Submitted:
30 December 2023
Posted:
03 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
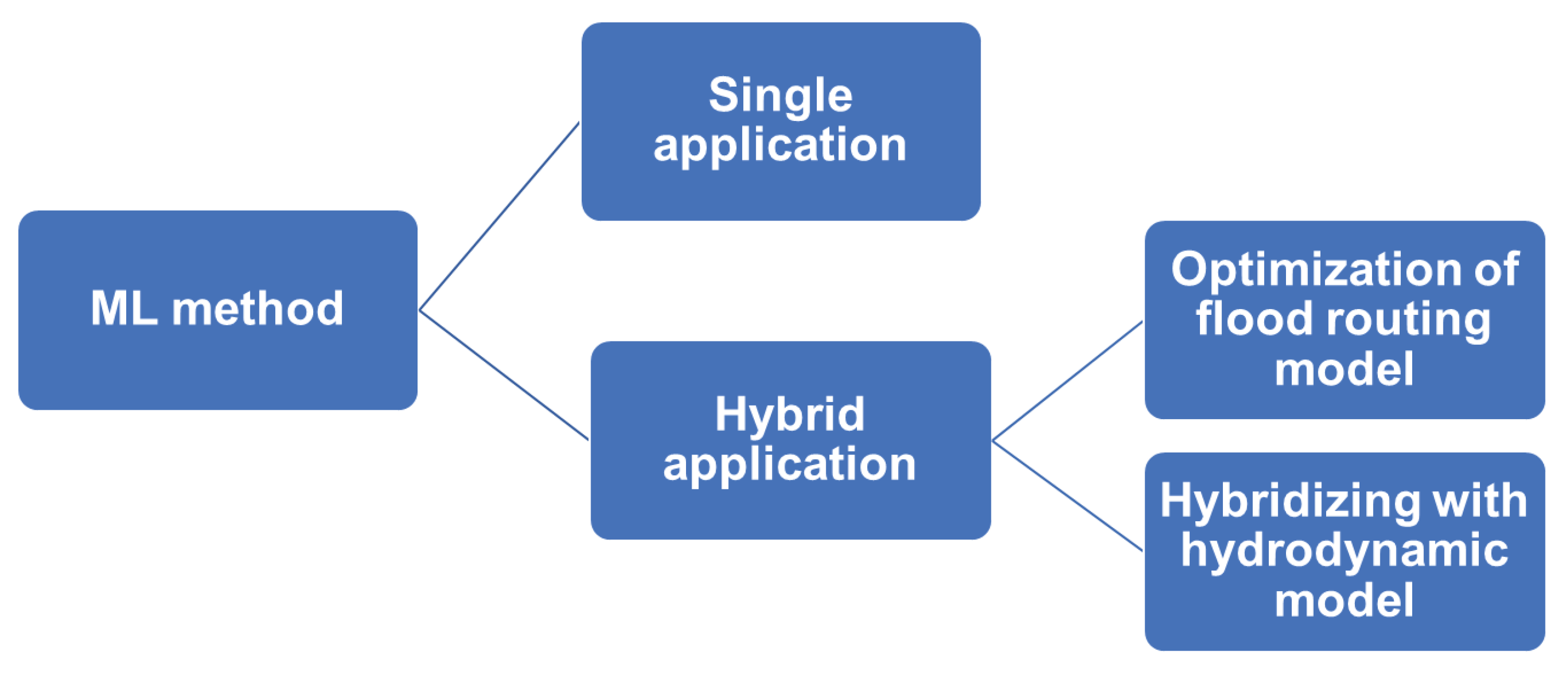
2. ML methods
2.1. Single application
2.1.1. Support vector regression (SVR)
2.1.2. Artificial neural network (ANN)
2.1.3. Recurrent neural network (RNN)
2.1.4. Random forest regression (RFR)
2.1.5. K-nearest neighbor (KNN)
2.1.6. Other ML methods
2.2. Hybrid application
2.2.1. ML-based optimization technique
2.2.2. Hybrid application of a hydraulic model and ML method
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| ACO | Ant colony optimization |
| ANFIS | Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system |
| ANN | Artificial neural network |
| ANSE | Arithmetic mean |
| ARIMA | Autoregressive integrated moving average |
| ARMA | Auto-regressive moving averageo-regressive m |
| BA | Bat algorithm |
| BFGS | Broyden-fletcher-goldfarb-shanno |
| BSA | Backtracking search algorithm |
| BT | Bagged tree |
| CC | Coefficient of correlation |
| CE | Coefficient of efficiency |
| CFBNN | Cascade forward backpropagation neural network |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| C-QPSO | Cuckoo quantum-behaviour particle swarm optimization |
| CSA | Clonal selection algorithm |
| DE | Differential evolution |
| DE | Differential evolution |
| DLCM | Discrete linear cascade model |
| DP | Difference in peak |
| DPF | Difference in peak flow |
| EA | Evolutionary algorithm |
| EEMD | Ensemble empirical mode decomposition |
| EMD | Empirical model decomposition |
| EQp | Error of peak discharge |
| ETp | Error of time to peak |
| FFBNN | Feed-forward backpropagation neural network |
| FMLP | Feed forward multilayer percetptron |
| GA | Genetic algorithm |
| GBM | Gradient-boosted machine |
| GEP | Gene expression programming |
| GMC | Gaussian mixture copula |
| GP | Genetic programming |
| GPR | Gaussian process regression |
| GRG | Generalized reduced gradient |
| GRP | Gaussian process regression |
| GRU | Gated recurrent unit |
| GWO | Grey wolf optimizer |
| HBSA | Hybrid bat-swarm algorithm |
| HPSO | Hybrid particle swarm optimization |
| HS | Harmony search |
| ICA | Imperialist competitive algorithm |
| ICSA | Immune clonal selectio algorithm |
| IOA | Index of agreement |
| KF | Kalman filter |
| KGE | Kling-Gupta efficiency |
| KN2K | KNN-KF |
| KNN | K-nearest neighbor |
| LM | Levenberg-Marquardt |
| LMM | Lagrange multiplier |
| LSSVM | Least squares support vector machine |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
| MBE | Mean bias error |
| MHBMO | Modified honey bee mating optimization |
| ML | Mahine Learning |
| MLFN | Multilayer-feedforward network |
| MLP | Multilayer perceptron |
| MRE | Mean relative error |
| MSE | Mean square error |
| MWLP | MLP-based water level prediction |
| NMM | Nonlinear Muskingum model |
| NMS | Nelder-mead simplex |
| NSE | Nash-Sutcliffe Coefficient |
| PCC | Pearson correlation coefficient |
| PI | Persistence index |
| PSF-HS | Parameter setting free-harmony search |
| PSO | Particle swarm optimization |
| PWRMSE | Peak-weighted root mean square error |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| RAPID | Routing application for parallel computation of discharge |
| RCM | Rating curve method |
| RF | Random forest |
| RFR | Random forest regression |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| RNN | Recurrent neural network |
| RWLP | RNN-based water level prediction |
| SA | Shark algorithm |
| SBA | Social-based algorithm |
| SDE | Standard deviation of the NSE |
| SFLA | Shuffled frog leaping algorithm |
| SI | Scatter index |
| S-LSM | segmented least square method |
| SSE | Sum of squared error |
| SSQ | Sum of the square of the deviations between the observed and routed outflows |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| SVR | Support vector regression |
| TDNN | Time delay neural network |
| TDRNN | Time delay recurrent neural network |
| TSS | Taylor skill score |
| VMD | Variational model decomposition |
| WI | Willmott’s index of agreement |
| WOA | Weed optimizatio algorithm |
| WPANFIS | Wavelet packet-based adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system |
| WPANN | Wavelet packet-based artificial neural network |
| XGBoost | Extream gradient boosting |
References
- Yuan, X.; Wu, X.; Tian, H.; Yuan, Y.; Adnan, R.M. Parameter identification of nonlinear Muskingum model with Backtracking Search Algorithm. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 2767–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Liu, P.; Cheng, L.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W. Determining dynamic water level control boundaries for a multi-reservoir system during flood seasons with considering channel storage. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, 13, e12586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Z.-L.; Wang, J.; Lin, P.; Liang, J.; Li, Z.; Gu, Z. Improving flood simulation capability of the WRF-Hydro-RAPID model using a multi-source precipitation merging method. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhote, P.R.; Thakur, P.K.; Domeneghetti, A.; Chouksey, A.; Garg, V.; Aggarwal, S.P.; Chauhan, P. The use of SARAL/AltiKa altimeter measurements for multi-site hydrodynamic model validation and rating curves estimation: An application to Brahmaputra River. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Kumar Villuri, V.G.; Pasupuleti, S.; Nune, R. Hydrodynamic modeling for identifying flood vulnerability zones in lower Damodar river of eastern India. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020, 11, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, C.; Förster, S.; Bronstert, A. Comparison of hydrodynamic models of different complexities to model floods with emergency storage areas. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 4695–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, F.; Jia-chun, L.; Qing-quan, L. Flood routing models in confluent and dividing channels. Appl. Math. Mech. 2004, 25, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Liu, K.; Cheng, L.; Bai, Y.; Jin, G. Optimizing flood diversion siting and its control strategy of detention basins: A case study of the Yangtze River, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 597, 126201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jun, K.S. Distributed parameter unsteady flow model for the Han River. J. Hydro-environ. Research 2018, 21, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jun, K.S. A hybrid approach to improve flood forecasting by combining a hydrodynamic flow model and artificial neural networks. Water 2022, 14, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, H.; Fang, H. Component-based Reconstruction Prediction of Runoff at Multi-time Scales in the Source Area of the Yellow River Based on the ARMA Model. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Mu, R.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, H. Flood risk analysis of reservoirs based on full-series ARIMA model under climate change. J. Hydrol. 2022, 610, 127979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, H.; Iplikci, S.; Yasar, M.; Gurarslan, G. River flow estimation from upstream flow records using support vector machines. J. Appl. Math. 2014, 714213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Kang, L. Comparative analysis of multiple machine learning methods for flood routing in the Yangtze River. Water 2023, 15, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, R.K.; Pramanik, N.; Bala, B. Simulation of river stage using artificial neural network and MIKE 11 hydrodynamic model. Computers & Geosciences 2010, 36, 735-745.
- Elsafi, S.H. Artificial neural networks (ANNs) for flood forecasting at Dongola Station in the River Nile, Sudan. Alexandria Eng. J. 2014, 53, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Liu, X.; Niu, J.; Lei, X.; Zhang, Z. Real-time water level prediction of cascaded channels based on multilayer perception and recurrent neural network. J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizi, Z.; Batki, B.; Ratki, L.; Szalanczi, S.; Rehevary, I.; Kozak, P.; Kiss, T. Water level prediction using long short-term memory neural network model for a lowland river: a case study on the Tisza River, Central Europe. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivapragasam, C.; Maheswaran, R.; Venkatesh, V. Genetic programming approach for flood routing in natural channels. Hydrol. Process 2008, 22(5), 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latt, Z.Z. Application of feedforward artificial neural network in Muskingum flood routing: a black-box forecasting approach for a natural river system. Water Resour. Manage. 2015, 29, 4995–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoo, M.; Ramezani, F.; Hadzima-Nyarko, M.; Nyarko, E.K.; Nikoo, M. Flood-routing modeling with neural network optimized by social-based algorithm. Nat. Hazards. 2016, 82, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanvand, M.R.; Karami, H.; Mousavi, S.-F. Investigation of neural network and fuzzy inference neural network and their optimization using meta-algorithms in river flood routing. Nat. Hazards 2018, 94, 1057–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayfur, G.; Singh, V.P.; Moramarco, T.; Barbetta, S. Flood hydrograph prediction using machine learning methods. Water 2018, 10(8), 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashazadeh, A.; Javan, M. Comparison of the gen expression programming, artificial neural network (ANN), and equivalent Muskingum inflow models in the flood routing of multiple branched rivers. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 139, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Yeh, H.-C.; Kao, S.-P.; Wei, C.; Su, P.-Y. Water level forecasting in tidal rivers during typhoon periods through ensemble empirical model decomposition. Hydrology 2023, 10(2), 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katipoglu, O.M.; Sarigo, M. Coupling machine learning with signal process techniques and particle swarm optimization for forecasting flood routing calculations in the Eastern Black Sea Basin, Turkiye. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 46074–46091. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katipoglu, O.M.; Sarigol, M. Prediction of flood routing results in the Central Anatolian region of Turkiye with various machine learning models. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 37, 1–20.
- Katipoglu, O.M.; Sarigol, M. Boosting flood routing prediction performance through a hybrid approach using empirical model decomposition and neural networks: a case of the Mera River in Ankara. Water Supply 2023c, 288.
- Safavi, H.R.; Esmikhani, M. Conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater: application of support vector machines (SVMs) and generic algorithms. Water Resour. Manage. 2013, 27, 2623–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbar, A.; Mirarabi, A.; Nakhaei, M.; Talkhabi, M.; Jamali, M. A Comparative Analysis of Data-Driven Models (SVR, ANFIS, and ANNs) for Daily Karst Spring Discharge Prediction. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 589–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarzad, M.; Eskandari, F.; Vanjani, N.J.; Arabasadi, A. Drought forecasting by ANN, ANFIS and SVM and comparison of the models. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, P.; Anctil, F.; Rasmussen, P.; Bobee, B. A recurrent neural networks approach using indices of low-frequency climatic variability to forecast regional annual runoff. Hydrol. Process 2000, 14, 2755–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.-B. Learning capability and storage capacity of two-hidden-layer feedforward networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2003, 14(2), 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiti, S.; Tiwari, R.K. A comparative study of artificial neural networks Bayesian neural networks and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system in groundwater level prediction. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 3147–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atashpaz-Gargari, E.; Lucas, C. Imperialist competitive algorithm: an algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. IEEE congress on evolutionary computation 2007, 4661–4666. [Google Scholar]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; McClelland, J.L.; James, L. Parallel distribution processing: exploration in the microstructure of cognition. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1986.
- Mohan, S. Parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models using genetic algorithm. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1997, 123(2), 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, R. Parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models using the Nelder-Mead simplex algorithm. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16(11), 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geem, Z.W. Parameter estimation for the nonlinear Muskingum model using the BFGS techniques. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2006, 132(5), 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Kang, L.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, M. Deep Learning Framework with Time Series Analysis Methods for Runoff Prediction. Water 2021, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Machine learning. 2001, 45(1), 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetnik, V.; Liaw, A.; Tong, C.; Culberson, J.C.; Sheridan, R.P.; Feuston, B.P. Random forest: a classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43(6), 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.J.; Chang, L.C. Applying particle swarm optimization to parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14(9), 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Kim, S. River stage forecasting using wavelet packet decomposition and data-driven models. Procedia Engineering 2016, 154, 1225–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Shaikh, A.A.; Mahato, S.K.; Bhunia, A.K. Applications of new hybrid algorithm based on advanced cuckoo search and adaptive Gaussian quantum behaved particle swarm optimization in solving ordinary differential equations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 172(15), 114646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy G.T. The unit hydrograph and flood routing. Proc., Conference of the North Atlantic Division, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, New London, CT, 1938.
- Akbari, K.; Hessami-kermani, M.-R. Parameter estimation of Muskingum model using grey wolf optimizer algorithm. MethodsX 2021, 101589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Geem, Z.W.; Kim, E.S. Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model using harmony search. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37(5), 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xie, J. Parameter estimation for nonlinear Muskingum model based on immune clonal selection algorithm. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15(10), 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geem, Z.W. Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum model using parameter-setting-free harmony search. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2011, 16(8), 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.M.; Qiu, L.; Chen, S.Y. Estimation of nonlinear Muskingum model parameter using Differential Evolution. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17(2), 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahan, H.; Gurarslan, G.; Aff.M.ASCE; Geem, Z.W. Parameter estimation of the nonlinear Muskingum flood-routing model using a hybrid harmony search algorithm. J. Hydro. Eng. 2013, 18, 352-360.
- Ouyang, A.; Li, K.; Truong, T.K.; Sallam, A.; Sha, E.H.M. Hybrid particle swarm optimization for parameter estimation of Muskingum model. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 1785–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, O.B.; Hamedi, F.; Fallah-Mehdipour, E.; Orouji, H.; Marino, M.A. Application of a hybrid optimization method in Muskingum parameter estimation. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2015, 141(12), 482-489.
- Niazkar, M.; Afzali, S.H. Assessment of modified honey bee mating optimization for parameter estimation of nonlinear Muskingum models. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20(4), 04014055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, F.; Bozorg-Haddad, O.; Pazoki, M.; Asgari, H.R.; Parsa, M.; Loaiciga, H.A. Parameter estimation of extended nonlinear Muskingum models with the weed optimization algorithm. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142(12), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, A.; Behmanesh, J.; Farsijani, A. Parameter estimation for the new four-parameter nonlinear Muskingum model using the particle swarm optimization. Water Resour. Manage. 2016, 30(7), 2143–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazkar, M.; Afzali, S.H. Application of new hybrid optimization technique for parameter estimation of new improved version of Muskingum model. Water Resour. Manage. 2016, 30(13), 4713–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehteram, M.; Othman, F.B.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Afan, H.A.; Allawi, M.F.; Malek, M.B.A.; Ahmed, A.N.; Shahid, S.; Singh, V.P.; EI-Shafie, A. Improving the Muskingum flood routing method using a hybrid of particle swarm optimization and bat algorithm. Water 2018, 1(6), 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, N.; Karami, H.; Farzin, S.; Ehteram, M.; Kisi, O.; Shafie, A.El. A new method for flood routing utilizing four-parameter nonlinear Muskingum an Shark algorithm. Water Resour. Manage. 2019, 33, 4879–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, R.; Hessami-Kermani, M.R.; Shojaee, S. Flood routing: improving outflow using a new nonlinear muskingum model with four variable parameters coupled with PSO-GA algorithm. Water Resour. Manage. 2020, 34(10), 3219–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, H.; Bazargan, J. Effects of uncertainty in determining the parameters of the linear Muskingum method using the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. J. Water and Climate Change 2021, 12(5), 2055–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkan, U.; Kirdemir, U. Locally tuned hybridized particle swarm optimization for the calibration of the nonlinear Muskingum flood routing model. J. Water Clim. Change 2020, 11(S1), 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, X.; Liu, H.-B.; Liu, L.-B. A new hybrid cuckoo quantum-behavior particle swarm optimization algorithm and its application in Muskingum model. Neural Processing Letters 2023, 55, 8309–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chadha, M.; Olsen, N.; Yeates, E.; Turner, J.; Gugaratshan, G.; Qian, G.; Todd, M.D.; Hu, Z. Machine learning-enabled calibration of river routing model parameters. J. Hydroinformatics 2023, 25(5), 1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Schmitz, G.; Cullmann, J. Flood routing modelling with Artificial Neural Network. Adv. Geosci. 2006, 9, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.R.; Theobald, S.; Nestmann, F. Simulation of flood flow in a river system using artificial neural networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9(4), 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, S.; Karamouz, M. Adaptive neural networks for flood routing in river systems. Water Int. 2007, 32(3), 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalkhani, H.; Golian, S.; Saghafian, B.; Farokhnia, A.; Shamseldin, A. Application of surrogate artificial intelligent models for real-time flood routing. Water Environ. J. 2013, 535, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, Z.; Yao, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Saifullah, M. Coupling the k-nearest neighbor procedure with the Kalman filter for real-time updating of the hydraulic model in flood forecasting. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2016, 31, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, S.; Patidar, S.; Xia, X.; Liang, Q.; Neal, J.; Pender, G. A deep convolutional neural network model for rapid prediction of fluvial flood inundation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, A.M. River flood routing using artificial neural networks. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 101904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, A.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Tian, Y. Effects of Training Data on the Learning Performance of LSTM Network for Runoff Simulation. Water Resour. Manag. 2022, 36, 2381–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Paper | No. of citations | Journal | Impact factor | Studied river | Adopted method | Compared models | Modeling performance criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | 73 | Hydrological Processes | 3.2 | Walla Walla River, USA | GP | NMM | RMSE, CC |
| [15] | 125 | Computers & Geosciences | 8.1 | Kushabhadra River, India | ANN | MIKE 11 HD | RMSE, R2, NSE, IOA, DP |
| [16] | 164 | Alexandria Engineering Journal | 6.8 | River Nile, Sudan | ANN | R2, RMSE | |
| [13] | 7 | Journal of Applied Mathematics | - | River Wyre, UK | SVM | Muskingum model | SSE |
| [20] | 19 | Water Resources Management | 4.2 | Chindwin River, Myanmar | ANN | CE, MRE, EQp, ETp | |
| [21] | 46 | Natural Hazards | 3.7 | Kheir Abad River, Iran | ANN (FF-SBA) | FF-GA, FF-PSO, Linear regression, Non-linear regression | R2, MSE |
| [22] | 18 | Natural Hazards | 3.7 | Maryam Negar River, Iran | ANN, ANFIS | MAE, RMSE, Bias, SI, SSQ | |
| [23] | 40 | Water | 3.4 | Tiber River, Italy | ANN | RCM, GA_RCM, PSO_RCM, ACO_RCM, Saint-Venant, PSO_NMM, ACO_NMM, GA_NMM | EQp, ETp, MAE, RMSE |
| [24] | 10 | Theoretical and Applied Climatology | 3.4 | Gharesoo River, Iran | GEP, ANN | Muskingum model | R2, RMSE |
| [17] | 53 | Journal of Hydrology | 6.4 | South-to-North water Diversion Project channel, China | MWLP, RWLP, LSTM, GRU | SVM, ANN | RMSE, MAE, NSE, PCC, PI |
| [25] | 3 | Hydrology | 3.2 | Tanshui River, Taiwan | EEMD and stepwise regression | CC, RMSE | |
| [26] | 4 | Environmental Science and Pollution Research | 5.8 | Turnasuyu Stream, Turkey | LSSVM, PSO-LSSVM, EMD-LSSVM, Wavelet-LSSVM, VMD-LSSVM | MAPE, NSE, MBE, R2 | |
| [27] | 1 | Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment | 4.2 | Mera Stream, Sarisu Stream, Kizilirmak River, Turkey | BT, GBM, KNN, RF, SVM, XGBoost | R2, RMSE, MAE | |
| [28] | 0 | Water Supply | 1.7 | Mera River, Turkey | EMD-CFBNN, EME-FFBNN | CFBNN, FFBNN | CC |
| [18] | 0 | Environmental Sciences Europe | 5.9 | Tisza River, Central Europe | LSTM | DLCM, MLP, Linear model, | MAE, RMSE, R2, WI |
| [14] | 2 | Water | 3.4 | Yangtze River, China | SVR, GPR, RFR, MLP, LSTM, GRU | MAPE, RMSE, NSE, TSS, KGE |
| Paper | No. of citations | Journal | Impact factor | Adopted method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | 261 | Journal of Hydraulic Engineering | 2.4 | GA |
| [48] | 278 | Journal of the American Water Resources Association | 2.4 | HS |
| [39] | 95 | Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering | 2.6 | BFGS |
| [19] | 73 | Hydrological Processes | 3.2 | GP |
| [43] | 87 | Journal of Hydrologic Engineering | 2.4 | PSO |
| [49] | 55 | Journal of Hydrologic Engineering | 2.4 | ICSA |
| [38] | 218 | Journal of Hydrologic Engineering | 2.4 | NMS algorithm |
| [50] | 65 | Journal of Hydrologic Engineering | 2.4 | Parameter-setting-free HS |
| [51] | 55 | Journal of Hydrologic Engineering | 2.4 | DE |
| [52] | 157 | Journal of Hydrologic Engineering | 2.4 | BFGS-HS |
| [53] | 55 | Neural Computing and Application | 6 | HPSO |
| [54] | 15 | Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering | 2.6 | SFLA-NMS |
| [55] | 65 | Journal of Hydrologic Engineering | 2.4 | MHBMO algorithm |
| [56] | 23 | Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering | 2.6 | WOA |
| [57] | 42 | Water Resources Management | 4.3 | PSO |
| [58] | 37 | Water Resources Management | 4.3 | MHBMO-GRG |
| [1] | 33 | Water Resources Management | 4.3 | BSA evolutionary algorithm |
| [59] | 39 | Water | 3.4 | HBSA |
| [23] | 40 | Water | 3.4 | PSO, ACO, GA |
| [60] | 11 | Water Resources Management | 4.3 | SA |
| [61] | 13 | Water Resources Management | 4.3 | PSO-GA |
| [62] | 9 | Water & Climate Change | 2.8 | PSO |
| [63] | 13 | Water & Climate Change | 2.8 | PSO-LM |
| [47] | 4 | MethodsX | 1.9 | GWO algorithm |
| [64] | 0 | Neural Processing Letters | 3.1 | C-QPSO |
| [65] | 0 | Hydroinformatics | 2.7 | GPR, GMC, RF, XGBoost |
| Paper | No. of citations | Journal | Impact factor | Studied river | Adopted method | Compared model | Modeling performance criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [67] | 88 | Hydrology and Earth System Science | 6.3 | Neckar River, Germany | ANN & a one-dimensional hydrodynamic numerical model | - | CE, R2, RMSE, DPF |
| [66] | 40 | Advances in Geosciences | 1.6 | Freiberger Mulde River, Germany | HEC-RAS & ANN | HEC-RAS | R2 |
| [68] | 14 | Water International | 2.6 | Karoon River, Iran | HEC-RAS & adaptive ANNs | HEC-RAS, Muskingum routing method | CE, PWRMSE, mean error of time to peak, volume error of highest peaks |
| [69] | 36 | Water and Environment Journal | 2 | Doogh River, Iran | HEC-RAS & ANN; HEC-RAS & ANFIS | HEC-RAS | NSE, MRE, RMSE |
| [70] | 64 | International Journal of Sediment Research | 3.6 | Huai River, China | KN2K & one-dimensional hydraulic model | KF & one-dimensional hydraulic model | NSE, ANSE, SDE |
| [71] | 101 | Journal of Hydrology | 6.4 | Eden Catchment, UK | LISFLOOD-FP & CNN | LISFLOOD-FP, SVR | NSE, RMSE |
| [10] | 0 | Water | 3.4 | Han River, South Korea | HM-ANN | HM, ANN | RMSE, NSE |
| [72] | 2 | Ain Shams Engineering Journal | 6 | HEC-RAS & ANN | HEC-RAS, Muskingum method | Standard error, etc. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





