Submitted:
23 January 2024
Posted:
23 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
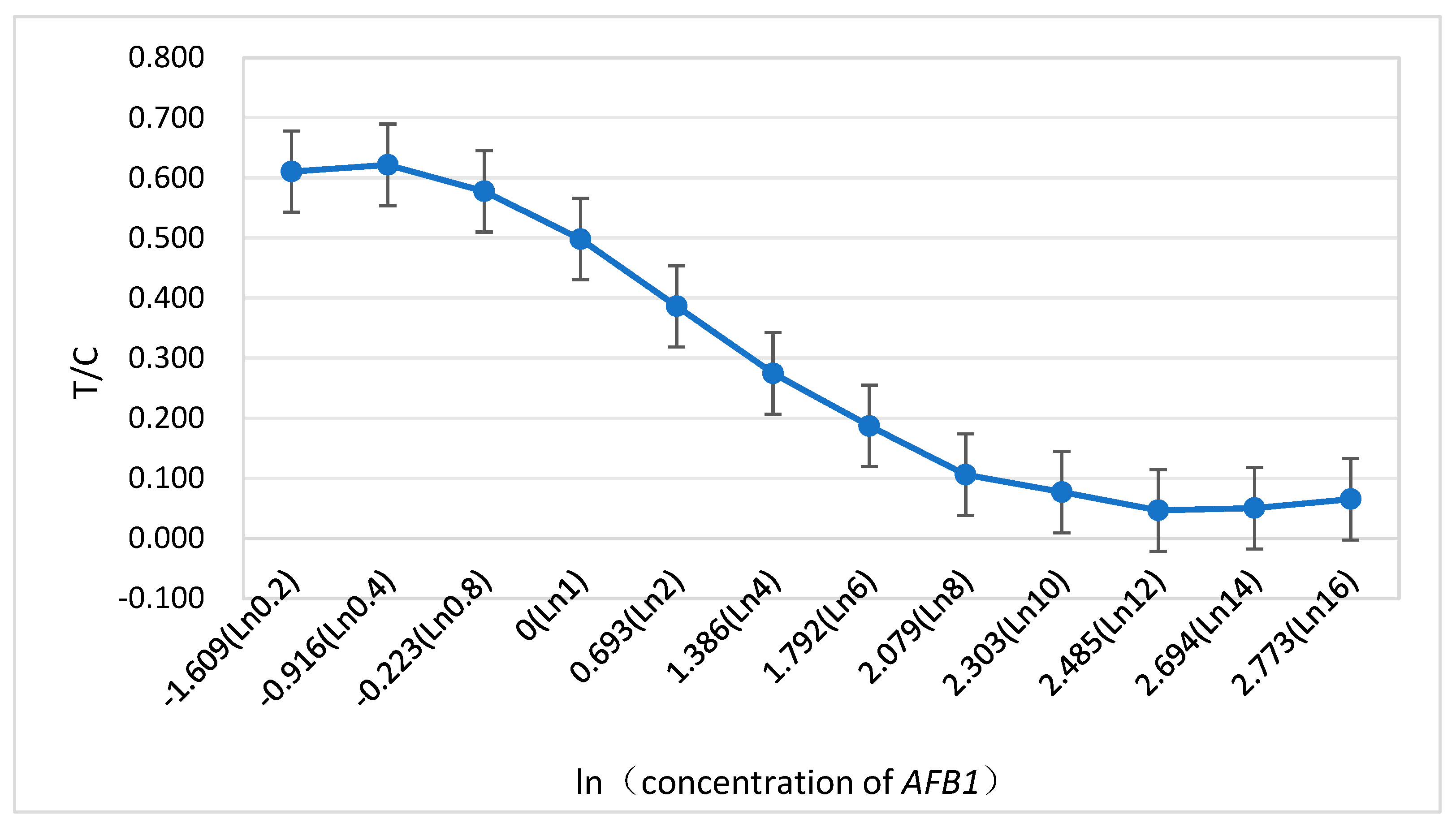
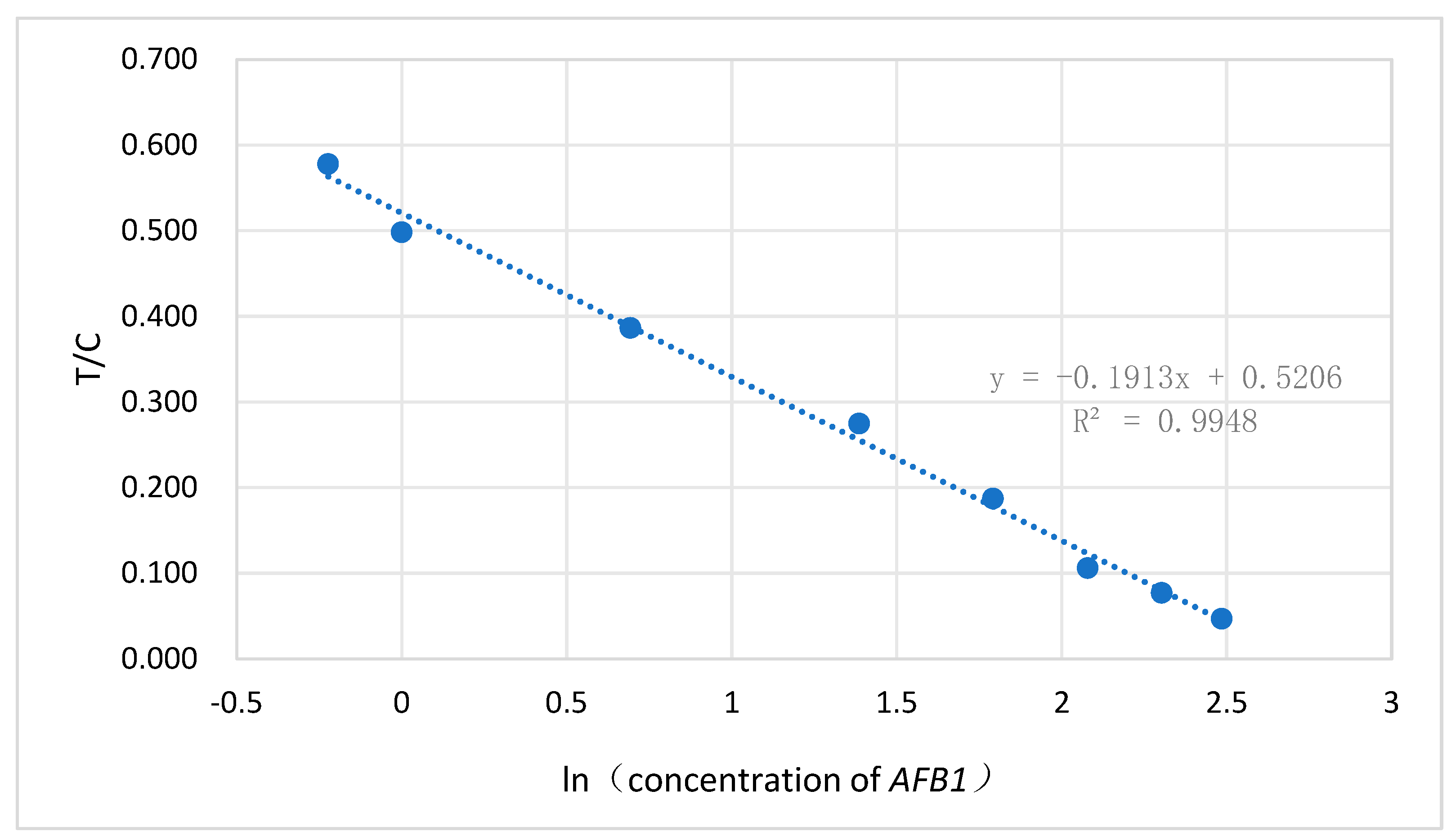
2.1. Detection limit and linear range of the method
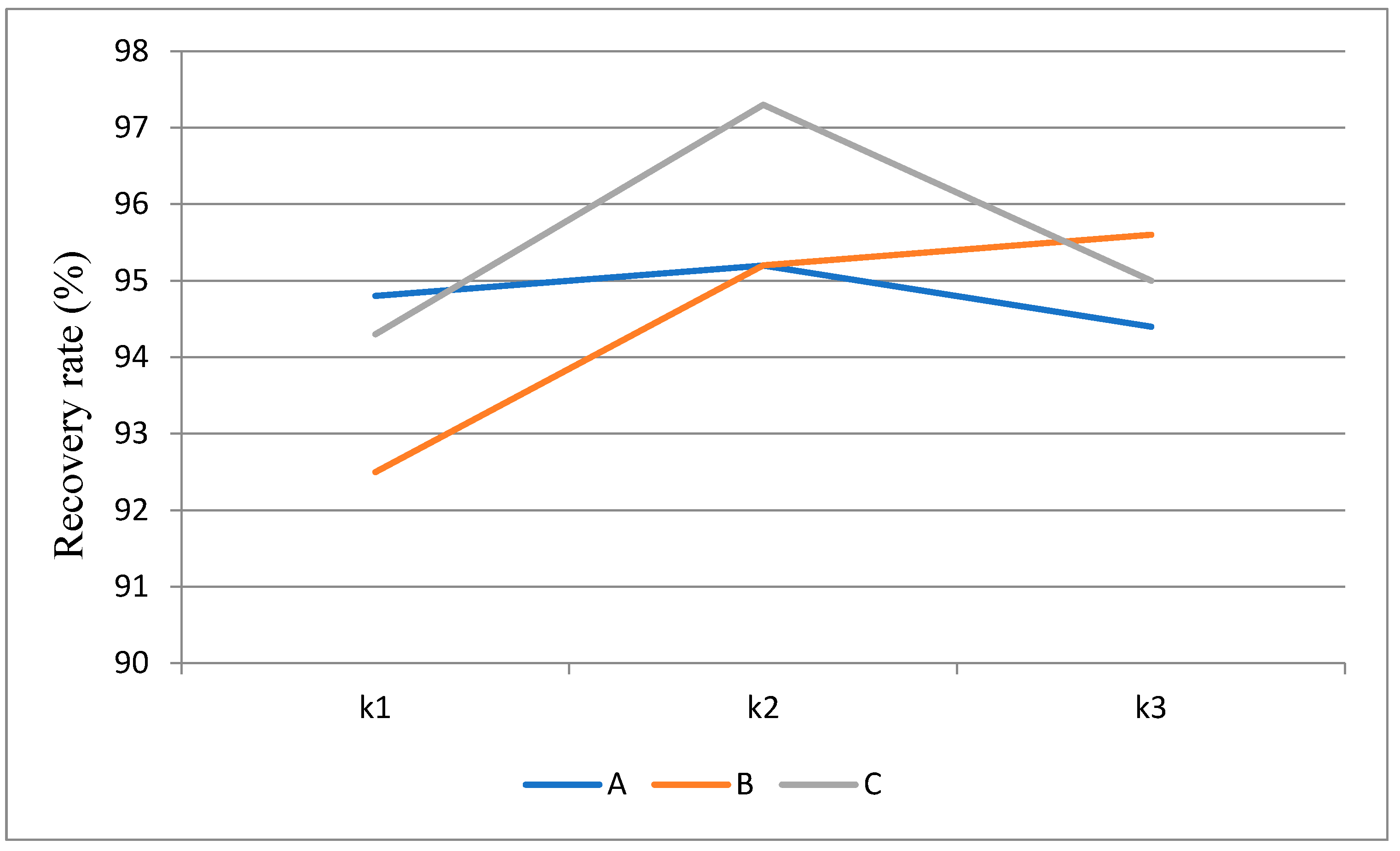
2.2. Preprocessing optimal reaction conditions
2.3. Accuracy and precision of the method
2.3.1. In-batch accuracy and precision of the method
2.3.2. Inter-batch accuracy and precision of the method
2.4. Comparison of results on AFB1 detection in actual sample test results between time-resolution fluorescence immunochromatographys and HPLC
Materials and Methods
3.1. Establish a standard curve
3.1.1. Preparation of sample diluent
3.1.2. Selection of blank matrix solution
3.1.3. Standard working solution preparation
3.2. Certain sample pretreatment optimal reaction conditions
3.2.1. Sample pretreatment and AFB1 content determine
3.2.2. Pretreatment for the optimal reaction conditions
|
Level Level Level Factor Factor |
A | B | C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oscillation time (min) | Reaction temperature (°C) |
Chromatography time (min) |
|
| 1 | 10 | 28 | 4 |
| 2 | 20 | 32 | 6 |
| 3 | 30 | 37 | 8 |
3.3. AFB1 detection limit and linear range
3.4. AFB1 detection of in-batch precision
3.5. AFB1 detection of inter-batch precision
3.6. Comparison of test results from actual samples betwen time-resolution fluorescence immunochromatography and HPLC
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- JI, X.F.; CHEN, X.Y.; WEI, W. Determination of aflatoxin B1 in bottled Chinese rice wine by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay ( ELISA). Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis.2015,27( 11) : 2006 -2010.
- WANG, D.; ZHANG, W.; LI, P.W.; ZHANG, Qi.; ZHANG, Z.W.; DING, X.X.; JIANG, J. Rapid and quantitative detection of aflatoxin B1 in plant grain and oilseeds products using colloid golden immuno - chromatographic method. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences.2014,36 ( 4): 529 - 532.
- REN, Q.; XU, J.L.; LIU, J.H. Safety risk and its control of yellow rice wine. Journal of Food Science and Technology.2016,34 ( 3) : 12 - 19. [CrossRef]
- ZHUANG, Z.H.; ZHENG, C.Q.; WANG, S.H. Optimization of Aspergillus flavus Culture Conditions and Extraction of Aflatoxin B1. Chin J Appl Environ Biol.2010,16 ( 5): 724-729.
- WILSON, C.L., DROBY, S. Microbial food contamination. New York: CRC Press.2001.
- GUO.X.; WEN.F.; ZHENG.N.; et al. Development of an ultrasensitive aptsensor for the detection of aflatoxin B1. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014, 56 (1): 340-344. [CrossRef]
- MAO, Q.Z.; LU, W.G.; CHEN, B.L.; YU, G.S.; WU, B.Y. Study and analysis on safety of rice wine. LIQUOR MAKING. 2006, (03)60- 65.
- YANG, X.D.; LUO, H.B.; YE, G.B.; LI, D.Y.; WANG, C.H.; WANG, Y. Verification of the Safety of Aflatoxin B1 in Nong-flavor Liquor Production by Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). LIQUOR-MAKING SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY.2013, (4)92-94.
- Han, X.W. Analysis Methods Development for Three Mycotoxins and Application in liquor production. Tianjin University of Science and Technology.2014.
- MAGATOMI, Y.; INOUE, T.; UYAMA, A.; et al. The fate of mycotoxins during the distillation process of barley shochu, a distilled alcoholic beverage. bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry.2012,76(1):202-204. [CrossRef]
- XU, Z.; TAN, S.M.; JIAO, Y.C.; ZHANG, Y.F. Determination of Aflatoxin B1 in Dry Capsicum by Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Food Science.2009,30 ( 10): 245 - 247.
- LIU, J.; XIONG, N.; LIU, L.; YU, D. Verification of rapid detection of Aflatoxin B1 in grain by immunochromatographic test parer method. Journal of Henan University of Technology.2011,32 ( 5) : 51 -57.
- LI, P.W.; MA, L.; YANG, J.E.; ZHANG, W.; YANG, C.H.; YANG, M.A. Reiew on analytical methods for aflatox in B1 in grains and oilseeds products. Chinese journal of oil crop sciences.2005,27 ( 2) : 77 - 81.
- Cusati. T.; Granucci. G.; Persico. M. Photodynamics and time-resolved fluorescence of azobenzene in solution: a mixed quantum-classical simulation. Journal of the American Chemical Society.2011, 133(13) : 5109-5123. [CrossRef]
- Mizukami. S.; Tonai. K.; Kaneko. M.; Kikuchi. K. Lanthanide-based protease activity sensors for time-resolved fluorescence measurements. Journal of the American Chemical Society.2008, 130(44): 14376-14377. [CrossRef]
- Bunzli. J.C.G.; Piguet. C. Taking advantage of luminescent lanthanide ions. Chemical Society Reviews. 2005, 34(12): 1048-1077. [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Huang, B.; Zhang, L.; Mi, X.l.; et al. Use of ultrasensitive time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for rapid detection of clenbuterol hydrochloride in urine. Journal of Hygiene Rrsearch.2006,35 ( 6): 798 - 801.
- Determination of AFB and AFG groups in food. National Food Safety Standards. GB 5009.22-2016:11-17.
- ZHANG, Z.W.; LI, P.W.; ZHANG, Q.; DING, X.X. Study on Time-Resolved Fluorescence Immunochromatography for Afaltoxin Determination in Agricultural Product. Scientia Agricultura Sinica.2014,47(18):3668-3674.
- Riterion on Quality Control of Laboratories-Chemical Testing of Food. Chinese National Standards. GB/T 27404-2008:29-27.
|
Level Level Factor FactorFG |
A | B | C | Empty column | Recovery rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oscillation time (min) | Reaction temperature (℃) | Chromatography time (min) | |||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 92.1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 95.6 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 96.7 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 92.9 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 95.7 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 96.9 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 92.5 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 94.2 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 98.4 |
| Extreme difference extreme Factor factorFactor |
A | B |
C | Empty column |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | 284.4 | 277.5 | 283.2 | 284.4 |
| K2 | 285.5 | 285.5 | 286.9 | 285.5 |
| K3 | 285.1 | 292 | 284.9 | 285.1 |
| K1 | 94.8 | 92.5 | 94.4 | 94.8 |
| K2 | 95.2 | 95.2 | 95.6 | 95.2 |
| K3 | 95.0 | 97.3 | 95.0 | 95.0 |
| R extreme | 0.4 | 4.8 | 1.2 | 0.9 |
| Source of variance | Square sum | Degree of freedom | Mean square | F value | F (2,2) A=0.05 |
Salience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.21 | 2 | 0.11 | 0.22 | 19 | Not significant |
| B | 35.17 | 2 | 17.59 | 36.64 | Significant | |
| C | 2.29 | 2 | 1.15 | 2.39 | Not significant | |
| Error | 0.96 | 2 | 0.48 | |||
| Sum total | 38.63 | 8 |
| Spiked level (μg·kg-1) |
Average finding (μg·kg-1) |
Standard deviation (μg·kg-1) |
Recovery (%) |
CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 5 10 |
0.779 4.987 10.569 |
0.0799 0.0663 0.0501 |
77.9% 97.7% 105.7% |
10.26 6.80 4.47 |
| Spiked level (μg·kg-1) |
Average finding (μg·kg-1) |
Standard deviation (μg·kg-1) |
Recovery (%) |
CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 5 10 |
0.759 4.210 8.980 |
0.1052 0.0682 0.0426 |
75.9% 84.2% 89.8% |
13.86 8.10 10.10 |
| Sample Number | Finding by TRFIA (μg·kg-1) |
Finding by HPLC (μg·kg-1) | Relative error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 0.949 | 1.051 | -9.70 |
| Sample 2 | N.D. | N.D. | |
| Sample 3 | 4.932 | 4.994 | -1.24 |
| Sample 4 | 1.754 | 1.839 |
-4.63 |
| Sample 5 | 6.710 | 6.910 |
-2.89 |
| Sample 6 | N.D. | N.D. | |
| Sample 7 | 1.200 |
1.330 |
-9.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





