Submitted:
18 December 2023
Posted:
28 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
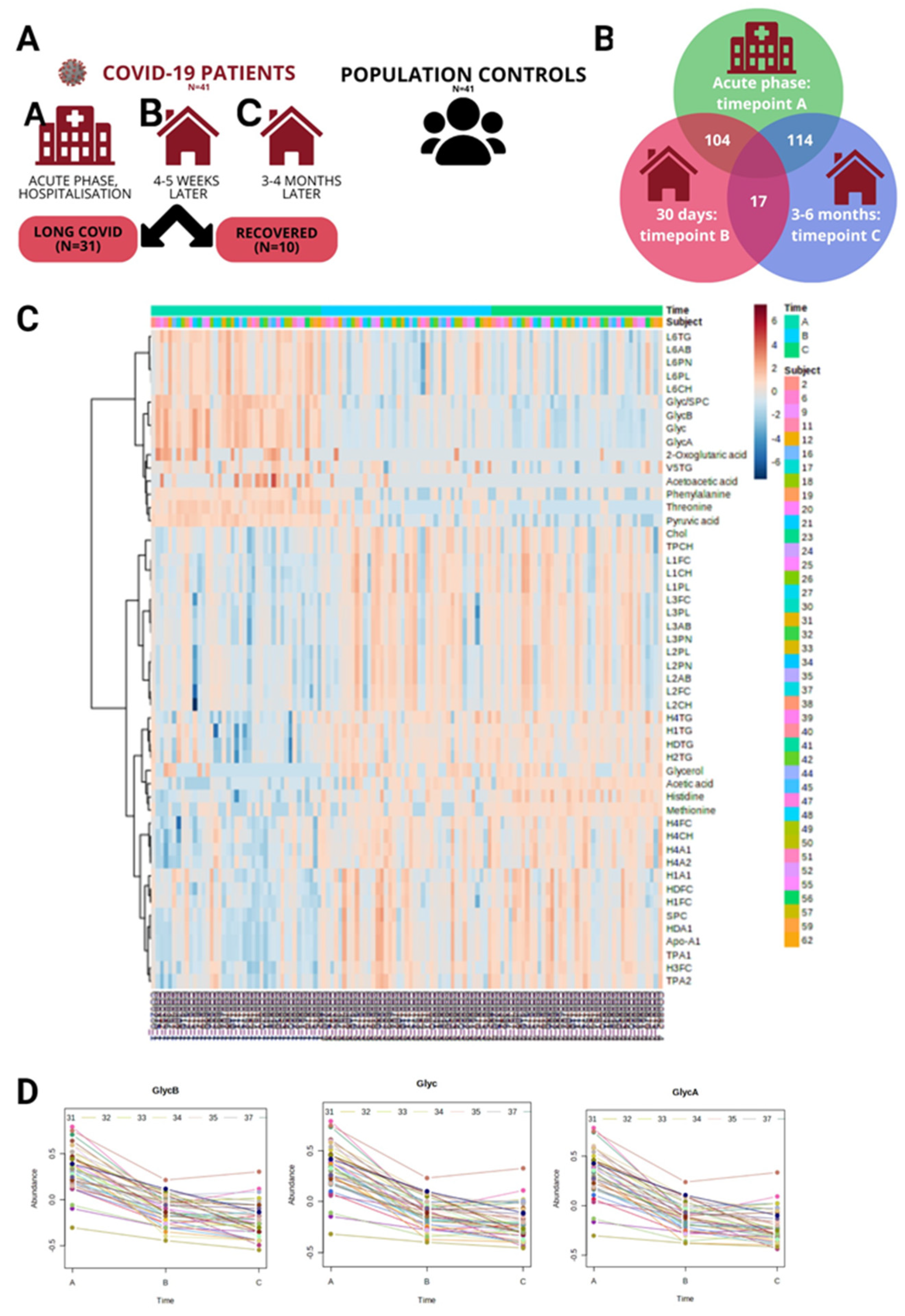
2. Results
| Variable, mean (SD) or n (%) | COVID-19 patients | Population controls | |||
| Male/ Female (n, %) | 17 (41.46%)/ 24 (58.54%) | 17 (41.46%)/ 24 (58.54%) | |||
| Age, average ± SD (years ± SD) | 56.63 ± 13.16 | 53.10 ± 11.41 | |||
| BML, average (kg/m2 ± SD) | 34.40 ± 22.95 | 27.08 ± 4.60 | |||
| Time in Hospital (days ± SD) | 9.18 ± 3.25 | - | |||
| Smoker/ non-smoker (n, %) | 3 (7.32%)/ 38 (92.68%) | 3 (7.32%)/ 38 (92.68%) | |||
| Comorbidities* | |||||
| Number of patients with comorbidities (yes/no) | 30 (73.17%)/ 11 (26.83%) | 23 (56.10%)/ 18 (43.90%) | |||
| Hypertension (n, %) | 17 (41.46%) | 9 (21.95%) | |||
| Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (n, %) | 3 (7.32%) | 3 (7.32%) | |||
| Other cardiovascular disease (n, %) | 10 (24.39%) | 13 (31.71%) | |||
| Oncological (n, %) | 2 (4.88%) | 3 (7.32%) | |||
| Clinical measurements ** | |||||
| Average (SD) | Acute COVID-19 | Recovery phase(1 month) | Recovery phase(3-4 months) | ||
| Leukocytes (μL) | 5.71 (2.15) | 6.19 (1.37) | 5.67 (1.67) | ||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.24 (1.45) | 137.87 (11.20) | 137.88 (28.15) | ||
| Hematocrit (%) | 39.91 (4.07) | 41.47 (3.08) | 41.26 (8.05) | ||
| Platelets (μL) | 173.13 (99.07) | 267.10 (49.20) | 238.17 (59.95) | ||
| Neutrophils (μL) | 1.51 (1.50) | 52.48 (9.58) | 50.92 (13.72) | ||
| Lymphocytes (μL) | 4.86 (12.89) | 32.74 (10.36) | 32.54 (12.67) | ||
| Monocytes (μL) | 27.99 (87.84) | 9.83 (2.42) | 8.42 (2.21) | ||
| Eosinophils (μL) | 0.03 (0.05) | 3.03 (1.70) | 3.05 (1.62) | ||
| ALT (U/l) | 23.82 (18.49) | 39.23 (28.53) | 30.95 (17.54) | ||
| AST (U/l) | 28.75 (13.74) | 28.45 (13.68) | 26.75 (12.91) | ||
| GGT (U/l) | 78.33 (99.33) | 44.43 (43.10) | 28.31 (30.13) | ||
| Bilirubin (μmol/l) | 6.64 (3.22) | 13.30 (5.31) | 11.26 (4.60) | ||
| LDH (U/L) | 295.00 (168.87) | 215.70 (38.10) | 189.67 (71.51) | ||
| Creatinine ((μmol/L) | 72.45 (19.87) | 68.65 (11.53) | 70.57 (18.49) | ||
| CRP (mg/L) | 35.05 (42.05) | 3.69 (2.80) | 3.39 (4.28) | ||
| D-dimer (mg/ml) | 0.60 (0.12) | 0.48 (0.31) | 0.25 (0.15) | ||
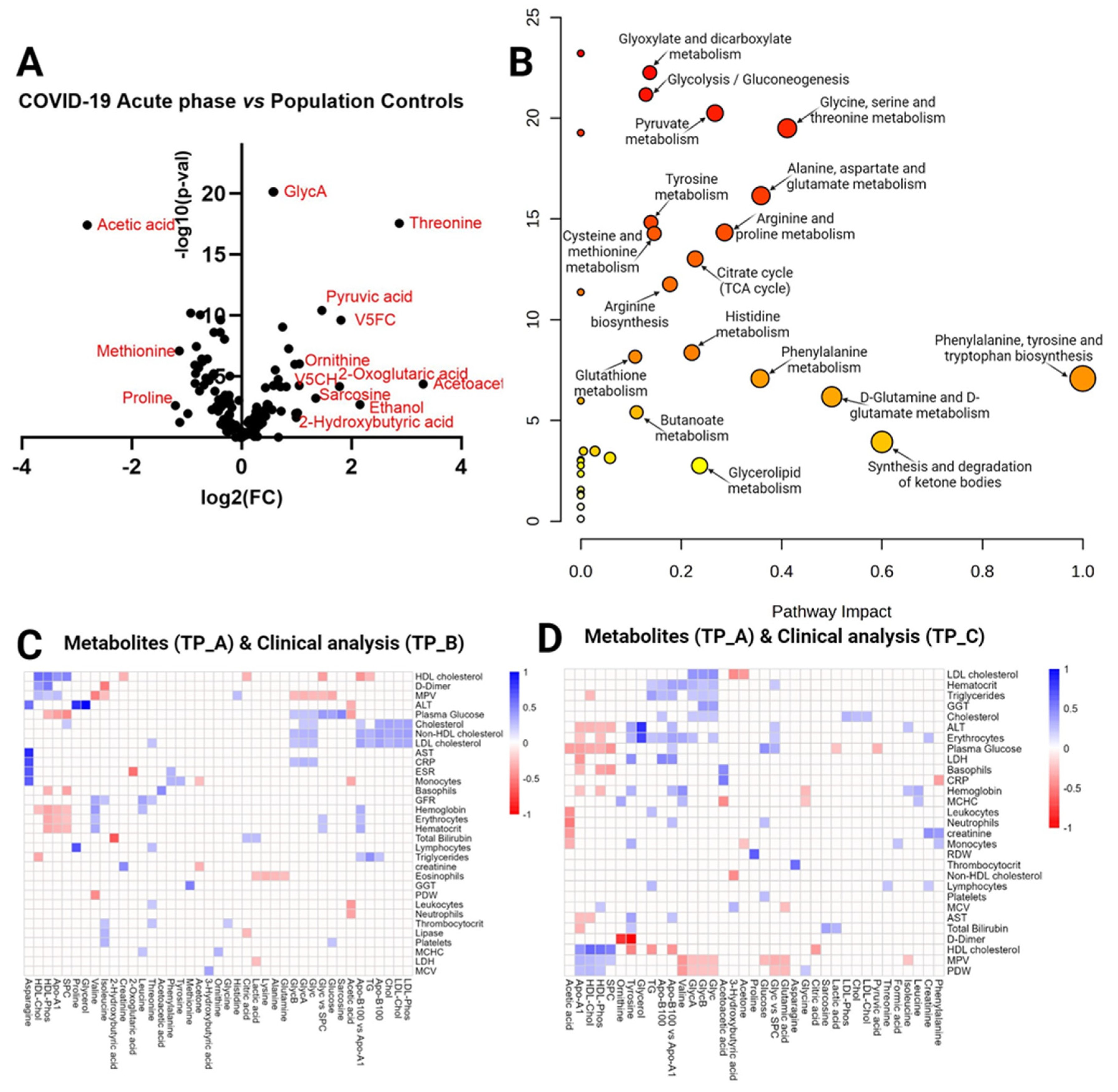
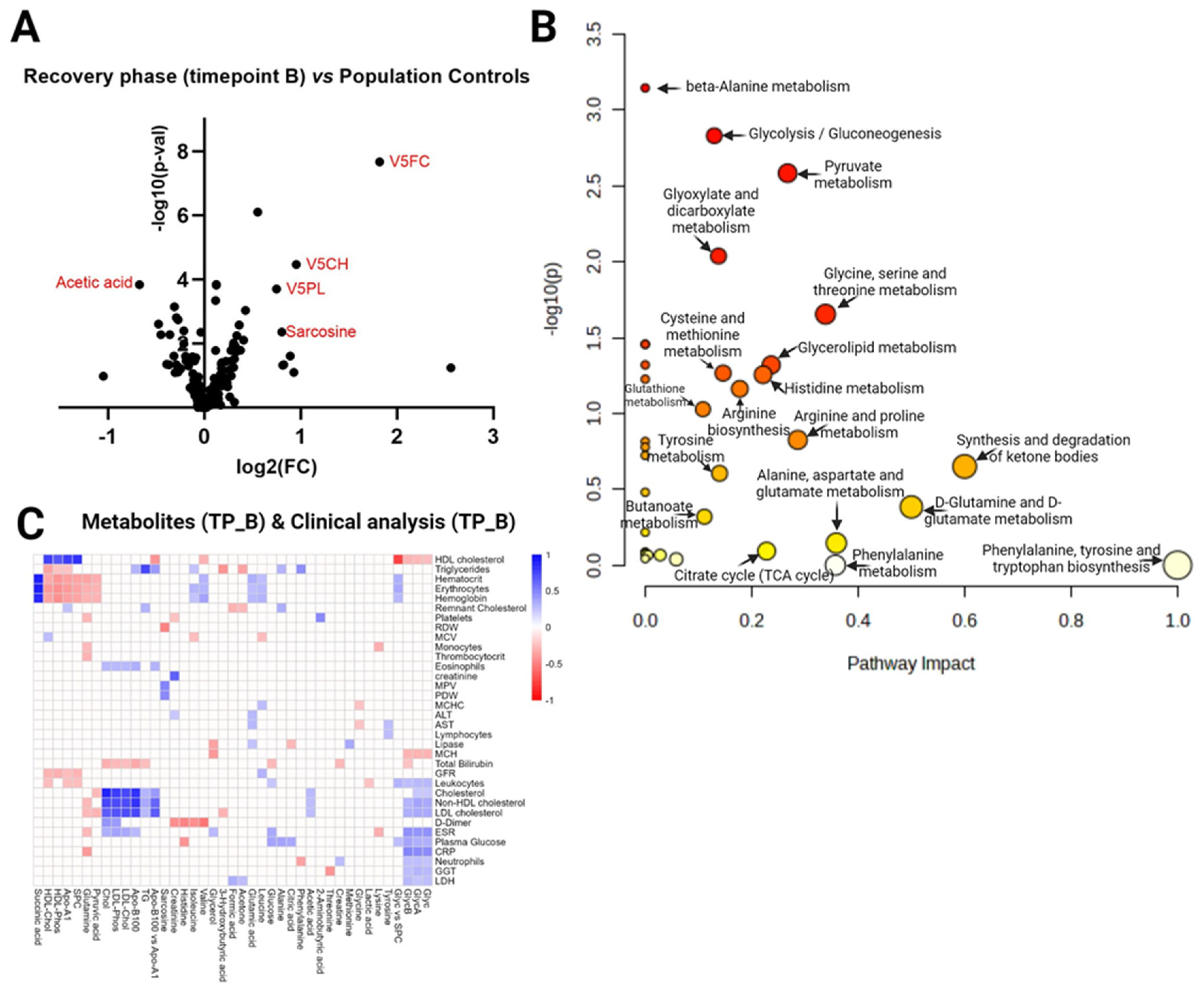
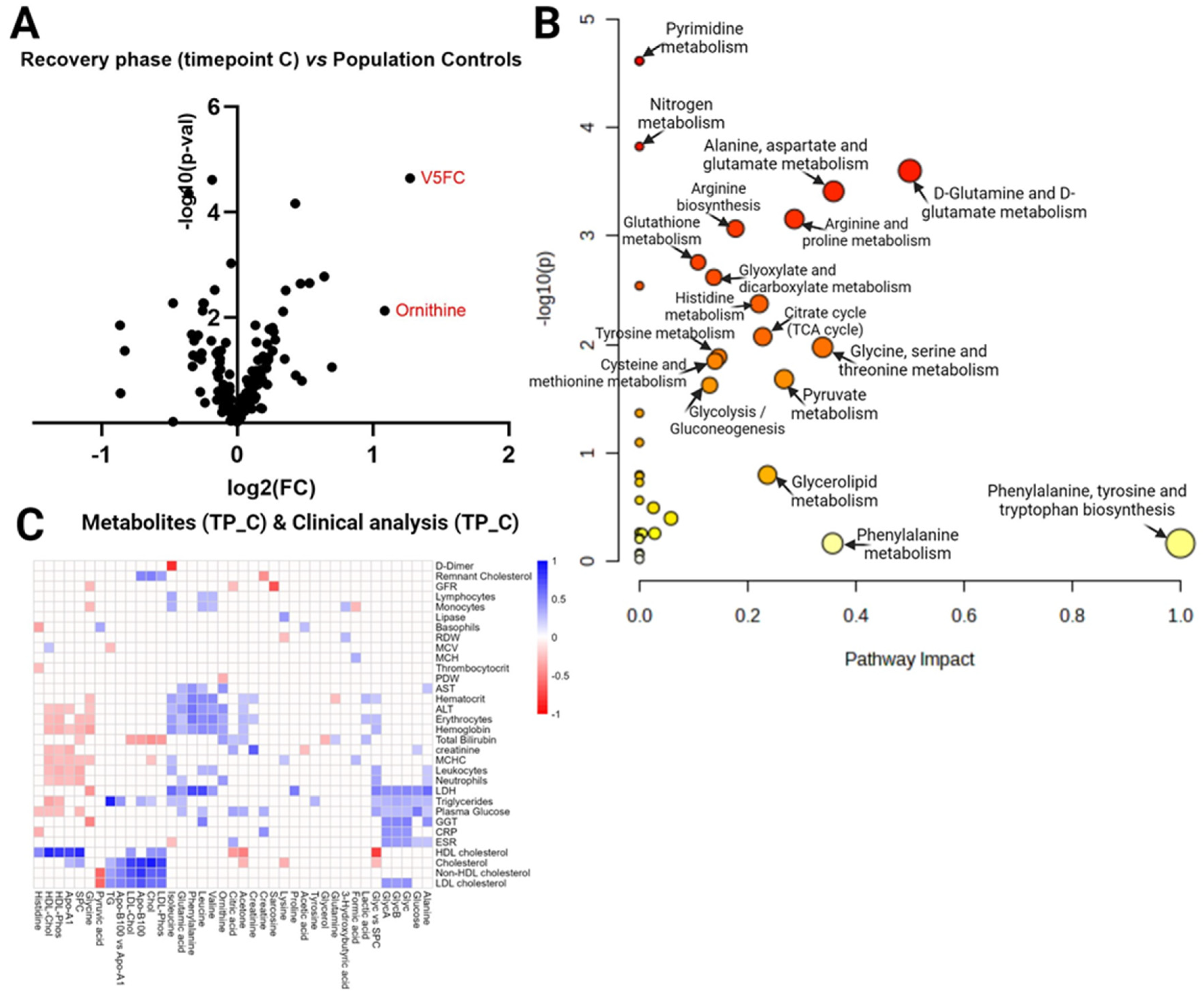
3. Discussion
3.1. Dysregulations in amino acid metabolism
3.2. Dyslipidemia in COVID-19
3.3. Glycoprotein level alterations
3.4. Energy metabolism disturbances
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carfì, A.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puntmann, V.O.; Carerj, M.L.; Wieters, I.; Fahim, M.; Arendt, C.; Hoffmann, J.; Shchendrygina, A.; Escher, F.; Vasa-Nicotera, M.; Zeiher, A.M.; et al. Outcomes of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients Recently Recovered From Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 1265–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, D.T. Rehabilitation after COVID-19: an evidence-based approach. Clin. Med. 2020, 20, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bian, J.; Morozyuk, D.; Schenck, E.J.; Khullar, D.; Nordvig, A.S.; Shenkman, E.A.; Rothman, R.L.; et al. Data-driven analysis to understand long COVID using electronic health records from the RECOVER initiative. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Leon, S.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Perelman, C.; Sepulveda, R.; Rebolledo, P.A.; Cuapio, A.; Villapol, S. More than 50 long-term effects of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Mahoney, L.L.; Routen, A.; Gillies, C.; Ekezie, W.; Welford, A.; Zhang, A.; Karamchandani, U.; Simms-Williams, N.; Cassambai, S.; Ardavani, A.; et al. The prevalence and long-term health effects of Long Covid among hospitalised and non-hospitalised populations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine, 2022, 55, 101762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zheng, B.; Daines, L.; Sheikh, A. Long-Term Sequelae of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of One-Year Follow-Up Studies on Post-COVID Symptoms. Pathogens 2022, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Haupert, S.R.; Zimmermann, L.; Shi, X.; Fritsche, L.G.; Mukherjee, B. Global Prevalence of Post-Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Condition or Long COVID: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 226, 1593–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Kishton, R.J.; Rathmell, J. A guide to immunometabolism for immunologists. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyajima, M. Amino acids: key sources for immunometabolites and immunotransmitters. Int. Immunol. 2020, 32, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caterino, M.; Costanzo, M.; Fedele, R.; Cevenini, A.; Gelzo, M.; Di Minno, A.; Andolfo, I.; Capasso, M.; Russo, R.; Annunziata, A.; et al. The Serum Metabolome of Moderate and Severe COVID-19 Patients Reflects Possible Liver Alterations Involving Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansone, L.; Briviba, M.; Silamikelis, I.; Terentjeva, A.; Perkons, I.; Birzniece, L.; Rovite, V.; Rozentale, B.; Viksna, L.; Kolesova, O.; et al. Amino Acid Metabolism is Significantly Altered at the Time of Admission in Hospital for Severe COVID-19 Patients: Findings from Longitudinal Targeted Metabolomics Analysis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e0033821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liptak, P.; Baranovicova, E.; Rosolanka, R.; Simekova, K.; Bobcakova, A.; Vysehradsky, R.; Duricek, M.; Dankova, Z.; Kapinova, A.; Dvorska, D.; et al. Persistence of Metabolomic Changes in Patients during Post-COVID Phase: A Prospective, Observational Study. Metabolites 2022, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berezhnoy, G.; Bissinger, R.; Liu, A.; Cannet, C.; Schäfer, H.; Kienzle, K.; Bitzer, M.; Häberle, H.; Göpel, S.; Trautwein, C.; et al. Maintained imbalance of triglycerides, apolipoproteins, energy metabolites and cytokines in long-term COVID-19 syndrome patients. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1144224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluck, G.E.G.; Yoo, J.-A.; Sakarya, E.H.; Trigatti, B.L. Good Cholesterol Gone Bad? HDL and COVID-19. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kuraishy, H.M.; Hussien, N.R.; Al-Niemi, M.S.; Fahad, E.H.; Al-Buhadily, A.K.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Al-Hamash, S.M.; Tsagkaris, C.; Papadakis, M.; Alexiou, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 induced HDL dysfunction may affect the host’s response to and recovery from COVID-19. Immunity, Inflamm. Dis. 2023, 11, e861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Risks and burdens of incident diabetes in long COVID: a cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. Web-based inference of biological patterns, functions and pathways from metabolomic data using MetaboAnalyst. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, M.; Uysal, B.B.; Ikitimur, H.; Ozcan, E.; Islamoğlu, M.S.; Aktepe, E.; Yavuzer, H.; Yavuzer, S. Effect of oral l-Glutamine supplementation on Covid-19 treatment. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 2020, 33, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldani, M.; Sandini, M.; Nespoli, L.; Coppola, S.; Bernasconi, D.P.; Gianotti, L. Glutamine Supplementation in Intensive Care Patients. Medicine 2015, 94, e1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obayan, A.O.E. Overview of the Rationale for L-Glutamine Treatment in Moderate-Severe COVID-19 Infection. J. Infect. Dis. Epidemiology 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; Szergyuk, I.; de Oliveira, M.H.S.; Abosamak, M.F.; Benoit, S.W.; Benoit, J.L.; Lippi, G. Alterations in the lipid profile associate with a dysregulated inflammatory, prothrombotic, anti-fibrinolytic state and development of severe acute kidney injury in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A study from Cincinnati, USA. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Risks and burdens of incident dyslipidaemia in long COVID: a cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khovidhunkit, W.; Memon, R.A.; Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Infection and Inflammation-Induced Proatherogenic Changes of Lipoproteins. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, S462–S472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteve, E.; Ricart, W.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Dyslipidemia and inflammation: an evolutionary conserved mechanism. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosino, P.; Calcaterra, I.L.; Mosella, M.; Formisano, R.; D’anna, S.E.; Bachetti, T.; Marcuccio, G.; Galloway, B.; Mancini, F.P.; Papa, A.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction in COVID-19: A Unifying Mechanism and a Potential Therapeutic Target. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, S.C.; Würtz, P.; Nath, A.P.; Abraham, G.; Havulinna, A.S.; Fearnley, L.G.; Sarin, A.-P.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Aalto, K.; et al. The Biomarker GlycA Is Associated with Chronic Inflammation and Predicts Long-Term Risk of Severe Infection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazenwadel, J.; Berezhnoy, G.; Cannet, C.; Schäfer, H.; Geisler, T.; Rohlfing, A.-K.; Gawaz, M.; Merle, U.; Trautwein, C. Stratification of hypertension and SARS-CoV-2 infection by quantitative NMR spectroscopy of human blood serum. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otvos, J.D.; Shalaurova, I.; Wolak-Dinsmore, J.; Connelly, M.A.; Mackey, R.H.; Stein, J.H.; Tracy, R.P. GlycA: A Composite Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Biomarker of Systemic Inflammation. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gornik, O.; Lauc, G. Glycosylation of Serum Proteins in Inflammatory Diseases. Dis. Markers 2008, 25, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duprez, D.; Neuhaus, J.; Otvos, J.; Neaton, J.D.; Lundgren, J.D. Abstract 14731: Glyc A, a Novel Marker of Inflammation, Predicts Cardiovascular Events in HIV-Positive Patients: Results of SMART Study. Circulation 2014, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhuenda-Egea, F.; Narro-Serrano, J. Evaluation of risk factors for COVID-19 severity or death and their relationship to metabolic pathways. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Hernández, Y.; Monárrez-Espino, J.; López, D.A.G.; Zheng, J.; Borrego, J.C.; Torres-Calzada, C.; Elizalde-Díaz, J.P.; Mandal, R.; Berjanskii, M.; Martínez-Martínez, E.; et al. The plasma metabolome of long COVID patients two years after infection. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, A.J.; Lamers, W.H.; Chamuleau, R.A.; Le Plénier, S.; Goron, A.; Sotiropoulos, A.; Archambault, E.; Guihenneuc, C.; Walrand, S.; Salles, J.; et al. Nitrogen metabolism and ornithine cycle function. Physiol. Rev. 1990, 70, 701–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaini, G.; Baracca, A.; Lenaz, G.; Sgarbi, G. Hypoxia and mitochondrial oxidative metabolism. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Bioenerg. 2010, 1797, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, Y.; De Sousa-Coelho, A.L.; Harata, I.; Aoun, C.; Weimer, S.; Shi, X.; Herrera, K.N.G.; Takahashi, H.; Doherty, C.; Noguchi, Y.; et al. l-Alanine activates hepatic AMP-activated protein kinase and modulates systemic glucose metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2018, 17, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui, L. Energy Metabolism in the Liver. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeigue, P.M.; McGurnaghan, S.; Blackbourn, L.; Bath, L.E.; McAllister, D.A.; Caparrotta, T.M.; Wild, S.H.; Wood, S.N.; Stockton, D.; Colhoun, H.M. Relation of Incident Type 1 Diabetes to Recent COVID-19 Infection: Cohort Study Using e-Health Record Linkage in Scotland. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wander, P.L.; Lowy, E.; Beste, L.A.; Tulloch-Palomino, L.; Korpak, A.; Peterson, A.C.; Kahn, S.E.; Boyko, E.J. The Incidence of Diabetes Among 2,808,106 Veterans with and Without Recent SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovite, V.; Wolff-Sagi, Y.; Zaharenko, L.; Nikitina-Zake, L.; Grens, E.; Klovins, J. Genome Database of the Latvian Population (LGDB): Design, Goals, and Primary Results. J. Epidemiology 2018, 28, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





