, device miniaturization is another important aspect that must be studied in the future for device application in real clinical fields.
Author Contributions
D.T.N.: investigation, data curation, writing—original draft. N.-F.C.: conceptualization, methodology, data curation, supervision, investigation, resources, methodology. Y.-S. H.: conceptualization, methodology. Y.-J. L.: conceptualization, methodology. H. S. N.:conceptualization, methodology. All the authors contributed equally and have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is sponsored by “Higher Education Sprout Project” of National Taiwan Normal University and the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China (ROC), Taiwan, for financially supporting this research under Contract No. MOST 108-2221-E-003 -020 -MY3, MOST 109-2221-E-003-028-MY3, and NSTC 112-2221-E-003 -016 -MY3.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cheng, N.; Du, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Xu, W.; Luo, Y.; Lin, Y. Recent Advances in Biosensors for Detecting Cancer-Derived Exosomes. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1236–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, S.M.I.; Hossain, F.B.; Nestorova, G.G. Advances in Biosensors Technology for Detection and Characterization of Extracellular Vesicles. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiei, M.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Razak, S.I.A.; Khan, M.U.A. A Comprehensive Review on the Applications of Exosomes and Liposomes in Regenerative Medicine and Tissue Engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2021, 13, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sałaga-Zaleska, K.; Kuchta, A.; Bzoma, B.; Chyła-Danił, G.; Safianowska, A.; Płoska, A.; Kalinowski, L.; Dębska-Ślizień, A.; Jankowski, M. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis of Urinary Extracellular Vesicle Proteins as a New Challenge in Laboratory Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Kastresana, A.; Jones, J.C. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Extracellular Vesicles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1545, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatanek, R.; Baj-Krzyworzeka, M.; Zimoch, J.; Lekka, M.; Siedlar, M.; Baran, J. The Methods of Choice for Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) Characterization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qie, Y.; Qin, W.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, M.; Guo, L.H. Emerging Immunoassay Technologies for the Rapid Detection of Exosomes. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2021, 345, 130336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.L.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A.P. Critical Overview on the Application of Sensors and Biosensors for Clinical Analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, F.; Jalili, R.; Amjadi, M.; Rashidi, M.R. SPR Signals Enhancement by Gold Nanorods for Cell Surface Marker Detection. BioImpacts 2019, 9, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, N.F.; Tai, M.J.; Nurrohman, D.T.; Lin, T.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Chen, C.Y. Immunoassay-Amplified Responses Using a Functionalized Mos2-Based Spr Biosensor to Detect Papp-A2 in Maternal Serum Samples to Screen for Fetal down’s Syndrome. Int. J. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 2715–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurrohman, D.T.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chiu, N.-F. Exploring Graphene and MoS2 Chips Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors for Diagnostic Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, N.F.; Kuo, C.T.; Lin, T.L.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, C.Y. Ultra-High Sensitivity of the Non-Immunological Affinity of Graphene Oxide-Peptide-Based Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors to Detect Human Chorionic Gonadotropin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Agarwal, S.; Pal, S.; Verma, A.; Kumar Prajapati, Y. Refractive Index Sensing Using MXene Mediated Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensor in Visible to near Infrared Regime. Measurement 2024, 224, 113682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, A.M.; Cvelbar, U.; Abdulhalim, I. A Comprehensive Review on Plasmonic-Based Biosensors Used in Viral Diagnostics. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, N.F.; Yang, C. Du; Chen, C.C.; Kuo, C.T. Stepwise Control of Reduction of Graphene Oxide and Quantitative Real-Time Evaluation of Residual Oxygen Content Using EC-SPR for a Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2018, 258, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.S.; Fan, S.K. Microfluidic Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors: From Principles to Point-of-Care Applications. Sensors (Switzerland) 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurrohman, D.T.; Chiu, N.F. Interaction Studies of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Immunosensor Based on Gold Nanoparticles. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 19262–19271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, S.; de Araujo, R.E. Engineering a Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Platform for Molecular Biosensing. Open J. Appl. Sci. 2018, 08, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellas, V.; Hu, D.; Mazouzi, Y.; Mimoun, Y.; Blanchard, J.; Guibert, C.; Salmain, M.; Boujday, S. Gold Nanorods for LSPR Biosensing: Synthesis, Coating by Silica, and Bioanalytical Applications. Biosensors 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, A.; Sekhon, J.S.; Verma, S.S. Scattering Efficiency and LSPR Tunability of Bimetallic Ag, Au, and Cu Nanoparticles. Plasmonics 2014, 9, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unser, S.; Bruzas, I.; He, J.; Sagle, L. Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensing: Current Challenges and Approaches. Sensors (Switzerland) 2015, 15, 15684–15716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajna, N.D.; Santhosh, C.; Tom, D.; Rajeev, K.S. LSPR-Based Sensing of Insulin Using Gold Nanostars. AIP Conf. Proc. 2023, 2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Li, A.; Hu, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, L.; Shen, Z. Recent Developments in Isolating Methods for Exosomes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Kaslan, M.; Lee, S.H.; Yao, J.; Gao, Z. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics 2017, 7, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Ma, L.; Larcher, L.M.; Chen, S.; Liu, N.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Progress, Opportunity, and Perspective on Exosome Isolation - Efforts for Efficient Exosome-Based Theranostics. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3684–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, J.X.; Jiang, F.; Ni, W.K.; Qu, L.S.; Ni, R.Z.; Lu, C.H.; Xiao, M.B. A Comparison of Traditional and Novel Methods for the Separation of Exosomes from Human Samples. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W. zhao; Ma, Z. jun; Kang, X. wen Current Status and Outlook of Advances in Exosome Isolation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 7123–7141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Cheng, W.; Wu, T.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Bai, H.; Ding, S.; Li, X.; et al. Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Exosome Detection Based on Reformative Tyramine Signal Amplification Activated by Molecular Aptamer Beacon. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Guan, M.; Liu, Y.; Lv, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Isolation of Circulating Exosomes and Identification of Exosomal PD-L1 for Predicting Immunotherapy Response. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 8995–9003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Koh, K.; Chen, H. A Simple and Direct SPR Platform Combining Three-in-One Multifunctional Peptides for Ultra-Sensitive Detection of PD-L1 Exosomes. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2021, 346, 130496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Noto, G.; Bugatti, A.; Zendrini, A.; Mazzoldi, E.L.; Montanelli, A.; Caimi, L.; Rusnati, M.; Ricotta, D.; Bergese, P. Merging Colloidal Nanoplasmonics and Surface Plasmon Resonance Spectroscopy for Enhanced Profiling of Multiple Myeloma-Derived Exosomes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zou, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Nie, W.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, K. Direct Quantification of Cancerous Exosomes via Surface Plasmon Resonance with Dual Gold Nanoparticle-Assisted Signal Amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Koh, K.; Chen, H. Tunable Au@SiO2/Au Film Metasurface as Surface Plasmon Resonance Enhancer for Direct and Ultrasensitive Detection of Exosomes. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 9663–9671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Xie, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Lin, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Label-Free Plasmonic Metasensing of PSA and Exosomes in Serum for Rapid High-Sensitivity Diagnosis of Early Prostate Cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 235, 115380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, X.; Kolay, J.; Wang, R.; Wan, Z.; Wang, S. Label-Free Imaging and Biomarker Analysis of Exosomes with Plasmonic Scattering Microscopy. Chem. Sci. 2022, 367, 12760–12768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sina, A.A.I.; Vaidyanathan, R.; Wuethrich, A.; Carrascosa, L.G.; Trau, M. Label-Free Detection of Exosomes Using a Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Liu, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Geng, X.; Zou, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, K. Surface Plasmon Resonance Assay for Exosomes Based on Aptamer Recognition and Polydopamine-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles for Signal Amplification. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Koh, K.; Hu, X.; Chen, H. Rapid and Sensitive Detection of PD-L1 Exosomes Using Cu-TCPP 2D MOF as a SPR Sensitizer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 201, 113954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, G.; Thakur, A.; Xu, C.; Ng, S.; Lee, Y.; Wu, C.L. Detection of Glioma-Derived Exosomes with the Biotinylated Antibody-Functionalized Titanium Nitride Plasmonic Biosensor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Fan, Y.; Qian, H.; Li, S.; Xiang, Y.; Ding, S. Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor Using Hydrogel-AuNP Supramolecular Spheres for Determination of Prostate Cancer-Derived Exosomes. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.M.; Park, J.S.; Jung, S.W.; Yeom, J.; Yoo, S.M. =Biosensing Applications Using Nanostructure-Based Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Lee, J.U.; Jeon, M.J.; Kim, S.; Sim, S.J. Detection of Multiplex Exosomal MiRNAs for Clinically Accurate Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Label-Free Plasmonic Biosensor Based on DNA-Assembled Advanced Plasmonic Architecture. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Huang, C.-H.; Gao, Z.; Shen, J.; He, J.; MacLachlan, A.; Ma, C.; Chang, Y.; Yang, W.; Cai, Y.; et al. Nanoplasmonic Sandwich Immunoassay for Tumor-Derived Exosome Detection and Exosomal PD-L1 Profiling. ACS Sensors 2021, 6, 3308–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, J.; Wei, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, C.; Xu, Z. Plasmonic Colorimetric Biosensor for Sensitive Exosome Detection via Enzyme-Induced Etching of Gold Nanobipyramid@MnO 2 Nanosheet Nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 15244–15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yue, S.; Lu, Y.; Yang, C.; Fang, J.; Xu, Z. Sensitive Multicolor Visual Detection of Exosomes via Dual Signal Amplification Strategy of Enzyme-Catalyzed Metallization of Au Nanorods and Hybridization Chain Reaction. ACS Sensors 2019, 4, 3210–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Geng, Z.; Su, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wang, S.; Fang, W.; Chen, H. Label-Free Exosome Detection Based on a Low-Cost Plasmonic Biosensor Array Integrated with Microfluidics. Langmuir 2019, 35, 9816–9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.L.; Huang, W.X.; Zhang, P.J.; Chen, L.; Lio, C.K.; Zhou, H.; Qing, L. Sen; Luo, P. Colorimetric Determination of the Early Biomarker Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Alpha (HIF-1α) in Circulating Exosomes by Using a Gold Seed-Coated with Aptamer-Functionalized Au@Au Core-Shell Peroxidase Mimic. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Qiu, G.; NG, S.P.; Guan, J.; Yue, J.; Lee, Y.; Wu, C.M.L. Direct Detection of Two Different Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles by SAM-AuNIs LSPR Biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, T.; Lu, L.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, B. Ultrasensitive Detection of Exosomes Using an Optical Microfiber Decorated with Plasmonic MoSe2-Supported Gold Nanorod Nanointerfaces. ACS Sensors 2022, 7, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).