Submitted:
31 March 2024
Posted:
02 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
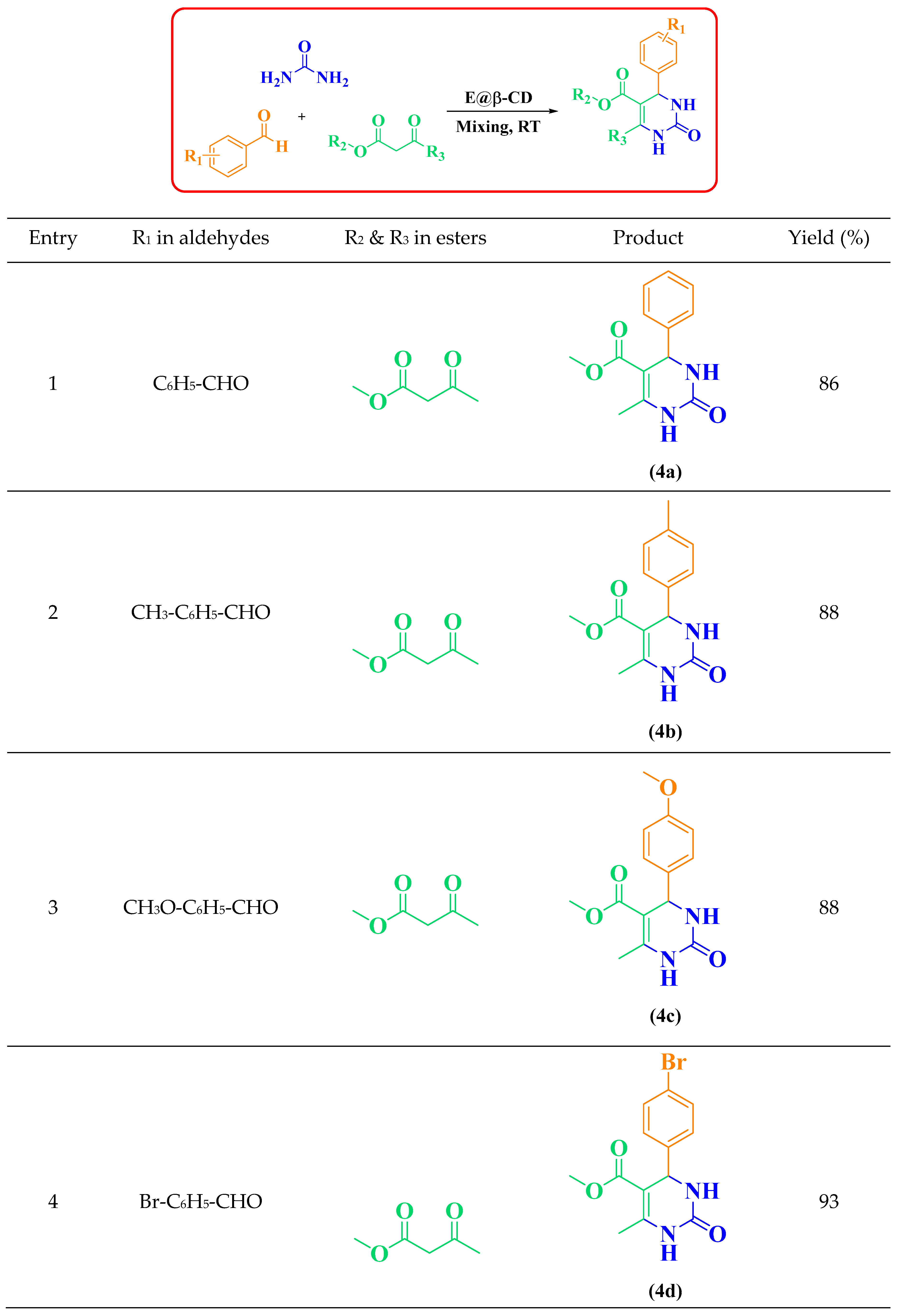
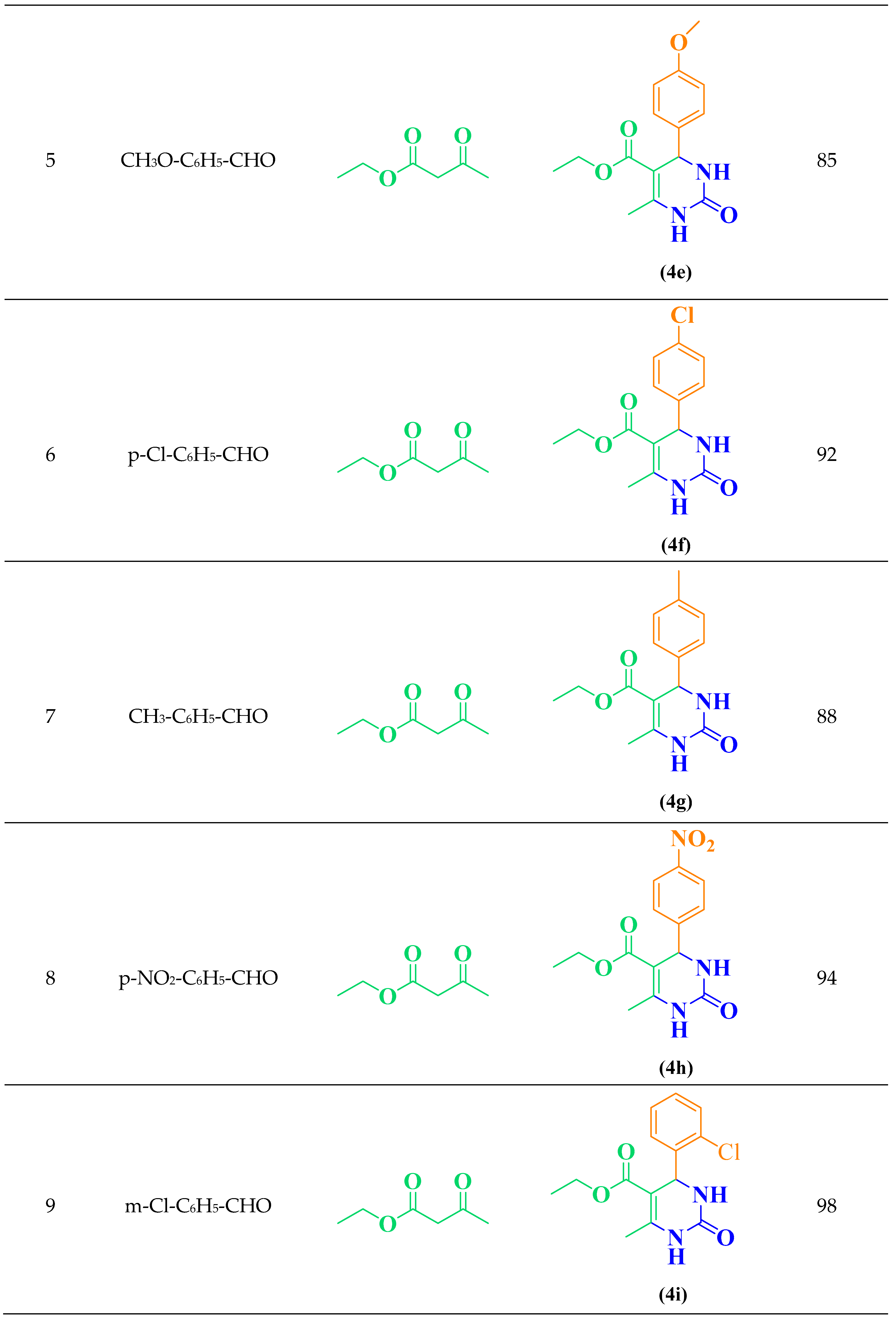
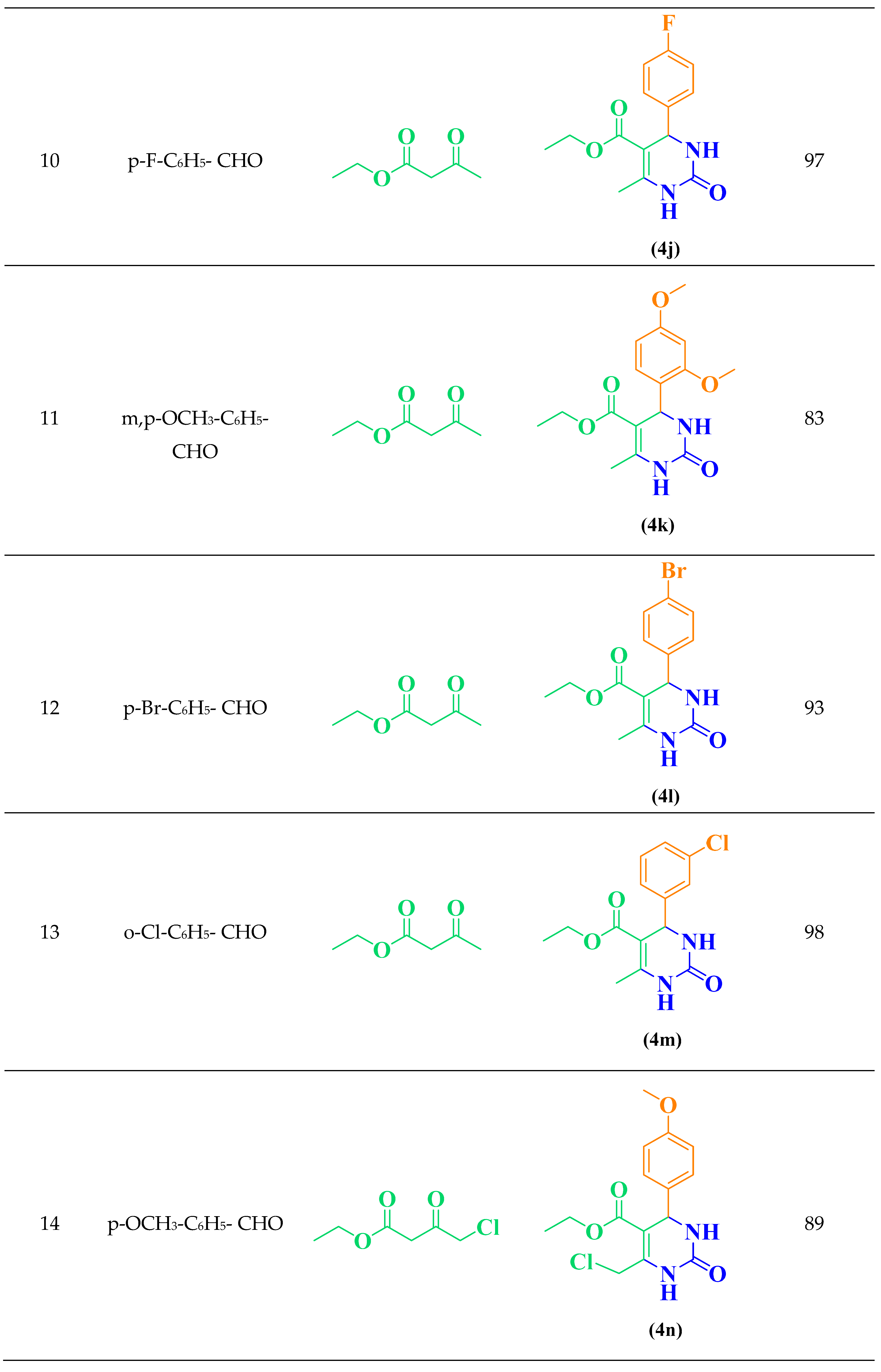
2.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones DHPMs (4 a-r)
2.2. Molecular Docking Studies
3. Result and Discussion
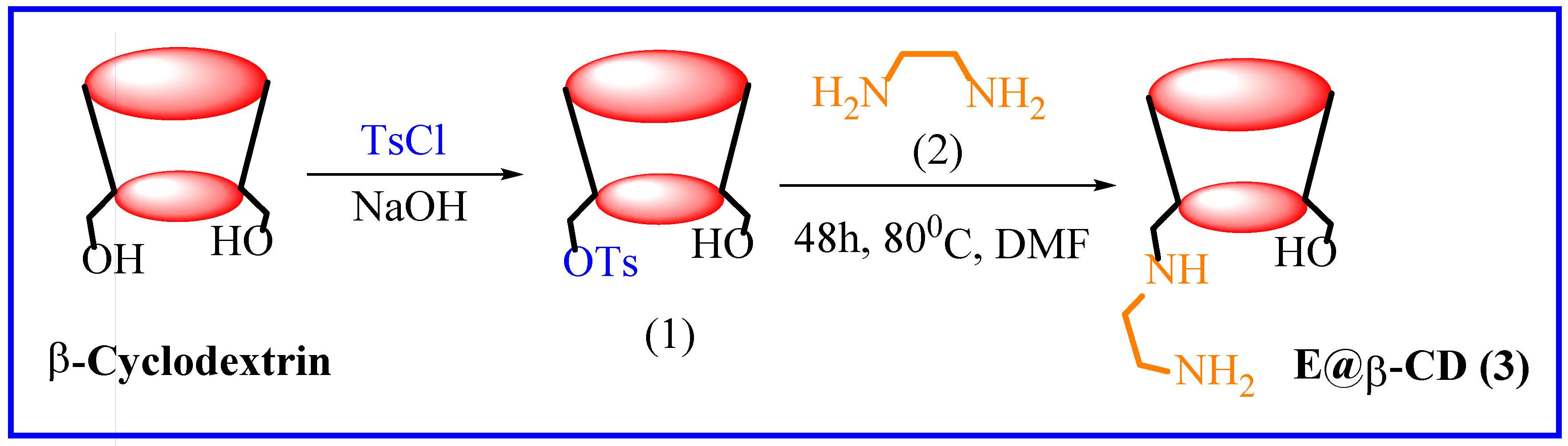
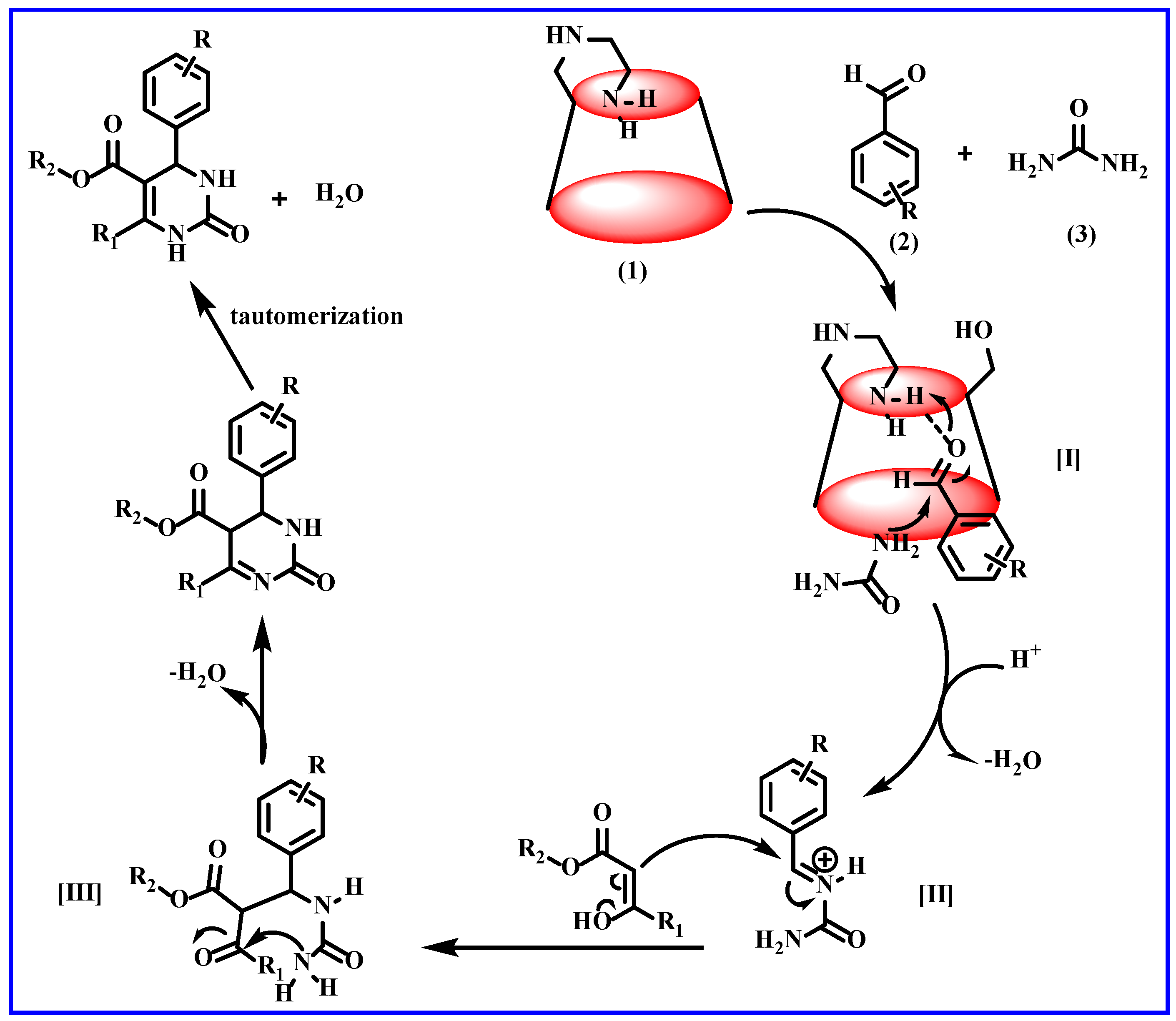
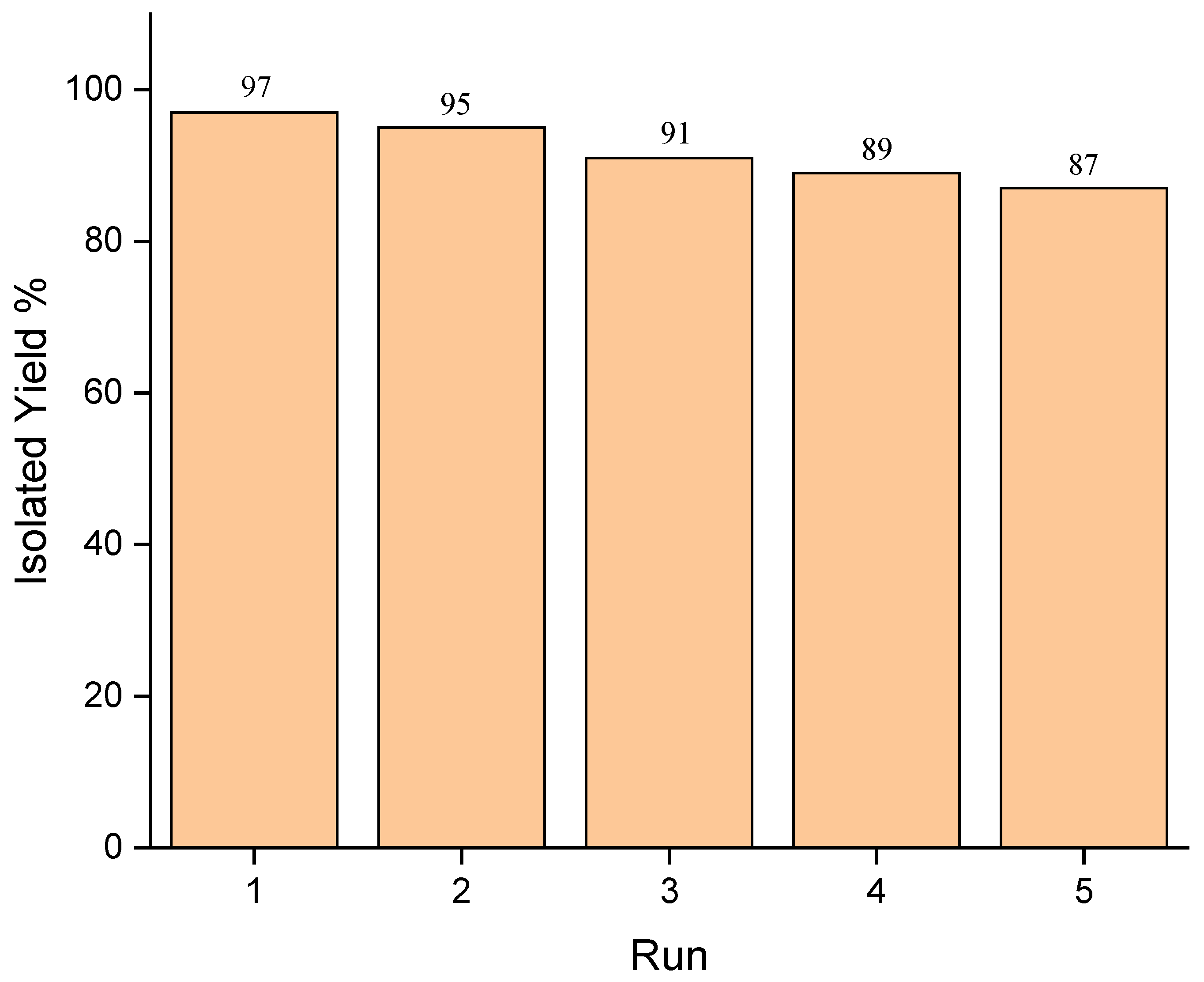
3.1. E@β-CD Catalyzed for Multi-Component Reactions
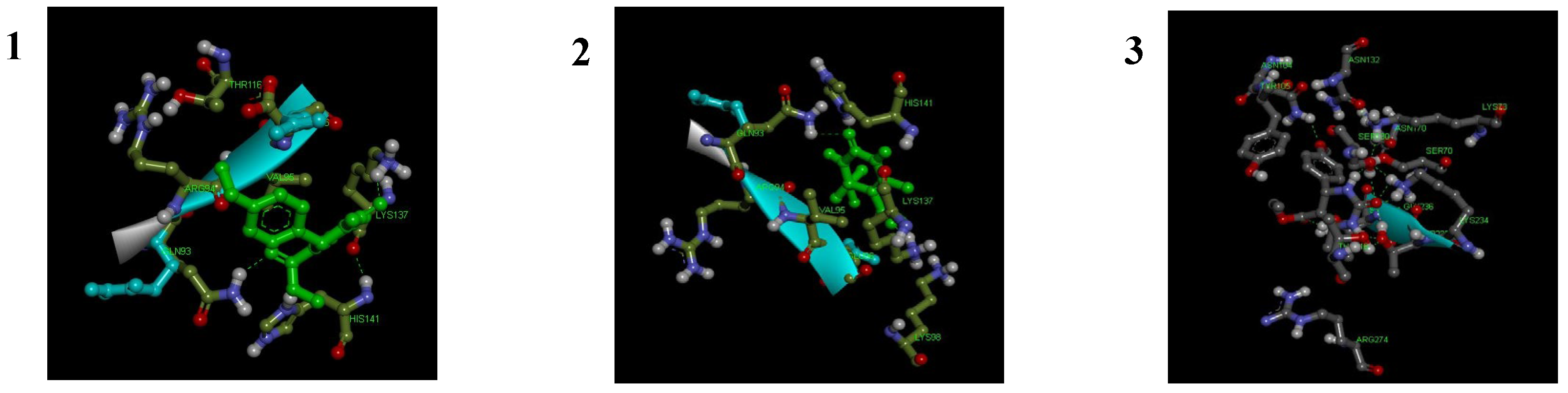
3.2. In-Silico Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethical Approval
Declaration of Competing Interest
Availability of Data and Materials
Acknowledgments
References
- Gregorio, C. (2014) Review : A History of Cyclodextrins Gre g. Chemical Reviews. [CrossRef]
- Mitra, B., Chandra Pariyar, G., Ghosh, P. (2021) β-Cyclodextrin: a supramolecular catalyst for metal-free approach towards the synthesis of 2-amino-4,6-diphenylnicotinonitriles and 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1 H )-one, RSC Advances, 11 1271–1281. [CrossRef]
- Jie K., Zhou, Y., Yao, Y., Huang, F., (2015) Macrocyclic amphiphiles, Chemical Society Reviews, 44 3568–3587. [CrossRef]
- Hapiot, F.; Monflier, E. Unconventional Approaches Involving Cyclodextrin-Based, Self-Assembly-Driven Processes for the Conversion of Organic Substrates in Aqueous Biphasic Catalysis. Catalysts 2017, 7, 173, . [CrossRef]
- Szejtli, J. Introduction and General Overview of Cyclodextrin Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1743–1754, . [CrossRef]
- Vyas, A., Saraf, S., Saraf, S. (2008) Cyclodextrin based novel drug delivery systems, Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry, 62 23–42. [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, S.; Shaabani, A.; Ng, S.W. One-Pot Synthesis of Coumarin-3-carboxamides Containing a Triazole Ring via an Isocyanide-Based Six-Component Reaction. ACS Comb. Sci. 2014, 16, 176–183, . [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Saha, A. Free-ZnO nanoparticles: a mild, efficient and reusable catalyst for the one-pot multicomponent synthesis of tetrahydrobenzo[b]pyran and dihydropyrimidone derivatives. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 4170–4175, . [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Chang, L.; Hou, Z.; Shang, D.; Liu, X.; Feng, X. An Enantioselective Biginelli Reaction Catalyzed by a Simple Chiral Secondary Amine and Achiral Brønsted Acid by a Dual-Activation Route. Chem. – A Eur. J. 2008, 14, 3177–3181, . [CrossRef]
- Shiri, L.; Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A.; Kazemi, M. Synthesis and characterization of DETA/Cu(NO3)2 supported on magnetic nanoparticles: a highly active and recyclable catalyst for the solvent-free synthesis of polyhydroquinolines. Monatshefte Fuer Chemie/chemical Mon. 2017, 148, 1131–1139, . [CrossRef]
- Kühl, O. N-heterocyclic germylenes and related compounds. Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2004, 248, 411–427, . [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Rico, J. L., Vidal-Ferran, A. (2013) [Ir(P−OP)]-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrogenation of Diversely Substituted C═N-Containing Heterocycles, Organic Letters, 15 2066–2069. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Hülsey, M.J.; Yan, N. One-Step Synthesis of N-Heterocyclic Compounds from Carbohydrates over Tungsten-Based Catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 11096–11104, . [CrossRef]
- Yam, V.W.-W.; Lee, J.K.-W.; Ko, C.-C.; Zhu, N. Photochromic Diarylethene-Containing Ionic Liquids and N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 912–913, . [CrossRef]
- Ruamps, M.; Lugan, N.; César, V. A Cationic N-Heterocyclic Carbene Containing an Ammonium Moiety. Organometallics 2017, 36, 1049–1055, . [CrossRef]
- Nayak, N.; Ramprasad, J.; Dalimba, U. New INH–pyrazole analogs: Design, synthesis and evaluation of antitubercular and antibacterial activity. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5540–5545, . [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.C.; Vaja, D.V.; Jadeja, K.A.; Joshi, S.B.; Khedkar, V.M. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Docking Study of Pyrazole, Pyrazoline Clubbed Pyridine as Potential Antimicrobial Agents. Anti-Infective Agents Med. Chem. (Formerly ‘Current Med. Chem. - Anti-Infective Agents) 2020, 18, 306–314, . [CrossRef]
- Amnerkar, N.D.; Bhusari, K.P. Synthesis, anticonvulsant activity and 3D-QSAR study of some prop-2-eneamido and 1-acetyl-pyrazolin derivatives of aminobenzothiazole. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 149–159, . [CrossRef]
- El-Malah, A., Mahmoud, Z., Hamed Salem, H., Abdou, A.M., Soliman, M.M.H., Hassan, R.A. (2021) Design, ecofriendly synthesis, anticancer and antimicrobial screening of innovative Biginelli dihydropyrimidines using β-aroylpyruvates as synthons, Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 14 221–233. [CrossRef]
- El-Sabbagh, O.I.; Baraka, M.M.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Pannecouque, C.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R.; Balzarini, J.; Rashad, A.A. Synthesis and antiviral activity of new pyrazole and thiazole derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 3746–3753, . [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Qin, S.; Jin, J. Efficient Biginelli Reaction Catalyzed by Sulfamic Acid or Silica Sulfuric Acid under Solvent-Free Conditions. Synth. Commun. 2007, 37, 47–52, . [CrossRef]
- Slimi, H., Moussaoui, Y., ben Salem, R. (2016) Synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones/thiones via Biginelli reaction promoted by bismuth(III)nitrate or PPh3 without solvent, Arabian Journal of Chemistry, 9 S510–S514. [CrossRef]
- Zahiri, S., Mokhtary, M. (2015) Bi(NO 3 ) 3 ·5H 2 O: An efficient catalyst for one-pot synthesis of 3-((aryl)(diethylamino)methyl)-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-ones and biscoumarin derivatives , Journal of Taibah University for Science, 9 89–94. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Siddiqui, Z.N. Sulphated silica tungstic acid as a highly efficient and recyclable solid acid catalyst for the synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidines and dihydropyrimidines. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2014, 387, 45–56, . [CrossRef]
- Salim, S.D.; Akamanchi, K.G. Sulfated tungstate: An alternative, eco-friendly catalyst for Biginelli reaction. Catal. Commun. 2011, 12, 1153–1156, . [CrossRef]
- Davoodnia, A., Allameh, S., Fazli, S., Tavakoli-Hoseini, N. (2011) One-pot synthesis of 2-amino-3-cyano-4-arylsubstituted tetrahydrobenzo[b] pyrans catalysed by silica gel-supported polyphosphoric acid (PPA-SiO 2) as an efficient and reusable catalyst, Chemical Papers, 65 714–720. [CrossRef]
- Salehi, P., Dabiri, M., Zolfigol M.A., Bodaghi Fard M.A. (2003) Silica sulfuric acid: an efficient and reusable catalyst for the one-pot synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones, Tetrahedron Letters, 44 2889–2891. [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi Reddy, Y., Rajitha, B., Narsimha Reddy, P., Sunil Kumar, B., Rao V.P. (2004) Bismuth Subnitrate Catalyzed Efficient Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-Ones: An Improved Protocol for the Biginelli Reaction, Synthetic Communications, 34 3821–3825. [CrossRef]
- Aswin, K., Mansoor, S.S., Logaiya, K., Sudhan, S.P.N. (2014) Triphenylphosphine: An efficient catalyst for the synthesis of 4,6-diphenyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2(1H)-thione under thermal conditions, Journal of King Saud University – Science, 26 141–148. [CrossRef]
- Khatri, C.K., Rekunge, D.S., Chaturbhuj, G.U. (2016) Sulfated polyborate: a new and eco-friendly catalyst for one-pot multi-component synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones/thiones via Biginelli reaction, New Journal of Chemistry, 40 10412–10417. [CrossRef]
- Sharghi, H. Jokar, M. (2009) ChemInform Abstract: Al 2 O 3 /MeSO 3 H: A Novel and Recyclable Catalyst for One-Pot Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidinones or Their Sulfur Derivatives in Biginelli Condensation. , ChemInform, 40 958–979. [CrossRef]
- Shaterian, H.R., Hosseinian, A., Ghashang, M. (2008) Reaction in dry media: Silica gel supported ferric chloride catalyzed synthesis of 1,8-dioxo-octahydroxanthene derivatives, Phosphorus, Sulfur and Silicon and the Related Elements, 183 3136–3144. [CrossRef]
- Nasr-Esfahani, M.; Taei, M. Aluminatesulfonic acid nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and application as a new and recyclable nanocatalyst for the Biginelli and Biginelli-like condensations. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 44978–44989, . [CrossRef]
- Angeles-Beltrán, D.; Lomas-Romero, L.; Lara-Corona, V.H.; González-Zamora, E.; Negrón-Silva, G. Sulfated Zirconia-Catalyzed Synthesis of 3,4-Dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones (DHPMs) Under Solventless Conditions: Competitive Multicomponent Biginelli vs. Hantzsch Reactions. Molecules 2006, 11, 731–738, . [CrossRef]
- Dilmaghani, K.A., Zeynizadeh, B., Parasajam, H. (2012) The efficient synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-(1H)-ones and their sulfur derivatives with H2SO4 immobilized on activated charcoal, Phosphorus, Sulfur and Silicon and the Related Elements, 187 544–553. [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Li, J.; Zheng, Z.; Shen, Y. One-pot synthesis of dihydropyrimidiones catalyzed by strontium(II) triflate under solvent-free conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 6037–6040, . [CrossRef]
- Safaei-Ghomi, J., Tavazo, M., Mahdavinia, G.H. (2018) Ultrasound promoted one-pot synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones/thiones using dendrimer-attached phosphotungstic acid nanoparticles immobilized on nanosilica, Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 40 230–237. [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liu, M.; Jiang, R.; Huang, H.; Huang, Q.; Wen, Y.; Tian, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Ultrafast fabrication of fluorescent organic nanoparticles with aggregation-induced emission feature through the microwave-assisted Biginelli reaction. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 165, 90–96, . [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, H., Shockravi, A. (2009) Imidazolium-based phosphinite ionic liquid as reusable catalyst and solvent for one-pot synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1 H )- (thio)ones, Heteroatom Chemistry, 20 284–288.
- Safari, J., Gandomi-Ravandi, S. (2014) Titanium dioxide supported on MWCNTs as an eco-friendly catalyst in the synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-(1H)-ones accelerated under microwave irradiation, New Journal of Chemistry, 38 3514–3521. [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, D.; Sharma, M.; Sharma, P.; Tomar, R. Synthesis and surfactant modification of clinoptilolite and montmorillonite for the removal of nitrate and preparation of slow release nitrogen fertilizer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227-228, 292–300, . [CrossRef]
- Ould M’hamed, M., Alshammari, A., Lemine, O., (2016) Green High-Yielding One-Pot Approach to Biginelli Reaction under Catalyst-Free and Solvent-Free Ball Milling Conditions, Applied Sciences, 6 431. [CrossRef]
- Dilmaghani, K.A., Zeynizadeh, B., Amirpoor, M. (2013) Ultrasound-mediated synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-(1H)-ones (or Thiones) with NaHSO4·H2O, Phosphorus, Sulfur and Silicon and the Related Elements, 188 1634–1642. [CrossRef]
- Suresh, P.; Pitchumani, K. Per-6-amino-β-cyclodextrin catalyzed asymmetric Michael addition of nitromethane and thiols to chalcones in water. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 2008, 19, 2037–2044, . [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, K., Pitchumani, K. (2013) The aminocyclodextrin/Pd(OAc) 2 complex as an efficient catalyst for the Mizoroki-Heck cross-coupling reaction, Chemistry - A European Journal, 19 14425–14431. [CrossRef]
- Suresh, P.; Pitchumani, K. Per-6-amino-β-cyclodextrin as an Efficient Supramolecular Ligand and Host for Cu(I)-Catalyzed N-Arylation of Imidazole with Aryl Bromides. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 9121–9124, . [CrossRef]
- Azath, I.A., Suresh, P., Pitchumani, K. (2012) Per-6-amino-β-cyclodextrin/CuI catalysed cyanation of aryl halides with K4[Fe(CN)6], New Journal of Chemistry, 36 2334. [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, K.; Suresh, P.; Pitchumani, K. Per-6-amino-β-cyclodextrin as a Reusable Promoter and Chiral Host for Enantioselective Henry Reaction. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4070–4073, . [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, K.; Pitchumani, K. Solvent-free multicomponent synthesis of pyranopyrazoles: per-6-amino-β-cyclodextrin as a remarkable catalyst and host. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 3312–3316, . [CrossRef]
- Azath, I.A., Puthiaraj, P., Pitchumani, K. (2013) One-pot multicomponent solvent-free synthesis of 2-amino-4H-benzo[b]pyrans catalyzed by per-6-amino-β-cyclodextrin, ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 1 174–179. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.I.; Pitchumani, K. A pyridinium modified β-cyclodextrin: an ionic supramolecular ligand for palladium acetate in C–C coupling reactions in water. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5518–5528, . [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X., Liu, X., Lu, M. (2014) β-cyclodextrin-capped palladium nanoparticle-catalyzed ligand-free Suzuki and Heck couplings in low-melting β-cyclodextrin/NMU mixtures, Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 28 635–640. [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; He, F.; Li, Z.; Guo, S.; Xie, Y.; Luo, D.; Wu, J. Facile construction of spiroindoline derivatives as potential anti-viral agent via three-component reaction in aqueous with β-cyclodextrin-SO3H as an efficient catalyst. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2022, 15, 139–152, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X.; Fang, G.; Tang, B. Cyclodextrin-based ocular drug delivery systems: A comprehensive review. Co-ord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 476, . [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, S. Efficient Synthesis of Heterocycles Using Highly Electrophilic Ethenetricarboxylates. HETEROCYCLES 2016, 92, 1561, . [CrossRef]
- Wu, J., Du, X., Ma, J., Zhang, Y., Shi, Q., Luo, L., Song, B., Yang, S., Hu, D. (2014) Preparation of 2,3-dihydroquinazolin-4(1H)-one derivatives in aqueous media with β-cyclodextrin-SO 3 H as a recyclable catalyst, Green Chem, 16 3210–3217. [CrossRef]
- Quintas, P.C.; Al-Salami, H.; Pfaff, A.; Li, D.; Koks, S. β-cyclodextrin based nano gene delivery using pharmaceutical applications to treat Wolfram syndrome. Ther. Deliv. 2022, 13, 449–462, . [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Chaudhary, S.; Kumar, K.; Gupta, M.K.; Rawal, R.K. Recent synthetic and medicinal perspectives of dihydropyrimidinones: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 132, 108–134, . [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.M.; Kumar, P.M.; Rambabu, D.; Kapavarapu, R.; Rani, S.S.; Misra, P.; Pal, M. Novel alkynyl substituted 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one derivatives as potential inhibitors of chorismate mutase. Bioorganic Chem. 2013, 51, 48–53, . [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, S.; Koohestani, F. Composite of cross-linked chitosan beads and a cyclodextrin nanosponge: A metal-free catalyst for promoting ultrasonic-assisted chemical transformations in aqueous media. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 156, 110157, . [CrossRef]
- Bigi, F., Carloni, S., Frullanti, B., Maggi, R., Sartori, G. (1999) A revision of the biginelli reaction under solid acid catalysis. Solvent-free synthesis of dihydropyrimidines over montmorillonite KSF, Tetrahedron Letters, 40 3465–3468. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Qian, C., Tian, H., Ma, Y. (2003) Lanthanide triflate catalyzed one-pot synthesis of dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-thiones by a three-component of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds, aldehydes, and thiourea using a solvent-free Biginelli condensation, Synthetic Communications, 33 1459–1468. [CrossRef]
- Lal, J., Sharma, M., Gupta, S., Parashar, P., Sahu, P., Agarwal, D.D. (2012) Hydrotalcite: A novel and reusable solid catalyst for one-pot synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidinones and mechanistic study under solvent free conditions, Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 352 31–37. [CrossRef]
- Aswin, K. Mansoor, S.S., Logaiya, K., Sudhan, P.N., Ahmed, R.N. (2014) Facile synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1 H )-ones and -thiones and indeno [1,2- d ]pyrimidines catalyzed by p -dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, Journal of Taibah University for Science, 8 236–247. [CrossRef]
- Liberto, N.A.; Silva, S.d.P.; de Fátima, .; Fernandes, S.A. β-Cyclodextrin-assisted synthesis of Biginelli adducts under solvent-free conditions. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 8245–8249, . [CrossRef]
- Gong, K., Wang, H., Wang, S., Ren, X., (2015) β-Cyclodextrin-propyl sulfonic acid: a new and eco-friendly catalyst for one-pot multi-component synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidones via Biginelli reaction, Tetrahedron, 71 4830–4834. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z., Larock, R.C. (2006) Facile N -Arylation of Amines and Sulfonamides and O -Arylation of Phenols and Arenecarboxylic Acids commonly found in a variety of biologically active and natural, The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 71 3198–3209.
- Kolvari, E.; Koukabi, N.; Armandpour, O. A simple and efficient synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2-(1H)-ones via Biginelli reaction catalyzed by nanomagnetic-supported sulfonic acid. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 1383–1386, . [CrossRef]
- Quan, Z.J., Da, Y.X., Zhang, Z., Wang, X.C. (2009) PS-PEG-SO3H as an efficient catalyst for 3,4-dihydropyrimidones via Biginelli reaction, Catalysis Communications. 10 1146–1148.
- Zamani, F.; Izadi, E. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonated-phenylacetic acid coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a novel acid magnetic catalyst for Biginelli reaction. Catal. Commun. 2013, 42, 104–108, . [CrossRef]
- Kalbasi, R.J.; Massah, A.R.; Daneshvarnejad, B. Preparation and characterization of bentonite/PS-SO3H nanocomposites as an efficient acid catalyst for the Biginelli reaction. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 55, 1–9, . [CrossRef]
- Suresh, Saini, A., Kumar, D., Sandhu, J.S. (2009) Multicomponent eco-friendly synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidine-2-(1H)-ones using an organocatalyst Lactic acid, Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews, 2 29–33.
- de Vasconcelos, A., Oliveira, P.S., Ritter, M., Freitag, R.A., Romano, R.L., Quina, F.H., Pizzuti, L., Pereira, C.M.P., Stefanello, F.M., Barschak, A.G. (2012) Antioxidant capacity and environmentally friendly synthesis of dihydropyrimidin-(2H)-ones promoted by naturally occurring organic acids, Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology, 26 155–161.
- Amarante, G.W., Coelho, F. (2009) Catalytic Synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones under Green Conditions and by Keggin type Heteropolyacid catalyst H7[PMo8V4O40], Química Nova, 32 469–481.
- Sehout, I.; Boulcina, R.; Boumoud, B.; Boumoud, T.; Debache, A. Solvent-free synthesis of polyhydroquinoline and 1,8-dioxodecahydroacridine derivatives through the Hantzsch reaction catalyzed by a natural organic acid: A green method. Synth. Commun. 2017, 47, 1185–1191, . [CrossRef]
- Kargar, M., Hekmatshoar, R., Mostashari, A., Hashemi, Z. (2011) Efficient and green synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-ones/thiones using imidazol-1-yl-acetic acid as a novel, reusable and water-soluble organocatalyst, Catalysis Communications, 15 123–126.
- Rajack, A.; Yuvaraju, K.; Praveen, C.; Murthy, Y. A facile synthesis of 3,4-dihydropyrimidinones/thiones and novel N-dihydro pyrimidinone-decahydroacridine-1,8-diones catalyzed by cellulose sulfuric acid. J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 2013, 370, 197–204, . [CrossRef]
- Ganwir, P., Gavali, K., Chaturbhuj, (2022) G.U. N -(Phenylsulfonyl)Benzenesulfonamide: A New Organocatalyst for One-Pot, Solvent-Free Synthesis of Biginelli’s 3,4-Dihydropyrimidine-2(1 H )-Thiones, Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, 1 1–10.
- Maryam, L.; Khan, A.U. Structural insight into mode of binding of Meropenem to CTX-M-15 type β-lactamase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 78–86, . [CrossRef]
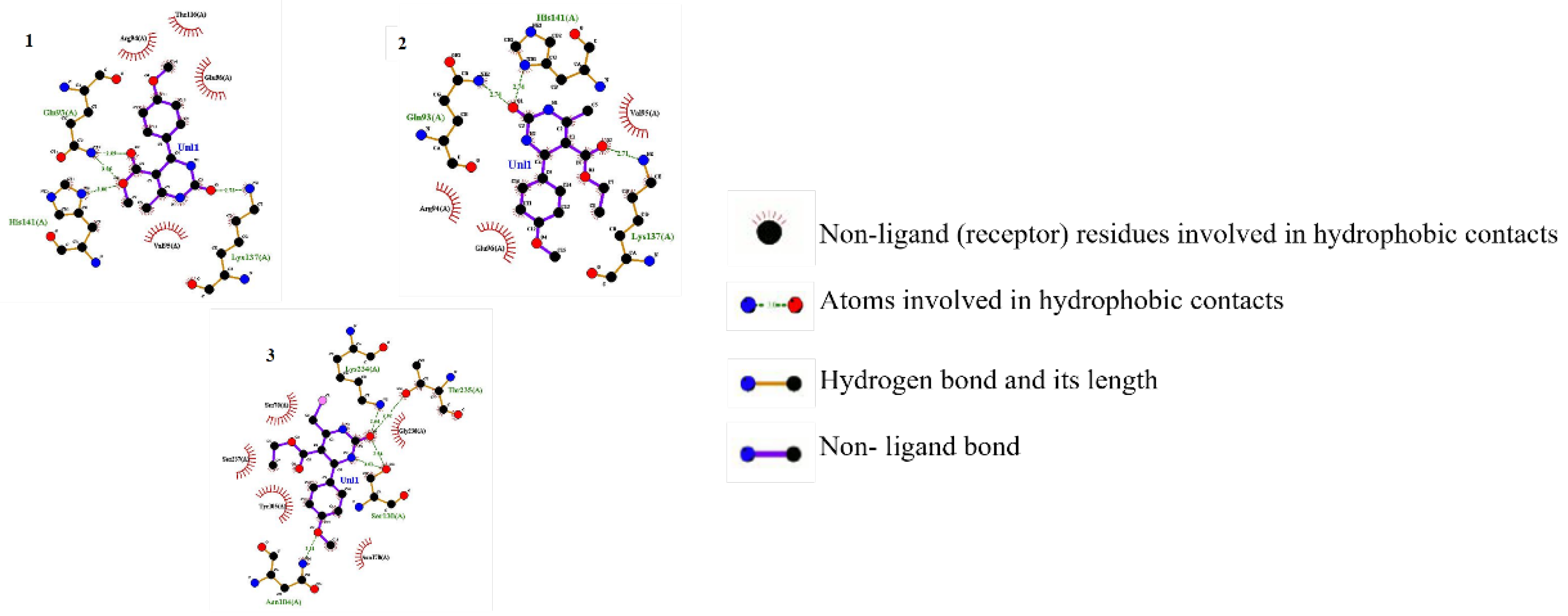
| Mode of Inclusion | ΔEa (Kcal.M-1) | |
| Di-amine group outside the pyr:β-CD cavity | (Mode A) | -64.8800 |
| Di-amine group inside the pyr:β-CD cavity. | (Mode B) | -50.8492 |
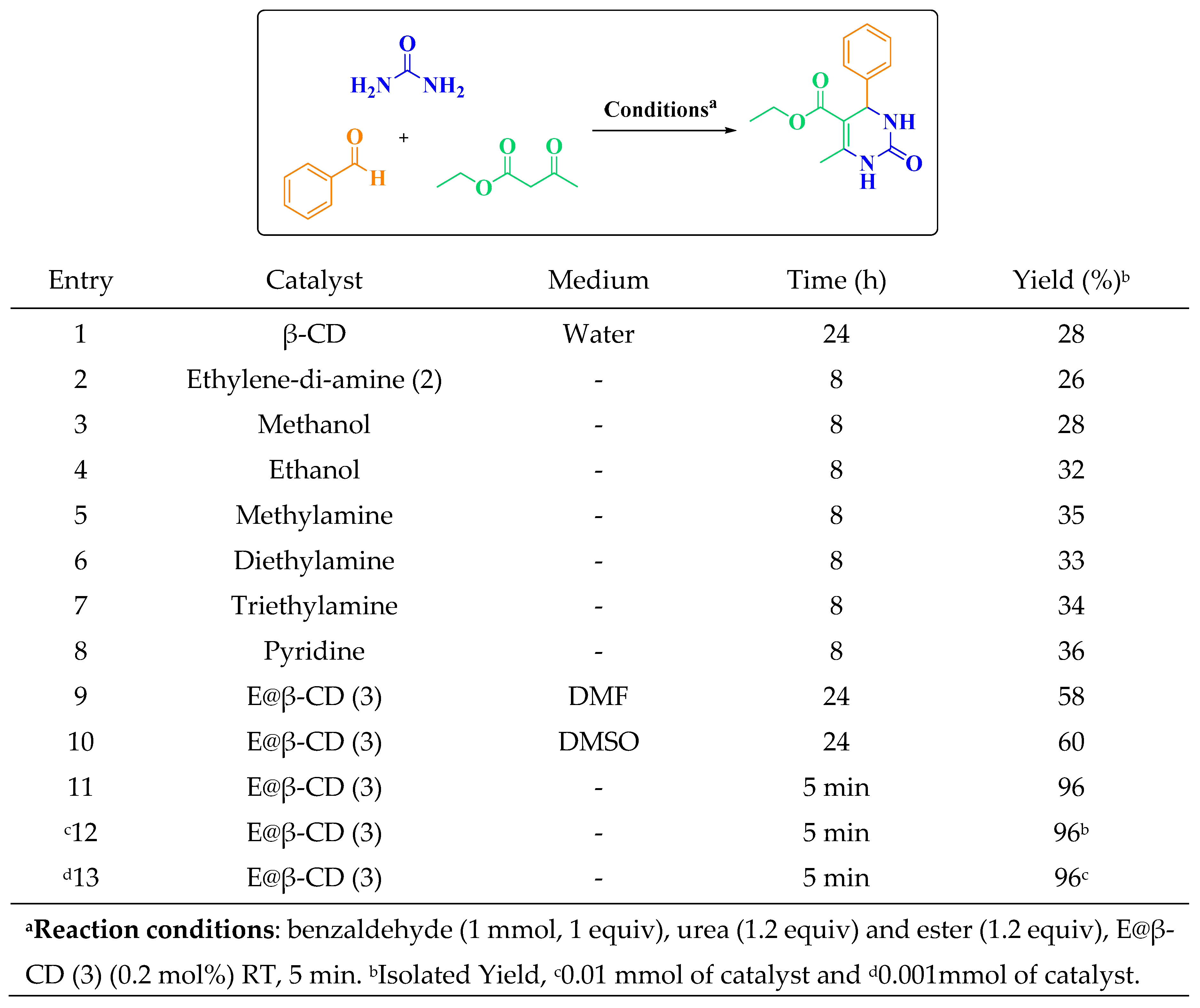

| Entry | Catalyst | Reaction condition | Time | Yield (%) | Ref |
| 1. | E@β-CD / SF | rt | 30 min | 97 | This work |
| 2. | KSF/SF | 130 0C | 48 h | 74–88 | [61] |
| 3. | Lanthanide triflate/ SF | 100 0C | 1–1.5 min | 81–91 | [62] |
| 4. | strontium(II) triflate/ SF | 70 0C | 4 h | 85–97 | [36] |
| 5. | Mg-Al-CO3 hydrotalcite/SF | 80 0C | 30–60 min | 71–74 | [63] |
| 6. | DBSA (5 mol %) / SF | 80 0C | 2.5–3h | 81–94 | [64] |
| 7. | β-CD SF | 100 0C | 3 h | 85 | [65] |
| 8 | β-CD-SO3H SF | 100 0C | 2 h | 83 | [66] |
| 9 | β-CD-HCl | EtOH/ reflux | 8 h | 92 | [67] |
| 10 | nano-γ-Fe2O3-SO3H SF | 60 ℃ | 3 h | 90 | [68] |
| 11 | PS-PEG-SO3H | Dioxane/80℃ | 10 h | 86 | [69] |
| 12 | Fe3O4/PAA-SO3H SF | RT | 120 min | 90 | [70] |
| 13 | Bentonite/PS-SO3H SF | 120 ℃ | 30 min | 89 | [71] |
| 14 | Tartaric acid | EtOH/Reflux | 4 h | 92 | [72] |
| 15 | Citric acid | EtOH/Reflux | 4 h | 96 | [73] |
| 16 | Lactic acids | EtOH/Reflux | 2.5 h | 92 | [74] |
| 17 | Ascorbic acid | Solvent free | 6 h | 85 | [75] |
| 18 | Imidazole-1yl-acetic acid | Water/reflux | 30 min | 94 | [76] |
| 19 | Sulfanilic acid | Water | 3 h | 98 | [77] |
| 20 | Phenyl Phosphonic acid | ACN/reflux | 4 h | 97 | [78] |
| SF – Solvent Free; DBSA – p-Deodecylbenzene sulfonic acid; β-CD- SO3H – Cyclodextrin modified Propyl Sulfonic acid; PS-PEG-SO3H – Polysterene-poly(ethylene glycol) sulfonic acid; PAA- SO3H – Pheylaceticacid sulfonic acid. | |||||
| Entry | vdW + H bond + electrostatic + dissolving energy (1) (kcal/mol) | Final total internal Energy (2) (kcal/mol) | Torsional free energy (3) (kcal/ mol) | Unbound system’s energy (4) (kcal/mol) | Estimated free energy of binding [1 + 2 + 3–4] (kcal/mol) |
| 4a | -7.53 | -2.83 | 1.49 | -2.83 | -6.04 |
| 4d | -7.21 | -2.28 | 1.49 | -2.28 | -5.72 |
| 4n | -6.21 | -2.88 | 1.69 | -2.25 | -4.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





