Submitted:
26 December 2023
Posted:
27 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Purpose of the Study
1.2. Scope and Methodology
2. Literature Review
2.1. Construction Project Cost Deviation and Risk Management Theory
2.2. Research on cost deviation in construction projects
3. Research Methodology
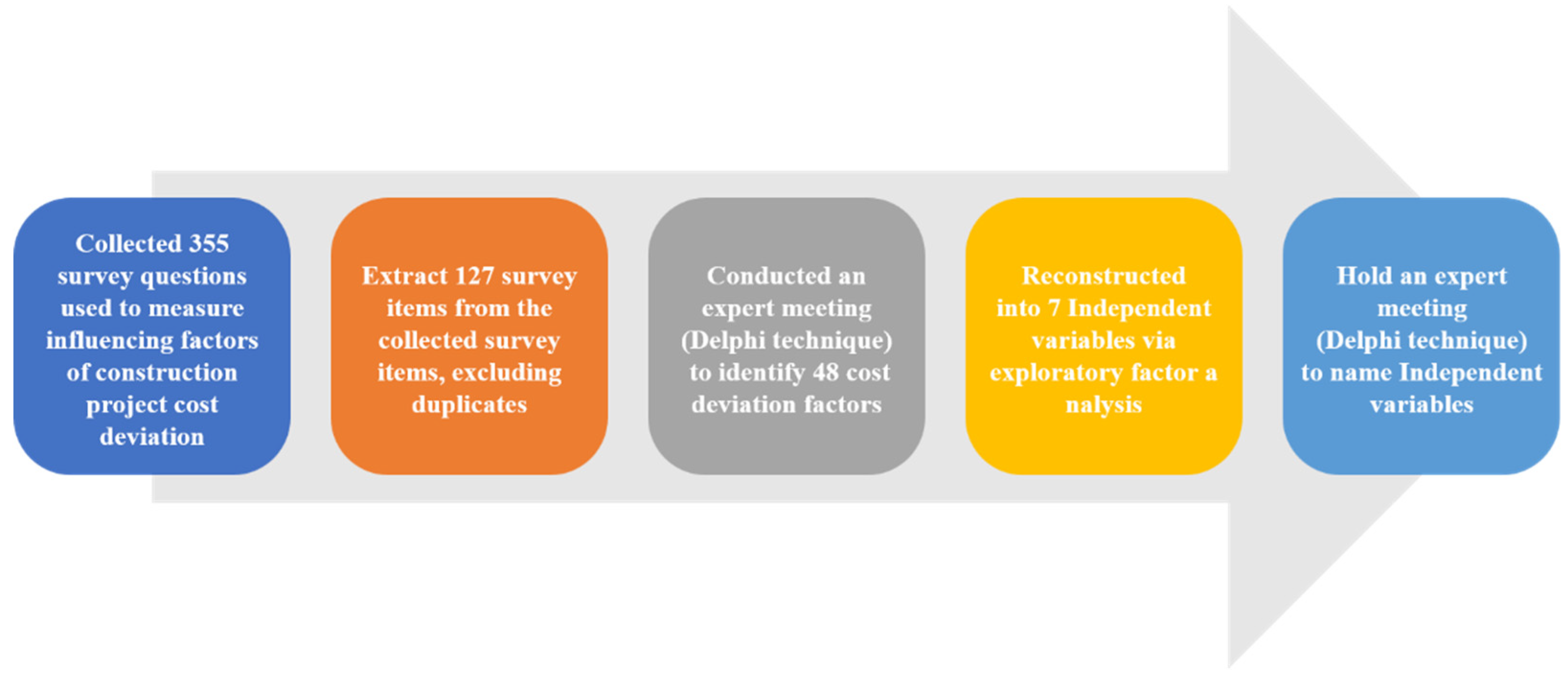
3.1. Deriving Cost Variation Influencing Factors
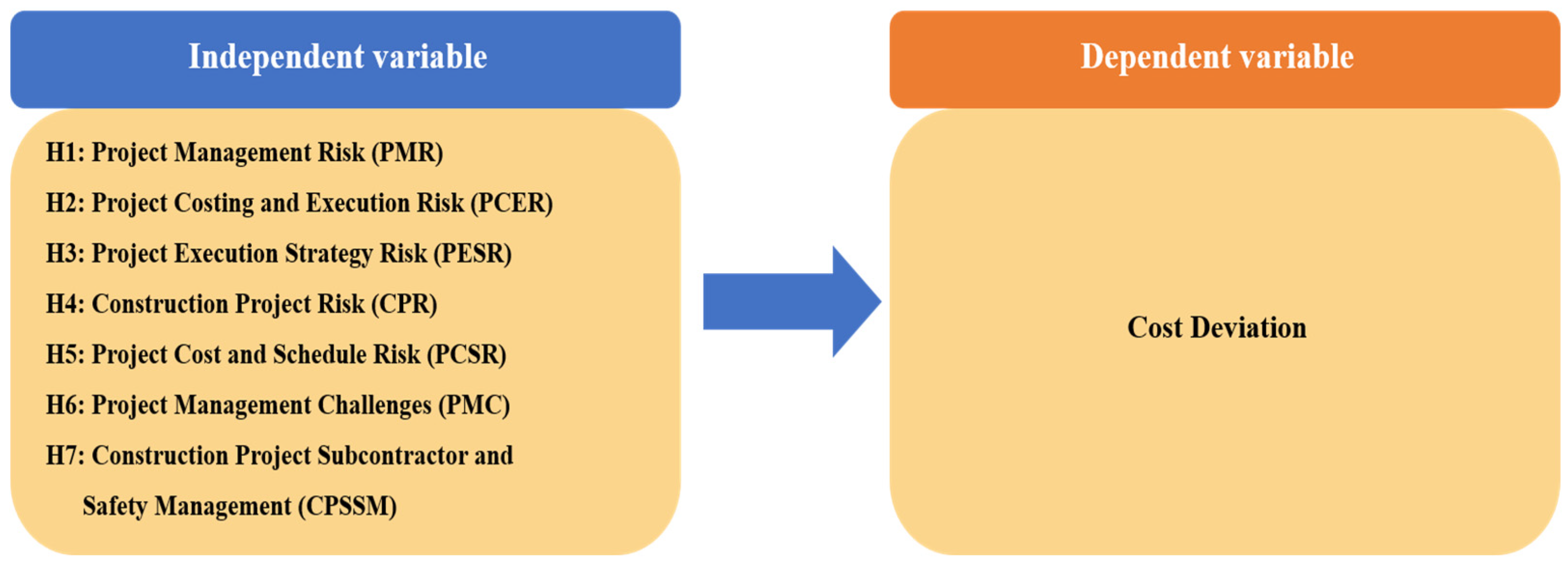
3.2. Research models and hypotheses
- H1
- PMR level has a significant effect on cost deviation in NDPP.
- H2
- PCER level has a significant effect on cost deviation in NDPP.
- H3
- PESR level has a significant effect on cost deviation in NDPP.
- H4
- CPR level has a significant effect on cost deviation in NDPP.
- H5
- PCSR level has a significant effect on cost deviation in NDPP.
- H6
- PMC level has a significant effect on cost deviation in NDPP.
- H7
- CPSSM level has a significant impact on cost deviation in NDPP.
3.3. Research analysis procedures
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Reliability and validity analysis
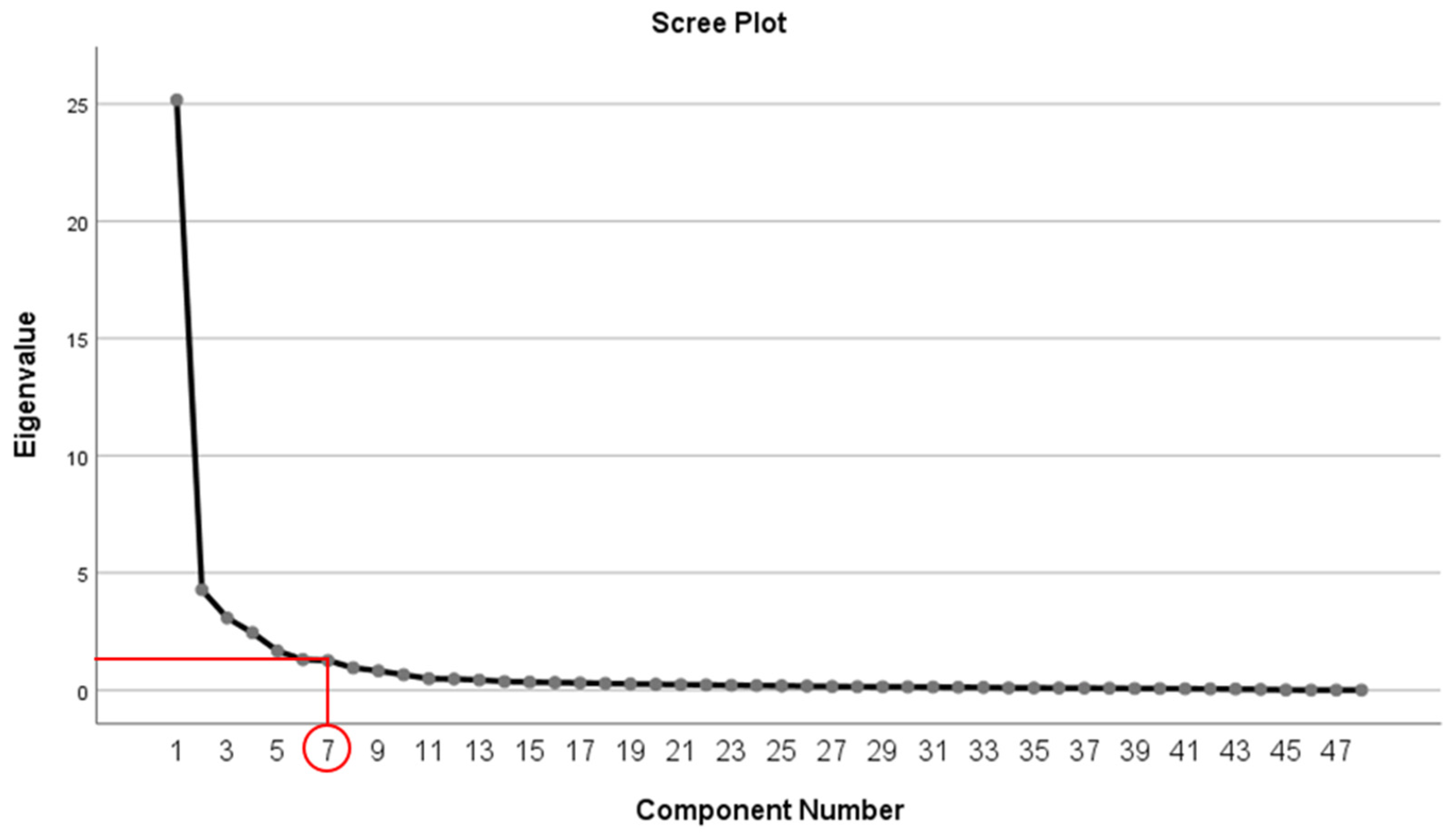
4.2. Exploratory factor and correlation analysis
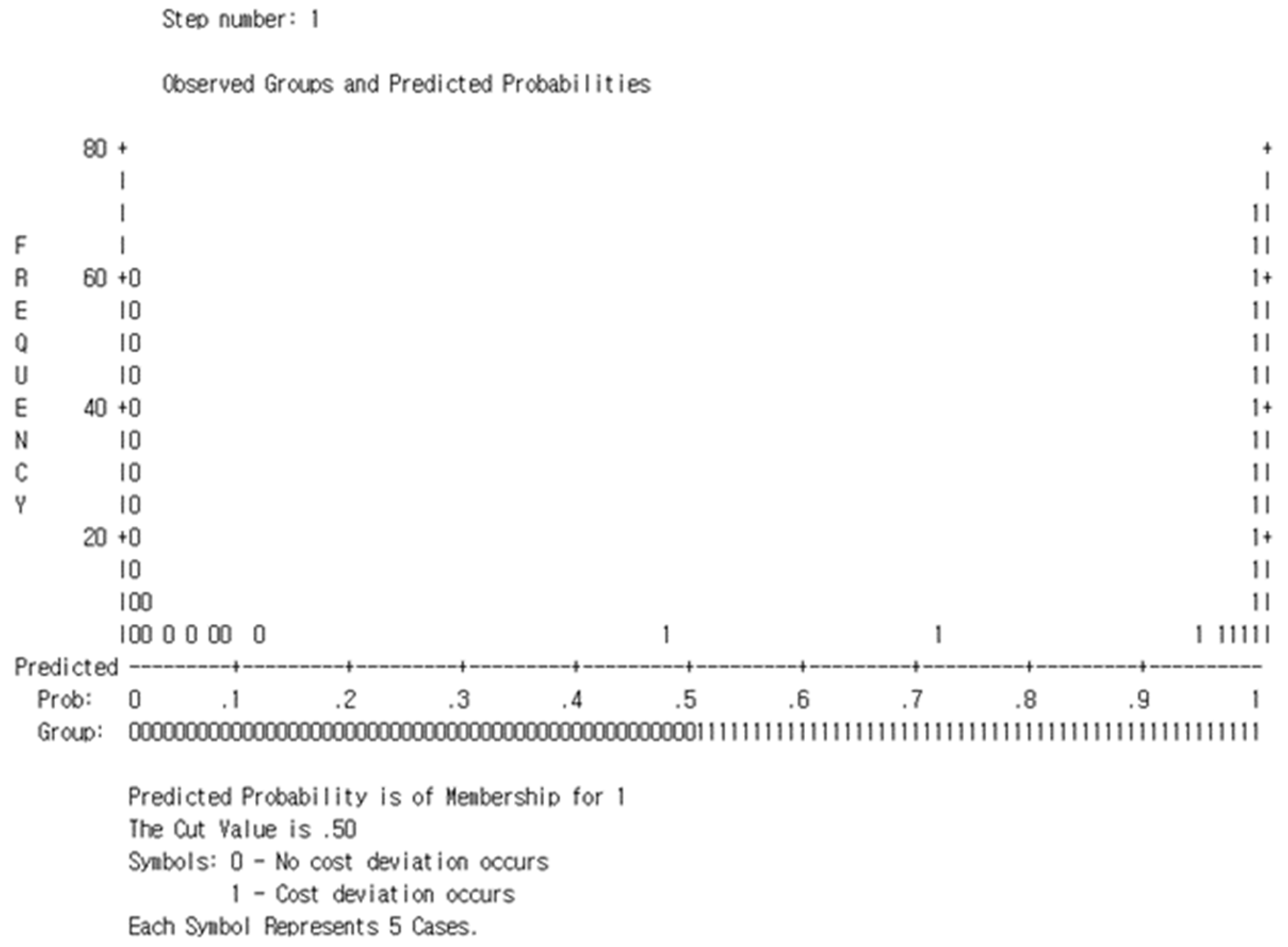
4.3. Binary logistic regression analysis
4.4. Analyze and discuss cost deviation influence factors
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Simonds, E.A.; Gobenciong, K.A.P.; Wilson, J.E.; Jiroutek, M.R.; Nugent, N.R.; van Tilburg, M.A.L. Trauma Functioning and Well-Being in Children Who Receive Mental Health Aid after Natural Disaster or War. Children. 2022, 9, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, D.S.; Development of an Integrated Management System for Disaster Prevention Centered on Living Areas. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 18, 35–44. Available online: https://www.earticle.net/Article/A424810 (accessed on 25.03.2023). (in Korean).
- Flyvbjerg, B.; Skamris Holm, M.K.; Buhl, S.L. How Common and How Large are Cost Overruns in Transport Infrastructure Projects? Transp. Rev. 2003, 23, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.H.; Elshwadfy, L.M. Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Construction Project Cost Estimation in Egypt. Jordan J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 15, 2021–2329. [Google Scholar]
- Raghib, A.T.; Belayutham, S.; Mohammad, M.Z.; Ibrahim, C. Causes, Effects and Potential Measures of Cost Deviations in High-Rise Building Projects in Egypt. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2023, 23, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyeongbuk Province. Gyeongbuk Province has Invested the Most in Natural Disaster Prevention Projects in the Country This Year. Available online: https://url.kr/orqkbg (accessed on 25.03.2023). (in Korean).
- Bhargava, A.; Labi, S.; Chen, S.; Saeed, T.U.; Sinha, K.C. Predicting Cost Escalation Pathways and Deviation Severities of Infrastructure Projects Using Risk-Based Econometric Models and Monte Carlo Simulation. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2017, 32, 620–640. [CrossRef]
- Gómez Cabrera, A. Identification of Factors Generating Time and Cost Deviation in Construction Projects: A Case Study in Rural Roads in Colombia. Available online: https://repositorio.uniandes.edu.co/handle/1992/52996 (accessed on 20.03.2023).
- Alsugair, A.M. Cost Deviation Model of Construction Projects in Saudi Arabia Using PLS-SEM. Sustainability. 2022, 14, 16391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalaisami, C.D.; Kuppuswamy, A. Managing Cost Risks: Toward a Taxonomy of Cost Overrun Factors in Building Construction Projects. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part A: Civ. Eng. 2021, 7, 04021021. [CrossRef]
- Górecki, J.; Diaz-Madronero, M. Who Risks and Wins?—Simulated Cost Variance in Sustainable Construction Projects. Sustainability. 2020, 12, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przywara, D.; Rak, A. Monitoring of Time and Cost Variances of Schedule Using Simple Earned Value Method Indicators. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.; Pimplikar, S.S.; Sawant, K. Effect of Project Cost and Time Monitoring on Progress of Construction Project. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2013, 2, 796–800. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, S.; Kure, A.M.; Palaniappan, S. Study on Time and Cost Overruns in Mega Infrastructure Projects in India. J. Inst. Eng. (India): Ser. A. 2019, 100, 139–145. [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.G. Investigation of Bid Price Competition Measured Through Prebid Project Estimates, Actual Bid Prices, and Number of Bidders. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2005, 131, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endut, I.R.; Akintoye, A.; Kelly, J. Cost and Time Overruns of Projects in Malaysia. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265377554 (accessed on 25.06.2023).
- Rahman, I.A.; Memon, A.H. The Way Forward in Sustainable Construction: Issues and Challenges. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2013, 2, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Monem, M.; Alshaer, K.T.; El-Dash, K. Assessing Risk Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Conceptual Cost Estimation in the Middle East. Buildings. 2022, 12, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, A.; Saeedi, A. Major Factors of Delay in Developing Countries Construction Projects: Critical Review. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355041672 (accessed on 25.06.2023). [CrossRef]
- Albtoush, F.; Shu Ing, D.; Rahman, R.A.; Aldiabat Al-Btoosh, F.A.; Faten Albtoush, A.M.; Doh, S.I.; Rahman, R.A.; Maria Zaidi, S. Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Cost Estimate in Construction Projects: A Review. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355041672 (accessed on 15.06.2023).
- Cho, J.-H.; Kim, B.-S. Risk Influencing Factors in Performance of River Disaster Prevention Project. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 40, 417–428. (in Korean). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, J.; Mbachu, J.; Domingo, J. Factors Influencing the Accuracy of Pre-Contract Stage Estimation of Final Contract Price in New Zealand. Int. J. Constr. Supply Chain Manag. 2014, 4, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azman, N.A.M.; Adeleke, A.Q. Effect of Time Overruns on Apartment Building among Kuantan Malaysian Construction Industries. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2018, 10, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Memon, A.H.; Rahman, I.A.; Abdullah, M.R.; Asmi, A.; Azis, A.; Factors Affecting Construction Cost in Mara Large Construction Project: Perspective of Project Management Consultant. Int. J. Sustain. Constr. Eng. Technol. 2010, 1, 41–54. Available online: https://penerbit.uthm.edu.my/ojs/index.php/IJSCET/article/view/62 (accessed on 25.06.2023).
- Mahamid, I.; Aichouni, M. Factors Affecting Accuracy of Pretender Post Estimate: Studies of Saudi Arabia. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265377554 (accessed on 05.06.2023]).

| Researcher | Country | Research Field | Cost-Related Factors | Item |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdel-Monem et al. [18] | Middle East | Construction projects | Project complexity, Site constraints, Design changes, Unavailability of skilled labor, Inflation, Market fluctuations, Changes in scope, Delays in construction, Acceleration, Claims and disputes | 57 |
| Alsugair [9] | Saudi Arabia | Construction projects | Scope quality, contractor organization, estimator performance, information quality, project characteristics, external factors, contractual procedures | 73 |
| Ibrahim and Elshwadfy [4] | Egypt | Construction projects | Consultants, design parameters, information and estimators, client characteristics, project characteristics, contract requirements, contractor characteristics, external factor | 70 |
| Albtoush et al. [20] | New Zealand | Construction projects | Project characteristics, client characteristics, contractor characteristics, design, consultant and tendering, external factors and market conditions, inaccurate cost estimating | - |
| Przywara and Rak [12] | Poland | multi-family housing | Time variances from the Schedule (T/S), Time variances from planned Costs (T/C) | - |
| Azman et al. [23] | Peninsular Malaysia | Construction industry |
Scope quality, information quality, uncertainty level, estimator performance, quality of estimating procedure | - |
| Gómez Cabrera [8] | Colombia | Rural road projects | Competitive bidding (Open Data), competitive bidding (Web Search) | 51 |
| Cong et al. [22] | New Zealand | Construction industry |
Project characteristics, client characteristics, contractor characteristics, tendering conditions, consultants and design, external factors and market condition, inaccuracies in cost estimation | 37 |
| Mahamid and Aichouni [25] | Saudi Arabia | Construction industry |
Client, consultants and design, cost estimating, project characteristics, contract and tendering, resources (labors, materials, equipments) | 43 |
| Raut et al. [13] | India | Roads & Highway etc |
Time, Cost, Quality | - |
| Memon et al. [24] | Malaysia | Construction projects | Causes affecting construction costs | 24 |
| Variable | Item | Questionnaire |
|---|---|---|
| Project Management Risk (PMR) |
Q22 | Budget variation due to material purchase and rental costs |
| Q21 | Difference between project cost and budget | |
| Q20 | Bond and warranty clauses | |
| Q15 | Environmental impact of the project | |
| Q19 | Allowable contingency | |
| Q16 | Non-provision of regulatory information | |
| Q18 | Number of bidders participating in the project | |
| Q17 | Cost variation due to price fluctuation | |
| Q25 | Possibility of complaints from stakeholders | |
| Q24 | Additional costs due to inappropriate budget planning | |
| Q26 | Possibility of design errors and omissions issues | |
| Q27 | Additional costs and schedule delays due to change orders | |
| Project Costing and Execution Risk (PCER) |
Q8 | Managerial labor cost estimation and project efficiency |
| Q10 | Reliability and completeness of cost information | |
| Q9 | Cost comparison and selection according to alternative methods | |
| Q7 | Allowable time for cost estimation preparation | |
| Q6 | Accuracy of estimation according to proper estimation method | |
| Q23 | Regulatory changes due to legal, institutional, and policy changes | |
| Q28 | Contract execution delay | |
| Project Execution Strategy Risk (PESR) |
Q3 | Fundraising and budget securing |
| Q2 | Experience and performance of management team | |
| Q4 | Information on loss/profit experience from similar projects | |
| Q5 | Relationship with subcontractors and suppliers | |
| Q1 | Feasibility of design and implementation | |
| Q14 | Financial situation and budget of the client | |
| Q11 | Detailed and clear specifications and drawings | |
| Q12 | Budget allocation and cost management according to project priority | |
| Q13 | Project duration | |
| Construction Project Risk (CPR) |
Q44 | Possibility of complaints from residents |
| Q42 | Winter construction suspension | |
| Q40 | Additional costs due to maintenance convenience considerations | |
| Q41 | Compensation delay | |
| Q43 | Imbalance between supply and demand of materials | |
| Project Cost and Schedule Risk (PCSR) |
Q37 | Productivity decline and additional costs due to weather conditions |
| Q38 | Budget increase during project progress due to low bidding | |
| Q39 | Lack of technical competence of the manager | |
| Q36 | Additional costs due to insufficient construction period | |
| Q35 | Cost reduction or change due to budget shortage | |
| Project Management Challenges (PMC) |
Q34 | Mismatch between design conditions and site conditions |
| Q30 | Cost increase and schedule delay due to additional work | |
| Q32 | Risk of delay in project commencement date and completion date | |
| Q31 | Conflict among consortium members | |
| Q29 | Risk of regulatory changes related to acquisition | |
| Q33 | Lack of project risk management experts | |
| Construction Project Subcontractor and Safety Management (CPSSM) |
Q46 | Lack of subcontractor technical skills |
| Q47 | Pressure to achieve target execution rate | |
| Q45 | Possibility of subcontractor bankruptcy risk occurrence | |
| Q48 | On-site accident-free pressure |
| Variable | Operational Definition | Component Matrix | Item |
|---|---|---|---|
| PMR | These issues include budget deviations, contract terms, environmental impacts, risk management, regulatory compliance, bidding processes, price fluctuation, and stakeholder responses. | Q22, Q21, Q20, Q15, Q19, Q16, Q18, Q17, Q25, Q24, Q26, Q27 | 12 |
| PCER | Issues related to managers’ labor costings, reliability of cost information, cost comparison according to alternative methods, time allowed for costing preparation, accuracy according to appropriate costing methods, regulatory changes due to legal/institutional changes, delays in contract execution, etc. | Q8, Q10, Q9, Q7, Q6, Q23, Q28 | 7 |
| PESR | Securing financing and budget, experience and performance of management, profit and loss experience information on similar projects, relationships with subcontractors and suppliers, design and implementation feasibility, client’s financial situation and budget, clear and specific specifications and drawings, project priorities. These are issues related to budget allocation, cost management, and project period according to ranking. | Q3, Q2, Q4, Q5, Q1, Q14, Q11, Q12, Q13 | 9 |
| CPR | These issues include the possibility of complaints from residents, construction suspension in winter, additional costs due to consideration of maintenance convenience, delayed compensation, and imbalance between material supply and demand. | Q44, Q42, Q40, Q41, Q43 | 5 |
| PCSR | Related issues include decreased productivity and additional costs due to weather conditions, budget increases during project progress due to low-priced bids, lack of technical capabilities of managers, additional costs due to insufficient construction period, and cost reduction or change due to lack of budget. | Q37, Q38, Q39, Q36, Q35 | 5 |
| PMC | Related issues include mismatch between design conditions and site conditions, cost increases and schedule delays due to additional work, risk of delaying project start and completion dates, conflicts among consortium members, risk of regulatory changes related to acquisitions, and lack of project risk management experts. | Q34, Q30, Q32, Q31, Q29, Q33 | 6 |
| CPSSM | These are related issues such as lack of technical capabilities of subcontractors, pressure to achieve target execution rate, possibility of subcontractor bankruptcy risk, and pressure for zero accidents on site. | Q46, Q47, Q45, Q48 | 4 |
| Category | N | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 216 | 96.43 |
| Female | 8 | 3.57 | |
| Sector | Owner | 8 | 3.57 |
| Construction project manager | 40 | 17.86 | |
| Construction manager | 176 | 78.57 | |
| Period of work | Less than 10 years | 146 | 65.18 |
| 11∼20 years | 66 | 29.46 | |
| More than 21 years | 12 | 5.36 | |
| Descriptive Statistics | Reliability Statistics | Communalities | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | N | Min | Max | M | SD | SMID | SVID | CITC | CAID | In | Ex |
| Q1 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 3.610 | 1.698 | 222.950 | 2422.980 | 0.516 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.626 |
| Q2 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 3.750 | 1.835 | 222.820 | 2396.052 | 0.627 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.827 |
| Q3 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 3.670 | 1.812 | 222.900 | 2389.043 | 0.676 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.903 |
| Q4 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 3.520 | 1.784 | 223.040 | 2403.859 | 0.600 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.793 |
| Q5 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 3.820 | 1.795 | 222.740 | 2401.466 | 0.610 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.733 |
| Q6 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.710 | 1.585 | 221.850 | 2393.391 | 0.749 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.886 |
| Q7 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.770 | 1.561 | 221.790 | 2395.521 | 0.747 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.872 |
| Q8 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.820 | 1.573 | 221.750 | 2393.635 | 0.754 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.954 |
| Q9 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.770 | 1.609 | 221.790 | 2394.615 | 0.729 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.892 |
| Q10 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.820 | 1.575 | 221.750 | 2393.491 | 0.753 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.947 |
| Q11 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.630 | 1.525 | 221.940 | 2393.243 | 0.781 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.832 |
| Q12 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.320 | 1.537 | 222.250 | 2403.325 | 0.706 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.692 |
| Q13 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.630 | 1.471 | 221.940 | 2403.628 | 0.737 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.743 |
| Q14 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.630 | 1.525 | 221.940 | 2393.243 | 0.781 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.832 |
| Q15 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.590 | 1.302 | 221.970 | 2420.403 | 0.702 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.770 |
| Q16 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.600 | 1.260 | 221.960 | 2416.914 | 0.756 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.756 |
| Q17 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.740 | 1.294 | 221.830 | 2416.422 | 0.739 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.695 |
| Q18 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.860 | 1.325 | 221.710 | 2413.195 | 0.746 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.747 |
| Q19 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 5.040 | 1.535 | 221.530 | 2410.600 | 0.657 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.682 |
| Q20 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 5.140 | 1.462 | 221.420 | 2412.819 | 0.676 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.788 |
| Q21 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.870 | 1.395 | 221.700 | 2417.755 | 0.673 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.806 |
| Q22 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.880 | 1.347 | 221.690 | 2427.857 | 0.621 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.745 |
| Q23 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.950 | 1.365 | 221.620 | 2399.843 | 0.825 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.792 |
| Q24 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.920 | 1.354 | 221.640 | 2402.258 | 0.814 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.753 |
| Q25 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.940 | 1.364 | 221.620 | 2400.926 | 0.817 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.756 |
| Q26 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.770 | 1.417 | 221.790 | 2400.272 | 0.791 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.685 |
| Q27 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.810 | 1.326 | 221.750 | 2411.327 | 0.760 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.645 |
| Q28 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.950 | 1.328 | 221.620 | 2406.238 | 0.799 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.724 |
| Q29 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.930 | 1.377 | 221.630 | 2398.350 | 0.829 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.867 |
| Q30 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.970 | 1.307 | 221.590 | 2404.215 | 0.828 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.878 |
| Q31 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.960 | 1.337 | 221.600 | 2403.801 | 0.812 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.835 |
| Q32 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 5.080 | 1.328 | 221.480 | 2408.278 | 0.783 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.815 |
| Q33 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.930 | 1.361 | 221.630 | 2402.574 | 0.807 | 0.978 | 1.000 | 0.808 |
| Q34 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.940 | 1.336 | 221.620 | 2410.380 | 0.761 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.800 |
| Q35 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 5.110 | 1.521 | 221.450 | 2417.298 | 0.618 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.816 |
| Q36 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.770 | 1.487 | 221.790 | 2430.884 | 0.539 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.804 |
| Q37 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.850 | 1.586 | 221.710 | 2429.335 | 0.513 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.867 |
| Q38 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 5.010 | 1.583 | 221.550 | 2434.446 | 0.481 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.845 |
| Q39 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 5.130 | 1.499 | 221.430 | 2428.103 | 0.553 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.846 |
| Q40 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.700 | 1.377 | 221.860 | 2416.676 | 0.691 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.983 |
| Q41 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.670 | 1.368 | 221.890 | 2418.907 | 0.679 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.932 |
| Q42 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.700 | 1.377 | 221.860 | 2416.676 | 0.691 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.983 |
| Q43 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.720 | 1.347 | 221.840 | 2415.615 | 0.715 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.944 |
| Q44 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.700 | 1.377 | 221.860 | 2416.676 | 0.691 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.983 |
| Q45 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.950 | 1.466 | 221.620 | 2415.242 | 0.657 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.799 |
| Q46 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 4.820 | 1.394 | 221.750 | 2421.805 | 0.644 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.834 |
| Q47 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 5.040 | 1.420 | 221.520 | 2413.309 | 0.694 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.876 |
| Q48 | 224 | 1 | 7.000 | 5.090 | 1.371 | 221.470 | 2422.672 | 0.649 | 0.979 | 1.000 | 0.804 |
| Variable | Item | Rotated Component Matrix | Reliability | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | α | ||
| PMR | Q22 | 0.796 | 0.189 | 0.035 | 0.087 | 0.067 | 0.115 | 0.223 | 0.956 |
| Q21 | 0.786 | 0.176 | 0.093 | 0.022 | 0.071 | 0.313 | 0.214 | ||
| Q20 | 0.766 | 0.235 | 0.076 | 0.059 | 0.050 | 0.337 | 0.142 | ||
| Q15 | 0.752 | 0.171 | 0.325 | 0.187 | 0.176 | 0.056 | 0.016 | ||
| Q19 | 0.725 | 0.112 | 0.228 | 0.114 | 0.121 | 0.249 | 0.053 | ||
| Q16 | 0.709 | 0.261 | 0.285 | 0.225 | 0.195 | 0.105 | 0.072 | ||
| Q18 | 0.664 | 0.396 | 0.092 | 0.222 | 0.173 | 0.101 | 0.227 | ||
| Q17 | 0.662 | 0.310 | 0.240 | 0.157 | 0.204 | 0.102 | 0.165 | ||
| Q25 | 0.502 | 0.419 | 0.178 | 0.201 | 0.215 | 0.328 | 0.319 | ||
| Q24 | 0.472 | 0.435 | 0.216 | 0.128 | 0.273 | 0.311 | 0.325 | ||
| Q26 | 0.455 | 0.309 | 0.232 | 0.221 | 0.239 | 0.349 | 0.317 | ||
| Q27 | 0.433 | 0.395 | 0.173 | 0.303 | 0.231 | 0.184 | 0.305 | ||
| PCER | Q8 | 0.290 | 0.844 | 0.303 | 0.174 | 0.033 | 0.163 | 0.084 | 0.964 |
| Q10 | 0.288 | 0.840 | 0.301 | 0.166 | 0.034 | 0.178 | 0.088 | ||
| Q9 | 0.278 | 0.815 | 0.264 | 0.188 | 0.025 | 0.194 | 0.081 | ||
| Q7 | 0.299 | 0.793 | 0.295 | 0.122 | 0.097 | 0.171 | 0.115 | ||
| Q6 | 0.304 | 0.792 | 0.318 | 0.151 | 0.046 | 0.157 | 0.123 | ||
| Q23 | 0.461 | 0.481 | 0.192 | 0.153 | 0.213 | 0.343 | 0.352 | ||
| Q28 | 0.385 | 0.459 | 0.248 | 0.188 | 0.239 | 0.223 | 0.402 | ||
| PESR | Q3 | 0.177 | 0.243 | 0.859 | 0.187 | 0.014 | 0.083 | 0.178 | 0.945 |
| Q2 | 0.123 | 0.224 | 0.835 | 0.146 | 0.017 | 0.138 | 0.153 | ||
| Q4 | 0.105 | 0.211 | 0.815 | 0.150 | 0.050 | 0.033 | 0.217 | ||
| Q5 | 0.112 | 0.287 | 0.760 | 0.147 | 0.009 | 0.155 | 0.119 | ||
| Q1 | 0.125 | 0.013 | 0.681 | 0.105 | 0.163 | 0.328 | -0.039 | ||
| Q14 | 0.489 | 0.338 | 0.612 | 0.213 | 0.209 | 0.108 | -0.055 | ||
| Q11 | 0.489 | 0.338 | 0.612 | 0.213 | 0.209 | 0.108 | -0.055 | ||
| Q12 | 0.370 | 0.288 | 0.595 | 0.144 | 0.295 | 0.104 | -0.010 | ||
| Q13 | 0.496 | 0.370 | 0.513 | 0.177 | 0.201 | 0.128 | -0.092 | ||
| CPR | Q44 | 0.163 | 0.164 | 0.192 | 0.897 | 0.141 | 0.164 | 0.202 | 0.992 |
| Q42 | 0.163 | 0.164 | 0.192 | 0.897 | 0.141 | 0.164 | 0.202 | ||
| Q40 | 0.163 | 0.164 | 0.192 | 0.897 | 0.141 | 0.164 | 0.202 | ||
| Q41 | 0.148 | 0.139 | 0.221 | 0.865 | 0.157 | 0.154 | 0.215 | ||
| Q43 | 0.176 | 0.188 | 0.175 | 0.848 | 0.171 | 0.193 | 0.248 | ||
| PCSR | Q37 | 0.129 | 0.034 | 0.133 | 0.176 | 0.888 | 0.094 | 0.059 | 0.885 |
| Q38 | 0.125 | 0.098 | -0.020 | 0.100 | 0.878 | 0.158 | 0.121 | ||
| Q39 | 0.287 | -0.017 | 0.099 | 0.097 | 0.833 | 0.097 | 0.203 | ||
| Q36 | 0.070 | 0.029 | 0.166 | 0.163 | 0.819 | 0.180 | 0.200 | ||
| Q35 | 0.164 | 0.199 | 0.070 | 0.123 | 0.774 | 0.171 | 0.319 | ||
| PMC | Q34 | 0.342 | 0.172 | 0.262 | 0.236 | 0.254 | 0.659 | 0.174 | 0.962 |
| Q30 | 0.338 | 0.333 | 0.233 | 0.281 | 0.248 | 0.655 | 0.171 | ||
| Q32 | 0.313 | 0.330 | 0.182 | 0.274 | 0.191 | 0.643 | 0.223 | ||
| Q31 | 0.356 | 0.279 | 0.240 | 0.272 | 0.210 | 0.630 | 0.240 | ||
| Q29 | 0.419 | 0.240 | 0.246 | 0.305 | 0.256 | 0.628 | 0.140 | ||
| Q33 | 0.363 | 0.278 | 0.222 | 0.236 | 0.299 | 0.603 | 0.204 | ||
| CPSSM | Q46 | 0.111 | 0.136 | 0.139 | 0.367 | 0.228 | 0.241 | 0.735 | 0.947 |
| Q47 | 0.339 | 0.096 | 0.065 | 0.364 | 0.287 | 0.152 | 0.714 | ||
| Q45 | 0.213 | 0.101 | 0.155 | 0.327 | 0.278 | 0.164 | 0.713 | ||
| Q48 | 0.207 | 0.165 | 0.082 | 0.312 | 0.329 | 0.120 | 0.712 | ||
| Initial Eigenvalues | 25.169 | 4.278 | 3.076 | 2.449 | 1.661 | 1.300 | 1.261 | ||
| % of Variance | 52.435 | 8.913 | 6.408 | 5.103 | 3.461 | 2.708 | 2.627 | ||
| Cumulative % | 52.435 | 61.348 | 67.756 | 72.859 | 76.320 | 79.028 | 81.655 | ||
| KMO=0.838, Bartlett’s Chi-Square=2138.321, df=1128 (p<.001) | |||||||||
| PMR | PCER | PESR | CPR | PCSR | PMC | CPSSM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMR | PC | 1.000 | 0.480** | 0.308** | 0.335** | 0.214** | 0.467** | 0.322** |
| Sig. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | |
| PCER | PC | 0.480** | 1.000 | 0.581** | 0.451** | 0.188** | 0.498** | 0.381** |
| Sig. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | |
| PESR | PC | 0.308** | 0.581** | 1.000 | 0.463** | 0.215** | 0.477** | 0.363** |
| Sig. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | |
| CPR | PC | 0.335** | 0.451** | 0.463** | 1.000 | 0.365** | 0.519** | 0.607** |
| Sig. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | |
| PCSR | PC | 0.214** | 0.188** | 0.215** | 0.365** | 1.000 | 0.421** | 0.383** |
| Sig. | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | |
| PMC | PC | 0.467** | 0.498** | 0.477** | 0.519** | 0.421** | 1.000 | 0.531** |
| Sig. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | |
| CPSSM | PC | 0.322** | 0.381** | 0.363** | 0.607** | 0.383** | 0.531** | 1.000 |
| Sig. | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||
| N | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | 224 | |
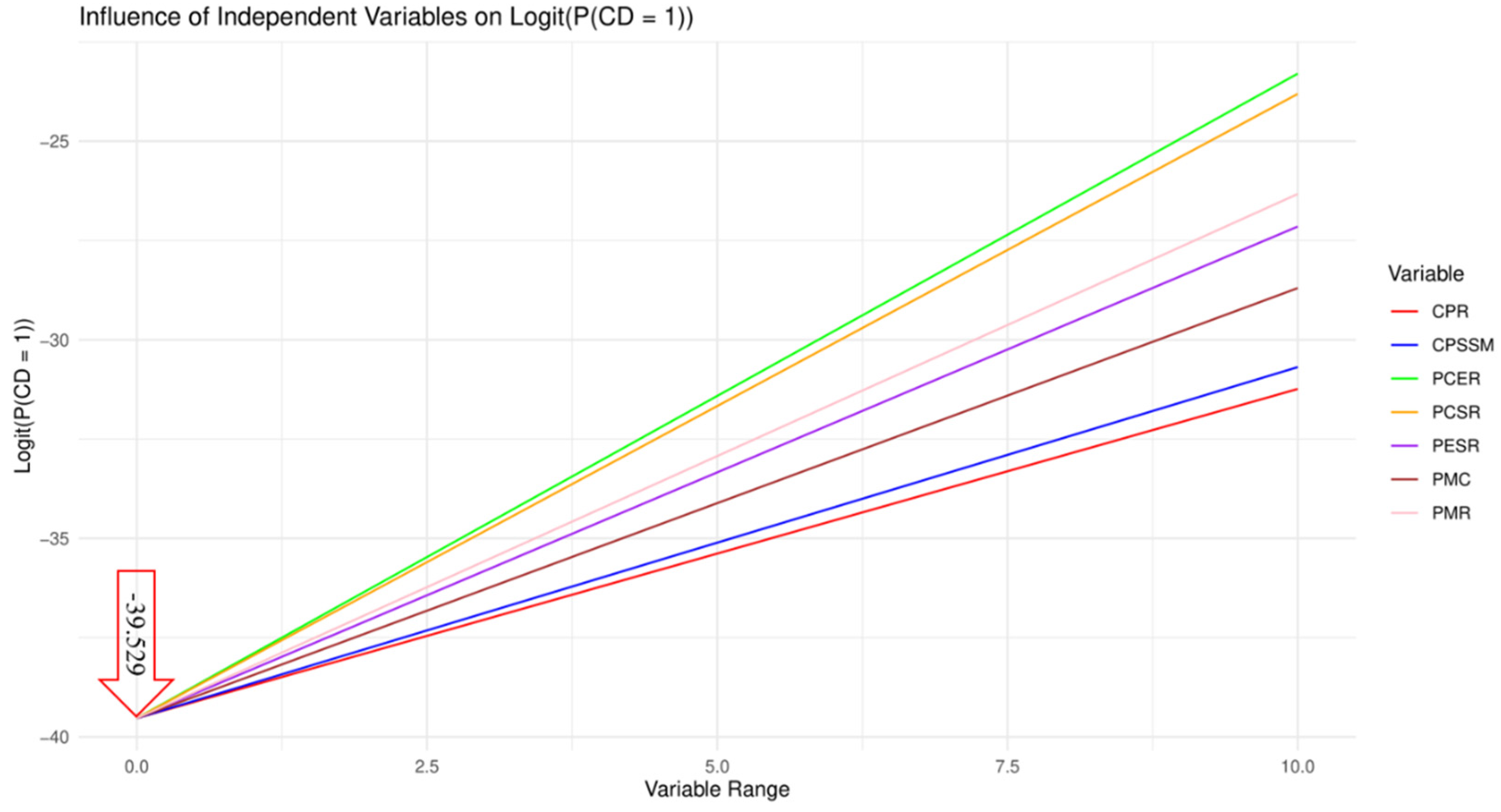
| H | DV | IV | B | S.E. | Wald | P | OR | 95% C.I.for EXP(B) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| H1 | CD | PMR | 1.320 | 0.416 | 10.082 | 0.001 | 3.744 | 1.657 | 8.457 |
| H2 | CD | PCER | 1.623 | 0.417 | 15.117 | 0.000 | 5.068 | 2.236 | 11.484 |
| H3 | CD | PESR | 1.238 | 0.317 | 15.265 | 0.000 | 3.447 | 1.853 | 6.413 |
| H4 | CD | CPR | 0.829 | 0.413 | 4.030 | 0.045 | 2.292 | 1.020 | 5.151 |
| H5 | CD | PCSR | 1.572 | 0.389 | 16.375 | 0.000 | 4.817 | 2.250 | 10.317 |
| H6 | CD | PMC | 1.083 | 0.363 | 8.929 | 0.003 | 2.954 | 1.452 | 6.013 |
| H7 | CD | CPSSM | 0.884 | 0.318 | 7.705 | 0.006 | 2.419 | 1.297 | 4.515 |
| Constant | -39.529 | 7.301 | 29.315 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||
| Omnibus Tests of Model Coefficients: Chi-square=243.734, df=7, P=0.000 | |||||||||
| Model Summary: -2 Log likelihood=66.635, Cox & Snell R Square=0.663, Nagelkerke R Square=0.884 | |||||||||
| Hosmer and Lemeshow Test: Chi-square=3.559, df=8, P=0.895 | |||||||||
| Classification Table: Observed Cost Diviation Predicted Percentage 0=95.4, 1=93.0, Overall Percentage=94.2 | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





