Submitted:
09 January 2024
Posted:
09 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hypothesis
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Objectives of the study
2.2.1.1. Primary objectives
2.2.1.2. Secondary objectives
2.2.3. Study population
2.2.4. Analyzed variables
2.2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
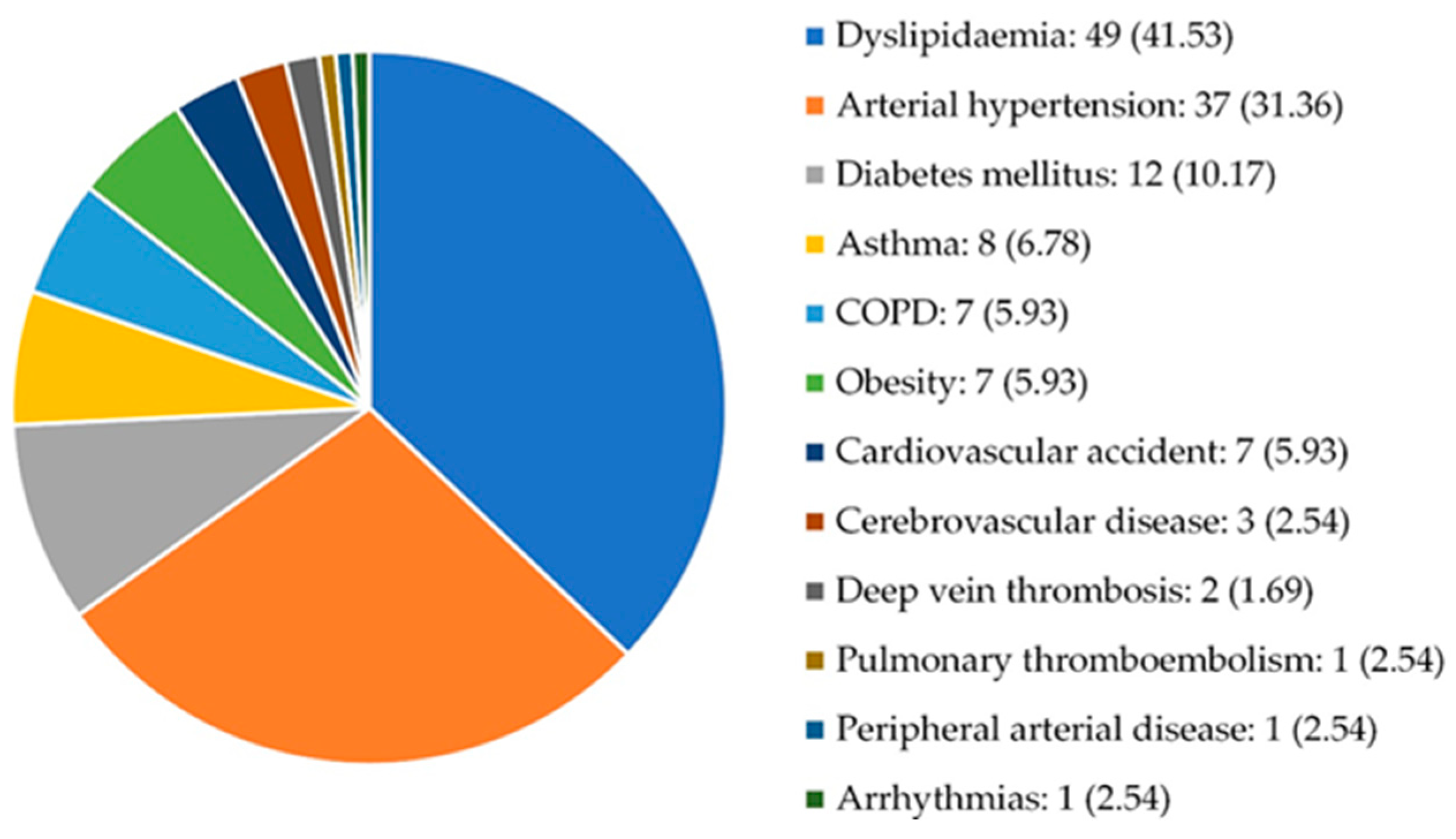
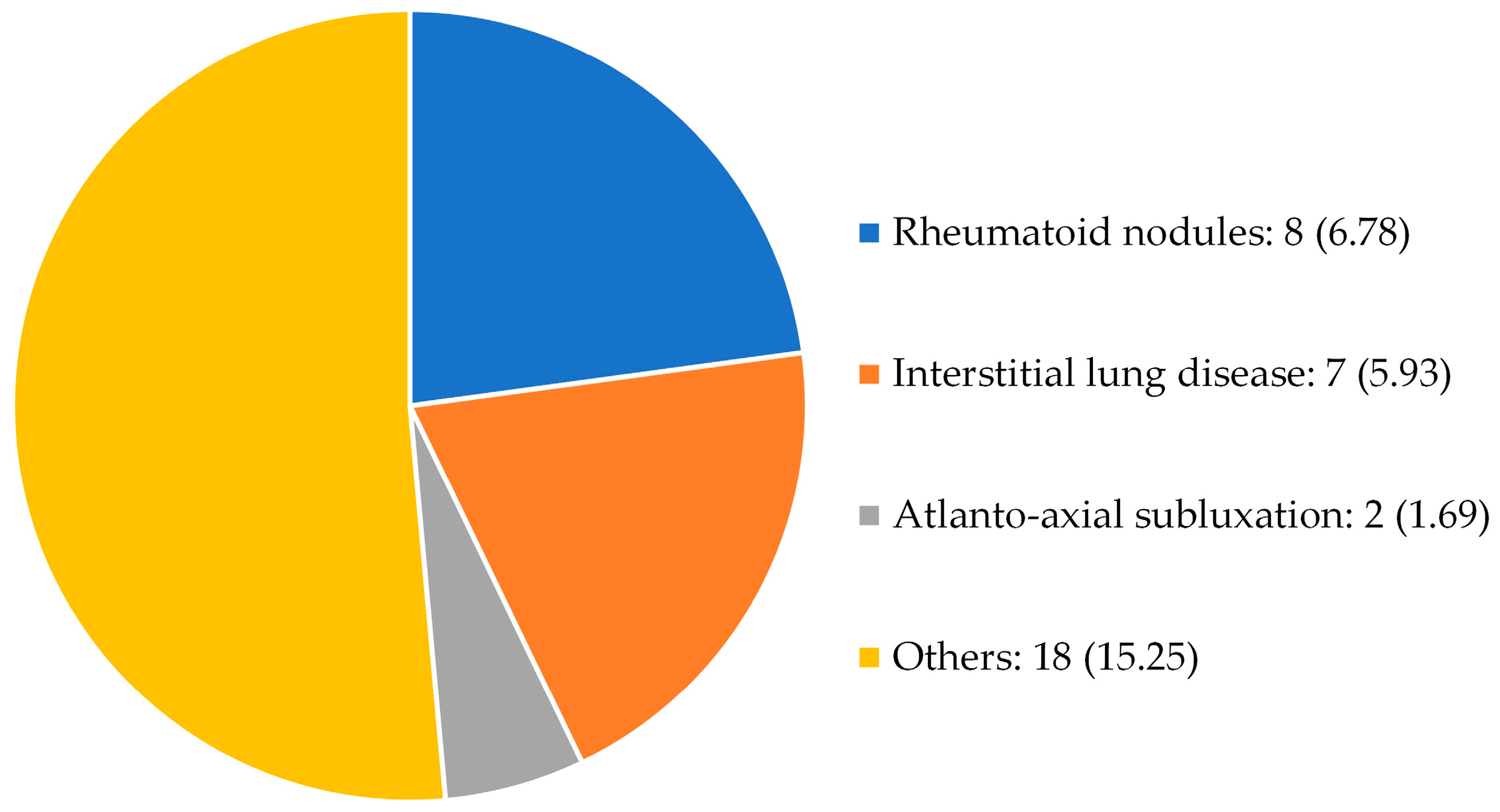
3.1. Characteristics of the study population
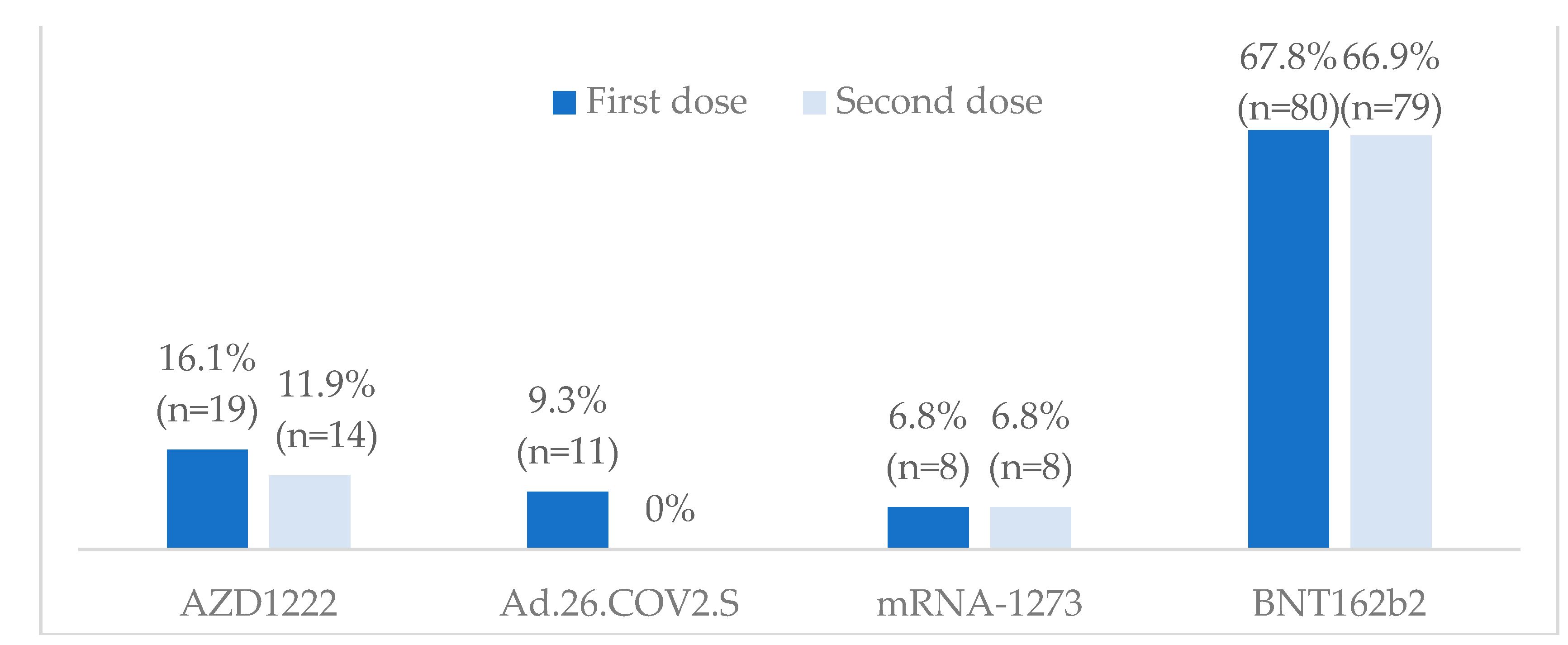
3.2. Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2
3.3. Vaccine efficacy and safety
3.3.1. Positive serological response and degree of response
3.3.2. Post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection
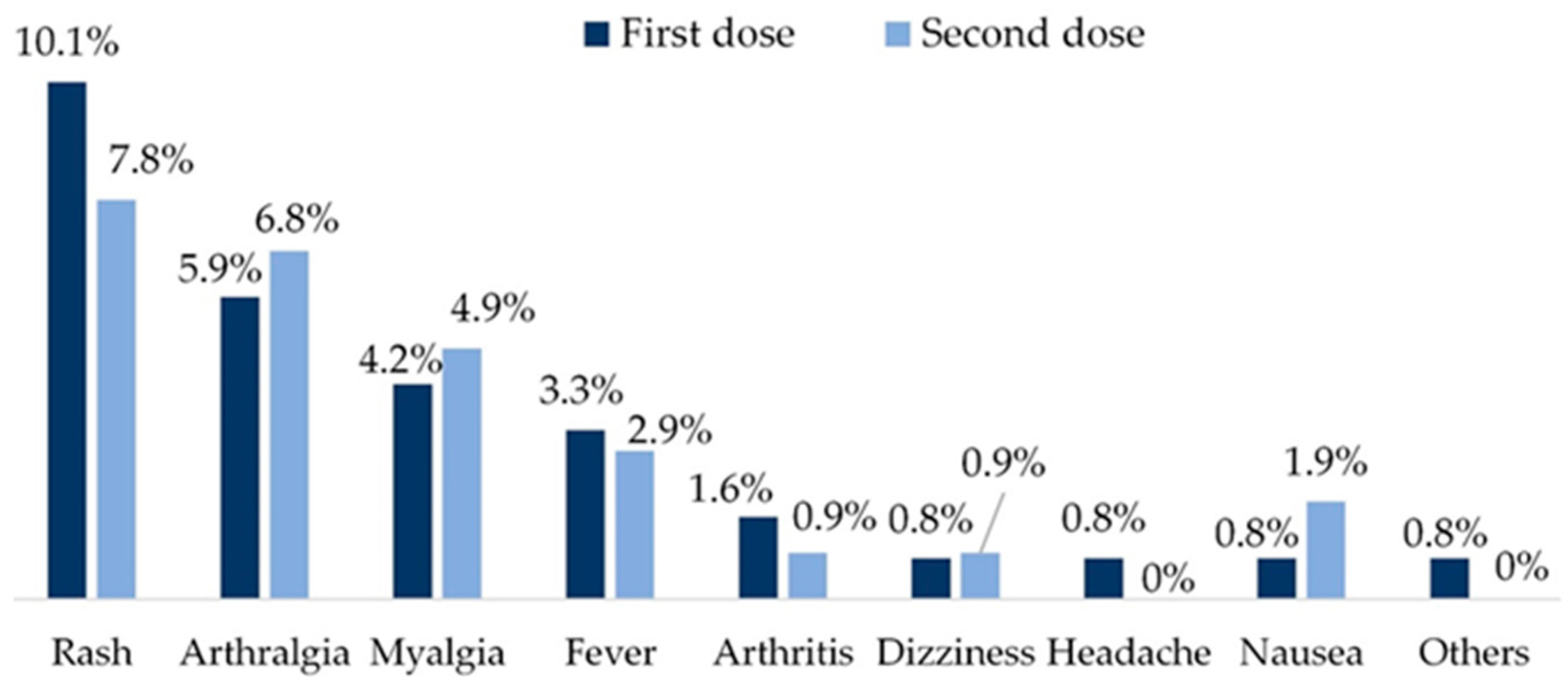
3.3.3. Vaccine safety
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Groups of variables | Type of variable | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic variables | Age | Years |
| Sex | Male, female | |
| Smoking | Pack-years | |
| Comorbidities | Presence Type: AHT, DM, DL, obesity, ischemic heart disease, thromboembolic disease, cardiovascular disease, stroke, peripheral arterial disease, arrhythmias, heart failure, thromboembolic disease, pulmonary thromboembolism, deep vein thrombosis, renal failure, COPD, asthma |
|
| RA characteristics | Onset date | Date |
| Diagnosis date | Date | |
| Rheumatoid factor | Presence, titer | |
| aCCP antibodies | Presence, titer | |
| Erosive RA | Yes / No | |
| Extra-articular manifestations |
Nodules, interstitial lung disease, atlanto-axial subluxation, others | |
| Disease activity and functionality | ESR, CRP, DAS28, HAQ | |
| RA treatment | Previous therapy | GC, MTX, OHCQ, SSZ, CsA, AZA, MPM, TACRO, TOFA, BARI, ANAK, ABA, RTX, TCZ, SARI, IFX, ETN, ADA, GOLI |
| Current therapy | Starting date and dosage of GC, MTX, OHCQ, SSZ, CsA, AZA, MPM, TACRO, TOFA, BARI, ANAK, ABA, RTX, TCZ, SARI, IFX, ETN, ADA and/or GOLI | |
|
Previous COVID-19 |
Diagnosis | Data, method (PCR / antigen test), place (Primary Care / Hospital Care) |
| Symptoms and complications |
Cough, fever, expectoration, nasal congestion, pneumonia, dyspnoea, desaturation, chest pain, palpitations, tachycardia, back pain, arthralgia, myalgia, arthritis, malaise, anosmia, ageusia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, headache, dizziness, rash, superinfection, thrombosis, arrhythmia, renal failure | |
| Severity | Hospital admission, ICU admission | |
| Sequelae | Free text for description | |
| RA activity at diagnosis of COVID-19 |
Remission, low, moderate, severe | |
| Treatments received | Anti-inflammatory, antiviral, respiratory support, modification of usual RA treatment | |
|
COVID-19 vaccine |
Type of vaccine | AZD1222, Ad.26.COV2.s, mRNA-1237, BNT162b2 |
| Number of vaccine doses | Number of doses administered | |
| First dose | Date, AE (fever, arthralgia, myalgia, arthritis, headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, rash, anaphylaxis, thrombosis), severe AE | |
| Second dose | Date, AE (fever, arthralgia, myalgia, arthritis, headache, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, rash, anaphylaxis, thrombosis), severe AE | |
| Humoral response* | Post-vaccine serology (BAU/mL), serology collection date | |
|
Post-vaccine COVID-19 |
Symptoms and signs | Cough, fever, expectoration, nasal congestion, pneumonia, dyspnoea, desaturation, chest pain, palpitations, tachycardia, back pain, arthralgia, myalgia, arthritis, malaise, anosmia, ageusia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, headache, dizziness, rash, superinfection, thrombosis, arrhythmia, renal failure |
| Severity | Hospital admission, ICU admission |
References
- Seoane-Mato, D.; Sánchez-Piedra, C.; Díaz-González, F.; et al. Prevalence of rheumatic diseases in adult population in Spain. EPISER 2016 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018, 77, 535–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García de Yébenes, M.J.; Loza, E. Rheumatoid arthritis: epidemiology and socio-health impact. Clinical Rheumatology Supplements 2018, 14, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, J.A. Rheumatoid arthritis (I). Etiopathogenesis, symptomatology, diagnosis and prognosis. OFFARM, 2021; 20, 94–100. [Google Scholar]
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Sisó-Almirall, A.; Flores-Chavez, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 676–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasseli, R.; Mueller-Ladner, U.; Hoyer, B.F.; et al. Older age, comorbidity, glucocorticoid use and disease activity are risk factors for COVID-19 hospitalisation in patients with inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. RMD Open 2021, 7, e001464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Koops, H.; Krueger, K.; Vallbracht, I.; et al. Increased risk for severe COVID-19 in patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases treated with rituximab. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021, 80, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, J.R.; Johnson, S.R.; Anthony, D.D.; et al. American College of Rheumatology Guidance for COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients With Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases: Version 3. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, e60–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Lee, E.B.; Shin, K.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: Clinical Guidance of the Korean College of Rheumatology. J Korean Med Sci. 2021, 36, e95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alten, R.; Bingham, C.O.; Cohen, S.B.; et al. Antibody response to pneumococcal and influenza vaccination in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving abatacept. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016, 17, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crnkic Kapetanovic, M.; Saxne, T.; Jönsson, G.; et al. Rituximab and abatacept but not tocilizumab impair antibody response to pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013, 15, R171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furer, V.; Rondaan, C.; Heijstek, M.W.; et al. 2019 update of EULAR recommendations for vaccination in adult patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020, 79, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Barnetche, T.; Combe, B.; Morel, J. Effect of methotrexate, anti-tumor necrosis factor α, and rituximab on the immune response to influenza and pneumococcal vaccines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2014, 66, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, E.Y.; et al. Effect of methotrexate discontinuation on efficacy of seasonal influenza vaccination in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017, 76, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Shin, K.; et al. Impact of temporary methotrexate discontinuation for 2 weeks on immunogenicity of seasonal influenza vaccination in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomised clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018, 77, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grupo de Trabajo Técnico de Vacunación COVID-19, de la Ponencia de Programa y Registro de Vacunaciones. Estrategia de vacunación frente a COVID-19 en España. Ministerio de Sanidad. Available online: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/profesionales/saludPublica/prevPromocion/vacunaciones/covid19/Actualizaciones_Estrategia_Vacunacion/docs/COVID-19_EstrategiaVacunacion.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Grupo de Trabajo Técnico de Vacunación COVID-19, de la Ponencia de Programa y Registro de Vacunaciones. Estrategia de vacunación frente a COVID-19 en España: actualización 3. Ministerio de Sanidad. Available online: https://www.sanidad.gob.es/profesionales/saludPublica/prevPromocion/vacunaciones/covid19/Actualizaciones_Estrategia_Vacunacion/docs/COVID-19_Actualizacion3_EstrategiaVacunacion.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2022).
- Curtis, J.R.; Johnson, S.R.; Anthony, D.D.; et al. American College of Rheumatology Guidance for COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients With Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases: Version 5. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, e1–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, F.C.; Edworthy, S.M.; Bloch, D.A.; et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros-Ribeiro, A.C.; Bonfiglioli, K.R.; Domiciano, D.S.; et al. Distinct impact of DMARD combination and monotherapy in immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022, 81, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, A.; Mishra, S.; Deepak, P.; et al. Response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in immune mediated inflammatory diseases: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev. 2022, 21, 102927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, D.; Vago, H.; Tothfalusi, L.; et al. Factors influencing the SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination induced immune response in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2022, 13, 960001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammitzbøll, C.; Thomsen, M.K.; Andersen, J.B.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination in patients with rheumatic diseases leads to a high seroconversion rate and reduced self-imposed isolation and shielding behaviour. Mod Rheumatol. 2023, 33, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmegna, I.; Valerio, V.; Amiable, N.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccine in Immunosuppressed Adults with Autoimmune rheumatic Diseases (COVIAAD): safety, immunogenicity and antibody persistence at 12 months following Moderna Spikevax primary series. RMD Open 2023, 9, e003400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiesisibieke, Z. L.; Liu, W. Y.; Yang, Y. P.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccinations: An Umbrella Meta-Analysis. Int J Public Health 2023, 68, 1605526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Moine, C.; Soyfoo, M.S.; Mekkaoui, L.; et al. Impaired Humoral Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2022, 49, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Fleta, P.; Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Triguero-Martínez, A.; et al. Beneficial effect of temporary methotrexate interruption on B and T cell responses upon SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis. NPJ Vaccines, 2024, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Ibarguengoitia, M.E.; Rivera-Salinas, D.; Sarti, R.; et al. Efficacy of Six Different SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines during a Six-Month Follow-Up and Five COVID-19 Waves in Brazil and Mexico. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitchon, C.A.; Mesa, C.; Bernstein, C.N.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of mixed COVID-19 vaccine regimens in patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases: a single-centre prospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e071397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, B.; Ross, R.L.; Bissell, L.A.; et al. Effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) on DMARDs: as determined by antibody and T cell responses. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limoges, M. A.; Lortie, A.; Demontier, É.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine-induced immune responses in rheumatoid arthritis. J Leuk Biol. 2023, 114, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moine, C.; Soyfoo, M. S.; Mekkaoui, L.; et al. Waning humoral immunity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in a rheumatoid arthritis cohort and the benefits of a vaccine booster dose. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2023, 41, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, J.M.; Breznik, J.A.; Ang, J.C.; et al. Immunomodulatory drugs have divergent effects on humoral and cellular immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in people living with rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 22846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammitzbøll, C.; Thomsen, M.K.; Andersen, J.B.; et al. Revaccination of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis without an initial COVID-19 vaccine response elicits seroconversion in half of the patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, M.W.; Dayam, R.M.; Shapiro, J.R.; et al. Third and Fourth Vaccine Doses Broaden and Prolong Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Adult Patients with Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. J Immunol. 2023, 211, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, B.; Moradi Hasan-Abad, A.; Piroozmand, A.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of the BBIBP-CorV vaccine in patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases undergoing mmunosuppressive therapy in a monocentric cohort. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023, 11, e858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frommert, L.M.; Arumahandi de Silva, A.N.; Zernicke, J.; et al. Type of vaccine and immunosuppressive therapy but not diagnosis critically influence antibody response after COVID-19 vaccination in patients with rheumatic disease. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, H.M.; O'Mara, M.; Auma, A.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and older age are associated with lower humoral and cellular immune response to primary series COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. Vaccine 2023, 41, 6112–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerike, M.; Parimi, V.P. ; D M; et al. Clinical and immunological responses to COVID-19 vaccination in rheumatoid arthritis patients on disease modifying antirheumatic drugs: a cross-sectional study. J Rheum Dis. 2024 31, 15-24. [CrossRef]
- Shirata, M.; Ito, I.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Impact of methotrexate on humoral and cellular immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Med. 2023, 23, 4707–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, S.K.; Solomon, D.H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Humoral and cellular immune responses in persons with rheumatoid arthritis after a third dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2023, 59, 152177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, C.S.R.; Medeiros-Ribeiro, A.C.; Saad, C.G.S.; Bonfiglioli, K.R.; et al. Two-week methotrexate discontinuation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis vaccinated with inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: a randomised clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022, 81, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermann, E.; Gieselmann, L.; Tober-Lau, P.; et al. Pausing methotrexate prevents impairment of Omicron BA.1 and BA.2 neutralisation after COVID-19 booster vaccination. RMD Open, 2022; 8, e002639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra López-Matencio, J.M.; Vicente-Rabaneda, E.F.; Alañón, E.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccination and Immunosuppressive Therapy in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11, 1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md Yusof, M.Y.; Arnold, J.; Saleem, B.; et al. Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections and prediction of moderate-to-severe outcomes during rituximab therapy in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases in the UK: a single-centre cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e88–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furer, V.; Eviatar, T.; Zisman, D.; et al. Predictors of Immunogenic Response to the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Treated with Rituximab. Vaccines 2022, 10, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Togt, C.J.T.; Ten Cate, D.F.; den Broeder, N.; et al. Humoral response to coronavirus disease-19 vaccines is dependent on dosage and timing of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2022, 61, SI175–SI179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, C.E.; Patel, N.J.; Fu, X.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 Vaccines Against COVID-19 Infection Among Patients With Systemic Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases on Immunomodulatory Medications. J Rheumatol. 2023, 50, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picchianti-Diamanti, A.; Navarra, A.; Aiello, A.; et al. Older Age, a High Titre of Neutralising Antibodies and Therapy with Conventional DMARDs Are Associated with Protection from Breakthrough Infection in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients after the Booster Dose of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picchianti Diamanti, A.; Navarra, A.; Cuzzi, G.; et al. The Third Dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine Does Not "Boost" Disease Flares and Adverse Events in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wallace, Z.S.; Sparks, J.A.; et al. Risk of COVID-19 Among Unvaccinated and Vaccinated Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: A General Population Study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2023, 75, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, R.; Parodis, I.; Joshi, M.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination in autoimmune diseases (COVAD) study: vaccine safety and tolerance in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2023, 62, 2366–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, L.; Balduzzi, S.; Bogliolo, L.; et al. Reactogenicity, safety and disease flares following BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients with chronic immune-inflammatory arthritis treated with biological and targeted synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2023, 41, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.Y.; Bernatsky, S.; Kwong, J.C.; et al. Safety and Health Care Use Following COVID-19 Vaccination Among Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Self-Controlled Case Series Analysis. J Rheumatol. 2023, jrheum, 2023–0355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boekel, L.; Kummer, L.Y.; van Dam, K.; et al. Adverse events after first COVID-19 vaccination in patients with autoimmune diseases. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e542–e545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszczyk, M.; Marciniak, Z.; Nessler, K.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine short-term adverse events in the real-life family practice in Krakow, Poland. Eur J Gen Pract. 2023, 29, 2147500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, P.M.; Lawson-Tovey, S.; Strangfeld, A.; et al. Safety of vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: results from the EULAR Coronavirus Vaccine (COVAX) physician-reported registry. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022, 81, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatani, A.; Iwamoto, N.; Koto, S.; Aramaki, T. , Terada, K., Ueki, Y., Kawakami, A., & Eguchi, K. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine on arthritis condition in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 2023; 14, 1256655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Santosa, A.; Fong, W.; et al. Post-mRNA vaccine flares in autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases: Results from the COronavirus National Vaccine registry for ImmuNe diseases SINGapore (CONVIN-SING). J Autoimmun. 2023, 134, 102959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rider, L.G.; Parks, C.G.; Wilkerson, J.; et al. Baseline Factors Associated with Self-reported Disease Flares Following COVID-19 Vaccination among Adults with Systemic Rheumatic Disease: Results from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Vaccine Survey. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2022, 61, SI143–SI150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striani, G.; Hoxha, A.; Lorenzin, M.; et al. The impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination on inflammatory arthritis: a cohort study. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1207015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Descriptive analysis | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65.47±11.69 | |
| Sex (female) | 103 (87.29) | |
| Smoking (pack-years) | 8.79±18.55 | |
| Comorbidities | 68 (57.63) | |
| RA evolution | 12.08±9.63 | |
| RA onset | 53.04±13.64 | |
| Rheumatoid factor (positive) | 79 (66.95) | |
| - Titer | 111.49±269.16 | |
| aCCP antibodies (positive) | 63 (53.39) | |
| - Titer | 201.53±255.74 | |
| Erosive RA | 32 (27.11) | |
| Extra-articular manifestations | 26 (22.03) | |
| ESR (mm/h) | 19.88±18.64 | |
| CRP (mg/dl) | 0.51±0.78 | |
| HAQ | 0.575±0.660 | |
| DAS28 | 2.39±1.07 | |
| Previous COVID-19 | 21 (17.8) | |
| Severe previous COVID-19* | 6 (5.08) | |
| Glucocorticoids | 11 (9.32) | |
| - Dose (mg/d) | 5.34±2.24 | |
| Methotrexate | 99 (83.89) | |
| - Dose (mg/w) | 13.18±4.55 | |
| Hydroxycloroquine | 6 (5.08) | |
| Sulfasalazine | 3 (2.54) | |
| Leflunomide | 20 (16.94) | |
| - Dose (mg/d) | 15.75±4.94 | |
| Tofacitinib | 2 (1.69) | |
| Baricitinib | 3 (2.54) | |
| Abatacept sc | 2 (1.69) | |
| Rituximab iv | 19 (16.10) | |
| Tocilizumab sc or iv | 2 (1.69) | |
| Sarilumab sc | 3 (2.54) | |
| Infliximab iv | 1 (0.85) | |
| Etarnecept sc | 14 (11.86) | |
| Adalimumab sc | 4 (3.39) | |
| Certolizumab sc | 4 (3.39) | |
| Golimumab sc | 1 (0.85) |
| Serological response | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | YES | NO | p |
| Age (years) | 65.25±11.67 | 67.14±12.10 | 0.233 |
| Sex (female) | 92 (88.46) | 11 (78.57) | 0.385 |
| Smoking (pack-years) | 6.87±15.23 | 23.01±31.83 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | 58 (55.77) | 10 (71.43) | 0.389 |
| RA evolution | 11.57±8.59 | 15.93±15.28 | 0.994 |
| RA onset | 53.50±13.06 | 49.61±17.58 | 0.319 |
| Rheumatoid factor (positive) | 72 (69.23) | 7 (50.00) | 0.151 |
| - Titer | 117.61±282.15 | 66.07±136.97 | 0.999 |
| aCCP antibodies (positive) | 52 (82.54) | 52 (94.55) | 0.051 |
| - Titer | 196.34±252.54 | 240.07±285.45 | 0.005 |
| Erosive RA | 26 (25.00) | 6 (42.86) | 0.158 |
| Extra-articular manifestations | 20 (19.23) | 6 (42.86) | 0.045 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 20.00±19.04 | 19.00±15.94 | 0.855 |
| CRP (mg/dl) | 0.47±0.64 | 0.82±1.44 | 0.239 |
| HAQ | 0.59±0.67 | 0.43±0.59 | 0.810 |
| DAS28 | 2.37±1.12 | 2.53±0.60 | 0.110 |
| Previous COVID-19 | 22 (20.19) | 0 (0) | 0.072 |
| Severe previous COVID-19* | 6 (5.77) | 0 (0) | 0.460 |
| Glucocorticoids | 8 (7.69) | 3 (21.43) | 0.124 |
| Methotrexate | 88 (84.62) | 11 (78.57) | 0.444 |
| Hydroxycloroquine | 6 (5.77) | 0 (0) | 0.356 |
| Sulfasalazine | 3 (2.88) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Leflunomide | 17 (16.35) | 3 (21.43) | 0.704 |
| Rituximab | 2 (1.92) | 0 (0) | 0.463 |
| Etarnecept | 3 (2.88) | 0 (0) | 0.215 |
| Adalimumab | 2 (1.92) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





