Submitted:
19 January 2024
Posted:
19 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
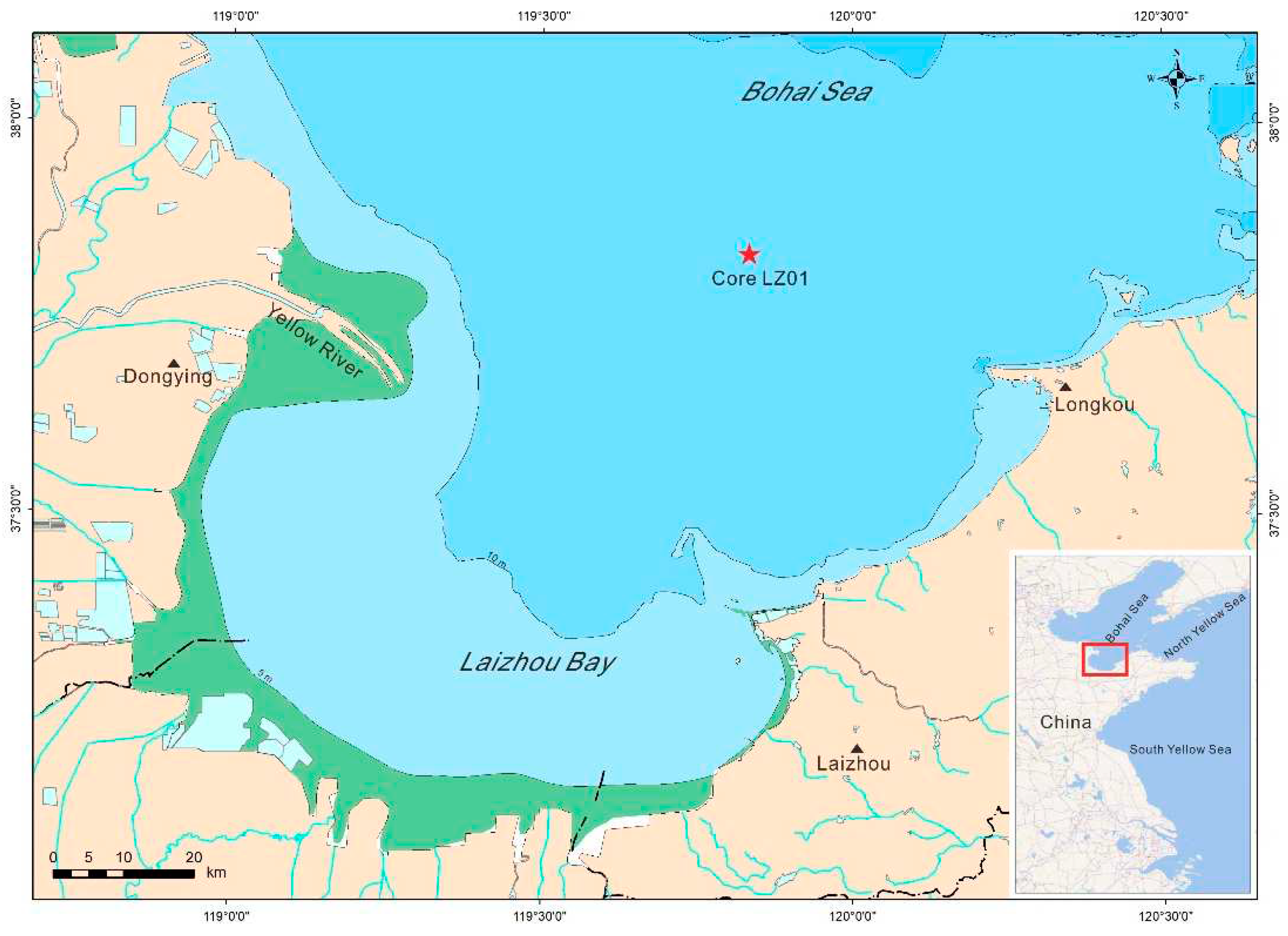
2.1. Sampling and Analytical Methods
2.2. Multivariate Analysis Method
2.3. Assessment Methods of Heavy Metal Pollution
2.3.1. Enrichment Factor
2.3.2. Geoaccumulation Index
2.3.3. Nemerow Pollution Index
2.3.4. Potential Ecological Risk Index
3. Results
3.1. Sedimentary Structure of the Core
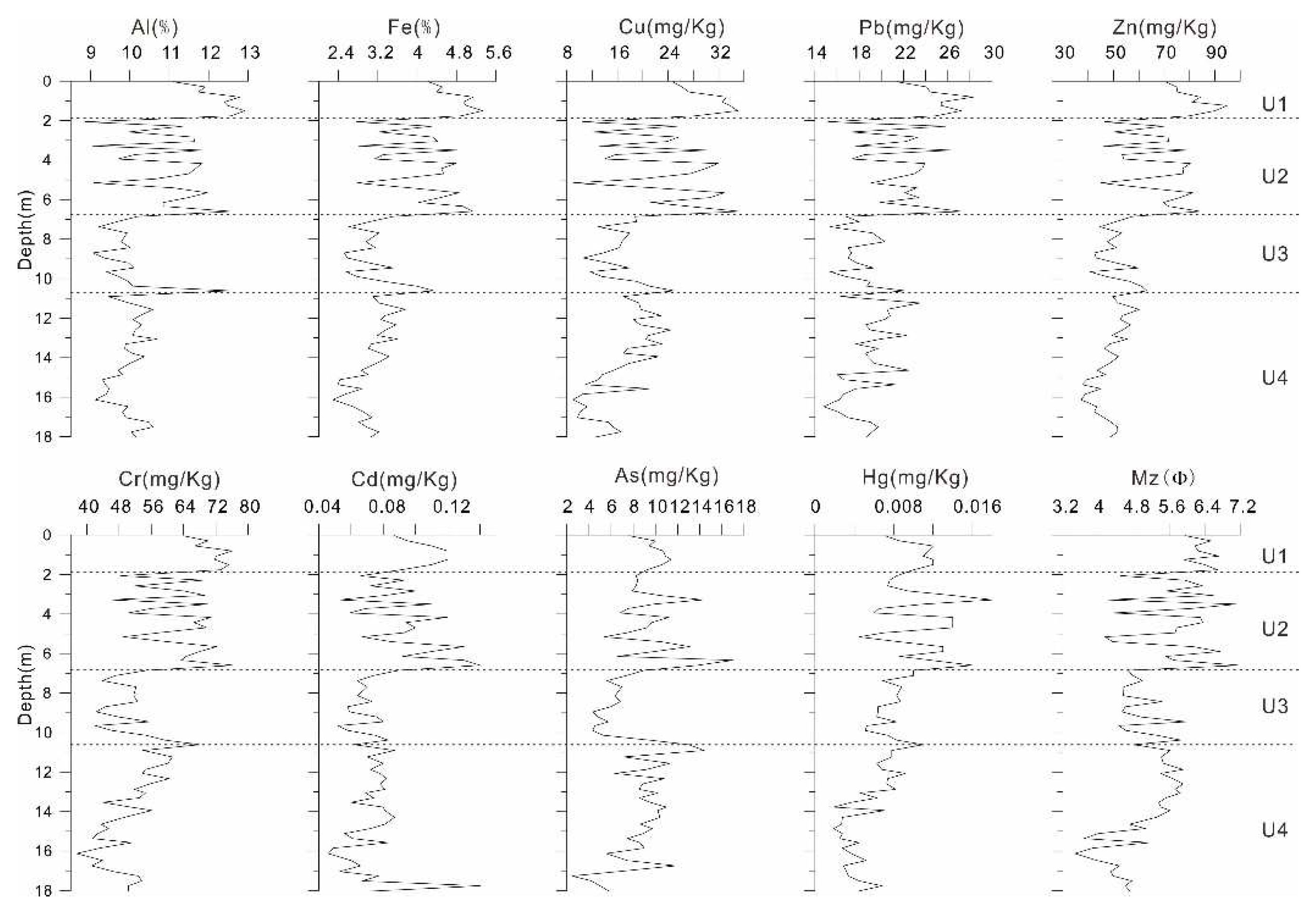
3.2. Concentration of Heavy Metals
4. Discussion
4.1. Assessment of Sediment Contamination
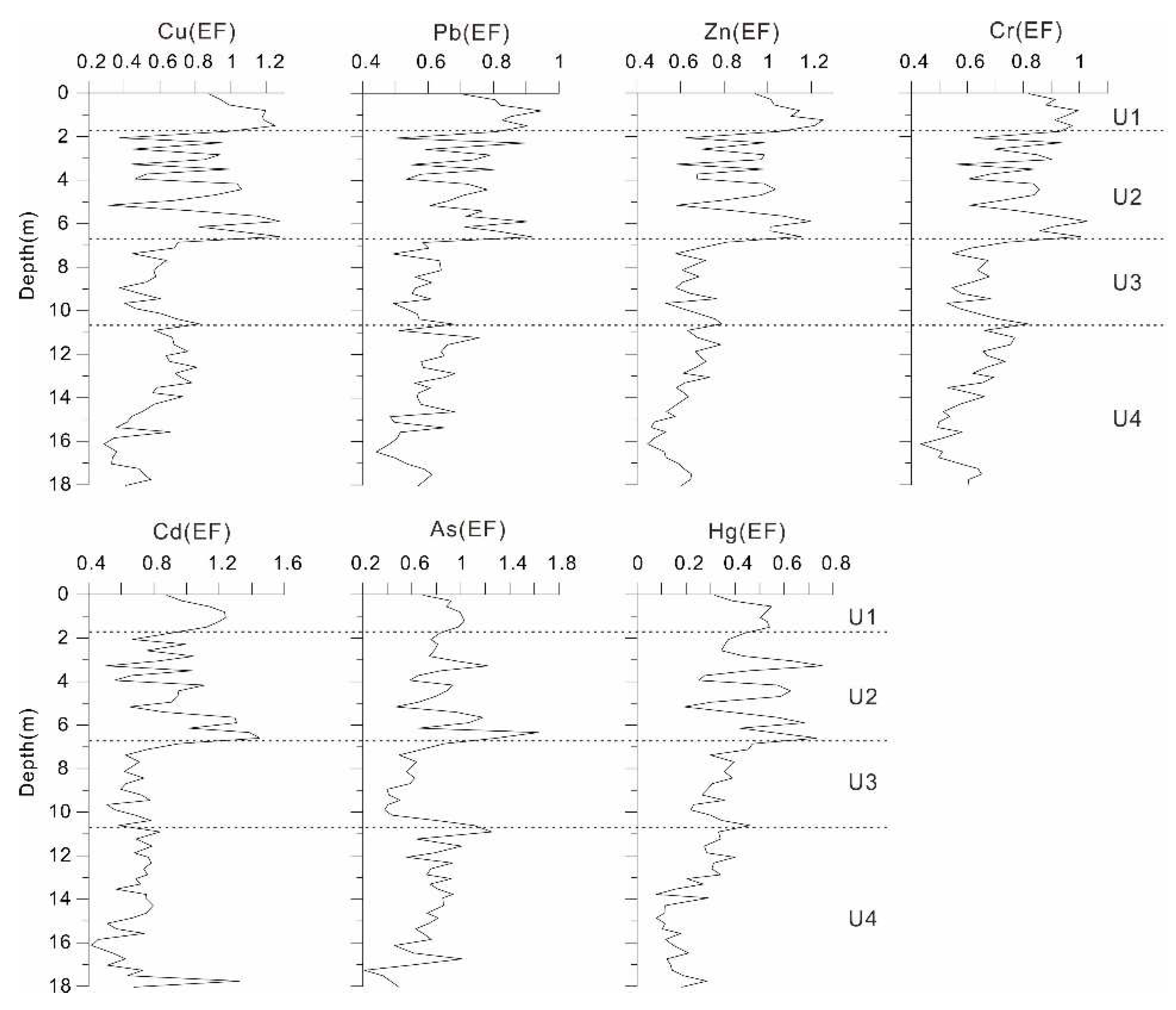

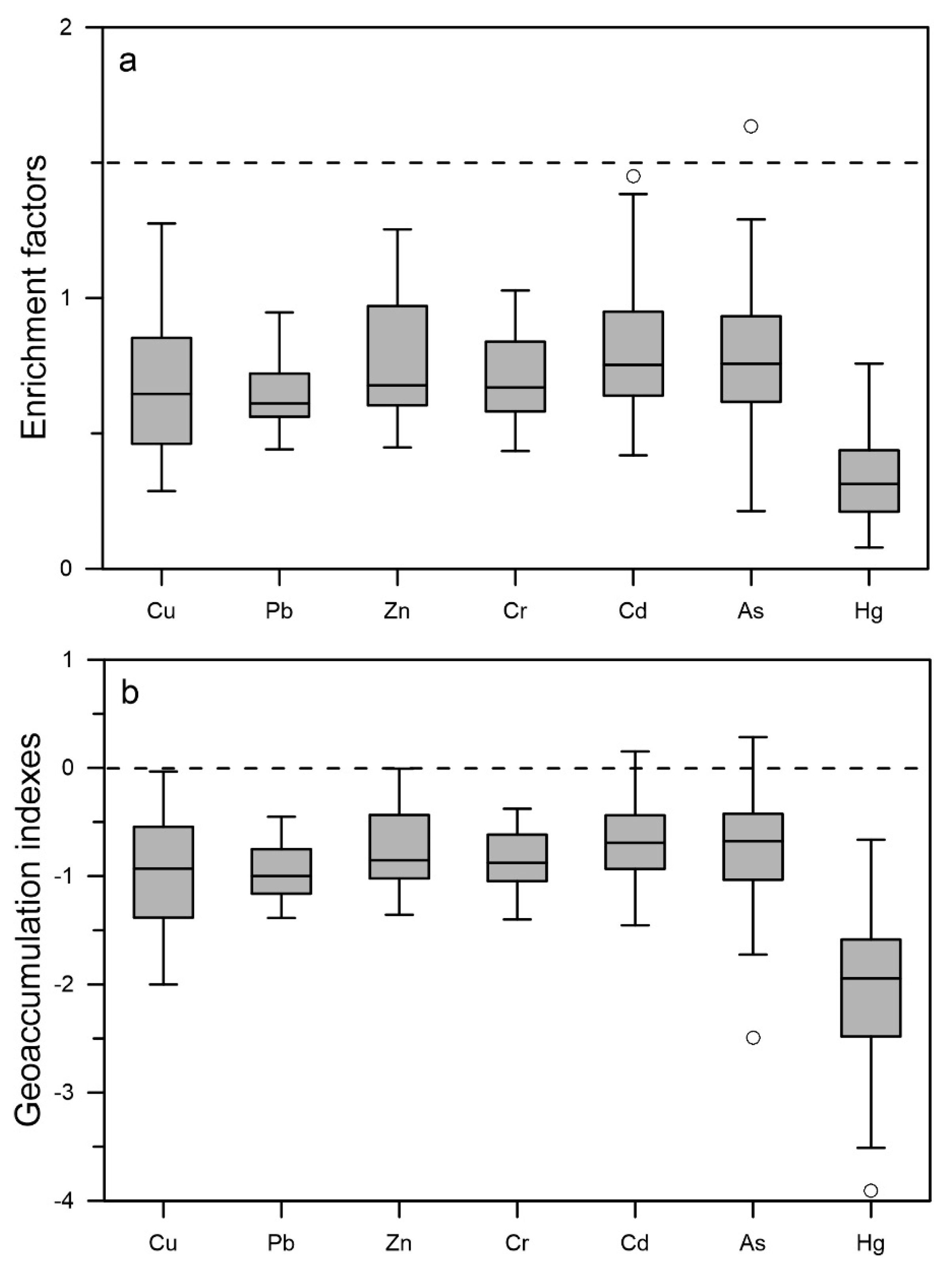
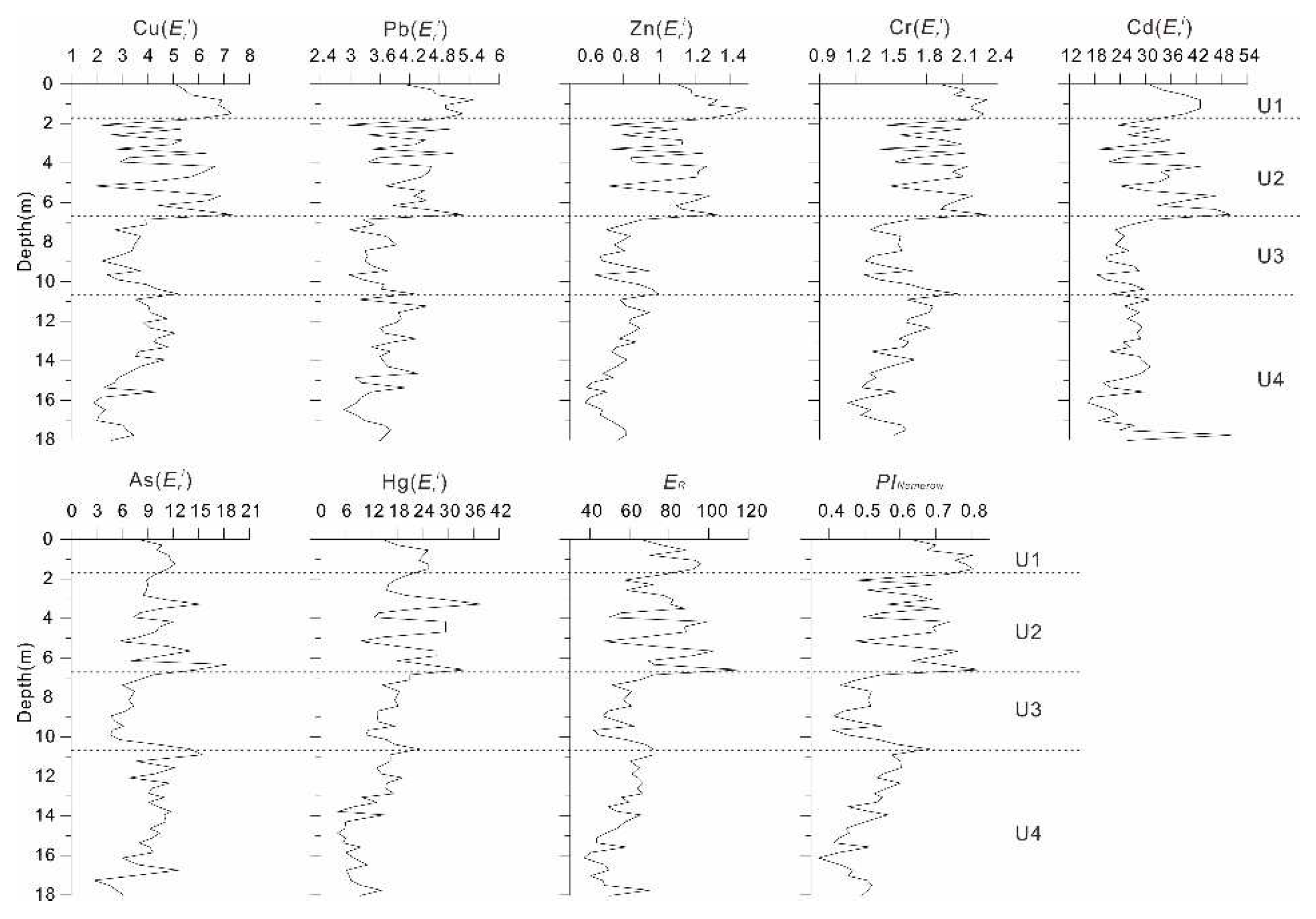
4.2. Source of the Heavy Metals
4.3. Selection of Elemental Background Values
5. Conclusions
References
- Gil, F.; Olmedo, P. Food safety heavy metals and metalloids, in: Encyclopedia of Human Nutrition. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Thorat, B.; Prasad, P.; Ram, A. Heavy metal accumulation in a moderately polluted Ulhas estuary, Western India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 60, 102818. [Google Scholar]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, T.; Naz, S.; Hussain, R.; Chatha, A.M.M.; et al. Exposure to heavy metals causes histopathological changes and alters antioxidant enzymes in fresh water fish (Oreochromis niloticus). Asian J. Agricul. Biol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, J.; Qiu, J.; et al. Spatio-temporal distribution and environmental risk of sedimentary heavy metals in the Yangtze river estuary and its adjacent areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 116, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Liao, X.; et al. Heavy metal pollution in coastal wetlands: A systematic review of studies globally over the past three decades. J. Hazard Mater. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onakpa, M.M.; Njan, A.A.; Kalu, O.C. A review of heavy metal contamination of food crops in Nigeria. Ann. Glob. Health 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strode, E.; Jansons, M.; Purina, I.; et al. Sediment quality assessment using survival and embryo malformation tests in amphipod crustaceans: The Gulf of Riga, Baltic Sea AS case study. J. Mar. Syst. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Hu, R.; Feng, X.; et al. Sedimentary records and implications for the evolution of sedimentary environments inferred from BH1302 during the late Quaternary in the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Geol. 2023, 456, 106986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Pei, S.; Liao, M.; et al. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay and their sources and pollution assessment. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2021, 41, 67–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Liu, R. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments off the Dongying coast, Bohai Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hu, B.; Bi, J.; et al. Heavy metals distribution and contamination in surface sediments of the coastal Shandong Peninsula (Yellow Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Liu, J.; Pei, S.; et al. Sediment properties and trace metal pollution assessment in surface sediments of the Laizhou Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11634–11647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, H.; Wei, X.; et al. Heavy metals and their ecological risk in the surface sediments of Laizhou Bay. Period. Ocean Uni. China 2021, 51, 74–85. [Google Scholar]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos river bar: a study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuiver, M.; Reimer, P.J.; Reimer, R.W. CALIB 8.2 [WWW Program]. 2020. at. http:// calib.org. accessed 2020-8-14.
- Aitken, M. An Introduction to Optical Dating: the Dating of Quaternary Sediments by the Use of Photon-stimulated Luminescence. 1998. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
- Marsh, R.; Prestwich, W.; Rink, W.; Brennan, B. Monte Carlo eterminations of the beta dose rate to tooth enamel. Radiat. Meas. 2002, 35, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Center (CNEMC). Chinese elemental background values for soils. 1990, Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing.
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.L. Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China-weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 1051–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Heavy-metals in sediment of the rhine-changes since 1971. Umschau in Wissenschaft und Technik 1979, 79, 778–783. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, G. Die Schwermetallbelastung der sediment des Neckars und seiner Nebenflusse: eine Bestandsaufnahme. Chemiker Zeitung 1981, 105, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- AQSIQ. (Administration of quality supervision, inspection and quarantine of the People's Republic of China). Marine Sediment Quality of China (GB 18668-2002). 2002. Standards Press of China, Beijing.
- Kowalska, J.; Mazurek, R.; Gąsiorek, M.; et al. Soil pollution indices conditioned by medieval metallurgical activity – A case study from Krakow (Poland). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, W.; Kong, L.; et al. Records of trace metals since the Holocene in sediments of Laizhou Bay, Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, S.; et al. Heavy metals distribution and environmental quality assessment for sediments off the southern coast of the Shandong Peninsula, China. Mar. Pollu. Bull. 2015, 100, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madadi, R.; Mejjad, N.; De-la-Torre, G.E. Geochemical speciation, ecological risk, and source identification of heavy metal(loid)s in sediments and waters from Musa Estuary, Persian Gulf. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Ra, K. Pollution and ecological risk assessments for heavy metals in coastal, river, and road-deposited sediments from Apia City in Upolu Island, Samoa. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrose, A.; Coynel, A.; Schäfer, J.; et al. Assessing the current state of the Gironde Estuary by mapping priority contaminant distribution and risk potential in surface sediment. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1912–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diagomanolin, V.; Farhang, M.; Ghazi-Khansari, M.; et al. Heavy metals (Ni, Cr, Cu) in the karoon waterway river, Iran. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 151, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Zhao, G.; Li, X.; et al. Regional distribution of heavy metals in surface sediments of Dafeng coastal wetlands in Yancheng, Jiangsu and its ecological implications. Mar. Geol. Front. 2018, 430, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in sediments of typical estuaries on the south coast of Laizhou Bay. 2020, Master Dissertation of Shandong Normal University.
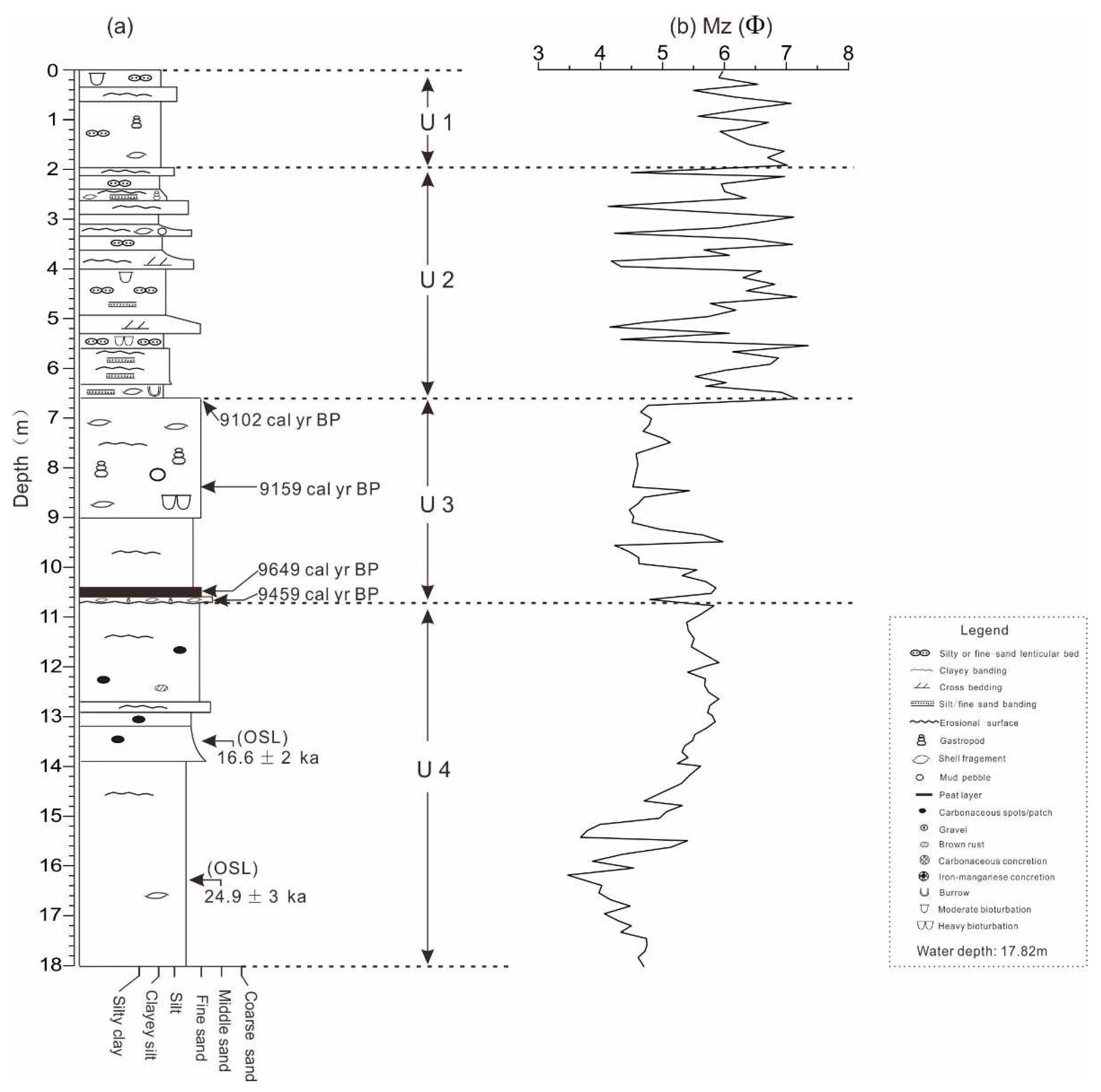
| Depth (m) | Materials | δ13C (permil) |
Conventional age(14C yr BP) | Calendar ages(Cal yr BP) | Beta No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | Range (2σ) | |||||
| 6.83 | Gastropod | -2.3 | 8310 ± 40 | 9102 | 9012-9191 | 372002 |
| 8.40 | Gastropod | -4.8 | 8350 ± 40 | 9159 | 9065-9253 | 372003 |
| 10.46 | Peat layer | -22.9 | 8720 ± 40 | 9649 | 9563-9734 | 372004 |
| 10.64 | Shell | +4.1 | 8610 ± 40 | 9459 | 9405-9512 | 372005 |
| Depth (m) | Water content (%) | U (ppm) | Th (ppm) | K (%) | DE (Gy) | Age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13.50 | 15.89 | 3.68 | 9.53 | 1.54 | 82.1 | 16.6 ± 2.0 |
| 16.27 | 16.97 | 2.75 | 6.7 | 1.59 | 102.16 | 24.9 ± 2.0 |
| Locations | time | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | Cd | As | Hg | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LZ01 | Avg. (n=71) | 19.77 | 20.17 | 57.70 | 56.02 | 0.08 | 8.68 | 0.008 | This study |
| U1 | 24.7-35 | 21.4-28.3 | 70.5-94.8 | 63.8-76.1 | 0.087-0.12 | 7.62-11.4 | 0.007-0.012 | ||
| Avg. (n=8) | 30.13 | 25.14 | 81.33 | 71.14 | 0.11 | 9.98 | 0.01 | ||
| U2 | 9.1-35.2 | 15.2-27.2 | 45-84.2 | 46.2-76.2 | 0.053-0.14 | 5.37-17 | 0.005-0.018 | ||
| Avg. (n=20) | 22.65 | 21.67 | 66.41 | 62.18 | 0.09 | 9.77 | 0.011 | ||
| U3 | 10.6-24.9 | 15.4-22.1 | 40.8-63.1 | 42.1-68 | 0.052-0.089 | 4.32-13 | 0.005-0.011 | ||
| Avg. (n=15) | 16.59 | 18.01 | 51.31 | 50.83 | 0.07 | 6.63 | 0.008 | ||
| U4 | 9-24.4 | 14.8-23.5 | 37.2-60.1 | 37.5-61.2 | 0.046-0.14 | 2.48-14.4 | 0.002-0.009 | ||
| Avg. (n=28) | 16.57 | 18.80 | 48.15 | 50.09 | 0.07 | 8.62 | 0.005 | ||
| Yellow River Estuary | 22.84 | 21.23 | 64.8 | 61.07 | 0.09 | 11.12 | 0.01 | [26] | |
| Dongying Coast | 22.5 | 21.6 | 70.2 | 66.4 | 0.12 | 12.8 | na | [11] | |
| Laizhou Bay | 19.06 | 20.3 | 55.98 | 60.1 | 0.11 | 11.72 | 0.038 | [10] | |
| Southern Shandong Peninsula | 23.1 | 25 | 71.1 | 64.3 | 0.08 | 11.4 | 0.032 | [27] | |
| Coastal Shandong Peninsula | 20 | 28.4 | 74.7 | 57.8 | na | na | na | [12] | |
| Musa Estuary, Iran | 23 | 7.33 | 51.5 | 105.5 | 0.18 | 2.48 | na | [28] | |
| Upolu Island, Samoa | 29 | 7.4 | 98.5 | 368 | 0.13 | 3.6 | 0.03 | [29] | |
| Element baseline in the soil of Shandong Peninsula | 24 | 25.8 | 63.5 | 66 | 0.084 | 9.3 | 0.019 | [19] | |
| Parameters | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | Cd | As | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mbackgrounda (mg/kg) | 24 | 25.8 | 63.5 | 66 | 0.084 | 9.3 | 0.019 |
| EF | 0.29-1.28 | 0.44-0.95 | 0.45-1.25 | 0.43-1.03 | 0.42-1.45 | 0.21-1.64 | 0.08-0.76 |
| 0.68 | 0.65 | 0.75 | 0.70 | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.34 | |
| Igeo | -2 to -0.03 | -1.39 to -0.45 | -1.36 to -0.01 | -1.4 to -0.38 | -1.45- 0.15 | -2.49-0.29 | -3.91 to -0.66 |
| -0.96 | -0.96 | -0.76 | -0.85 | -0.67 | -0.76 | -2.07 | |
| 1.88-7.33 | 2.87-5.48 | 0.59-1.49 | 1.14-2.31 | 16.43-50 | 2.67-18.28 | 4-37.89 | |
| 4.12 | 3.91 | 0.91 | 1.7 | 29.26 | 9.33 | 16.15 |
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER | 66.55-96.01 | 46.97-114.76 | 41.95-72.18 | 36.93-72.07 |
| Avg. | 82.53 | 76.55 | 57.76 | 54.89 |
| PINemerow | 0.64-0.8 | 0.47-0.82 | 0.41-0.68 | 0.37-0.6 |
| Avg. | 0.74 | 0.64 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| Al | Fe | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | Cd | As | Hg | Mz | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 1 | |||||||||
| Fe | 0.94** | 1 | ||||||||
| Cu | 0.90** | 0.94** | 1 | |||||||
| Pb | 0.86** | 0.85** | 0.85** | 1 | ||||||
| Zn | 0.93** | 0.98** | 0.93** | 0.84** | 1 | |||||
| Cr | 0.93** | 0.96** | 0.92** | 0.85** | 0.96** | 1 | ||||
| Cd | 0.73** | 0.82** | 0.82** | 0.78** | 0.81** | 0.77** | 1 | |||
| As | 0.44** | 0.56** | 0.53** | 0.40** | 0.46** | 0.47** | 0.54** | 1 | ||
| Hg | 0.61** | 0.71** | 0.70** | 0.57** | 0.73** | 0.72** | 0.57** | 0.46** | 1 | |
| Mz | 0.73** | 0.80** | 0.82** | 0.68** | 0.78** | 0.81** | 0.68** | 0.42** | 0.57** | 1 |
| Parameter | PC1 |
|---|---|
| Al | 0.93 |
| Fe | 0.98 |
| Cu | 0.96 |
| Pb | 0.87 |
| Zn | 0.97 |
| Cr | 0.97 |
| Cd | 0.90 |
| As | 0.55 |
| Hg | 0.75 |
| Mz | 0.84 |
| Eigenvalues | 7.82 |
| Percentage of variances | 78.21 |
| Cumulative % eigenvectors | 78.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




