Submitted:
03 January 2024
Posted:
04 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials needed for the experiment
2.2. Synthesis of the three-component deep eutectic solvent
2.3. Preparation of deep eutectic solvent/carbon nanotube composites
2.4. Preparation of PVA hydrogel and CNTs/PEG-PVA hydrogel
2.5. Desulfurization of simulated oil and recovery of hydrogels
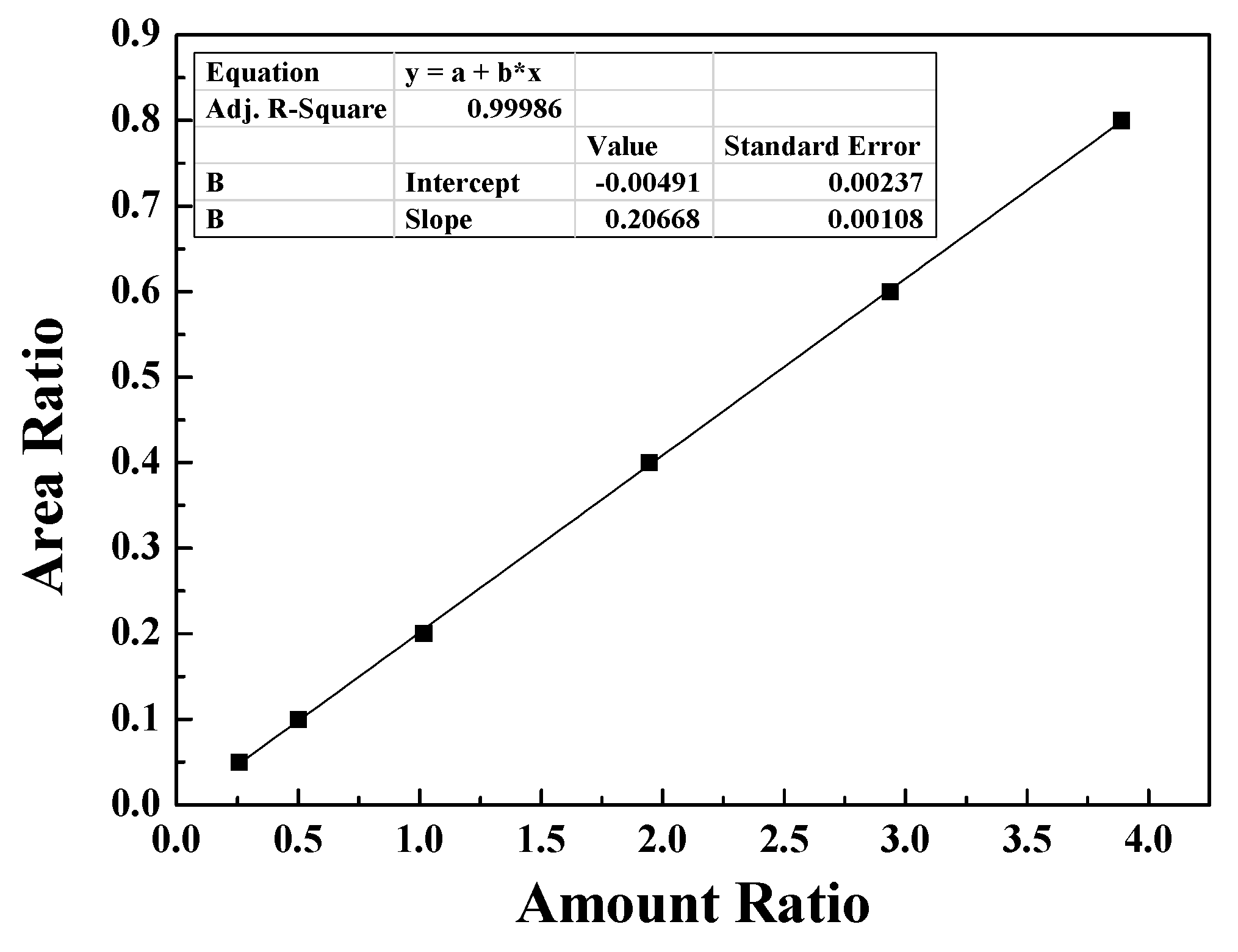
2.6. Analytical method
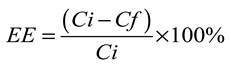
3. Results and discussions
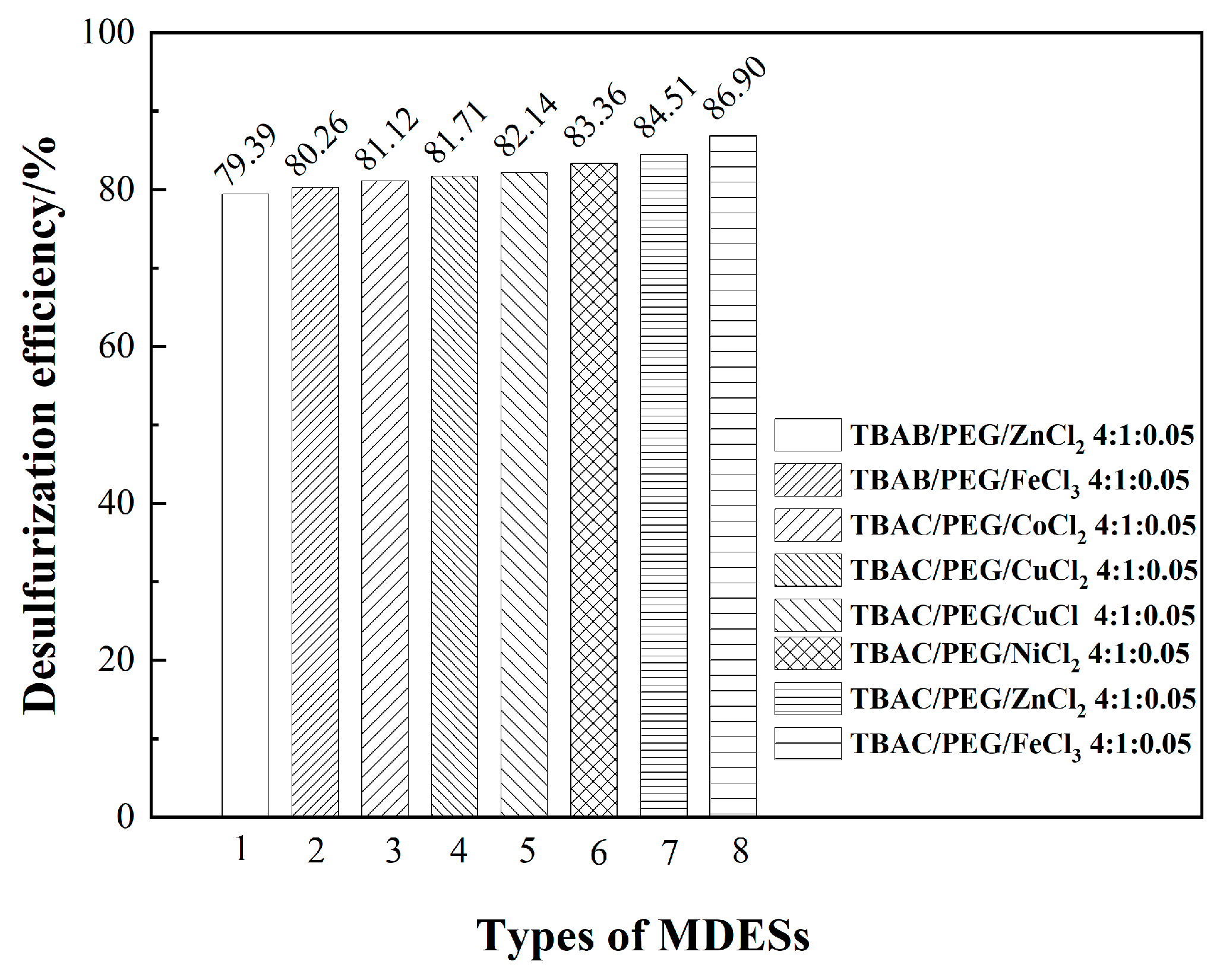
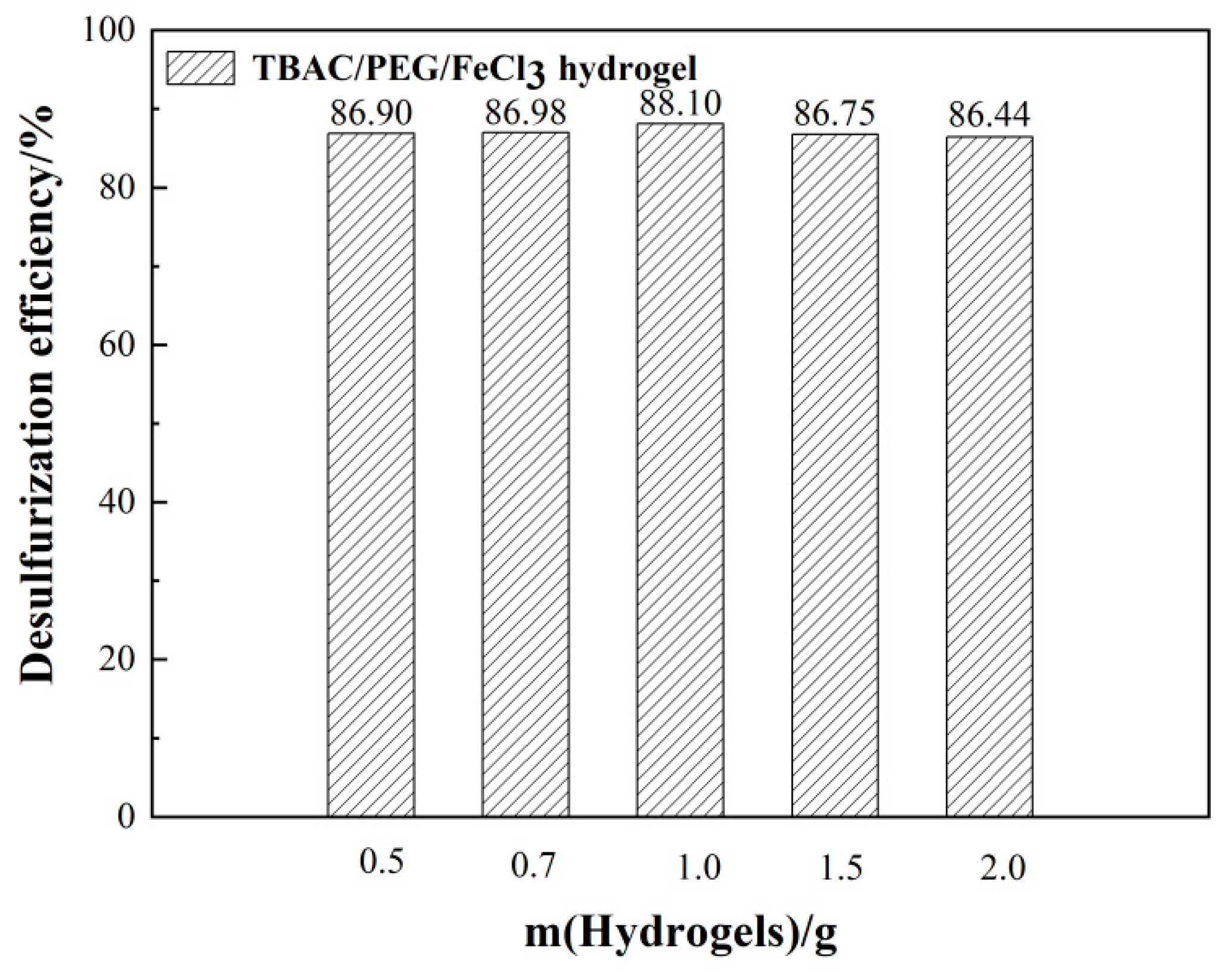
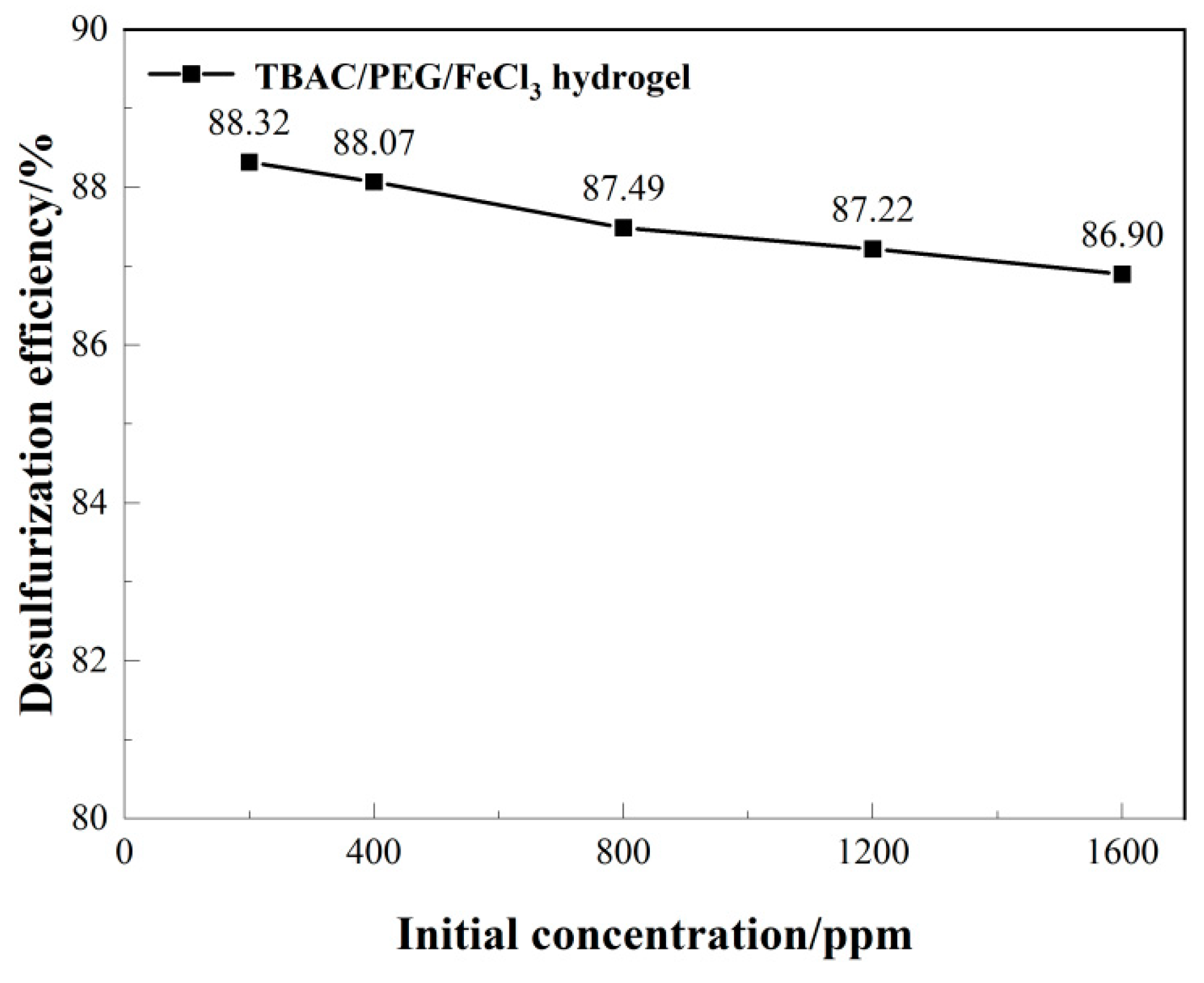
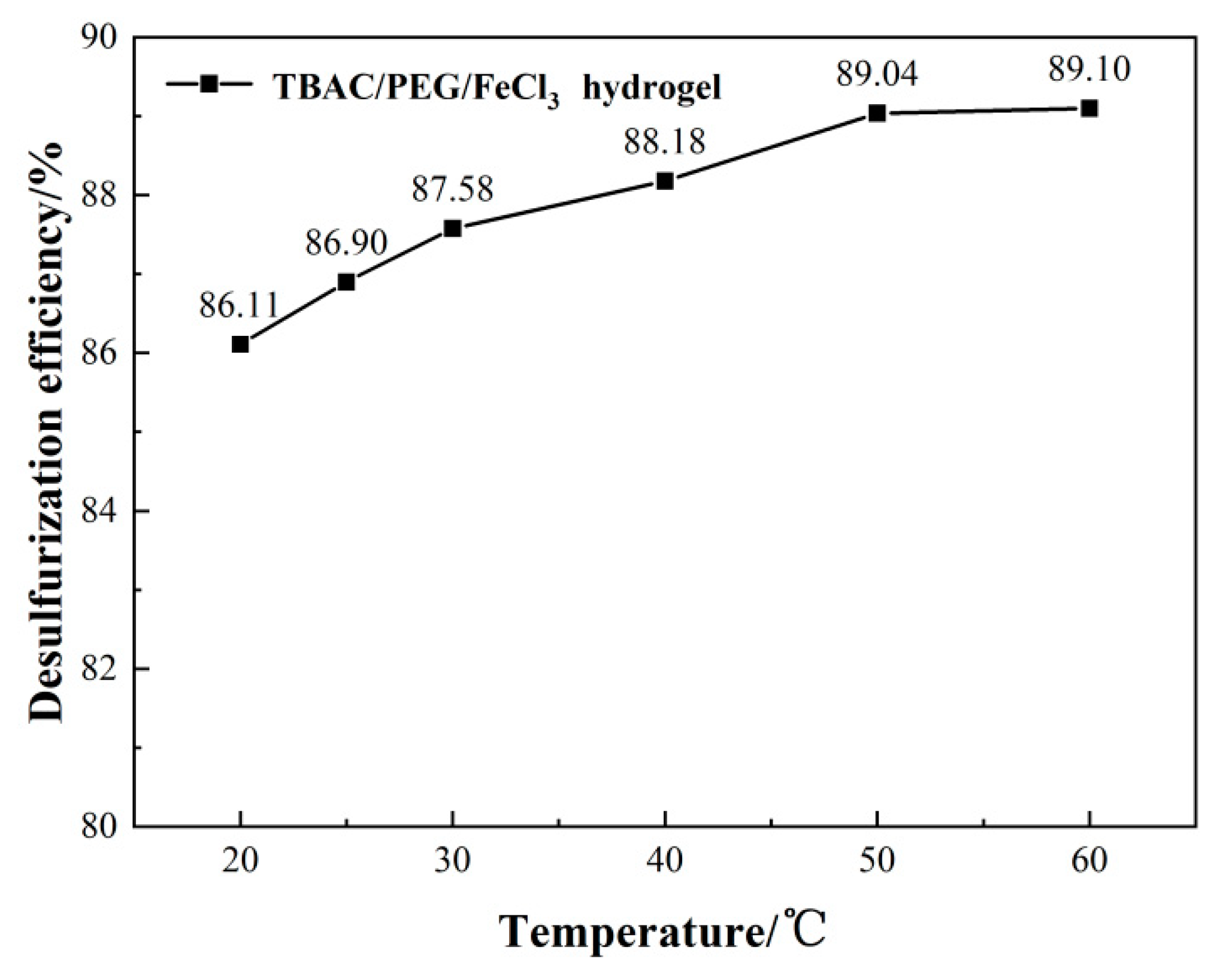
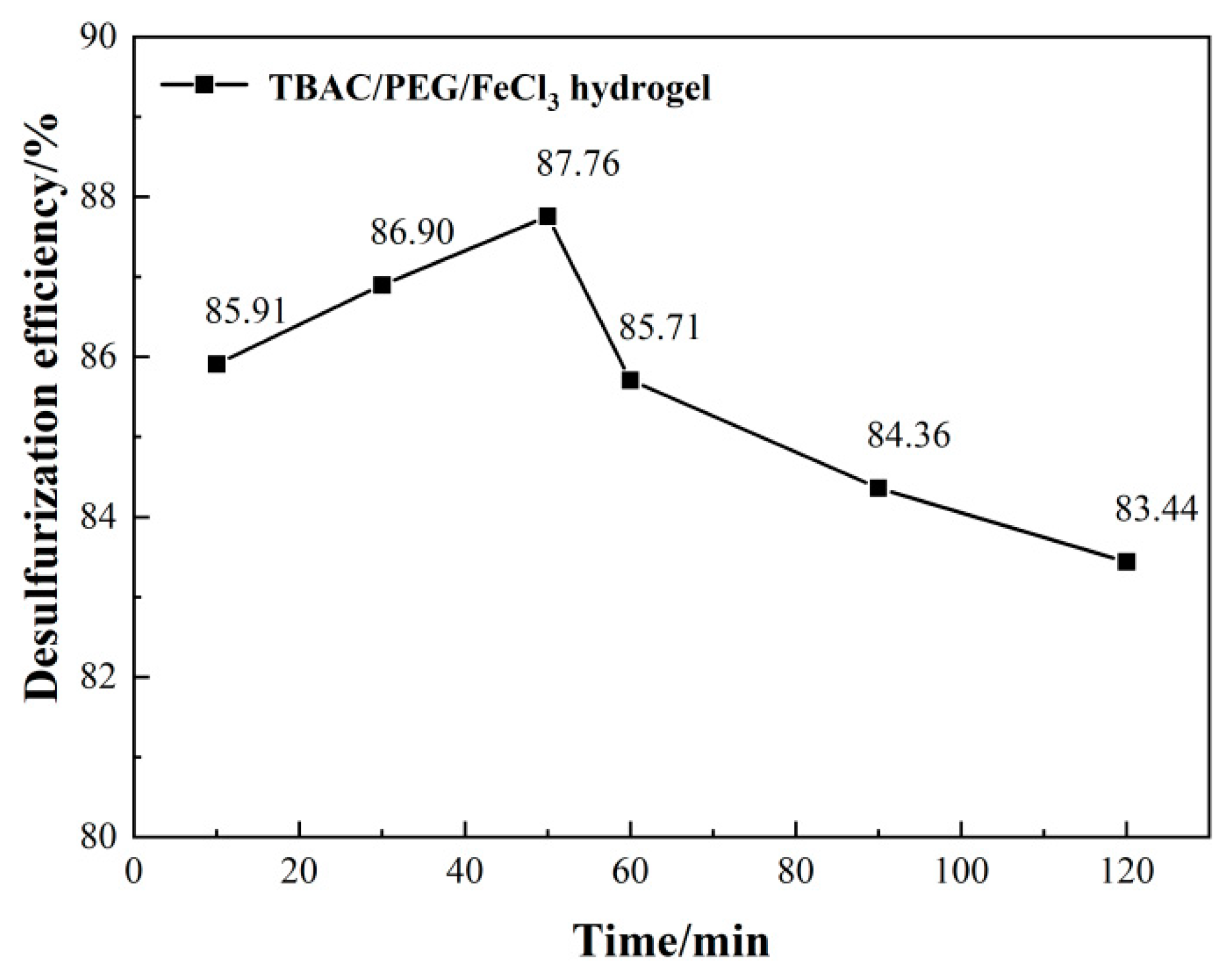
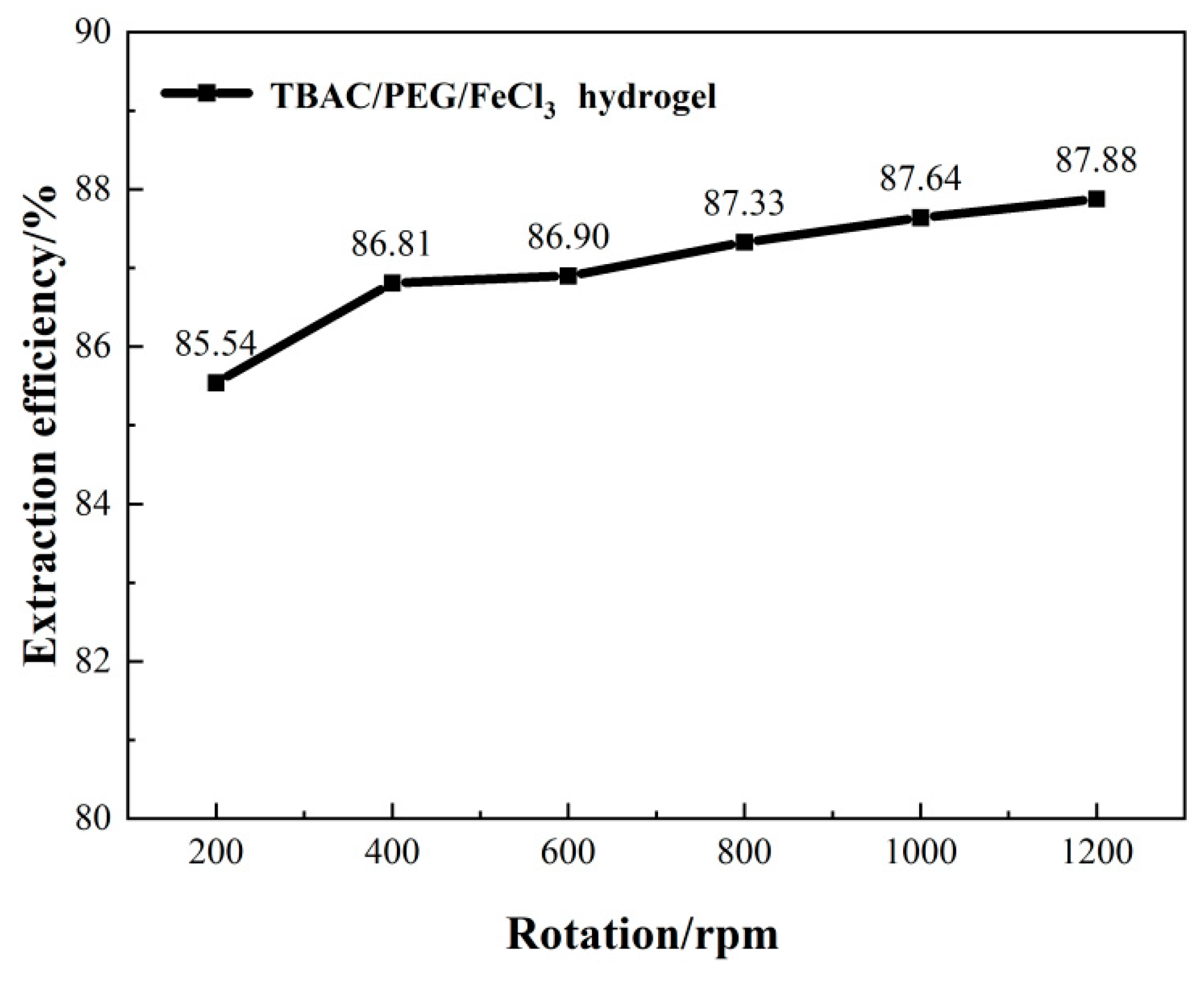
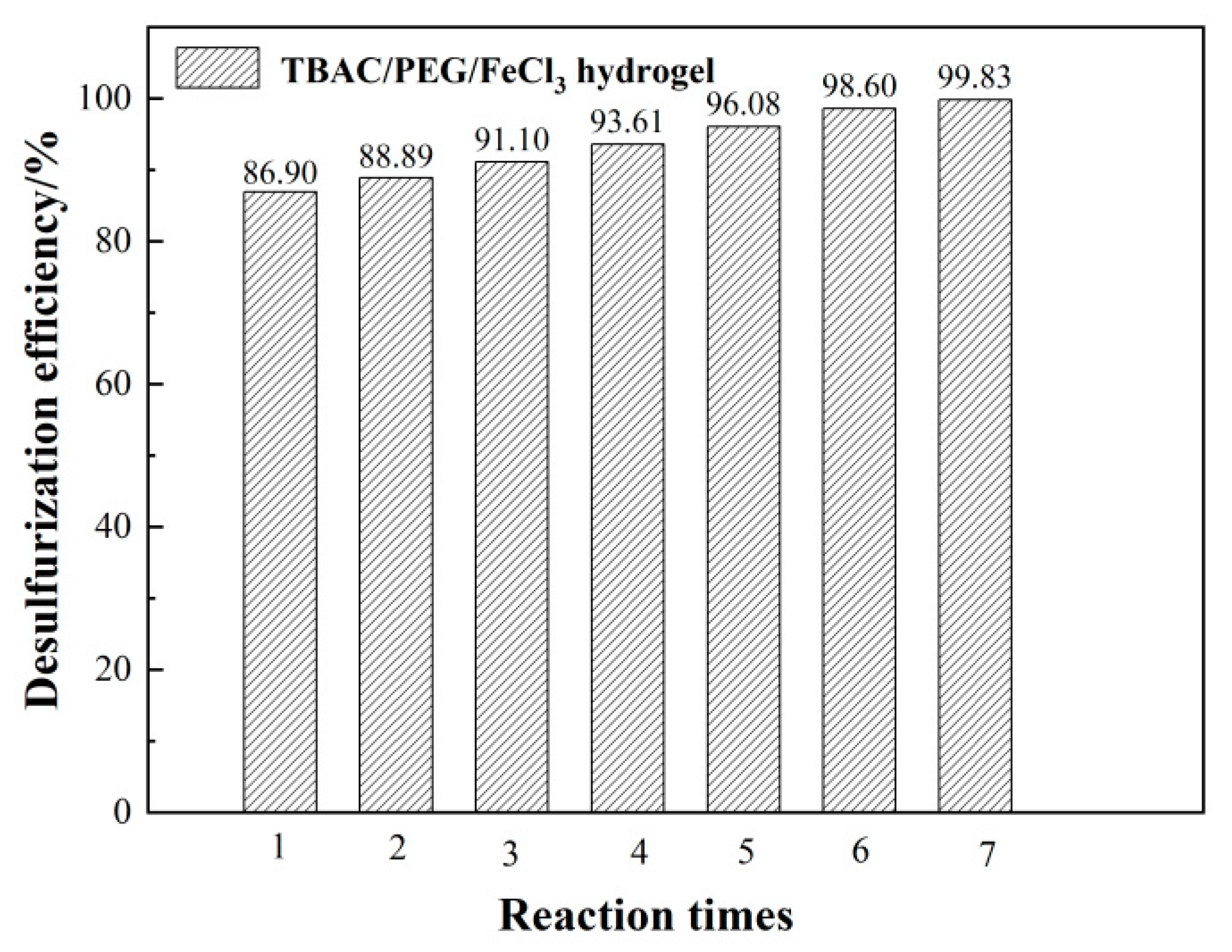
3.1. Optimizing desulfurization conditions
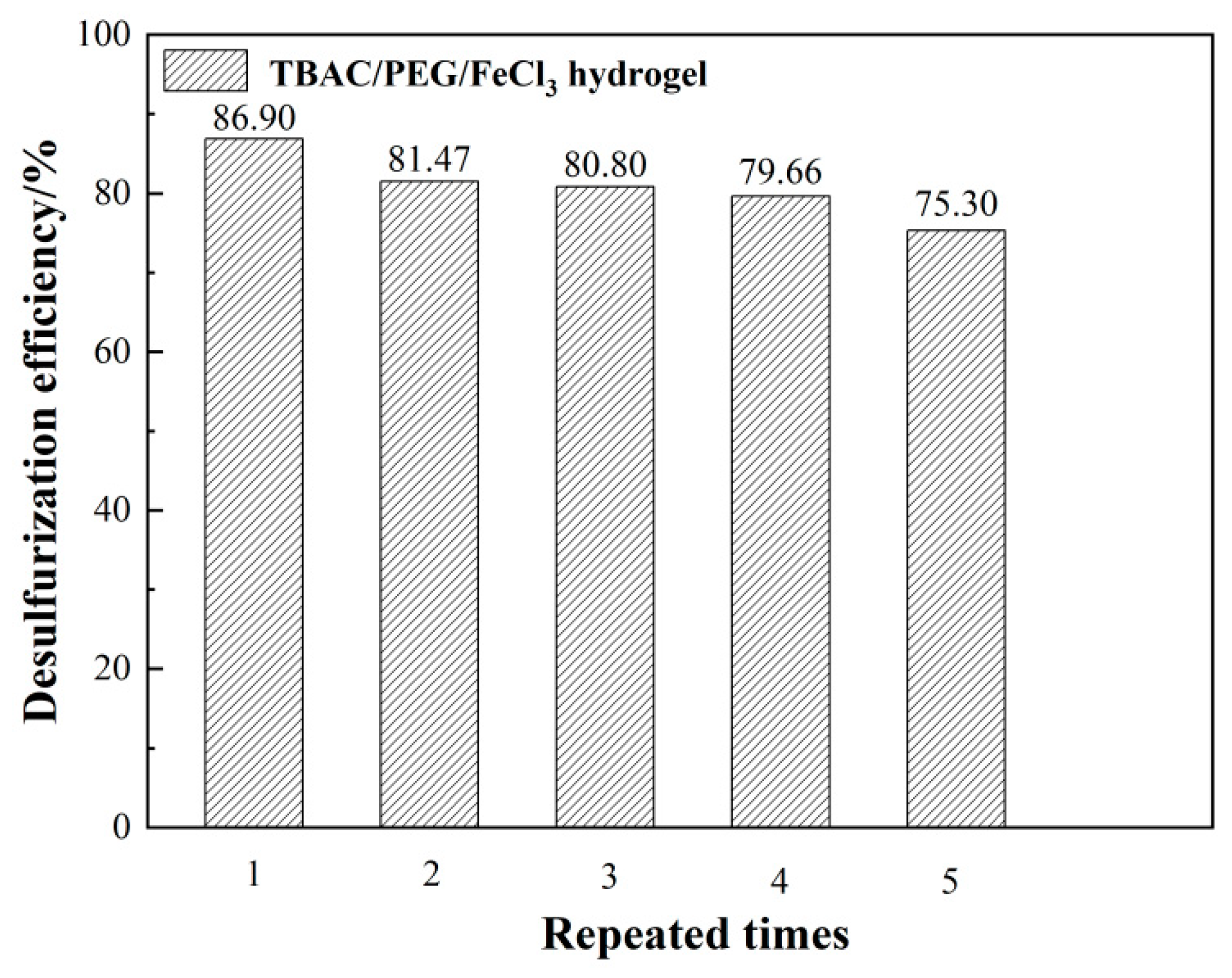
3.2. Repeated recycling of CNTs/PEG-PVA hydrogels
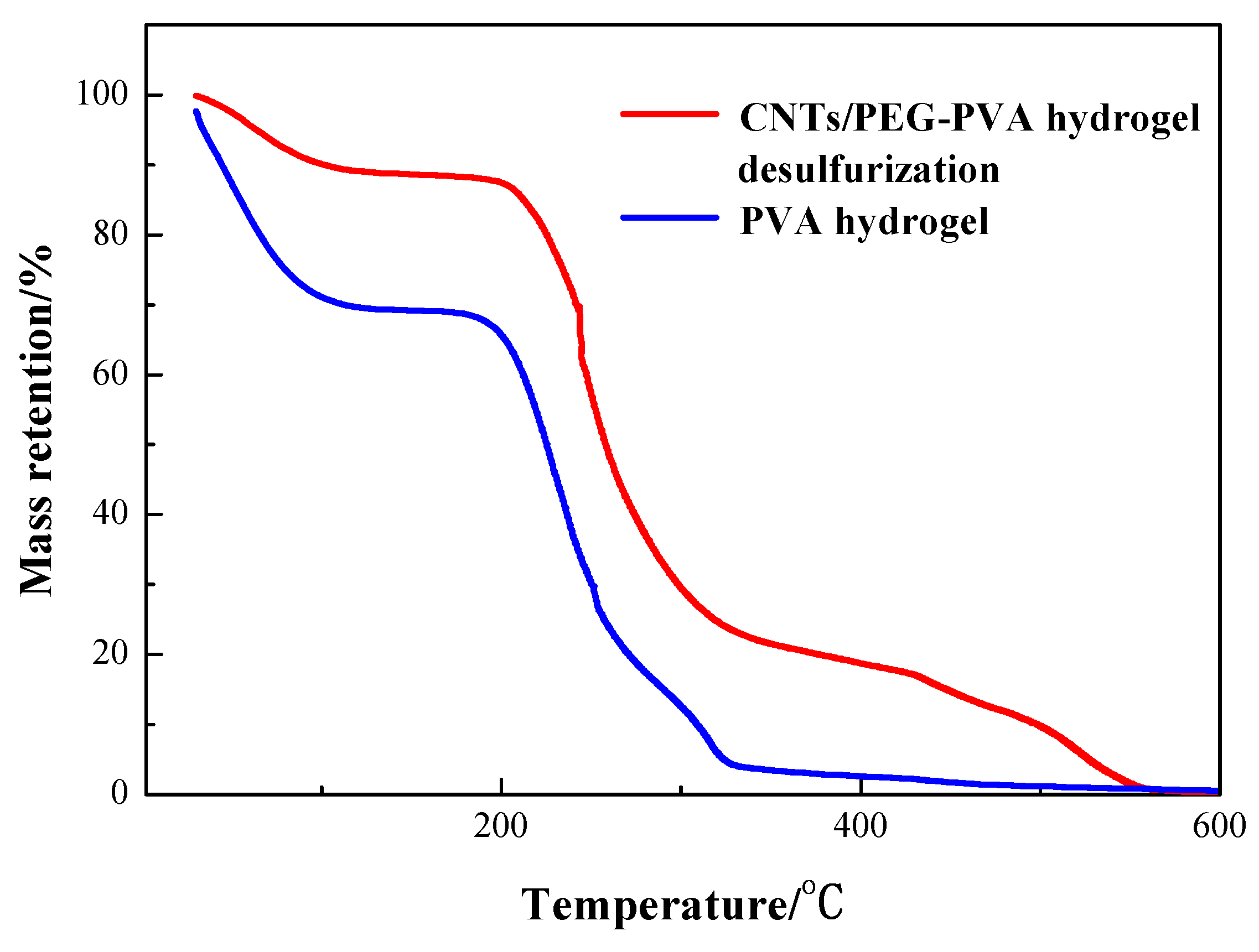
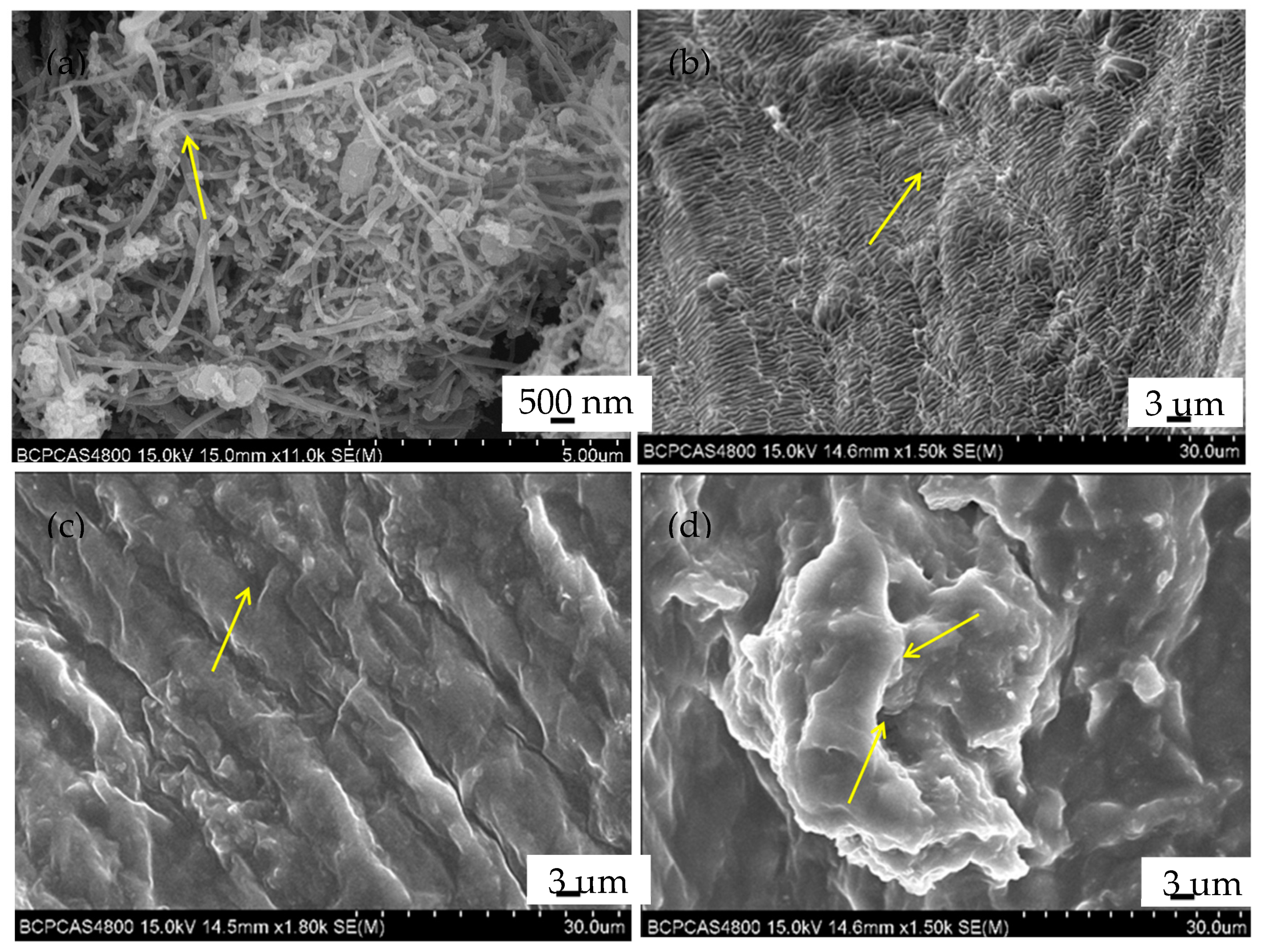
3.3. Study on Adsorption Mechanism
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgements
References
- Song, C.S. An overview of new approaches to deep desulfurization for ultra-clean gasoline, diesel fuel and jet fuel. Catalysis Today 2003, 86, 211–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; He, J.; Nguyen, T.; Petzold, F.; Fonseca, D.; Jasinski, J.B.; Sunkara, M.K. "Nanowire catalysts for ultra-deep hydro-desulfurization and aromatic hydrogenation". Applied Catalysis B-Environmental 2016, 180, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y. Efficient oxidative desulfurization of diesel fuel using amide-based ionic liquids. Chemical Engineering Journal 2016, 283, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, S.O.; Juliao, D.; Cunha-Silva, L.; Domingues, V.F.; Valenca, R.; Ribeiro, J.C.; de Castro, B.; Balula, S.S. Catalytic oxidative/extractive desulfurization of model and untreated diesel using hybrid based zinc-substituted polyoxometalates. Fuel 2016, 166, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, D.; Zou, S.; Li, Z.; Yin, J.; Wang, A.; Cui, Y.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, Q. Extraction desulfurization process of fuels with ammonium-based deep eutectic solvents. Green Chemistry 2013, 15, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadj-Kali, M.K.; Mulyono, S.; Hizaddin, H.F.; Wazeer, I.; El-Blidi, L.; Ali, E.; Hashim, M.A.; AlItashef, I.M. Removal of Thiophene from Mixtures with <i>n</i>-Heptane by Selective Extraction Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2016, 55, 8415–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Sun, T. Extractive desulfurisation of gasoline with tetrabutyl ammonium chloride-based deep eutectic solvents. Separation Science and Technology 2016, 51, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Song, H.; Meng, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, C.; Lei, Z.; Chen, B. Polyethylene glycol oligomers as green and efficient extractant for extractive catalytic oxidative desulfurization of diesel. Fuel Processing Technology 2017, 158, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zheng, D.; Xun, S.; Qin, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Li, H. Polyoxometalate-based ionic liquid supported on graphite carbon induced solvent-free ultra-deep oxidative desulfurization of model fuels. Fuel 2017, 190, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.F.; Al-Malki, A.; El-Ali, B.; Martinie, G.; Siddiqui, M.N. Deep desulphurization of gasoline and diesel fuels using non-hydrogen consuming techniques. Fuel 2006, 85, 1354–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, H.F.M.; Kait, C.F.; Mutalib, M.I.A. Extractive deep desulfurization of diesel using choline chloride-glycerol eutectic-based ionic liquid as a green solvent. Fuel 2017, 192, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharaskar, S.A.; Varma, M.N.; Shende, D.Z.; Yoo, C.K.; Wasewar, K.L. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of 1-Butyl-3 Methylimidazolium Chloride as Green Material for Extractive Desulfurization of Liquid Fuel. Scientific World Journal, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gano, Z.S.; Mjalli, F.S.; Al-Wahaibi, T.; Al-Wahaibi, Y.; AlNashef, I.M. Extractive desulfurization of liquid fuel with FeCl<sub>3</sub>-based deep eutectic solvents: Experimental design and optimization by central-composite design. Chemical Engineering and Processing-Process Intensification 2015, 93, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Maldonado, A.J.; Yang, R.T. Desulfurization of transportation fuels by adsorption. Catalysis Reviews-Science and Engineering 2004, 46, 111–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Maldonado, A.J.; Yang, R.T. New sorbents for desulfurization of diesel fuels via π-complexation. Aiche Journal 2004, 50, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang Phuoc, H.; Kasinathan, P.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Woo, H.C. Deep desulfurization of fuel gas by adsorption on Cu-impregnated activated carbons in practical conditions. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering 2016, 33, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Ahmadi, M.; Khosravi-Nikou, M.R. Adsorptive desulfurization and denitrogenation of model fuel by mesoporous adsorbents (MSU-S and CoO-MSU-S). Petroleum Science and Technology 2017, 35, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wan, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, H. An improvement of MCM-41 supported phosphoric acid catalyst for alkylation desulfurization of fluid catalytic cracking gasoline. Fuel 2015, 143, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.-d.; Zhang, Y.-f.; Li, J.-j.; Zhu, Y.-q.; Qing, D.-y.; Deng, Y.-x. Deep Extractive Desulfurization with Arenium Ion Deep Eutectic Solvents. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2015, 54, 4625–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chemical Reviews 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhou, X.; Cui, Y.; Yin, J. Deep desulfurization performance of thiophene with deep eutectic solvents loaded carbon nanotube composites. Royal Society Open Science 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mixtures. Journal of Solution Chemistry 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel solvent properties of choline chloride/urea mixtures. Chemical Communications, 2003; 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, C.; Garcia-Alvarez, J.; Hernan-Gomez, A.; Kennedy, A.R.; Hevia, E. Introducing Deep Eutectic Solvents to Polar Organometallic Chemistry: Chemoselective Addition of Organolithium and Grignard Reagents to Ketones in Air. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 2014, 53, 5969–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Alvarez, J.; Hevia, E.; Capriati, V. The Future of Polar Organometallic Chemistry Written in Bio-Based Solvents and Water. Chemistry-a European Journal 2018, 24, 14854–14863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnodo, D.; Ghinato, S.; Nejrotti, S.; Blangetti, M.; Prandi, C. Lateral lithiation in deep eutectic solvents: regioselective functionalization of substituted toluene derivatives. Chemical Communications 2020, 56, 2391–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios-Lombardia, N.; Cicco, L.; Yamamoto, K.; Hernandez-Fernandez, J.A.; Moris, F.; Capriati, V.; Garcia-Alvarez, J.; Gonzalez-Sabin, J. Deep eutectic solvent-catalyzed Meyer-Schuster rearrangement of propargylic alcohols under mild and bench reaction conditions. Chemical Communications 2020, 56, 15165–15168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, M.D.; Mezzetta, A.; Guazzelli, L.; Scanlan, E.M. Radical-mediated thiol-ene 'click' reactions in deep eutectic solvents for bioconjugation. Green Chemistry 2022, 24, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cui, Y.; Li, C.; Shen, Y. Deep desulfurization of fuels based on deep eutectic theory. Separation and Purification Technology 2019, 219, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
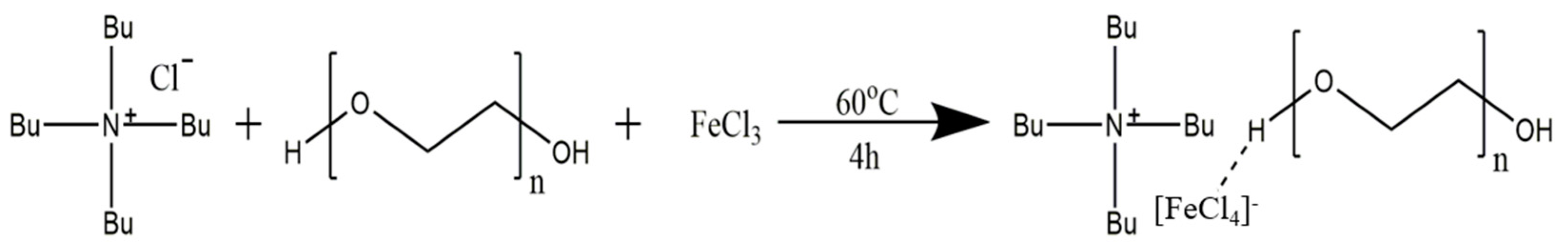

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




