Submitted:
19 January 2024
Posted:
23 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategies
- #1 sarcopenia OR Sarcopenias OR composition, body OR body composition OR Body Compositions OR Compositions, Body OR muscle mass OR muscle volume OR muscle quality OR skeletal muscle loss OR muscle loss
- #2 Ca prostate OR cancer in the prostate OR cancer of the prostate OR cancer, prostate OR carcinogenesis of the prostate OR malignancies of the prostate OR malignancy of the prostate OR malignant neoplasm of the prostate OR malignant prostate tumor OR malignant prostate tumour OR malignant prostatic tumor OR malignant prostatic tumour OR malignant tumor of the prostate OR prostate cancerogenesis OR prostate carcinogenesis OR prostate gland cancer OR prostate malignancies OR prostate malignancy OR prostate malignant neoplasm OR prostate malignant tumor OR prostate malignant tumour OR prostatic cancer OR prostatic cancerogenesis OR prostatic carcinogenesis OR prostatic malignancies OR prostatic malignancy OR prostate cancer OR Prostatic Neoplasms OR Prostate Neoplasms OR Neoplasms, Prostate OR Neoplasm, Prostate OR Prostate Neoplasm OR Neoplasms, Prostatic OR Neoplasm, Prostatic OR Prostatic Neoplasm OR Cancers, Prostate OR Prostate Cancers OR Cancer, Prostatic OR Cancers, Prostatic OR Prostatic Cancers OR Cancer of Prostate
- #3 Antagonists, Androgen OR Antiandrogens OR Androgen Antagonist OR Antagonist, Androgen OR Antiandrogen OR Anti-Androgen Effect OR Anti Androgen Effect OR Effect, Anti-Androgen OR Antiandrogen Effect OR Effect, Antiandrogen OR Antiandrogen Effects OR Effects, Antiandrogen OR Anti-Androgen Effects OR Anti Androgen Effects OR Effects, Anti-Androgen OR Androgen Antagonists OR ADT OR androgen deprivation therapy OR androgen suppresion therapy OR anti androgen OR antiandrogen agent OR antiandrogenic agent OR antiandrogenic drug OR nonsteroidal anti androgen OR nonsteroidal anti androgens OR nonsteroidal anti-androgen OR nonsteroidal anti-androgens OR nonsteroidal antiandrogen OR nonsteroidal antiandrogens OR gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist OR gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists OR gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist OR gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists OR LHRH agonist OR LHRH antagonist OR MAB OR maximum androgen blockade OR CAB OR complete androgen blockade OR gonadorelin antagonist OR antigonadorelin OR gonadorelin, anti OR gonadorelin antagonist OR gonadorelin agonist OR gonadorelin agonist OR gnrh antagonist OR gonadotropin releasing factor antagonist OR gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonist OR gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonists OR lh rh antagonist OR lrf antagonist OR luliberin antagonist OR luteinising hormone releasing hormone antagonist OR luteinizing hormone releasing hormone antagonist OR gnrh agonist OR gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist OR luteinising hormone releasing hormone agonist OR luteinizing hormone releasing hormone agonist OR orchectomy OR orcheotomy OR testectomy OR testis removal OR orchiectomy OR Orchidectomy OR Orchiectomies OR Orchidectomies OR Castration, Male OR Castrations, Male OR Male Castration OR Male Castrations
- #1 AND #2 AND #3
3.2. Study Selection
3.3. Data Extraction and Analysis
3.4. Risk of Bias
4. Results
| Study | Year | Country | Study design | Study population | Control population | Baseline | Follow up | ADT implementation: prior/post baseline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AT BASELINE AND FOLLOW-UP | ||||||||
| Chiang et al [24] | 2021 | Italy | Retrospective observational study, single-center | 125 | No | Before initiation of ADT+radiotherapy | Within one year after treatment initiation | Post |
| Korczak et al [21] | 2023 | Poland | Prospective observational study, single-centre | HSPC 34 CRPC 30 |
No | HSCPC: before initiation of ADT+docetaxel±radiotherapy CRPC: during ADT+abiraterone or enzalutamide±radiotherapy±prostatectomy |
At the moment of biochemical progression | HSPC post CRPC prior+post; no information about prior treatment |
| Sheean et al [22] | 2022 | USA | Retrospective observational study | 74 Subgroup at baseline: 54 Subgroup at follow-up: 19 |
No | Before initiation of ADT±docetaxel | At the moment of death or last contact | Post |
| Couderc et al [25] | 2020 | France | Prospective observational study, single-centre | 31 Subgroup at follow-up: 6 |
No | Before initiation of ADT+radiotherapy | At the end of the treatment | Post |
| Sheikhbahaei et al [26] | 2020 | USA | Retrospective observational study, single-center | 22 | No | Before initiation of neoadjuvant therapy: ADT+docetaxel | I: 1 month after the completion of neoadjuvant therapy II: approximately 1 year after initiation of neoadjuvant therapy. |
Post |
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AS A SINGLE MEASURMENT DURING ADT | ||||||||
| Owen et al [27] | 2019 | Australia | Cross-sectional study | 70 | Non-ADT prostate cancer: 52 Healthy: 70 |
During ADT treatment ± chemotherapy | Prior | |
| Kimura et al [28] | 2019 | Japan | Cross-sectional study | 89 | No | During ADT | Prior | |
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopez, P.; Newton, R.U.; Taaffe, D.R.; Singh, F.; Buffart, L.M.; Spry, N.; Tang, C.; Saad, F.; Galvão, D.A. Associations of Fat and Muscle Mass with Overall Survival in Men with Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussing, A.; Mikkelsen, M.; Villumsen, B.; Wejlgaard, J.; Bistrup, P.; Birkefoss, K.; Bandholm, T. Supervised Exercise Therapy Compared with No Exercise Therapy to Reverse Debilitating Effects of Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Patients with Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PROSTATE CANCER AND PROSTATIC DISEASES 2022, 25, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Zhang, H.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Y. The Effects of Exercise on Body Composition of Prostate Cancer Patients Receiving Androgen Deprivation Therapy: An Update Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0263918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European Consensus on Definition and Diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICD-10 Version:2019. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en#/M62.5 (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- ICD-11 Coding Tool Mortality and Morbidity Statistics (MMS). Available online: https://icd.who.int/ct11/icd11_mms/en/release (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association 2020, 21, 300–307.e2. [CrossRef]
- Clay, C.A.; Perera, S.; Wagner, J.M.; Miller, M.E.; Nelson, J.B.; Greenspan, S.L. Physical Function in Men with Prostate Cancer on Androgen Deprivation Therapy. Phys Ther 2007, 87, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, D.A.; Taaffe, D.R.; Spry, N.; Joseph, D.; Turner, D.; Newton, R.U. Reduced Muscle Strength and Functional Performance in Men with Prostate Cancer Undergoing Androgen Suppression: A Comprehensive Cross-Sectional Investigation. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2009, 12, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibhai, S.M.H.; Breunis, H.; Timilshina, N.; Johnston, C.; Tomlinson, G.; Tannock, I.; Krahn, M.; Fleshner, N.E.; Warde, P.; Canning, S.D.; et al. Impact of Androgen-Deprivation Therapy on Physical Function and Quality of Life in Men with Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010, 28, 5038–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibhai, S.M.H.; Breunis, H.; Timilshina, N.; Naglie, G.; Tannock, I.; Krahn, M.; Warde, P.; Fleshner, N.E.; Canning, S.D.; Tomlinson, G. Long-Term Impact of Androgen-Deprivation Therapy on Physical Function and Quality of Life. Cancer 2015, 121, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basaria, S.; Lieb, J. 2nd; Tang, A.M.; DeWeese, T.; Carducci, M.; Eisenberger, M.; Dobs, A.S. Long-Term Effects of Androgen Deprivation Therapy in Prostate Cancer Patients. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2002, 56, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overkamp, M.; Houben, L.H.P.; van der Meer, S.; van Roermund, J.G.H.; Bos, R.; Kokshoorn, A.P.J.; Larsen, M.S.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Beelen, M.; Beijer, S. Onset of Androgen Deprivation Therapy Leads to Rapid Deterioration of Body Composition, Physical Performance, Cardiometabolic Health and Quality-of-Life in Prostate Cancer Patients. Scand J Urol 2023, 57, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Joseph, D.J.; Ebert, M.A.; Galvão, D.A.; Taaffe, D.R.; Denham, J.W.; Newton, R.U.; Spry, N.A. Effect of Androgen Deprivation Therapy on Muscle Attenuation in Men with Prostate Cancer. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 2014, 58, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.R.; Saad, F.; Egerdie, B.; Sieber, P.R.; Tammela, T.L.J.; Ke, C.; Leder, B.Z.; Goessl, C. Sarcopenia during Androgen-Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. J Clin Oncol 2012, 30, 3271–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Castro, E.; Fizazi, K.; Heidenreich, A.; Ost, P.; Procopio, G.; Tombal, B.; Gillessen, S. Prostate Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up†. Annals of Oncology 2020, 31, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- McGrath, S.; Zhao, X.; Steele, R.; Benedetti, A. Estmeansd: Estimating the Sample Mean and Standard Deviation from Commonly Reported Quantiles in Meta-Analysis 2022.
- Companion R Package for the Guide Doing Meta-Analysis in R. Available online: https://dmetar.protectlab.org/ (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Korczak, J.; Mardas, M.; Litwiniuk, M.; Bogdański, P.; Stelmach-Mardas, M. Androgen Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Influences Body Composition Increasing Risk of Sarcopenia. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheean, P.M.; O’Connor, P.; Joyce, C.; Vasilopoulos, V.; Badami, A.; Stolley, M. Clinical Features and Body Composition in Men with Hormone-Sensitive Metastatic Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study Examining Differences by Race. Prostate Cancer 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying Heterogeneity in a Meta-Analysis. Stat Med 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, P.-K.; Tsai, W.-K.; Chiu, A.W.-H.; Lin, J.-B.; Yang, F.-Y.; Lee, J. Muscle Loss During Androgen Deprivation Therapy Is Associated With Higher Risk of Non-Cancer Mortality in High-Risk Prostate Cancer. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 722652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couderc, A.L.; Muracciole, X.; Nouguerede, E.; Rey, D.; Schneider, S.; Champsaur, P.; Lechevallier, E.; Lalys, L.; Villani, P. HoSAGE: Sarcopenia in Older Patients before and after Treatment with Androgen Deprivation Therapy and Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. J Nutr Health Aging 2020, 24, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhbahaei, S.; Reyes, D.K.; Rowe, S.P.; Pienta, K.J. CT-Based Assessment of Body Composition Following Neoadjuvant Chemohormonal Therapy in Patients with Castration-Naïve Oligometastatic Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2021, 81, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, P.J.; Daly, R.M.; Dalla Via, J.; Mundell, N.L.; Livingston, P.M.; Rantalainen, T.; Fraser, S.F. Does Use of Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT) in Men with Prostate Cancer Increase the Risk of Sarcopenia? Calcif Tissue Int 2019, 105, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, Y.; Yamada, M.; Ohji, S.; Ishiyama, D.; Nishio, N.; Otobe, Y.; Koyama, S.; Suzuki, M.; Ichikawa, T.; Ito, D.; et al. Presence of Sarcopenic Obesity and Evaluation of the Associated Muscle Quality in Japanese Older Men with Prostate Cancer Undergoing Androgen Deprivation Therapy. J Geriatr Oncol 2019, 10, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narici MV.; Maffulli N. Sarcopenia: characteristics, mechanisms and functional significance. Br Med Bull 2010, 95, 139-59. [CrossRef]
- Nam YS.; Lee G, Yun JM.; Cho B. Testosterone Replacement, Muscle Strength, and Physical Function. World J Mens Health 2018, May 36(2), 110-122. [CrossRef]
- Griggs RC.; Kingston W.; Jozefowicz RF.; Herr BE.; Forbes G.; Halliday D. Effect of testosterone on muscle mass and muscle protein synthesis. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989, Jan 66(1), 498-503. [CrossRef]
- Kaluźniak-Szymanowska A.; Krzymińska-Siemaszko R.; Deskur-Śmielecka E.; Lewandowicz M.; Kaczmarek B.; Wieczorowska-Tobis K.; Malnutrition, Sarcopenia, and Malnutrition-Sarcopenia Syndrome in Older Adults with COPD. Nutrients 2021, Dec 23, 14(1):44. [CrossRef]
- Son SW.; Song DS.; Chang UI.; Yang JM.; Definition of Sarcopenia in Chronic Liver Disease. Life (Basel) 2021, Apr 16, 11(4):349. [CrossRef]
- Smith MR.; Changes in fat and lean body mass during androgen-deprivation therapy for prostate cancer. Urology 2004, 63(4); 742-5. [CrossRef]
- Shahinian VB.; Kuo YF.; Freeman JL.; Goodwin JS. Risk of fracture after androgen deprivation for prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2005,;352(2); 154-64. [CrossRef]
- Storer TW.; Miciek R.; Travison TG.; Muscle function, physical performance and body composition changes in men with prostate cancer undergoing androgen deprivation therapy. Asian J Androl. 2012 ; 2; 204-21. doi: 10.1038/aja.2011.104. Epub 2012 Feb 27. [CrossRef]
- de Pablos-Rodríguez P, Del Pino-Sedeño T, Infante-Ventura D, de Armas-Castellano A, Ramírez Backhaus M, Ferrer JFL, de Pablos-Velasco P, Rueda-Domínguez A, Trujillo-Martín MM. Prognostic Impact of Sarcopenia in Patients with Advanced Prostate Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. J Clin Med. 2022 Dec 21;12(1):57. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010057. PMID: 36614862; PMCID: PMC982150138. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chiang PK.; Tsai WK.; Chiu AW.; Lin JB.; Yang FY.; Lee J. Muscle Loss During Androgen Deprivation Therapy Is Associated With Higher Risk of Non-Cancer Mortality in High-Risk Prostate Cancer. Front Oncol. 2021; Sep 17; 11:722652. [CrossRef]
- McGovern J.; Dolan RD.; Horgan PG.; Laird BJ.; McMillan DC. Computed tomography-defined low skeletal muscle index and density in cancer patients: observations from a systematic review. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021 Dec;12(6):1408-1417. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12831. Epub 2021 Oct 18. PMID: 34664431; PMCID: PMC8718024. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Amato MC, Giordano C, Galia M, Criscimanna A, Vitabile S, Midiri M, Galluzzo A; AlkaMeSy Study Group. Visceral Adiposity Index: a reliable indicator of visceral fat function associated with cardiometabolic risk. Diabetes Care. 2010; ;33(4); 920-2. [CrossRef]
- Di Bella CM.; Howard LE.; Oyekunle T.; De Hoedt AM.; Salama JK.; Song H.; Freedland SJ.; Allott EH. Abdominal and pelvic adipose tissue distribution and risk of prostate cancer recurrence after radiation therapy. Prostate 2020; 80(14); 1244-1252. [CrossRef]
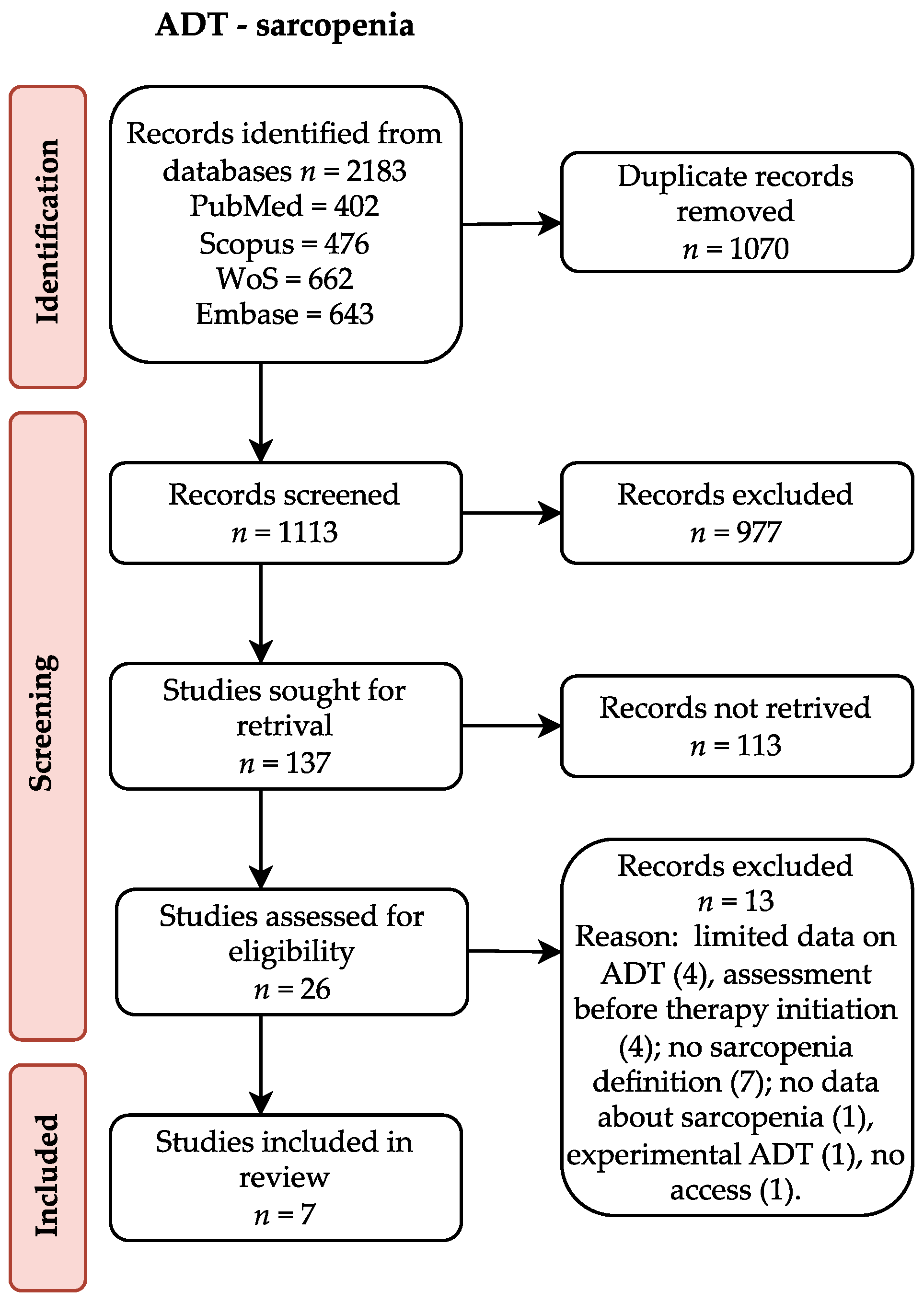
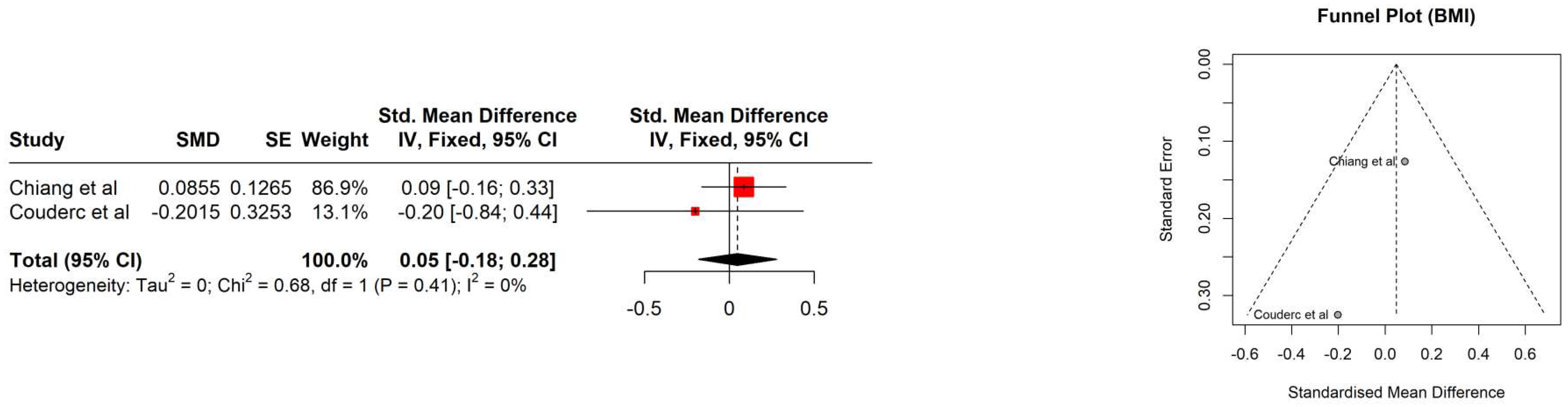
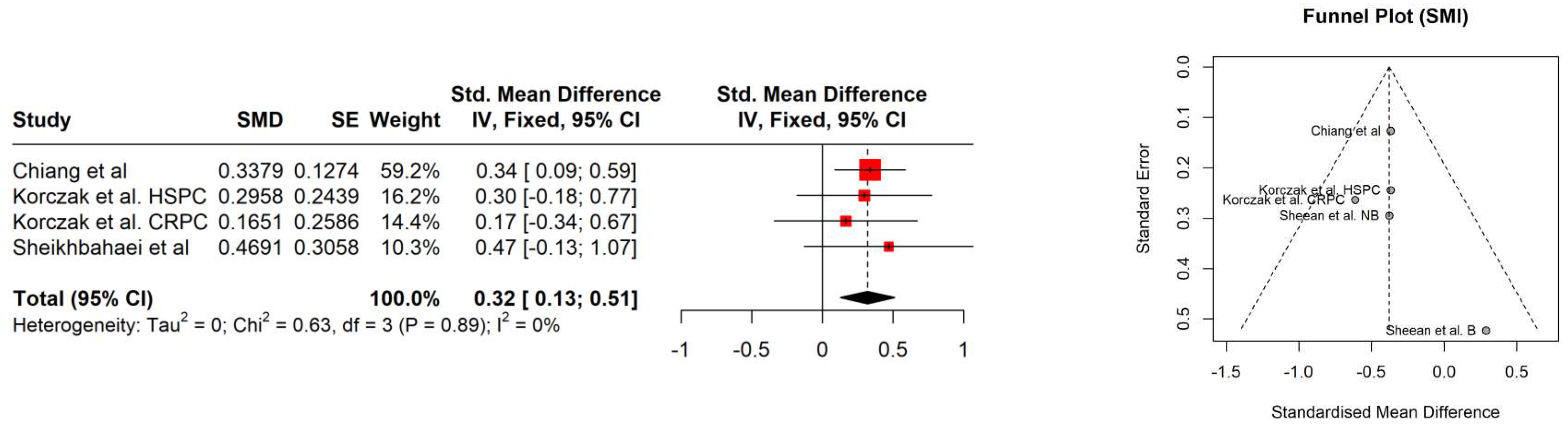
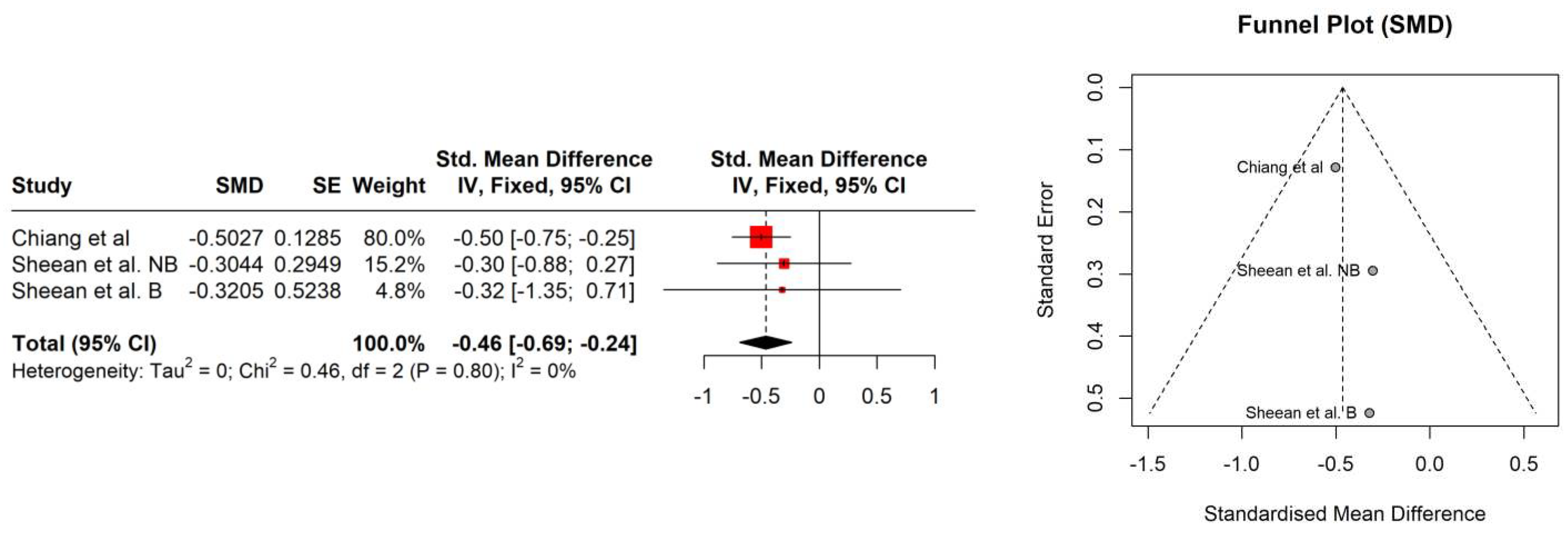
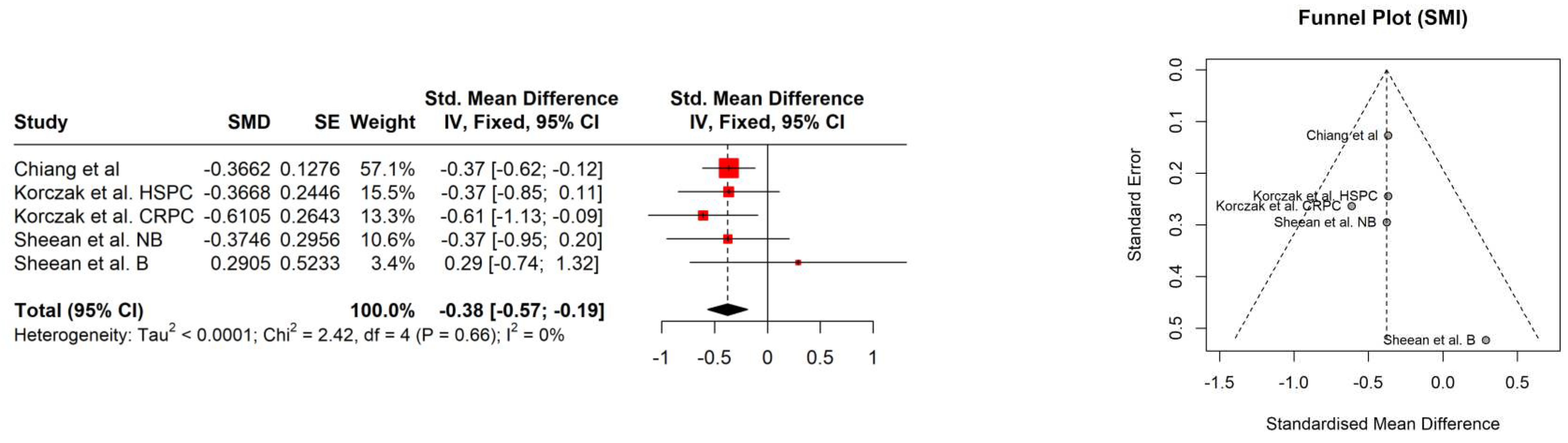
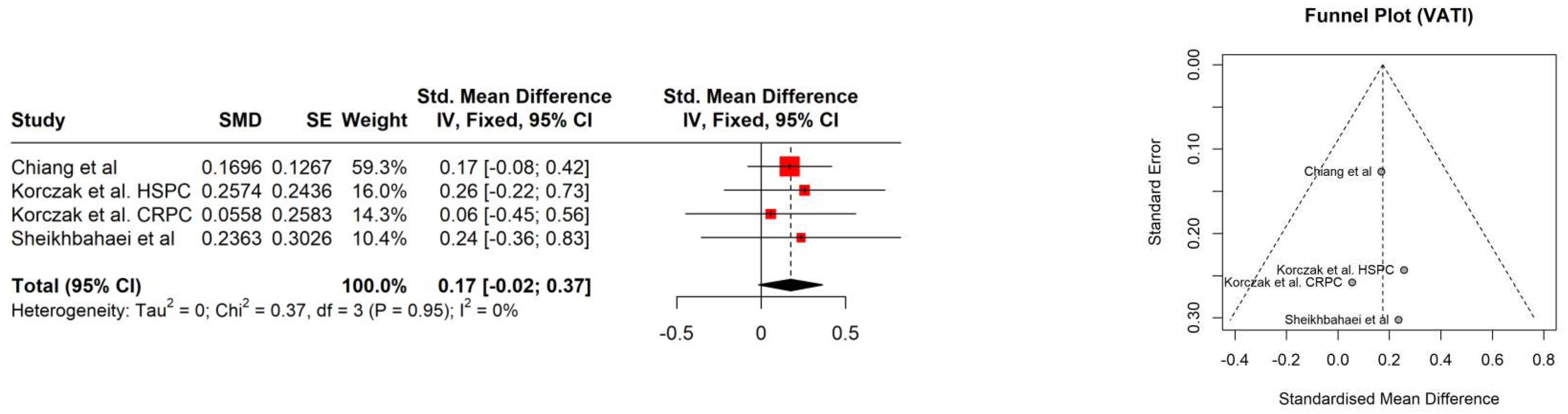
| Study | Age [years] | PSA [ng/ml] | Gleason score | Albumin [g/L] | Hb [mmol/l] | Performance status | Comorbidities | BMI [kg/m2] | BMI category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AT BASELINE AND FOLLOW-UP | |||||||||
| Chiang et al [24] | 73 median, 67–78 IQR | 27.8 median, 21.2-60.5 IQR | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Age-adjusted CCI: 4 median, 3-5 IQR | 24.2±3.5 | N/A |
| Korczak et al [21] | HSPC: 68.6±7.1 CRPC: 72.0±7.5 |
HSPC: 206.3±547.6 CRPC: 82±155.5 |
HSPC: 8 median, 5-9 range CRPC: 7 median, 4-9 range |
N/A | HSPC: 8.176±0,.8370 CRPC: 8.778±1.406 |
WHO HSPC: 0, 6%; 1, 70%; 2, 24% CRPC: 0, 100% |
Diabetes HSPC: 26.5; CRPC: 16.6 Hypertension HSPC: 61.8; CRPC: 66.7 Ischemic heart disease HSPC: 14.7; CRPC: 46.76 Other HSPC: 44.1; CRPC: 40.0 |
HSPC: 28.5±4.9 CRPC: 29.3±4.4 |
HSPC: underweight 3%; normal: 20%; overweight: 35%; obesity: 42% CRPC: underweight 0%; normal: 19%; overweight: 37%; obesity: 44% |
| Sheean et al [22] | 71 median, 63–79 IQR | N=511 110 median, IQR 35–677 |
7, 36% 8-10, 64% |
N=701 36 median, 34.0–41.0 IQR g/dL |
N=711 7.76 median, 6.83–8.5 IQR |
ECOG 0, 80% ≥1, 20% |
2 median, 1-3 IQR 28% diabetes |
N=711 27.6 median, 24.8–31.1 IQR |
N=551 Normal 22%, overweight 46%, obesity 32% |
| Couderc et al [25] | 80.5±4.3 , 70-88 range | N/A | N/A | 41.8±2.5, 37.6-47.9 range | N/A | N/A | Number of comorbidities 3.4±1.6, 0-7 range ≥5 drugs 58.1% |
26.6±3.6, 21-42 range | N/A |
| Sheikhbahaei et al [26] | 58 median, 54.3–64.3 IQR, 48–75 range | 14 median, 7.2–44 IQR | 8 median, 8–9 IQR, 7–10 range | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 29.3 median, 25.1–33.4 IQR | Normal 22.7%; overweight 27.3%; obese 50% |
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AS A SINGLE MEASURMENT DURING ADT | |||||||||
| Owen et al [27] | 71±6 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | Yes 88.6% If yes, mean 3±1 |
28.8±5.0 | N/A |
| Kimura et al [28] | 79.8±6.4 | 0.67±1.69 | ≤6 16.8% ≤7 27.0% ≥8 56.2% |
N/A | N/A | N/A | ≥3, 16.9% | 23.1±3.0 | N/A |
| Study | Cancer | Metastasis sites | Current therapy | ADT drug | ADT duration | Other drugs or intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AT BASELINE AND FOLLOW-UP | ||||||
| Chiang et al [24] |
NCCN: high-risk 72.0%; very high-risk 28.0% | N/A | ADT+EBRT; 72-76Gy Followed by 2-3 years of adjuvant ADT |
N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Korczak et al [21] |
Metastatic HSPC and CRPC | Bones HSPC: 94%; CRPC: 70% Lymph nodes HSPC: 74%; CRPC: 53% Parenchymal organs HSPC: 3%; CRPC: 0 |
HSPC: ADT+docetaxel 75 mg/m2 79.5%/docetaxel 50mg/m2 20.5%, with radiotherapy 11.8%, prostatectomy 0 CRPC: ADT+abiraterone +predniosne 70%/enzalutamide 30% with radiotherapy 63.3%, prostatectomy 13.3% |
N/A | N/A | Dietary consultation HSPC: 20%; CRPC: 38%; ONS2 for approx. 50% of them if NRS ≥3 |
| Sheean et al [22] |
Metastatic HSPC | Total distant metastases 1 median, 1-2 IQR Bone metastases 76% |
ADT±docetaxel 34% | Androgen receptor inhibitors; gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues; gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists | N/A | N/A |
| Couderc et al [25] |
High-risk 45.2%; intermediate 45.2% |
N/A | N=191 ADT+radiotherapy mean 75.6 Gy |
N/A | N=191 6 months 42.11% 15 months 52.63% 18 months 5.26% |
N/A |
| Sheikhbahaei et al [26] |
Castration naïve oligometastatic cancer | N/A | Neoadjuvant ADT+docetaxel 75/55/35 mg/m2+dexamethasone 2/day, beginning the day before chemotherapy, for 3 days. 45,45%: concurrent abiraterone+prednisone for 1-16 weeks. N=211 radical prostatectomy+radiation therapy to the prostatic/pelvic bed+consolidative stereotactic radiation to metastases |
Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists | Neoadjuvant therapy 9 weeks median, 9–11 IQR From neoadjuvant therapy to prostatectomy 9 weeks median, 7–10 IQR N=211 ADT for 12 months after prostatectomy |
N/A |
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AS A SINGLE MEASURMENT DURING ADT | ||||||
| Owen et al [27] |
Localised/removed 64.3%; advanced 7.1%; unknown 28.6% |
N/A | ADT±prior therapy | Goserelin 57.1% Leuprorelin 20% Goserelin+bicalutamide 7.1% Leuprorelin+bicalutamide 4.3% Triptorelin 4.3% Degarelix 2.9% Abiraterone 1.4% Degarelix+bicalutamide 1.4% Enzalutamide 1.4% |
Min 12 weeks; 25±36 months | Previous prostatectomy 48.6% Previous radiotherapy 68.6% Previous chemotherapy 15.7% |
| Kimura et al [28] |
T1 10.1%; T2 39.3%; T3/T4 50.6% | N/A | ADT±prior therapy | N/A | 83.6±57.6 months | Prostatectomy 6.7% Radiation 21.3% |
| Study | BMI [kg/m2] baseline | BMI [kg/m2] follow up | Appendicular mass [kg/m2] | PMI [cm2 /m2] baseline | PMI [cm2 /m2] follow up | SMI [cm2/m2] baseline | SMI [cm2/m2] follow up | SMD [HU] baseline | SMD [HU] follow up | SATI [cm2/m2] baseline | SATI [cm2/m2] follow up | VATI [cm2/m2] baseline | VATI [cm2/m2] follow up | TATI [cm2/m2] baseline | TATI [cm2/m2] follow up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AT BASELINE AND FOLLOW-UP | |||||||||||||||
| Chiang et al [24] | 24.2±3.5 | 24.5±3.5 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 47.2±7.4 | 44.5±7.3 | 37.8±5.6 | 34.9±5.9 | 39.9±13.6 | 44.7±14.7 | 55.2±28.0 | 60.1±29.6 | 95.1±37.7 | 104.6±40.4 |
| Korczak et al [21] | HSPC: 28.5 ± 4.9 CRPC: 29.3 ±4.4 |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | HSPC: 54.01± 9.85 CRPC: 52.0±8.311 |
HSPC: 50.4 ±9.61 CRPC: 47.4±6.46 |
N/A | N/A | HSPC: 66.47±33.36 CRPC: 86.1±29.7 |
HSPC: 78.2±39.2 CRPC: 92.01±40.2 |
HSPC: 90.40± 44.2 CRPC: 110.2±37.9 |
HSPC: 101.7±42.6 CRPC: 112.4±39.89 |
N/A | N/A |
| Sheean et al [22] | N = 711 27.6 median, 24.8–31.1 IQR |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N=551 49.8 median, 40.2–56.2 IQR |
Non-black N=141: −3.7 median, (−8.5)–(−0.4) IQR (7% loss) Black N=51: −1.2 median, (−1.8)–12.5) IQR (2% gain) |
N=551 33.8, median 26.3–41.8 IQR | Non-black N=141: −5.7 median, (−9.6)−(3.2) IQR (14%) Black N=51: −5.3 median, (−7.2)−(−1.4) IQR (12%) |
N=551 51.9 median, 33.3–69.4 IQR |
Subcutaneous adipose tissue change [cm2] Non-black N=141: 23.2 median, (−6.5)−51.5 IQR (5% gain) Black N=51: 95.2 median, (89.4–172.3) IQR (8% gain) |
N=551 61.6 median, 33.6–98.9 IQR |
Visceral adipose tissue change [cm2] Non-black N=141: −16.0 median, (−32.2)−3.5 IQR (1% gain) Black N=51: median 40.1, 29.4–41.0 IQR (2% gain) |
N/A | N/A |
| Couderc et al [25] | N=191 26.1±2.6, 21-32 range |
N=191 25.5±3.2, 18-31.9 range |
ASSM/height2 <7.0 for 2 patients | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Sheikhbahaei et al [26] | 29.3 median, 25.1–33.4 IQR | N/A | N/A | 8.7 median, 8.11–11.3 IQR Psoas muscle mass 27.5 median, 24.6–36.7 IQR |
Psoas muscle area I: −13.9% (−7.6, −16.5) II: −13.2(−6, −11.2)) |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 72.4 median, 51.0–107.1 IQR Subcutaneous adiposity [cm2]: 217 median, 159.8–340.9 IQR |
Subcutaneous fat [cm2] I: +8.9(+5.1, +21.5) II: +18.9(+6.1, +33.8) |
81.6 median, 46.4–102.9 IQR Visceral adiposity [cm2]: 261.3 median, 142.4–326.9 IQR |
Visceral fat [cm2] I: −1.6(−9.9, +18,7) II: +8.4(−1.7, +23.8) |
Total adiposity [cm2] 476.8 median, 389.8–685 IQR |
Total adiposity[cm2] I: +5.7(+0.8, +15.2) II: +10.3(+2.7, +28.5) |
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AS A SINGLE MEASURMENT DURING ADT | |||||||||||||||
| Owen et al [27] | 28.8 ±5.0 | ALMI 8.07±0.95 ALMBMI 0.875±0.117 |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||
| Kimura et al [28] | 23.1±3.0 | N/A | N/A | 7.23±1.10 [kg/m2] | 0.20±0.04 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||
| Study | Sarcopenia definition | Assessment | Assessment methodology | Sarcopenia at baseline | Sarcopenia at follow up | Time to follow up | Significance of outcomes | Correlation between survival and sarcopenia |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AT BASELINE AND FOLLOW-UP | ||||||||
| Chiang et al [24] |
SMI: <43.2cm2/m2 | CT: L3 level | One blinded researcher. | 33.6% | 48.0% | 180 days median, 146-223 IQR | p=0.001 | Sarcopenia at baseline was not associated with 3-year non-cancer-specific survival and 3-year prostate cancer-specific survival. |
| Korczak et al [21] |
SMI: 1. 53cm2/m2 2. 43cm2/m2for BMI <25 kg/m2 3. Sarcopenic obesity: <53cm2/m2 for BMI >30kg/m2 |
CT: L3 level | Software CoreSlicer.com. Manual correction. | HSPC: 47.06% CRPC: 46.67% |
HSPC: 58% CRPC: 79.3% |
12.33 months median, 5.4-26 range | HSPC: NS CRPC: p=0.015 |
Sarcopenia was not correlated with progression-free survival. |
| Sheean et al [22] |
SMI: 1. 53cm2/m2 2. 43cm2/m2for BMI <25kg/m2 3. Sarcopenic obesity: <53cm2/m2for BMI >30kg/m2 |
CT: L3 level | Automated tissue demarcation. Manual correction. 10 images were assessed for quality assurance. | N=55 49% (15% of N=55 had sarcopenic obesity) |
N=8 0% |
12.5 months median |
N/A | Sarcopenia was not correlated with overall survival. |
| Couderc et al [25] |
EWGSOP2 guidelines Hand-grip <27kg DXA ASSM/height² <7.0kg/m2 |
Baseline: hand-grip strength Follow-up: DXA |
Hand-grip strength test was performed according to ASHT recommendations. | N=311 Probable sarcopenia 25% |
N=61 1 patient |
N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Sheikhbahaei et al [26] |
PMI <5.7cm2/m2 Sarcopenic obesity: PMI <5.7cm2/m2 for BMI >30kg/m2 |
CT: L3-L4 level | Manual analysis of anonymized images twice at different time points. Third reviewer assessed differences. | Sarcopenic obesity 9.1% | No change at both follow up CTs | First: 3 months median, 2–3 IQR Second: 12 months median, 10.5–17.5 IQR |
N/A | N/A |
| SARCOPENIA ASSESSED AS A SINGLE MEASURMENT | ||||||||
| Owen et al [27] |
ALMHFM ≤−1.816 and weak handgrip strength and/ or slow gait speed based on EWGSOP1, EWGSOP2, FNIH and IWGS |
Handgrip dynamometer 4 m walk test DXA |
Six tests, three for each hand, were performed for dynamometry (the highest). Dynamometer Jamar Plus Digital. Three test for gait speed were performed (the fastest). For DXA researchers were blinded. Software 12.30.008 (Lunar iDXA, GE Lunar Corp., Madison, USA). |
ADT group: FNIH 1.0% EWGSOP1 1.0% EGSOP2 or IWGS 0 No-ADT group: EWGSOP1 1.92% Healthy group EWGSOP1 1.43% |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Kimura et al [28] |
Walking speed <0.8m/s and/or handgrip strength <26kg+ SMI <7.0kg/m2 Sarcopenic obesity: sarcopenic criteria+body fat ≥25% |
Handgrip dynamometer 5m walking BIA |
Two tests were performed for dynamometry (the highest) and walking test (average). Dynamometer TKK 5401. BMI system MC-780A. | Sarcopenia non-obese 15.7% Sarcopenic obesity 13.5% |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





