1. Introduction
The genus
Flavivirus includes a group of enveloped arthropod-borne viruses [
1]. There are 53 distinct members, of which Dengue virus (DENV), Zika virus (ZIKV), Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), and West Nile virus (WNV) are predominantly implicated in affecting human health. The flavivirus genome is an approximately 11 kb positive-sense single-stranded RNA that encodes a single open reading frame (ORF) flanked by highly conserved 5' and 3' untranslated regions. The ORF encodes 3 structural proteins (capsid [C], pre-membrane [prM], and envelope [E]) and seven non-structural proteins (NS1, NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, and NS5) [
2]. This group is known for its widespread infection across many global regions. The clinical manifestations of human flavivirus infection can be dichotomized into two principal groups: hemorrhagic diseases such as dengue and yellow fever, encompassing systemic infection, hemorrhagic disease, and pyrexia; and neurological diseases including congenital Zika syndrome and Japanese encephalitis, predominantly resulting in neurological sequelae.
The viral life cycle of flaviviruses can be delineated into three primary stages: the initial phase of binding and entry, the subsequent phase of translation and replication, and the final phase of assembly and egress [
2]. In the initial stage of the flavivirus life cycle, virions initially adhere to the cell membrane followed by the binding of the viral E protein to specific cell receptors, triggering endocytosis. Within the endosomal compartment, which is characterized by a slightly acidic milieu, uncoating of the virions occurs. This process culminates in the fusion of the viral envelope with the endosomal membrane [
3]. In the ensuing translation and replication stage, the fusion event facilitates the release of the positive-strand viral RNA genome into the cytoplasm. This genomic RNA serves as a template for the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, namely NS5. NS5 synthesizes an intermediate negative-strand RNA, which subsequently guides the production of progeny positive-strand RNA. These nascent RNAs are then packaged into immature viral particles [
4,
5]. During the final assembly and egress phase, these immature virions are transported to the trans-Golgi network for maturation. The mature virions are then released from the cell through a mechanism that remains to be fully elucidated.
An appropriate animal model is critical for characterizing the pathogenesis of flavivirus infection and evaluating the effectiveness of therapeutic drugs and vaccine candidates. This review demonstrates a comprehensive assessment of current animal models utilized in the research field of eight flaviviruses and delves into the strengths and limitations of each model in detail, helping researchers select the most suitable animal model for flavivirus research based on the findings presented in this paper.
2. Flavivirus infection in humans
2.1. Dengue Virus (DENV)
Globally, four distinct serotypes of the virus have been identified, designated as DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, and DENV-4 [
6]. Each serotype encompasses multiple genotypes, defined by nucleotide variations in the viral genome. Infection with one serotype imparts lifelong immunity against it, while concurrently offering only temporary and partial immunity against the other serotypes. This partial immunity, rather than being protective, predisposes to more severe disease upon subsequent infections with heterologous serotypes, a phenomenon known as antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) [
7]. Same to ZIKV, the principal vectors transmitting DENV are
Aedes aegypti and
Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. Annually, over 100 countries report incidences of dengue fever, placing approximately 3.6 billion individuals at the risk of contracting the infection. Notably, the prevalence of dengue fever has escalated by thirtyfold in the past five decades [
8,
9]. Dengue fever exhibits a broad spectrum of severity. The patients usually manifest symptoms akin to influenza, predominantly characterized by fever, headache, nausea, vomiting, skin rashes, and musculoskeletal pain. In exceptional instances, the disease may progress to more severe diseases such as Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever and Dengue Shock Syndrome, both of which bear a potential for fatality.
2.2. Japanese Encephalitis Virus (JEV)
JEV stands as the predominant etiological agent of viral encephalitis in humans, particularly in some regions across Asia [
10]. JEV spreads between humans and affected animal hosts mainly through the bite of culex tritaeniorhynchus mosquitoes [
11]. Notably, in scenarios devoid of these vectors, JEV transmission among animals can occur via alternative routes, including direct contact, aerosols, and transplacental transfer [
12,
13,
14,
15]. JEV is a neurotropic virus that manifests symptoms such as fever, convulsions, and motor deficits. These manifestations can progress to long-term neuropsychiatric complications [
16]. Individuals under the age of fifteen years are the most susceptible to experiencing the impacts of this viral infection [
17]. Additionally, JEV is capable of inducing peripheral neurological disorders, exemplified by Guillain-Barre syndrome, which is characterized by symptoms including debilitation, paralysis, and respiratory distress [
18,
19]. Furthermore, it is observed that approximately 50% of individuals who survive the JEV infection may subsequently develop a range of enduring complications, encompassing neurological, psychiatric, cognitive, and behavioral disturbances [
20].
2.3. Kyasanur Forest disease virus (KFDV)
KFDV, a member of the tick-borne flavivirus group, is responsible for inducing acute encephalitis and hemorrhagic fever in human populations. Annual estimates show that approximately 500 cases of human KFDV infections occur, accompanied by a case fatality rate ranging from 3 to 5% [
21,
22]. The principal vector facilitating the transmission of KFDV is identified as ticks of the species Haemaphysalis spinigera [
21,
23,
24,
25]. Ticks, particularly in various developmental stages, ingest vertebrate blood and facilitate the transmission of KFDV to a range of avian and mammalian hosts through a process known as co-ingestion. Significantly, the activity period of the adult haemaphysalis spinner overlaps with the spring and summer months, which coincides with the observed increase in KFDV infection incidence among human populations [
26]. The incubation period for Kyasanur Forest disease (KFD) in humans typically ranges from 2 to 4 days [
21,
27]. KFD is clinically characterized by an abrupt onset of high fever and headache, followed by a constellation of symptoms including body aches, diarrhea, anorexia, insomnia, vomiting, myalgia, coughing, and photophobia. Additionally, hemorrhagic manifestations are notable in KFD, evidenced by bleeding from the gums, nasal cavity, or gastrointestinal tract [
27,
28]. Approximately 10 to 20% of KFD cases experience febrile relapses accompanied by a range of neurological symptoms. These manifestations may encompass psychiatric disturbances, lethargy, transient disorientation, confusion, convulsive episodes, tremors, and, in some instances, a loss of consciousness [
28,
29].
2.4. Powassan virus (POWV)
POWV was identified in 1958 and is the only virus present in North America in the tick-borne encephalitis serogroups [
30]. Although the reported cases have remained relatively limited, epidemiological evidence suggests that the prevalence of POWV may be greater than currently acknowledged [
31]. Infection with POWV can manifest as asymptomatic or exhibit moderate to severe symptoms, potentially leading to fatal outcomes. The initial symptoms of acute Powassan disease typically include fever and fatigue. But, approximately 95% of documented cases exhibit neuroinvasive characteristics. The majority of patients with neuroinvasive disease present with encephalitis or meningoencephalitis, characterized by symptoms such as headache, confusion, muscle weakness, focal neurological deficits, and seizures [
31]. The mortality rate associated with POWV infection is approximately 10%. Notably, the case fatality rate (CFR) for encephalitis caused by POWV exceeds 30%, and survivors often experience long-term neurological sequelae [
30,
32].
2.5. Tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV)
TBEV is an endemic tick-borne pathogen in Europe. Over the past four decades, there has been a significant rise in its incidence[
33], with an estimated 10,000 to 13,000 cases globally each year [
34,
35]. TBEV is a neurotropic virus and primarily infects neuronal cells within the host's brain. The clinical manifestations range from mild influenza-like symptoms to more severe forms, such as encephalitis or encephalomyelitis. TBEV is classified into three major subtypes based on phylogenetic analysis: the European, Siberian, and Far Eastern subtypes. Notably, the mortality rate associated with TBEV infection varies depending on the specific subtype of the virus [
36]. In the European context, the mortality rate associated with TBEV typically ranges from 1% to 2%. The fatal outcomes predominantly occur within a span of five to seven days following the emergence of neurological symptoms [
37]. Conversely, infecting with subtypes prevalent in the Far East results in a more severe disease course, with the mortality rate ranging from 5% to 20% [
38]. Additionally, it is observed that approximately 10% to 20% of patients endure long-term or permanent neuropsychiatric sequelae [
39].
2.6. West Nile virus (WNV)
WNV was initially discovered in Uganda in 1937 and still spread in the transmission cycle involving birds and mosquitoes. Humans, serving as incidental hosts, are susceptible to infection primarily through the bites of culex mosquitoes carrying WNV [
40]. Furthermore, infections might occur via blood transfusion, organ transplantation, breast milk feeding, and vertical transmission during pregnancy [
41,
42,
43,
44]. Approximately 80% of human infections are asymptomatic. Of the symptomatic cases, the majority are characterized by fever, headache, and influenza-like symptoms [
45]. Nevertheless, approximately one in every 150 infections with WNV culminates in neurological complications that manifest as meningitis, encephalitis, or acute flaccid paralysis.
2.7. Yellow fever virus (YFV)
YFV is mainly endemic in the tropical regions of South America and Africa, accounting for an estimated 170,000 severe cases and 29,000 to 60,000 deaths annually [
46,
47]. The transmission of YFV has a 'forest cycle' and 'urban cycle' with the latter currently serving as the primary mode of transmission in human populations [
48,
49]. Infection with YFV results in yellow fever, a disease characterized by hemorrhagic fever and multi-organ failures, leading to significant damage to vital organs, including the liver, kidneys, and heart [
50]. Notably, the CFR for patients requiring hospitalization can reach up to 67% in fatal cases.
2.8. Zika virus (ZIKV)
ZIKV was initially identified in Uganda in 1947 and caused an outbreak in Brazil after being dormant for over half a century in 2015-2016 [
51]. ZIKV possesses approximately 10.7 kilobases of RNA genome which encodes a polypeptide composed of roughly 3,400 amino acids [
52,
53,
54]. According to the phylogenetic analysis result, ZIKV can be classified into three phylogenetic lineages, namely, West African lineage, East African lineage, and Asian/American lineage [
55]. In addition to the main transmission route via mosquitoes (
Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus), ZIKV exhibits alternative transmission routes, including the vertical route, unprotected sexual route, and hematogenous (bloodborne) route [
56]. Approximately 80% of ZIKV infections are asymptomatic, while the remaining 20% typically cause only mild illnesses. Crucially, ZIKV infection in pregnant women during the first three months of pregnancy can affect fetal development, leading to microcephaly and ocular defects [
57]. In certain instances, ZIKV infection is associated with the onset of Guillain-Barré syndrome in adults [
58]. As of now, there are no specifically authorized vaccines or pharmaceutical treatments for ZIKV infection.
3. Animal models of flavivirus infection
Appropriate animal models are essential tools for researchers aiming to elucidate the pathogenesis of flavivirus infection, as well as to develop vaccines, antiviral drugs, or antibodies against flaviviruses. In the field of flavivirus research, the most commonly used animal models fall into two main categories: mouse models and non-human primate (NHP) models. Mouse models are further divided into immunocompetent and immunodeficient mice. NHP models typically include Cynomolgus macaques, Rhesus macaques, and Pigtailed macaques.
3.1. Immunocompetent Mice
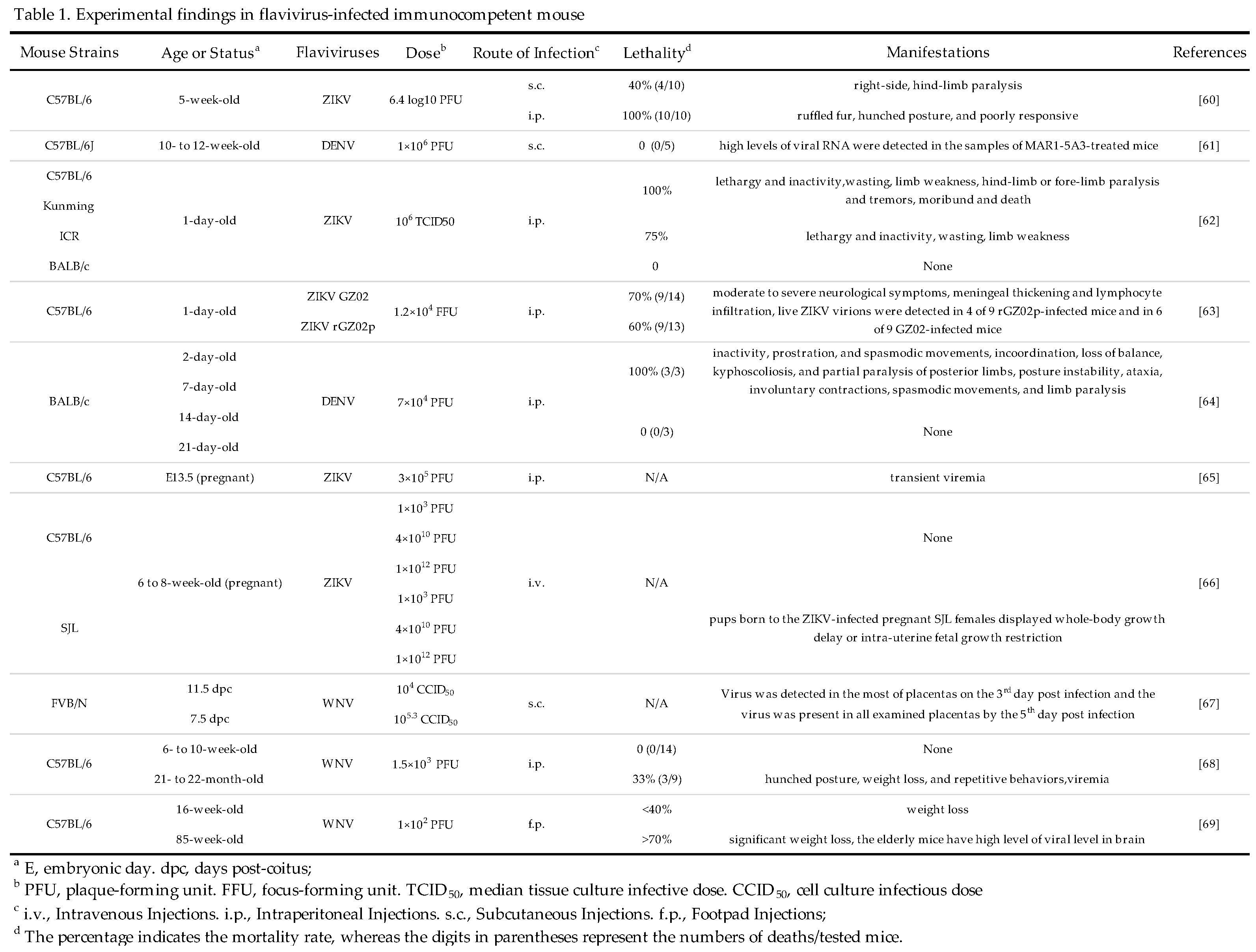
Immunocompetent mice, specifically the BALB/c and C57BL/6 strains, are commonly used as animal models for flavivirus research. Since adult immunocompetent mice naturally resist flavivirus infection, researchers employ four strategies to make these mice as suitable models: Antibody-Mediated Receptor-Blocked Mice, Neonatal Mice, Pregnant Mice, and Elderly Mice.
3.1.1. Antibody-Mediated Receptor-Blocked Mice
Early study has shown that mice lacking interferon (IFN) receptors are more susceptible to flavivirus infections as compared to wild-type (WT) immunocompetent mice[
59]. This discovery led researchers to explore if blocking IFN receptors could enable flavivirus infection in immunocompetent mice. In a pivotal study, Darci R. Smith and colleagues disrupted the Type I IFN response of adult immunocompetent mice by administering Type I IFN receptor (IFNAR1)-blocking antibody (MAb-5A3) intraperitoneally (i.p.) one day before, on the day of, and four days after infection. The mice were infected with ZIKV via subcutaneous (s.c.) or i.p. routes. The team recorded mouse deaths daily and collected blood for viral load analysis on the 4
th day post-infection or at euthanasia time. Control mice, which did not receive MAb-5A3, survived the infection. However, antibody-treated mice exhibited variable mortality rates: 40% for s.c. infection and 100% for i.p. infection. Viremia levels in antibody-treated mice were higher than those in control mice, regardless of the infection route[
60]. In a similar DENV study conducted by Lucas Wilken et al., adult C57BL/6J mice were pre-treated with MAb-5A3 or isotype control antibody and then infected with DENV. The IFNAR1
-/- mice were used as a control group. Following s.c. infection, IFNAR1
-/- mice rapidly lost body weight and met euthanasia criteria within 5 days, while the antibody-treated C57BL/6J mice survived until the end of the observation period. Notably, the viral RNA levels in the sera of MAb-5A3-treated mice were significantly higher than those in the isotype control-treated mice [
61].
These results suggest that adult immunocompetent mice can support flavivirus replication and succumb to lethal flavivirus infection after being blocked the Type I IFN receptor function, which represents a convenient, and easy-to-use platform for the development of next-generation vaccines and antiviral drugs against flaviviruses. But, IFNAR1-blocking antibody is very expensive and required to inject multiple times to maintain the infection status of mice, which limits the widespread application of this animal model.
3.1.2. Neonatal Mice
The innate immune system of adult immunocompetent mice is typically resistant to multiple flaviviruses, including ZIKV and DENV. To explore this further, Shuxuan Li and colleagues selected one-day-old mice from four different strains (C57BL/6, KM, ICR, and BALB/c) and infected them with ZIKV through i.p. injection. They found that all strains, except for BALB/c mice, were susceptible to ZIKV infection. The infected mice exhibited significant weight loss, paralysis in their hind or forelimbs, and tremors. ZIKV replication was also confirmed in multiple organs of neonatal C57BL/6 mice by RT-qPCR[
62]. In one study conducted by Xianmiao Ye et al., newborn C57BL/6 mice were infected with ZIKV via i.p. injection, and the mouse weight loss and mortality were recorded daily. The results indicated that the infected neonatal mice experienced severe growth retardation and had a mortality rate exceeding 60%. Additionally, about 50% of the virus-infected neonates displayed moderate to severe neurological symptoms and had detectable viral loads in the tissues [
63]. Furthermore, Myriam Lucia Velandia-Romero and colleagues infected neonatal (2, 7, 14, or 21 days old) BALB/c mice with DENV via i.p. injection. The results showed that mice aged 2 and 7 days postnatal exhibited neurological symptoms, such as inactivity, prostration, and spasmodic movements. The virus was present in the brains of the infected mice, with a 2 to 3-log increase observed by day 6 post-infection. However, no neurological symptoms were observed in mice infected at 14 and 21 days postnatal, even though the virus in the brain was detectable [
64].
These findings demonstrate that the immature immune system of neonatal mice presents a heightened susceptibility to flavivirus, making them suitable as an animal model for flavivirus infection. However, breeding and manipulating newborn mice can be cumbersome, and they may experience noninfection-induced death in the first few days after virus infection.
3.1.3. Pregnant Mice
Since some flaviviruses particularly ZIKV can across the placental barrier of pregnant women and infect the fetus[
57], it is necessary to set up an animal model of vertical transmission for studying flaviviruses. Kong-Yan Wu et al. successfully established a vertical transmission mouse model of ZIKV infection by injecting ZIKV into the peritoneum of pregnant C57BL/6 mice at embryonic day 13.5 (E13.5) and observed that the viremia level of the offspring of pregnant mice was significantly higher than that of the control group at one day post-infection. On the 3
rd day after infection, viral RNA was identified in the placentas of 5 out of 9 pregnant mice, suggesting that ZIKV can effectively across the placental barrier and infect placentas [
65]. In addition, researchers utilized pregnant mice from SJL and C57BL/6 strains to investigate the effects of ZIKV infection on the development of the fetus. They injected intravenously (i.v.) ZIKV into pregnant mice on days 10-13 of gestation and immediately examined the neonates post-birth. They found that the neonates born to infected pregnant mice exhibited pronounced generalized growth retardation and had viral RNA in multiple organs including the brain, kidneys, liver, and spleen. This study underscores the neurotropic propensity of ZIKV and provides direct experimental evidence supporting the hypothesis that ZIKV can lead to birth defects like microcephaly by promoting cell death via apoptosis and autophagy[
66]. In a pioneering study conducted by Justin G. Julander and colleagues, a WNV vertical infection model was established for the first time. Pregnant mice, 11.5 days post-coital (dpc), were s.c. injected with WNV, and placenta samples were collected on the 3
rd, 4
th, and 5
th day post-infection. The results showed that the virus was detectable in 6 out of 8 placentas on the 3
rd day post-infection and the virus was present in all examined placentas by the 5
th day post-infection. The researchers also observed a higher rate of fetal infection with WNV when the WNV infection occurred 7.5 dpc [
67]. Given that pregnant women also face the risk of WNV infection, this intrauterine WNV infection model is highly beneficial for future research.
These findings demonstrate the feasibility of an intrauterine infection model for flaviviruses, offering a suitable approach for the development of therapeutics or antibodies to interrupt intrauterine transmission of flaviviruses.
3.1.4. Elderly Mice
Due to the weakened immune system, the elderly people are more susceptible to various viruses than young people. Therefore, it is necessary to explore whether flavivirus, particularly attenuated flavivirus strains, could establish infection in the elderly mouse. In a study conducted by Guorui Xie and colleagues, the elderly mice were used to examine the protective efficacy of attenuated WNV strain (WNV NS4B-P38G). Both 21- to 22-month-old elderly C57BL/6 mice and 6- to 10-week-old young mice were injected i.p. with WNV NS4B-P38G. The results showed that no young mice died or exhibited clinical symptoms. In contrast, 40% of elderly mice displayed severe neurological symptoms, with a 33% mortality rate. The serum viral loads in the elderly mice were approximately three folds higher than those in young mice on the 3
rd day post-infection. The viral loads in the elderly mice showed a 45-fold increase on the 13
th day post-infection [
68]. In comparison, Kristen E Funk et al. injected 85-week-old mice and 16-week-old mice with WNV through footpad (f.p.) injection. As a result, the mortality rate of the elderly mice was significantly higher than that of the young mice, and the degree of weight loss in the elderly mice was more pronounced [
69].
These studies indicate that the elderly mice, due to their diminished immune function, can also be developed as animal models for flavivirus infection. Compared to other fully immunocompetent mouse models, they do not require additional manipulation and can be utilized for the development of vaccines or drugs targeted towards the elderly population. It should be noted that the elderly mice are prone to various diseases, especially tumors, which may affect the stability of this animal models. More details for immunocompetent mouse models are shown in
Table 1.
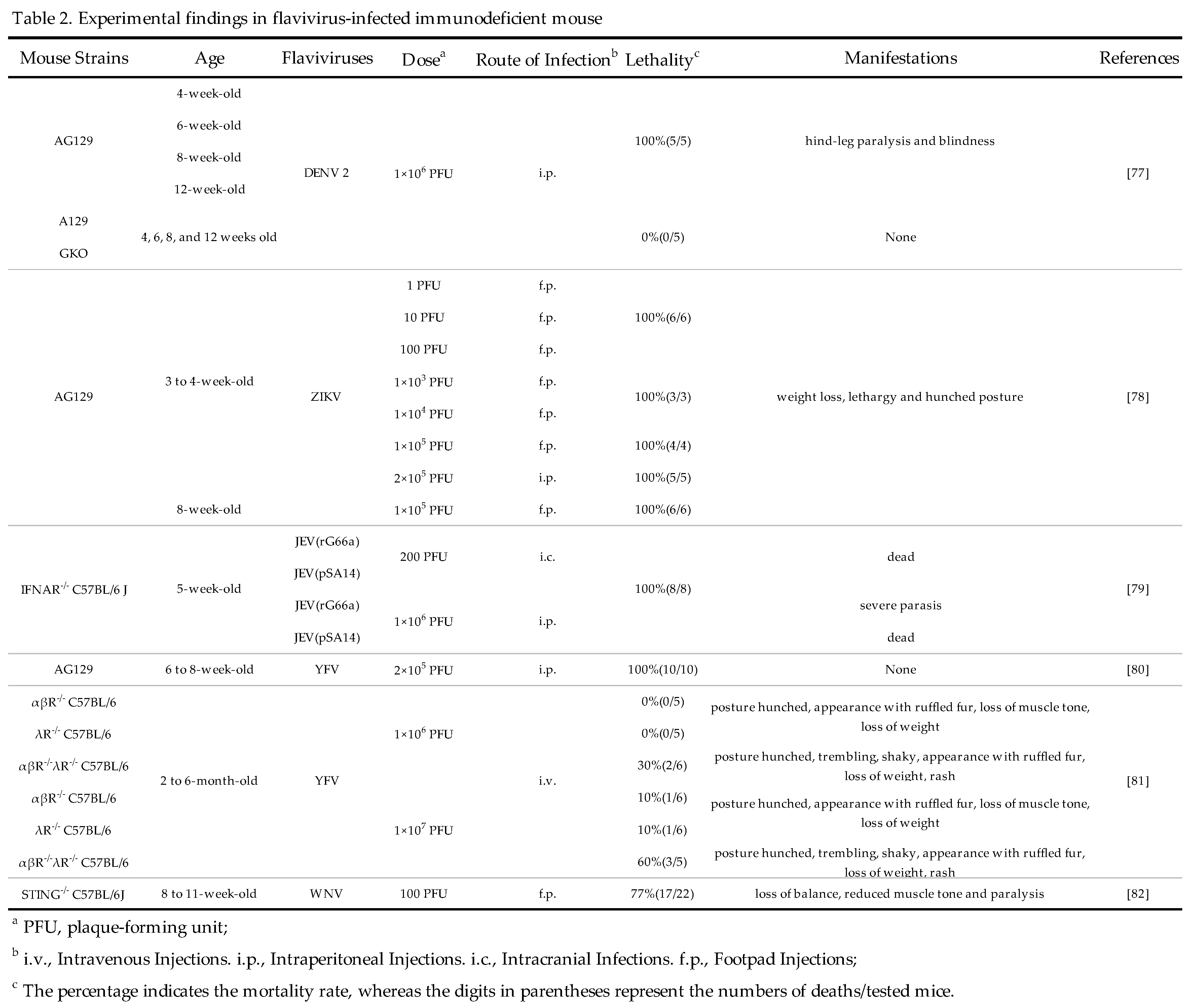
3.2. Immunodeficient Mice
Immunocompetent mice are the well-characterized and widely accepted experimental animal model for JEV infection research [
70], however, this kind of mouse model has above-mentioned limitations which limit their widespread application in some flaviviruses such as DENV, ZIKV, WNV, YFV, and TBEV [
71,
72,
73,
74,
75]. Therefore, the scientists constructed immunodeficient mice models that support flavivirus infection and demonstrate more efficiency than immunocompetent mice in evaluating vaccine and antiviral agents [
76]. Immunodeficient mice refer to mice with deficiencies in one or more components of the immune system either due to congenital genetic mutations or artificial methods.
For examples, Johnson AJ et al. evaluated the infectivity of DENV in AG129 mice (lacking IFN-α/β and IFN-γ receptors genes) of different ages (4-, 6-, 8-, or 12-week-old). They administered the DENV via i.p. injection into the mouse's abdominal cavities, and then found that mice of different age groups all exhibited neurological abnormalities (hind-limbs paralysis and blindness) on the 7
th day post-infection and all mice died on the 12
th day after infection. In comparison, no WT mice had clinical symptoms [
77]. Similarly, Aliota MT et al. reported that ZIKV infection could cause 100% mortality in 3- to 8-week-old AG129 mice. Although having no paralysis during the whole experimental period, all infected mice displayed signs of illness like weight loss, lethargy, and hunching by the 5
th day post-infection [
78]. In addition, Zhou D et al. compared the pathogenicity of two strains (pSA14 and rG66A) of JEV using 5-week-old C57BL/6 mice and INFAR
-/- mice. All C57BL/6 mice infected with the pSA14 strain via i.p. injection succumbed within nine days post-infection whereas mice infected with rG66A strain just exhibited a 30% mortality. In contrast, all INFAR
-/- mice, irrespective of virus strains, died within six days post-infection, suggesting that INFAR
-/- mice are more susceptible to JEV infection than WT mice [
79]. In fact, AG129 mice are also applicable animal models for YFV infection[
80]. To understand the role of type III IFN in YFV infection, Douam F et al. constructed a range of mouse models including αβR
-/-(IFN-α/β receptor knockout), λR
-/-( IFN-λ receptor knockout), and αβR
-/-λR
-/- mice (both IFN-α/β and IFN-λ receptors knockout) mice. Two different doses (1 × 10
6 and 1 × 10
7 PFU, representing low and high doses, respectively) of YFV (YFV-17D strain) were injected to the tail vein of mice. Collected data revealed the obvious difference in mortality rate among three mouse models, with αβR
-/-λR
-/-mice exhibiting increased susceptibility to YFV. Specifically, αβR
-/-λR
-/-mice presented a mortality rate of 30% at the low dose of YFV and a mortality rate of 60% at the high dose of YFV. In contrast, the mortality rates in the other two mouse models were limited to 10% even at the high dose of YFV [
81].
STING (stimulator of interferon genes), primarily recognized for initiating the production of type I interferon and the innate immune response to cytosolic DNA, is essential for defending against neurotropic RNA viruses. Studies have shown that mice lacking STING (STING
-/- mice) exhibit more significant neurological symptoms compared to WT mice following WNV infection. These neurological symptoms in affected STING
-/- mice include loss of balance, diminished muscle tone and reflexes, especially in the pelvic limbs, along with increased paresis and paralysis. This suggests more severe damage to the hindbrain and spinal cord [
82].
In general, knocking out key molecules involved in the interferon signaling pathway could promote flaviviruses to infect mice more effectively, resulting in significant clinical symptoms and increased mortality rates. Therefore, immunodeficient mice represent a good animal models for studying flaviviruses infection. More details for immunodeficient mouse models are shown in
Table 2.
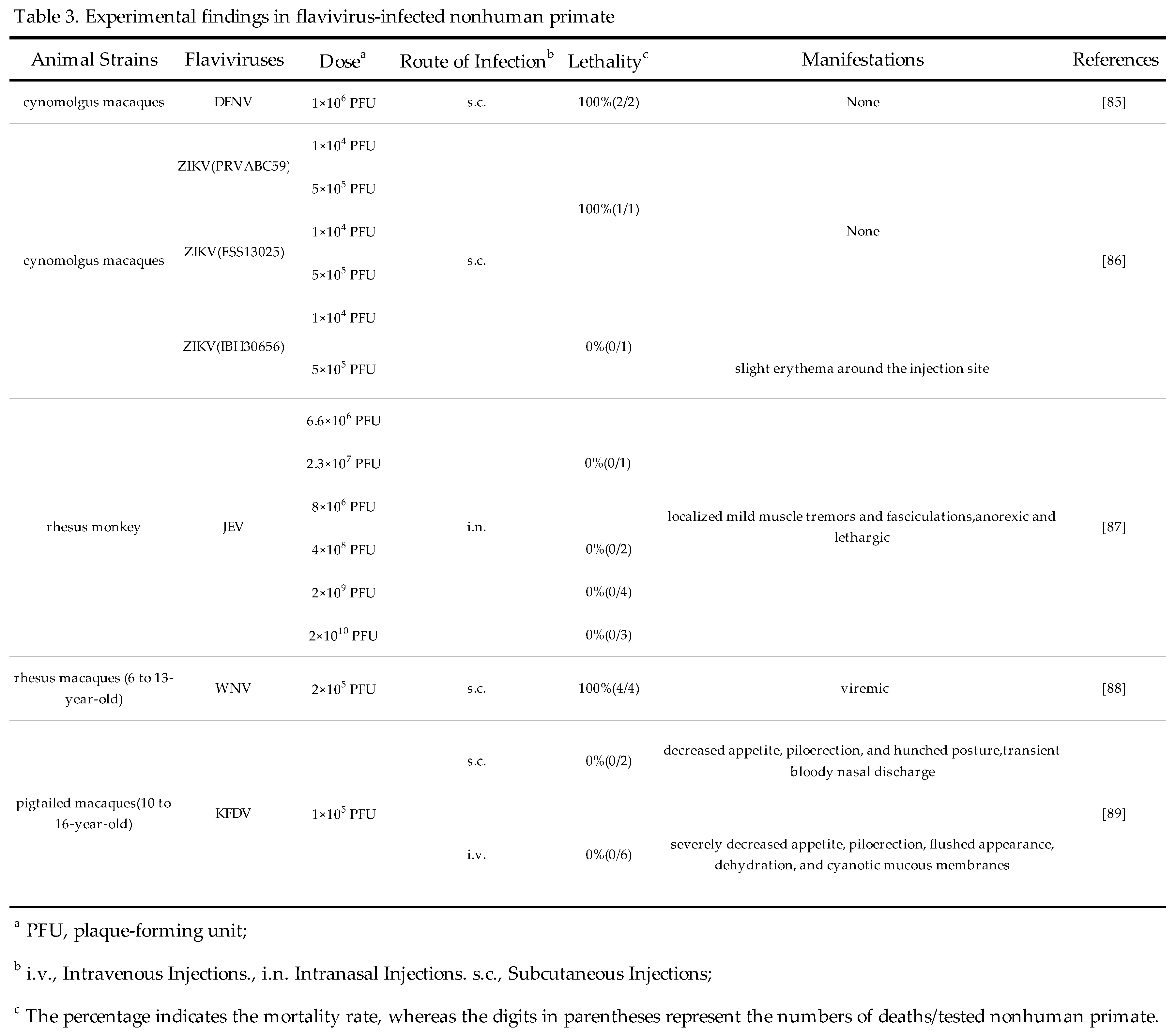
3.3. Non-human primates (NHP)
The main natural hosts of flaviviruses are humans and mosquitoes. Although there are no obvious clinical symptoms after infection with a few flaviviruses like DENV and ZIKV, NHP can develop viremia and immune responses. Therefore, NHP can be used to study the immune response to flavivirus infection, the pathogenic mechanism of infection, and evaluate the efficacy of vaccine candidates[
83,
84].
3.3.1. Cynomolgus macaques
Cynomolgus macaques are primarily used for the evaluation of DENV vaccines. After being infected with 10
6 PFU of DENV, the viremia in these
cynomolgus macaques occurred from the 2
rd day to the 9
th day post-infection[
85]. In addition, Koide F et al. reported the infectivity of ZIKV in Mauritian
cynomolgus macaques. In this study, six
cynomolgus macaques were subdivided into three cohorts with a male and female each and challenged with different doses of ZIKV Asian (PRVABC59 or FSS13025)or African (IBH30656) lineages. Asian lineage-induced viremia is detectable up to day 10, but, FSS13025 induced viremia lasting only up to 6 days. Therefore,
cynomolgus macaques could be suitable alternative models for the evaluation of ZIKV vaccine and antiviral agents[
86]. Thus, scientists have a choice of
cynomolgus macaques as an alternative NHP model for the study of DENV and ZIKV infection in the future.
3.3.2. Rhesus macaques
As for JEV research, the researchers used intranasal injection aiming to simulate a more natural infection route as a method of infecting
rhesus macaques with JEV. JEV infection induced non-suppurative encephalitis in the
rhesus macaques, characterized by neuronal cell death, proliferation of microglia, and astrocyte hyperplasia. All infected rhesus macaques displayed neurological symptoms that appeared approximately 7–10 days post-inoculation, which is consistent with human cases of JEV infection [
87]. As for WNV, Poore EA et al. constructed a
rhesus macaque model to evaluate the efficacy of attenuated WNV vaccines. All
rhesus macaques inoculated s.c. with attenuated WNV-NY99 strain developed viremia [
88]. In brief,
rhesus macaques could work as appropriate experimental models for evaluating the effectiveness of flavivirus vaccine and deepening researchers' understanding of flavivirus pathogenesis and antiviral agents.
3.3.3. Pigtailed macaques
In one study conducted by Broeckel RM et al, the feasibility of using
Pigtailed macaques as an animal model for KFDV infection was evaluated. The
pigtailed macaques infected with 10
5 PFU of KFDV displayed detectable viremia between 2 and 4 days following inoculation. Throughout infection, animals developed lymphocytopenia, thrombocytopenia, and elevated liver enzymes. Infected
pigtailed macaques exhibited typical symptoms of human KFDV infection, characterized by a flushed appearance, piloerection, dehydration, loss of appetite, weakness, and hemorrhagic signs including epistaxis[
89]. This study suggests that
pigtailed macaques can be used as an alternative NPH model for experimental KFDV infection. More details for non-human primate models are shown in
Table 3.
4. Conclusions
Animal models of various flaviviruses have been developed for a long time, however, there is still a lot waiting to be explored. There are no effective antiviral agents available for the specific treatments of most flaviviruses, and vaccines are available for only a few of them. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the pathogenesis of the disease, and develop antiviral drugs and related vaccines, all of which cannot be achieved without animal models. Animal models should simulate human diseases as closely as possible to facilitate the effective translation of research into clinical applications. However, certain factors affecting human flavivirus pathogenesis, such as genetic variations and underlying diseases, can never be accurately simulated using animal models.
Before selecting a suitable animal model, the following points should be considered: firstly, the natural infection should be simulated as closely as possible, e.g., if the pathogen is transmitted via arthropods, the infection should be carried out using subcutaneous injections; secondly, in the study of flavivirus pathogenesis, doses of the virus similar to those used in natural infections should be utilized; and thirdly, the NHP is the most appropriate animal model for most flaviviruses, however, feeding costs and ethical issues need to be considered. In general, researchers first select animal models from various types of small animals with low cost and short lifespans, such as mice, guinea pigs, and hamsters. After the study has been conducted to a certain extent, they then move to the more costly and restrictive NHPs.
Although mammals are anatomically, physiologically, and immunologically similar to humans, care must be taken when extrapolating results. Researchers need to continually deepen their understanding of extrapolation, which will facilitate progress in a variety of studies and reduce the number of experimental animals used. Overall, animal models play an indispensable role in flavivirus pathogenesis research, new drug preparation, and vaccine development.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.Y.Z. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Y.Z., L.J. and J.Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.W.; project administration, J.W.; funding acquisition, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY22C010004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070162 and 31870159), Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo Municipality (2022J131), and K.C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University. The APC was funded by grant number 32070162.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kummerer BM: Establishment and Application of Flavivirus Replicons. Adv Exp Med Biol 2018, 1062:165-173. [CrossRef]
- van Leur SW, Heunis T, Munnur D, Sanyal S: Pathogenesis and virulence of flavivirus infections. Virulence 2021, 12(1):2814-2838. [CrossRef]
- Zaitseva E, Yang ST, Melikov K, Pourmal S, Chernomordik LV: Dengue virus ensures its fusion in late endosomes using compartment-specific lipids. PLoS Pathog 2010, 6(10):e1001131. [CrossRef]
- Neufeldt CJ, Cortese M, Acosta EG, Bartenschlager R: Rewiring cellular networks by members of the Flaviviridae family. Nat Rev Microbiol 2018, 16(3):125-142. [CrossRef]
- Cortese M, Goellner S, Acosta EG, Neufeldt CJ, Oleksiuk O, Lampe M, Haselmann U, Funaya C, Schieber N, Ronchi P et al: Ultrastructural Characterization of Zika Virus Replication Factories. Cell Rep 2017, 18(9):2113-2123. [CrossRef]
- Bhatt S, Gething PW, Brady OJ, Messina JP, Farlow AW, Moyes CL, Drake JM, Brownstein JS, Hoen AG, Sankoh O et al: The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature 2013, 496(7446):504-507. [CrossRef]
- Ngono AE, Shresta S: Immune Response to Dengue and Zika. Annu Rev Immunol 2018, 36:279-308. [CrossRef]
- Shepard DS, Undurraga EA, Halasa YA, Stanaway JD: The global economic burden of dengue: a systematic analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2016, 16(8):935-941. [CrossRef]
- Diamond MS, Pierson TC: Molecular Insight into Dengue Virus Pathogenesis and Its Implications for Disease Control. Cell 2015, 162(3):488-492. [CrossRef]
- van den Hurk AF, Ritchie SA, Mackenzie JS: Ecology and geographical expansion of Japanese encephalitis virus. Annu Rev Entomol 2009, 54:17-35. [CrossRef]
- Pearce JC, Learoyd TP, Langendorf BJ, Logan JG: Japanese encephalitis: the vectors, ecology and potential for expansion. J Travel Med 2018, 25(suppl_1):S16-S26. [CrossRef]
- Chai C, Palinski R, Xu Y, Wang Q, Cao S, Geng Y, Zhao Q, Wen Y, Huang X, Yan Q et al: Aerosol and Contact Transmission Following Intranasal Infection of Mice with Japanese Encephalitis Virus. Viruses 2019, 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Nicolas O, Braun RO, Milona P, Lewandowska M, Dijkman R, Alves MP, Summerfield A: Targeting of the Nasal Mucosa by Japanese Encephalitis Virus for Non-Vector-Borne Transmission. J Virol 2018, 92(24). [CrossRef]
- Ricklin ME, Garcia-Nicolas O, Brechbuhl D, Python S, Zumkehr B, Nougairede A, Charrel RN, Posthaus H, Oevermann A, Summerfield A: Vector-free transmission and persistence of Japanese encephalitis virus in pigs. Nat Commun 2016, 7:10832. [CrossRef]
- Chapagain S, Pal Singh P, Le K, Safronetz D, Wood H, Karniychuk U: Japanese encephalitis virus persists in the human reproductive epithelium and porcine reproductive tissues. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2022, 16(7):e0010656. [CrossRef]
- Basumatary LJ, Raja D, Bhuyan D, Das M, Goswami M, Kayal AK: Clinical and radiological spectrum of Japanese encephalitis. J Neurol Sci 2013, 325(1-2):15-21. [CrossRef]
- Heffelfinger JD, Li X, Batmunkh N, Grabovac V, Diorditsa S, Liyanage JB, Pattamadilok S, Bahl S, Vannice KS, Hyde TB et al: Japanese Encephalitis Surveillance and Immunization - Asia and Western Pacific Regions, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2017, 66(22):579-583. [CrossRef]
- Xiang JY, Zhang YH, Tan ZR, Huang J, Zhao YW: Guillain-Barre syndrome associated with Japanese encephalitis virus infection in China. Viral Immunol 2014, 27(8):418-420. [CrossRef]
- Wang G, Li H, Yang X, Guo T, Wang L, Zhao Z, Sun H, Hou X, Ding X, Dou C et al: Guillain-Barre Syndrome Associated with JEV Infection. N Engl J Med 2020, 383(12):1188-1190. [CrossRef]
- Ooi MH, Lewthwaite P, Lai BF, Mohan A, Clear D, Lim L, Krishnan S, Preston T, Chieng CH, Tio PH et al: The epidemiology, clinical features, and long-term prognosis of Japanese encephalitis in central sarawak, malaysia, 1997-2005. Clin Infect Dis 2008, 47(4):458-468. [CrossRef]
- Shah SZ, Jabbar B, Ahmed N, Rehman A, Nasir H, Nadeem S, Jabbar I, Rahman ZU, Azam S: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Control of a Tick-Borne Disease- Kyasanur Forest Disease: Current Status and Future Directions. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2018, 8:149. [CrossRef]
- Holbrook MR: Kyasanur forest disease. Antiviral Res 2012, 96(3):353-362. [CrossRef]
- Work TH: Russian spring-summer virus in India: Kyasanur Forest disease. Prog Med Virol 1958, 1:248-279.
- Boshell J, Rajagopalan PK: Preliminary studies on experimental transmission of Kyasanur Forest disease virus by nymphs of Ixodes petauristae Warburton, 1933, infected as larvae on Suncus murinus and Rattus blanfordi. Indian J Med Res 1968, 56(4):589-593.
- Trapido H, Rajagopalan PK, Work TH, Varma MG: Kyasanur Forest disease. VIII. Isolation of Kyasanur Forest disease virus from naturally infected ticks of the genus Haemaphysalis. Indian J Med Res 1959, 47(2):133-138.
- Stone R: Monkey fever unbound. Science 2014, 345(6193):130-131, 133. [CrossRef]
- Munivenkatappa A, Sahay RR, Yadav PD, Viswanathan R, Mourya DT: Clinical & epidemiological significance of Kyasanur forest disease. Indian J Med Res 2018, 148(2):145-150. [CrossRef]
- Bhatia B, Meade-White K, Haddock E, Feldmann F, Marzi A, Feldmann H: A live-attenuated viral vector vaccine protects mice against lethal challenge with Kyasanur Forest disease virus. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6(1):152. [CrossRef]
- Bhatia B, Feldmann H, Marzi A: Kyasanur Forest Disease and Alkhurma Hemorrhagic Fever Virus-Two Neglected Zoonotic Pathogens. Microorganisms 2020, 8(9). [CrossRef]
- Hermance ME, Thangamani S: Powassan Virus: An Emerging Arbovirus of Public Health Concern in North America. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2017, 17(7):453-462. [CrossRef]
- Piantadosi A, Solomon IH: Powassan Virus Encephalitis. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2022, 36(3):671-688. [CrossRef]
- Hinten SR, Beckett GA, Gensheimer KF, Pritchard E, Courtney TM, Sears SD, Woytowicz JM, Preston DG, Smith RP, Jr., Rand PW et al: Increased recognition of Powassan encephalitis in the United States, 1999-2005. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2008, 8(6):733-740. [CrossRef]
- Petri E, Gniel D, Zent O: Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) trends in epidemiology and current and future management. Travel Med Infect Dis 2010, 8(4):233-245. [CrossRef]
- Lindquist L, Vapalahti O: Tick-borne encephalitis. Lancet 2008, 371(9627):1861-1871. [CrossRef]
- Beaute J, Spiteri G, Warns-Petit E, Zeller H: Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe, 2012 to 2016. Euro Surveill 2018, 23(45). [CrossRef]
- Kovalev SY, Mukhacheva TA: Tick-borne encephalitis virus subtypes emerged through rapid vector switches rather than gradual evolution. Ecol Evol 2014, 4(22):4307-4316. [CrossRef]
- Kaiser R: Tick-borne encephalitis. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2008, 22(3):561-575, x. [CrossRef]
- Suss J: Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and beyond--the epidemiological situation as of 2007. Euro Surveill 2008, 13(26).
- Kaiser R: Tick-borne encephalitis: Clinical findings and prognosis in adults. Wien Med Wochenschr 2012, 162(11-12):239-243. [CrossRef]
- Colpitts TM, Conway MJ, Montgomery RR, Fikrig E: West Nile Virus: biology, transmission, and human infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 2012, 25(4):635-648. [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease C, Prevention: Investigations of West Nile virus infections in recipients of blood transfusions. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2002, 51(43):973-974.
- Iwamoto M, Jernigan DB, Guasch A, Trepka MJ, Blackmore CG, Hellinger WC, Pham SM, Zaki S, Lanciotti RS, Lance-Parker SE et al: Transmission of West Nile virus from an organ donor to four transplant recipients. N Engl J Med 2003, 348(22):2196-2203. [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease C, Prevention: Possible West Nile virus transmission to an infant through breast-feeding--Michigan, 2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2002, 51(39):877-878.
- Centers for Disease C, Prevention: Intrauterine West Nile virus infection--New York, 2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2002, 51(50):1135-1136.
- Martinez AA, Espinosa BA, Adamek RN, Thomas BA, Chau J, Gonzalez E, Keppetipola N, Salzameda NT: Breathing new life into West Nile virus therapeutics; discovery and study of zafirlukast as an NS2B-NS3 protease inhibitor. Eur J Med Chem 2018, 157:1202-1213. [CrossRef]
- Garske T, Van Kerkhove MD, Yactayo S, Ronveaux O, Lewis RF, Staples JE, Perea W, Ferguson NM, Yellow Fever Expert C: Yellow Fever in Africa: estimating the burden of disease and impact of mass vaccination from outbreak and serological data. PLoS Med 2014, 11(5):e1001638. [CrossRef]
- Paules CI, Fauci AS: Yellow Fever - Once Again on the Radar Screen in the Americas. N Engl J Med 2017, 376(15):1397-1399. [CrossRef]
- Cardoso Jda C, de Almeida MA, dos Santos E, da Fonseca DF, Sallum MA, Noll CA, Monteiro HA, Cruz AC, Carvalho VL, Pinto EV et al: Yellow fever virus in Haemagogus leucocelaenus and Aedes serratus mosquitoes, southern Brazil, 2008. Emerg Infect Dis 2010, 16(12):1918-1924. [CrossRef]
- Faria NR, Kraemer MUG, Hill SC, Goes de Jesus J, Aguiar RS, Iani FCM, Xavier J, Quick J, du Plessis L, Dellicour S et al: Genomic and epidemiological monitoring of yellow fever virus transmission potential. Science 2018, 361(6405):894-899. [CrossRef]
- Davis EH, Wang B, White M, Huang YS, Sarathy VV, Wang T, Bourne N, Higgs S, Barrett ADT: Impact of yellow fever virus envelope protein on wild-type and vaccine epitopes and tissue tropism. NPJ Vaccines 2022, 7(1):39. [CrossRef]
- Li C, Xu D, Ye Q, Hong S, Jiang Y, Liu X, Zhang N, Shi L, Qin CF, Xu Z: Zika Virus Disrupts Neural Progenitor Development and Leads to Microcephaly in Mice. Cell stem cell 2016, 19(1):120-126.
- Prasad VM, Miller AS, Klose T, Sirohi D, Buda G, Jiang W, Kuhn RJ, Rossmann MG: Structure of the immature Zika virus at 9 A resolution. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2017, 24(2):184-186. [CrossRef]
- Kostyuchenko VA, Lim EX, Zhang S, Fibriansah G, Ng TS, Ooi JS, Shi J, Lok SM: Structure of the thermally stable Zika virus. Nature 2016, 533(7603):425-428. [CrossRef]
- Hasan SS, Sevvana M, Kuhn RJ, Rossmann MG: Structural biology of Zika virus and other flaviviruses. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2018, 25(1):13-20. [CrossRef]
- Lanciotti RS, Lambert AJ, Holodniy M, Saavedra S, Signor Ldel C: Phylogeny of Zika Virus in Western Hemisphere, 2015. Emerg Infect Dis 2016, 22(5):933-935. [CrossRef]
- Tabata T, Petitt M, Puerta-Guardo H, Michlmayr D, Wang C, Fang-Hoover J, Harris E, Pereira L: Zika Virus Targets Different Primary Human Placental Cells, Suggesting Two Routes for Vertical Transmission. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20(2):155-166. [CrossRef]
- Mlakar J, Korva M, Tul N, Popovic M, Poljsak-Prijatelj M, Mraz J, Kolenc M, Resman Rus K, Vesnaver Vipotnik T, Fabjan Vodusek V et al: Zika Virus Associated with Microcephaly. The New England journal of medicine 2016, 374(10):951-958.
- Martines RB, Bhatnagar J, Keating MK, Silva-Flannery L, Muehlenbachs A, Gary J, Goldsmith C, Hale G, Ritter J, Rollin D et al: Notes from the Field: Evidence of Zika Virus Infection in Brain and Placental Tissues from Two Congenitally Infected Newborns and Two Fetal Losses--Brazil, 2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2016, 65(6):159-160. [CrossRef]
- Lazear HM, Govero J, Smith AM, Platt DJ, Fernandez E, Miner JJ, Diamond MS: A Mouse Model of Zika Virus Pathogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19(5):720-730. [CrossRef]
- Smith DR, Hollidge B, Daye S, Zeng X, Blancett C, Kuszpit K, Bocan T, Koehler JW, Coyne S, Minogue T et al: Neuropathogenesis of Zika Virus in a Highly Susceptible Immunocompetent Mouse Model after Antibody Blockade of Type I Interferon. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017, 11(1):e0005296. [CrossRef]
- Wilken L, Stelz S, Prajeeth CK, Rimmelzwaan GF: Transient Blockade of Type I Interferon Signalling Promotes Replication of Dengue Virus Strain D2Y98P in Adult Wild-Type Mice. Viruses 2023, 15(4). [CrossRef]
- Li S, Armstrong N, Zhao H, Hou W, Liu J, Chen C, Wan J, Wang W, Zhong C, Liu C et al: Zika Virus Fatally Infects Wild Type Neonatal Mice and Replicates in Central Nervous System. Viruses 2018, 10(1). [CrossRef]
- Ye X, Liu X, Shu T, Deng W, Liao M, Zheng Y, Zheng X, Zhang X, Li T, Fan W et al: A Live-Attenuated Zika Virus Vaccine with High Production Capacity Confers Effective Protection in Neonatal Mice. J Virol 2021, 95(14):e0038321. [CrossRef]
- Velandia-Romero ML, Acosta-Losada O, Castellanos JE: In vivo infection by a neuroinvasive neurovirulent dengue virus. J Neurovirol 2012, 18(5):374-387. [CrossRef]
- Wu KY, Zuo GL, Li XF, Ye Q, Deng YQ, Huang XY, Cao WC, Qin CF, Luo ZG: Vertical transmission of Zika virus targeting the radial glial cells affects cortex development of offspring mice. Cell Res 2016, 26(6):645-654. [CrossRef]
- Cugola FR, Fernandes IR, Russo FB, Freitas BC, Dias JL, Guimaraes KP, Benazzato C, Almeida N, Pignatari GC, Romero S et al: The Brazilian Zika virus strain causes birth defects in experimental models. Nature 2016, 534(7606):267-271. [CrossRef]
- Julander JG, Winger QA, Olsen AL, Day CW, Sidwell RW, Morrey JD: Treatment of West Nile virus-infected mice with reactive immunoglobulin reduces fetal titers and increases dam survival. Antiviral Res 2005, 65(2):79-85. [CrossRef]
- Xie G, Luo H, Pang L, Peng BH, Winkelmann E, McGruder B, Hesse J, Whiteman M, Campbell G, Milligan GN et al: Dysregulation of Toll-Like Receptor 7 Compromises Innate and Adaptive T Cell Responses and Host Resistance to an Attenuated West Nile Virus Infection in Old Mice. J Virol 2016, 90(3):1333-1344. [CrossRef]
- Funk KE, Arutyunov AD, Desai P, White JP, Soung AL, Rosen SF, Diamond MS, Klein RS: Decreased antiviral immune response within the central nervous system of aged mice is associated with increased lethality of West Nile virus encephalitis. Aging Cell 2021, 20(8):e13412. [CrossRef]
- Frank JC, Song BH, Lee YM: Mice as an Animal Model for Japanese Encephalitis Virus Research: Mouse Susceptibility, Infection Route, and Viral Pathogenesis. Pathogens 2023, 12(5). [CrossRef]
- Brinton MA, Perelygin AA: Genetic resistance to flaviviruses. Adv Virus Res 2003, 60:43-85. [CrossRef]
- Brien JD, Uhrlaub JL, Hirsch A, Wiley CA, Nikolich-Zugich J: Key role of T cell defects in age-related vulnerability to West Nile virus. J Exp Med 2009, 206(12):2735-2745. [CrossRef]
- Zellweger RM, Shresta S: Mouse models to study dengue virus immunology and pathogenesis. Front Immunol 2014, 5:151. [CrossRef]
- Beasley DW, McAuley AJ, Bente DA: Yellow fever virus: genetic and phenotypic diversity and implications for detection, prevention and therapy. Antiviral Res 2015, 115:48-70. [CrossRef]
- Morrison TE, Diamond MS: Animal Models of Zika Virus Infection, Pathogenesis, and Immunity. J Virol 2017, 91(8). [CrossRef]
- Na W, Yeom M, Choi IK, Yook H, Song D: Animal models for dengue vaccine development and testing. Clin Exp Vaccine Res 2017, 6(2):104-110. [CrossRef]
- Johnson AJ, Roehrig JT: New mouse model for dengue virus vaccine testing. J Virol 1999, 73(1):783-786. [CrossRef]
- Aliota MT, Caine EA, Walker EC, Larkin KE, Camacho E, Osorio JE: Characterization of Lethal Zika Virus Infection in AG129 Mice. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2016, 10(4):e0004682. [CrossRef]
- Zhou D, Jia F, Li Q, Zhang L, Chen Z, Zhao Z, Cui M, Song Y, Chen H, Cao S et al: Japanese Encephalitis Virus NS1' Protein Antagonizes Interferon Beta Production. Virol Sin 2018, 33(6):515-523. [CrossRef]
- Calvert AE, Dixon KL, Piper J, Bennett SL, Thibodeaux BA, Barrett AD, Roehrig JT, Blair CD: A humanized monoclonal antibody neutralizes yellow fever virus strain 17D-204 in vitro but does not protect a mouse model from disease. Antiviral Res 2016, 131:92-99. [CrossRef]
- Douam F, Soto Albrecht YE, Hrebikova G, Sadimin E, Davidson C, Kotenko SV, Ploss A: Type III Interferon-Mediated Signaling Is Critical for Controlling Live Attenuated Yellow Fever Virus Infection In Vivo. mBio 2017, 8(4). [CrossRef]
- McGuckin Wuertz K, Treuting PM, Hemann EA, Esser-Nobis K, Snyder AG, Graham JB, Daniels BP, Wilkins C, Snyder JM, Voss KM et al: STING is required for host defense against neuropathological West Nile virus infection. PLoS Pathog 2019, 15(8):e1007899. [CrossRef]
- Koraka P, Benton S, van Amerongen G, Stittelaar KJ, Osterhaus AD: Characterization of humoral and cellular immune responses in cynomolgus macaques upon primary and subsequent heterologous infections with dengue viruses. Microbes Infect 2007, 9(8):940-946. [CrossRef]
- Yoshida T, Omatsu T, Saito A, Katakai Y, Iwasaki Y, Kurosawa T, Hamano M, Higashino A, Nakamura S, Takasaki T et al: Dynamics of cellular immune responses in the acute phase of dengue virus infection. Arch Virol 2013, 158(6):1209-1220. [CrossRef]
- Ong EZ, Budigi Y, Tan HC, Robinson LN, Rowley KJ, Winnett A, Hobbie S, Shriver Z, Babcock GJ, Ooi EE: Preclinical evaluation of VIS513, a therapeutic antibody against dengue virus, in non-human primates. Antiviral Res 2017, 144:44-47. [CrossRef]
- Koide F, Goebel S, Snyder B, Walters KB, Gast A, Hagelin K, Kalkeri R, Rayner J: Development of a Zika Virus Infection Model in Cynomolgus Macaques. Front Microbiol 2016, 7:2028. [CrossRef]
- Myint KS, Raengsakulrach B, Young GD, Gettayacamin M, Ferguson LM, Innis BL, Hoke CH, Jr., Vaughn DW: Production of lethal infection that resembles fatal human disease by intranasal inoculation of macaques with Japanese encephalitis virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1999, 60(3):338-342. [CrossRef]
- Poore EA, Slifka DK, Raue HP, Thomas A, Hammarlund E, Quintel BK, Torrey LL, Slifka AM, Richner JM, Dubois ME et al: Pre-clinical development of a hydrogen peroxide-inactivated West Nile virus vaccine. Vaccine 2017, 35(2):283-292. [CrossRef]
- Broeckel RM, Feldmann F, McNally KL, Chiramel AI, Sturdevant GL, Leung JM, Hanley PW, Lovaglio J, Rosenke R, Scott DP et al: A pigtailed macaque model of Kyasanur Forest disease virus and Alkhurma hemorrhagic disease virus pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog 2021, 17(12):e1009678. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).