Submitted:
10 January 2024
Posted:
11 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related work
2.1. Pairwise registration
2.2. Global refinement
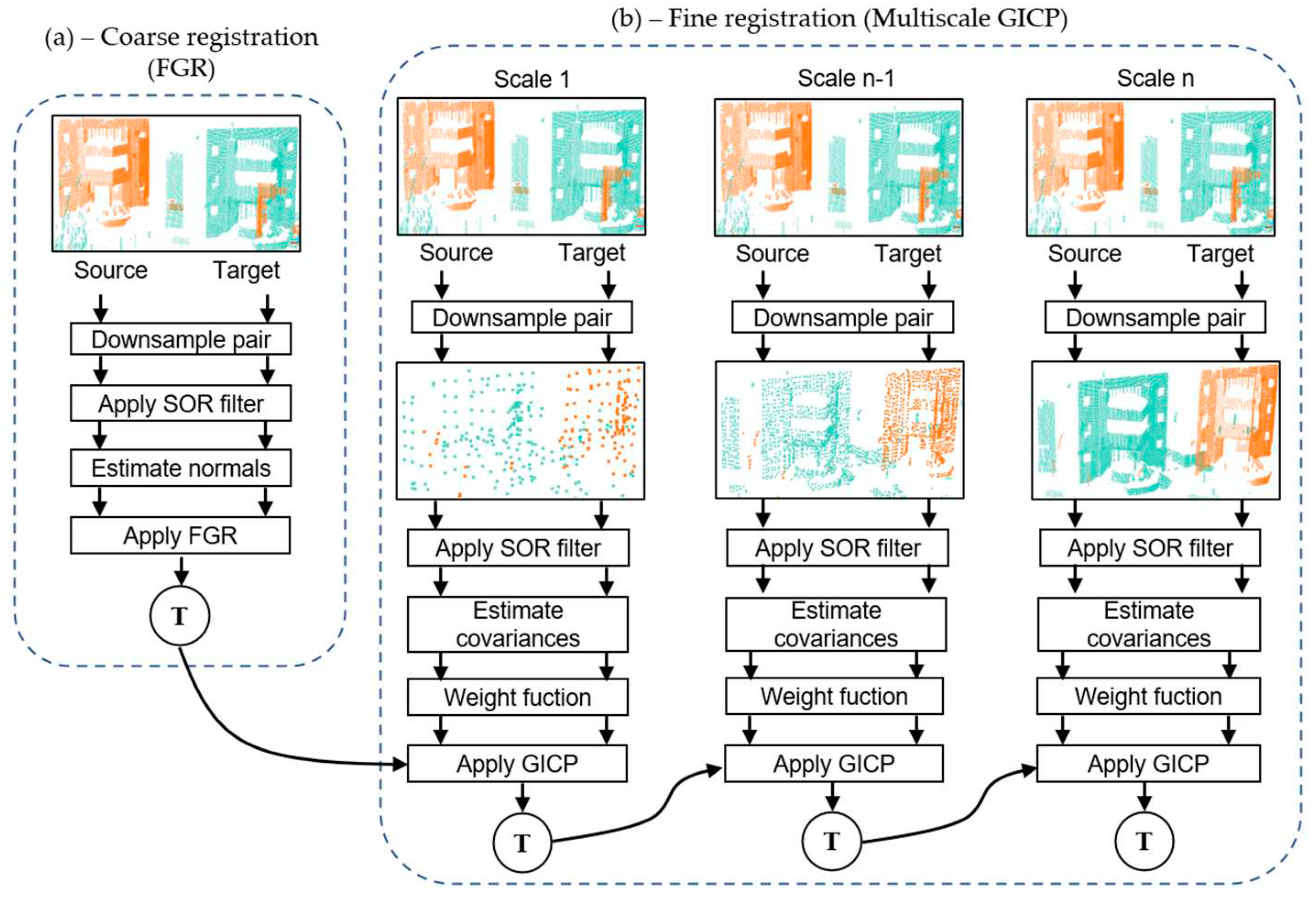
3. Method
3.1. Pairwise registration
3.1.1. Voxel Sizes
3.1.2. Maximum Correspondence Distances
3.1.3. Neighborhood of the Multiscale SOR Filter
3.1.4. Neighborhood for Normal and Covariance Estimation
3.2. Proposed Global Refinement Model
4. Experiments and discussion
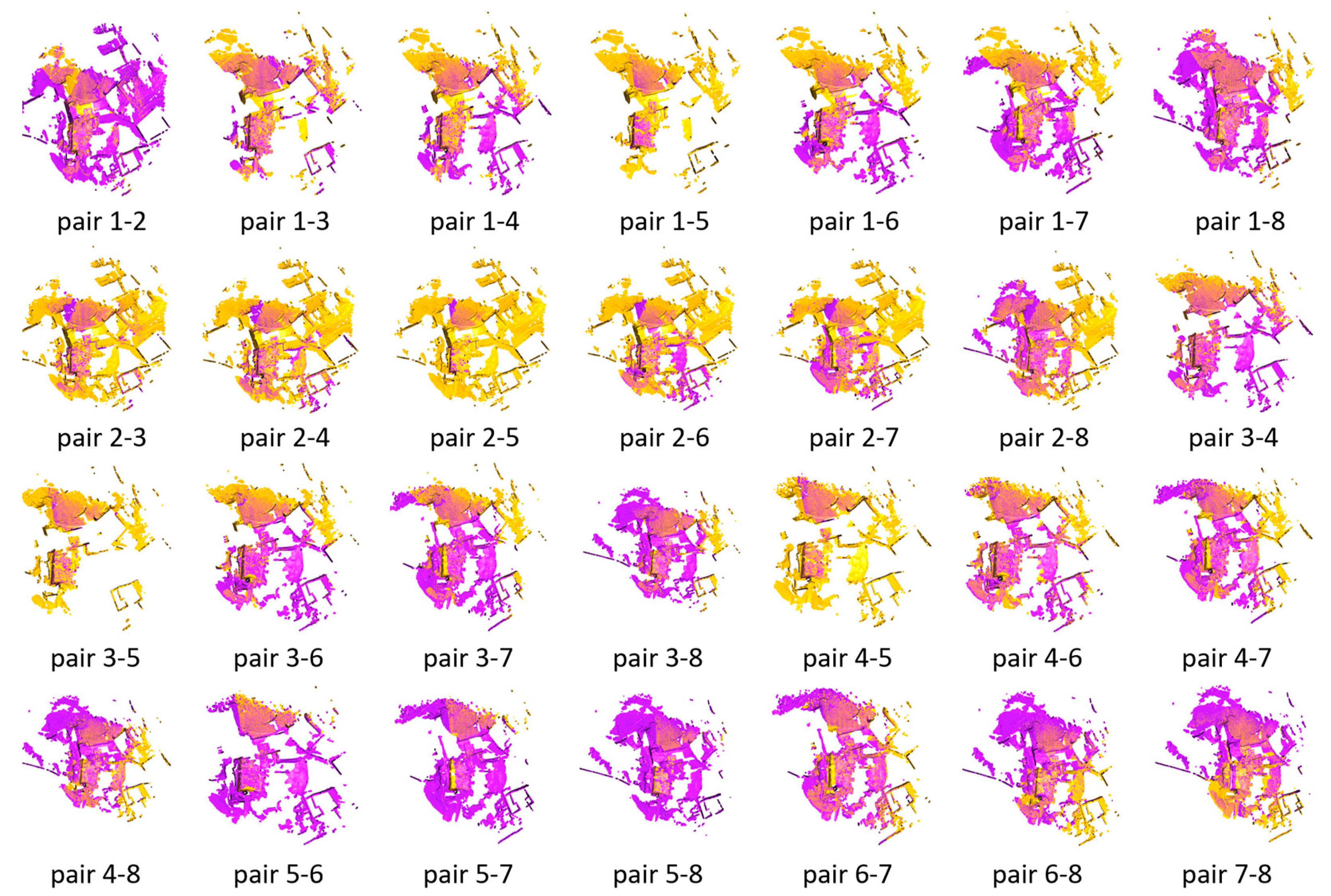
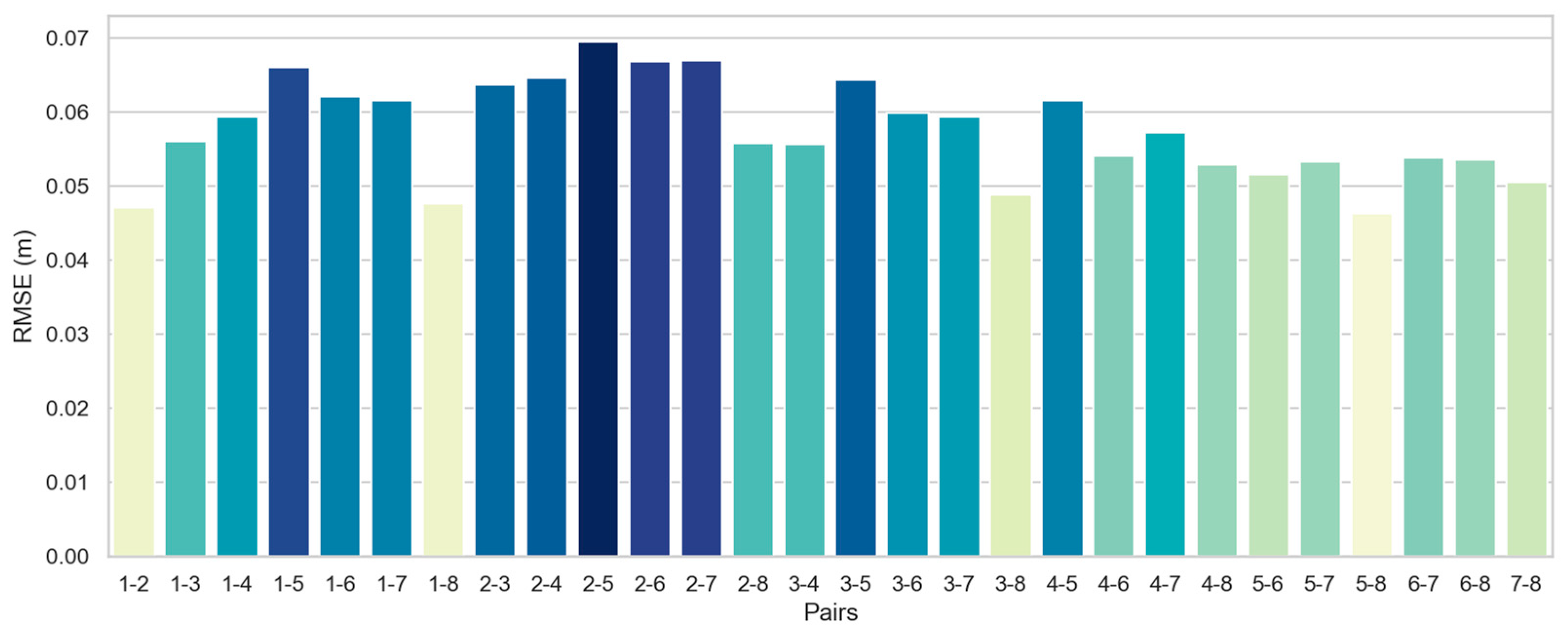
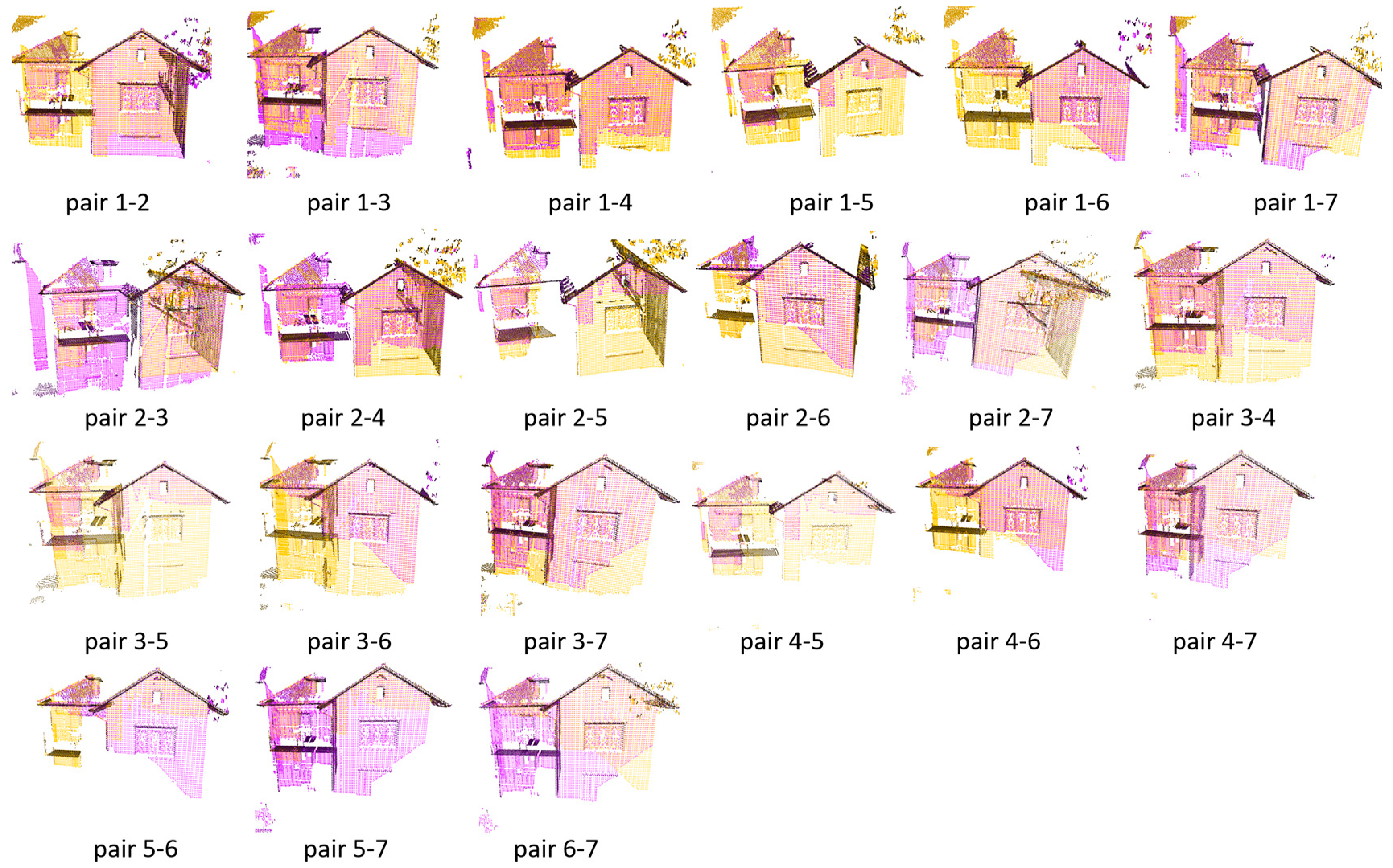
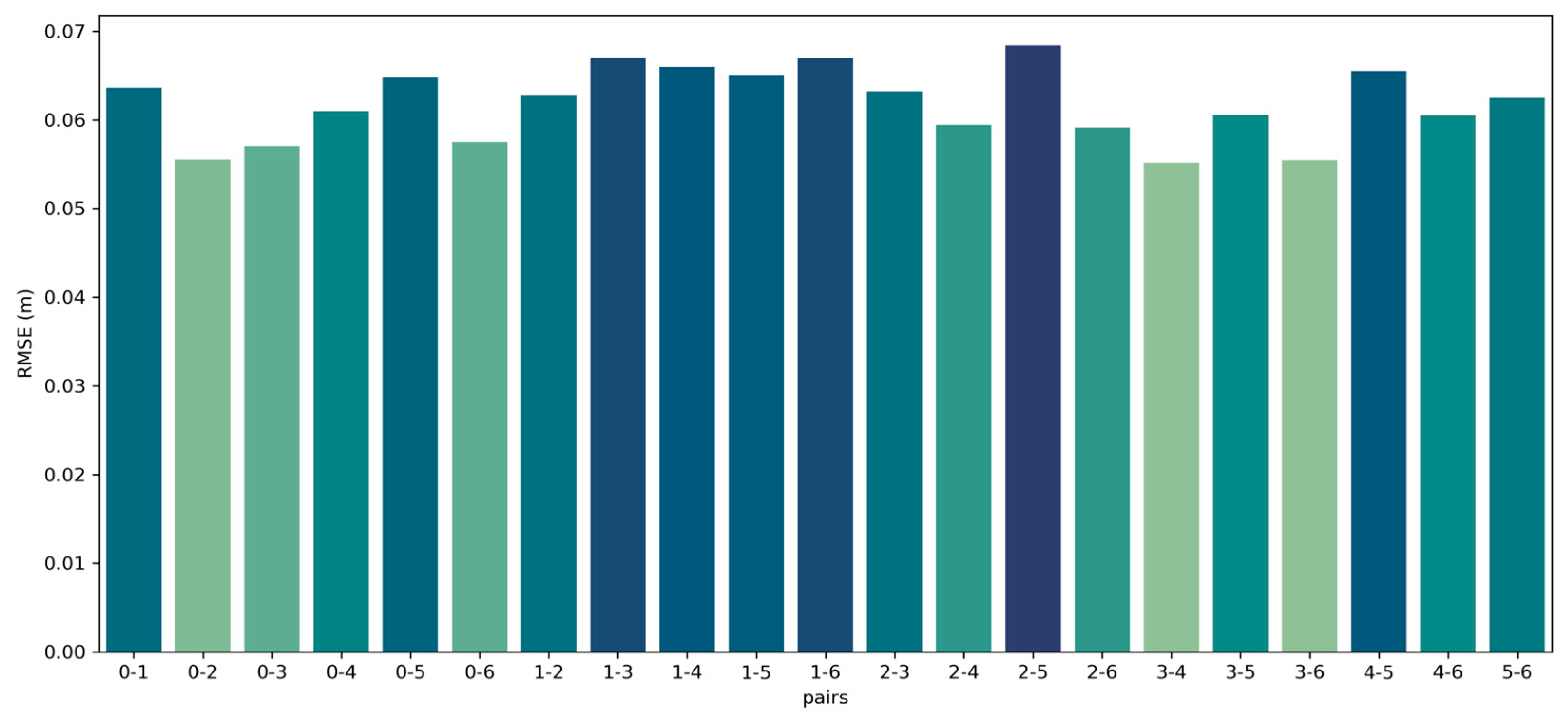
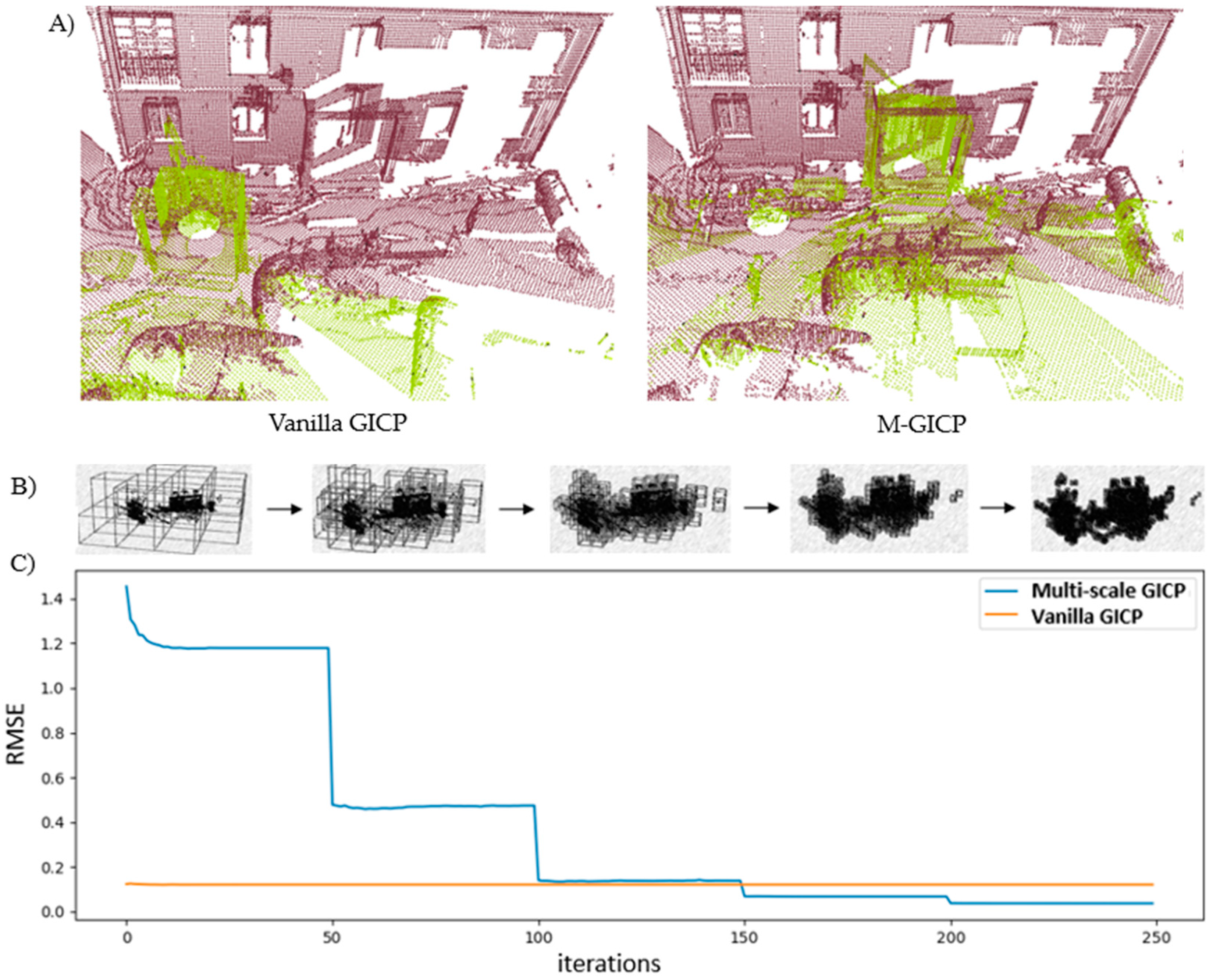
4.1. Pairwise registration of the dataset Courtyard
4.2. Pairwise registration of the dataset Facade
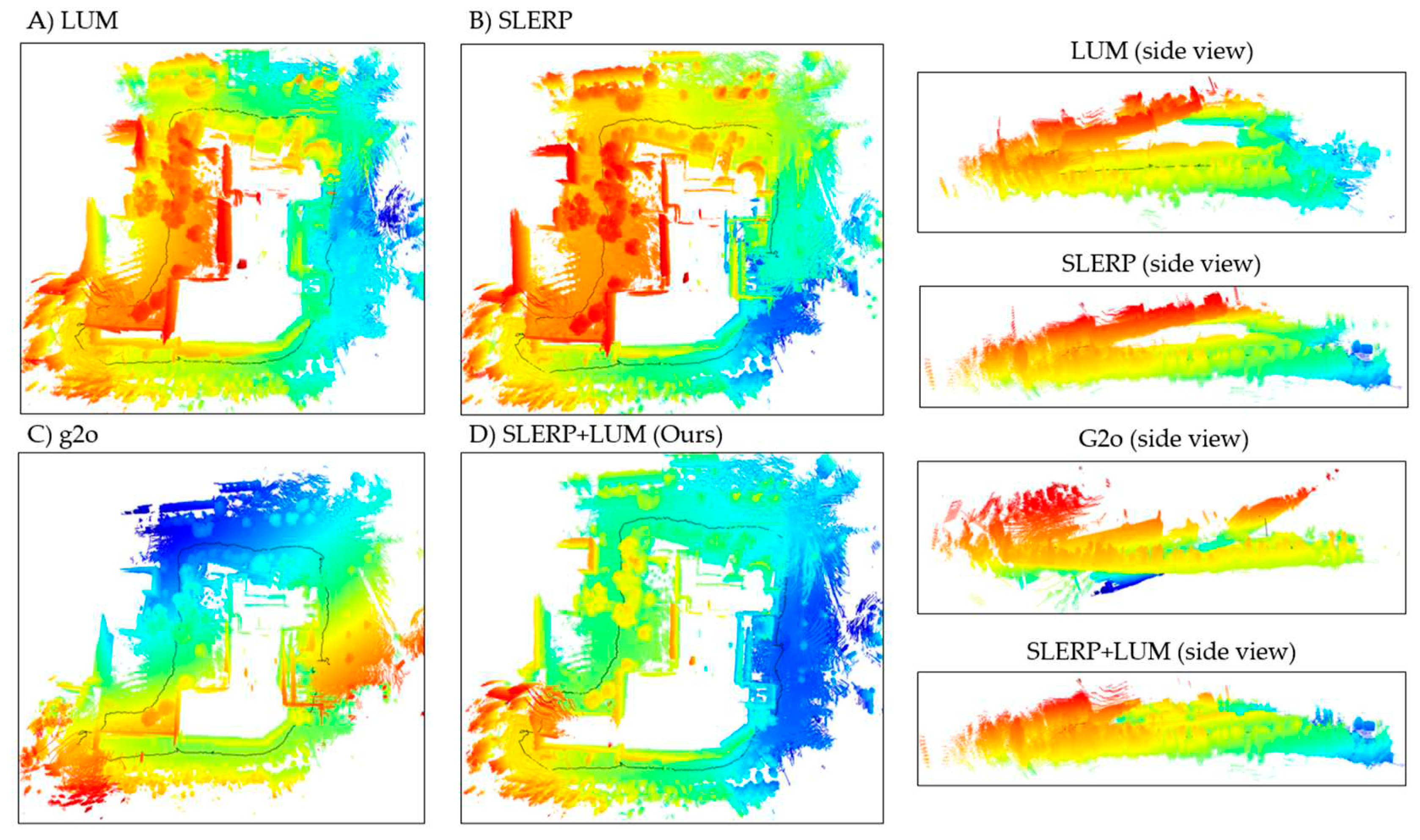
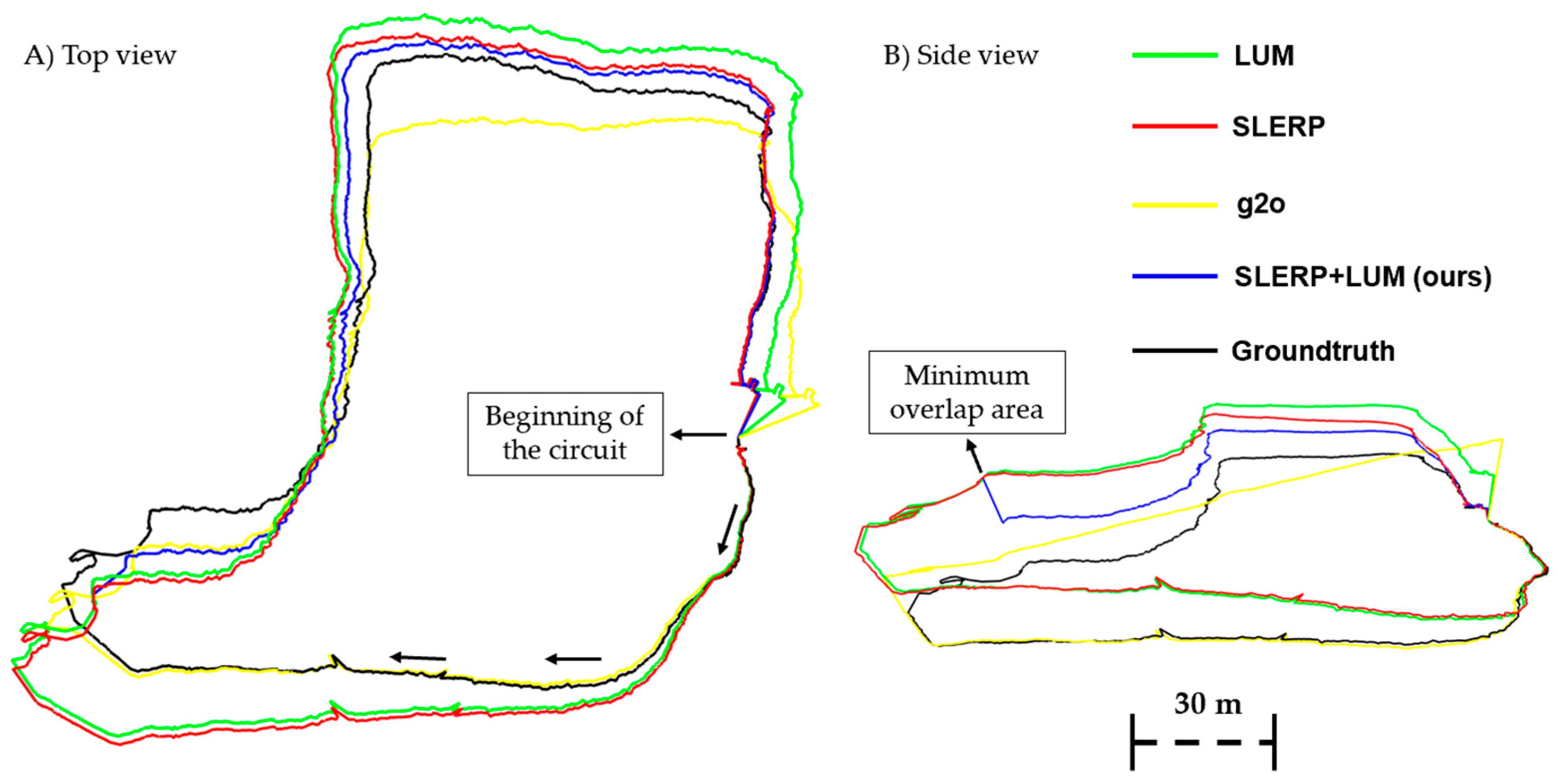
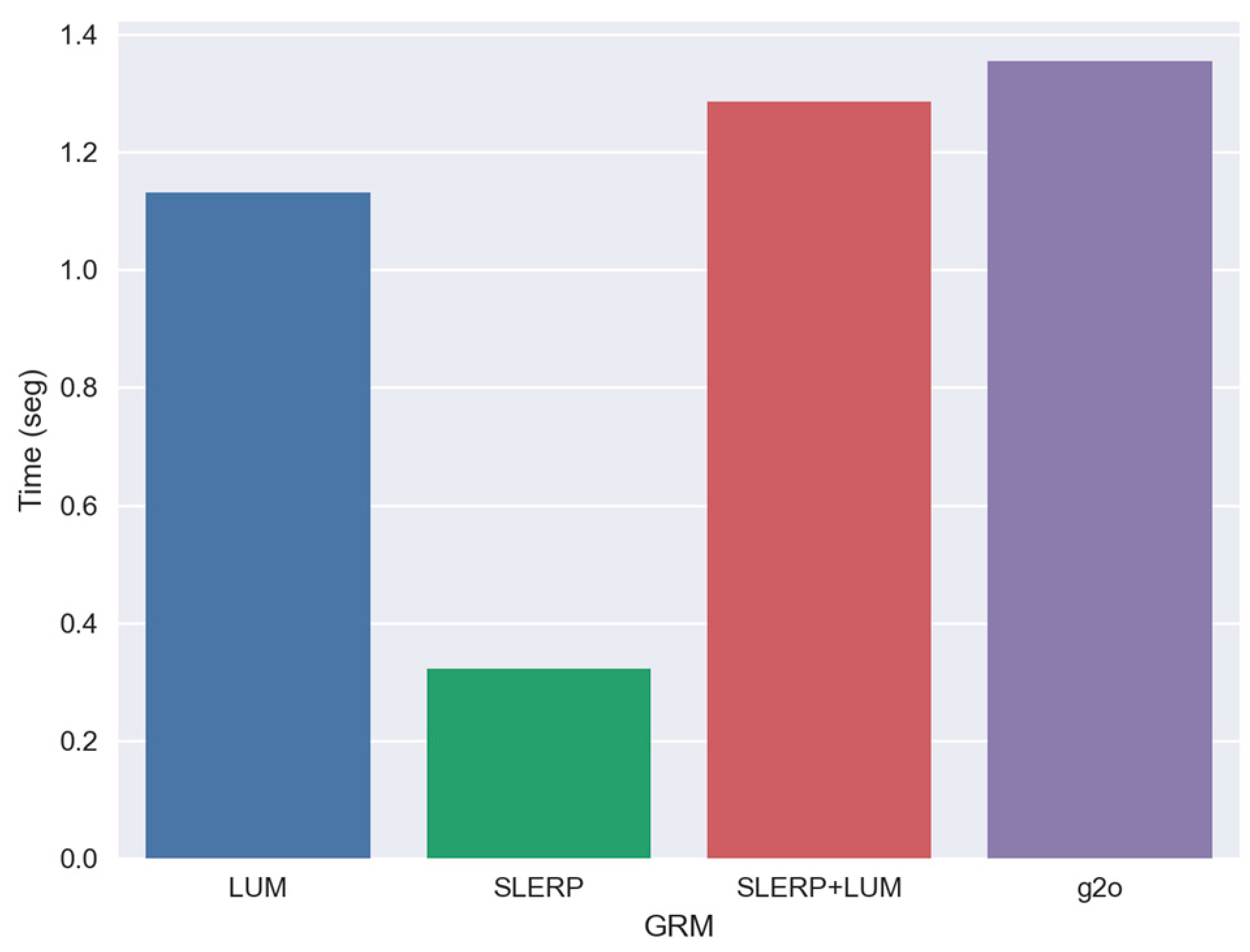
4.3. Global Refinement Model SLERP+LUM
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cadena, C.; Carlone, L.; Carrillo, H.; Latif, Y.; Scaramuzza, D.; Neira, J.; Reid, I.; Leonard, J.J. Past, present, and future of simultaneous localization and mapping: Toward the robust-perception age. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2016, 32, 1309–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, Y.; Roure, F.; Lladó, X.; Salvi, J. A qualitative review on 3D coarse registration methods. ACM Comput. Surv. 2015, 47, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kümmerle, R.; Grisetti, G.; Strasdat, H.; Konolige, K.; Burgard, W. g 2 o: A general framework for graph optimization. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation; IEEE, 2011; pp. 3607–3613. [Google Scholar]
- Gavin, H.P. The Levenberg-Marquardt Algorithm for Nonlinear Least Squares Curve-Fitting Problems; Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Duke University: 2019; Volume 19.
- Theiler, P.W.; Wegner, J.D.; Schindler, K. Globally consistent registration of terrestrial laser scans via graph optimization. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2015, 109, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlevaris-Bianco, N.; Ushani, A.K.; Eustice, R.M. University of Michigan North Campus long-term vision and lidar dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 35, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetverikov, D.; Svirko, D.; Stepanov, D.; Krsek, P. The trimmed iterative closest point algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Pattern Recognition; IEEE, 2002; pp. 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, A.; Haehnel, D.; Thrun, S. Generalized-icp. In Robotics: Science and Systems; Seattle, WA, USA, 2009; p. 435.
- Yang, J.; Li, H.; Campbell, D.; Jia, Y. Go-ICP: A Globally Optimal Solution to 3D ICP Point-Set Registration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 2241–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerleau, F.; Colas, F.; Siegwart, R. A review of point cloud registration algorithms for mobile robotics. Found. Trends Robot. 2015, 4, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, R.B.; Blodow, N.; Beetz, M. Fast point feature histograms (FPFH) for 3D registration. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation; IEEE, 2009; pp. 3212–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, R.B.; Cousins, S. 3d is here: Point cloud library (pcl). In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation; IEEE, 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.-Y.; Park, J.; Koltun, V. Fast global registration. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision; Springer, 2016; pp. 766–782. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.-Y.; Park, J.; Koltun, V. Open3D: A modern library for 3D data processing. arXiv Prepr. arXiv1801.09847. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiger, D.; Mitra, N.J.; Cohen-Or, D. 4-points congruent sets for robust pairwise surface registration. ACM Trans. Graph. 2008, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hilton, A. Evaluation of 3D feature descriptors for multi-modal data registration. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on 3D Vision-3DV 2013, Seattle, WA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Tombari, F.; Salti, S.; Stefano, L.D. Unique signatures of histograms for local surface description. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Hebert, M. Using spin images for efficient object recognition in cluttered 3D scenes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1999, 21, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körtgen, M.; Park, G.-J.; Novotni, M.; Klein, R. 3D shape matching with 3D shape contexts. In Proceedings of the 7th central European seminar on computer graphics; Citeseer, 2003; pp. 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Zhou, Q.-Y.; Koltun, V. Robust reconstruction of indoor scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2015; pp. 5556–5565. [Google Scholar]
- Mellado, N.; Aiger, D.; Mitra, N.J. Super 4pcs fast global pointcloud registration via smart indexing. Comput. Graph. Forum 2014, 33, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, B.; Ulrich, M.; Navab, N.; Ilic, S. Model globally, match locally: Efficient and robust 3D object recognition. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; IEEE, 2010; pp. 998–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Shi, J.; Carlone, L. Teaser: Fast and certifiable point cloud registration. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 37, 314–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Liang, F.; Li, B.; Zang, Y. A novel binary shape context for 3D local surface description. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2017, 130, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Sedaghat, N.; Zolfaghari, M.; Amiri, E.; Brox, T. Orientation-boosted voxel nets for 3D object recognition. arXiv Prepr. arXiv1604.03351 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Birdal, T.; Ilic, S. Ppfnet: Global context aware local features for robust 3d point matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2018; pp. 195–205. [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer, P.J. Reconstruction of real-world objects via simultaneous registration and robust combination of multiple range images. Int. J. Shape Model. 1997, 3, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Bennamoun, M. Simultaneous registration of multiple corresponding point sets. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2001, 81, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Milios, E. Globally consistent range scan alignment for environment mapping. Auton. Robot. 1997, 4, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.F.; Hebert, M. Fully automatic registration of multiple 3D data sets. Image Vis. Comput. 2003, 21, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Yang, B.; Liang, F.; Huang, R.; Scherer, S. Hierarchical registration of unordered TLS point clouds based on binary shape context descriptor. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2018, 144, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Bennamoun, M. Multiple view 3D registration using statistical error models. In Vision modeling and visualization; 1999.
- Pavan, N.L.; Santos, D.R.D. A global closed-form refinement for consistent TLS data registration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaminck, M.; Luong, H.; Philips, W. Have I seen this place before? A fast and robust loop detection and correction method for 3D lidar SLAM. Sensors 2019, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemake, K. Animating rotation with quaternion curves. In Proceedings of the 12th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques; 1985; pp. 245–254.
- Babin, P.; Giguere, P.; Pomerleau, F. Analysis of robust functions for registration algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA); IEEE, 2019; pp. 1451–1457. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, R.B.; Marton, Z.C.; Blodow, N.; Dolha, M.; Beetz, M. Towards 3D Point cloud based object maps for household environments. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2008, 56, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muja, M.; Lowe, D.G. Fast approximate nearest neighbors with automatic algorithm configuration. VISAPP 2009, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Voxel size | 0.1 for FGR [0.5; 0.4, 0.3, 0.2, 0.1] for M-GICP |
Used to reduce the number of points and uniformize the density along the point cloud pair |
| Maximum correspondence distance | 2 × voxel_size for FGR [3, 2.5, 2.0, 1.5, 1.0] × voxel_size for M-GICP |
Maximum distance to search for correspondences between source and target point cloud |
| Standard Deviation of SOR filter |
1.0 for FGR and 1.0 for all scales of M-GICP |
Used to filter the point cloud pair given a neighborhood |
| Neighborhood of the SOR filter | 30 knn for FGR 30 knn for all scales of M-GICP |
Number of neighbors used by the SOR filter |
| Neighborhood for normal estimation | 20 knn or 2 × voxel_size for FGR 20 knn or 2 × voxel_size for all scales of M-GICP |
Neighborhood used for normal estimation |
| Neighborhood for FPFH estimation | 200 knn or 10 × voxel_size | Neighborhood of the FPFH descriptor, we use a hybrid approach that can leverage a maximum radius or a value of knn. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





