Submitted:
04 January 2024
Posted:
05 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Mechanisms of Kidney Damage in Diabetes
2.1. Glomerular Hemodynamic Perturbations
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
2.2. Inflammatory and Fibrotic Factors
2.3. Metabolic Factors
2.4. Dietary AGEs and Gut Microbiome Variation
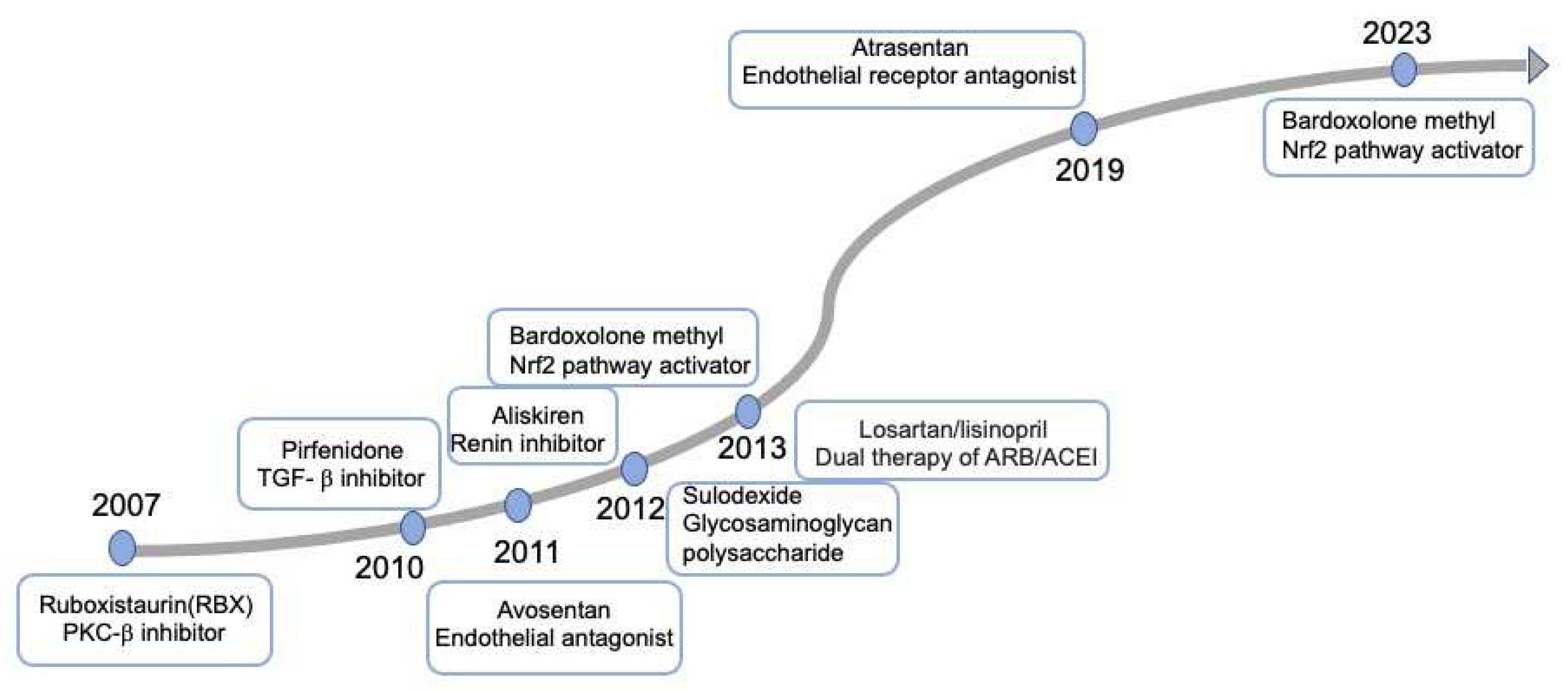
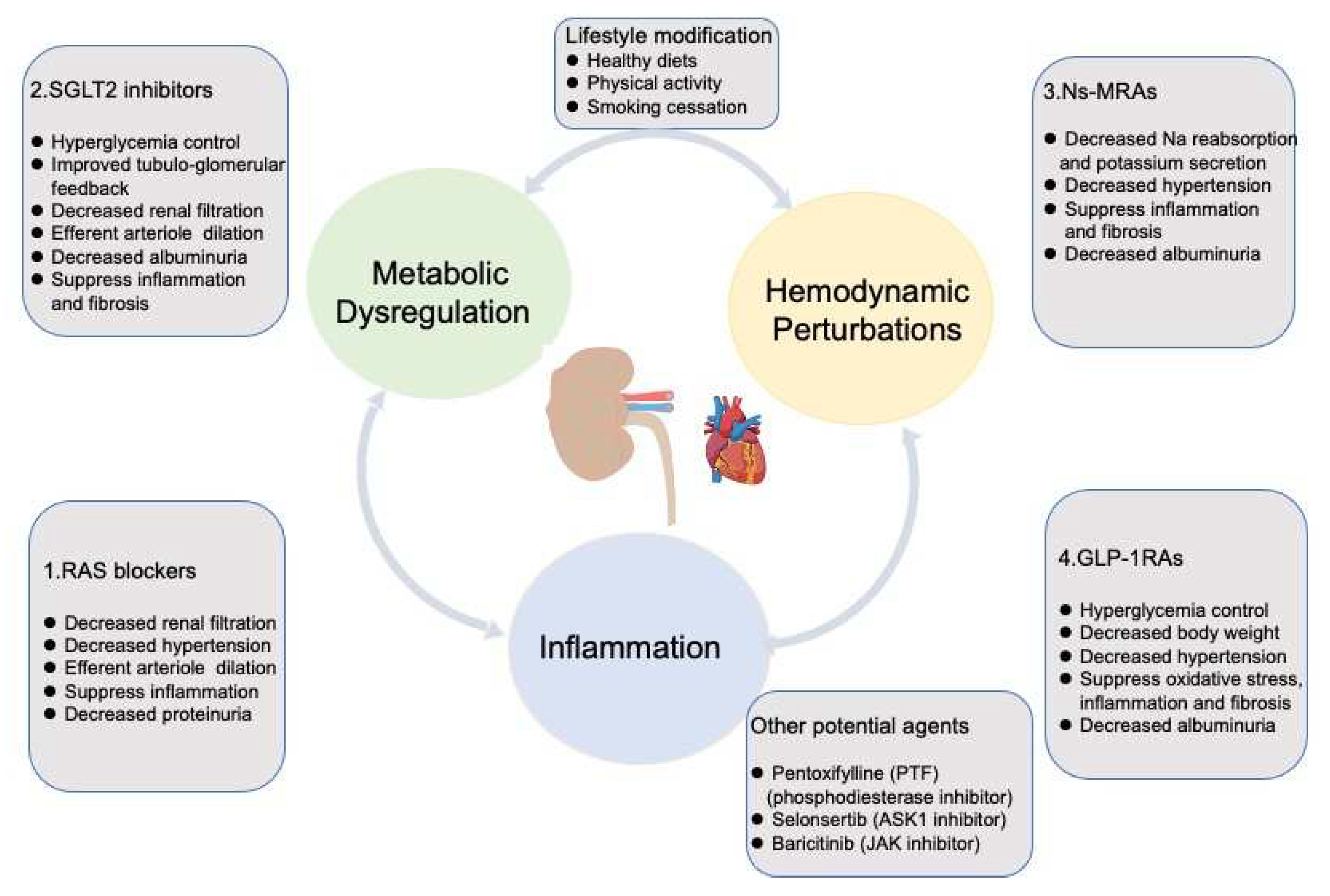
3. Targeting Mechanisms and Recent Advances in the Therapy of DKD
3.1. RAS Blockades
3.2. SGLT2 Inhibitors
3.3. NS-MRAs
3.4. GLP1-RAs
3.5. Other Agents
3.6. Lifestyle
4. The Value of Drug Combination Therapy in Clinical Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jager, K.J.; Kovesdy, C.; Langham, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Jha, V.; Zoccali, C. A single number for advocacy and communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2019, 34, 1803–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Rooney, M.T.; Tuttle, K.R. Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, Progress, and Possibilities. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2017, 12, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaboration, N.C.D.R.F. Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet 2016, 387, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan JC, N.; Mbanya, J.C.; Pavkov, M.E.; Ramachandaran, A.; Wild, S.H.; James, S.; Herman, W.H.; Zhang, P.; Bommer, C.; Kuo, S.; Boyko, E.J.; Magliano, D.J. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, T.; Ninomiya, T.; Jha, V.; Neal, B.; Patrice, H.M.; Okpechi, I.; Zhao, M.H.; Lv, J.; Garg, A.X.; Knight, J.; Rodgers, A.; Gallagher, M.; Kotwal, S.; Cass, A.; Perkovic, V. Worldwide access to treatment for end-stage kidney disease: a systematic review. Lancet 2015, 385, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Agarwal, R.; Alpers, C.E.; Bakris, G.L.; Brosius, F.C.; Kolkhof, P.; Uribarri, J. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets for diabetic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2022, 102, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Diabetes Work, G. KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int 2022, 102, S1–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, A.K.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Lloyd, A.; James, M.T.; Manns, B.J.; Klarenbach, S.; Tonelli, M.; Alberta Kidney Disease, N. Associations among estimated glomerular filtration rate, proteinuria, and adverse cardiovascular outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2011, 6, 1418–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, S.; James, M.; Wiebe, N.; Hemmelgarn, B.; Manns, B.; Klarenbach, S.; Tonelli, M.; Alberta Kidney Disease, N. Cause of Death in Patients with Reduced Kidney Function. J Am Soc Nephrol 2015, 26, 2504–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Bain, R.P.; Rohde, R.D. The effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition on diabetic nephropathy. The Collaborative Study Group. N Engl J Med 1993, 329, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulov, V. [Infusion treatment and parenteral feeding of the newborn]. Akush Ginekol (Sofiia) 1977, 16, 387–393. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, B.M.; Cooper, M.E.; de Zeeuw, D.; Keane, W.F.; Mitch, W.E.; Parving, H.H.; Remuzzi, G.; Snapinn, S.M.; Zhang, Z.; Shahinfar, S.; Investigators, R.S. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2001, 345, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lin, C.; Cai, X.; Hu, S.; Zhu, X.; Lv, F.; Yang, W.; Ji, L. Baseline eGFR, albuminuria and renal outcomes in patients with SGLT2 inhibitor treatment: an updated meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol 2023, 60, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintscher, U.; Bakris, G.L.; Kolkhof, P. Novel non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in cardiorenal disease. Br J Pharmacol 2022, 179, 3220–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes, A. 9. Pharmacologic Approaches to Glycemic Treatment: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, S111–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, F.; Grant, P.J.; Aboyans, V.; Bailey, C.J.; Ceriello, A.; Delgado, V.; Federici, M.; Filippatos, G.; Grobbee, D.E.; Hansen, T.B.; Huikuri, H.V.; Johansson, I.; Juni, P.; Lettino, M.; Marx, N.; Mellbin, L.G.; Ostgren, C.J.; Rocca, B.; Roffi, M.; Sattar, N.; Seferovic, P.M.; Sousa-Uva, M.; Valensi, P.; Wheeler, D.C.; Group, E.S.C.S.D. 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J 2020, 41, 255–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaman, A.M.; Bain, S.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Buse, J.B.; Idorn, T.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann JF, E.; Nauck, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.; Rossing, P.; Wolthers, B.; Zinman, B.; Perkovic, V. Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Semaglutide and Liraglutide on Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Pooled Analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and LEADER. Circulation 2022, 145, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naaman, S.C.; Bakris, G.L. Diabetic Nephropathy: Update on Pillars of Therapy Slowing Progression. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R. Back to the Future: Glomerular Hyperfiltration and the Diabetic Kidney. Diabetes 2017, 66, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Neumiller, J.J.; Johnson, E.J.; Dieter, B.; Tuttle, K.R. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetes 2019, 68, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.; VanBeusecum, J.P.; Inscho, E.W. Endothelin and the renal microcirculation. Semin Nephrol 2015, 35, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytvyn, Y.; Bjornstad, P.; van Raalte, D.H.; Heerspink, H.L.; Cherney DZ, I. The New Biology of Diabetic Kidney Disease-Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Endocr Rev 2020, 41, 202–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohan, D.E.; Barton, M. Endothelin and endothelin antagonists in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int 2014, 86, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, D.Z.; Miller, J.A.; Scholey, J.W.; Nasrallah, R.; Hebert, R.L.; Dekker, M.G.; Slorach, C.; Sochett, E.B.; Bradley, T.J. Renal hyperfiltration is a determinant of endothelial function responses to cyclooxygenase 2 inhibition in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1344–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premaratne, E.; Verma, S.; Ekinci, E.I.; Theverkalam, G.; Jerums, G.; MacIsaac, R.J. () The impact of hyperfiltration on the diabetic kidney. Diabetes Metab 2015, 41, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.J.; Huber, T.B.; Isermann, B.; Schiffer, M. CKD in diabetes: diabetic kidney disease versus nondiabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 2018, 14, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochett, E.B.; Cherney, D.Z.; Curtis, J.R.; Dekker, M.G.; Scholey, J.W.; Miller, J.A. Impact of renin angiotensin system modulation on the hyperfiltration state in type 1 diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006, 17, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfriend, T.L.; Elliott, M.E.; Catt, K.J. Angiotensin receptors and their antagonists. N Engl J Med 1996, 334, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, R.M.; Wang, Z.Q.; Siragy, H.M. Role of the angiotensin type 2 receptor in the regulation of blood pressure and renal function. Hypertension 2000, 35, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilatovskaya, D.V.; Blass, G.; Palygin, O.; Levchenko, V.; Pavlov, T.S.; Grzybowski, M.N.; Winsor, K.; Shuyskiy, L.S.; Geurts, A.M.; Cowley, A.W., Jr.; Birnbaumer, L.; Staruschenko, A. A NOX4/TRPC6 Pathway in Podocyte Calcium Regulation and Renal Damage in Diabetic Kidney Disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2018, 29, 1917–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Lorenzo, O.; Suzuki, Y.; Ruperez, M.; Egido, J. Proinflammatory actions of angiotensins. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2001, 10, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesch, G.H. Macrophages and diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 2010, 30, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, E.; Tomaschitz, A. Aldosterone, a vasculotoxic agent--novel functions for an old hormone. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2009, 24, 2302–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.C.; Chan, L.Y.; Leung, J.C.; Cheng, A.S.; Chan, K.W.; Lan, H.Y.; Lai, K.N. Bradykinin and high glucose promote renal tubular inflammation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2010, 25, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.C.W.; Yiu, W.H. Innate immunity in diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 2020, 16, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z. Non-genetic mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy. Front Med 2017, 11, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caamano, J.; Hunter, C.A. NF-kappaB family of transcription factors: central regulators of innate and adaptive immune functions. Clin Microbiol Rev 2002, 15, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewczas, M.A.; Pavkov, M.E.; Skupien, J.; Smiles, A.; Md Dom, Z.I.; Wilson, J.M.; Park, J.; Nair, V.; Schlafly, A.; Saulnier, P.J.; Satake, E.; Simeone, C.A.; Shah, H.; Qiu, C.; Looker, H.C.; Fiorina, P.; Ware, C.F.; Sun, J.K.; Doria, A.; Kretzler, M.; Susztak, K.; Duffin, K.L.; Nelson, R.G.; Krolewski, A.S. A signature of circulating inflammatory proteins and development of end-stage renal disease in diabetes. Nat Med 2019, 25, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Johnson, E.J.; Tuttle, K.R. Inflammatory Mechanisms as New Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Diabetic Kidney Disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 2018, 25, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Atkin, S.L.; Sahebkar, A. Interleukin-18 and diabetic nephropathy: A review. J Cell Physiol 2019, 234, 5674–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.P.; Zhou, H.; Setia, O.; Liu, B.; Kanasaki, K.; Koya, D.; Dardik, A.; Fernandez-Hernando, C.; Goodwin, J. Loss of endothelial glucocorticoid receptor accelerates diabetic nephropathy. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichler, R.; Afkarian, M.; Dieter, B.P.; Tuttle, K.R. Immunity and inflammation in diabetic kidney disease: translating mechanisms to biomarkers and treatment targets. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2017, 312, F716–F731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrauben, S.J.; Shou, H.; Zhang, X.; Anderson, A.H.; Bonventre, J.V.; Chen, J.; Coca, S.; Furth, S.L.; Greenberg, J.H.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Ix, J.H.; Lash, J.P.; Parikh, C.R.; Rebholz, C.M.; Sabbisetti, V.; Sarnak, M.J.; Shlipak, M.G.; Waikar, S.S.; Kimmel, P.L.; Vasan, R.S.; Feldman, H.I.; Schelling, J.R.; Consortium, C.K.D.B.; the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort Study, I. Association of Multiple Plasma Biomarker Concentrations with Progression of Prevalent Diabetic Kidney Disease: Findings from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study. J Am Soc Nephrol 2021, 32, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, F.; Ma, Q. Up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases-9 in the kidneys of diabetic rats and the association with neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin. BMC Nephrol 2021, 22, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Yeh, J.N.; Chiang, J.Y.; Sung, P.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Liu, F.; Yip, H.K. Intrarenal arterial administration of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells effectively preserved the residual renal function of diabetic kidney disease in rat. Stem Cell Res Ther 2022, 13, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Morales, R.E.; Del Pino, M.D.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Ortiz, A.; Mora-Fernandez, C.; Navarro-Gonzalez, J.F. Inflammation in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Nephron 2019, 143, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiteras, R.; Flaquer, M.; Cruzado, J.M. Macrophage in chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J 2016, 9, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, L.M.; Lever, J.M.; Agarwal, A. Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis: A Double-edged Sword. J Histochem Cytochem 2019, 67, 663–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, R.; Yang, C. Renal tubular epithelial cells: the neglected mediator of tubulointerstitial fibrosis after injury. Cell Death Dis 2018, 9, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.L.; Liu, T.T.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-Beta as a Master Regulator of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Chen, X.C.; Li, Z.H.; Wu, H.L.; Jing, K.P.; Huang, X.R.; Ye, L.; Wei, B.; Lan, H.Y.; Liu, H.F. SMAD3 promotes autophagy dysregulation by triggering lysosome depletion in tubular epithelial cells in diabetic nephropathy. Autophagy 2021, 17, 2325–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.; Cai, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhong, F.; Ni, Z.; Cai, G.; Chen, X.M.; He, J.C.; Lee, K. Modulation of transforming growth factor-beta-induced kidney fibrosis by leucine-rich ⍺-2 glycoprotein-1. Kidney Int 2022, 101, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Typiak, M.; Piwkowska, A. Antiinflammatory Actions of Klotho: Implications for Therapy of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, N.; Mukoyama, M.; Yanagita, M.; Yokoi, H. CTGF in kidney fibrosis and glomerulonephritis. Inflamm Regen 2018, 38, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.J.; Vaughan, D.E.; Fogo, A.B. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and fibrinolysis in progressive renal disease. Semin Nephrol 2002, 22, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zou, Y.; Liu, F. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta1 in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemis, V.; Ghura, H.; Federico, G.; Wurfel, C.; Bentmann, A.; Gretz, N.; Miyazaki, T.; Grone, H.J.; Nakchbandi, I.A. Circulating fibronectin contributes to mesangial expansion in a murine model of type 1 diabetes. Kidney Int 2017, 91, 1374–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Li, H.Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, G.; Lin, S.; Liao, C.; Zhou, T. Administration of mesenchymal stem cells in diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.C.; Tang, S.Q.; Liu, Y.T.; Li, A.M.; Zhan, M.; Yang, M.; Song, N.; Zhang, W.; Wu, X.Q.; Peng, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S. AMPK agonist alleviate renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis via activating mitophagy in high fat and streptozotocin induced diabetic mice. Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Hu, F.; Xue, M.; Jia, Y.J.; Zheng, Z.J.; Li, Y.; Xue, Y.M. Early growth response protein-1 upregulates long noncoding RNA Arid2-IR to promote extracellular matrix production in diabetic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2019, 316, C340–C352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liles, J.T.; Corkey, B.K.; Notte, G.T.; Budas, G.R.; Lansdon, E.B.; Hinojosa-Kirschenbaum, F.; Badal, S.S.; Lee, M.; Schultz, B.E.; Wise, S.; Pendem, S.; Graupe, M.; Castonguay, L.; Koch, K.A.; Wong, M.H.; Papalia, G.A.; French, D.M.; Sullivan, T.; Huntzicker, E.G.; Ma, F.Y.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Altuhaifi, T.; Yang, H.; Fogo, A.B.; Breckenridge, D.G. ASK1 contributes to fibrosis and dysfunction in models of kidney disease. J Clin Invest 2018, 128, 4485–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertow, G.M.; Pergola, P.E.; Chen, F.; Kirby, B.J.; Sundy, J.S.; Patel, U.D.; Investigators, G.-U.-. . Effects of Selonsertib in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2019, 30, 1980–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reidy, K.; Kang, H.M.; Hostetter, T.; Susztak, K. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest 2014, 124, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, C.C.; Zhang, H.; Schin, M.; Henger, A.; Nelson, R.G.; Yee, B.; Boucherot, A.; Neusser, M.A.; Cohen, C.D.; Carter-Su, C.; Argetsinger, L.S.; Rastaldi, M.P.; Brosius, F.C.; Kretzler, M. Enhanced expression of Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription pathway members in human diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2009, 58, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looker, H.C.; Lin, C.; Nair, V.; Kretzler, M.; Mauer, M.; Najafian, B.; Nelson, R.G. Serum Level of Polyubiquitinated PTEN and Loss of Kidney Function in American Indians With Type 2 Diabetes. Am J Kidney Dis 2022, 79, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, Q.; Li, C.; Liang, K.; Xiang, Y.; Hsiao, H.; Nguyen, T.K.; Park, P.K.; Egranov, S.D.; Ambati, C.R.; Putluri, N.; Hawke, D.H.; Han, L.; Hung, M.C.; Danesh, F.R.; Yang, L.; Lin, C. PTEN-induced partial epithelial-mesenchymal transition drives diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest 2019, 129, 1129–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Choi, J.; Lee, H.S. Palmitate induces mitochondrial superoxide generation and activates AMPK in podocytes. J Cell Physiol 2017, 232, 3209–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susztak, K.; Raff, A.C.; Schiffer, M.; Bottinger, E.P. Glucose-induced reactive oxygen species cause apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2006, 55, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanji, N.; Markowitz, G.S.; Fu, C.; Kislinger, T.; Taguchi, A.; Pischetsrieder, M.; Stern, D.; Schmidt, A.M.; D'Agati, V.D. Expression of advanced glycation end products and their cellular receptor RAGE in diabetic nephropathy and nondiabetic renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000, 11, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Q.; Zhang, D.D.; Wang, Y.N.; Tan, Y.Q.; Yu, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y. AGE/RAGE in diabetic kidney disease and ageing kidney. Free Radic Biol Med 2021, 171, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Jourde-Chiche, N. Endothelial Toxicity of High Glucose and its by-Products in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschopp, J.; Schroder, K. NLRP3 inflammasome activation: The convergence of multiple signalling pathways on ROS production? Nat Rev Immunol 2010, 10, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Y.; Han, W.; Song, S.; Mu, L.; Du, C.; Shi, Y. Inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome ameliorates podocyte damage by suppressing lipid accumulation in diabetic nephropathy. Metabolism 2021, 118, 154748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojs, R.; Ekart, R.; Bevc, S.; Hojs, N. Markers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Development and Progression of Renal Disease in Diabetic Patients. Nephron 2016, 133, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribarri, J.; Woodruff, S.; Goodman, S.; Cai, W.; Chen, X.; Pyzik, R.; Yong, A.; Striker, G.E.; Vlassara, H. Advanced glycation end products in foods and a practical guide to their reduction in the diet. J Am Diet Assoc 2010, 110, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H.; Striker, L.J.; Teichberg, S.; Fuh, H.; Li, Y.M.; Steffes, M. Advanced glycation end products induce glomerular sclerosis and albuminuria in normal rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1994, 91, 11704–11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garay-Sevilla, M.E.; Beeri, M.S.; de la Maza, M.P.; Rojas, A.; Salazar-Villanea, S.; Uribarri, J. The potential role of dietary advanced glycation endproducts in the development of chronic non-infectious diseases: a narrative review. Nutr Res Rev 2020, 33, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelson, M.; Tan, S.M.; Clarke, R.E.; de Pasquale, C.; Thallas-Bonke, V.; Nguyen, T.V.; Penfold, S.A.; Harcourt, B.E.; Sourris, K.C.; Lindblom, R.S.; Ziemann, M.; Steer, D.; El-Osta, A.; Davies, M.J.; Donnellan, L.; Deo, P.; Kellow, N.J.; Cooper, M.E.; Woodruff, T.M.; Mackay, C.R.; Forbes, J.M.; Coughlan, M.T. Processed foods drive intestinal barrier permeability and microvascular diseases. Sci Adv 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, A.; Raj, D.S. The gut microbiome, kidney disease, and targeted interventions. J Am Soc Nephrol 2014, 25, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chadban, S.J.; Zhao, C.Y.; Chen, X.; Kwan, T.; Panchapakesan, U.; Pollock, C.A.; Wu, H. TLR4 activation promotes podocyte injury and interstitial fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. PLoS One 2014, 9, e97985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Chen, X.; Kwan, T.K.; Loh, Y.W.; Singer, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Tan, J.; Macia, L.; Mackay, C.R.; Chadban, S.J.; Wu, H. Dietary Fiber Protects against Diabetic Nephropathy through Short-Chain Fatty Acid-Mediated Activation of G Protein-Coupled Receptors GPR43 and GPR109A. J Am Soc Nephrol 2020, 31, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; McGill, J.B.; Haney, D.J.; Lin, T.E.; Anderson, P.W.; Pkc-Drs, P.-D.; Groups, P.-D. S. Kidney outcomes in long-term studies of ruboxistaurin for diabetic eye disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2007, 2, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.F.; Green, D.; Jamerson, K.; Ruilope, L.M.; Kuranoff, S.J.; Littke, T.; Viberti, G.; Group, A.S. Avosentan for overt diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2010, 21, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Parving, H.H.; Andress, D.L.; Bakris, G.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Hou, F.F.; Kitzman, D.W.; Kohan, D.; Makino, H.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Melnick, J.Z.; Miller, M.G.; Pergola, P.E.; Perkovic, V.; Tobe, S.; Yi, T.; Wigderson, M.; de Zeeuw, D.; Committees, S.; Investigators. Atrasentan and renal events in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (SONAR): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1937–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossing, P.; Caramori, M.L.; Chan, J.C.N.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Hurst, C.; Khunti, K.; Liew, A.; Michos, E.D.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Olowu, W.A.; Sadusky, T.; Tandon, N.; Tuttle, K.R.; Wanner, C.; Wilkens, K.G.; Zoungas, S.; Craig, J.C.; Tunnicliffe, D.J.; Tonelli, M.A.; Cheung, M.; Earley, A.; de Boer, I.H. Executive summary of the KDIGO 2022 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: an update based on rapidly emerging new evidence. Kidney Int 2022, 102, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, K.; Ix, J.H.; Mathew, A.V.; Cho, M.; Pflueger, A.; Dunn, S.R.; Francos, B.; Sharma, S.; Falkner, B.; McGowan, T.A.; Donohue, M.; Ramachandrarao, S.; Xu, R.; Fervenza, F.C.; Kopp, J.B. Pirfenidone for diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2011, 22, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packham, D.K.; Wolfe, R.; Reutens, A.T.; Berl, T.; Heerspink, H.L.; Rohde, R.; Ivory, S.; Lewis, J.; Raz, I.; Wiegmann, T.B.; Chan, J.C.; de Zeeuw, D.; Lewis, E.J.; Atkins, R.C.; Collaborative Study, G. Sulodexide fails to demonstrate renoprotection in overt type 2 diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2012, 23, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parving, H.H.; Brenner, B.M.; McMurray, J.J.; de Zeeuw, D.; Haffner, S.M.; Solomon, S.D.; Chaturvedi, N.; Persson, F.; Desai, A.S.; Nicolaides, M.; Richard, A.; Xiang, Z.; Brunel, P.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Investigators, A. Cardiorenal end points in a trial of aliskiren for type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2012, 367, 2204–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Zeeuw, D.; Akizawa, T.; Audhya, P.; Bakris, G.L.; Chin, M.; Christ-Schmidt, H.; Goldsberry, A.; Houser, M.; Krauth, M.; Lambers Heerspink, H.J.; McMurray, J.J.; Meyer, C.J.; Parving, H.H.; Remuzzi, G.; Toto, R.D.; Vaziri, N.D.; Wanner, C.; Wittes, J.; Wrolstad, D.; Chertow, G.M.; Investigators, B.T. Bardoxolone methyl in type 2 diabetes and stage 4 chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 2013, 369, 2492–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangaku, M.; Kanda, H.; Takama, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Hase, H.; Akizawa, T. Randomized Clinical Trial on the Effect of Bardoxolone Methyl on GFR in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients (TSUBAKI Study). Kidney Int Rep 2020, 5, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangaku, M.; Takama, H.; Ichikawa, T.; Mukai, K.; Kojima, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Watada, H.; Wada, T.; Ueki, K.; Narita, I.; Kashihara, N.; Kadowaki, T.; Hase, H.; Akizawa, T. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study of bardoxolone methyl in patients with diabetic kidney disease: design and baseline characteristics of the AYAME study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2023, 38, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.J.; Hunsicker, L.G.; Clarke, W.R.; Berl, T.; Pohl, M.A.; Lewis, J.B.; Ritz, E.; Atkins, R.C.; Rohde, R.; Raz, I.; Collaborative Study, G. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin-receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2001, 345, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fried, L.F.; Emanuele, N.; Zhang, J.H.; Brophy, M.; Conner, T.A.; Duckworth, W.; Leehey, D.J.; McCullough, P.A.; O'Connor, T.; Palevsky, P.M.; Reilly, R.F.; Seliger, S.L.; Warren, S.R.; Watnick, S.; Peduzzi, P.; Guarino, P.; Investigators, V.N.-D. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2013, 369, 1892–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Perco, P.; Mulder, S.; Leierer, J.; Hansen, M.K.; Heinzel, A.; Mayer, G. Canagliflozin reduces inflammation and fibrosis biomarkers: a potential mechanism of action for beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 1154–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes, A. 11. Microvascular Complications and Foot Care: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2020. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, S135–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, C.; Marx, N. SGLT2 inhibitors: the future for treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and other chronic diseases. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2134–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; Cannon, C.P.; Capuano, G.; Chu, P.L.; de Zeeuw, D.; Greene, T.; Levin, A.; Pollock, C.; Wheeler, D.C.; Yavin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zinman, B.; Meininger, G.; Brenner, B.M.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Investigators, C.T. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefansson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Toto, R.D.; Langkilde, A.M.; Wheeler, D.C.; Committees, D.-C. T.; Investigators. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salah, H.M.; Al'Aref, S.J.; Khan, M.S.; Al-Hawwas, M.; Vallurupalli, S.; Mehta, J.L.; Mounsey, J.P.; Greene, S.J.; McGuire, D.K.; Lopes, R.D.; Fudim, M. Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on cardiovascular and kidney outcomes-Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Am Heart J 2021, 232, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, E.-K. C. G.; Herrington, W.G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Hauske, S.J.; Emberson, J.R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.J.; Ng, S.Y.A.; Sammons, E.; Zhu, D.; Hill, M.; Stevens, W.; Wallendszus, K.; Brenner, S.; Cheung, A.K.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, J.; Hooi, L.S.; Liu, W.; Kadowaki, T.; Nangaku, M.; Levin, A.; Cherney, D.; Maggioni, A.P.; Pontremoli, R.; Deo, R.; Goto, S.; Rossello, X.; Tuttle, K.R.; Steubl, D.; Petrini, M.; Massey, D.; Eilbracht, J.; Brueckmann, M.; Landray, M.J.; Baigent, C.; Haynes, R. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Neumiller, J.J.; Johnson, E.J.; Dieter, B.; Tuttle, K.R. Erratum. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetes 2019, 68, 248–257. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Chimal, J.; Girerd, S.; Jaisser, F. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists and kidney diseases: pathophysiological basis. Kidney Int 2019, 96, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.S.; Tostes, R.C.; Paradis, P.; Schiffrin, E.L. Aldosterone, Inflammation, Immune System, and Hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2021, 34, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesch, G.H.; Young, M.J. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Signaling as a Therapeutic Target for Renal and Cardiac Fibrosis. Front Pharmacol 2017, 8, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Hayashi, K.; Naruse, M.; Saruta, T. Effectiveness of aldosterone blockade in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Hypertension 2003, 41, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miric, G.; Dallemagne, C.; Endre, Z.; Margolin, S.; Taylor, S.M.; Brown, L. Reversal of cardiac and renal fibrosis by pirfenidone and spironolactone in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Br J Pharmacol 2001, 133, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Bohm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Celutkiene, J.; Chioncel, O.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Farmakis, D.; Gilard, M.; Heymans, S.; Hoes, A.W.; Jaarsma, T.; Jankowska, E.A.; Lainscak, M.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lyon, A.R.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Mebazaa, A.; Mindham, R.; Muneretto, C.; Francesco Piepoli, M.; Price, S.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Ruschitzka, F.; Kathrine Skibelund, A. Corrigendum to: 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2021, 42, 4901. [Google Scholar]
- Charytan, D.M.; Himmelfarb, J.; Ikizler, T.A.; Raj, D.S.; Hsu, J.Y.; Landis, J.R.; Anderson, A.H.; Hung, A.M.; Mehrotra, R.; Sharma, S.; Weiner, D.E.; Williams, M.; DiCarli, M.; Skali, H.; Kimmel, P.L.; Kliger, A.S.; Dember, L.M.; Hemodialysis Novel Therapies, C. Safety and cardiovascular efficacy of spironolactone in dialysis-dependent ESRD (SPin-D): a randomized, placebo-controlled, multiple dosage trial. Kidney Int 2019, 95, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Filippatos, G.; Pitt, B.; Anker, S.D.; Rossing, P.; Joseph, A.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Gebel, M.; Ruilope, L.M.; Bakris, G.L.; Fidelio, D.K.D.; investigators, F.-D. Cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with finerenone in patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease: the FIDELITY pooled analysis. Eur Heart J 2022, 43, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; Filippatos, G.; Investigators, F.-D. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Pitt, B.; Palmer, B.F.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Burgess, E.; Filippatos, G.; Malyszko, J.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossignol, P.; Rossing, P.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Anker, S.D.; Joseph, A.; Lawatscheck, R.; Wilson, D.; Gebel, M.; Bakris, G.L. A comparative post hoc analysis of finerenone and spironolactone in resistant hypertension in moderate-to-advanced chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J 2023, 16, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Kashihara, N.; Shikata, K.; Nangaku, M.; Wada, T.; Okuda, Y.; Sawanobori, T. Esaxerenone (CS-3150) in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Microalbuminuria (ESAX-DN): Phase 3 Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2020, 15, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolkhof, P.; Hartmann, E.; Freyberger, A.; Pavkovic, M.; Mathar, I.; Sandner, P.; Droebner, K.; Joseph, A.; Huser, J.; Eitner, F. Effects of Finerenone Combined with Empagliflozin in a Model of Hypertension-Induced End-Organ Damage. Am J Nephrol 2021, 52, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Kristensen, S.L.; Bengtsson, O.; Bohm, M.; de Boer, R.A.; Docherty, K.F.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Katova, T.; Kober, L.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Langkilde, A.M.; Lindholm, D.; Martinez, M.F.A.; O'Meara, E.; Nicolau, J.C.; Petrie, M.C.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M.S.; Schou, M.; Sjostrand, M.; Solomon, S.D.; Jhund, P.S.; McMurray, J.J.V. Dapagliflozin in HFrEF Patients Treated With Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists: An Analysis of DAPA-HF. JACC Heart Fail 2021, 9, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, J.P.; Zannad, F.; Pocock, S.J.; Anker, S.D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Brueckmann, M.; Jamal, W.; Steubl, D.; Schueler, E.; Packer, M. Interplay of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists and Empagliflozin in Heart Failure: EMPEROR-Reduced. J Am Coll Cardiol 2021, 77, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Joseph, A.; Anker, S.D.; Filippatos, G.; Rossing, P.; Ruilope, L.M.; Pitt, B.; Kolkhof, P.; Scott, C.; Lawatscheck, R.; Wilson, D.J.; Bakris, G.L.; Investigators, F.-D. Hyperkalemia Risk with Finerenone: Results from the FIDELIO-DKD Trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 2022, 33, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossing, P.; Filippatos, G.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Chan, J.C.N.; Kooy, A.; McCafferty, K.; Schernthaner, G.; Wanner, C.; Joseph, A.; Scheerer, M.F.; Scott, C.; Bakris, G.L.; Investigators, F.-D. Finerenone in Predominantly Advanced CKD and Type 2 Diabetes With or Without Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Therapy. Kidney Int Rep 2022, 7, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes management in chronic kidney disease: a consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int 2022, 102, 974–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Cox, E.J.; Neumiller, J.J.; Tuttle, K.R. Incretin drugs in diabetic kidney disease: biological mechanisms and clinical evidence. Nat Rev Nephrol 2021, 17, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes Diabetes Work, G. KDIGO 2020 Clinical Practice Guideline for Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int 2020, 98, S1–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Lakshmanan, M.C.; Rayner, B.; Busch, R.S.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Woodward, D.B.; Botros, F.T. Dulaglutide versus insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic kidney disease (AWARD-7): a multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018, 6, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; Rosenstock, J.; Gerstein, H.C. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.; Tendal, B.; Mustafa, R.A.; Vandvik, P.O.; Li, S.; Hao, Q.; Tunnicliffe, D.; Ruospo, M.; Natale, P.; Saglimbene, V.; Nicolucci, A.; Johnson, D.W.; Tonelli, M.; Rossi, M.C.; Badve, S.V.; Cho, Y.; Nadeau-Fredette, A.C.; Burke, M.; Faruque, L.I.; Lloyd, A.; Ahmad, N.; Liu, Y.; Tiv, S.; Millard, T.; Gagliardi, L.; Kolanu, N.; Barmanray, R.D.; McMorrow, R.; Raygoza Cortez, A.K.; White, H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Rodriguez, A.F.; Gonzalez-Colmenero, A.D.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Sutanto, S.; Solis, R.C.; Diaz Gonzalez-Colmenero, F.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, R.; Walsh, M.; Guyatt, G.; Strippoli, G.F.M. Sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2021, 372, m4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; Steinberg, W.M.; Stockner, M.; Zinman, B.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buse, J.B.; Committee, L.S.; Investigators, L.T. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jodar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; Woo, V.; Hansen, O.; Holst, A.G.; Pettersson, J.; Vilsboll, T.; Investigators, S.-. . Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Sattar, N.; Rosenstock, J.; Ramasundarahettige, C.; Pratley, R.; Lopes, R.D.; Lam, C.S.P.; Khurmi, N.S.; Heenan, L.; Del Prato, S.; Dyal, L.; Branch, K.; Investigators, A.-O. T. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Efpeglenatide in Type 2 Diabetes. N Engl J Med 2021, 385, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathy, H.; Henriquez, G.; Abramowitz, M.K.; Kramer, H.; Rosas, S.E.; Johns, T.; Kumar, J.; Skversky, A.; Kaskel, F.; Melamed, M.L. Abdominal Obesity, Race and Chronic Kidney Disease in Young Adults: Results from NHANES 1999-2010. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0153588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejerblad, E.; Fored, C.M.; Lindblad, P.; Fryzek, J.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Nyren, O. Obesity and risk for chronic renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006, 17, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossing, P.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Bakris, G.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Gislum, M.; Gough, S.C.L.; Idorn, T.; Lawson, J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.E.; Mersebach, H.; Perkovic, V.; Tuttle, K.; Pratley, R. The rationale, design and baseline data of FLOW, a kidney outcomes trial with once-weekly semaglutide in people with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2023, 38, 2041–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.K.; Carr, M.J.; Kontopantelis, E.; Leelarathna, L.; Thabit, H.; Emsley, R.; Buchan, I.; Mamas, M.A.; van Staa, T.P.; Sattar, N.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Rutter, M.K. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular and Heart Failure Events With SGLT2 Inhibitors, GLP-1 Receptor Agonists, and Their Combination in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davila-Esqueda, M.E.; Martinez-Morales, F. Pentoxifylline diminishes the oxidative damage to renal tissue induced by streptozotocin in the rat. Exp Diabesity Res 2004, 5, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Gonzalez, J.F.; Mora-Fernandez, C.; Muros de Fuentes, M.; Chahin, J.; Mendez, M.L.; Gallego, E.; Macia, M.; del Castillo, N.; Rivero, A.; Getino, M.A.; Garcia, P.; Jarque, A.; Garcia, J. Effect of pentoxifylline on renal function and urinary albumin excretion in patients with diabetic kidney disease: the PREDIAN trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 2015, 26, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Gonzalez, J.F.; Sanchez-Nino, M.D.; Donate-Correa, J.; Martin-Nunez, E.; Ferri, C.; Perez-Delgado, N.; Gorriz, J.L.; Martinez-Castelao, A.; Ortiz, A.; Mora-Fernandez, C. Effects of Pentoxifylline on Soluble Klotho Concentrations and Renal Tubular Cell Expression in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1817–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Brosius, F.C.; 3rd, Adler, S. G.; Kretzler, M.; Mehta, R.L.; Tumlin, J.A.; Tanaka, Y.; Haneda, M.; Liu, J.; Silk, M.E.; Cardillo, T.E.; Duffin, K.L.; Haas, J.V.; Macias, W.L.; Nunes, F.P.; Janes, J.M. JAK1/JAK2 inhibition by baricitinib in diabetic kidney disease: results from a Phase 2 randomized controlled clinical trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2018, 33, 1950–1959. [Google Scholar]
- Fragoulis, G.E.; McInnes, I.B.; Siebert, S. JAK-inhibitors. New players in the field of immune-mediated diseases, beyond rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2019, 58, i43–i54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, G.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Joshi, S. The Effects of High-Protein Diets on Kidney Health and Longevity. J Am Soc Nephrol 2020, 31, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassara, H.; Uribarri, J. Advanced glycation end products (AGE) and diabetes: cause, effect, or both? Curr Diab Rep 2014, 14, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, K.E.; Kelly, J.T.; Palmer, S.C.; Khalesi, S.; Strippoli, G.F.M.; Campbell, K.L. Healthy Dietary Patterns and Incidence of CKD: A Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2019, 14, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.D. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Garg, S.; Khunger, M.; Darden, D.; Ayers, C.; Kumbhani, D.J.; Mayo, H.G.; de Lemos, J.A.; Berry, J.D. Dose-Response Relationship Between Physical Activity and Risk of Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis. Circulation 2015, 132, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowlby, W.; Zelnick, L.R.; Henry, C.; Himmelfarb, J.; Kahn, S.E.; Kestenbaum, B.; Robinson-Cohen, C.; Utzschneider, K.M.; de Boer, I.H. Physical activity and metabolic health in chronic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study. BMC Nephrol 2016, 17, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmadakis, G.C.; John, S.G.; Clapp, E.L.; Viana, J.L.; Smith, A.C.; Bishop, N.C.; Bevington, A.; Owen, P.J.; McIntyre, C.W.; Feehally, J. Benefits of regular walking exercise in advanced pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012, 27, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; He, L.; Su, X. Cigarette smoking and chronic kidney disease in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2017, 32, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhee, J.H.; Joo, Y.S.; Kee, Y.K.; Jung, S.Y.; Park, S.; Yoon, C.Y.; Han, S.H.; Yoo, T.H.; Kang, S.W.; Park, J.T. Secondhand Smoke and CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2019, 14, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, M.; Jardine, M.J.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Cannon, C.P.; Charytan, D.M.; de Zeeuw, D.; Edwards, R.; Greene, T.; Levin, A.; Lim, S.K.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Neal, B.; Pollock, C.; Rosenthal, N.; Wheeler, D.C.; Zhang, H.; Zinman, B.; Perkovic, V.; Heerspink, H.J.L. Insights from CREDENCE trial indicate an acute drop in estimated glomerular filtration rate during treatment with canagliflozin with implications for clinical practice. Kidney Int 2021, 99, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, B.J.; Weir, M.R.; Bakris, G.L.; Mattheus, M.; Cherney, D.Z.I.; Sattar, N.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Ritter, I.; von Eynatten, M.; Zinman, B.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Wanner, C.; Koitka-Weber, A. Characterization and implications of the initial estimated glomerular filtration rate 'dip' upon sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibition with empagliflozin in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. Kidney Int 2021, 99, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, M.; Puchades, M.J.; Garofalo, C.; Jongs, N.; D'Marco, L.; Andreucci, M.; De Nicola, L.; Gorriz, J.L.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; group, R.-s. , and members, R.-s. g. Albuminuria-Lowering Effect of Dapagliflozin, Eplerenone, and Their Combination in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Randomized Crossover Clinical Trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 2022, 33, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.B.; Mottl, A.K.; Bakris, G.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Mann, J.F.E.; McGill, J.B.; Nangaku, M.; Rossing, P.; Scott, C.; Gay, A.; Agarwal, R. Design of the COmbinatioN effect of FInerenone anD EmpaglifloziN in participants with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes using a UACR Endpoint study (CONFIDENCE). Nephrol Dial Transplant 2023, 38, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




