Submitted:
09 January 2024
Posted:
09 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Instability behavior
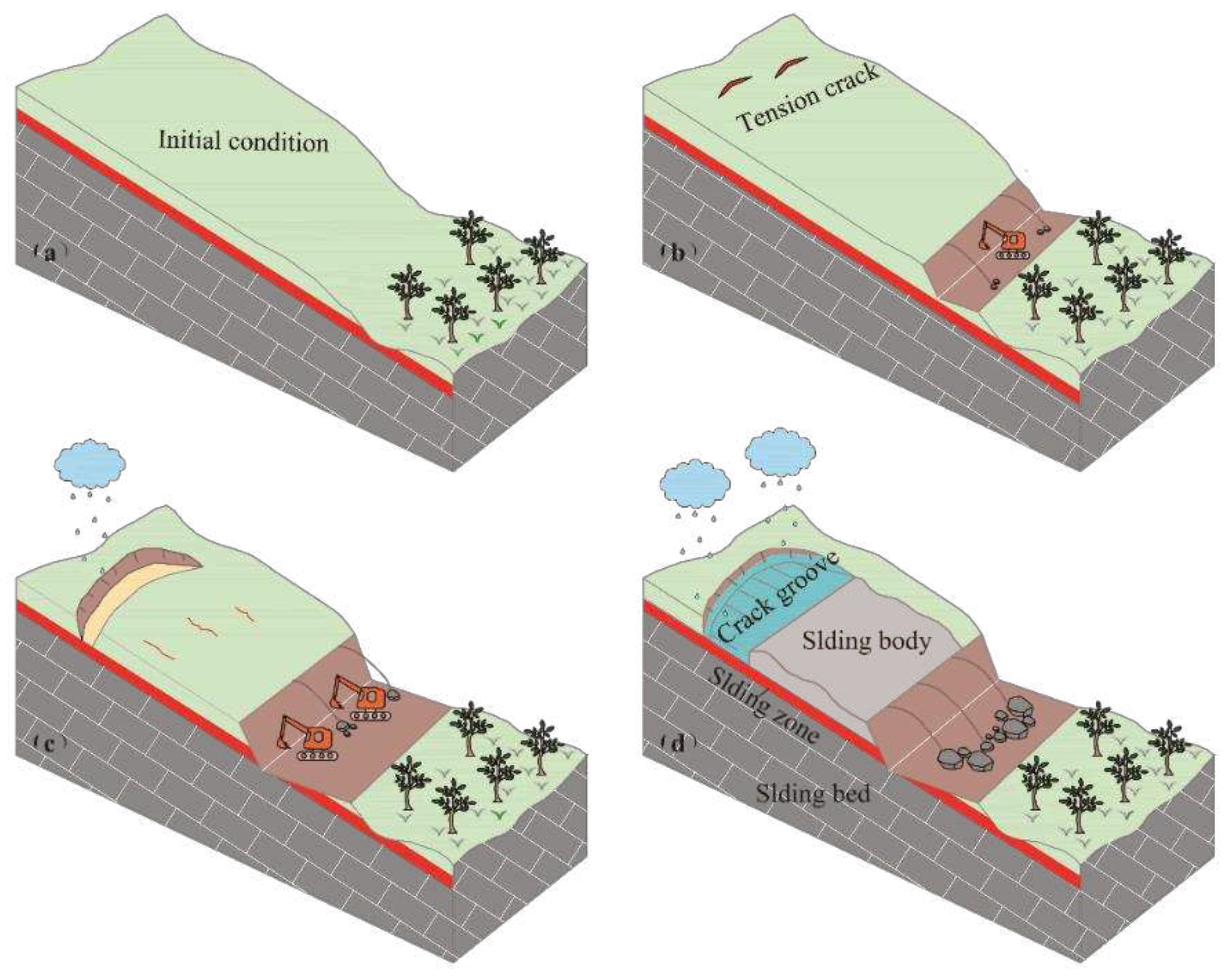
3.1. Evolution process
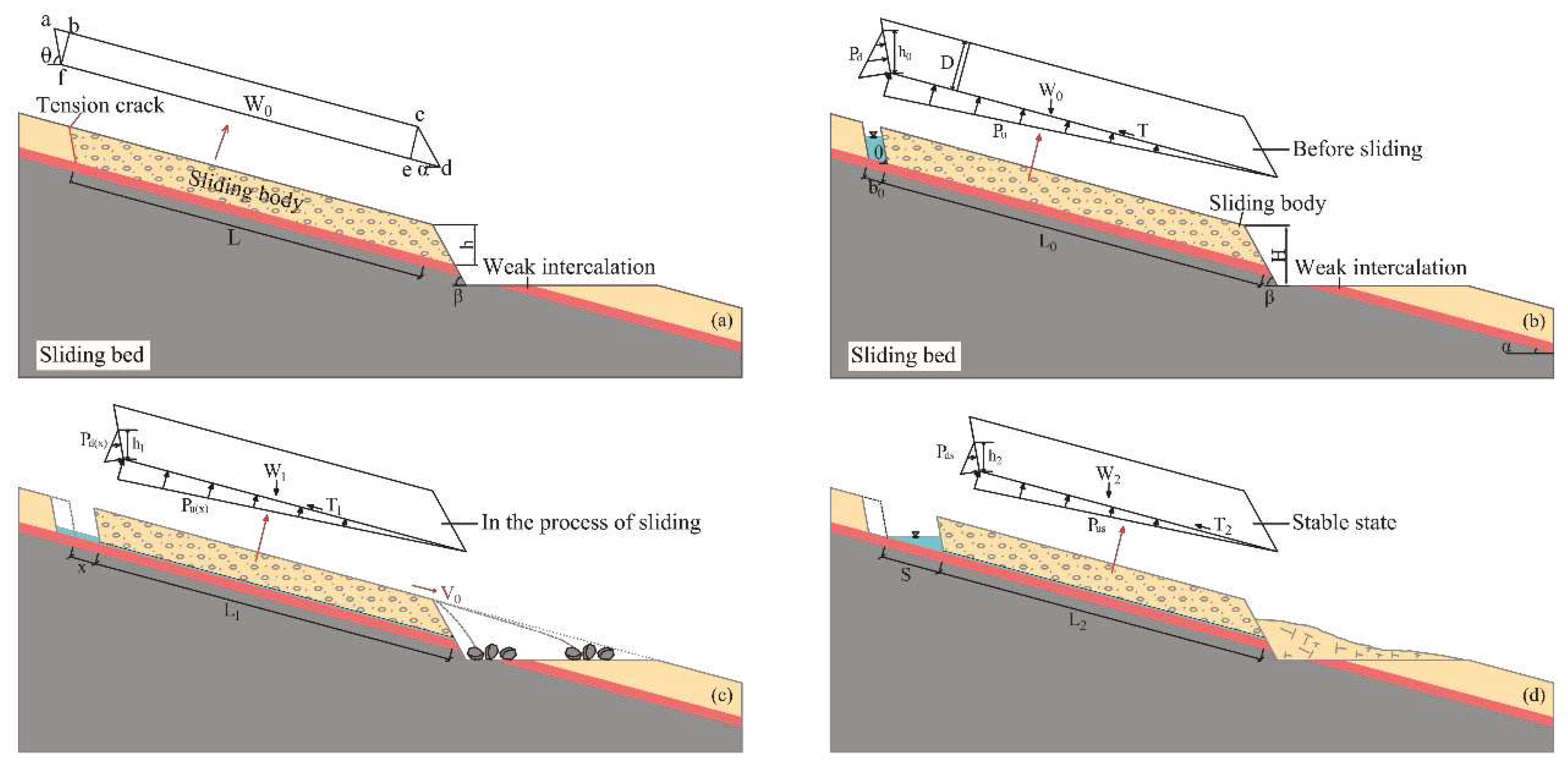
3.2. Mechanical analysis
3.2.1. Instability length
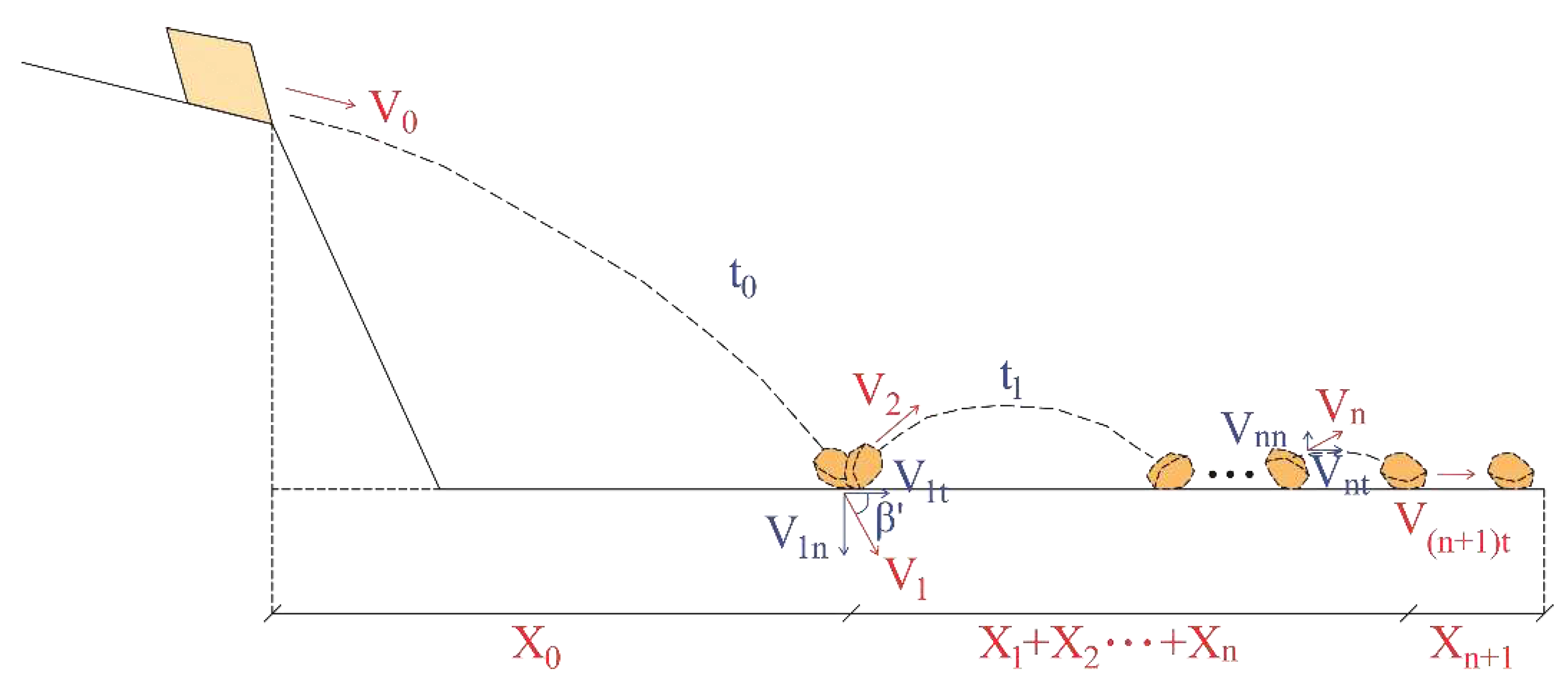
3.2.2. Runout distance
4. Case verification
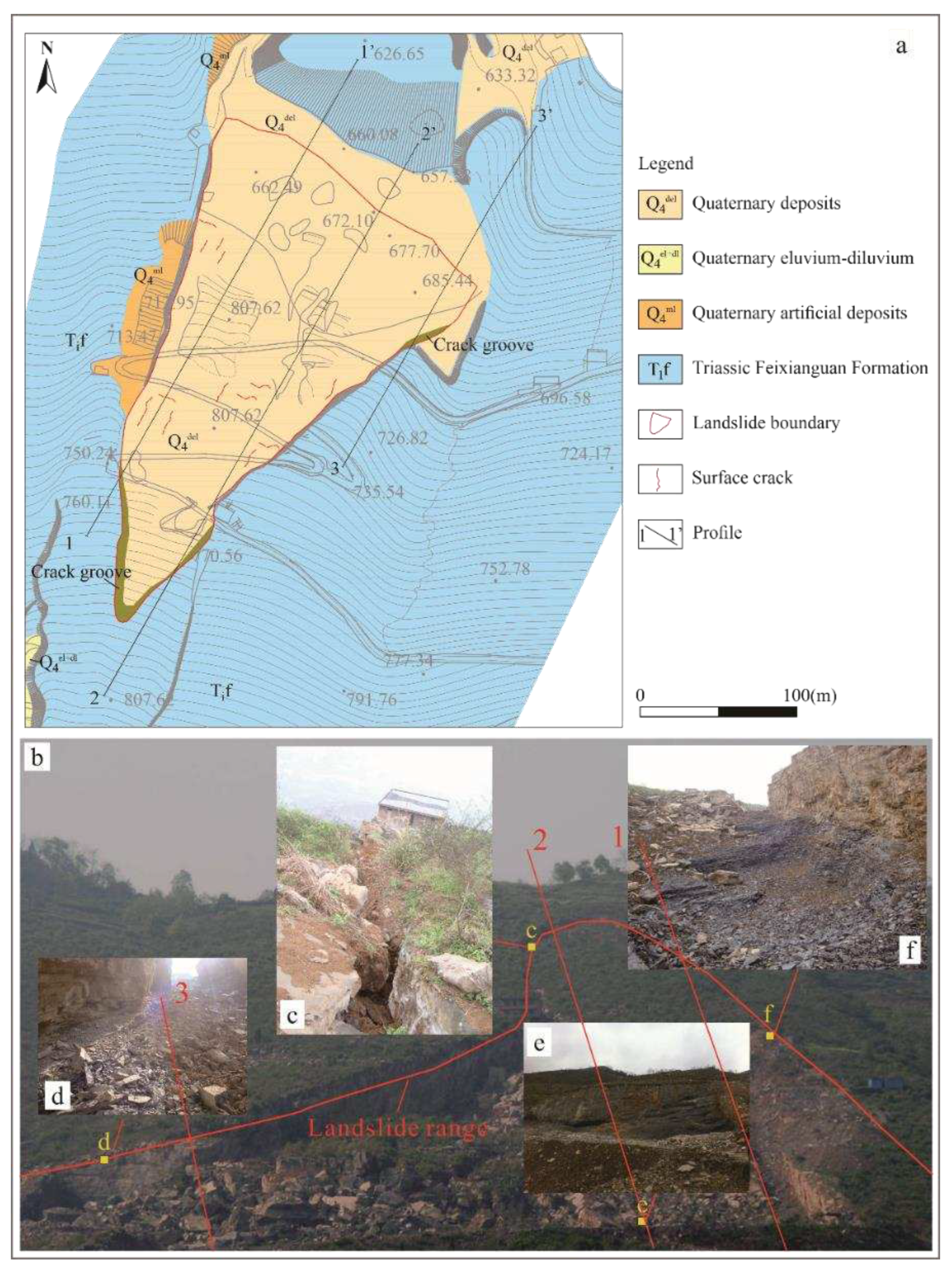
4.1. Case analysis
4.2. Numerical simulation analysis
4.2.1. Model implementation and parameter determination
4.2.2. Result of numerical tests
5. Discussion
6. Conclusion
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
References
- Wu, Lili, et al. "Research on the excavation stability evaluation method of Chaqishan ancient landslide in China." Engineering Failure Analysis 2022, 141, 106664. [CrossRef]
- Y. Togashi, K.Y. Togashi, K. Mizuo; et al. Evaluating Changes in the Degree of Saturation in Excavation Disturbed Zones Using a Stochastic Differential Equation. Computers and Geotechnics 2022, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. Liu, Y. Xie, Z.H. Feng; et al. Better Understanding the Failure Modes of Tunnels Excavated in the Boulder-Cobble Mixed Strata by Distinct Element Method. Engineering Failure Analysis 2020, 116, 104712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S.S. Xu, H. Lei, C. Li; et al. Model Test on Mechanical Characteristics of Shallow Tunnel Excavation Failure in Gully Topography. Engineering Failure Analysis 2021, 119, 104978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Bayer, A. Simoni, D. Schmidt. Using Advanced InSAR Techniques to Monitor Landslide Deformations Induced by Tunneling in the Northern Apennines Italy. Engineering Geology 2017, 226, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Changbao, et al.; et al. Study of an ancient landslide reactivation mechanism based on centrifuge model testing: an example of the Jiangdingya ancient landslide reactivation in 2018, Gansu Province, China. Landslides 2023, 20, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Chonglei, et al; et al. Large-scale shaking table test on seismic behaviour of anti-slide pile-reinforced bridge foundation and gravel landslide: a case study. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 2021, 80, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Jian, et al.; et al. The effect of topography on landslide kinematics: a case study of the Jichang town landslide in Guizhou, China. Landslides 2020, 17, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E. Botero, E. Ovando, M.J. Mendoza. Successful prediction of slope failure in an excavation trial. Engineering Failure Analysis. 2020, 109, 104392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- K.R. Praveen, J. Chophel, J. Wangchuk; et al. IBIS-FM Radar as A Tool for Monitoring Hill Slopes During Excavations in Hydropower Projects: A Case Study from Bhutan Himalayas. Energy Geoscience. 2021; 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Florin, L. Maria, D. Ciprian. IzabelaMaria, Investigations on the Stability of the Right Slope in the Area of Anina Wastewater Treatment Plant, Revista Minelor / Mining Revue. 2022, 27, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du J, Shi X, Chai B; et al. Force and energy equilibrium-based analytical method for progressive failure analysis of translational rockslides: formulation and comparative study. Landslides 2023, 20, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang W, Song H, Zhang Z; et al. Landslide Multi-attitude Data Measurement of Bedding Rock Slope Model[J]. International Journal of Parallel Programming 2020, 48, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng Y, Dong S, Lu Z; et al. A method for calculating permanent displacement of seismic-induced bedding rock landslide considering the deterioration of the structural plane. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2023; 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai Z, Zhang L, Wang Y; et al. Deformation and failure response characteristics and stability analysis of bedding rock slope after underground adverse slope mining. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 2021, 80, 4405–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X., Gong. Study of the slope deformation characteristics and landslide mechanisms under alternating excavation and rainfall disturbance. Bull Eng Geol Environ 2021, 80, 7171–7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang J Y, Li L, Zheng D G, et a1. Characteristics of Apparent Dip Slide and Movement Process of the "8.12" Shanyang Rockslide. Journal of Catastrophology (in Chinese with English abstract). 2018, 33, 111–116. [CrossRef]
- Zhu X, Xie L, Tang Y; et al. Progressive Formation of Retrogressive Landslide and the Lateral Length of Instability. Applied Sciences 2023, 13, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li J, Chen S, Yu F; et al. Reinforcement mechanism and optimisation of reinforcement approach of a high and steep slope using prestressed anchor cables. Applied Sciences 2019, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu Z, Qiu H, Ma S; et al. Surface displacement and topographic change analysis of the Changhe landslide on September 14, 2019, China. Landslides 2021, 18, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari A, Mousavi S. An analytical probabilistic analysis of slopes based on limit equilibrium methods. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 2019, 78, 4333–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng H, Zhou X. A novel displacement-based rigorous limit equilibrium method for three-dimensional landslide stability analysis. Can Geotech J 2015, 52, 2055–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou XP, Cheng H. Analysis of stability of three-dimensional slopes using the rigorous limit equilibrium method. Eng Geol 2013, 160, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengani F, Allopi D. Accuracy of Two-Dimensional Limit Equilibrium Methods in Predicting Stability of Homogenous Road-Cut Slopes. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng J, Zhou D P, Jiang N. On the Extent of Bedding Slipping Rockmass of Consequent Rock Slope. Journal of Mountain Science (In Chinese with English abstract). 2007, 3, 376–380. [Google Scholar]
- Deng R G, Zhou D P, Li A H; et al. On the Critical Length of Unstable Rock Stratum on bedrock slope. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering (in Chinese with English abstract). 2002, 24, 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Su X, Wei W, Ye W; et al. Predicting landslide sliding distance based on energy dissipation and mass point kinematics. Natural Hazards 2019, 96, 1367–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattanji T, Moriwaki H. Morphometric analysis of relic landslides using detailed landslide distribution maps: implications for forecasting travel distance of future landslides. Geomorphology 2009, 103, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo D P, Hamada M, He C. An empirical model for landslide travel distance prediction in Wenchuan earthquake area. Landslides 2014, 11, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo C B, Zhang Y S, Montgomery D R; et al. How unusual is the long-runout of the earthquake-triggered giant Luanshibao landslide, Tibetan Plateau, China? Geomorphology 2016, 259, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungr, O. A model for the runout analysis of rapid flow slides, debris flows, and avalanches. Can Geotech J 1995, 32, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao T D, Liu Z Y, Niu Y H. A sliding block model for the runout prediction of high-speed landslides. Can Geotech J 2001, 38, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang J D, Xiao S F, Zhang Z Y. The mechanism for movement of irrigation-induced high-speed loess landslide. J Eng Geol (In Chinese with English abstract). 2001, 9, 241–246. [Google Scholar]
- He S M, Liu W, Wang J. Dynamic simulation of landslide based on thermo-poroelastic approach. Comput. Geosci. 2015, 75, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaringi G, Fan X, Xu Q; et al. Some considerations on the use of numerical methods to simulate past landslides and possible new failures: the case of the recent Xinmo landslide (Sichuan, China). Landslides 2018, 15, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang Y, Li G, Xiong M. Stochastic assessment of slope failure run-out triggered by earthquake ground motion. Nat. Hazards 2020, 101, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell A, McDougall S, Nolde N; et al. Rock avalanche runout prediction using stochastic analysis of a regional dataset. Landslides 2020, 17, 777–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang Z, Zeng R, Meng X; et al. Estimating landslide sliding distance based on an improved Heim sled model. Catena 2021, 204, 105401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang P, Chen J J. Displacement prediction of landslide based on generalized regression neural networks with K -fold cross-validation. Neurocoputing 2016, 198, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Xu C, Huang B; et al. Landslide displacement prediction based on multi-source data fusion and sensitivity states. Engineering Geology. 2020, 271, 105608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li X, Tang X, Zhao S; et al. MPM evaluation of the dynamic runout process of the giant Daguangbao landslide. Landslides 2021, 18, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang C, Yin Y, Yan H; et al. Centrifuge modeling of multi-row stabilizing piles reinforced reservoir landslide with different row spacings. Landslides 2022, 20, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou C, Cao Y, Yin K; et al. Characteristic comparison of seepage-driven and buoyancy-driven landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Engineering Geology 2022, 301, 106590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge Y F, Tang H M, Li Wei; et al. Evaluation for Deposit Areas of Rock Avalanche Based on Features of Rock Mass Structure. Earth Science (In Chinese with English abstract). 2016, 41, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar]
- Dai X R, Zhao J J, Lai Q Y; et al. Movement Process and Formation Mechanism of Rock Avalanche in Chada, Tibet Plateau. Earth Science. (In Chinese with English abstract). 2022, 47, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang R, Xu Q, Wu B; et al. Method of sliding distance calculation for translational landslides. Rock and Soil Mechanics. (In Chinese with English abstract). 2017, 39, 1009–1019+1070. [Google Scholar]
- Yang L, Wang Y, Zhang Q et al.; et al. A theoretical model about runout distance of bedding rock landslide under excavation uploading [J/OL]. Earth Science:1-15[2023-06-05]. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20230-420.1013.002.html.
- Itasca, 2004. UDEC Version 4.0 Universal Distinct Element Code. Itasca Consulting Group, Inc.
- Li X M, Yan E C, YanY; et al. Deformation Zoning and Treatment of a Toppling Deformation Slope Beside the Diversion Channel of a Hydropower Station. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology (In Chinese with English abstract). 2019, 38, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Mu C, L. 2017. Study on deformation instability evolution mechanism and prediction during excavating process of bedded rock slope - A case of slope as the studied object in the Gasoline construction site. Doctoral dissertation. Chengdu University of Technology.
- Zhang Y H, Zhang M X, Cheng Q. Kinematics analysis for calculating distance of rockfalls on typical loose media slope. Journal Of ShangHai University (Natural Science). 2017, 23, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang R Q, Liu W H. Study on the movement characteristics of rolling rock blocks on platform. Advances in Earth Science. (In Chinese with English abstract). 2008, 5, 517–523. [Google Scholar]
- Huang D, Gu D M, Song Y X; et al. Towards a complete understanding of the triggering mechanism of a large reactivated landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir. Engineering Geology 2018, 238, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi Y, Cappa F, Binet S. Coupling between hydrogeology and deformation of mountainous rock slopes: Insights from La Clapière area (southern Alps, France). Comptes Rendus Geoscience 2005, 337, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
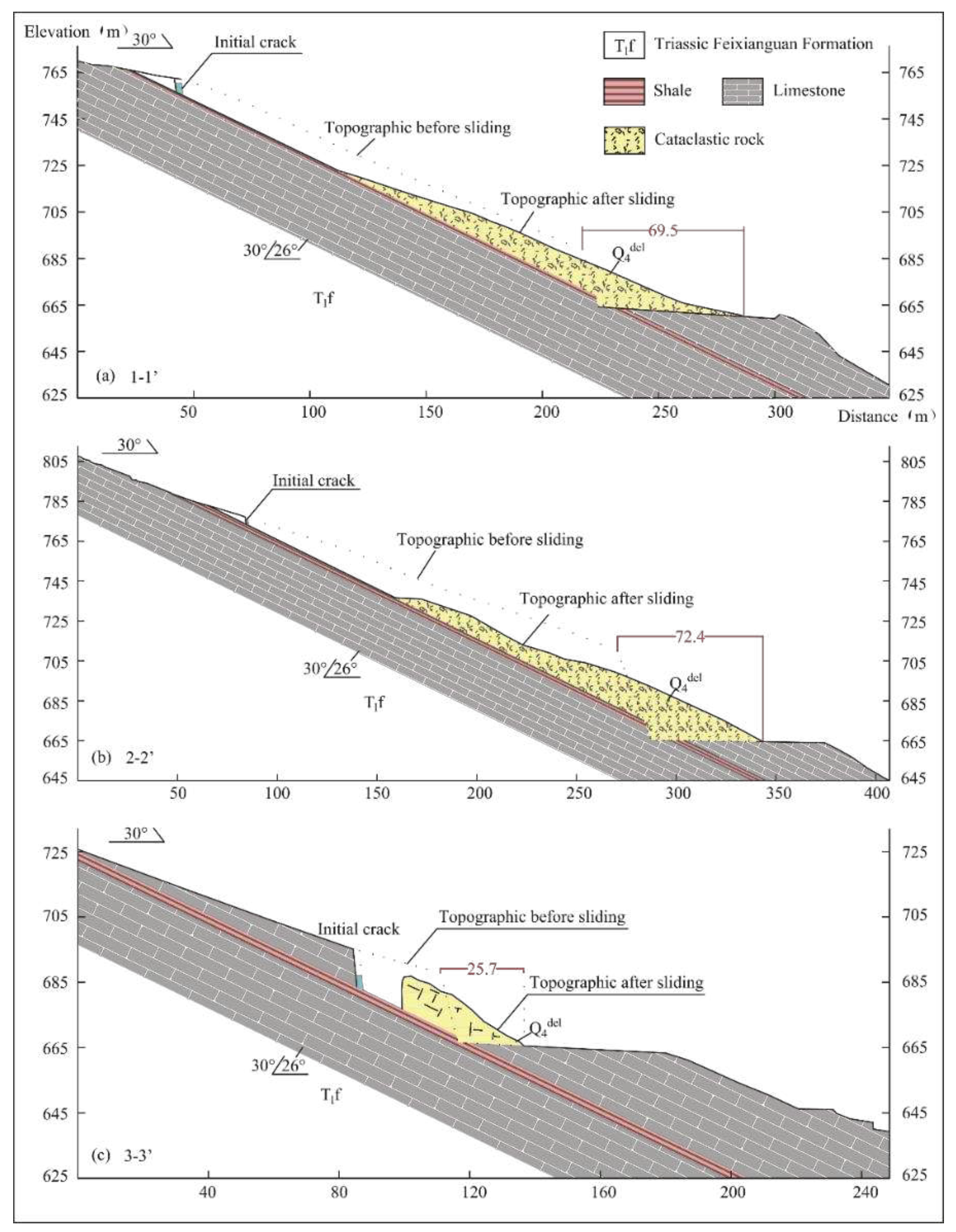
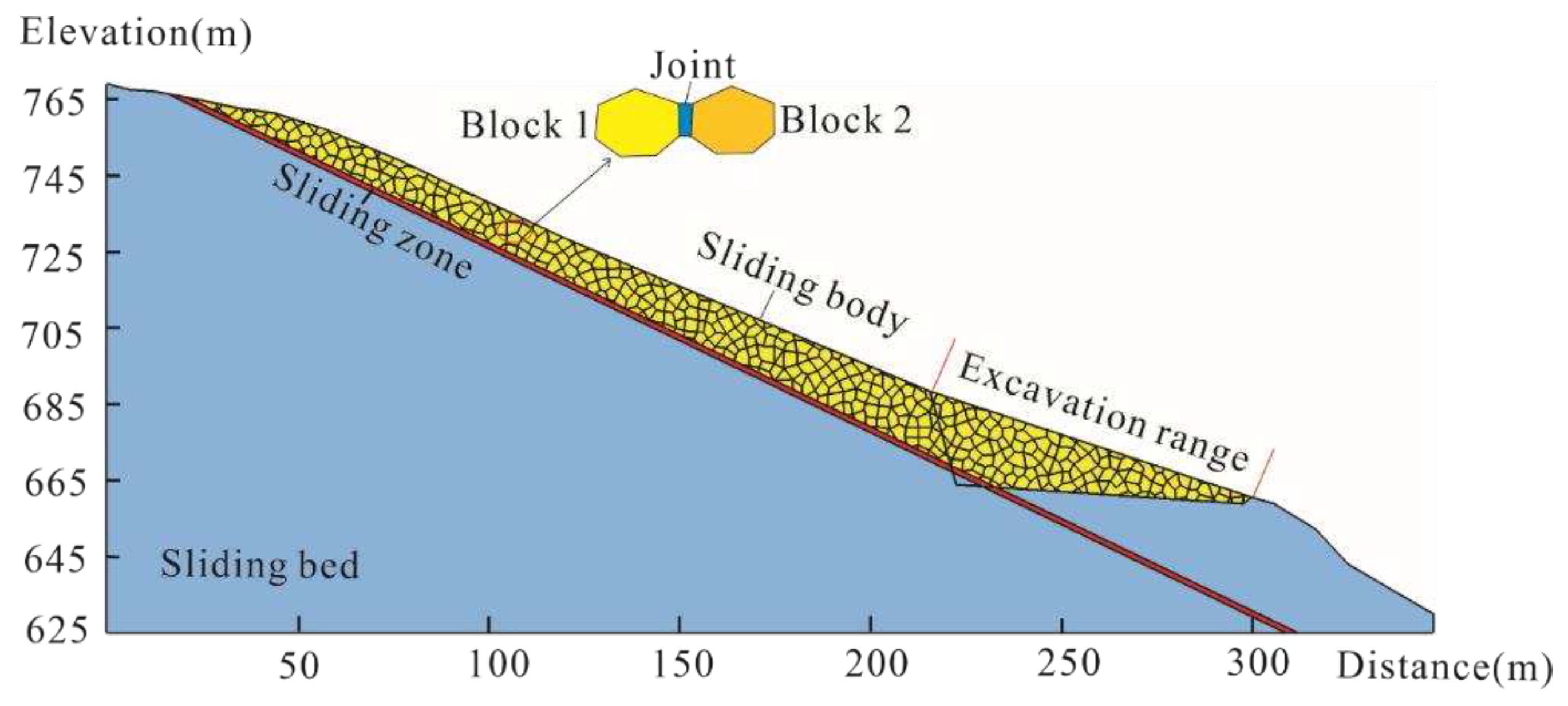
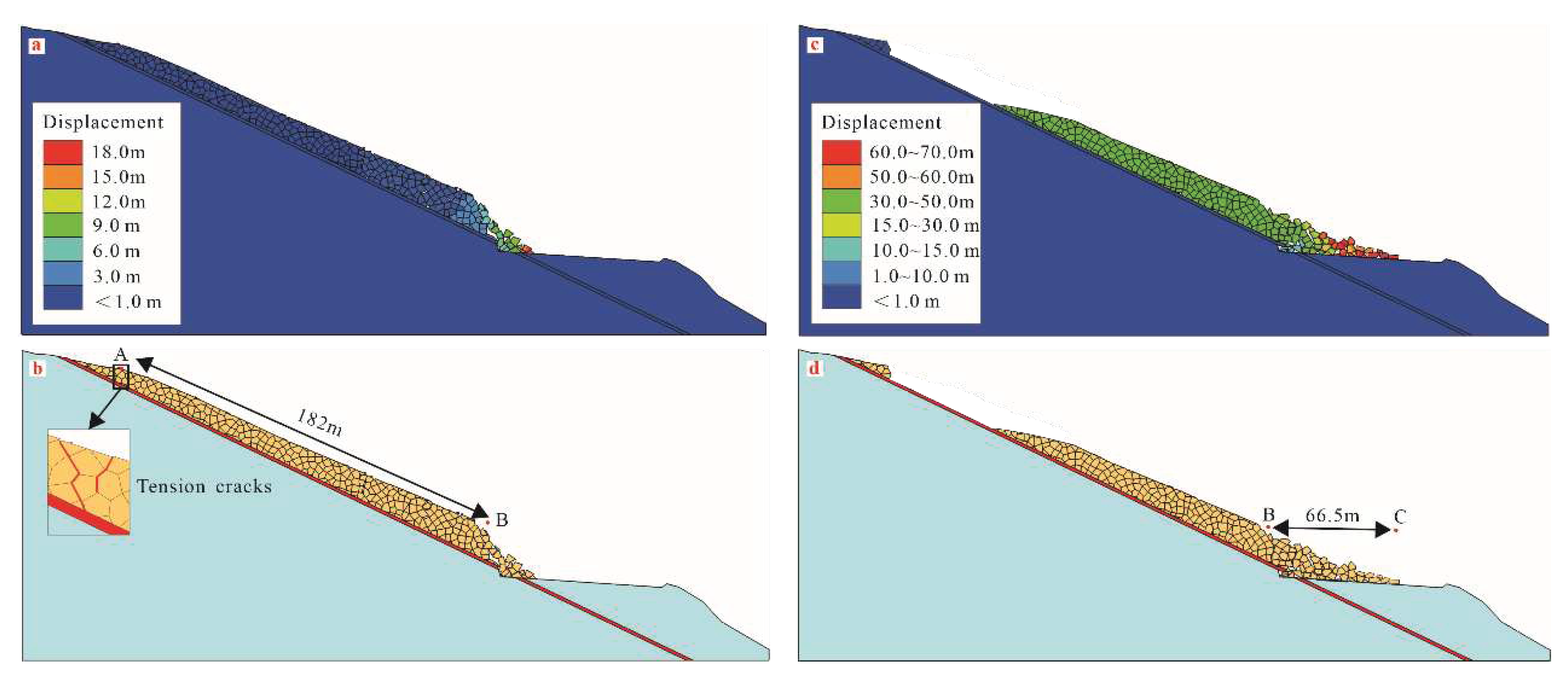
| Profile | γ (kN/m3) | ɵ(°) | β(°) | h(m) | b0 (m) | h0 (m) | L0 (m) | W0 (kN/m) | H (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1’ | 21.5 | 82 | 74 | 19.4 | 1.5 | 5.5 | 196.0 | 62975.50 | 28.0 |
| 2-2’ | 21.5 | 82 | 69 | 34.7 | 1.2 | 5.5 | 216.0 | 114972.54 | 42.6 |
| 3-3’ | 21.5 | 82 | 76 | 19.1 | 2.2 | 3.5 | 30.0 | 9323.86 | 21.7 |
| Profile | lac (m) | lac’ (m) | Xt (m) | Xt’ (m) | absolute error | relative error |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-1’ | 170.5 | 187.2 | 75.22 | 69.5 | 16.7/5.72 | 8.9%/8.23% |
| 2-2’ | 175.2 | 197.7 | 82.5 | 72.4 | 22.5/1.83 | 11.38%/13.95% |
| 3-3’ | 20.8 | 25.7 | 27.14 | 25.7 | 4.0/0.15 | 19.07%/5.6% |
| Stage | Position | γ (kN/m3) | B (Pa) | S (Pa) | c (kPa) | φ (°) | T(Mpa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excavation | 1 | 21.5 | 7.2×109 | 5.5×109 | 26.3 | 24.4 | 1.5 |
| 2 | 19.5 | 3.8×108 | 2.1×108 | 19.5 | 21.5 | 0.35 | |
| 3 | 25.5 | 8.9×1011 | 6.9×1011 | 95 | 50 | 120 | |
| Hydrostatic pressure | 1 | 20.6 | 2.1×109 | 1.5×109 | 20.6 | 13.8 | 0.8 |
| 2 | 18.6 | 8.6×107 | 7.6×107 | 13.5 | 9.5 | 0.2 | |
| 3 | 24.8 | 8.9×1011 | 6.9×1011 | 95 | 50 | 120 |
| Stage | Position | Jkn (GPa/m) | Jks (GPa/m) | Jc (kpa) | Jt (Mpa) | Jf (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Excavation | 1 | 12.0 | 4.0 | 24.5 | 0.8 | 23.2 |
| Hydrostatic pressure | 1 | 10.0 | 2.5 | 19.8 | 0.4 | 12.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




