1. Introduction
Geosynthetic materials, such as geotextiles, geomembranes, and geogrids, are of-ten made from recycled or recyclable materials. Their use in civil engineering projects helps in reducing the dependency on natural resources and minimizes environmental footprints [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. Soilbags are a form of application of geosynthetic materials in civil engineering [
6]. Traditionally, due to their limited durability, soilbags are primarily employed in constructing temporary embankments during floods and for building temporary structures in post-disaster scenarios [
7]. However, following aging tests conducted by Matsuoka and Liu [
8], it was asserted that soilbags exhibit enhanced durability when manufactured with anti-aging agents in the woven bags. This advancement has led to the gradual adoption of these enhanced soilbags in permanent infrastructure projects. Consequently, they are now extensively utilized in reinforcing foundations [
9,
10,
11], building retaining structures [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16], stabilizing slopes [
17,
18], and constructing small dams [
19].
The soilbag reinforced retaining structure is an important form in which soilbags applied in engineering, and several application cases and the well performance of this new type of structure have been reported [
14]. To establish a well-supported design guideline for scientifically engineering these structures, Fan et al. [
13] explored the distribution of earth pressures behind soilbag reinforced retaining walls through laboratory experiments. The stability of such walls is intricately linked to the interlayer friction of the soilbags. Addressing this, Liu et al. [
20] conducted comprehensive laboratory tests to examine the impact of the materials filled in the bags, the layered arrangement of the soilbags, and the influence of water on this interlayer friction. Fan et al. [
13] then developed a method for analyzing the sliding stability of the wall, based on the equilibrium of earth pressure and the interface resistance of soilbags. Additionally, Wang et al. [
16,
21] investigated the effects of soilbag arrangements and tail length on the displacement and earth pressure of the wall. They proposed a method for estimating the wall’s safety using the upper-bound approach. These studies collectively contribute valuable insights for designing soilbag reinforced retaining structures.
In a large number of retaining structure projects, additional surcharge loads, such as those from vehicles and buildings, are often present on the surface of the backfill behind the structures. These loads negatively impact the stability of the retaining structure [
22,
23,
24]. It is therefore essential to determine the earth pressure exerted on soilbag reinforced retaining walls when subjected to such surcharge loads. However, existing research has primarily focused on soilbag reinforced retaining walls under limit states [
13,
16]. In practical engineering situations, this state of limit equilibrium is often not reached, resulting in a non-limit state for the wall. This divergence is attributed to factors such as the restricted movement of soilbags and the complex behavior of soil. As a result, there is a need for a more sophisticated approach to accurately estimate the active earth pressure on soilbag reinforced retaining walls under surcharge loads in a non-limited state, to better mirror the actual conditions faced by these structures.
In this study, physical model tests were performed to investigate the earth pressure exerted on the soilbag reinforced retaining wall subjected to surcharge loads under the non-limited state. To predict the non-limited lateral earth pressure, an analytical method grounded in the force equilibrium of differential elements was formulated. The validity and effectiveness of this analytical approach were subsequently corroborated by the results derived from these model tests.
2. Experimental Investigations
2.1. Model Test
Fan et al. [
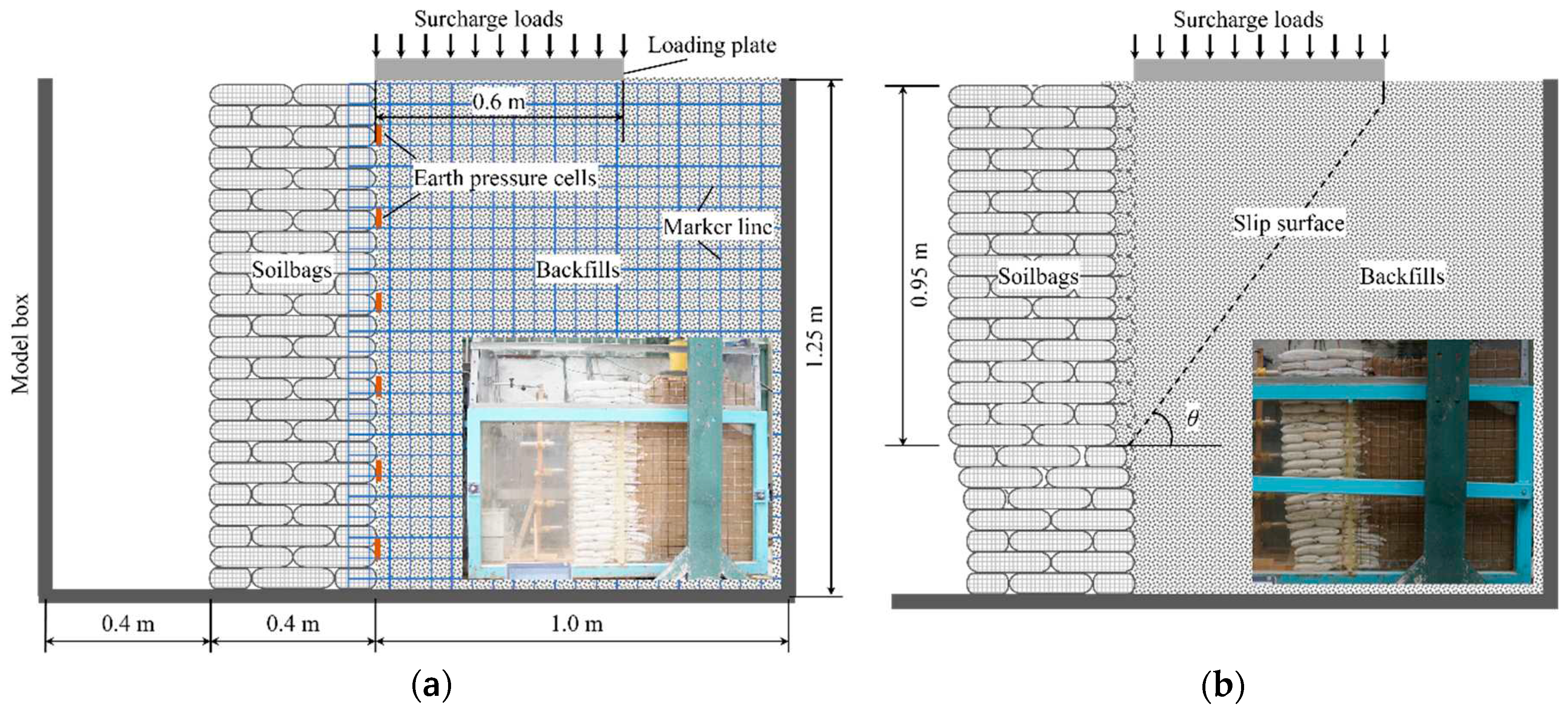
13] investigated the failure mode and earth pressure distribution of the soilbags reinforced retaining wall subjected to surcharge loads in the limited state through a model test depicted in
Figure 1. During this test, a notable phenomenon was observed when the surcharge stress reached 8.7 kPa: a sliding surface emerged in the backfill behind the wall, which aligned nearly as a straight line. This sliding surface formed an angle of 60 ° with the horizontal plane, closely resembling the theoretical angle of 45 degrees plus half the internal friction angle (φ/2), as illustrated in
Figure 1b. Within the structure of the soilbag reinforced retaining wall, a unique stepped sliding surface was identified, which penetrated through three layers of soilbags. This ladder-like sliding surface formation is attributed to the interlayer insertion of soilbags [
5]. Additionally, the upper portion of this stepped sliding surface exhibited horizontal movement. The critical height of the sliding wall (H_crit) in this scenario was measured at 0.95 m.
This present research employs the same experimental framework but focuses on assessing the earth pressure on the wall subjected to surcharge loads under non-limited conditions. In the model tests, a soilbag reinforced retaining wall measuring 80cm in length, 40 cm in width, and 120 cm in height, were constructed from two sizes of staggered soilbags, one set measuring 20 cm × 20 cm × 5 cm and the other 20 cm × 10 cm × 5 cm. The soilbags were made of woven bags with a weight of 150 g/m
2. Details on the main performance parameters of the woven bags are provided in
Table 1. The bag is filled with river sand, which was also used as the backfill soil for the wall, with a density of 1.76 g/cm
3. The maximum and minimum dry densities of the sand are 1.66 g/cm
3 and 1.89 g/cm
3, respectively, with an unevenness coefficient of
Cu=2.0, a curvature coefficient of
Cc=1.28, and an internal friction angle of 35.4°. It belongs to medium sand. A 1 m wide section of backfills lies behind the wall, with a 0.6 m wide loading plate placed at top near the wall. A centrally positioned hydraulic jack on this plate applies a consistent vertical load to the backfill, increasing the vertical load by 2 kPa each time until the wall fails. Lateral earth pressure on the soilbag reinforced retaining wall during this process are monitored using soil pressure cells, as depicted in
Figure 1a.
2.2. Test Result
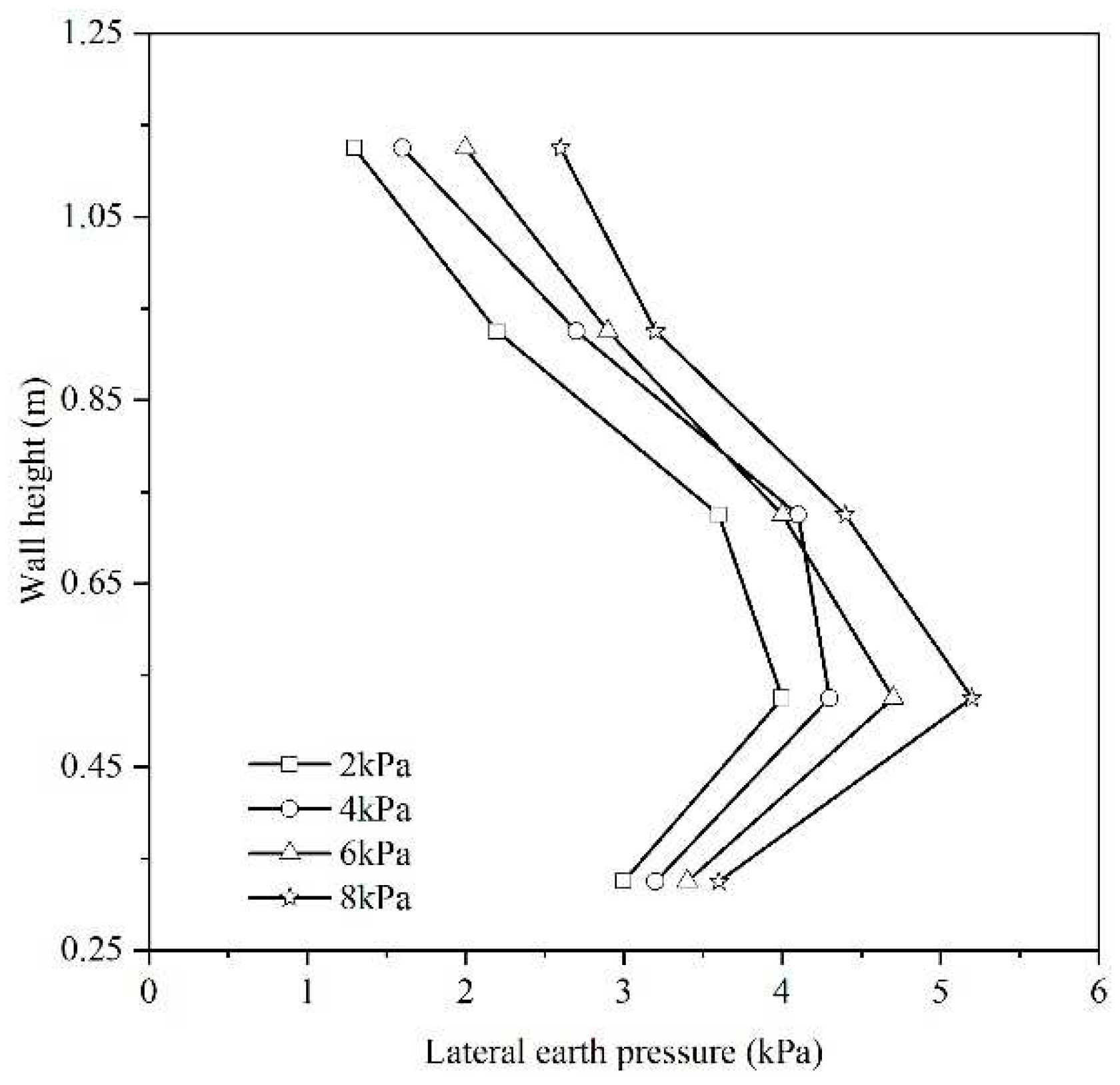
Figure 2 shows the variation in lateral earth pressure distribution along the wall height at different stages of surcharge stress, specifically at 2 kPa, 4 kPa, 6 kPa, and 8 kPa. Notably, during these stages, the retaining wall remains undamaged. The distribution of lateral earth pressure on the wall is characterized as non-linear. As the surcharge stress increases, there is a corresponding increase in the lateral earth pressure exerted on the wall.
3. Analytical Approaches
The assessment of earth pressure is a crucial component in studies focusing on retaining structures, as it significantly influences both the stability and the cost of retaining walls. Within this realm, the Rankine and Coulomb earth pressure theories are recognized as foundational approaches for estimating earth pressure. However, a limitation shared by these theories is their assumption of soil remaining static, disregarding any wall displacement. Through comprehensive model experiments, Tazaghi [
25] demonstrated that the active earth pressure displays a nonlinear pattern when retaining walls experience either translation or rotation, thereby rendering traditional earth pressure theories inadequate. Consequently, numerous academics have developed alternative approaches for calculating earth pressure under varying displacement scenarios of retaining walls. Widely adopted methods include the differential element method [
24] and the finite element numerical method [
26,
27,
28]. The differential element method, specifically, is formulated based on conditions involving a retaining wall with a vertical back, sandy soil fill, and a horizontal surface behind the wall. This method segments the sliding wedge behind the wall into horizontal soil elements, presuming a uniform vertical stress distribution across these elements. Subsequently, the earth pressure calculation solution is derived by considering both the static and moment equilibrium of the soil elements, revealing a nonlinear soil pressure distribution. This method has been effectively applied in calculating active earth pressure for various types of retaining walls, yielding favorable results [
29,
30,
31,
32].
Originally, the differential element method was utilized predominantly for calculating the active earth pressure of retaining walls in a limit state. To extend its application to non-limit states, several scholars have refined this approach. Notably, Tang and Chen [
33] contributed by developing theoretical formulations linking wall displacement to the friction angle in non-limit states. Subsequent methodologies introduced by other researchers have largely followed the foundational principles set by Tang and Chen, with variations in computing the effective friction angle under non-limit state scenarios [
34].
In the conducted model test, it was observed that the active earth pressure exerted on the soilbag reinforced retaining wall under non-limit conditions displayed a nonlinear behavior. Furthermore, the conditions under which the wall operated were consistent with the prerequisites for applying the differential element method. As a result, this method was effectively employed to compute the non-linear earth pressures that were recorded in the test.
3.1. Basic Equation for Non-Limited Active Earth Pressure
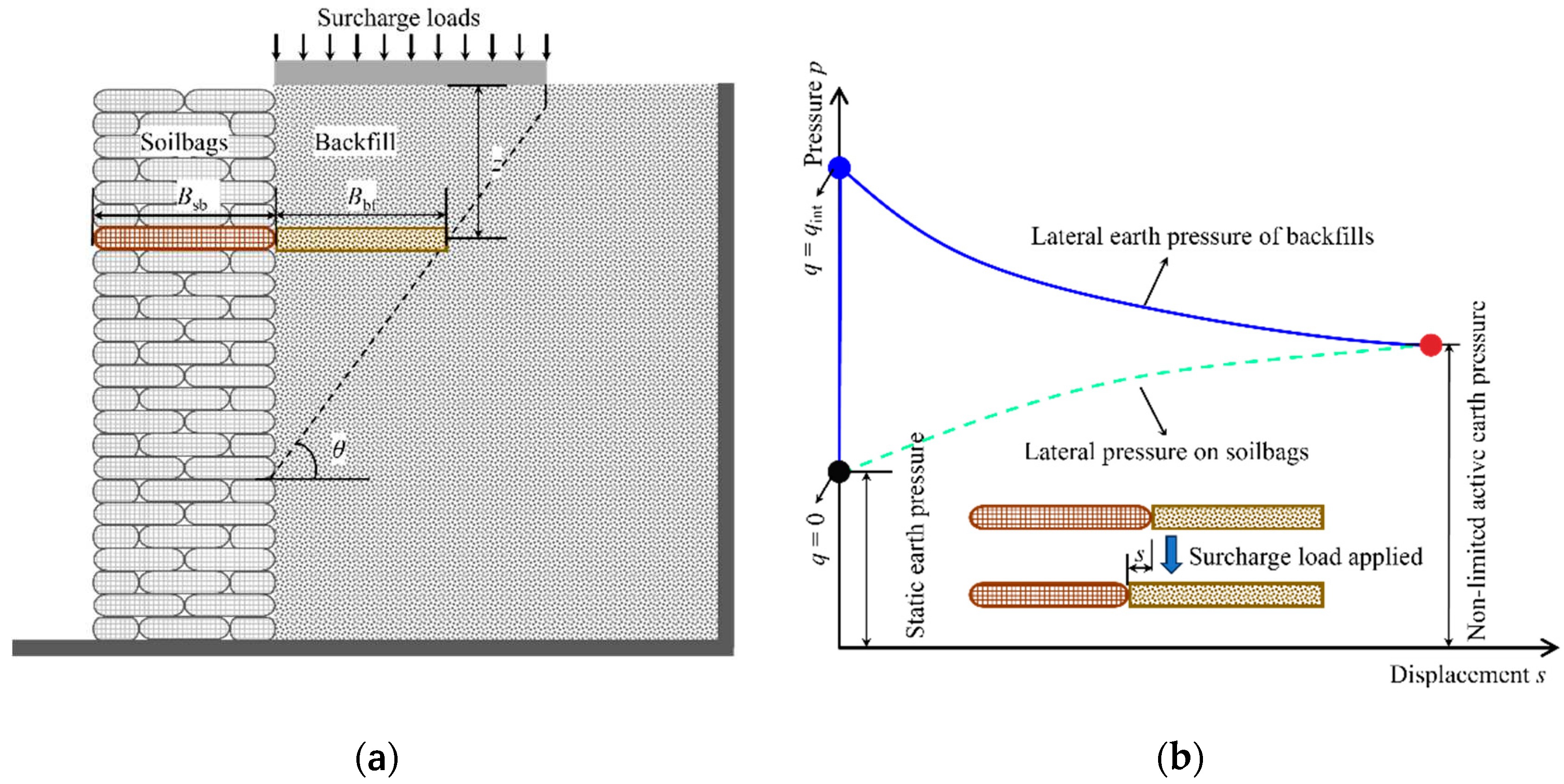
In the context of analyzing a sliding wedge as an isolated entity, as depicted in
Figure 3a, a differential flat element with a thickness of
dz is selected from the wedge, positioned at a depth
z beneath the backfill surface. In conditions where surcharge stress is absent (
q=0), the pressure exerted by the backfill due to filling is characterized as static earth pressure. Conversely, when surcharge stress, which does not compromise the integrity of the retaining wall (
q=
qint), is applied to the backfill, the soil’s immediate response is hindered, leading to a swift increase in lateral earth pressure, as demonstrated in
Figure 3b. This escalation in lateral earth pressure consequently prompts compression in the neighboring soilbag, resulting in augmented compression deformation of the soilbag. Concurrently, there is an observable increase in the swelling deformation along with a decrease in the backfill’s lateral earth pressure. Equilibrium is attained once the lateral earth pressure equilibrates with the lateral compressive stress applied on the soilbag. At this juncture, the lateral swelling deformation of the backfill matches the lateral compressive deformation of the soilbag, as shown in
Figure 3b. The relationship established upon achieving equilibrium following the application of surcharge stress
qint is as follows:
where
px-bf and
εx-bf are the lateral earth pressure and strain of the backfill,
σx-sb and
εx-sb are the lateral compressed stress and strain of soilbag,
Bbf is the width of differential flat element, and
Bsb is the width of the soilbag reinforced retaining wall.
Building upon the findings of Wang [
23], the lateral earth pressure exerted by the backfill can be expressed as:
where
Kq and Kγ are the surcharge pressure coefficient and the backfill pressure coefficient, respectively. These coefficients are inherently linked to the strain experienced by the differential flat element.
The lateral compressed stress of soilbags can be expressed as:
where
Ex-sb is the elastic modulus of soilbag, and
K0 is the static earth pressure coefficient of the backfill.
By solving simultaneous Equations (1-3), the non-limited active earth pressure exerted on soilbags reinforced retaining walls subjected to surcharge loads can be determined.
3.2. Determination of Kq and Kγ
In limited-state scenarios, retaining walls exhibit complete sliding wedges, where the backfill’s internal friction angle (
φcirt) and the friction angle at the backfill-wall interface (
δcrit) peak. In contrast, non-limited states yield only partial wedge development, resulting in lower, or intermediate, friction angles (
φint for backfill internal friction and
δint for backfill-wall friction). These intermediate values, lower than
φcirt and
δcrit, indicate a less intense stress condition. Fan et al. [
35] outline a procedure to calculate
φint and
δint,, suggesting these angles lie between their initial (
φ0 and
δ0, representing the starting internal and interface friction angles) and critical states. This approach helps in precisely gauging the frictional behavior of retaining walls under varying conditions.
The calculation equations provided by Fan et al. for
φint and
δint are as follows:
where
scrit is the critical lateral displacement necessary to reach the fully active state of the backfill. For walls with layered backfill,
δ0 is proposed to be half of
φcirt (i.e.,
δ0 =
φcirt/2), and
φ0 can be derived from Equation (6):
Sherif et al. [
36] provided an empirical equation for
scrit in retaining walls with varying densities of sand through model tests:
By solving Equations (4-7), the values of φint and δint can be determined.
From the equilibrium analysis of horizontal and vertical forces, as well as the moment equilibrium about the midpoint on the sliding surface of a differential flat element, a set of equations can be derived:
Equation (8) represents the balance of horizontal forces:
Equation (9), addressing the vertical force equilibrium, are given by:
Equation (10) pertains to the moment equilibrium:
In those equations, θ is the sliding angle (θ=45°+ φ/2), qbf is the force on the top of the element, Rbf is the normal reaction of the backfillsoil at rest, and dW is the weight of the element (dWbf =γ(Hcrit-z)cotθdz).
Equations (8) and (10) can be simplified as:
Ignoring the second-order differential terms yields, Equation (9) can be expressed as:
Substituting Equation (12) into Equation (13) yields
Substituting Equation (14) into Equation (12) yields:
where
N = 1/ (cot
δintcot(
θ-φint)-1).
By differentiation, the general solution of Equation (15) is
where C is a constant, which can be determined by the boundary condition (
z = 0,
qbf =
q,).
C is determined as
Thus, Equation (16) can also be expressed as:
Substituting Equation (18) into Equation (14),
px-bf can be obtained:
Solving for Equations (19) and (2) yields:
3.3. Determination of Ex-sb
The lateral compressive stress-strain characteristics of soilbags were investigated using a direct shear test apparatus, details of which are elaborated in the work of Fan et al. [
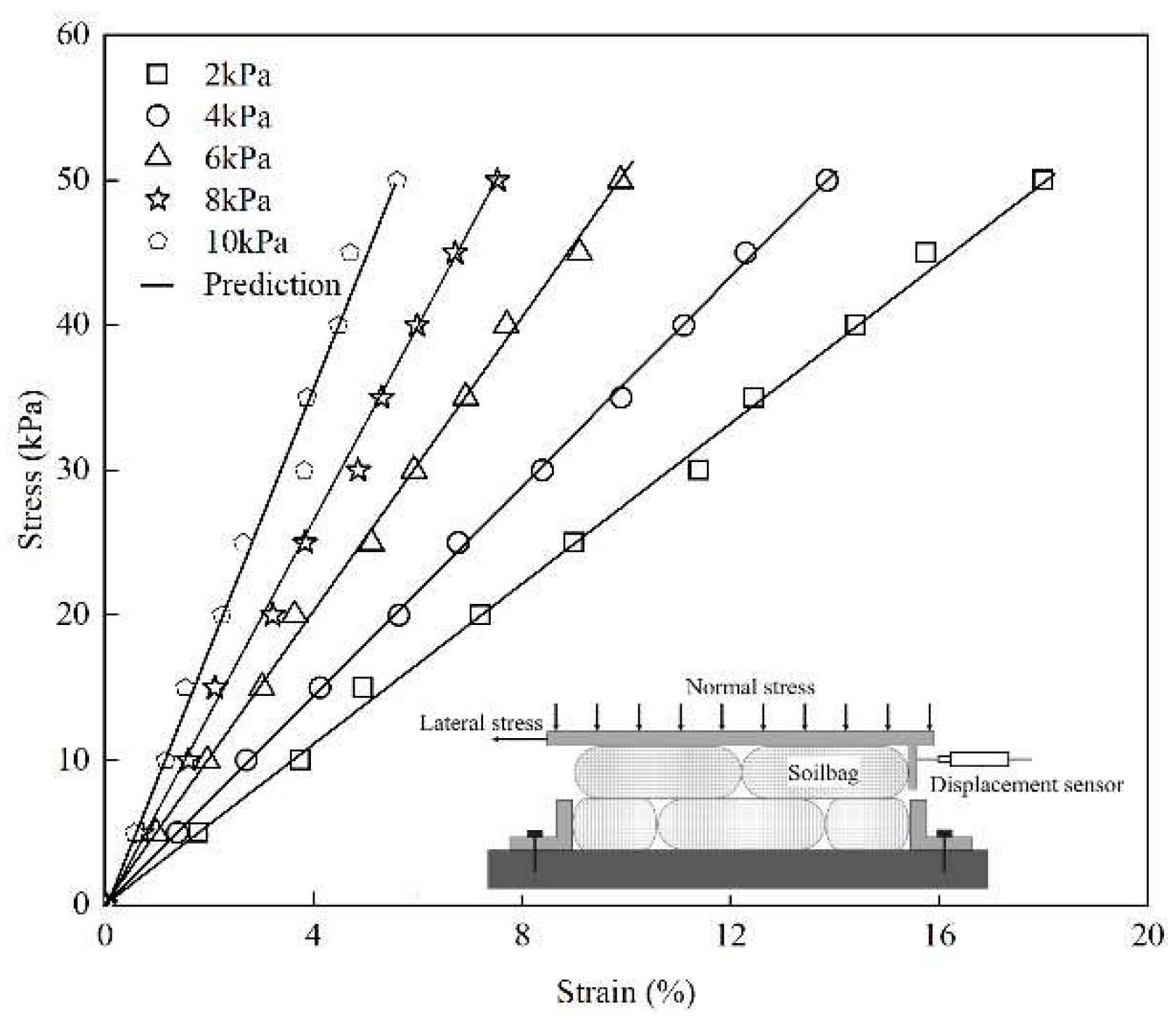
5]. In this setup, two layers of soilbags were positioned on the apparatus’s base. The lower layer was anchored using two plates fixed to the base, ensuring stability during testing. Above the soilbags, a loading plate was placed, accompanied by a right-side plate. This arrangement was designed to apply normal stresses to the soilbags. A critical component of the setup was a displacement sensor attached to the right-side plate. This sensor’s role was to precisely track any lateral displacement that occurred during the testing process. For the application of lateral force, a controlled speed of 1 mm/min was maintained, and a load cell was incorporated to measure the lateral force exerted.
The results of these tests are depicted in
Figure 4, which illustrates the lateral compressive stress-strain relationship of the soilbags under varying normal stresses. The data indicates a roughly linear relationship between lateral stress and strain across different levels of normal stress. This linear trend suggests a consistent response of the soilbags to lateral compression.
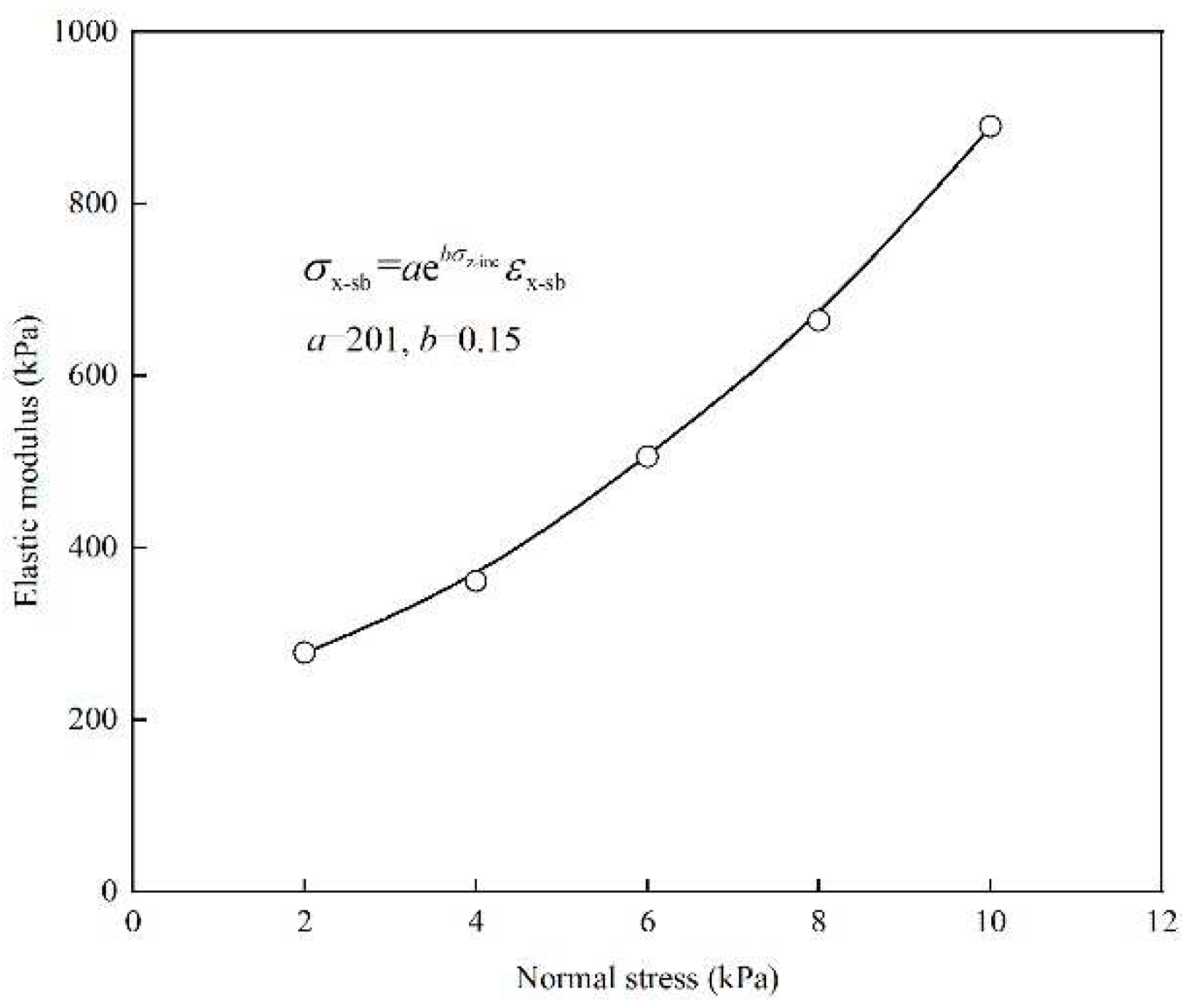
Figure 5 presents the correlation between the lateral compressive modulus (
Ex-sb) and the normal stress (
σz-sb) of the soilbag. This relationship reveals that the
Ex-sb value progressively increases as
σz-sb increases, demonstrating a distinct exponential connection between these two parameters. This observed relationship can be quantitatively described by an exponential function, where the lateral stress-strain relationship of the soilbag is modeled as:
Further simplification leads to the expression for the lateral compressive modulus (
Ex-sb) as:
3.4. Validation
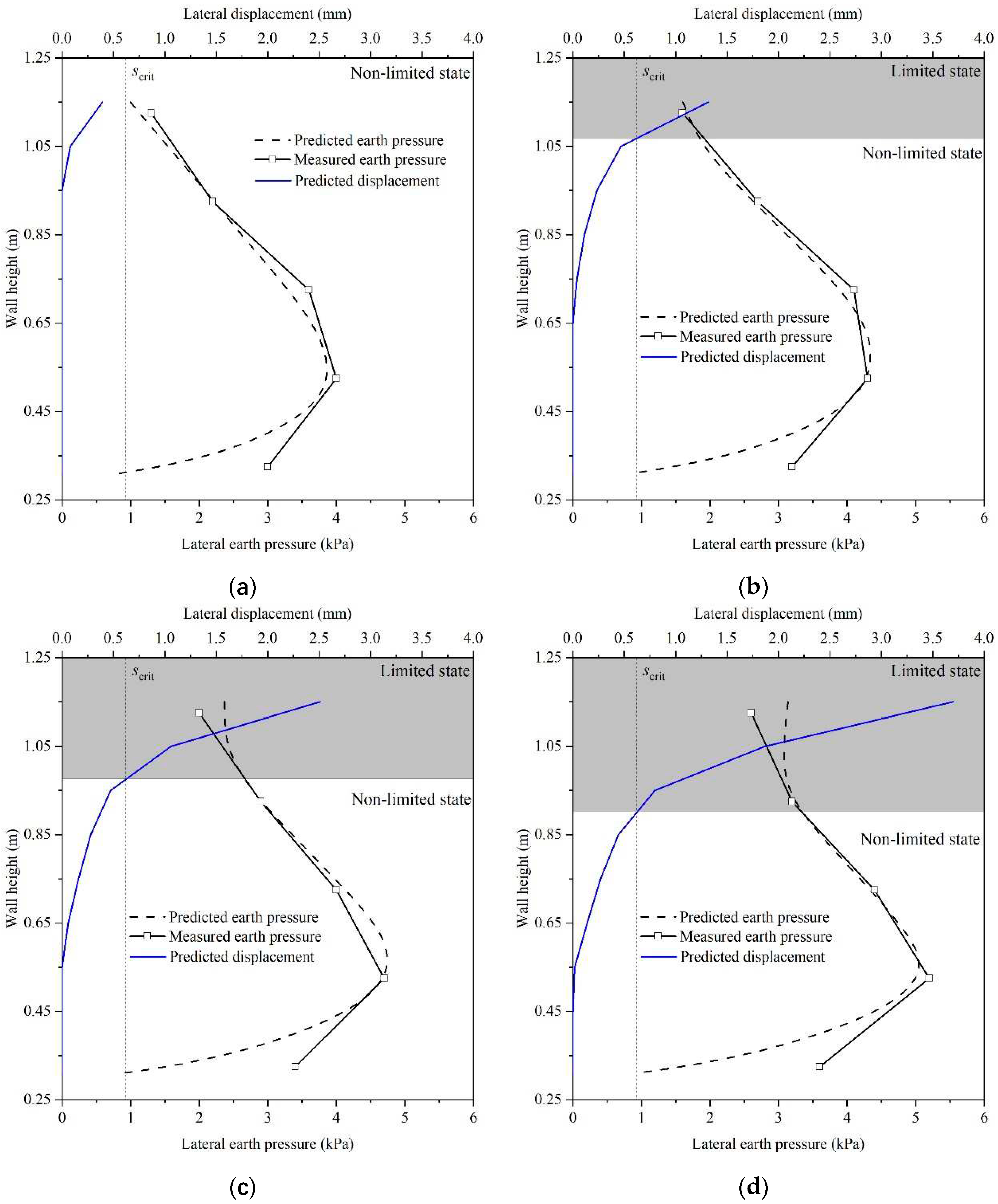
In the described model test, key parameters include the unit weight of the backfill (γ) at 17.6 kN/m3, the internal friction angle (φcrit) at 35.4°, the frictional angle between the back of the soilbag and the backfill (δcrit) at 28.1°, the width of the soilbag reinforced retaining wall (Bsb) at 0.4 m, and the critical height of the wall (Hcrit) at 0.95 m. Utilizing the previously mentioned equations, the lateral displacement and lateral earth pressures of the backfill along the wall height were calculated under varying surcharge loads of 2 kPa, 4 kPa, 6 kPa, and 8 kPa.
The findings revealed that under a 2 kPa surcharge load, the calculated lateral displacement along the wall height remained below the critical lateral displacement (
scrit). This suggests that, in this scenario, the wall did not reach its limit state, as depicted in
Figure 6a. However, as the surcharge load increased to 4 kPa, a notable change was observed. The lateral displacement of the soilbag at the upper part of the wall exceeded
scrit, indicating that this portion of the wall had reached the limit state, as shown in
Figure 6b. Furthermore, the extent of the wall reaching the limit state increased progressively with the increment of the surcharge loads, as shown in
Figure 6c,d.
Another key observation from
Figure 6a to d is the close agreement between the calculated earth pressure and the experimental data. This alignment validates the accuracy of the calculations and the effectiveness of the equations used in predicting the behavior of the soilbag and the retaining wall under different loading conditions.
4. Conclusions
Model tests on the soilbag reinforced retaining wall subjected to surcharge loads under the non-limited state were carried out to analyze the non-limited earth pressures. The findings yielded several key insights:
The lateral earth pressure distribution on the soilbag reinforced retaining wall subjected to surcharge loads under the non-limited state is non-linear. As the surcharge loads increased, there was a corresponding increase in the earth pressure.
It was determined through experimentation that the lateral stress-strain behavior of the soilbags adheres to a linear model. Furthermore, an exponential relationship between the lateral compression modulus of the soilbags and the normal stress was established.
The analytical solution, developed based on the force equilibrium of differential elements, proved to be highly effective in predicting the non-limited lateral earth pressure on the soilbag reinforced retaining wall under surcharge loads. The close agreement of this analytical solution with the experimental data highlights its potential as a reliable and accurate tool for predicting lateral earth pressure in similar scenarios.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.B. and K.F.; methodology, R.L. and Z.L.; validation, C.B., Z.W. and K.F.; formal analysis, R.L.; investigation, C.B.; resources, Z.L. and K.F.; data curation, C.B.; writing—original draft preparation, C.B.; writing—review and editing, R.L. and Z.L.; visualization, C.B. and R.L.; supervision, Z.L., Z.W. and K.F.; project administration, Z.L. and Z.W.; funding acquisition, Z.L. and Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Project (Grant number 2023YFC3206200), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number U2243219), and the Outstanding Youth and Excellent Youth Science Funds of Henan Province (Grant number 222300420013 and number 232300421065).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study may be available on reasonable request from the first or corresponding author
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Palmeira, E.M.; Araújo, G.L.S.; Santos, E.C.G. Sustainable Solutions with Geosynthetics and Alternative Construction Materials—A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Pei, Q.; Liu, L.; Han, Z.; Zou, W. Strength and microstructure of a lignin fiber-reinforced expansive soil in cold regions. Geosynth. Int. 2022, 29, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimoldi, P.; Shamrock, J.; Kawalec, J.; Touze, N. Sustainable Use of Geosynthetics in Dykes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska, J.; Kiersnowska, A.; Zięba, Z.; Trach, Y. Sustainability of Geosynthetics-Based Solutions. Environments 2023, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Zou, W.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y. Laboratory investigation and theoretical analysis of lateral pressure exerted by expansive soils on retaining walls with expanded polystyrene geofoam block upon water infiltration. Geotext. Geomembranes 2023, 52, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Liu, S.H.; Cheng, Y.P.; Liao, J. Effect of infilled materials and arrangements on shear characteristics of stacked soilbags. Geosynth. Int. 2020, 27, 662–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Freeman, M.; FitzPatrick, B.T.; Nevius, D.B.; Plaut, R.H.; Filz, G.M. Use of an apron to stabilize geomembrane tubes for fighting floods. Geotext. Geomembranes 2004, 22, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, H.; Liu, S.H. New earth reinforcement method by soilbags (‘Donow’). Soils Found. 2003, 43, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, G.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Hu, X. Effect of sand bags on vibration reduction in road subgrade. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2017, 100, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.Y.; Wu, J.L.; Wang, J.; Fu, H.T.; Liu, F.Y. Experimental study on vibration reduction by using soilbag cushions under traffic loads. Geosynth. Int. 2018, 25, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-H.; Gao, J.-J.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Weng, L.-P. Experimental study on vibration reduction by using soilbags. Geotext. Geomembranes 2014, 42, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-J.; Liu, S.-H.; Zhou, B. Experimental study on the inclusion of soilbags in retaining walls constructed in expansive soils. Geotext. Geomembranes 2015, 43, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Liu, S.H.; Cheng, Y.P.; Wang, Y. Sliding stability analysis of a retaining wall constructed by soilbags. Géotechnique Lett. 2019, 9, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fan, K.; Xu, S. Field study of a retaining wall constructed with clay-filled soilbags. Geotext. Geomembranes 2019, 47, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Jiang, E.; Fan, K.; Liu, S.H.; Wang, Y. Full-scale tests on soilbag-constructed retaining walls with a panel. Geosynth. Int. 2023, 30, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Liu, K.; Li, X.; Ren, Q.-B.; Li, L.-L.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Li, M.-C. Experimental and upper-bound study of the influence of soilbag tail length on the reinforcement effect in soil slopes. Geotext. Geomembranes 2019, 47, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Bai, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Treatment for Expansive Soil Channel Slope with Soilbags. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2012, 26, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, C.; Fan, K.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Shen, C.; Han, Z. Repairing expansive soil channel slope with soilbags. Geosynth. Int. 2023, 30, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, K.; Aqil, U.; Mohri, Y.; Tatsuoka, F. Shear strength and deformation characteristics of geosynthetic soil bags stacked horizontal and inclined. Geosynth. Int. 2008, 15, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Fan, K.W.; Chen, X.; Jia, F.; Mao, H.; Lin, Y. Experimental studies on interface friction characteristics of soilbags. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 38, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, Y.-L.; Liu, K.; Li, X.; Yang, F. Slope displacement and soil pressure of soilbag-retaining wall influenced by arrangement. Geosynth. Int. 2023, 30, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, T.; Dasaka, S. Transition of earth pressure on rigid retaining walls subjected to surcharge loading. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2012, 6, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Yan, J.; Zou, W.; Han, Z.; Lai, Z. Active earth pressure on non-yielding retaining walls with geofoam blocks and granular backfills. Transp. Geotech. 2022, 33, 100712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Z. Distribution of earth pressure on a retaining wall. Géotechnique 2000, 50, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K. Large retaining-wall tests. I. Pressure of dry sand. Eng. News Rec. 1934, 102, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Jamsawang, P.; Voottipruex, P.; Jongpradist, P.; Likitlersuang, S. Field and three-dimensional finite element investigations of the failure cause and rehabilitation of a composite soil-cement retaining wall. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 127, 105532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.-H.; Zheng, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W. An improved semi-implicit material point method for simulating large deformation problems in saturated geomaterials. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 161, 105614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.-H.; Liu, M.; Guo, N.; Dai, B.-B.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. A temporal stable smoothed particle finite element method for large deformation problems in geomechanics. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 156, 105298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Nimbalkar, S.; Chiaro, G. Determination of Active Earth Pressure on Rigid Retaining Wall Considering Arching Effect in Cohesive Backfill Soil. Int. J. Geomech. 2016, 16, 04015082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Lin, Y.-L.; Guo, D.-D.; Xing, H.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, J.-Y. A modified Newmark block method for determining the seismic displacement of a slope reinforced by prestressed anchors. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 162, 105697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-Q.; Lin, C.; Lin, L.-B.; Huang, M. Active earth pressure of narrow cohesive backfill on rigid retaining wall of rotation about the bottom. Soils Found. 2021, 61, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Jin, J.; Jiang, Z.H.; Liu, W.; Liu, H.D.; Li, R.F.; Liu, X. Seismic response of combined retaining structure with inclined rock slope. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2022, 84, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, J.G. Calculation of Active Earth Pressure in the Non-Limit State Based on Wedge Unit Method. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 2020, 56, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xiao, S.G. Calculation method for displacement-dependent earth pressure on a rigid wall rotating around its base. Int. J. Geomech. 2021, 21, 04021132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Yang, G.; Zou, W.; Han, Z.; Shen, Y. Lateral earth pressure of granular backfills on retaining walls with expanded polystyrene geofoam inclusions under limited surcharge loading: Experimental Studies and Analytical Approaches. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherif, M.A.; Ishibashi, I.; Lee, C.D. Earth Pressures against Rigid Retaining Walls. J. Geotech. Eng. Div. 1982, 108, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).