Submitted:
15 January 2024
Posted:
16 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Synthesis of catalysts
2.2. Characterization of the catalyst
2.3. Ozone decomposition test
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylan, O.; Alkabaa, A.S.; Alamoudi, M.; Basahel, A.; Balubaid, M.; Andejany, M.; Alidrisi, H. Air Quality Modeling for Sustainable Clean Environment Using ANFIS and Machine Learning Approaches. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, S.; Yu, S.; Bai, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Ma, S. Characteristics of ozone pollution and the sensitivity to precursors during early summer in central plain, China. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2021, 99, 354–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touati, H.; Mehri, A.; Karouia, F.; Richard, F.; Batiot-Dupeyrat, C.; Daniele, S.; Clacens, J.-M. Low-Temperature O3 Decomposition over Pd-TiO2 Hybrid Catalysts. Catalysts 2022, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Cheng, D.; Guo, Y.; Liang, Y. Supported gold catalysts used for ozone decomposition and simultaneous elimination of ozone and carbon monoxide at ambient temperature. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2001, 33, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Han, N.; Chen, Y. Facile solution synthesis of Cu2O–CuO–Cu(OH)2 hierarchical nanostructures for effective catalytic ozone decomposition. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2018, 20, 3096–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Kang, S.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; He, H. Role of Structural Defects in MnOx Promoted by Ag Doping in the Catalytic Combustion of Volatile Organic Compounds and Ambient Decomposition of O3. Environmental Science & Technology 2019, 53, 10871–10879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, L.; Guan, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, G.; Fan, G.; Wang, H.; Han, N.; Chen, Y. Highly efficient ozone elimination by metal doped ultra-fine Cu2O nanoparticles. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, B.; Ma, Q.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, P.; Chen, T.; Feng, Q.; Wang, C.; Yang, N.; Ma, H.; et al. Air Pollutant Correlations in China: Secondary Air Pollutant Responses to NOx and SO2 Control. Environmental Science & Technology Letters 2020, 7, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukta, T.A.; Hoque, M.M.M.; Sarker, M.E.; Hossain, M.N.; Biswas, G.K. Seasonal variations of gaseous air pollutants (SO2, NO2, O3, CO) and particulates (PM2.5, PM10) in Gazipur: an industrial city in Bangladesh. Advances in Environmental Technology 2020, 6, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.J.; Bell, J.N.B.; Brimblecombe, P.; Clark, C.M.; Dise, N.B.; Fowler, D.; Lovett, G.M.; Wolseley, P.A. The impact of air pollution on terrestrial managed and natural vegetation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 2020, 378, 20190317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjith, K.S.; Ranjith Kumar, D.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K.; Uyar, T.; Rajendra Kumar, R.T. Promotional Effect of Cu2S–ZnS Nanograins as a Shell Layer on ZnO Nanorod Arrays for Boosting Visible Light Photocatalytic H2 Evolution. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2020, 124, 3610–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.Z.; Faraz, M.; Munjal, S.; Kumar, V.; Khare, N. Highly dispersible and uniform size Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles for photocatalytic application. Advanced Powder Technology 2017, 28, 2402–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, Q.; Wen, X.; Li, X.-y.; Yang, S. Thermal oxidation of Cu2S nanowires: A template method for the fabrication of mesoscopic CuxO (x = 1,2) wires. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2002, 4, 3425–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Wu, W.; Li, Z.; Luo, J. First-order transition in LK-99 containing Cu2S. Matter 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.S.; Mohammed, R.Y. The Effect of Deposition Parameters on Morphological and Optical Properties of Cu2S Thin Films Grown by Chemical Bath Deposition Technique. Photonics 2022, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-W.; Rajaji, U.; Chen, S.-M.; Govindasamy, M.; Paul Selvin, S.S.; Manavalan, S.; Arumugam, R. Sonochemical synthesis of graphene oxide sheets supported Cu2S nanodots for high sensitive electrochemical determination of caffeic acid in red wine and soft drinks. Composites Part B: Engineering 2019, 158, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarnezhad, R.; Fathinia, M.; Khataee, A. Mechanical production and sonocatalytic application of Cu2S nanoparticles for degradation of isopropylxanthic acid: Kinetic modeling via white and black box methods. Journal of Molecular Liquids 2019, 287, 110899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Chu, Y.-T.; Song, Y.-F.; Huang, M.H. Cu2O Nanocrystal-Templated Growth of Cu2S Nanocages with Encapsulated Au Nanoparticles and In-Situ Transmission X-ray Microscopy Study. Advanced Functional Materials 2011, 21, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Yin, L. Double-walled heterostructured Cu2−xSe/Cu7S4 nanoboxes with enhanced electrocatalytic activity for quantum dot sensitized solar cells. CrystEngComm 2017, 19, 5640–5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandapani, B.; Oyama, S.T. Gas phase ozone decomposition catalysts. Applied Catalysis B-Environmental 1997, 11, 129–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gao, Z.; Han, H.; Wu, D.; Xu, F.; Wang, H.; Jiang, K. Mesoporous Cu2O submicro-spheres, facile synthesis and the selective adsorption properties. Chemical Engineering Journal 2012, 185-186, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Qu, F. Template-Free Synthesis of Porous Cu<sub>2</sub>O Nanospheres at Room Temperature and Investigation on Their Adsorption Property. Journal of Nanomaterials 2013, 2013, 378919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J.; Guan, J.; Han, N.; Chen, Y. Gram-scale synthesis of ultra-fine Cu2O for highly efficient ozone decomposition. RSC Advances 2020, 10, 5212–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minguez-Bacho, I.; Courté, M.; Fan, H.J.; Fichou, D. Conformal Cu<sub>2</sub>S-coated Cu<sub>2</sub>O nanostructures grown by ion exchange reaction and their photoelectrochemical properties. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 185401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusak, A.M.; Tu, K.N. Interaction between the Kirkendall effect and the inverse Kirkendall effect in nanoscale particles. Acta Materialia 2009, 57, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Wu, X.F.; Han, N.; Chen, Y.F. In-situ synthesis of Cu2O/reduced graphene oxide composite as effective catalyst for ozone decomposition. Catalysis Communications 2018, 106, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, L.; Chen, J. How M0S2 assisted sulfur vacancies featured Cu2S in hollow Cu2S@MoS2 nanoboxes to activate H2O2 for efficient sulfadiazine degradation? Chemical engineering journal 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H., ChanZeng, HanxuanWu, HuiyingYang, LingfangDeng, LinShi, Zhou. ZIF-8 assisted synthesis of magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@CuS nanoparticles for efficient sulfadiazine degradation via H2O2 activation: Performance and mechanism. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2021, 594.
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Zeng, H.; Deng, L.; Shi, Z. Can Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoparticles be used as heterogeneous catalysts for sulfadiazine degradation? Journal of Hazardous Materials 2020, 395, 122613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, S.; Grzybek, G.; Stelmachowski, P.; Sojka, Z.; Kotarba, A. Bulk, Surface and Interface Promotion of Co3O4 for the Low-Temperature N2O Decomposition Catalysis. Catalysts 2020, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Joo, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.-E.; Kang, K.-S.; Jung, H.; Yoon, J. Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Activity of TiO2 Nanotubes Decorated with Lanthanide Ions for Hydrogen Production. Catalysts 2022, 12, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huo, F.; Wang, A.; Chai, S.; Guan, J.; Fan, G.; Yang, W.; Ma, G.; Han, N.; Chen, Y. Coordination-Controlled Catalytic Activity of Cobalt Oxides for Ozone Decomposition. Inorganic Chemistry 2023, 62, 9178–9189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Gibbs, G.V.; Oyama, S.T. Mechanism of Ozone Decomposition on a Manganese Oxide Catalyst. 1. In Situ Raman Spectroscopy and Ab Initio Molecular Orbital Calculations. Journal of the American Chemical Society 1998, 120, 9041–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; He, H. Detrimental role of residual surface acid ions on ozone decomposition over Ce-modified γ-MnO2 under humid conditions. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2020, 91, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrogiacomi, D.; Sannino, D.; Magliano, A.; Ciambelli, P.; Tuti, S.; Indovina, V. The catalytic activity of CuSO4/ZrO2 for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 in the presence of excess O2. 2002, 36, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chen, S.; Mosconi, E.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Y.; et al. Stabilizing halide perovskite surfaces for solar cell operation with wide-bandgap lead oxysalts. Science 2019, 365, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlqvist, M.; Shchukarev, A. XPS spectra and electronic structure of Group IA sulfates. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena 2007, 156-158, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, M.Y.; Kalinkin, A.V.; Pashis, A.V.; Sorokin, A.M.; Noskov, A.S.; Kharas, K.C.; Bukhtiyarov, V.I. Interaction of Al2O3 and CeO2 Surfaces with SO2 and SO2 + O2 Studied by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2005, 109, 11712–11719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Tang, W.; Wang, A.; Zhang, L.; Guan, J.; Han, N.; Chen, Y. Heterojunctioned CuO/Cu2O catalyst for highly efficient ozone removal. Journal of Environmental Sciences 2023, 125, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, F.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X. The size controlled synthesis of Cu2S/P25 hetero junction solar-energy-materials and their applications in photocatalytic degradation of dyes. RSC Advances 2017, 7, 50056–50063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-Y.; Chang, H.-H.; Hsu, Y.-K.; Lin, Y.-G. Facile synthesis of Cu2S nanoarchitectures in application of surface enhanced Raman scattering. In Proceedings of the Nanophotonic Materials XI; 2014; pp. 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, H.E.; Fang, P.; Xie, G.Q.; Xie, Y.L.; Luo, M.F. Characterization of CuO Species in CuO/CeO_2-Al_2O_3 Catalysts by In-situ XRD, Raman Spectroscopy and TPR. Acta Physico-chimica Sinica 2005, 21, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
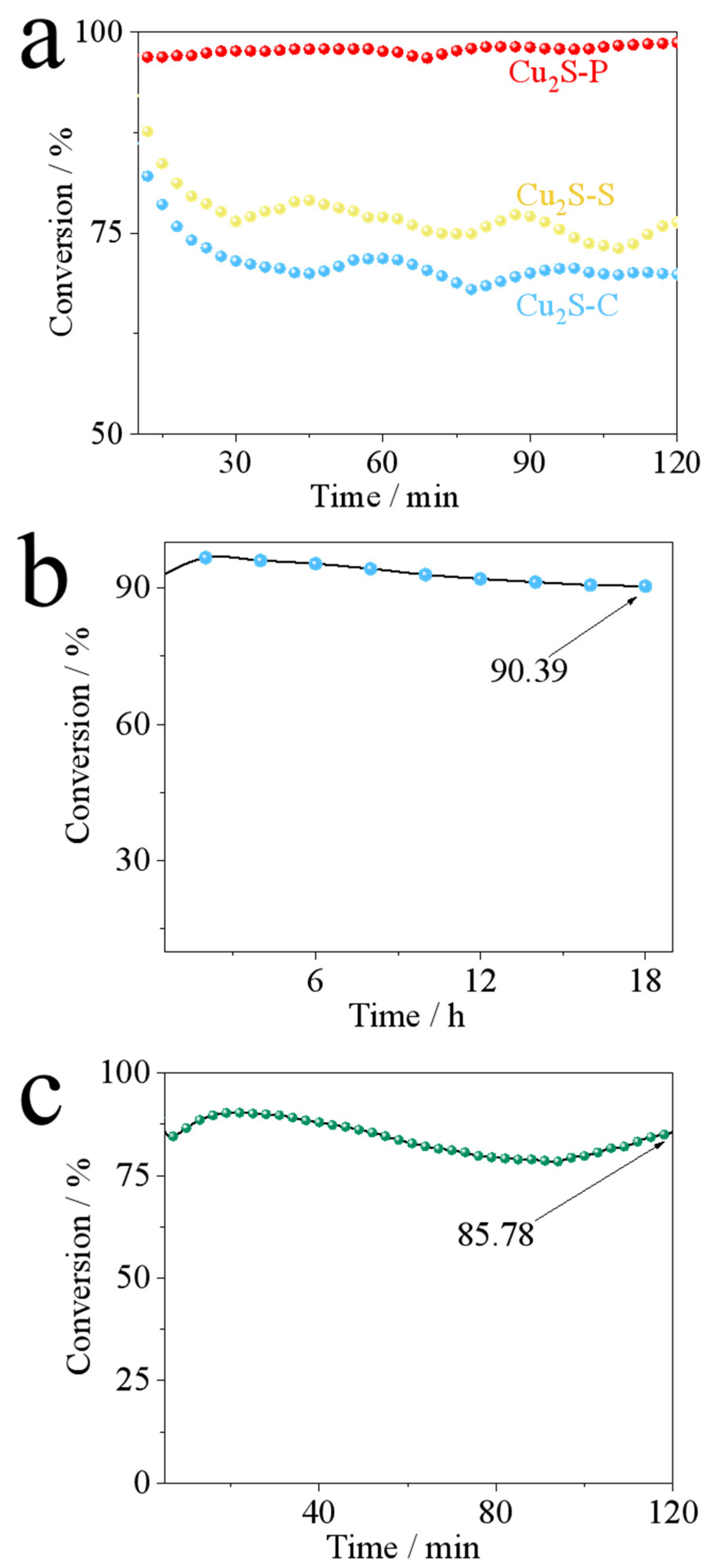
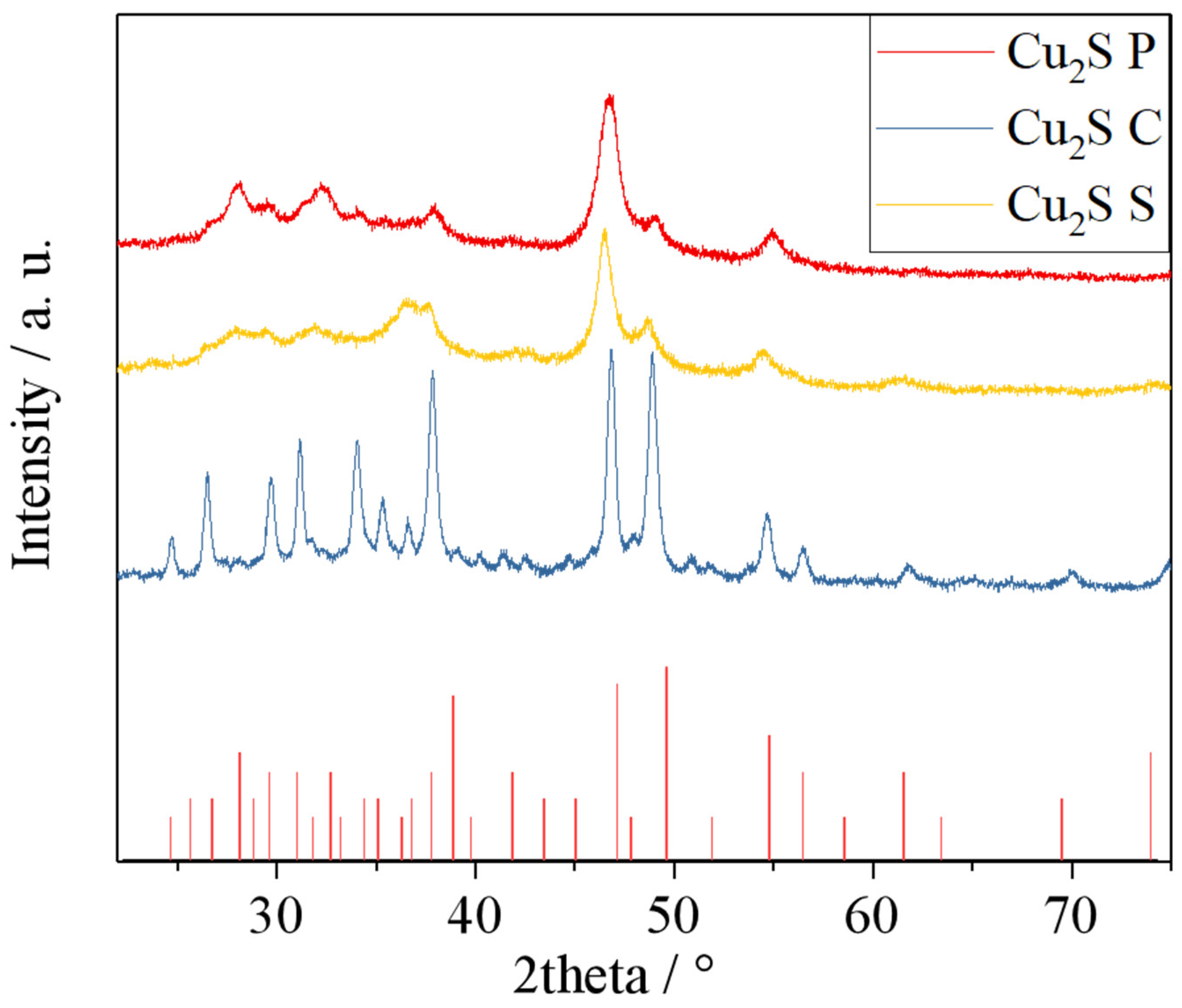
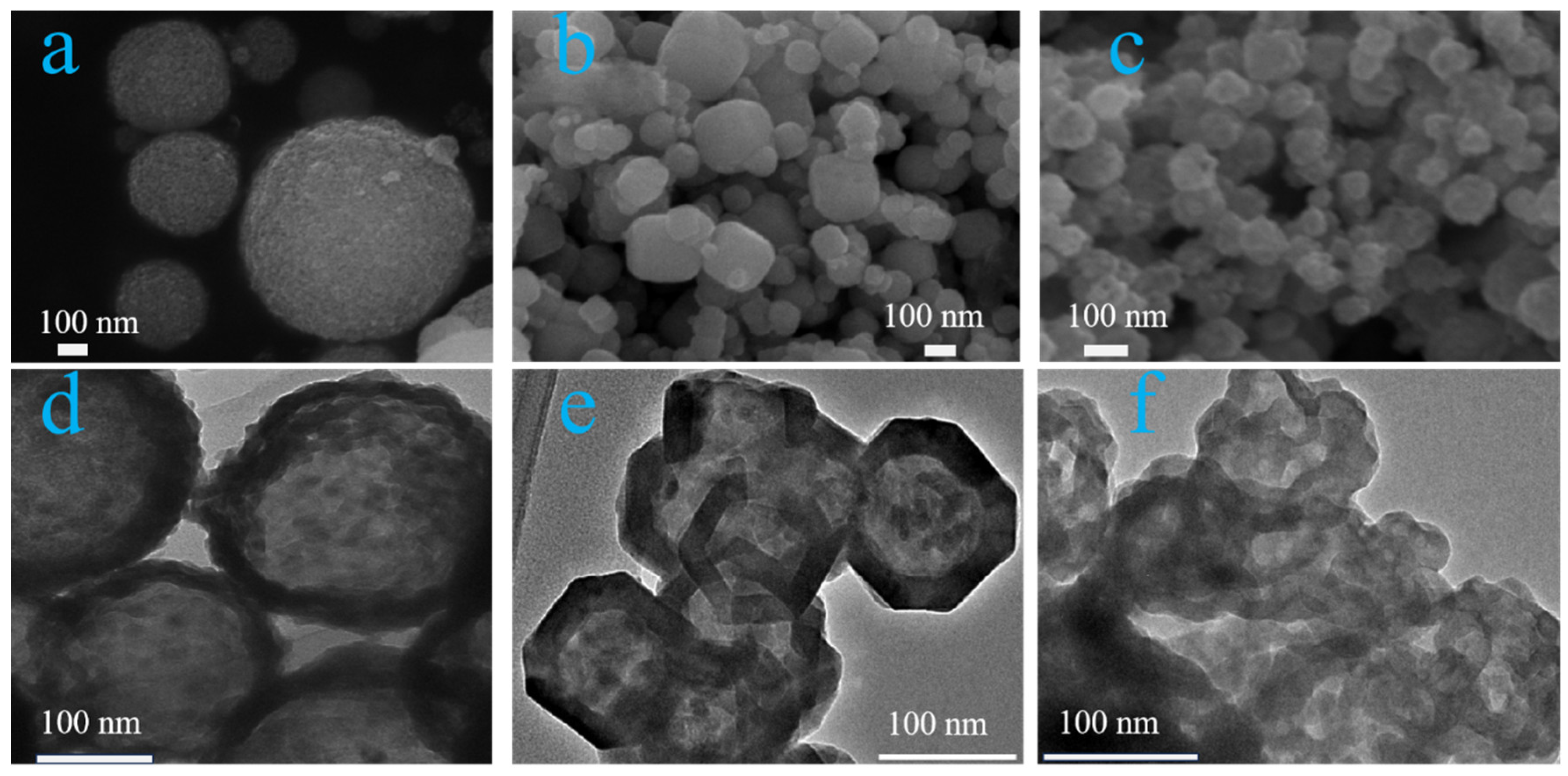
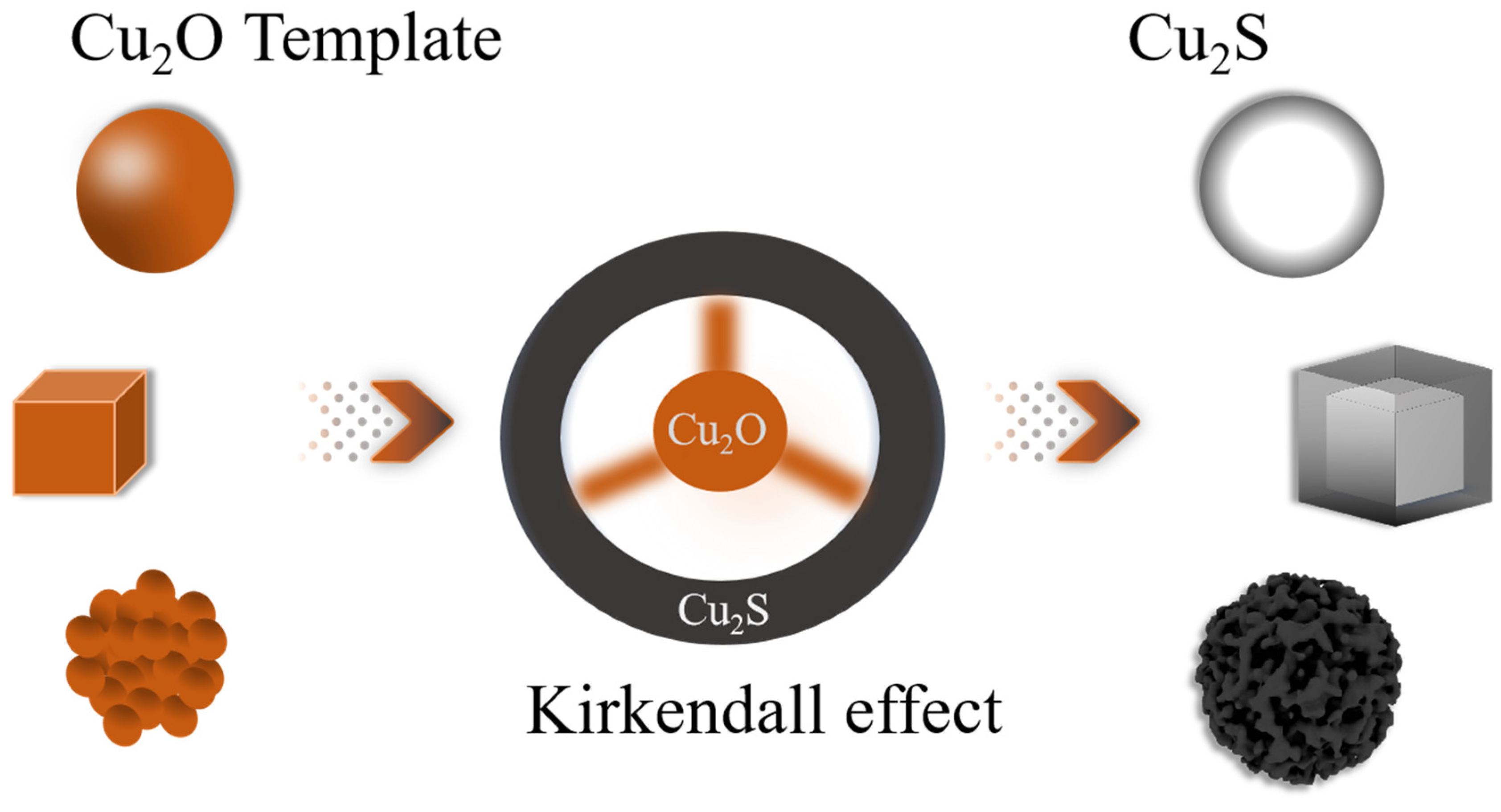

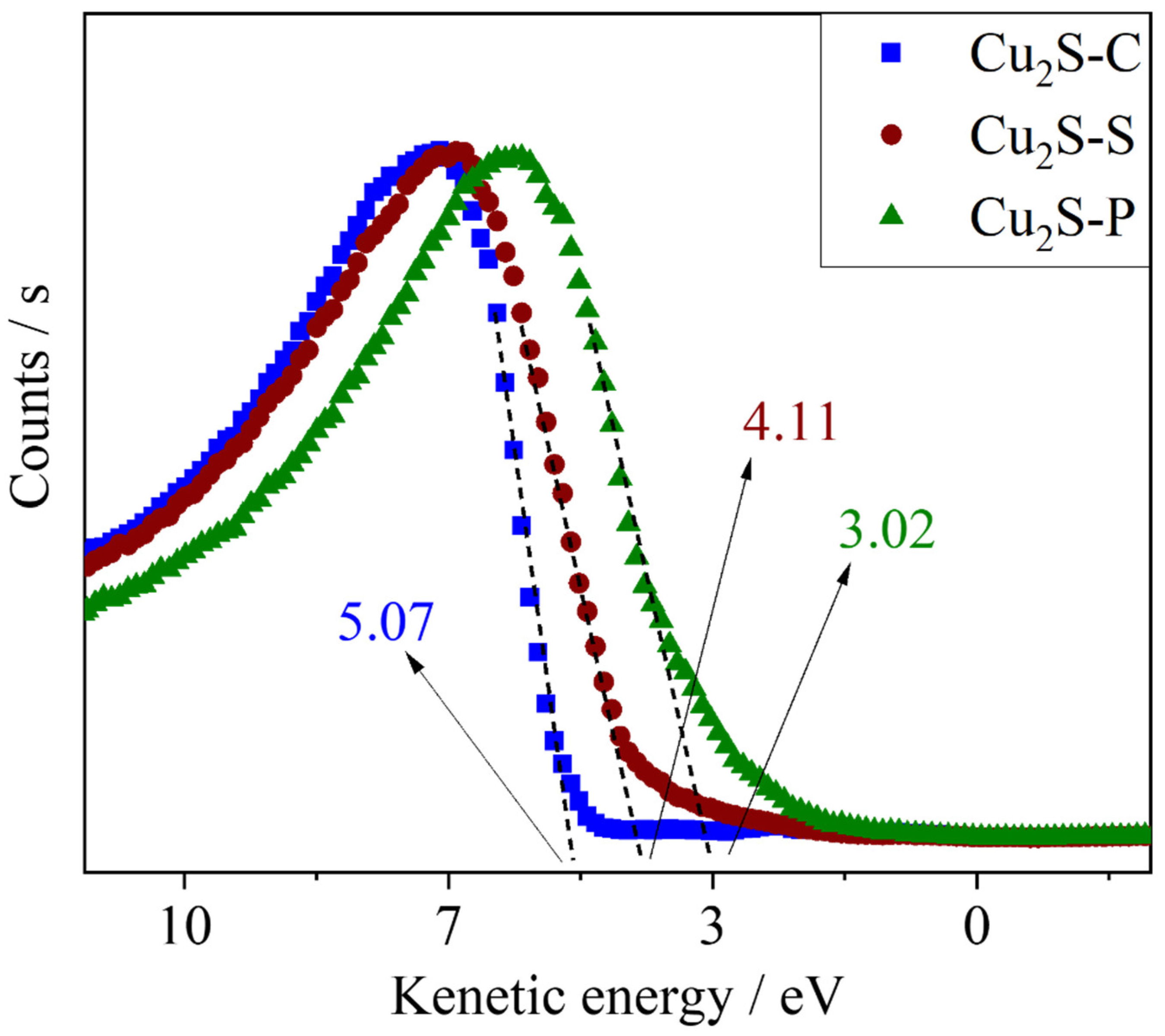
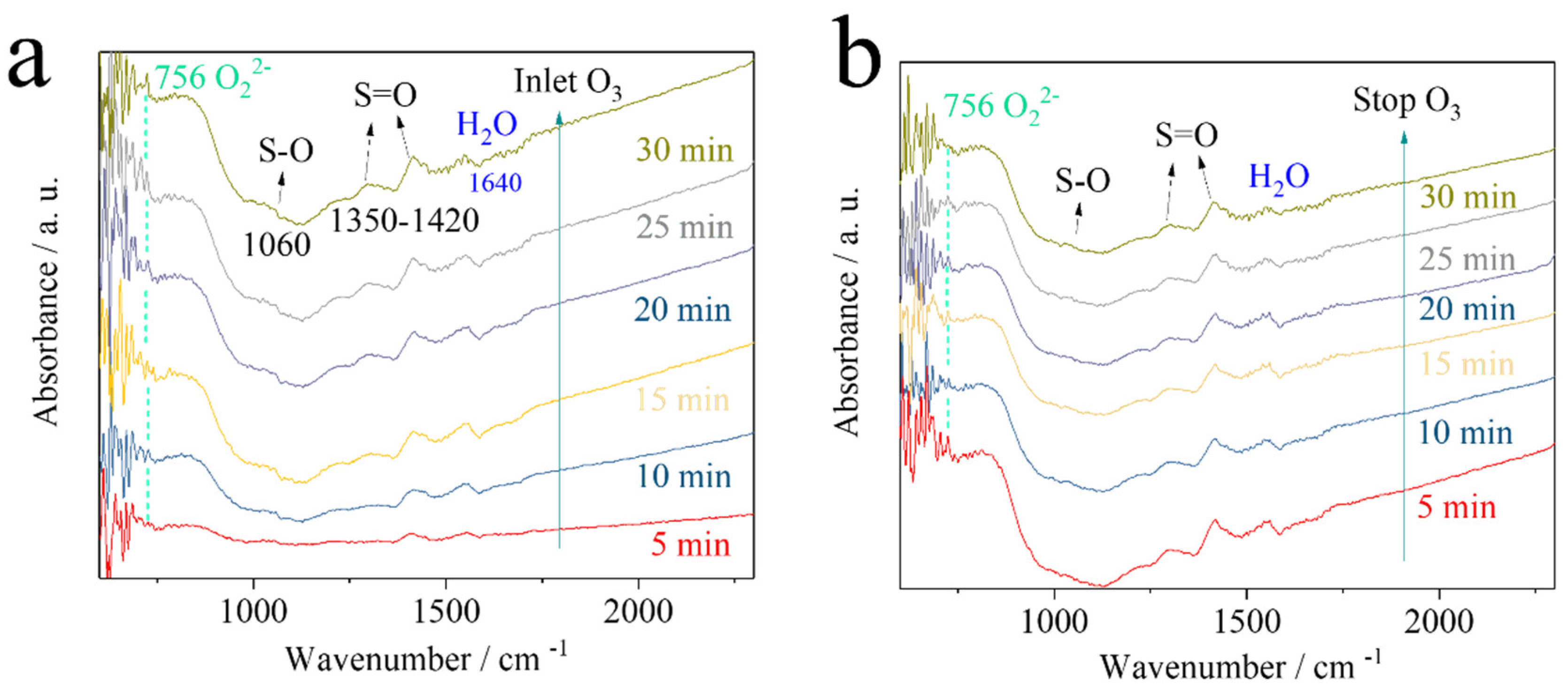
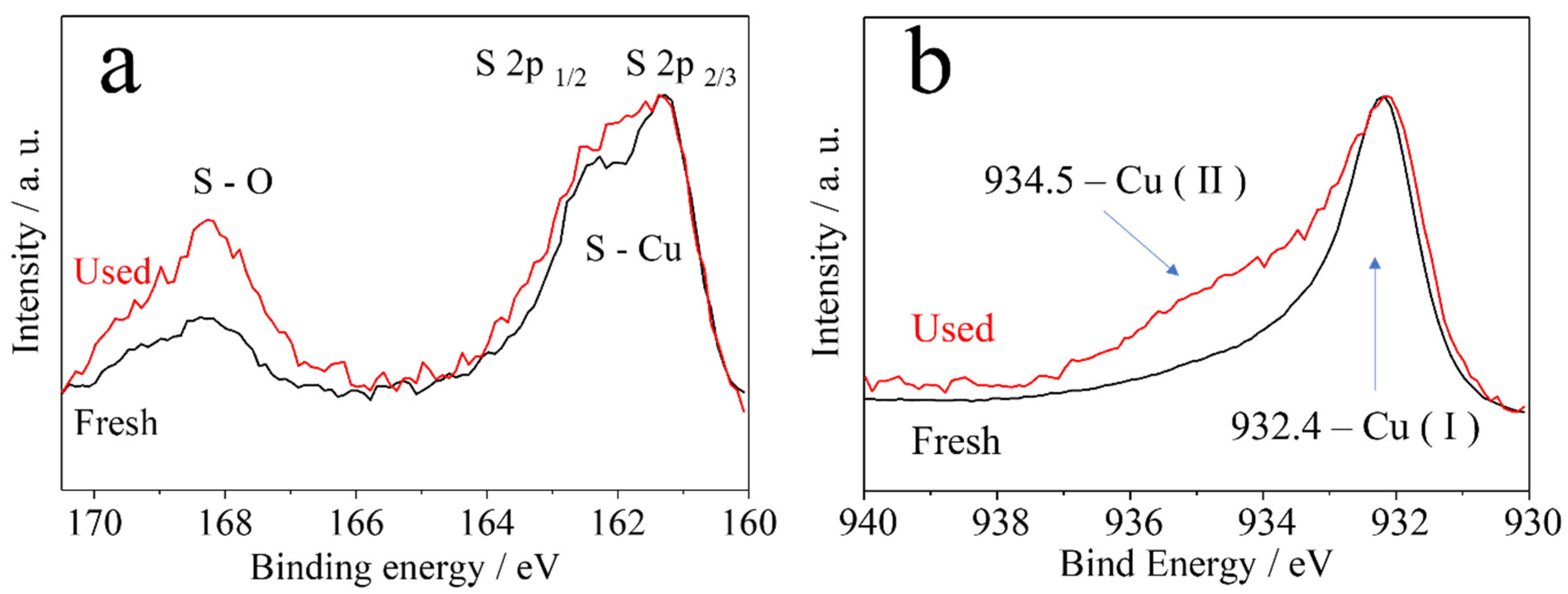
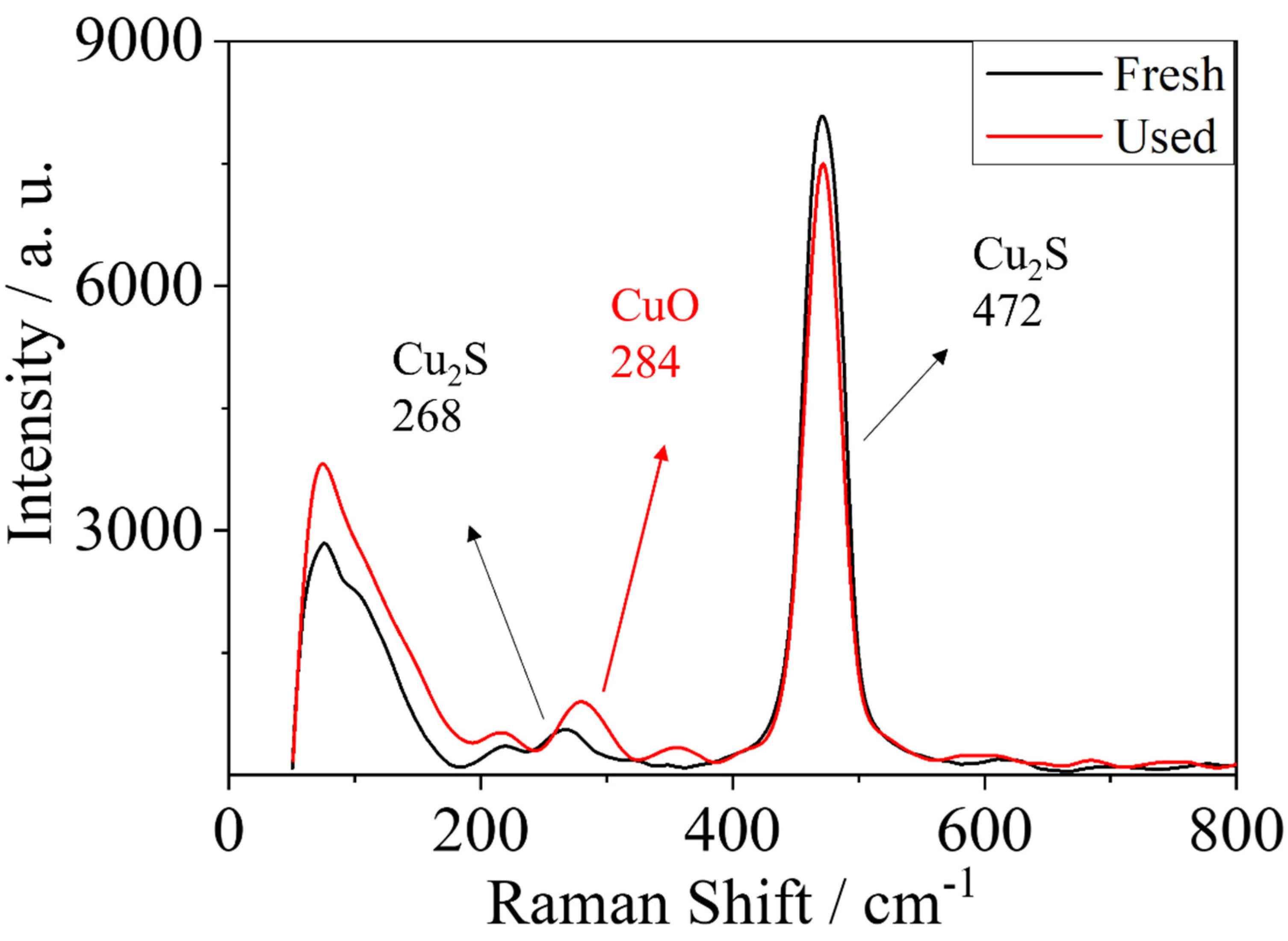
| Sample | BET Surface Area (m²/g) | Pore Size (Å) | Pore Volume (cm³/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cu2S-C | 11.48 | 71.31 | 0.02047 |
| Cu2S-S | 7.31 | 111.75 | 0.02043 |
| Cu2S-P | 14.67 | 59.25 | 0.02174 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





