Submitted:
18 January 2024
Posted:
19 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Physicochemical Properties of CNS Drugs
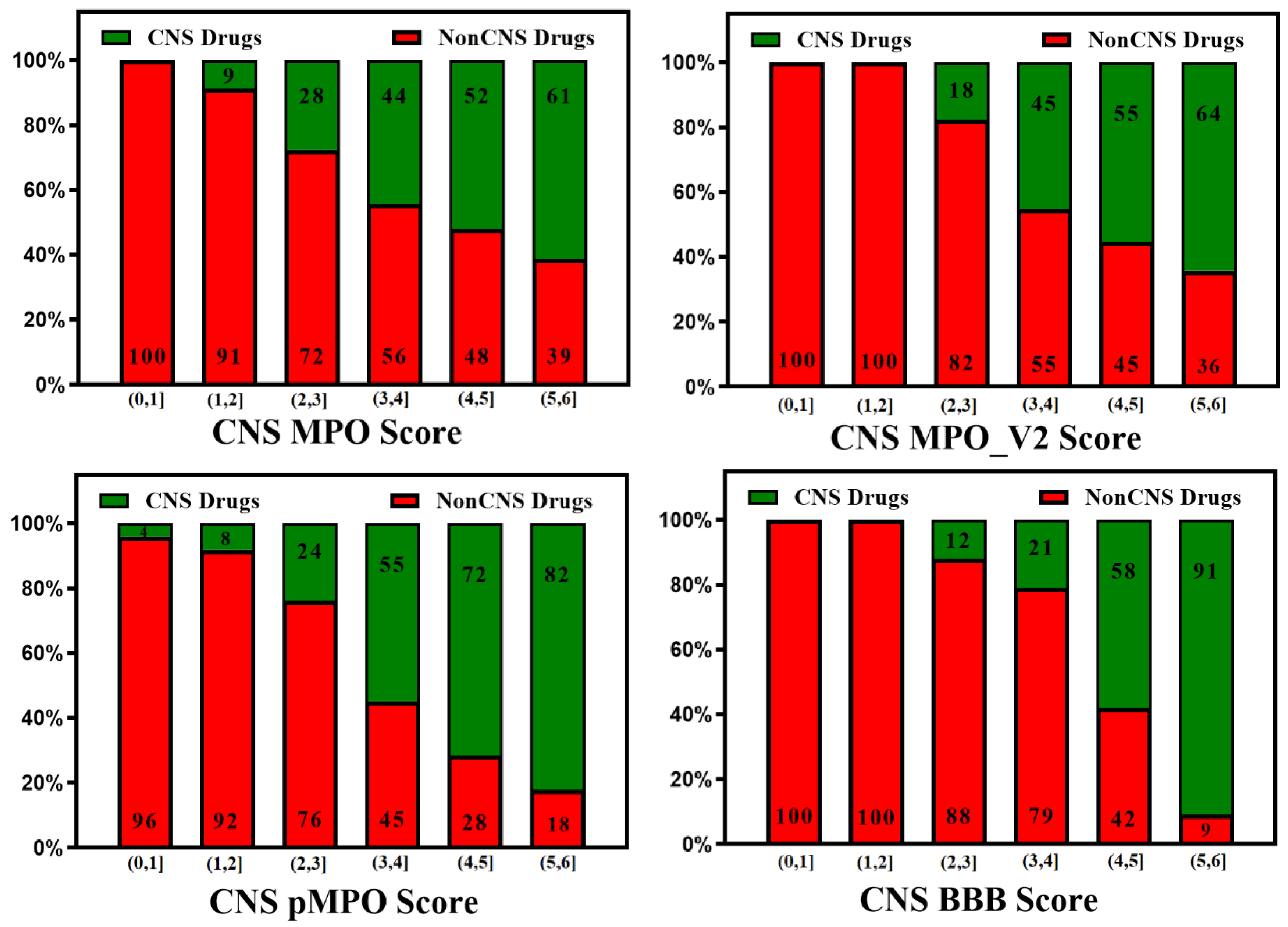
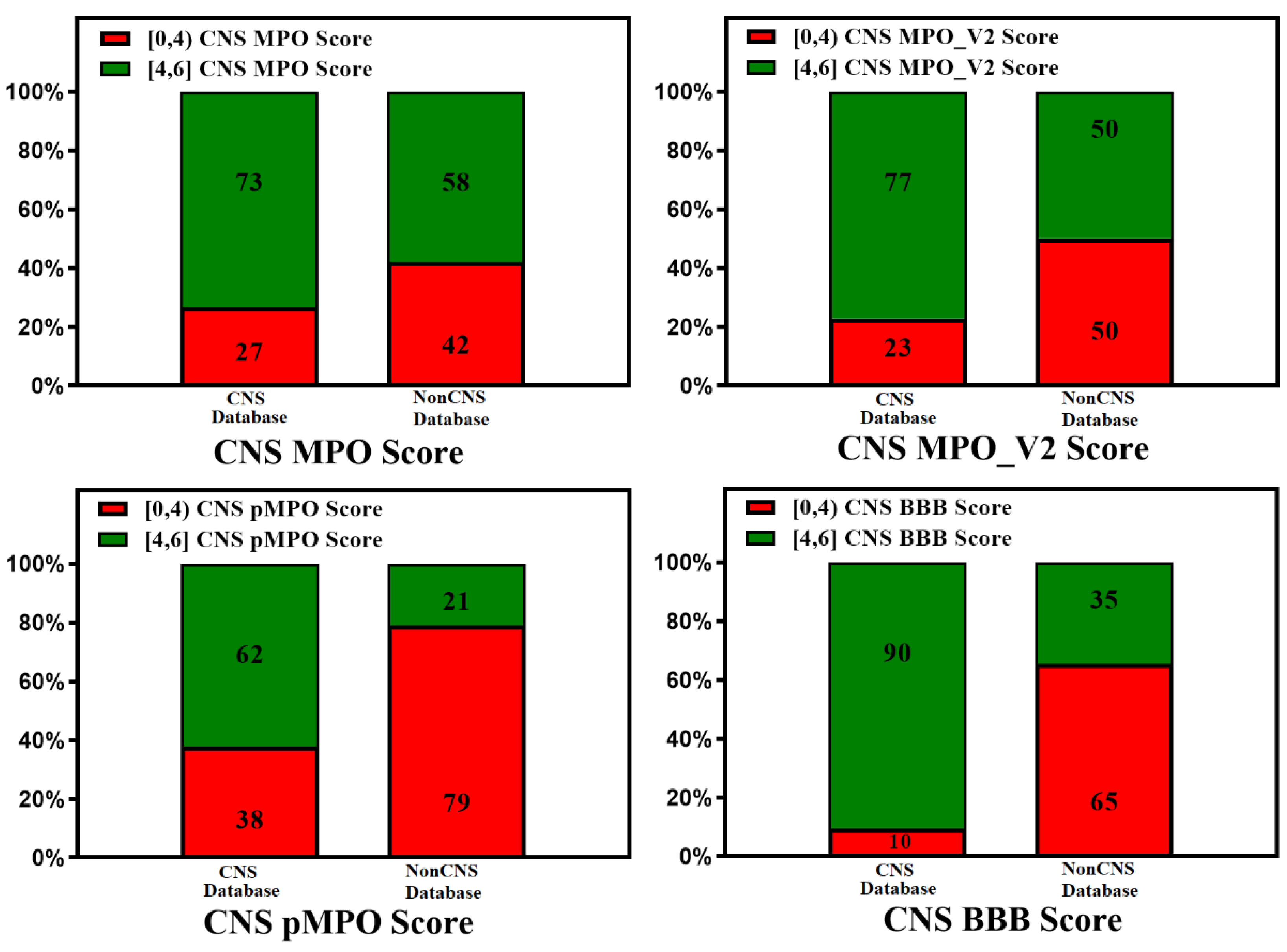
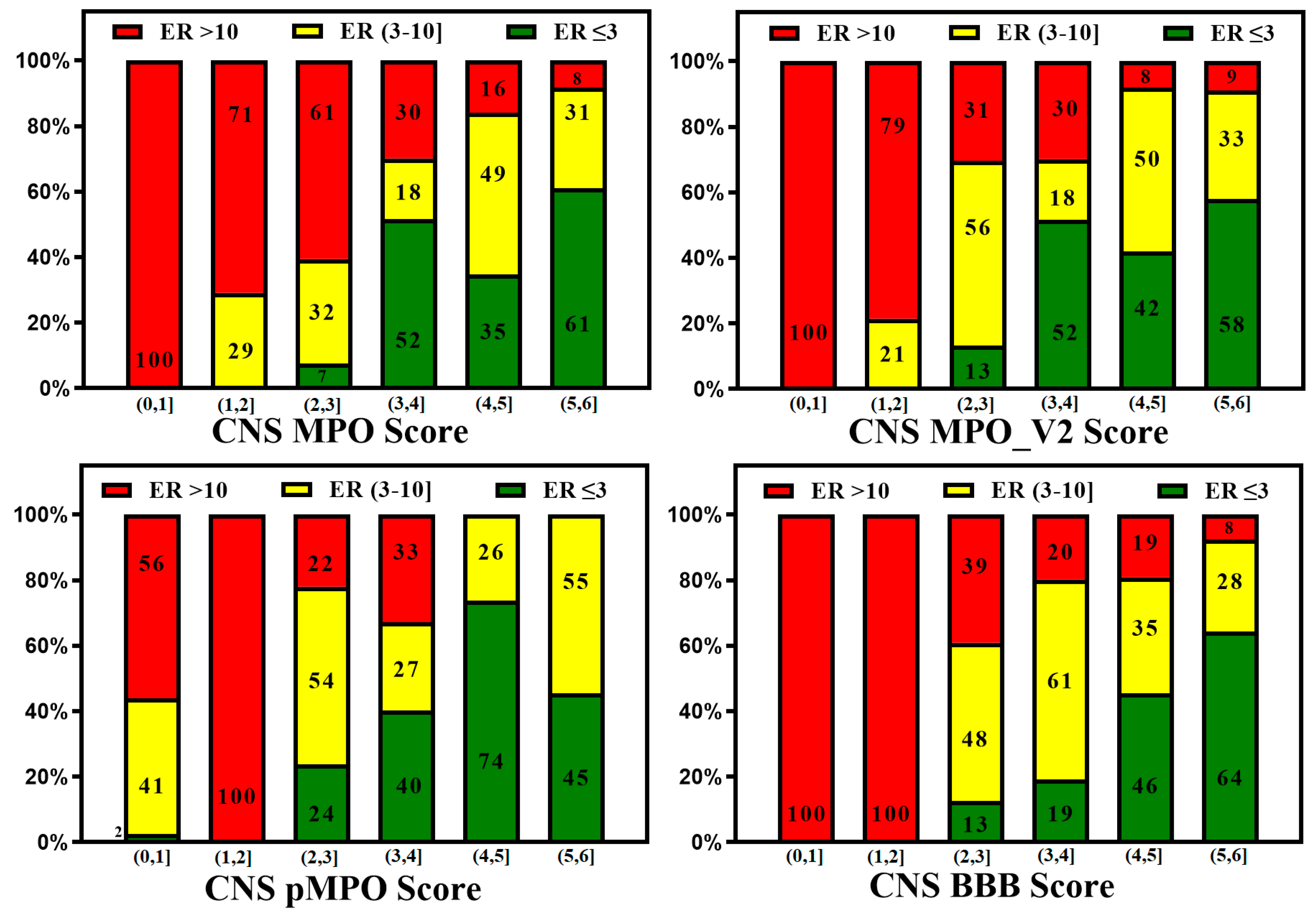
3. BBB Penetration Scoring Schemes for Predicting Brain Penetrance across BBB Primarily by Passive Diffusion
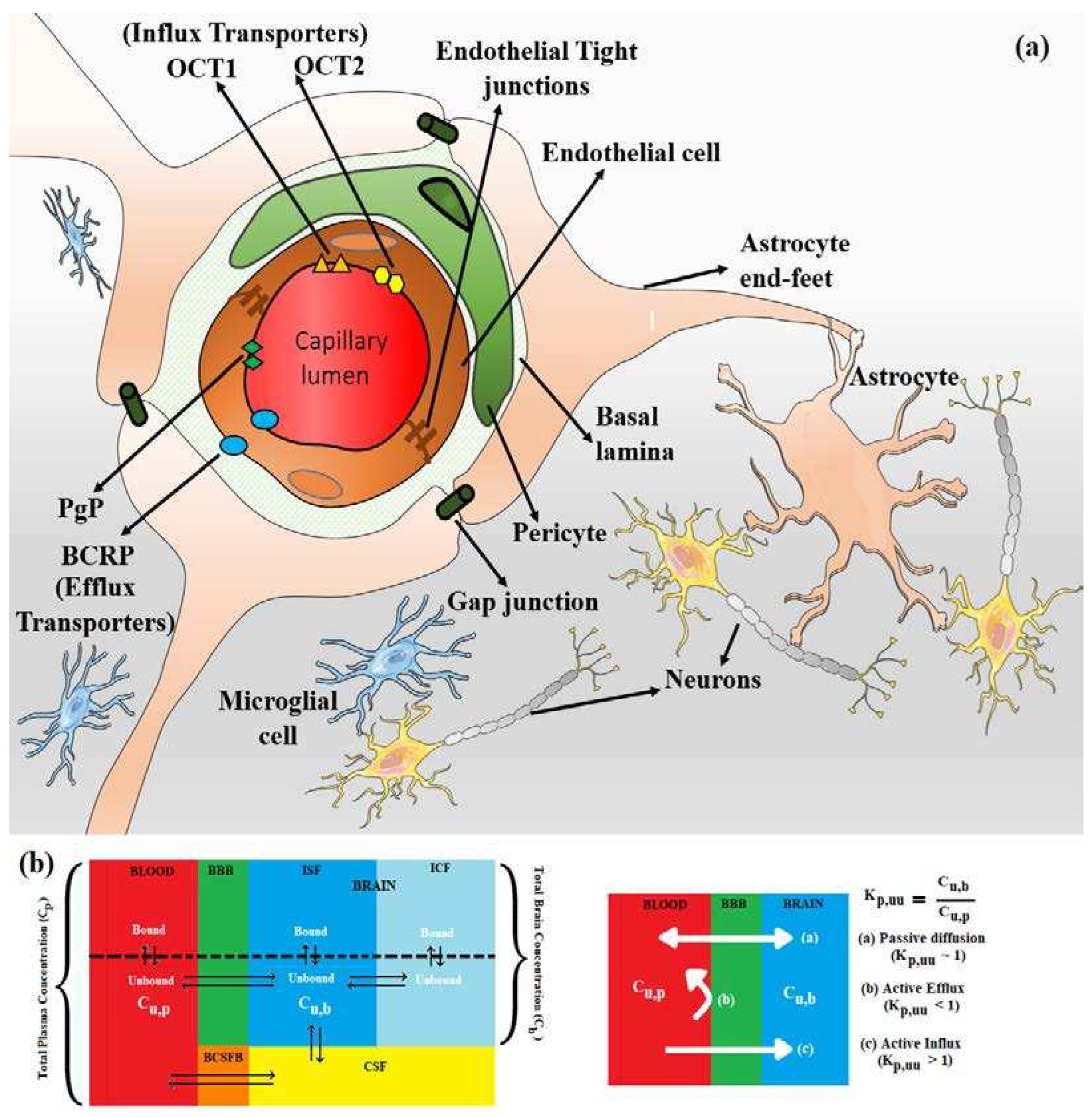
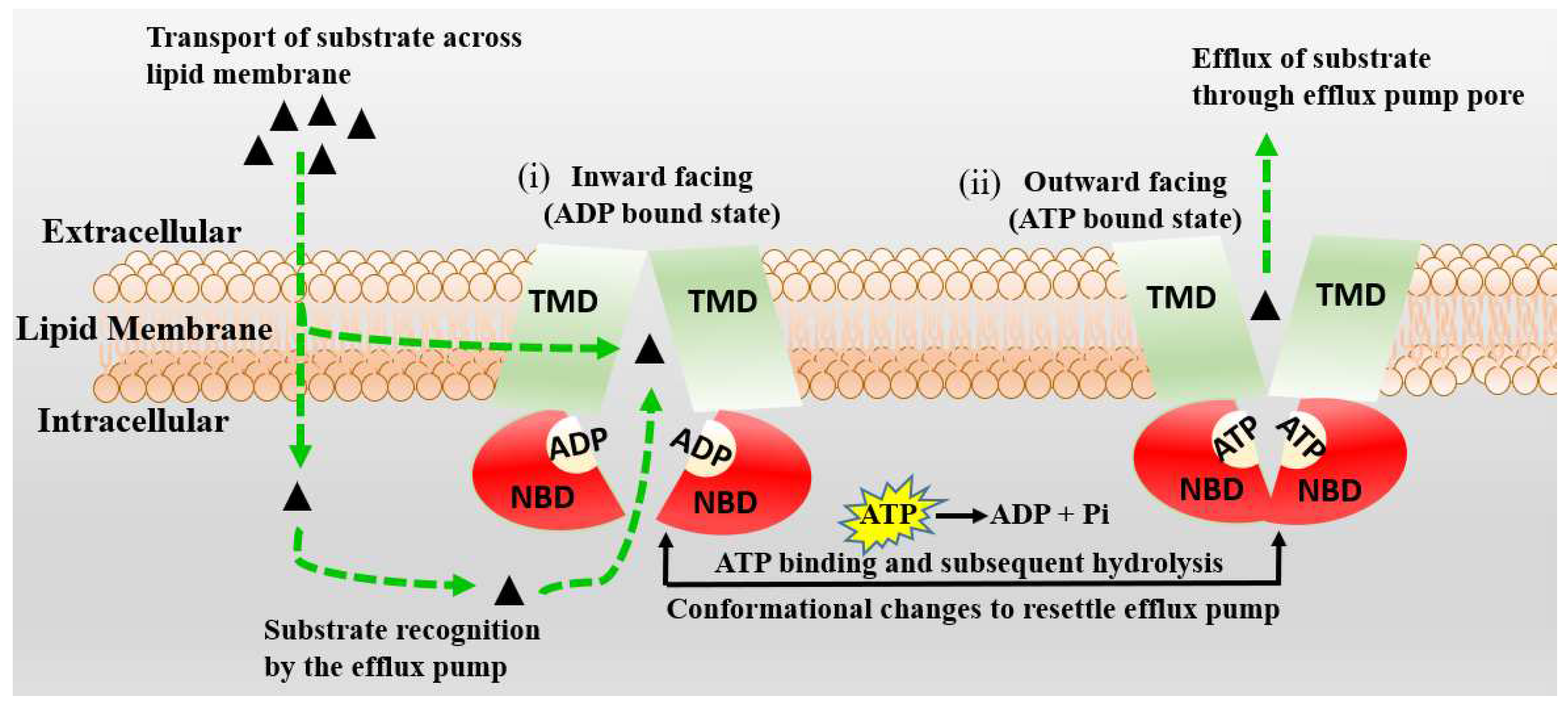
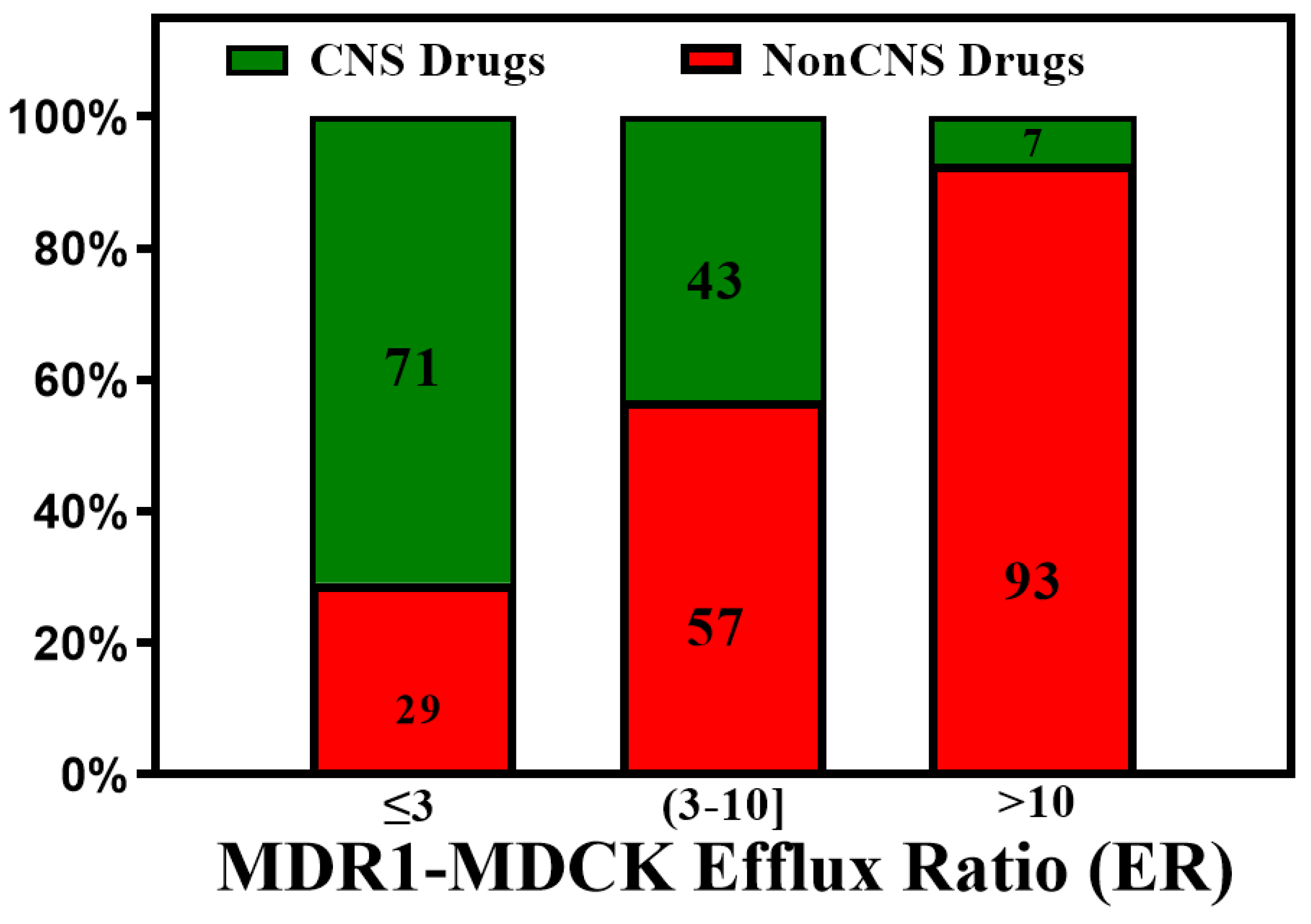
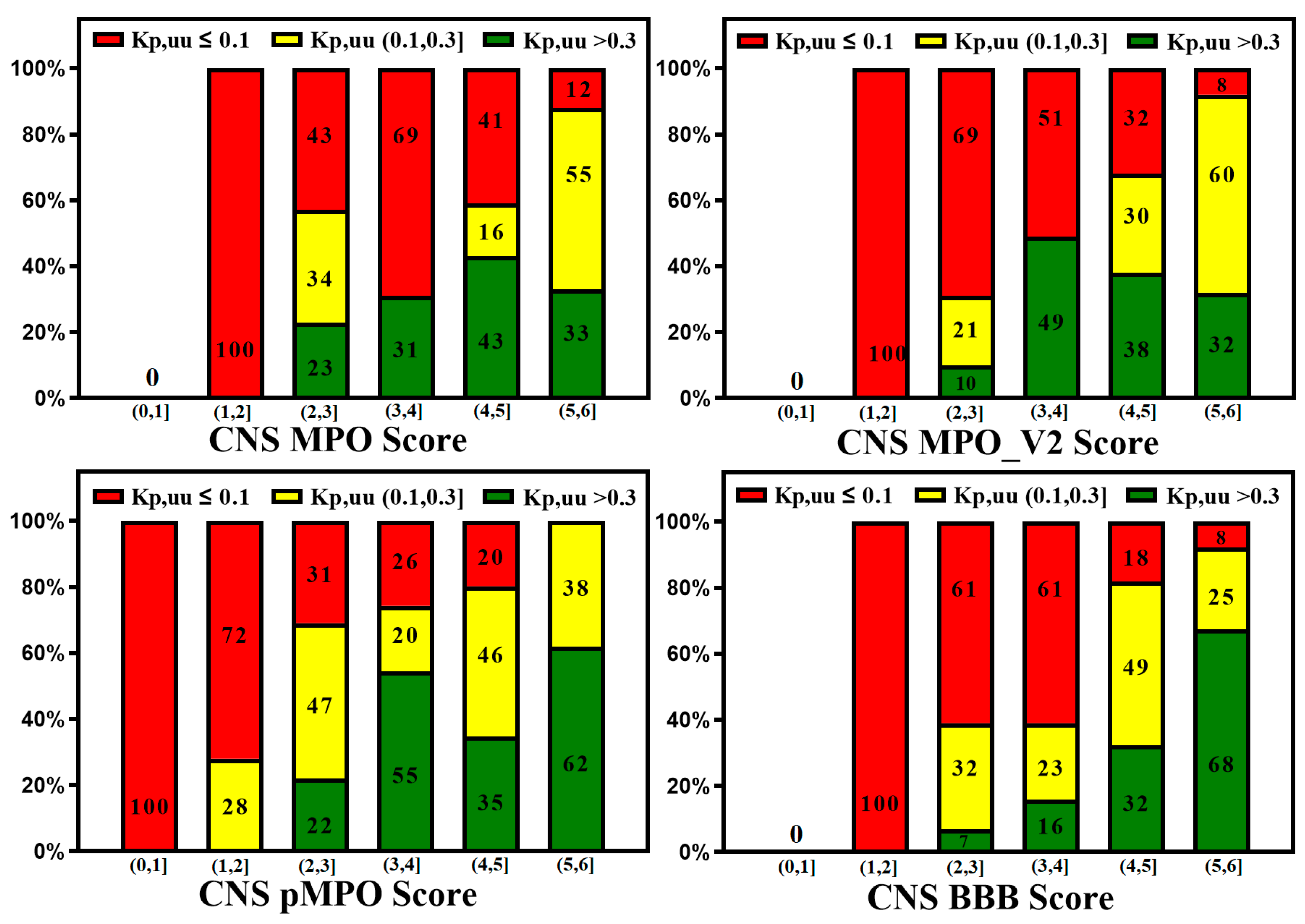
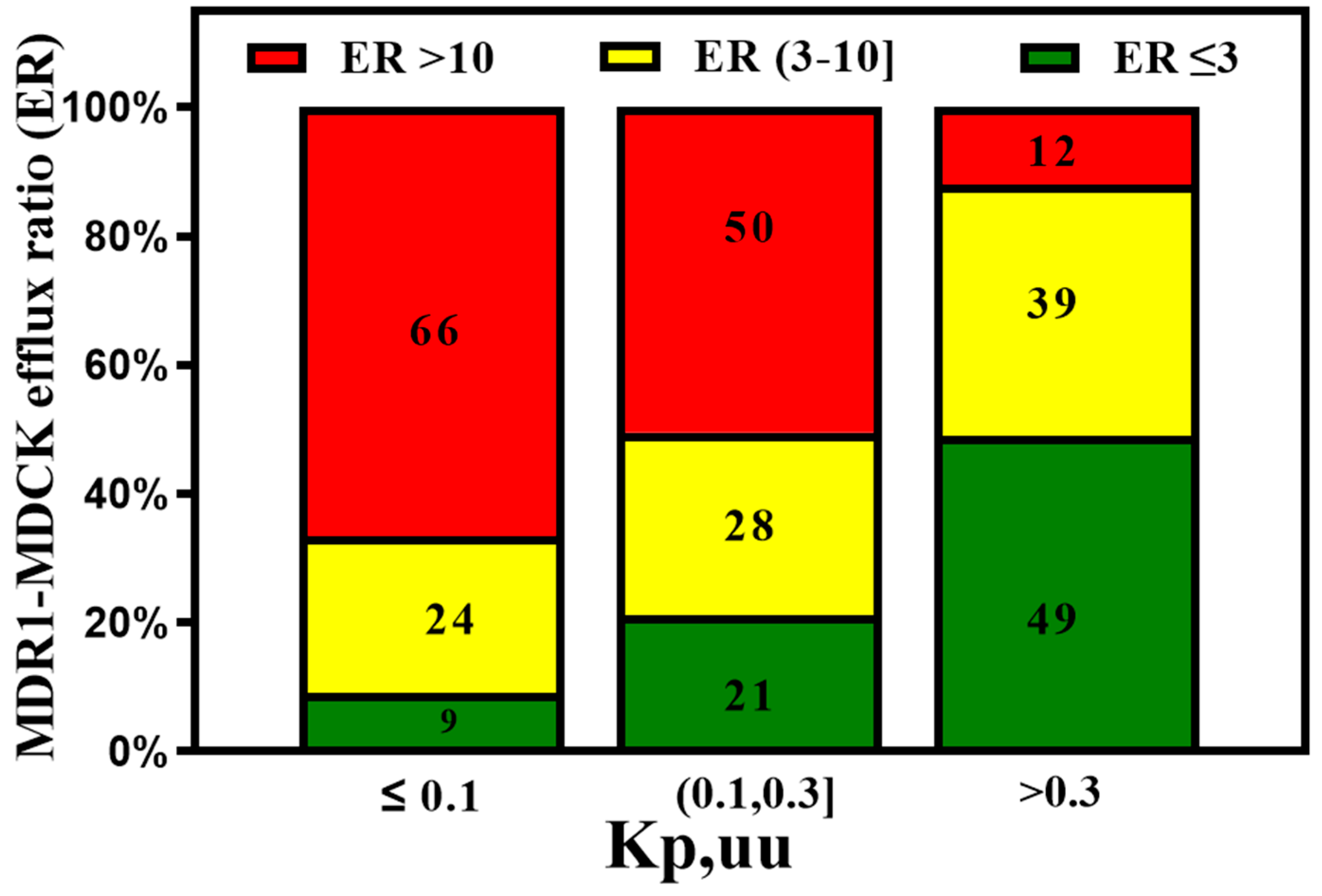
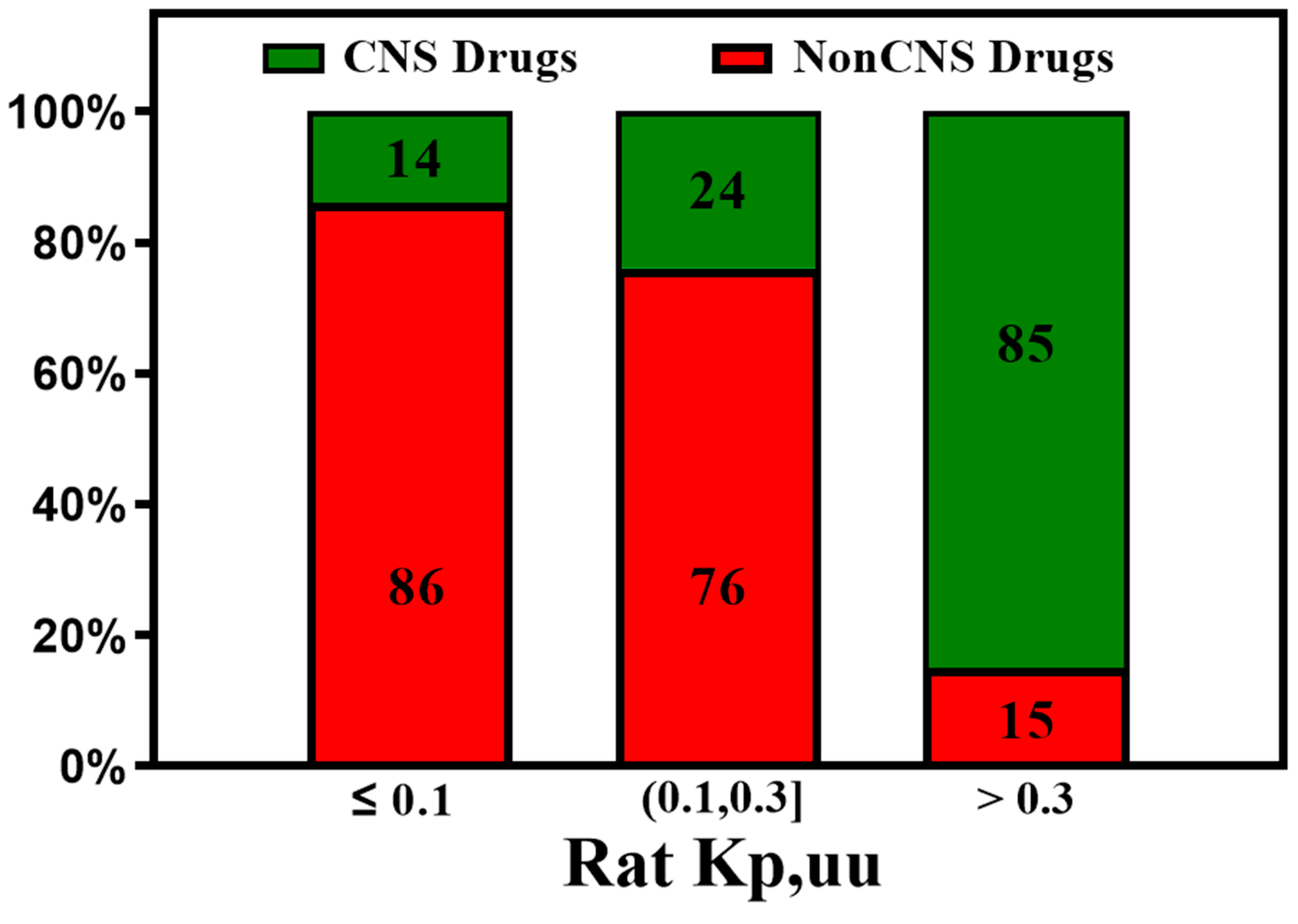
3. Active Transport across BBB (Efflux Transporters, Influx Transporters and Kp,uu)
4. In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Correlations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sweeney, M.D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A.R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-Brain Barrier: From Physiology to Disease and Back. Physiological Reviews 2019, 99, 21–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Ye, M.; Levy, A.; Rothstein, J.; Bergles, D.; Searson, P. The blood-brain barrier: an engineering perspective. Frontiers in Neuroengineering 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nau, R.; Sörgel, F.; Eiffert, H. Penetration of Drugs through the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid/Blood-Brain Barrier for Treatment of Central Nervous System Infections. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 2010, 23, 858–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, R.H.; O’Neill, C.A.; Bennett, J.; Humphrey, M.; Henry, B.; Rowland, M.; Warhurst, G. Resolution of P-glycoprotein and non-P-glycoprotein effects on drug permeability using intestinal tissues from mdr1a (−/−) mice. British Journal of Pharmacology 2002, 135, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickens, D.; Radisch, S.; Pirmohamed, M. Chapter 5 Drug Transporters at the Blood–Brain Barrier. In Drug Transporters: Volume 1: Role and Importance in ADME and Drug Development; The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2016; Vol. 1; pp 151-183.
- Gomez-Zepeda, D.; Taghi, M.; Scherrmann, J.-M.; Decleves, X.; Menet, M.-C. ABC Transporters at the Blood–Brain Interfaces, Their Study Models, and Drug Delivery Implications in Gliomas. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Potschka, H. Blood-brain barrier active efflux transporters: ATP-binding cassette gene family. NeuroRX 2005, 2, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Chatelain, P.; Massingham, R.; Jonsson, E.N.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M. Brain Distribution of Cetirizine Enantiomers: Comparisons of Three Different Tissue to Plasma Partition Coefficients. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 2006; 34, 318–323. [Google Scholar]
- Radchenko, E.V.; Dyabina, A.S.; Palyulin, V.A. Towards Deep Neural Network Models for the Prediction of the Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability for Diverse Organic Compounds. Molecules 2020, 25, 5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, R.K.; McAllister, C.B.; Inoue, M.; Wilkinson, G.R. Plasma binding and transport of diazepam across the blood-brain barrier. No evidence for in vivo enhanced dissociation. J Clin Invest 1989, 84, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammarlund-Udenaes, M.; Fridén, M.; Syvänen, S.; Gupta, A. On the rate and extent of drug delivery to the brain. Pharm Res 2008, 25, 1737–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajouhesh, H.; Lenz, G.R. Medicinal chemical properties of successful central nervous system drugs. NeuroRX 2005, 2, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Steward, A.R.; Anderson, S.M.; Bentley, D.L. Parabolic dependence of drug action upon lipophilic character as revealed by a study of hypnotics. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 1968, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Waterbeemd, H.; Camenisch, G.; Folkers, G.; Chretien, J.R.; Raevsky, O.A. Estimation of Blood-Brain Barrier Crossing of Drugs Using Molecular Size and Shape, and H-Bonding Descriptors. Journal of Drug Targeting 1998, 6, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelder, J.; Grootenhuis, P.D.J.; Bayada, D.M.; Delbressine, L.P.C.; Ploemen, J.-P. Polar Molecular Surface as a Dominating Determinant for Oral Absorption and Brain Penetration of Drugs. Pharmaceutical Research 1999, 16, 1514–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar Doan, K.M.; Humphreys, J.E.; Webster, L.O.; Wring, S.A.; Shampine, L.J.; Serabjit-Singh, C.J.; Adkison, K.K.; Polli, J.W. Passive permeability and P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux differentiate central nervous system (CNS) and non-CNS marketed drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2002, 303, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norinder, U.; Haeberlein, M. Computational approaches to the prediction of the blood–brain distribution. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2002, 54, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didziapetris, R.; Japertas, P.; Avdeef, A.; Petrauskas, A. Classification analysis of P-glycoprotein substrate specificity. J Drug Target 2003, 11, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeson, P.D.; Davis, A.M. Time-Related Differences in the Physical Property Profiles of Oral Drugs. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2004, 47, 6338–6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchcock, S.A.; Pennington, L.D. Structure−Brain Exposure Relationships. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2006, 49, 7559–7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankovic, Z. CNS Drug Design: Balancing Physicochemical Properties for Optimal Brain Exposure. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2015, 58, 2584–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loryan, I.; Sinha, V.; Mackie, C.; Van Peer, A.; Drinkenburg, W.H.; Vermeulen, A.; Heald, D.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M.; Wassvik, C.M. Molecular Properties Determining Unbound Intracellular and Extracellular Brain Exposure of CNS Drug Candidates. Molecular Pharmaceutics 2015, 12, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, B.B., 3rd; Yang, L.; Rankovic, Z. Practical approaches to evaluating and optimizing brain exposure in early drug discovery. Eur J Med Chem 2019, 182, 111643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wager, T.T.; Chandrasekaran, R.Y.; Hou, X.; Troutman, M.D.; Verhoest, P.R.; Villalobos, A.; Will, Y. Defining desirable central nervous system drug space through the alignment of molecular properties, in vitro ADME, and safety attributes. ACS Chem Neurosci 2010, 1, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wager, T.T.; Hou, X.; Verhoest, P.R.; Villalobos, A. Moving beyond rules: the development of a central nervous system multiparameter optimization (CNS MPO) approach to enable alignment of druglike properties. ACS Chem Neurosci 2010, 1, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wager, T.T.; Hou, X.; Verhoest, P.R.; Villalobos, A. Central Nervous System Multiparameter Optimization Desirability: Application in Drug Discovery. ACS Chem Neurosci 2016, 7, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaydin, H. Probabilistic Approach to Generating MPOs and Its Application as a Scoring Function for CNS Drugs. ACS Med Chem Lett 2016, 7, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Herbertz, T.; Hudkins, R.L.; Dorsey, B.D.; Mallamo, J.P. Knowledge-Based, Central Nervous System (CNS) Lead Selection and Lead Optimization for CNS Drug Discovery. ACS Chemical Neuroscience 2012, 3, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankovic, Z. CNS Physicochemical Property Space Shaped by a Diverse Set of Molecules with Experimentally Determined Exposure in the Mouse Brain. J Med Chem 2017, 60, 5943–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rankovic, Z. Retraction of “CNS Physicochemical Property Space Shaped by a Diverse Set of Molecules with Experimentally Determined Exposure in the Mouse Brain”. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2019, 62, 1699–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Lee, H.J.; Barden, C.J.; Weaver, D.F. The Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) Score. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2019, 62, 9824–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhan, C.-G. Improved Prediction of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability Through Machine Learning with Combined Use of Molecular Property-Based Descriptors and Fingerprints. The AAPS Journal 2018, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Winiwarter, S.; Friden, M.; Antonsson, M.; Engkvist, O. In silico prediction of unbound brain-to-plasma concentration ratio using machine learning algorithms. J Mol Graph Model 2011, 29, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadharajan, S.; Winiwarter, S.; Carlsson, L.; Engkvist, O.; Anantha, A.; Kogej, T.; Fridén, M.; Stålring, J.; Chen, H. Exploring In Silico Prediction of the Unbound Brain-to-Plasma Drug Concentration Ratio: Model Validation, Renewal, and Interpretation. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2015, 104, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridén, M.; Winiwarter, S.; Jerndal, G.; Bengtsson, O.; Wan, H.; Bredberg, U.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M.; Antonsson, M. Structure−Brain Exposure Relationships in Rat and Human Using a Novel Data Set of Unbound Drug Concentrations in Brain Interstitial and Cerebrospinal Fluids. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2009, 52, 6233–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, D.; Sharma, A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Kumar, R. Development of Machine Learning Based Blood-brain Barrier Permeability Prediction Models Using Physicochemical Properties, MACCS and Substructure Fingerprints. Current Bioinformatics 2021, 16, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durant, J.L.; Leland, B.A.; Henry, D.R.; Nourse, J.G. Reoptimization of MDL keys for use in drug discovery. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 2002, 42, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Xia, L.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Huang, H.-H.; Liang, Y. Improved Classification of Blood-Brain-Barrier Drugs Using Deep Learning. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 8802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsenan, S.; Al-Turaiki, I.; Hafez, A. A Recurrent Neural Network model to predict blood–brain barrier permeability. Computational Biology and Chemistry 2020, 89, 107377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Ding, Y. Identification of Key Features of CNS Drugs Based on SVM and Greedy Algorithm. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des 2020, 16, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, D.; Sharma, A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Kumar, R. Blood Brain Barrier Permeability Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques: An Update. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2019, 20, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, F.J.; Montoto, S.S.; Fagiolino, P.; Ruiz, E.M. Current State and Future Perspectives in QSAR Models to Predict Blood- Brain Barrier Penetration in Central Nervous System Drug R&D. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry 2017, 17, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Dong, K.; Zhang, W.; Summerfield, S.G.; Terstappen, G.C. Prediction of brain:blood unbound concentration ratios in CNS drug discovery employing in silico and in vitro model systems. Drug Discov Today 2018, 23, 1357–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNGERSTEDT, U. Microdialysis—principles and applications for studies in animals and man. Journal of Internal Medicine 1991, 230, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, A.; Chefer, V.I.; Shippenberg, T.S. Microdialysis in rodents. Current protocols in neuroscience, 2009; Chapter 7, Unit7.2–Unit7.2. [Google Scholar]
- Chefer, V.I.; Thompson, A.C.; Zapata, A.; Shippenberg, T.S. Overview of brain microdialysis. Current protocols in neuroscience, 2009; Chapter 7, Unit7.1–Unit7.1. [Google Scholar]
- de Lange, E.C.M.; de Boer, B.A.G.; Breimer, D.D. Microdialysis for pharmacokinetic analysis of drug transport to the brain. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 1999, 36, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurasia, C.S.; Müller, M.; Bashaw, E.D.; Benfeldt, E.; Bolinder, J.; Bullock, R.; Bungay, P.M.; DeLange, E.C.M.; Derendorf, H.; Elmquist, W.F.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M.; Joukhadar, C.; Kellogg, D.L.; Lunte, C.E.; Nordstrom, C.H.; Rollema, H.; Sawchuk, R.J.; Cheung, B.W.Y.; Shah, V.P.; Stahle, L.; Ungerstedt, U.; Welty, D.F.; Yeo, H. AAPS-FDA Workshop White Paper: Microdialysis Principles, Application and Regulatory Perspectives. Pharmaceutical Research 2007, 24, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, K.D.; Braggio, S. Assessing brain free fraction in early drug discovery. Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology 2010, 6, 337–344. [Google Scholar]
- Cory Kalvass, J.; Maurer, T.S. Influence of nonspecific brain and plasma binding on CNS exposure: implications for rational drug discovery. Biopharmaceutics & Drug Disposition 2002, 23, 327–338. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H.; Rehngren, M.; Giordanetto, F.; Bergström, F.; Tunek, A. High-Throughput Screening of Drug−Brain Tissue Binding and in Silico Prediction for Assessment of Central Nervous System Drug Delivery. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2007, 50, 4606–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, S.; Liu, X. Evaluation of the Utility of Brain Slice Methods to Study Brain Penetration. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 2006, 34, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, S.G.; Stevens, A.J.; Cutler, L.; del Carmen Osuna, M.; Hammond, B.; Tang, S.P.; Hersey, A.; Spalding, D.J.; Jeffrey, P. Improving the in vitro prediction of in vivo central nervous system penetration: integrating permeability, P-glycoprotein efflux, and free fractions in blood and brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2006, 316, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, S.G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Examining the Uptake of Central Nervous System Drugs and Candidates across the Blood-Brain Barrier. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2016, 358, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culot, M.; Fabulas-da Costa, A.; Sevin, E.; Szorath, E.; Martinsson, S.; Renftel, M.; Hongmei, Y.; Cecchelli, R.; Lundquist, S. A simple method for assessing free brain/free plasma ratios using an in vitro model of the blood brain barrier. PloS one 2013, 8, e80634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridén, M.; Ducrozet, F.; Middleton, B.; Antonsson, M.; Bredberg, U.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M. Development of a High-Throughput Brain Slice Method for Studying Drug Distribution in the Central Nervous System. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 2009, 37, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridén, M.; Gupta, A.; Antonsson, M.; Bredberg, U.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M. In Vitro Methods for Estimating Unbound Drug Concentrations in the Brain Interstitial and Intracellular Fluids. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 2007, 35, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spreafico, M.; Jacobson, M.P. In silico prediction of brain exposure: drug free fraction, unbound brain to plasma concentration ratio and equilibrium half-life. Current topics in medicinal chemistry 2013, 13, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgikh, E.; Watson, I.A.; Desai, P.V.; Sawada, G.A.; Morton, S.; Jones, T.M.; Raub, T.J. QSAR Model of Unbound Brain-to-Plasma Partition Coefficient, Kp,uu,brain: Incorporating P-glycoprotein Efflux as a Variable. J Chem Inf Model 2016, 56, 2225–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Liu, H.; Summerfield, S.G.; Luscombe, C.N.; Sahi, J. Integrating in Silico and in Vitro Approaches To Predict Drug Accessibility to the Central Nervous System. Molecular Pharmaceutics 2016, 13, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanevskij, K.; Japertas, P.; Didziapetris, R. Improving the prediction of drug disposition in the brain. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2013, 9, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The International Transporter, C.; Giacomini, K.M.; Huang, S.-M.; Tweedie, D.J.; Benet, L.Z.; Brouwer, K.L.R.; Chu, X.; Dahlin, A.; Evers, R.; Fischer, V.; Hillgren, K.M.; Hoffmaster, K.A.; Ishikawa, T.; Keppler, D.; Kim, R.B.; Lee, C.A.; Niemi, M.; Polli, J.W.; Sugiyama, Y.; Swaan, P.W.; Ware, J.A.; Wright, S.H.; Wah Yee, S.; Zamek-Gliszczynski, M.J.; Zhang, L. Membrane transporters in drug development. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2010, 9, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, K.; Zhang, W.; Summerfield, S.G.; Terstappen, G.C. Prediction of brain:blood unbound concentration ratios in CNS drug discovery employing in silico and in vitro model systems. Drug Discovery Today 2018, 23, 1357–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigues, A.; Escargueil, A.E.; Orlowski, S. The multidrug transporter, P-glycoprotein, actively mediates cholesterol redistribution in the cell membrane. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2002, 99, 10347–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajeva, I.K.; Globisch, C.; Wiese, M. Combined Pharmacophore Modeling, Docking, and 3D QSAR Studies of ABCB1 and ABCC1 Transporter Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1883–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombar, V.K.; Polli, J.W.; Humphreys, J.E.; Wring, S.A.; Serabjit-Singh, C.S. Predicting P-glycoprotein substrates by a quantitative structure–activity relationship model. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2004, 93, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzotti, J.E.; Lamb, M.L.; Evensen, E.; Grootenhuis, P.D.J. A Computational Ensemble Pharmacophore Model for Identifying Substrates of P-Glycoprotein. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2002, 45, 1737–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajeva, I.K.; Wiese, M. Pharmacophore Model of Drugs Involved in P-Glycoprotein Multidrug Resistance: Explanation of Structural Variety (Hypothesis). Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2002, 45, 5671–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikadi, Z.; Hazai, I.; Malik, D.; Jemnitz, K.; Veres, Z.; Hari, P.; Ni, Z.; Loo, T.W.; Clarke, D.M.; Hazai, E.; Mao, Q. Predicting P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Drug Transport Based On Support Vector Machine and Three-Dimensional Crystal Structure of P-glycoprotein. PloS one 2011, 6, e25815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Wang, Y.; Grater, R.; Kapadnis, S.; Black, C.; Trapa, P.; Sciabola, S. Prospective Validation of Machine Learning Algorithms for Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion Prediction: An Industrial Perspective. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2023, 63, 3263–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, R.; Watanabe, R.; Esaki, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Torimoto-Katori, N.; Watanabe, T.; Ogasawara, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Tsukimoto, M.; Mizuguchi, K. Development of Simplified in Vitro P-Glycoprotein Substrate Assay and in Silico Prediction Models To Evaluate Transport Potential of P-Glycoprotein. Mol Pharm 2019, 16, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broccatelli, F.; Larregieu, C.A.; Cruciani, G.; Oprea, T.I.; Benet, L.Z. Improving the prediction of the brain disposition for orally administered drugs using BDDCS. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2012, 64, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broccatelli, F. QSAR models for P-glycoprotein transport based on a highly consistent data set. J Chem Inf Model 2012, 52, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polli, J.W.; Wring, S.A.; Humphreys, J.E.; Huang, L.; Morgan, J.B.; Webster, L.O.; Serabjit-Singh, C.S. Rational Use of in Vitro P-glycoprotein Assays in Drug Discovery. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2001, 299, 620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, R.; de Morais, S.M.; Kalvass, J.C. In vitro P-glycoprotein efflux ratio can predict the in vivo brain penetration regardless of biopharmaceutics drug disposition classification system class. Drug Metab Dispos 2013, 41, 2012–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgikh, E.; Watson, I.A.; Desai, P.V.; Sawada, G.A.; Morton, S.; Jones, T.M.; Raub, T.J. QSAR Model of Unbound Brain-to-Plasma Partition Coefficient, Kp,uu,brain: Incorporating P-glycoprotein Efflux as a Variable. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2016, 56, 2225–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Bogdanowicz, T.; Reed, M.A.; Barden, C.J.; Weaver, D.F. The Brain Exposure Efficiency (BEE) Score. ACS Chemical Neuroscience 2020, 11, 205–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosugi, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Santos, C.; Sato, S.; Hosea, N.; Zientek, M. Direct Comparison of the Prediction of the Unbound Brain-to-Plasma Partitioning Utilizing Machine Learning Approach and Mechanistic Neuropharmacokinetic Model. The AAPS Journal 2021, 23, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Ott, G.R.; Hudkins, R.L. Technically Extended MultiParameter Optimization (TEMPO): An Advanced Robust Scoring Scheme To Calculate Central Nervous System Druggability and Monitor Lead Optimization. ACS Chemical Neuroscience 2017, 8, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broccatelli, F. QSAR Models for P-Glycoprotein Transport Based on a Highly Consistent Data Set. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling 2012, 52, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridén, M.; Winiwarter, S.; Jerndal, G.; Bengtsson, O.; Wan, H.; Bredberg, U.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M.; Antonsson, M. Structure-brain exposure relationships in rat and human using a novel data set of unbound drug concentrations in brain interstitial and cerebrospinal fluids. J Med Chem 2009, 52, 6233–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, R.; Esaki, T.; Ohashi, R.; Kuroda, M.; Kawashima, H.; Komura, H.; Natsume-Kitatani, Y.; Mizuguchi, K. Development of an In Silico Prediction Model for P-glycoprotein Efflux Potential in Brain Capillary Endothelial Cells toward the Prediction of Brain Penetration. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 64, 2725–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.C.; Feng, B.; Hou, X.; West, M.A.; Trapa, P.E.; Sciabola, S.; Verhoest, P.; Liras, J.L.; Maurer, T.S.; Wager, T.T. Harnessing Preclinical Data as a Predictive Tool for Human Brain Tissue Targeting. ACS Chemical Neuroscience 2021, 12, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Matsumiya, K.; Tohyama, K.; Kosugi, Y. Translational CNS Steady-State Drug Disposition Model in Rats, Monkeys, and Humans for Quantitative Prediction of Brain-to-Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid-to-Plasma Unbound Concentration Ratios. Aaps j 2021, 23, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.; Weaver, D.F. Alzheimer’s: The ABCDE Paradigm. ACS Chemical Neuroscience 2022, 13, 1355–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Physical Chemical Properties | CNS | Non-CNS |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 319 (151–655) | 330 (163–671) |
| ClogP | 3.43* (0.16–6.59) | 2.78* (−2.81–6.09) |
| ClogD | 2.08 (−1.34–6.57) | 1.07 (−2.81–5.53) |
| PSA | 40.5 (4.63–108) | 56.1 (3.25–151) |
| Hydrogen bond donors | 0.85* (0–3) | 1.56* (0–6) |
| Hydrogen bond acceptors | 3.56 (1–10) | 4.51 (1–11) |
| Flexibility (rotatable bonds) | 1.27* (0–5) | 2.18* (0–4) |
| Aromatic rings | 1.92 (0–4) | 1.93 (0–4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





