Submitted:
02 January 2024
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Experiment Procedures
3. Results and Discussions
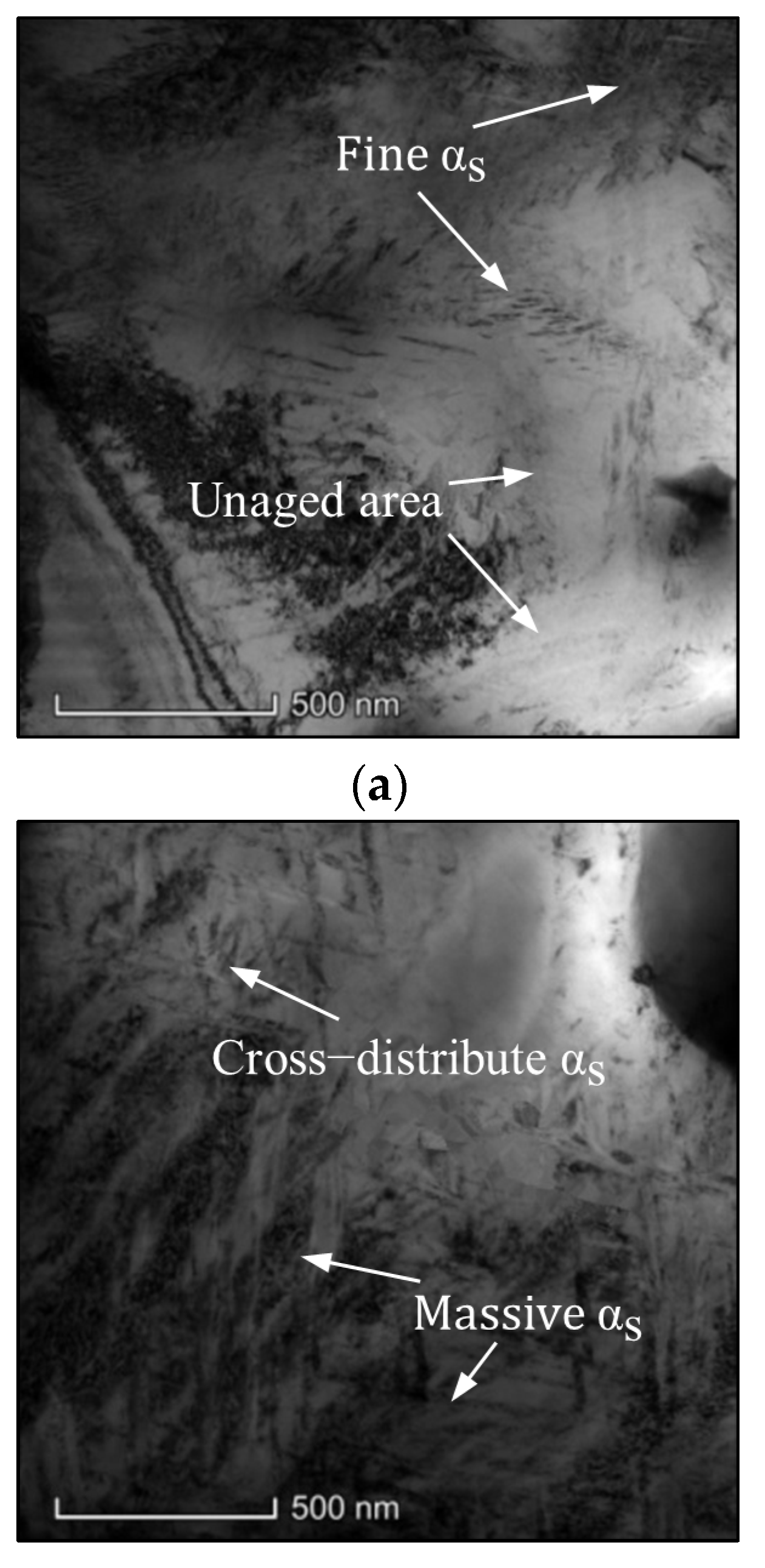
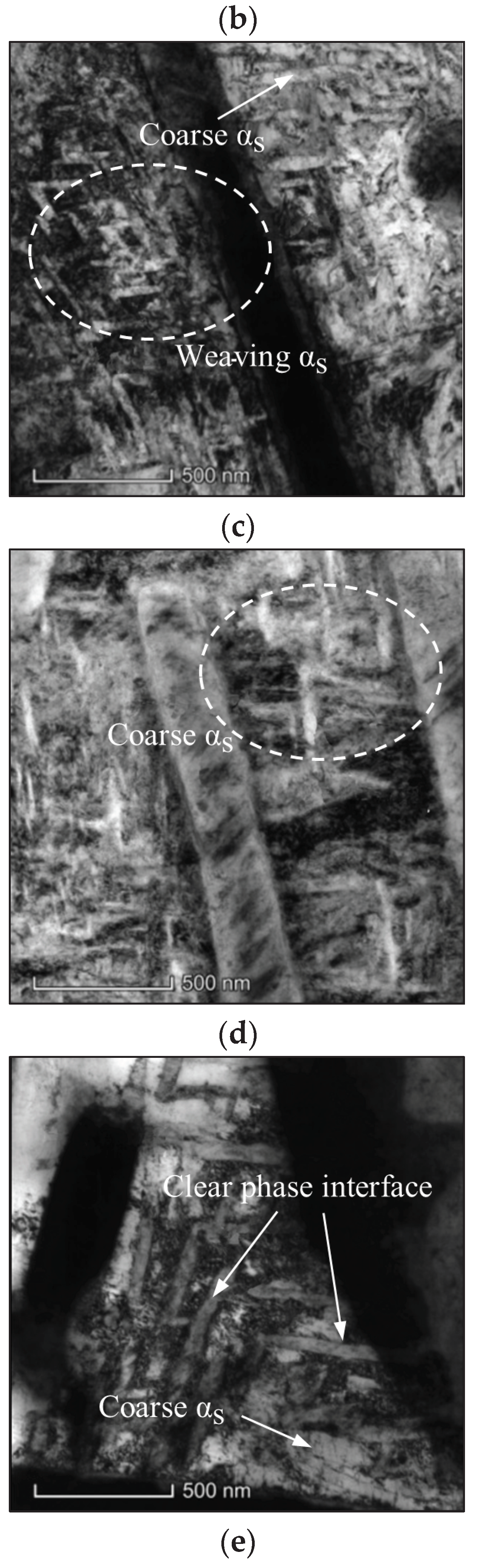
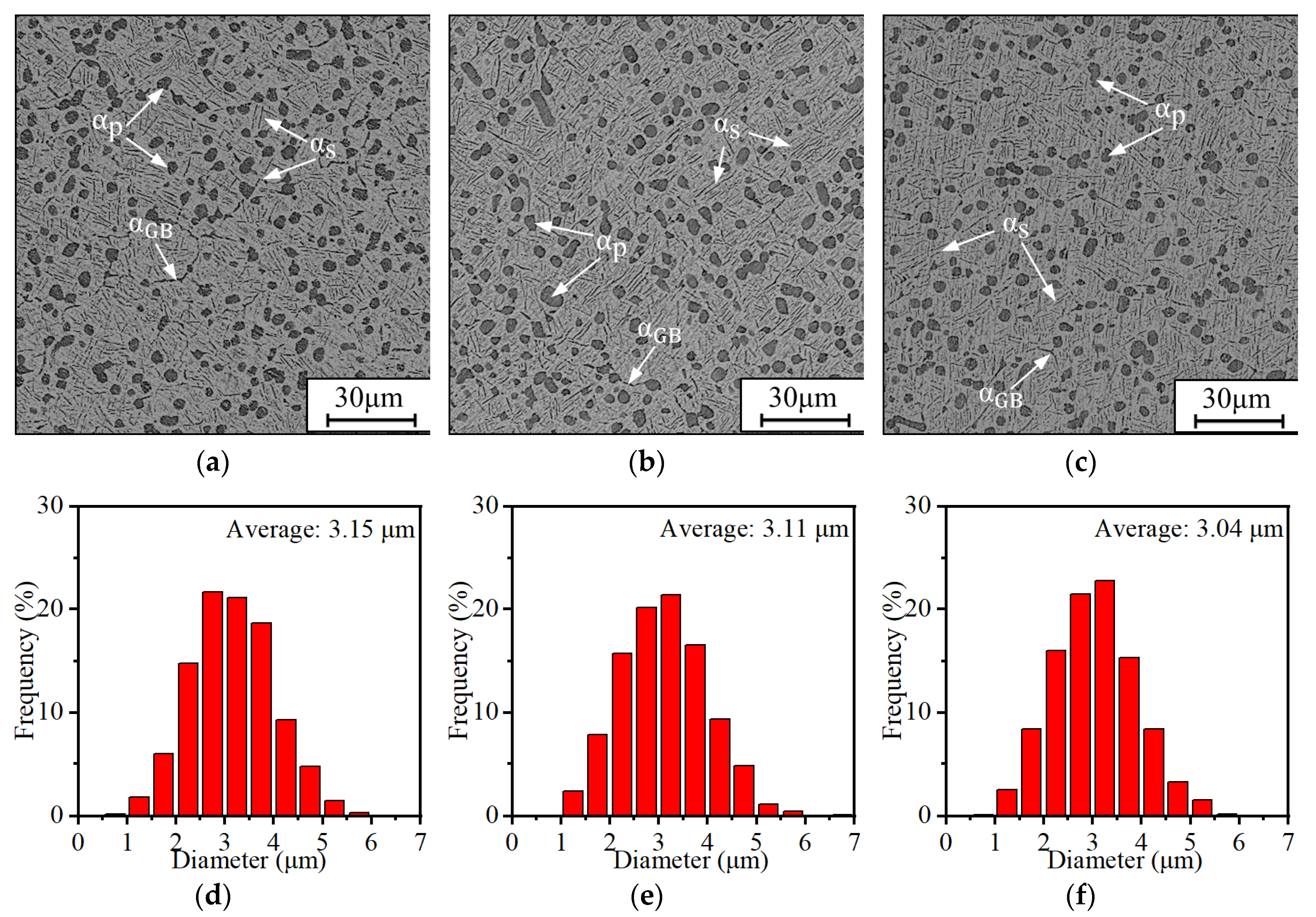
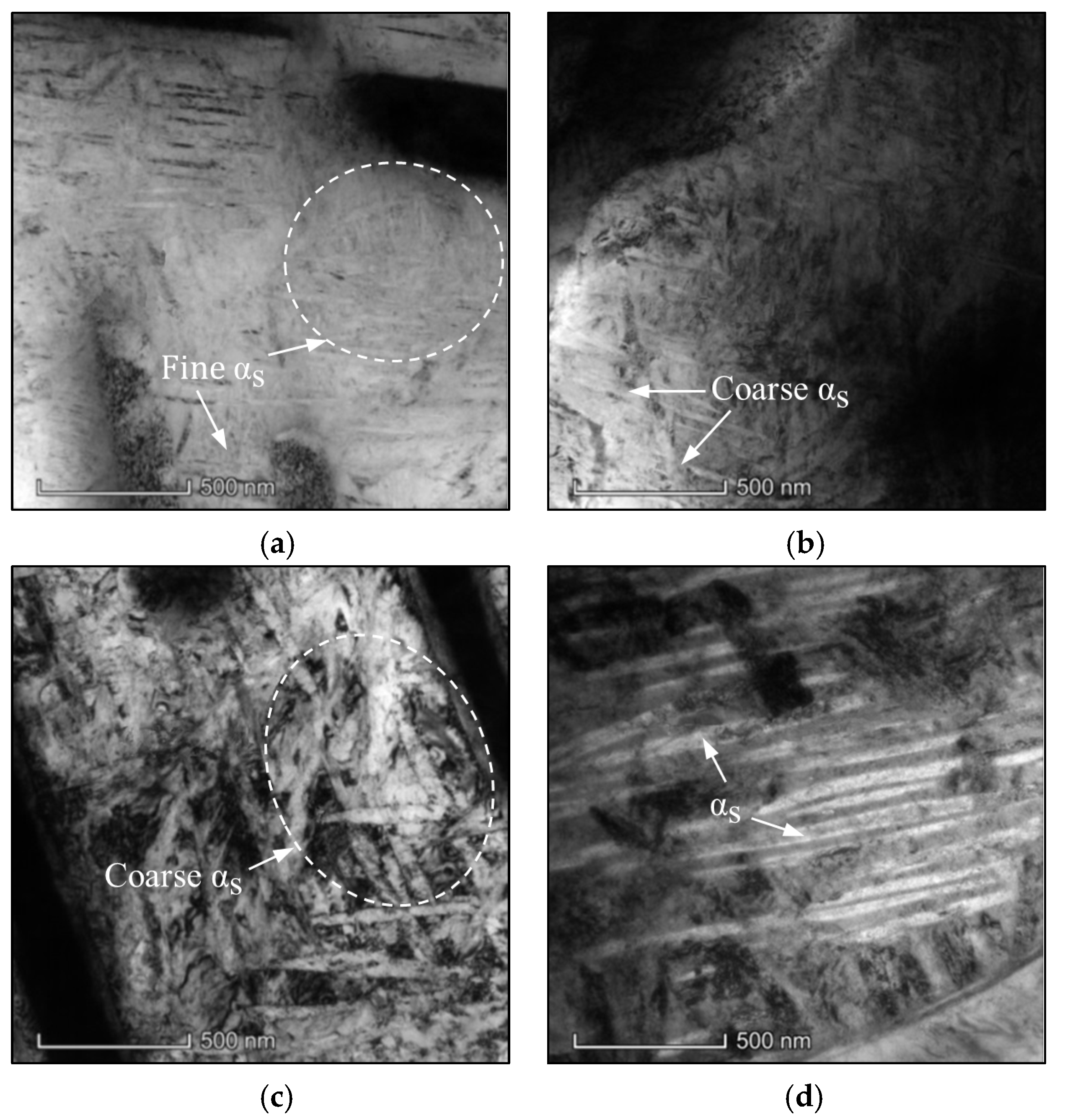
3.1. Effects of Ageing Conditions on Microstructures
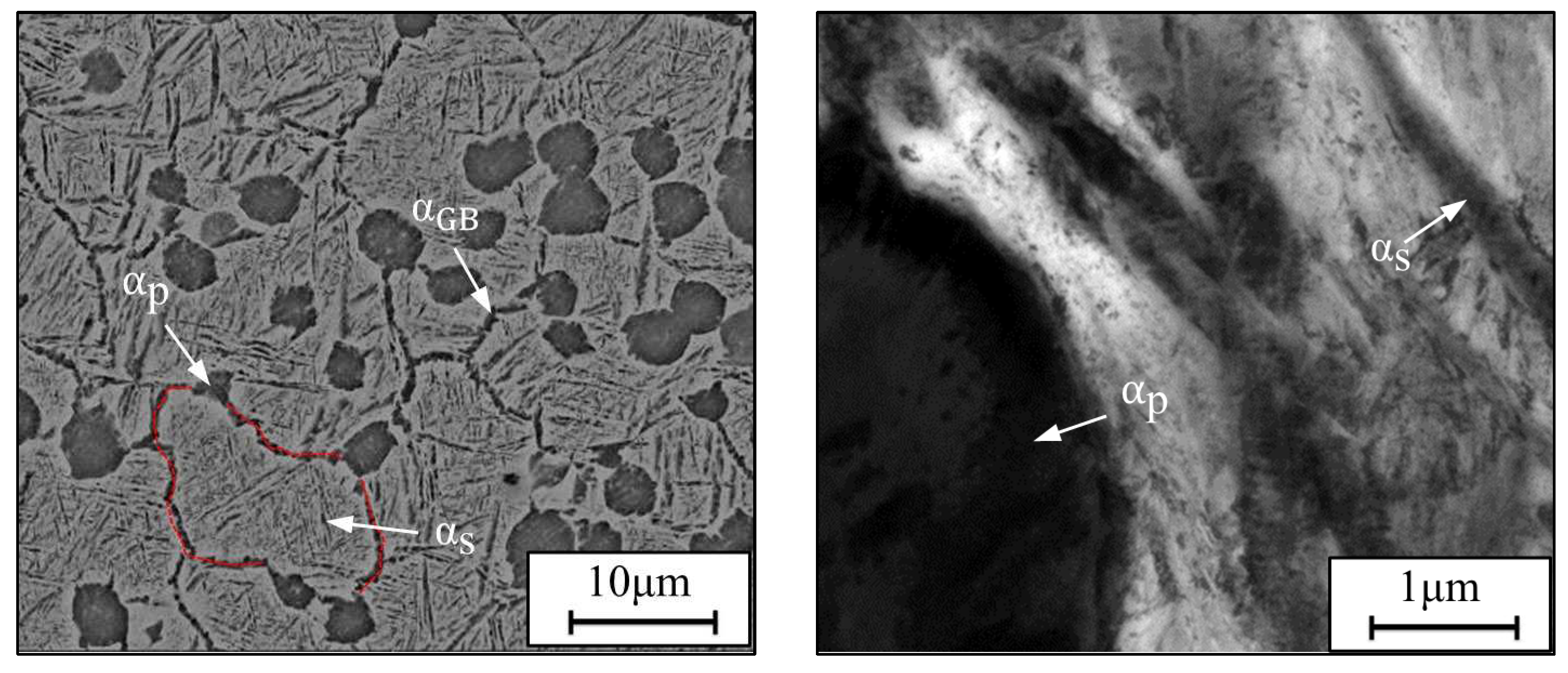
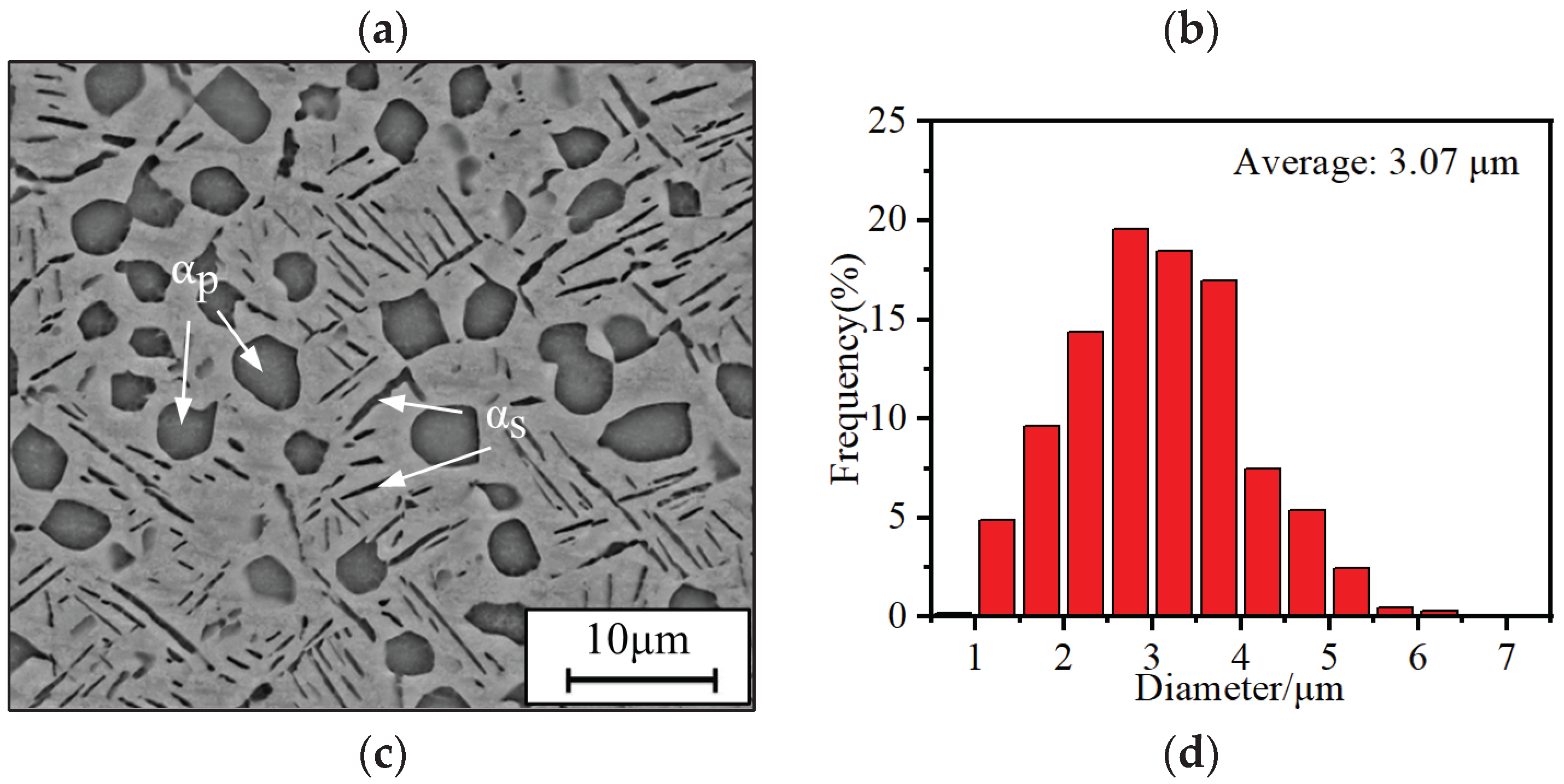
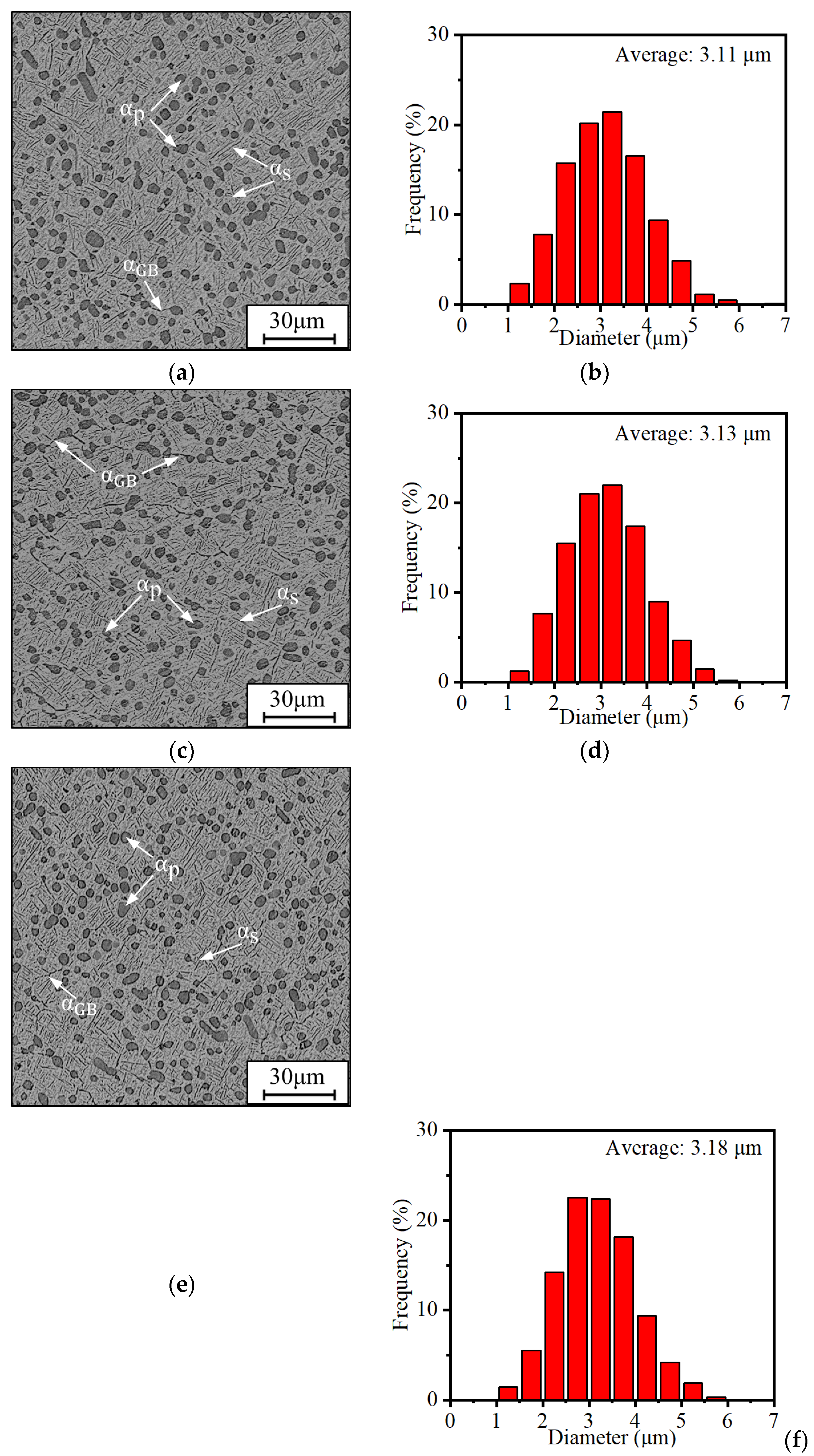
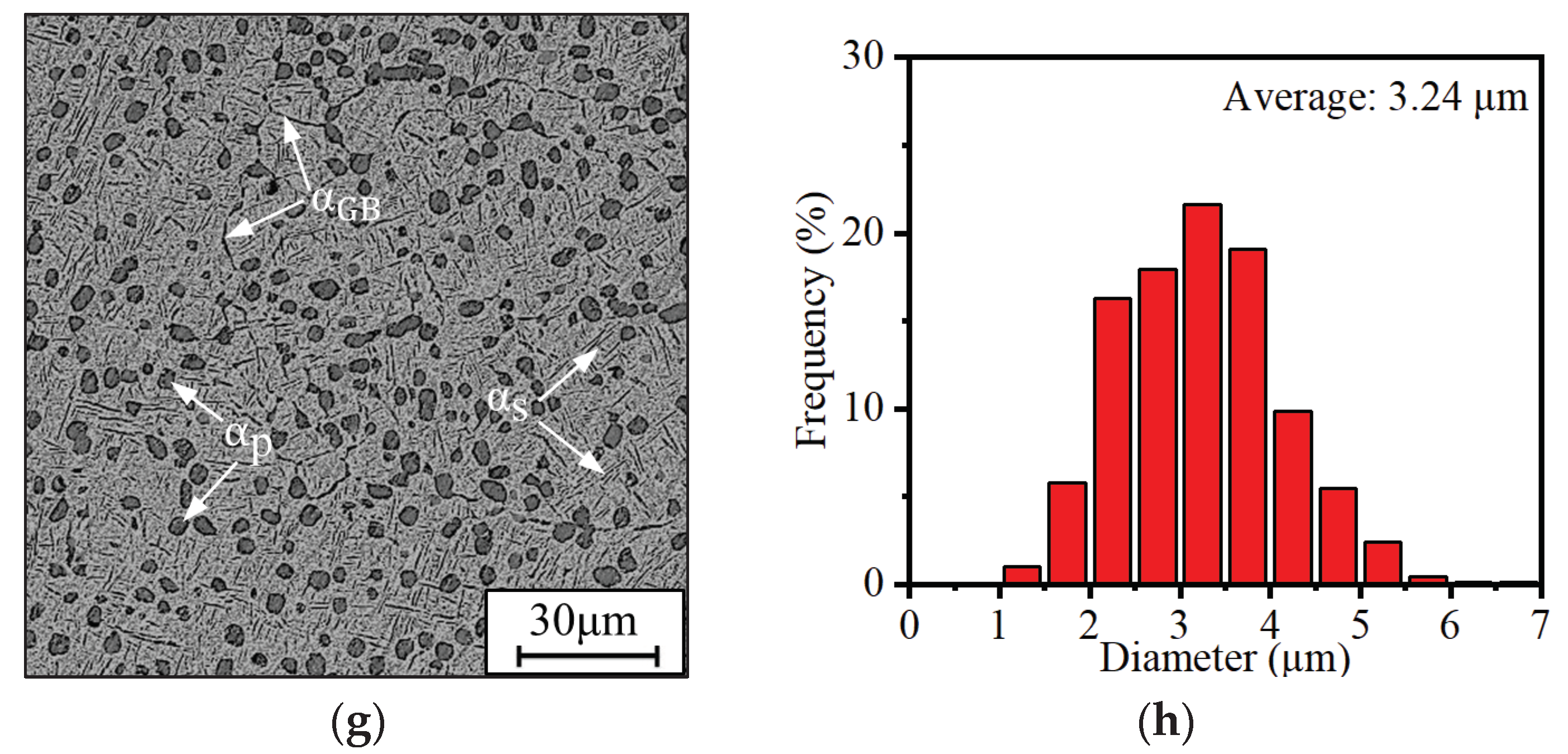
3.1.1. Effects of ageing temperature
3.1.2. Effects of Ageing Time
3.2. Effects of Ageing Conditions on Tensile Properties
3.2.1. Tensile Properties of the Aged TC18 Alloy
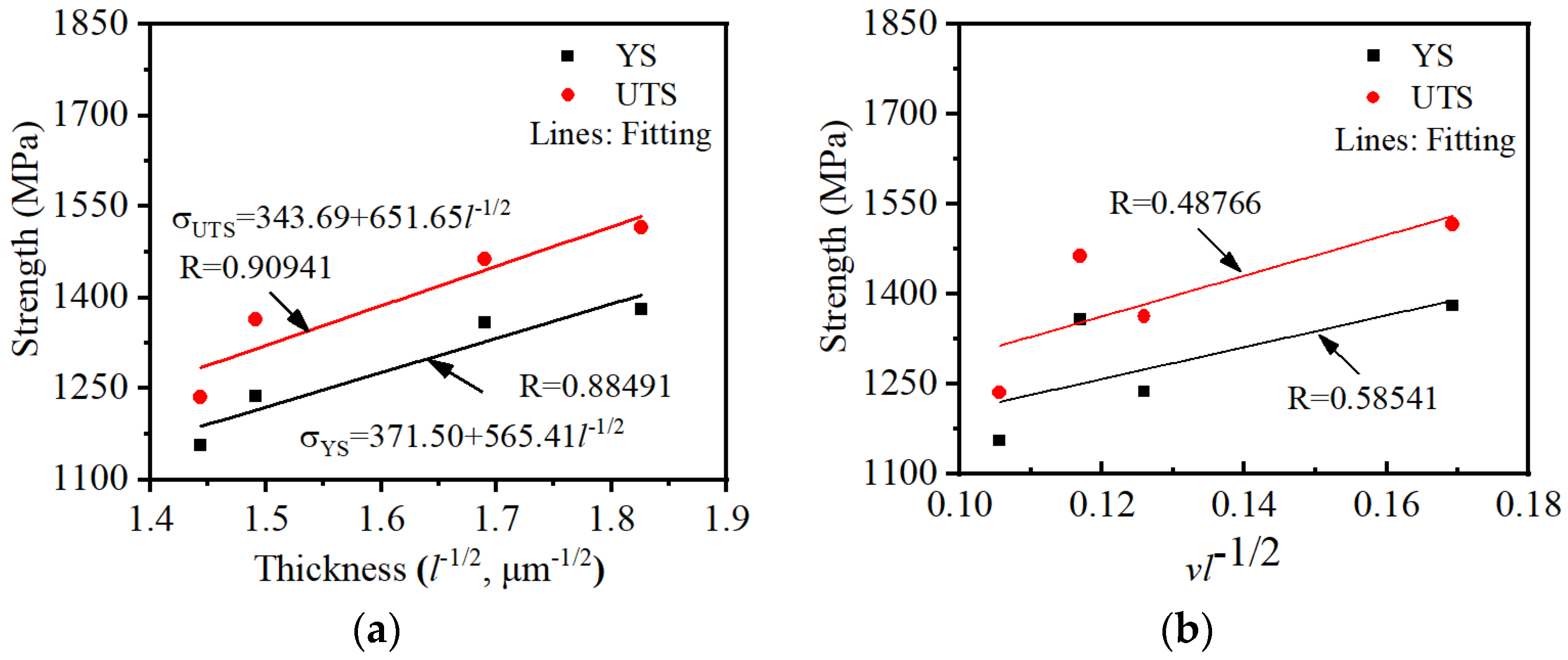
3.2.2. Effects of microstructural features on tensile properties of the aged TC18 alloy
3.2.3. Crucial roles of affecting tensile strengths for TC18 alloy
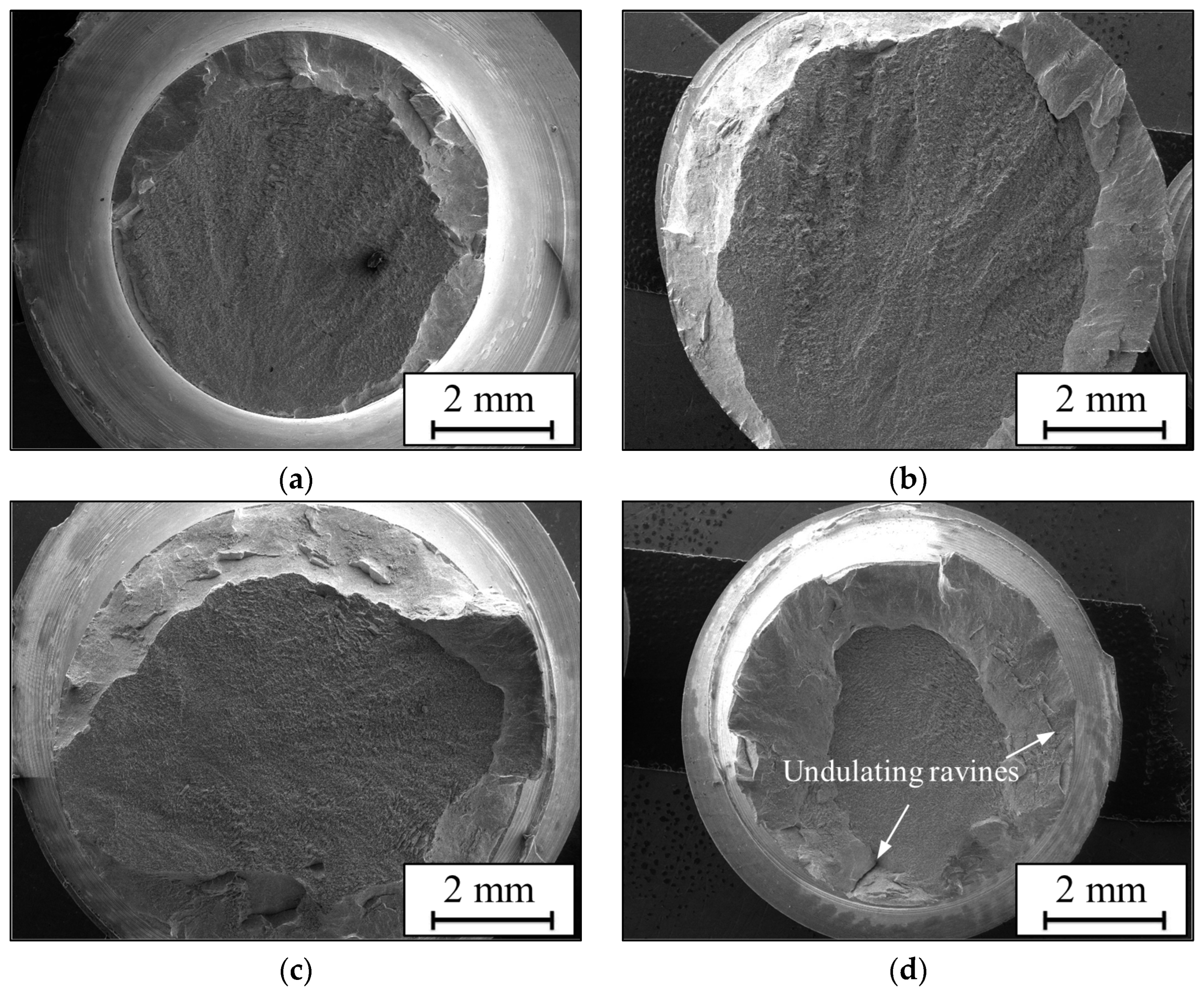
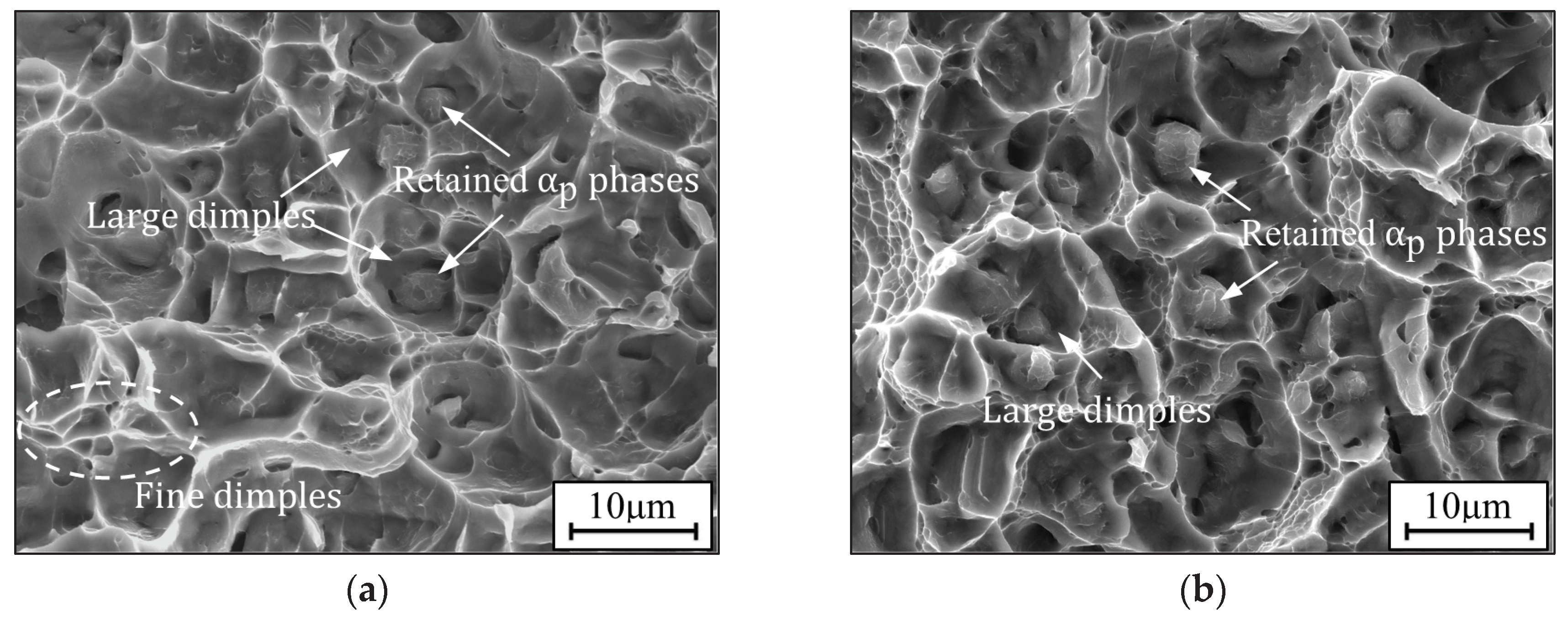
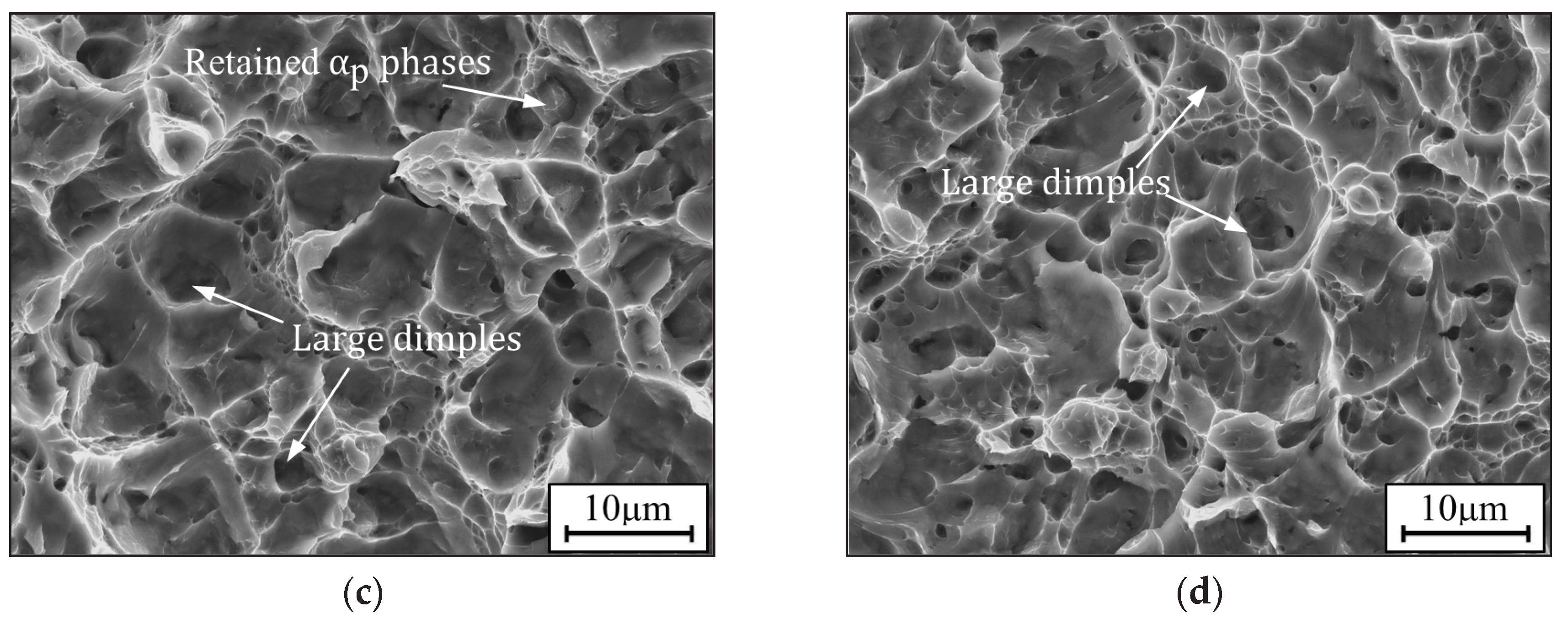
3.3. Fractographies and Fracture Mechanisms
3.3.1. Fractographies of TC18 alloy
3.3.2. Fracture Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, Y.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Pang, G.D.; Wang, D.; Zhou, K.C. A dislocation density-based model and processing maps of Ti-55511 alloy with bimodal microstructures during hot compression in α+β region. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 790, 139692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Zhu, Y.X.; Zhu, J.C.; Wang, C.W.; Liu, X.; Han, K.N.; Wang, B.W.; Yang, Q.; Bai, C.Y. Studies on the life, damage evolution, and crack propagation behaviors of TC18 titanium alloy under repeated impact loading. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 179, 108074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.M.; Morakkabati, M.; Sheikhali, A.H.; Momeni, A. Hot deformation behavior of beta titanium Ti-13V-11Cr-3Al alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 5201–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, A.; Abbasi, S.M.; Sadeghpour, S. A comparative study on the hot deformation behavior of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr and newly developed Ti-4Al-7Mo-3V-3Cr alloys. Vacuum 2019, 161, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Liu, X.G.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, D.D.; Chen, C.; Zhou, K.C. Precipitation behavior of a β-quenched Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe alloy during high-temperature compression. Mater. Charact. 2019, 151, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Yang, F.; Torrens, R.; Bolzoni, L. Evaluation of the hot workability and deformation mechanisms for a metastable beta titanium alloy prepared from powder. Mater. Charact. 2019, 149, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Gockel, B.T.; Balachandran, S.; Banerjee, D.; Rollett, A.D. Simulation of plastic deformation in Ti-5553 alloy using a self-consistent viscoplastic model. Int. J. Plast. 2017, 94, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, R.N.; El-Hadad, S.; Nofal, A. Influence of heat treatment processes on microstructure evolution, tensile and tribological properties of Ti6Al4V alloy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, X.G.; Xu, H.; He, Y.N.; Ke, Y.J.; Zhang, W.W. Relationship between Β→α dynamic transformation and dynamic recrystallization under thermomechanical coupling in Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 179, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobbili, R.; Ramudu, B.V.; Madhu, V. A physically-based constitutive model for hot deformation of Ti-10-2-3 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, T.; Rahimi, S.; Hopper, C.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, J. Unravelling thermal-mechanical effects on microstructure evolution under superplastic forming conditions in a near alpha titanium alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 4285–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.X.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, Y.B.; Wang, W.H.; Li, J.J. Constitutive modeling hot tensile behavior of Ti6Al4V alloy by considering phase transformation and damage mechanisms. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 890, 145887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, P.S.L.; Rakshit, R.; Mandal, S.; Gopal Roy, G.; Panda, S.K. Uniaxial tensile deformation behaviour of electron beam welded commercially pure titanium and Ti6Al4V joints: experimental and metallurgical characterization. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 76, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.J.; Jiang, X.; Han, J.C.; Zhang, S.Z.; Peng, P.; Feng, H.; Wang, T.; Cao, P. Probing the texture transition sequence of near β titanium matrix composites by observing the uneven hot deformation microstructure. Mater. Charact. 2023, 198, 112728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zeng, W.D.; Hong, Q. The effect of microstructure on the mechanical properties of TC4-DT titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 792 (2020) 139822. 2013, 563, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.B.; Yan, H.G.; Zhu, H.M.; Chen, J.H.; Xia, W.J.; Sun, Y.P.; Su, B.; Deng, Y.F.; Song, M. Dynamic recrystallization behavior and mechanism of bimodal TC17 titanium alloy during high strain rate hot compression. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, A.; Abdi, A.; Fatemi, S.A.; Marchese, G.; Biamino, S.; Mirzadeh, H. Hot deformation behavior and flow stress modeling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced via electron beam melting additive manufacturing technology in single β-phase field. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 792, 139822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.Q.; Lin, Y.C.; Zhao, C.Y.; Chen, M.S.; He, D.G. A new method to increase the spheroidization rate of lamellar α microstructure during hot deformation of a Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, J.T.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y.H.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.G.; Huang, W.D. Grain morphology evolution and texture characterization of wire and arc additive manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 768, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.T.; Zeng, W.D.; Xu, J.W.; Chen, W. The effects of microstructure evolution on the fracture toughness of BT-25 titanium alloy during isothermal forging and subsequent heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 745, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Savvakin, D.G.; Ivasishin, O.M.; Pereloma, E.V. The effect of ageing on microstructure and mechanical properties of powder Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-1Cr-1Fe alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 605, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.G.; Su, G.; Lin, Y.C.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.J.; Yan, X.T.; Xia, Y.C.; Xie, Y.C. Microstructural variation and a physical mechanism model for a Ti-55511 alloy during double-stage hot deformation with stepped strain rates in the β region. Materials 2021, 14, 6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.C.; Zeng, W.D.; Zhao, Z.B.; Wang, S.M.; Xu, J.W.; Wang, Q.J. Growth mechanism of αp and interface relationships between αp and αs during cooling of a near α titanium alloy. Mater. Des. 2022, 223, 111191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lypchanskyi, O.; Śleboda, T.; Łukaszek-Sołek, A.; Zyguła, K.; Wojtaszek, M. Application of the strain compensation model and processing maps for description of hot deformation behavior of metastable β titanium alloy. Materials 2021, 14, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.Z.; Li, F.G.; Wang, C.P. Micromechanical behavior study of α phase with different morphologies of Ti-6Al-4V alloy by microindentation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 580, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Xiao, W.L.; Chang, H.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Ma, C.L.; Zhou, L. Microstructural tailoring and mechanical properties of a multi-alloyed near β titanium alloy Ti-5321 with various heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Pang, G.D.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Liu, X.G.; Zhang, X.Y.; Chen, C.; Zhou, K.C. Hot compressive deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of a Ti-55511 alloy with basket-weave microstructures. Vacuum 2019, 169, 108878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.J.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, L.J. Rheological law and mechanism for superplastic deformation of Ti-6Al-4V. Materials 2019, 12, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhar, S.; Sarkar, R.; Kar, S.K.; Bhattacharjee, A. Effect of solution treatment and aging on microstructure and tensile properties of high strength β titanium alloy, Ti-5Al-5V-5Mo-3Cr. Mater. Des. 2015, 66, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, R.; Geetha, M.; Saxena, V.K.; Nageswararao, M. Studies on single and duplex aging of metastable beta titanium alloy Ti-15V-3Cr-3Al-3Sn. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 605, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Zhang, S.; Liang, Y.L.; Ou, M.G. Influence of multi-stage heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 titanium alloy. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Saxena, K.K. Effect of heat-treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti alloys: An overview. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 26, 2546–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeby-Gautier, E.; Denand, B.; Teixeira, J.; Dehmas, M.; Appolaire, B.; Settefrati, A. Influence of microstructure on tensile properties of β-metastable Ti 17 alloy. 12th World Conf. Titan. (Ti-2011) 2012, 2, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, L.; He, S.Y.; Chen, C.J.; Jiang, B.B.; Hao, Y.L.; Ye, H.Q.; Yang, R.; Du, K. Diffusional-displacive transformation in a metastable β titanium alloy and its strengthening effect. Acta Mater. 2020, 195, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhan, M. Microstructural evolution, mechanical properties and fracture toughness of near β titanium alloy during different solution plus aging heat treatments. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 805, 1144–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.K.; Li, J.S.; Kou, H.C.; Hua, K.; Tang, B.; Zhang, Y.D. Influence of solution treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of a near β titanium alloy Ti-7333. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Wu, Q.; Pang, G.D.; Jiang, X.Y.; He, D.G. Hot tensile deformation mechanism and dynamic softening behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with thick lamellar microstructures. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 1901193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshaer, R.N.; Ibrahim, K.M. Effect of cold deformation and heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of TC21 Ti alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2020, 30, 1290–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, L.; Quesne, C.; Penelle, R. Microstructure, and tensile properties of a near beta-titanium treatments and tensile properties. J. Mater. Res. 1996, 12, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantounas, I.; Dye, D.; Lindley, T.C. The Role of microtexture on the faceted fracture morphology in Ti-6Al-4V subjected to high-cycle fatigue. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3908–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Wang, L.H.; Wu, Q.; Xiao, Y.W.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, X.Y. Effects of solution temperature and cooling rate on α phases and mechanical properties of a forged Ti-55511 alloy. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1165h2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.G.; Ng, F.L.; Seet, H.L.; Nai, S.M.L. Tailoring the microstructure and mechanical property of laser powder bed fusion fabricated Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo via heat treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 895, 162648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wan, M.P.; Huang, C.W.; Lei, M. Strength and fracture toughness of TC21 alloy with multi-level lamellar microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 740–741, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.Y.; Lu, Y.F.; Guo, D.Z.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, L. Tensile deformation and fracture of Ti-5Al-5V-5Mo-3Cr-1.5Zr-0.5Fe alloy at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 587, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Liu, S.G.; Zhang, X.; Chen, B.H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ma, M.Z.; Liu, R.P. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of hot-rolled Ti-30Zr-5Al-2.5Sn alloy with mixed α and α′ phases. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 792, 139812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.W.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Xin, S.W.; Zhou, W.; Li, Q.; Zeng, W.D. Effect of microstructure on tensile properties of Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr-1Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, T.R.; Fallahi, A.; Ng, B.C.; Kumar, D.; Crimp, M.A.; Simkin, B.A.; Zamiri, A.; Pourboghrat, F.; Mason, D.E. Fracture initiation/propagation parameters for duplex TiAl grain boundaries based on twinning, slip, crystal orientation, and boundary misorientation. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Route No. | Pretreatment | Ageing Condition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (oC) | Hold Time (h) | Cooling Method | ||
| 1 | 780 oC/1h/WQ | 400 | 4 | AC |
| 2 | 450 | |||
| 3 | 500 | |||
| 4 | 550 | |||
| 5 | 600 | |||
| 2-1 | 450 | 1 | ||
| 2-2 | 450 | 2 | ||
| 2-3 | 450 | 8 | ||
| Ageing Condition d | The content of α phases (%) | The content of αp phases (%) | The diameter of αp phases (μm) | The content of αs phases (%) | The thickness of αs phases (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 450 oC | 27.61 | 18.34 | 3.11 | 9.27 | 0.30 |
| 500 oC | 23.79 | 16.87 | 3.13 | 6.92 | 0.35 |
| 550 oC | 27.01 | 18.56 | 3.18 | 8.45 | 0.45 |
| 600 oC | 25.89 | 18.57 | 3.24 | 7.32 | 0.47 |
| Pre-treatment | Ageing conditions | Yield strength (YS)/MPa | Ultimate tensile strength (UTS)/MPa | Elongation(δ)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 780 oC/1 h/WQ | / | 1220.2 | 1359.9 | 9.1 |
| 400 ℃/4 h/AC | 1157.9 | 1248.2 | 11.3 | |
| 450 ℃/2 h/AC | 1263.4 | 1406.9 | 12.5 | |
| 450 ℃/4 h/AC | 1381.6 | 1516.8 | 9.3 | |
| 450 ℃/8 h/AC | 1353.7 | 1516.9 | 11.2 | |
| 500 ℃/4 h/AC | 1358.3 | 1463.5 | 9.0 | |
| 550 ℃/4 h/AC | 1238.6 | 1363.2 | 10.3 | |
| 600 ℃/4 h/AC | 1156.8 | 1236.7 | 15.1 |
| Temperature | The content of α phases | The thickness of αs phases | The tensile strength | Ductility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 450→500 oC | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ |
| 500→550 oC | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
| 550→600 oC | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ | ↑ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





