Submitted:
20 January 2024
Posted:
22 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Proteomics research for AD biomarkers
Proteomics based biomarker research
Proteomics and Aβ cascade hypothesis
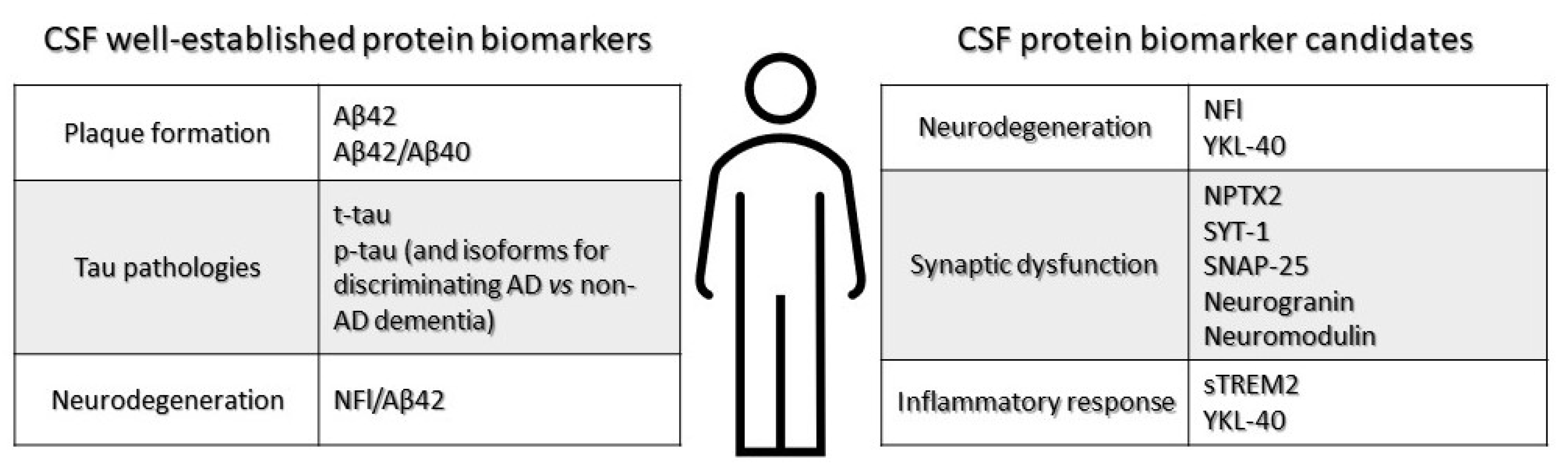
Cerebrospinal (CSF) fluid biomarkers
Plasma biomarkers
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2M | Alpha2 Macroglobulin |
| A | Amyloid beta protein |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| AMPA | -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| ApoA-1 | Apolipoprotein 1 |
| ApoE | Apolipoprotein E |
| APP | Amyloid precursor protein |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| ESI | Electrospray ionization |
| FABP3 | Fatty acid binding protein 3 |
| FTLD | Frontotemporal lobe dementia |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| IGFBP2 | Insulin like growth factor binding protein 2 |
| JAM-B | Junctional adhesion molecule B |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| LBD | Lewy body dementia |
| MALDI | Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization |
| Man-Tf | Mannosylated glycan transferrin |
| MMP9 | Metallo proteinase 9 |
| MMP10 | Metalloproteinase 10 |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRM | Multiple reaction monitoring |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| NCAM1 | Neuronal cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| NFl | Neurofilament light |
| NFTs | Neurofibrillary tangles |
| NMDA | N-methyl-D-aspartate |
| NPTX2 | Neuropentraxin 2 |
| p-tau | Hyperphosphorylated tau protein |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| PKM | Protein kinase M |
| PRDX3 | Mitochondrial thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase |
| SNAP-25 | Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 |
| sTREM2 | Soluble triggering receptor of myeloid cells 2 |
| SYT-1 | Synaptotagmin-1 |
| S100A9 | S100 calcium binding protein A9 |
| t-tau | Total tau protein |
| TOF | Time-of-flight |
| UCHL1 | Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 |
| YKL-40 | Astrocyte-derived chitinase-3-like protein 1 |
References
- Winblad, B.; Amouyel, P.; Andrieu, S.; Ballard, C.; Brayne, C.; Brodaty, H.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Dubois, B.; Edvardsson, D.; Feldman, H.; et al. Defeating Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: a priority for European science and society. The Lancet Neurology 2016, 15, 455–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beason-Held, L.L.; Goh, J.O.; An, Y.; Kraut, M.A.; O’Brien, R.J.; Ferrucci, L.; Resnick, S.M. Changes in brain function occur years before the onset of cognitive impairment. Journal of Neuroscience 2013, 33, 18008–18014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association, A. 2010 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2010, 6, 158–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubbelman, M.A.; Jutten, R.J.; Tomaszewski Farias, S.E.; Amariglio, R.E.; Buckley, R.F.; Visser, P.J.; Rentz, D.M.; Johnson, K.A.; Properzi, M.J.; Schultz, A.; et al. Decline in cognitively complex everyday activities accelerates along the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy 2020, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, T.; Matsuda, H.; Tabira, T.; Asada, T.; Uno, M. Changes in Brain Morphology in Alzheimer Disease and Normal Aging: Is Alzheimer Disease an Exaggerated Aging Process? American Journal of Neuroradiology 2001, 22, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Humpel, C. Identifying and validating biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Trends in Biotechnology 2011, 29, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xia, W. Proteomic profiling of plasma and brain tissue from Alzheimer’s disease patients reveals candidate network of plasma biomarkers. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2020, 76, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askenazi, M.; Kavanagh, T.; Pires, G.; Ueberheide, B.; Wisniewski, T.; Drummond, E. Compilation of reported protein changes in the brain in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K. Cerebrospinal fluid protein biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoop, A.; Singh, P.K.; Jacob, R.S.; Maji, S.K.; et al. CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. International journal of Alzheimer’s disease 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrowder, D.A.; Miller, F.; Vaz, K.; Nwokocha, C.; Wilson-Clarke, C.; Anderson-Cross, M.; Brown, J.; Anderson-Jackson, L.; Williams, L.; Latore, L.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: current evidence and future perspectives. Brain Sciences 2021, 11, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korecka, M.; Shaw, L.M. Mass spectrometry-based methods for robust measurement of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in biological fluids. Journal of neurochemistry 2021, 159, 211–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunes, S.; Aizawa, Y.; Sugashi, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Rodrigues, P.P. Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in the current state: A narrative review. International journal of molecular sciences 2022, 23, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Dhariwal, R.; Patil, N.; Ojha, S.; Tendulkar, R.; Tendulkar, M.; Dhanda, P.S.; Yadav, A.; Kaushik, P. Unveiling the Molecular Footprint: Proteome-Based Biomarkers for Alzheimer’s Disease. Proteomes 2023, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, M.; Mubeen, S.; Khan, A.; Ibrahim, S.; Meer, B. Plasma biomarkers: potent screeners of Alzheimer’s disease. American Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease & Other Dementias® 2019, 34, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Buckley, N.J.; Bos, I.; Engelborghs, S.; Sleegers, K.; Frisoni, G.B.; Wallin, A.; Lléo, A.; Popp, J.; Martinez-Lage, P.; et al. Plasma proteomic biomarkers relating to Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis based on our own studies. Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2021, 13, 712545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, N.J.; Ide, M.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. Salivary biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Neurology and Therapy 2019, 8, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Guan, Y.; Xie, F.; Cai, X.; Deng, J.; Wei, Y.; He, R.; Fang, Z.; et al. Systematic evaluation of urinary formic acid as a new potential biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2022, 14, 1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
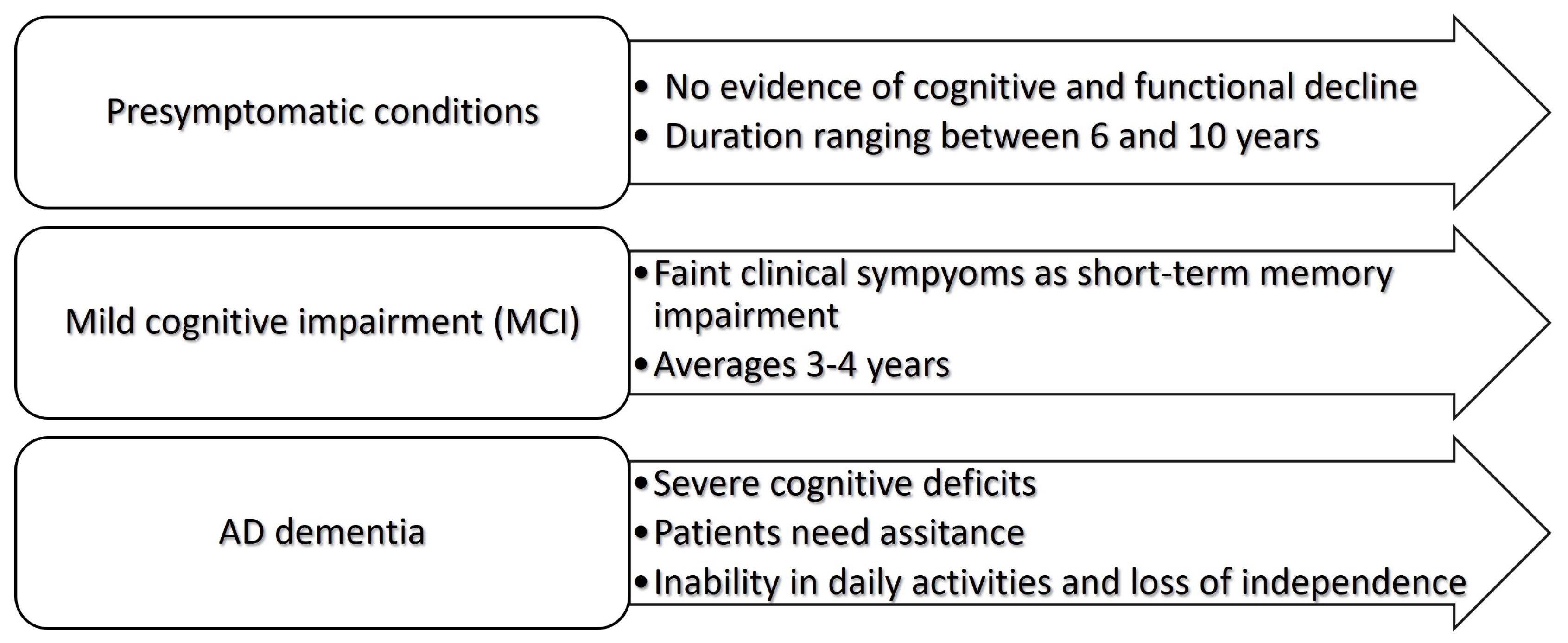
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermunt, L.; Sikkes, S.A.; Van Den Hout, A.; Handels, R.; Bos, I.; Van Der Flier, W.M.; Kern, S.; Ousset, P.J.; Maruff, P.; Skoog, I.; et al. Duration of preclinical, prodromal, and dementia stages of Alzheimer’s disease in relation to age, sex, and APOE genotype. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2019, 15, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.O.; Aakre, J.A.; Kremers, W.K.; Vassilaki, M.; Knopman, D.S.; Mielke, M.M.; Alhurani, R.; Geda, Y.E.; Machulda, M.M.; Coloma, P.; et al. Prevalence and outcomes of amyloid positivity among persons without dementia in a longitudinal, population-based setting. JAMA neurology 2018, 75, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathe, G.; Na, C.H.; Renuse, S.; Madugundu, A.K.; Albert, M.; Moghekar, A.; Pandey, A. Quantitative proteomic profiling of cerebrospinal fluid to identify candidate biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. PROTEOMICS–Clinical Applications 2019, 13, 1800105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Vanderwall, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Poudel, S.; Wang, H.; Dey, K.K.; Chen, P.C.; Yang, K.; Peng, J. Proteomic landscape of Alzheimer’s Disease: novel insights into pathogenesis and biomarker discovery. Molecular neurodegeneration 2021, 16, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, V.; Dhankhar, P.; Biswas, S. Proteomics as a Potential Tool for Biomarker Discovery. In High Altitude Sickness–Solutions from Genomics, Proteomics and Antioxidant Interventions; Springer, 2022; pp. 119–141. [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, S.; Spellman, D.S.; Hatcher, N.G. Proteomic Discovery and Validation of Novel Fluid Biomarkers for Improved Patient Selection and Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Alzheimer’s Disease Patient Cohorts. Proteomes 2022, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hippius, H.; Neundörfer, G. The discovery of Alzheimer’s disease. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience 2003, 5, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J.; Hardy, J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO molecular medicine 2016, 8, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheltens, P.; Blennow, K.; Breteler, M.M.; De Strooper, B.; Frisoni, G.B.; Salloway, S.; Van der Flier, W.M. Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet 2016, 388, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvěřová, M. Clinical aspects of Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical biochemistry 2019, 72, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’brien, R.J.; Wong, P.C. Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annual review of neuroscience 2011, 34, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Hanse, E. Amyloid β and APP as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Experimental gerontology 2010, 45, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, F.H.; Frisoni, G.B.; Johnson, S.C.; Chen, X.; Engelborghs, S.; Ikeuchi, T.; Paquet, C.; Ritchie, C.; Bozeat, S.; Quevenco, F.C.; et al. Clinical application of CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: From rationale to ratios. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring 2022, 14, e12314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahaman, Y.A.R.; Embaye, K.S.; Huang, F.; Li, L.; Zhu, F.; Wang, J.Z.; Liu, R.; Feng, J.; Wang, X. Biomarkers used in Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Ageing research reviews 2022, 74, 101544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurk, S.; Koren, S.; Rhie, A.; Rautiainen, M.; Bzikadze, A.V.; Mikheenko, A.; Vollger, M.R.; Altemose, N.; Uralsky, L.; Gershman, A.; et al. The complete sequence of a human genome. Science 2022, 376, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoni, V. The effect of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) genotype on biomarkers of amyloidogenesis, tau pathology and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine 2011, 49, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nature Reviews Neurology 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack Jr, C.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA research framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Provenzano, F.A.; Small, S.A.; Initiative, A.D.N. A deep learning MRI approach outperforms other biomarkers of prodromal Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy. [CrossRef]
- Saleem, T.J.; Zahra, S.R.; Wu, F.; Alwakeel, A.; Alwakeel, M.; Jeribi, F.; Hijji, M. Deep Learning-Based Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine 2022, 12, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.J.; Dammer, E.B.; Wang, G.; Seyfried, N.T.; Levey, A.I. Proteomics of protein post-translational modifications implicated in neurodegeneration. Translational neurodegeneration 2014, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, G.; Na, C.H.; Renuse, S.; Madugundu, A.; Albert, M.; Moghekar, A.; Pandey, A. Phosphotyrosine profiling of human cerebrospinal fluid. Clinical proteomics 2018, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, A.R.; Bach, S.B.; Perry, G. Analysis of post-translational modifications in Alzheimer’s disease by mass spectrometry. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease 2019, 1865, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.S.; Kayed, R.; Abate, G.; Uberti, D.; Kinnon, P.; Piccirella, S. Post-translational Modifications of the p53 Protein and the Impact in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review of the Literature. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2022, 14, 835288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, R.; Jacquemin, C.; Villain, N.; Fenaille, F.; Lamari, F.; Becher, F. Mass spectrometry for neurobiomarker discovery: The relevance of post-translational modifications. Cells 2022, 11, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouton, P.R.; Martin, L.J.; Calhoun, M.E.; Dal Forno, G.; Price, D.L. Cognitive decline strongly correlates with cortical atrophy in Alzheimer’s dementia. Neurobiology of aging 1998, 19, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestor, S.M.; Rupsingh, R.; Borrie, M.; Smith, M.; Accomazzi, V.; Wells, J.L.; Fogarty, J.; Bartha, R.; Initiative, A.D.N. Ventricular enlargement as a possible measure of Alzheimer’s disease progression validated using the Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative database. Brain 2008, 131, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.L.; Ganaraja, B.; Murlimanju, B.; Joy, T.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Agrawal, A. Hippocampus and its involvement in Alzheimer’s disease: a review. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beata, B.K.; Wojciech, J.; Johannes, K.; Piotr, L.; Barbara, M. Alzheimer’s disease—biochemical and psychological background for diagnosis and treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meftah, S.; Gan, J. Alzheimer’s disease as a synaptopathy: Evidence for dysfunction of synapses during disease progression. Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience 2023, 15, 1129036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Oliveros, A.; Jang, M.H. Dysfunctional mitochondrial bioenergetics and synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer disease. International neurourology journal 2019, 23, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Ma, X.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X. Mitochondria dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recent advances. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2020, 15, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Sabatini, B.L.; Südhof, T.C. Synapses and Alzheimer’s disease. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 2012, 4, a005777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Rawal, R.; Sharma, P.; Singh, T.; Singh, M.; Singh, V. Mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: opportunities for drug development. Current Neuropharmacology 2022, 20, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuzy, A.; Ashton, N.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Dodich, A.; Boccardi, M.; Corre, J.; Drzezga, A.; Nordberg, A.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. 2020 update on the clinical validity of cerebrospinal fluid amyloid, tau, and phospho-tau as biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in the context of a structured 5-phase development framework. European journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging 2021, 48, 2121–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Strooper, B.; Karran, E. The cellular phase of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 2016, 164, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyck, C.H. Anti-amyloid-β monoclonal antibodies for Alzheimer’s disease: pitfalls and promise. Biological psychiatry 2018, 83, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintun, M.A.; Lo, A.C.; Duggan Evans, C.; Wessels, A.M.; Ardayfio, P.A.; Andersen, S.W.; Shcherbinin, S.; Sparks, J.; Sims, J.R.; Brys, M.; et al. Donanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2021, 384, 1691–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s disease. New England Journal of Medicine 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenaro, E.; Piacentino, G.; Constantin, G. The blood-brain barrier in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of disease 2017, 107, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hye, A.; Lynham, S.; Thambisetty, M.; Causevic, M.; Campbell, J.; Byers, H.; Hooper, C.; Rijsdijk, F.; Tabrizi, S.; Banner, S.; et al. Proteome-based plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2006, 129, 3042–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodes, R.J.; Buckholtz, N. Accelerating medicines partnership: Alzheimer’s disease (AMP-AD) knowledge portal aids Alzheimer’s drug discovery through open data sharing. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets 2016, 20, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, M.; Hernández, F.; Avila, J. Protein biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease at different stages of neurodegeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, L.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, D.; Asthana, M.K.; Lalhlenmawia, H.; Kumar, A.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Kumar, D. Promising protein biomarkers in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Metabolic Brain Disease 2022, 37, 1727–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klyucherev, T.O.; Olszewski, P.; Shalimova, A.A.; Chubarev, V.N.; Tarasov, V.V.; Attwood, M.M.; Syvänen, S.; Schiöth, H.B. Advances in the development of new biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Translational Neurodegeneration 2022, 11, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haytural, H.; Benfeitas, R.; Schedin-Weiss, S.; Bereczki, E.; Rezeli, M.; Unwin, R.D.; Wang, X.; Dammer, E.B.; Johnson, E.C.; Seyfried, N.T.; et al. Insights into the changes in the proteome of Alzheimer disease elucidated by a meta-analysis. Scientific data 2021, 8, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetterberg, H. Biofluid-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease–related pathologies: An update and synthesis of the literature. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2022, 18, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penque, D. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry for biomarker discovery. Proteomics–Clinical Applications 2009, 3, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catherman, A.D.; Skinner, O.S.; Kelleher, N.L. Top down proteomics: facts and perspectives. Biochemical and biophysical research communications 2014, 445, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Takio, K.; Ogawara, M.; Selkoe, D. Mass spectrometry of purified amyloid beta protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1992, 267, 17082–17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Morishima-Kawashima, M.; Takio, K.; Suzuki, M.; Titani, K.; Ihara, Y. Protein sequence and mass spectrometric analyses of tau in the Alzheimer’s disease brain. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1992, 267, 17047–17054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, E.; Nayak, S.; Faustin, A.; Pires, G.; Hickman, R.A.; Askenazi, M.; Cohen, M.; Haldiman, T.; Kim, C.; Han, X.; et al. Proteomic differences in amyloid plaques in rapidly progressive and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Acta neuropathologica 2017, 133, 933–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, F.; Ge, W.; Ma, C. Quantitative proteomics reveals distinct composition of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2019, 15, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, R.; Hurtado, M.L.; Jackson, R.J.; Eaton, S.L.; Herrmann, A.G.; Colom-Cadena, M.; Tzioras, M.; King, D.; Rose, J.; Tulloch, J.; et al. Comparative profiling of the synaptic proteome from Alzheimer’s disease patients with focus on the APOE genotype. Acta neuropathologica communications 2019, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.Y.K.; Nouwens, A.S.; Dodd, P.R.; Etheridge, N. The synaptic proteome in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2013, 9, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Park, J.E.; Sze, S.K. Quantitative profiling brain proteomes revealed mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular brain 2019, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.C.; Dammer, E.B.; Duong, D.M.; Ping, L.; Zhou, M.; Yin, L.; Higginbotham, L.A.; Guajardo, A.; White, B.; Troncoso, J.C.; et al. Large-scale proteomic analysis of Alzheimer’s disease brain and cerebrospinal fluid reveals early changes in energy metabolism associated with microglia and astrocyte activation. Nature medicine 2020, 26, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereczki, E.; Branca, R.M.; Francis, P.T.; Pereira, J.B.; Baek, J.H.; Hortobágyi, T.; Winblad, B.; Ballard, C.; Lehtiö, J.; Aarsland, D. Synaptic markers of cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases: a proteomic approach. Brain 2018, 141, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, B.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.C.; Yu, K.; Dey, K.K.; Yarbro, J.M.; Han, X.; Lutz, B.M.; Rao, S.; et al. Deep multilayer brain proteomics identifies molecular networks in Alzheimer’s disease progression. Neuron 2020, 105, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Mucke, L. Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell 2012, 148, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.A.; Higgins, G.A. Alzheimer’s disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Science 1992, 256, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glenner, G.G.; Wong, C.W. The nature and pathogenesis of the amyloid deposits in Alzheimer’s disease. In Amyloidosis; Springer, 1986; pp. 227–242. [CrossRef]
- Goldgaber, D.; Lerman, M.I.; McBride, O.W.; Saffiotti, U.; Gajdusek, D.C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer’s disease. Science 1987, 235, 877–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goate, A.; Chartier-Harlin, M.C.; Mullan, M.; Brown, J.; Crawford, F.; Fidani, L.; Giuffra, L.; Haynes, A.; Irving, N.; James, L.; et al. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 1991, 349, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, F.A. A unifying hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: from plaques to neurodegeneration. Trends in neurosciences 2019, 42, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.w. The γ-secretase complex: from structure to function. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 2014, 8, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, M.; Giacomazza, D.; San Biagio, P. Alzheimer’s disease: biological aspects, therapeutic perspectives and diagnostic tools. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2012, 24, 244102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villemagne, V.L.; Burnham, S.; Bourgeat, P.; Brown, B.; Ellis, K.A.; Salvado, O.; Szoeke, C.; Macaulay, S.L.; Martins, R.; Maruff, P.; et al. Amyloid β deposition, neurodegeneration, and cognitive decline in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: a prospective cohort study. The Lancet Neurology 2013, 12, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.T.; Lourenco, M.V.; Oliveira, M.M.; De Felice, F.G. Soluble amyloid-β oligomers as synaptotoxins leading to cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in cellular neuroscience 2015, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koffie, R.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Spires-Jones, T.L. Alzheimer’s disease: synapses gone cold. Molecular neurodegeneration 2011, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, A.; Monjazeb, S.; Milton, S.; Glabe, C.G. Familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations within the amyloid precursor protein alter the aggregation and conformation of the amyloid-β peptide. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2017, 292, 3172–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barykin, E.P.; Mitkevich, V.A.; Kozin, S.A.; Makarov, A.A. Amyloid β modification: a key to the sporadic Alzheimer’s disease? Frontiers in genetics 2017, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.B.; Janelidze, S.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Kvartsberg, H.; Brinkmalm, A.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Stomrud, E.; Smith, R.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Untangling the association of amyloid-β and tau with synaptic and axonal loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2021, 144, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattson, M.P.; Chan, S.L. Neuronal and glial calcium signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell calcium 2003, 34, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, J.W.; Bemiller, S.M.; Murtishaw, A.S.; Leisgang, A.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Lamb, B.T. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Translational Research & Clinical Interventions 2018, 4, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustbader, J.W.; Cirilli, M.; Lin, C.; Xu, H.W.; Takuma, K.; Wang, N.; Caspersen, C.; Chen, X.; Pollak, S.; Chaney, M.; et al. ABAD directly links Aß to mitochondrial toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 2004, 304, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Ma, L.; Wei, W.; Li, Z.; Chang, S.; Wen, J.; Sun, J.; Li, H. Role of Aβ in Alzheimer’s-related synaptic dysfunction. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 2022, 10, 964075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Martinez, L.; Maccioni, R.B.; Andrade, V.; Navarrete, L.P.; Pastor, M.G.; Ramos-Escobar, N. Neuroinflammation as a common feature of neurodegenerative disorders. Frontiers in pharmacology 2019, 10, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.W. Role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedical reports 2016, 4, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, L. Targeting autophagy for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: challenges and opportunities. Frontiers in molecular neuroscience 2019, 12, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciarelli, R.; Fedele, E. The amyloid cascade hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: it’s time to change our mind. Current neuropharmacology 2017, 15, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Goernitz, A.; Buerger, K. Advances in the development of biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: from CSF total tau and Aβ1–42 proteins to phosphorylated tau protein. Brain research bulletin 2003, 61, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapiola, T.; Alafuzoff, I.; Herukka, S.K.; Parkkinen, L.; Hartikainen, P.; Soininen, H.; Pirttilä, T. Cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid 42 and tau proteins as biomarkers of Alzheimer-type pathologic changes in the brain. Archives of neurology 2009, 66, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, H.; Shigemoto, Y.; Sato, N. Neuroimaging of Alzheimer’s disease: focus on amyloid and tau PET. Japanese journal of radiology 2019, 37, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfried, N.T.; Dammer, E.B.; Swarup, V.; Nandakumar, D.; Duong, D.M.; Yin, L.; Deng, Q.; Nguyen, T.; Hales, C.M.; Wingo, T.; et al. A multi-network approach identifies protein-specific co-expression in asymptomatic and symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Cell systems 2017, 4, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Kim, S.J.; Hong, S.; Kim, Y. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease utilizing amyloid and tau as fluid biomarkers. Experimental & molecular medicine 2019, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, M.N.; Shi, J.; Arnold, L.; McGeer, P. [P2–255]: SALIVARY AMYLOID-BETA PROTEIN LEVELS CAN DIAGNOSE ALZHEIMER DISEASE AND PREDICT ITS FUTURE ONSET. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2017, 13, P710–P711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Sheikh, Z.; Subramanian, M. The Eye as a Diagnostic Tool for Alzheimer’s Disease. Life 2023, 13, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiner, S.; Sauer, M.; Visser, P.J.; Tijms, B.M.; Vorontsov, E.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Gobom, J. Optimized sample preparation and data analysis for TMT proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid applied to the identification of Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Clinical Proteomics 2022, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami, A. Alzheimer’s disease: The role of proteins in formation, mechanisms, and new therapeutic approaches. Neuroscience Letters, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewczuk, P.; Esselmann, H.; Meyer, M.; Wollscheid, V.; Neumann, M.; Otto, M.; Maler, J.M.; Rüther, E.; Kornhuber, J.; Wiltfang, J. The amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide pattern in cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer’s disease: evidence of a novel carboxyterminally elongated Aβ peptide. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 2003, 17, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, P.E.; Verbeek, M.M.; van Groen, T.; Claassen, J.A. Reviewing reasons for the decreased CSF Abeta42 concentration in Alzheimer disease 2012. [CrossRef]
- Begcevic, I.; Brinc, D.; Brown, M.; Martinez-Morillo, E.; Goldhardt, O.; Grimmer, T.; Magdolen, V.; Batruch, I.; Diamandis, E.P. Brain-related proteins as potential CSF biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: A targeted mass spectrometry approach. Journal of Proteomics 2018, 182, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Harten, A.C.; Visser, P.J.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.; Teunissen, C.E.; Blankenstein, M.A.; Scheltens, P.; van der Flier, W.M. Cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42 is the best predictor of clinical progression in patients with subjective complaints. Alzheimer’s & dementia 2013, 9, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjögren, M.; Gisslén, M.; Vanmechelen, E.; Blennow, K. Low cerebrospinal fluid β-amyloid 42 in patients with acute bacterial meningitis and normalization after treatment. Neuroscience letters 2001, 314, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewczuk, P.; Riederer, P.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Verbeek, M.M.; Dubois, B.; Visser, P.J.; Jellinger, K.A.; Engelborghs, S.; Ramirez, A.; Parnetti, L.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid and blood biomarkers for neurodegenerative dementias: An update of the Consensus of the Task Force on Biological Markers in Psychiatry of the World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry. The world journal of biological psychiatry 2018, 19, 244–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H.; Buchhave, P.; Andreasson, U.; Londos, E.; Minthon, L.; Blennow, K. Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease using the CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Dementia and geriatric cognitive disorders 2007, 23, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Mattsson, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Vanderstichele, H.; Lindberg, O.; van Westen, D.; Stomrud, E.; Minthon, L.; Blennow, K.; et al. CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 and Aβ42/Aβ38 ratios: better diagnostic markers of Alzheimer disease. Annals of clinical and translational neurology 2016, 3, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewczuk, P.; Esselmann, H.; Otto, M.; Maler, J.M.; Henkel, A.W.; Henkel, M.K.; Eikenberg, O.; Antz, C.; Krause, W.R.; Reulbach, U.; et al. Neurochemical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s dementia by CSF Aβ42, Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio and total tau. Neurobiology of aging 2004, 25, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fandos, N.; Pérez-Grijalba, V.; Pesini, P.; Olmos, S.; Bossa, M.; Villemagne, V.L.; Doecke, J.; Fowler, C.; Masters, C.L.; Sarasa, M.; et al. Plasma amyloid β 42/40 ratios as biomarkers for amyloid β cerebral deposition in cognitively normal individuals. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring 2017, 8, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H.; Vanmechelen, E.; Vanderstichele, H.; Andreasson, U.; Londos, E.; Wallin, A.; Minthon, L.; Blennow, K. Evaluation of plasma Aβ40 and Aβ42 as predictors of conversion to Alzheimer’s disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiology of aging 2010, 31, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, G.S. Amyloid-β and tau: the trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA neurology 2014, 71, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Takio, K.; Ogawara, M.; Selkoe, D.J. Mass spectrometry of purified amyloid beta protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1992, 267, 17082–17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sweeney, D.; Gandy, S.E.; Sisodia, S.S. The Profile of Soluble Amyloid β Protein in Cultured Cell Media: detection and quantification of amyloid β protein and variants by immunoprecipitation-mass spectrometry. Journal of Biological Chemistry 1996, 271, 31894–31902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oe, T.; Ackermann, B.L.; Inoue, K.; Berna, M.J.; Garner, C.O.; Gelfanova, V.; Dean, R.A.; Siemers, E.R.; Holtzman, D.M.; Farlow, M.R.; et al. Quantitative analysis of amyloid β peptides in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease patients by immunoaffinity purification and stable isotope dilution liquid chromatography/negative electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry: An International Journal Devoted to the Rapid Dissemination of Up-to-the-Minute Research in Mass Spectrometry 2006, 20, 3723–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, I.; Vos, S.; Verhey, F.; Scheltens, P.; Teunissen, C.; Engelborghs, S.; Sleegers, K.; Frisoni, G.; Blin, O.; Richardson, J.C.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of neurodegeneration, synaptic integrity, and astroglial activation across the clinical Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2019, 15, 644–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, P.J.; Reus, L.M.; Gobom, J.; Jansen, I.; Dicks, E.; Van der Lee, S.J.; Tsolaki, M.; Verhey, F.R.; Popp, J.; Martinez-Lage, P.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid tau levels are associated with abnormal neuronal plasticity markers in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular neurodegeneration 2022, 17, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthélemy, N.R.; Gabelle, A.; Hirtz, C.; Fenaille, F.; Sergeant, N.; Schraen-Maschke, S.; Vialaret, J.; Buée, L.; Junot, C.; Becher, F.; et al. Differential mass spectrometry profiles of tau protein in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, and dementia with lewy bodies. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2016, 51, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Ortiz, F.; Kac, P.R.; Brum, W.S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Karikari, T.K. Plasma phospho-tau in Alzheimer’s disease: towards diagnostic and therapeutic trial applications. Molecular neurodegeneration 2023, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashton, N.J.; Benedet, A.L.; Pascoal, T.A.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Brum, W.S.; Mathotaarachchi, S.; Therriault, J.; Savard, M.; Chamoun, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid p-tau231 as an early indicator of emerging pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. EBioMedicine 2022, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metaxas, A.; Kempf, S.J. Neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease: elucidation of the molecular mechanism by immunohistochemistry and tau protein phospho-proteomics. Neural regeneration research 2016, 11, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herukka, S.K.; Simonsen, A.H.; Andreasen, N.; Baldeiras, I.; Bjerke, M.; Blennow, K.; Engelborghs, S.; Frisoni, G.B.; Gabryelewicz, T.; Galluzzi, S.; et al. Recommendations for cerebrospinal fluid Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in the diagnostic evaluation of mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2017, 13, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottiez, G.; Yang, L.; Stewart, T.; Song, N.; Aro, P.; Galasko, D.R.; Quinn, J.F.; Peskind, E.R.; Shi, M.; Zhang, J. Mass-spectrometry-based method to quantify in parallel tau and amyloid β 1–42 in CSF for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of proteome research 2017, 16, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppälä, T.; Nerg, O.; Koivisto, A.; Rummukainen, J.; Puli, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Pyykkö, O.; Helisalmi, S.; Alafuzoff, I.; Hiltunen, M.; et al. CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer disease correlate with cortical brain biopsy findings. Neurology 2012, 78, 1568–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blennow, K.; Hampel, H.; Weiner, M.; Zetterberg, H. Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer disease. Nature Reviews Neurology 2010, 6, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strozyk, D.; Blennow, K.; White, L.; Launer, L. CSF Aβ 42 levels correlate with amyloid-neuropathology in a population-based autopsy study. Neurology 2003, 60, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardanaz, C.G.; Ramírez, M.J.; Solas, M. Brain metabolic alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummel, N.G.; Butterfield, D.A. Altered metabolism in Alzheimer disease brain: Role of oxidative stress. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2022, 36, 1289–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, I.V.; Proza, J.F.; Sohrabji, F.; Lawler, J.M. Vascular and metabolic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: a review. Experimental biology and medicine 2011, 236, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webers, A.; Heneka, M.T.; Gleeson, P.A. The role of innate immune responses and neuroinflammation in amyloid accumulation and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Immunology and cell biology 2020, 98, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuppo, E.E.; Arias, H.R. The role of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology 2005, 37, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, A.; Phillips, E.; Zheng, R.; Biju, M.; Kuruvilla, T. Evidence for neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Progress in Neurology and Psychiatry 2016, 20, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, S.E.; Allison, E.K.; El Khoury, J. Microglial dysfunction and defective β-amyloid clearance pathways in aging Alzheimer’s disease mice. Journal of Neuroscience 2008, 28, 8354–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markesbery, W.R. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 1997, 23, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, D. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: a reappraisal. Trends in pharmacological sciences 2008, 29, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagno, E.; Guglielmotto, M.; Vasciaveo, V.; Tabaton, M. Oxidative stress and beta amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Which comes first: The chicken or the egg? Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galasko, D.; Montine, T.J. Biomarkers of oxidative damage and inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomarkers in medicine 2010, 4, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, J.M.; Geyer, P.E.; Müller, J.B.; Strauss, M.T.; Koch, M.; Leypoldt, F.; Koertvelyessy, P.; Bittner, D.; Schipke, C.G.; Incesoy, E.I.; et al. Proteome profiling in cerebrospinal fluid reveals novel biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular systems biology 2020, 16, e9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehiman, S.H.; Lim, S.M.; Neoh, C.F.; Majeed, A.B.A.; Chin, A.V.; Tan, M.P.; Kamaruzzaman, S.B.; Ramasamy, K. Proteomics as a reliable approach for discovery of blood-based Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing research reviews 2020, 60, 101066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buccellato, F.R.; D’Anca, M.; Fenoglio, C.; Scarpini, E.; Galimberti, D. Role of oxidative damage in alzheimer’s disease and neurodegeneration: From pathogenic mechanisms to biomarker discovery. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, M.M.; Syrjanen, J.A.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Vemuri, P.; Skoog, I.; Machulda, M.M.; Kremers, W.K.; Knopman, D.S.; Jack Jr, C.; et al. Plasma and CSF neurofilament light: relation to longitudinal neuroimaging and cognitive measures. Neurology 2019, 93, e252–e260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, K.; Gupta, V.B.; Villemagne, V.L.; Eratne, D.; Graham, P.L.; Fowler, C.; Bourgeat, P.; Li, Q.X.; Collins, S.; Bush, A.I.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid neurofilament light concentration predicts brain atrophy and cognition in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia: Diagnosis, Assessment & Disease Monitoring 2020, 12, e12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoonsari, P.E.; Häggmark, A.; Lönnberg, M.; Mikus, M.; Kilander, L.; Lannfelt, L.; Bergquist, J.; Ingelsson, M.; Nilsson, P.; Kultima, K.; et al. Analysis of the cerebrospinal fluid proteome in Alzheimer’s disease. PloS one 2016, 11, e0150672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsson, P.; Sjögren, M. The use of proteomics in biomarker discovery in neurodegenerative diseases. Disease markers.
- Ho, L.; Sharma, N.; Blackman, L.; Festa, E.; Reddy, G.; Pasinetti, G.M. From proteomics to biomarker discovery in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain research reviews 2005, 48, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilento, E.M.; Jin, L.; Stewart, T.; Shi, M.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, J. Mass spectrometry: A platform for biomarker discovery and validation for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Journal of neurochemistry 2019, 151, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Haque, R.U.; Dammer, E.B.; Duong, D.M.; Ping, L.; Johnson, E.C.; Lah, J.J.; Levey, A.I.; Seyfried, N.T. Targeted mass spectrometry to quantify brain-derived cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Clinical proteomics 2020, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, C.M.; Dammer, E.B.; Ping, L.; Duong, D.M.; Modeste, E.; Carter, E.K.; Johnson, E.C.; Levey, A.I.; Lah, J.J.; Roberts, B.R.; et al. Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Protein Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Scientific Data 2023, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandi, J.; Noberini, R.; Bonaldi, T.; Cecconi, D. Advances in enrichment methods for mass spectrometry-based proteomics analysis of post-translational modifications. Journal of Chromatography A, 4633. [Google Scholar]
- Sarihan, M.; Albayrak, M.G.B.; Kasap, M.; Akpinar, G.; Kocyigit, E. An experimental workflow for enrichment of low abundant proteins from human serum for the discovery of serum biomarkers. Journal of biological methods 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellar, N.A.; Karnoup, A.S.; Albers, D.R.; Langhorst, M.L.; Young, S.A. Immunodepletion of high abundance proteins coupled on-line with reversed-phase liquid chromatography: a two-dimensional LC sample enrichment and fractionation technique for mammalian proteomics. Journal of Chromatography B 2009, 877, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldacci, F.; Lista, S.; Cavedo, E.; Bonuccelli, U.; Hampel, H. Diagnostic function of the neuroinflammatory biomarker YKL-40 in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Expert review of proteomics 2017, 14, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroudis, I.; Chowdhury, R.; Petridis, F.; Karantali, E.; Chatzikonstantinou, S.; Balmus, I.M.; Luca, I.S.; Ciobica, A.; Kazis, D. YKL-40 as a Potential Biomarker for the Differential Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Medicina 2021, 58, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gispert, J.D.; Monté, G.C.; Falcon, C.; Tucholka, A.; Rojas, S.; Sánchez-Valle, R.; Antonell, A.; Lladó, A.; Rami, L.; Molinuevo, J.L. CSF YKL-40 and pTau181 are related to different cerebral morphometric patterns in early AD. Neurobiology of aging 2016, 38, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heslegrave, A.; Heywood, W.; Paterson, R.; Magdalinou, N.; Svensson, J.; Johansson, P.; Öhrfelt, A.; Blennow, K.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.; et al. Increased cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 concentration in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular neurodegeneration 2016, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yin, X.S.; Guo, H.; Han, R.K.; He, R.D.; Chi, L.J.; et al. Elevated osteopontin levels in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Mediators of inflammation 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangishetti, U.; Christina Howell, J.; Perrin, R.J.; Louneva, N.; Watts, K.D.; Kollhoff, A.; Grossman, M.; Wolk, D.A.; Shaw, L.M.; Morris, J.C.; et al. Non-beta-amyloid/tau cerebrospinal fluid markers inform staging and progression in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s research & therapy 2018, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Aguilar, C.; Kiddle, S.J.; Doyle, O.; Thambisetty, M.; Muehlboeck, S.; Sattlecker, M.; Newhouse, S.; Lovestone, S.; Dobson, R.; et al. A subset of cerebrospinal fluid proteins from a multi-analyte panel associated with brain atrophy, disease classification and prediction in Alzheimer’s disease. PloS one 2015, 10, e0134368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordengen, K.; Kirsebom, B.E.; Henjum, K.; Selnes, P.; Gísladóttir, B.; Wettergreen, M.; Torsetnes, S.B.; Grøntvedt, G.R.; Waterloo, K.K.; Aarsland, D.; et al. Glial activation and inflammation along the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Journal of neuroinflammation 2019, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaz, I.; Lerer-Goldshtein, T.; Okamoto, H.; Appelbaum, L. Reduced synaptic density and deficient locomotor response in neuronal activity-regulated pentraxin 2a mutant zebrafish. The FASEB Journal 2015, 29, 1220–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.F.; Xu, D.; Craig, M.T.; Pelkey, K.A.; Chien, C.C.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Resnick, S.; Pletnikova, O.; Salmon, D.; et al. NPTX2 and cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Elife 2017, 6, e23798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, A.; Willette, A.; Initiative, A.D.N.; et al. Neuronal Pentraxin 2 predicts medial temporal atrophy and memory decline across the Alzheimer’s disease spectrum. Brain, behavior, and immunity 2016, 58, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumm, C.; Hiebel, C.; Hanstein, R.; Purrio, M.; Nagel, H.; Conrad, A.; Lutz, B.; Behl, C.; Clement, A.B. Cannabinoid receptor 1 deficiency in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease leads to enhanced cognitive impairment despite of a reduction in amyloid deposition. Neurobiology of aging 2013, 34, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporesi, E.; Nilsson, J.; Brinkmalm, A.; Becker, B.; Ashton, N.J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Fluid biomarkers for synaptic dysfunction and loss. Biomarker insights 2020, 15, 1177271920950319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayon, L.; Núñez Galindo, A.; Wojcik, J.; Cominetti, O.; Corthésy, J.; Oikonomidi, A.; Henry, H.; Kussmann, M.; Migliavacca, E.; Severin, I.; et al. Alzheimer disease pathology and the cerebrospinal fluid proteome. Alzheimer’s research & therapy 2018, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blennow, K. A review of fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: moving from CSF to blood. Neurology and therapy 2017, 6, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dey, K.K.; Chen, P.C.; Li, Y.; Niu, M.; Cho, J.H.; Wang, X.; Bai, B.; Jiao, Y.; Chepyala, S.R.; et al. Integrated analysis of ultra-deep proteomes in cortex, cerebrospinal fluid and serum reveals a mitochondrial signature in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecular neurodegeneration 2020, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashleigh, T.; Swerdlow, R.H.; Beal, M.F. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2023, 19, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, L.; He, F.; Meng, F.; Liu, X.; Su, Y.; Su, X.; Luo, B.; Peng, G. Identification of Candidate Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease via Multiplex Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum Proteomics. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 14225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öhrfelt, A.; Johansson, P.; Wallin, A.; Andreasson, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Svensson, J. Increased cerebrospinal fluid levels of ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Dementia and geriatric cognitive disorders extra 2016, 6, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasserini, D.; Parnetti, L.; Andreasson, U.; Zetterberg, H.; Giannandrea, D.; Calabresi, P.; Blennow, K. CSF levels of heart fatty acid binding protein are altered during early phases of Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2010, 22, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciotti, S.; Wojdała, A.L.; Bellomo, G.; Toja, A.; Chipi, E.; Piersma, S.R.; Pham, T.V.; Gaetani, L.; Jimenez, C.R.; Parnetti, L.; et al. Potential diagnostic value of CSF metabolism-related proteins across the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy 2023, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginbotham, L.; Ping, L.; Dammer, E.B.; Duong, D.M.; Zhou, M.; Gearing, M.; Hurst, C.; Glass, J.D.; Factor, S.A.; Johnson, E.C.; et al. Integrated proteomics reveals brain-based cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in asymptomatic and symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. Science advances 2020, 6, eaaz9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelan, C.D.; Mattsson, N.; Nagle, M.W.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Hyde, C.; Janelidze, S.; Stomrud, E.; Lee, J.; Fitz, L.; Samad, T.A.; et al. Multiplex proteomics identifies novel CSF and plasma biomarkers of early Alzheimer’s disease. Acta neuropathologica communications 2019, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miners, J.S.; Baig, S.; Palmer, J.; Palmer, L.E.; Kehoe, P.G.; Love, S. SYMPOSIUM: Clearance of Aβ from the Brain in Alzheimer’s Disease: Aβ-Degrading Enzymes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain pathology 2008, 18, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshi, K.; Ito, H.; Abe, E.; Fuwa, T.J.; Kanno, M.; Murakami, Y.; Abe, M.; Murakami, T.; Yoshihara, A.; Ugawa, Y.; et al. Transferrin biosynthesized in the brain is a novel biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. Metabolites 2021, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.L. The clinical plasma proteome: a survey of clinical assays for proteins in plasma and serum. Clinical chemistry 2010, 56, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, N.L.; Anderson, N.G. The human plasma proteome: history, character, and diagnostic prospects. Molecular & cellular proteomics 2002, 1, 845–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, A.L.; Westwood, S.; Lovestone, S. Blood-based proteomic biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Frontiers in neurology 2015, 6, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood–brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nature Reviews Neurology 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budelier, M.M.; Bateman, R.J. Biomarkers of Alzheimer disease. The journal of applied laboratory medicine 2020, 5, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, P.; Hampel, H.; Buerger, K. Biological marker candidates of Alzheimer’s disease in blood, plasma, and serum. CNS neuroscience & therapeutics 2009, 15, 358–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citron, M.; Vigo-Pelfrey, C.; Teplow, D.B.; Miller, C.; Schenk, D.; Johnston, J.; Winblad, B.; Venizelos, N.; Lannfelt, L.; Selkoe, D.J. Excessive production of amyloid beta-protein by peripheral cells of symptomatic and presymptomatic patients carrying the Swedish familial Alzheimer disease mutation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1994, 91, 11993–11997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Kaneko, N.; Villemagne, V.L.; Kato, T.; Doecke, J.; Doré, V.; Fowler, C.; Li, Q.X.; Martins, R.; Rowe, C.; et al. High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2018, 554, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Grijalba, V.; Romero, J.; Pesini, P.; Sarasa, L.; Monleon, I.; San-Jose, I.; Arbizu, J.; Martinez-Lage, P.; Munuera, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plasma Aβ42/40 ratio detects early stages of Alzheimer’s disease and correlates with CSF and neuroimaging biomarkers in the AB255 study. The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease 2019, 6, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthélemy, N.R.; Horie, K.; Sato, C.; Bateman, R.J. Blood plasma phosphorylated-tau isoforms track CNS change in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2020, 217, e20200861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhatwal, J.P.; Schultz, A.P.; Dang, Y.; Ostaszewski, B.; Liu, L.; Yang, H.S.; Johnson, K.A.; Sperling, R.A.; Selkoe, D.J. Plasma N-terminal tau fragment levels predict future cognitive decline and neurodegeneration in healthy elderly individuals. Nature communications 2020, 11, 6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Zetterberg, H.; Lopera, F.; Stomrud, E.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Serrano, G.E.; Leuzy, A.; et al. Discriminative accuracy of plasma phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders. Jama 2020, 324, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, A.; Karikari, T.K.; Poole, T.; Ashton, N.J.; Lantero Rodriguez, J.; Khatun, A.; Swift, I.; Heslegrave, A.J.; Abel, E.; Chung, E.; et al. Plasma phospho-tau181 in presymptomatic and symptomatic familial Alzheimer’s disease: a longitudinal cohort study. Molecular psychiatry 2021, 26, 5967–5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnov, D.S.; Ashton, N.J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Simrén, J.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Karikari, T.K.; Hiniker, A.; Rissman, R.A.; Salmon, D.P.; et al. Plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in relation to neuropathology and cognitive change. Acta neuropathologica 2022, 143, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissot, C.; L. Benedet, A.; Therriault, J.; Pascoal, T.A.; Lussier, F.Z.; Saha-Chaudhuri, P.; Chamoun, M.; Savard, M.; Mathotaarachchi, S.S.; Bezgin, G.; et al. Plasma pTau181 predicts cortical brain atrophy in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simrén, J.; Leuzy, A.; Karikari, T.K.; Hye, A.; Benedet, A.L.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Schöll, M.; Mecocci, P.; Vellas, B.; et al. The diagnostic and prognostic capabilities of plasma biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2021, 17, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janelidze, S.; Mattsson, N.; Palmqvist, S.; Smith, R.; Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; Chai, X.; Proctor, N.K.; Eichenlaub, U.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nature medicine 2020, 26, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, E.R.; Beiser, A.S.; O’Donnell, A.; Yang, Q.; Ghosh, S.; Gonzales, M.M.; Himali, J.J.; Satizabal, C.L.; Johnson, K.A.; Tracy, R.P.; et al. Blood phosphorylated tau 181 as a biomarker for amyloid burden on brain PET in cognitively healthy adults. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2022, 87, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, B.; Lautner, R.; Andreasson, U.; Öhrfelt, A.; Portelius, E.; Bjerke, M.; Hölttä, M.; Rosén, C.; Olsson, C.; Strobel, G.; et al. CSF and blood biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Neurology 2016, 15, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nature Reviews Neurology 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiki, A.; Kamada, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Terao, C.; Shimoda, F.; Tomita, N.; Arai, H.; Furukawa, K. Glial fibrillar acidic protein in the cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Journal of neurochemistry 2016, 136, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, K.B.; Aggarwal, N.T.; McAninch, E.A.; Weuve, J.; Barnes, L.L.; Wilson, R.S.; DeCarli, C.; Evans, D.A. Remote blood biomarkers of longitudinal cognitive outcomes in a population study. Annals of neurology 2020, 88, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicognola, C.; Janelidze, S.; Hertze, J.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Hansson, O. Plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein detects Alzheimer pathology and predicts future conversion to Alzheimer dementia in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s research & therapy 2021, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, J.A.; Maxwell, S.; Bena, J.; Bekris, L.M.; Rao, S.M.; Chance, M.; Lamb, B.T.; Leverenz, J.B.; Initiative, A.D.N. Key inflammatory pathway activations in the MCI stage of Alzheimer’s disease. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology 2019, 6, 1248–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Meri, S. Yin and Yang: complement activation and regulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Progress in neurobiology 2003, 70, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Suzuki, H.; Meno, K.; Liu, S.; Korenaga, T.; Uchida, K. Identification of Plasma Proteins as Biomarkers for Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease Using Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 13064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.T.; Wang, L.; Prabakaran, S.; Wengenroth, M.; Lockstone, H.; Koethe, D.; Gerth, C.; Gross, S.; Schreiber, D.; Lilley, K.; et al. Independent protein-profiling studies show a decrease in apolipoprotein A1 levels in schizophrenia CSF, brain and peripheral tissues. Molecular psychiatry 2008, 13, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Namkoong, H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.; Hwang, D.W.; Na, H.R.; Ha, S.A.; Kim, J.R.; Kim, J.W. Fibrinogen gamma-A chain precursor in CSF: a candidate biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. BMC neurology 2007, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, E.M.; Hohman, T.J.; Jefferson, A.L.; Initiative, A.D.N. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 interactions with Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Brain imaging and behavior 2017, 11, 1779–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Jia, X.; Shankar, S.; Olofsson, A.; Brännström, T.; Mu, Y.; Gräslund, A.; Morozova-Roche, L.A.; Jarvet, J.; Wang, C.; et al. The role of pro-inflammatory S100A9 in Alzheimer’s disease amyloid-neuroinflammatory cascade 2013. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Iashchishyn, I.A.; Pansieri, J.; Nyström, S.; Klementieva, O.; Kara, J.; Horvath, I.; Moskalenko, R.; Rofougaran, R.; Gouras, G.; et al. S100A9-driven amyloid-neuroinflammatory cascade in traumatic brain injury as a precursor state for Alzheimer’s disease. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kononikhin, A.S.; Zakharova, N.V.; Semenov, S.D.; Bugrova, A.E.; Brzhozovskiy, A.G.; Indeykina, M.I.; Fedorova, Y.B.; Kolykhalov, I.V.; Strelnikova, P.A.; Ikonnikova, A.Y.; et al. Prognosis of Alzheimer’s disease using quantitative mass spectrometry of human blood plasma proteins and machine learning. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiddle, S.J.; Sattlecker, M.; Proitsi, P.; Simmons, A.; Westman, E.; Bazenet, C.; Nelson, S.K.; Williams, S.; Hodges, A.; Johnston, C.; et al. Candidate blood proteome markers of Alzheimer’s disease onset and progression: a systematic review and replication study. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2014, 38, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudart, J.B.; Djerada, Z.; Nonnonhou, V.; Badr, S.; Bertholon, L.A.; Dammak, A.; Jaidi, Y.; Novella, J.L.; Pallet, N.; Gillery, P.; et al. Incremental Value of CSF Biomarkers in Clinically Diagnosed AD and Non-AD Dementia. Frontiers in Neurology 2020, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Bautista, C.; Álvarez-Sánchez, L.; Pascual, R.; Moreno, M.J.; Baquero, M.; Cháfer-Pericás, C. Clinical usefulness of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 2023, 53, e13910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K. From cerebrospinal fluid to blood: the third wave of fluid biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease 2018, 64, S271–S279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Zetterberg, H.; Masters, C.L.; Lista, S.; Kiddle, S.J.; Batrla, R.; Blennow, K. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer disease: mapping the road to the clinic. Nature Reviews Neurology 2018, 14, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




