Abstrac: tPericyte and their tunnelling nanotubes (P-TNTs) have been described as involved in the early phases of angiogenesis in the human normal developing brain and glioblastoma, being a common feature of combined endothelium/pericyte vessel sprouts. Based on the few data available so far about this ‘alternative’ pericyte-TNT-driven mode of angiogenesis, whose precise function in vessel growth through vascular cells communication, has still to be determined, this study aims to cast light on the regulative molecules involved in this process, governed by intimate pericyte-endothelial interactions. After considering the existence of the sprout guiding pericyte and P-TNT, as shown by pioneering ultrastructural studies as well as by more recent observations with NG2/CD146 pericyte markers and basal lamina molecules, a step-by-step profile of the process has been suggested and an investigation undertaken on ‘unconventional’, pro-angiogenic ligand/receptor systems, that may have a role aside from the canonical pathways. In this context, a possible candidate worthy of investigation is the c-KIT receptor, a member of the tyrosine kinase family of proteins, which also includes the well-known VEGFR and PDGFR. According to the obtained results showing a primary localization of c-KIT on endothelial cells and pointing out a differential distribution of the receptor on normal vs glioblastoma vessels, it seems conceivable to propose the stem cell factor/c-KIT signaling as a key factor in pericyte-TNT-driven angiogenesis, advancing this alternative mode of angiogenesis and the c- KIT pathway as possible targets for devising effective antiangiogenic therapeutic strategies.
Introduction
Among the variety of cell nanostructures, denoted as tunnelling nanotubes (TNTs), a specific type, whose cell source has been identified as pericytes of the central nervous system (CNS), intervenes in angiogenesis, neurovascular coupling, and in cell cross-talk within the neurovascular unit (NVU) [
1,
2,
3]. In previous studies on human fetal brain and human glioblastoma vascularization, pericyte-TNTs (P-TNTs) have been unveiled by NG2 and CD146 as markers of pericytes, in association with the endothelial cell-specific marker CD31 and vessel basal lamina (VBL) molecules, such as fibronectin, laminin, collagen (COL) IV, COL VI [
1,
4]. Interactions between cell surface integrins and fibronectin or laminin have been demonstrated to be essential in the formation of immune cell TNTs [
5], and retinal vessel pericytes, labelled by NG2-DsRed/laminin, have been detected to give origin to TNTs enwrapped by basal lamina molecules [
2]. These observations support the effectiveness of the VBL in revealing pericyte conduits and P-TNTs, distinguishing them from ‘string vessels’, described as formed by VBL residues after endothelial cell death and vessel remodeling in stroke pathology [
6]. Indeed, after exposure to experimental conditions of hypoxia and ischemia, aspects of neo-angiogenesis, characterized by P-TNT-like structures, have been detected as a tissue response and an attempt at vascular recovery [
7]. Endothelium-free pericyte conduits and segments of growing sprouts were firstly revealed by Ozerdem and colleagues in mouse retina and gliomas [
8,
9], and have subsequently been confirmed in human developing brain and glioblastoma, where P-TNTs have also been unveiled, and appear to be involved in the pericyte-driven mode of vessel growth [
1,
4,
10,
11,
12,
13].
Human Brain Vascularization Analyzed by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) - A Lesson Learned from the Pioneering Studies by G. Allsopp and H. J. Gamble
An important pillar of the understanding of the pericyte-guided mode of vessel growth lies in the pioneering ultrastructural studies by G. Allsopp and H. J. Gamble. These Authors analyzed the complex interrelationships that govern endothelial cells and pericytes during human brain vascularization on TEM serial sections, [
14,
15]. In these studies, very early aspects of angiogenesis were revealed by the presence of single cell capillaries, without junctional complexes, enwrapped in a basal lamina and pericyte processes (Supplementary
Figure 1A; see also [
4]). Thanks to serial sections, ‘seamless' capillaries and their blind end were also reconstructed (Supplementary
Figure 1B, C) and show endothelial filopodial processes that pass through pericyte gaps (Supplementary
Figure 1D) and pericyte processes that leave the capillary to penetrate the surrounding microenvironment (Supplementary
Figure 1E). In addition,
“a long endothelial cell process enwrapped by a pericyte, dissecting its way through the surrounding neuropil”, associated to a very electrodense VBL, is reported as the ‘
most striking’ observation in the study (Supplementary
Figure 1F). The ultrastructural details of the earliest phases of angiogenesis revealed in the human developing brain support the existence of P-TNTs and endothelial cells in combined forms of sprouts that identify a P-TNT-driven mode of angiogenesis [
1,
4]. As discussed by Gerhardt and Betsholtz [
16], the common view of a late recruitment and stabilizing role of pericytes during vessel growth, in both brain and retina vascular networks, conflicts with evidence of pericytes as plastic, dynamic, and challenging cells, with mesenchymal (or better ectomesenchymal) background and, therefore, running close to assume the role of other cells, including endothelial cells, according to specific angiogenic timing and environment signals [
17,
18,
19].
Investigating Pericyte-TNT-Driven Angiogenesis by c-KIT Receptor, a Member of the Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) Family of Proteins
Pro-angiogenic molecules and signaling pathways, involved in the canonical endothelial mode of angiogenic vessel sprouting, have been deeply investigated in normal and pathological conditions [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30]. Among these are the kinase receptors VEGFR, PDGFR, RET, and c-KIT; the latter, having received little attention as a pro-angiogenic molecule, is the focus of the present study, which aims to investigate regulative molecules possibly involved in the ‘unconventional’ pericyte-TNT-driven mode of angiogenesis. In humans, 58 receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are divided into classes according to specific structures of the amino (N)-terminal ligand binding ectodomains [
31]. c-KIT belongs to Class III, which also includes platelet-derived growth factor α and β receptors (PDGFR α/β), colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor, fms-like RTK 3 [
32]. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB), and its receptor PDGFR-β play well-established roles in endothelial-pericyte interactions, vessel growth/stabilization and, blood-brain barrier differentiation [
33,
34]. c-KIT RTK protein is also referred to as CD117 or stem cell factor (SCF) receptor due to its association with the ligand SCF. SCF/c-KIT interaction induces the dimerization of the receptor and its activity as both an enzyme and a self-substrate, as initially demonstrated in hemangioblastic progenitors [
35]. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) express both the ligand and the receptor, whose signaling promotes endothelial cell survival, migration, and capillary tube formation, thus replicating the pro-angiogenic activities of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) [
36] but with different levels of phosphorylation of the Erk1/2 and PI3K-Akt pathways [
36]. In our studies of human brain and human glioblastoma vascularization [
1,
4,
10,
11,
12,
37,
38,
39,
40,
41,
42], we have focused our attention on analysis of c-KIT protein and its relations with the pericyte-TNT-driven mode of angiogenesis. To allow the 3D reconstruction of pericyte-guided angiogenesis led by P-TNT, that are in the front line tracing the way for the pericyte growing sprout, we have carried out our analysis ‘ex vivo’ on human fetal brain and glioblastoma samples, according to protocols previously established for preserving TNT structure, on free-floating 20-μm vibratome sections examined under high-resolution confocal microscopy [
1]. Cellular and subcellular c-KIT immunolocalization was performed by double staining with COL IV as a major component of the vessel basal lamina (VBL) functionally shared in the intimate pericyte/endothelial cells coupling.
Material and Methods
Fetal Specimen Histology and Immunostaining
Fetal brain specimens were dissected from fetuses at 18 and 22 weeks of gestation (wg; 2 for each of the examined ages) spontaneously aborted due to preterm rupture of the placental membranes and with no history of neurological pathologies. Fetal tissue was collected after informed consent from the mother at the end of the abortion procedure. The sampling and handling of the specimens conformed to the ethical rules of the Department of Emergency and Organ Transplantation, Division of Pathology, University of Bari School of Medicine, and approval was gained from the local Ethics Committee of the National Health System in compliance with the principles stated in the Declaration of Helsinki. The fetal age was estimated based on the crown-rump length and/or pregnancy records (counting from the last menstrual period). At autopsy, the fetuses did not reveal macroscopic structural abnormalities and/or malformations of the central nervous system. The dorso-lateral wall of each telencephalic vesicle (future cerebral cortex), was dissected, along the coronal planes, in slices (n = 6) about 0.5 cm thick, fixed for 2–3 h at 4 °C by immersion in 2% paraformaldehyde (PFA) plus 0.2% glutaraldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline solution (PBS, pH 7.6) and then washed in PBS. For each fetus, 3–4 samples were serially cut using a vibrating microtome (Leica Microsystem; Milton Keynes, UK) into 20-µm sections, parts of which were processed for routine histological analysis with toluidine blue staining to rule out the presence of microscopic malformations. All the other sections were stored at 4 °C in PBS plus 0.02% PFA for immunolabeling and fluorescence microscopy. Single and multiple immunostainings were carried out with the following polyclonal (pAb) and monoclonal (mAb) antibodies diluted in blocking buffer (BB; 1% bovine serum albumin and 2% fetal calf serum in PBS): pAb anti-NG2 (kindly provided by William Stallcup, The Sanford-Burnham Institute for Medical Research, La Jolla, CA, USA), mAb anti-CD146 (Abcam; Cambridge, UK; Cat. AB49492), mAb anti-CD31 (Dako; Santa Clara, CA, US; Cat. M0823), pAb anti-c-KIT (Dako, Cat. A4502), mAb anti-COL type IV (Dako, Cat. M0785). Free-floating sections were incubated with 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS for 30 min at room temperature (RT), BB 30 min at RT, followed by incubation, with single or combined primary antibodies, overnight at 4 °C and with appropriate fluorophore-conjugated secondary antibodies (fluorophore 488, 555, and 633; Thermo Fisher Scientific; Waltham, MA, USA) or biotinylated secondary antibodies for 45 min at RT, the latter subsequently revealed by fluorophore-conjugated streptavidin (Streptavidin-Alexa 488, Streptavidin-Alexa 555; Thermo Fisher Scientific). After each incubation step the sections were washed 3 times for 5 min with PBS. The sections were then post-fixed in 4% PFA for 10 min and nuclear counterstaining was performed by incubations in TOPRO-3 (diluted 1:10 K in PBS; Thermo Fisher Scientific). Finally, the sections were allowed to adhere on polylysine slides (Menzel-Glaser, GmbH, Braunschweig, Germany) by drying for 10 min at RT, coverslipped with Vectashield (Vector Laboratories Inc., Burlingame, CA, USA), and sealed with nail varnish. Negative controls were prepared by omitting the primary antibodies and by mismatching the secondary antibodies.
Glioblastoma Histology and Immunostaining
Glioblastoma samples (n = 6) were collected from primary tumors specimens obtained in a previous study, in which the imaging techniques and histological analysis were specified in detail [
38]. The six GB patients were 4 males, aged 30 to 55 years-old, and 2 females, of 52 and 53 years-old, who underwent surgery at the Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital Zurich (Switzerland). Written informed consent was obtained from patients before study entry. All procedures were approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Bari Medical School and by the Ethics Committee of Canton Zurich, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Glioma samples were classified according to the WHO 2021 criteria. The samples were dissected (≤ 0.5 cm in thickness) and then fixed for 2–3 h at 4 °C by immersion in 2% PFA plus 0.2% glutaraldehyde in phosphate-buffered saline solution (PBS, pH 7.6). Specimens were then washed in PBS, and serially cut using a vibrating microtome (Leica Microsystem; Milton Keynes, UK); 20-μm sections were stored at 4 °C in PBS plus 0.02% PFA for immunolabeling and fluorescence microscopy. Double immunostainings were carried out with pAb anti-c-KIT and mAb anti-COL type IV, as described for fetal section. Negative controls were prepared by omitting the primary antibodies and by mismatching the secondary antibodies.
Laser Confocal Microscopy Analysis
Sections were examined with a Leica TCS SP5 confocal laser-scanning microscope (Leica Microsystems, Mannheim, Germany) using a sequential scanning procedure and, when appropriate, an overexposed laser setting. Confocal images were taken at 0.35 µm intervals through the z-axis of the sections, with 40× and 63× oil lenses associated with zoom factors from 1.5 to 3. Single, serial optical planes and z-stacks (projection images) were analyzed by Leica confocal software (Multicolour Package; Leica Microsystems).
Results
Preliminary Analysis of Steps That Characterize the Pericyte-TNT-Driven Neuro-Angiogenesis
The alternative, pericyte-guided mode of vessel growth, described in human developing brain and glioblastoma tissues [
1,
4,
10], can be suggested to take place according to a sequence of steps that also includes a role for P-TNTs and can be summarized as follows: i) appearance on the parental vessel of a pericyte ‘cone of extrusion’, ii) emergence of the leading P-TNT, iii) elongation of the pericyte proximal cone in a pericyte conduit, iv) engagement of the endothelial tip cell in the pericyte conduit, v) endothelial lumen formation (Supplementary
Figure 2). Similar pericyte-guided vessel growth events have also been described in corpus luteus vascularization, including elongation and migration of pericytes at the leading tip of the sprout and the presence of endothelial cells behind the leading front [
43]. According to our previous results, and as a preliminary step in this study, the pro-angiogenic potency of pericytes involved in the pericyte-guided angiogenesis has been further investigated by double labelling with NG2/CD146, as pericyte markers, and by NG2/CD31, the latter as a reliable endothelial cell marker, on sections from developing fetal brains (Supplementary
Figure 2). The results show NG2
+ pericyte conduits inhabited by engaged CD31
+ endothelial tip cells and NG2
+ pericyte-TNTs at the leading front of the combined sprouts (Supplementary
Figures 2A-D). Pericyte-TNTs, bridging facing capillaries, are also revealed by NG2/CD146 double staining (Supplementary
Figure 2E, F, F’). On these fields, the pericyte-guided sprout and the entire length of the leading pericyte-TNT are clearly shown by the pericyte marker CD146 (Supplementary
Figures 2F, F’). The analysis of gene expression in retinal pericytes and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and the evaluation of their similarity in angiogenesis-related gene expression, confirmed a direct correlation between CD146 expression and the angiogenic pericytes differentiation pathway [
17]. CD146
+ pericytes co-seeded with endothelial cells on Matrigel™ revealed their angiogenic potential to support neovascularization [
19] and improve sprout integrity and formation of pericyte-endothelial cords in cocultures [
44]. Moreover, more recent studies have demonstrated that subsets of CD146
+ pericytes develop strong angiogenic interactions with endothelial cells and stimulate endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis in spheroid assays [
45], and that CD146 identifies MSC-like pericytes that play an important pro-angiogenic role in the growth phase of infantile hemangiomas [
46].
c-KIT Cellular and Subcellular Immunolocalization in Human Developing Brain
On sections of the human fetal brain, double immunolabeled for c-KIT and COL IV, a high number of neuronal cell progenitors migrating through the layers that form the fetal telencephalon (future cerebral cortex and subcortical white matter) are recognizable as c-KIT
+ cells. Neuroblasts, clearly distinguishable by their rounded euchromatic nucleus, reveal a dual c-KIT immunostaining on the nucleus and their leading process (
Figure 1A, B, D). On these fields, penetrating, radial capillaries, whose vascular profile appears well marked by their COL IV-enriched VBL, often appear bridged by regularly spaced pericyte-TNTs marked by COL IV (
Figure 1A, B). This developing vascular network includes c-KIT immunolabeled capillaries (
Figure 1) and capillaries that do not stain for the receptor (
Figure 2A, B). The in-depth analysis of the c-KIT
+ developing microvessels allowed us to recognize details of the receptor subcellular distribution on vascular cells. The endothelial cells appear c-KIT
+, whereas pericytes, recognizable as embedded in the COL IV VBL, do not show any c-KIT signal (
Figure 1,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). As observed for cerebral cortex neuroblasts, the endothelial cells are characterized by a dual subcellular c-KIT reactivity, a strong nuclear reactivity together with a well detectable c-KIT staining of the endothelial cell membrane (
Figure 1-3). At the sites of pericyte-TNT emergence, endothelial cells, pre-engaged/engaged in the pericyte conduit, are c-KIT
+ on both their nucleus and cell membrane, as the other endothelial cells of the parental vessel to which they belong (
Figure 1,
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). Analyzing P-TNTs bridging two facing microvessels, it seems that only the one that corresponds to the pre-engaged endothelial cell is c-KIT reactive (
Figure 1A-C), whereas at the opposite side, the purported receiving capillary shows endothelial cells with a weak or absent c-KIT staining both at the nucleus and cell membrane (
Figure 1D). It is noteworthy that in the combined endothelium/pericyte vessel sprouts, the
leading pericytes placed at the origin of the P-TNT
do not reveal any c-KIT reactivity (Figures 2A, C, D and 3C).
c-KIT Cellular and Subcellular Immunolocalization in Glioblastoma
In glioblastoma samples, tumoral cells mainly show a nuclear c-KIT reactivity (
Figures 4), while only a few are characterized by a plasmalemmal c-KIT staining (
Figure 4B, D). Interestingly, some of these cells can be recognized as tumoral astrocytes, whose processes appear also stained by c-KIT (
Figure 4A). The tumoral vessels, revealed by their COL IV-enriched VBL, appear irregularly arranged and connected by a network of P-TNTs (
Figure 4). At a subcellular level, the endothelial cells of glioma vessels show a low c-KIT
+ plasma membrane and an unlabelled nucleus (
Figure 4B-D). As already observed in the developing brain, on glioblastoma sections, pericytes at the origin of TNTs do not appear immunostained by c-KIT (
Figure 4C, D).
Discussion
Cellular Expression of c-KIT and Its Subcellular Localization in Human Developing Brain and Human Glioblastoma
The evaluation of c-KIT receptor tyrosine kinase by confocal microscopy immunofluorescence, during fetal development and in human glioblastoma, allowed us to trace the general distribution of the receptor in these tissues and to focus on the analysis of c-KIT on their vascular cellular components. The core findings of the study are: the detection of a dual localization of c-KIT, in the nucleus and at the cell membrane of neural, tumoral and vascular cell types; the demonstration of a differential expression of c-KIT on vascular cells, c-KIT
+ endothelial cells
vs c-KIT
- pericytes; the observation of different levels and distribution of the endothelial c-KIT in glioma vessels, c-KIT
low, compared to normal brain microvessels, c-KIT
high. Overall, during cerebral cortex neurogenesis, the c-KIT immunosignal was detected on both the nucleus and the leading process of neural cell precursors, a similar dual localization being observed on a subset of glioblastoma tumor cells. These results are consistent with the demonstrated activity of the SCF/c-KIT signal on cell proliferation, survival, and migration during human normal and tumoral tissues development [
36] and should be further investigated by ‘specific’ essential markers for phenotyping and identifying c-KIT
+ cells in human developing brain and glioblastoma.
Endothelial c-KIT and Angiogenically Activated Microvessels
The focus of the study on fetal brain and glioblastoma vascular components and on pericyte-TNT-driven vessel growth contributed original data to the pro-angiogenic profile of c-KIT and, indirectly, to the involvement of the c-KIT ligand, the SCF, as an angiogenic cytokine [
36]. During brain vascularization, angiogenically activated microvessels have been identified by the endothelial dual localization of c-KIT. In glioblastoma tissue, the endothelial cells of the tumoral vessels also express the tyrosine kinase receptor c-KIT, although on these cells, its immunosignal is lower and the receptor appears to be restricted to the cell membrane. Pioneering studies have demonstrated that human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) constitutively express SCF and c-KIT mRNA and that SCF-specific transcripts increase by inflammatory stimuli [
47,
48,
49]. Early studies have also demonstrated a role of endothelial SCF in endothelial survival and migration, as well as in capillary tube formation; activities that are independent from those of angiogenic factors, such as VEGF, bFGF, and HGF [
36]. The exposure of HUVECs to SCF triggers tyrosine phosphorylation of Akt, Erk1/2, and c-KIT, while the c-KIT inhibitor STI-571 has been reported to inhibit the SCF-promoted formation of capillary tubes [
36]. Especially Akt, strongly phosphorylated by SCF, in comparison to VEGF, promotes tube formation by endothelial cells at a locus downstream of SCF/c-KIT signaling, confirming that overall the SCF and VEGF pathways are partly different and independent and that Akt and Erk1/2 have a dominant role in capillary tube formation under SCF/c-KIT control [
36]. In addition, it has been highlighted that c-KIT deficiency hindered vascular endothelial stem cell proliferation and blocked angiogenesis
in vivo [
50].
c-KIT and Pericyte-TNT-Driven Vessel Sprouting
The importance of SCF/c-KIT system activation in angiogenesis has been associated with the canonical mechanisms of endothelial sprouting in normal and pathological conditions [
51,
52]. Herein, we investigated cell distribution and immunolocalization of the c-KIT receptor to unveil its possible involvement in ‘alternative’ pro-angiogenic signaling pathways associated with ‘unconventional’ pericyte-TNT-driven vessel sprouts to promote endothelial proliferation, migration, and lumenization. The results support this hypothesis, detecting high levels of c-KIT protein on the nucleus and cell membrane of endothelial cells engaged in the pericyte conduit during brain vascularization, as well as lower levels of the receptor localized at the cell membrane of tumoral endothelial cells. During both brain vascularization and glioblastoma tumor vessel growth, like in the physiological, repetitive event of bovine corpus luteum vascularization, pericytes establish close interactions with endothelial cells and play an active role in vessel sprouting being regularly associated with the leading front of the capillary sprouts, where they serve as guiding structures aiding the outgrowth of the endothelial cells [
43]. Ultrastructural analysis has shown early capillary sprouts preceded by slender, bipolar pericytes, surrounded by a basal lamina, and migrating at the tips of the sprouts, together forming combined cylindrical projections with comigrating endothelial cells that soon acquire a slit-like lumen [
43]. The results obtained by high-resolution confocal microscopy were able to add further details to this description of pericyte-guided angiogenesis, demonstrating the presence of a ‘sensing’ pericyte-TNT at the leading front of the growing sprout. During corpus luteum angiogenesis, in response to the hypoxia conditions, endothelial cell-released nitric oxide (NO), together with VEGF/VEGFR1 endothelium/pericyte signaling, spark endothelial and pericyte paracrine as well as autocrine loops, coordinating the earlier angiogenesis steps [
53,
54,
55,
56]. It should be emphasized that hypoxia also stimulates quiescent pericytes to an effective response, including their activation to a pro-angiogenic state [
57,
58]. Therefore, pericyte SCF and endothelium SCF, as biologically active soluble and membrane-bound forms, may activate c-KIT receptors on endothelial cells and intervene in both the loops. Endothelial SCF may prevent the endocytosis of c-KIT receptor on endothelial cells and offer a mechanism of self-survival, while pericyte SCF can trigger the c-KIT signaling, stimulating endothelial cell proliferation, survival, and migration [
49,
59], intervening in NO production from endothelial cells, and increasing vascular leakage [
60]. In human fetal and adult bone marrow the subset of CD146
+ CXCL12
+ JAGGED-1
+ ANGPT-1
+ pericytes surrounding the sinusoids has been demonstrated to be the major producer of SCF [
61] followed by endothelial cells [
59] [
49]. These data suggest the possible role of pericytes in a paracrine/juxtracrine SCF/c-KIT-mediated regulative loop of the described pericyte-guided vessel sprouting.
The Dual, Nuclear and Cell Membrane, Endothelial c-KIT Protein Immunolocalization
This study, therefore, confirms and adds new data to the pioneering studies that revealed the unconventional nuclear localization of c-KIT in addition to its classical transmembrane localization [
62] and offers confirmation that c-KIT, like several other transmembrane RTKs, is not only expressed at the cell membrane level but can also translocate in the nucleus, where it can play a number of roles including acting as a transcriptional factor. It has been suggested that the localization of the c-KIT receptor in the nucleus may be a result that suffers from potential artifacts [
63]. The improved methodological approach adopted allowed the analysis of subcellular compartments providing morphofunctional data supporting the understanding of the mechanistic roles of the tyrosine kinase receptor in its translocation to the nucleus [
64]. Transmembrane proteins, that can move to the cell nucleus through a variety of mechanisms, at this site may provide a number of functions and are defined as nuclear localized membrane proteins (NLMPs). The receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are among the more representative in the class of NLMPs. RTKs also play roles as transcription factors in cancer cells, thereby becoming important targets for possible cancer therapies [
65,
66]. Interestingly, it has recently been demonstrated that a member of the RTK family, the receptor MET, in its nuclear form, regulates cancer stem-like cells self-renewal, thus promoting cancer recurrence and playing a Janus role in cell death and cell survival [
67]. Although the association of the nuclear form of a number of human RTK subfamilies has been associated with pharmacological resistance and signaling related DNA replication, few data are so far available about c-KIT behavior as an NLMP [
66,
67,
68]. Accordingly, the finding of a dual, nuclear and plasmalemmal, c-KIT immunolocalization in endothelial cells opens a new perspective on a potential different role in developing brain
vs glioblastoma. In the latter, c-KIT is absent in the endothelial nucleus, while barely detectable at the endothelial cell membrane. It is noteworthy that in chronic myeloid leukemia, therapy-resistant hemopoietic stem cells responsible for the disease relapse and drug-resistance have been identified by a low c-KIT expression and pose a challenge to the efficacy of tyrosine kinase inhibitor-based therapies [
69].
Conclusions
In conclusion, our data clearly emphasize the importance of c-KIT expression in endothelial cells of the developing and tumoral brain vascular networks and at the site of pericyte-guided vessel growth, suggesting that in both the examined conditions, SCF/c-KIT signaling may play complex and cell-specific autocrine and paracrine/juxtracrine pro-angiogenic roles, as well as being involved as an ‘alternative’ signaling pathway in the activation of the ‘unconventional’ pericyte-TNT-driven mode of human brain angiogenesis. These data extend the comprehension of the mechanisms involved in pathophysiological angiogenic events, suggesting the c-KIT pathway as a potential target for devising effective antiangiogenic therapeutic strategies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.E., D.V.; Methodology, T.A., I.D.T.; Validation, M.E.; Formal Analysis, T.W.; Investigation, M.E., T.A., A.d’A., I.D.T., T.W., F.G., D.V.; Resources, M.E., F.G., T.W., DV.; Data Curation, I.D.T., M.E.; Writing – Original Draft Preparation, M.E., T.A., A.d’A., I.D.T., F.G., D.V.; Writing – Review & Editing, M.E., T.W., F.G., D.V.; Visualization, M.E.; Supervision, M.E., D.V.; Funding Acquisition, D.V.
Funding
The authors declare no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Bari Medical Committee and of the National Health System Ethics Committee of Canton Zurich. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank M.V.C. Pragnell, BA, for language help, Michelina de Giorgis for technical and confocal microscopy assistance and Francesco Fumai for general laboratory assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Errede, M., D. Mangieri, G. Longo, F. Girolamo, I. de Trizio, A. Vimercati, G. Serio, K. Frei, R. Perris, and D. Virgintino. Tunneling Nanotubes Evoke Pericyte/Endothelial Communication During Normal and Tumoral Angiogenesis. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 1, 28. [CrossRef]
- Alarcon-Martinez, L., D. Villafranca-Baughman, H. Quintero, J. B. Kacerovsky, F. Dotigny, K. K. Murai, A. Prat, P. Drapeau, and A. Di Polo. Interpericyte Tunnelling Nanotubes Regulate Neurovascular Coupling. Nature 2020, 585, 7823, 91-95. [CrossRef]
- Pisani, F., V. Castagnola, L. Simone, F. Loiacono, M. Svelto, and F. Benfenati. Role of Pericytes in Blood-Brain Barrier Preservation During Ischemia through Tunneling Nanotubes. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 7, 582. [CrossRef]
- Girolamo, F., I. de Trizio, M. Errede, G. Longo, A. d'Amati, and D. Virgintino. Neural Crest Cell-Derived Pericytes Act as Pro-Angiogenic Cells in Human Neocortex Development and Gliomas. Fluids Barriers CNS 2021, 18, 1, 14. [CrossRef]
- Osteikoetxea-Molnár, A., E. Szabó-Meleg, E. A. Tóth, Á Oszvald, E. Izsépi, M. Kremlitzka, B. Biri, L. Nyitray, T. Bozó, P. Németh, M. Kellermayer, M. Nyitrai, and J. Matko. The Growth Determinants and Transport Properties of Tunneling Nanotube Networks between B Lymphocytes. Cell Mol Life Sci 2016, 73, 23, 4531-45. [CrossRef]
- Zille, M., M. Ikhsan, Y. Jiang, J. Lampe, J. Wenzel, and M. Schwaninger. The Impact of Endothelial Cell Death in the Brain and Its Role after Stroke: A Systematic Review. Cell Stress 2019, 3, 11, 330-47. [CrossRef]
- Girolamo, F., Y. P. Lim, D. Virgintino, B. S. Stonestreet, and X. F. Chen. Inter-Alpha Inhibitor Proteins Modify the Microvasculature after Exposure to Hypoxia-Ischemia and Hypoxia in Neonatal Rats. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 7. [CrossRef]
- Ozerdem, Ugur, and William B. Stallcup. Early Contribution of Pericytes to Angiogenic Sprouting and Tube Formation. Angiogenesis 2003, 6, 3, 241-49. [CrossRef]
- Ozerdem, U., and W. B. Stallcup. Pathological Angiogenesis Is Reduced by Targeting Pericytes Via the Ng2 Proteoglycan. Angiogenesis 2004, 7, 3, 269-76. [CrossRef]
- Virgintino, D., U. Ozerdem, F. Girolamo, L. Roncali, W. B. Stallcup, and R. Perris. Reversal of Cellular Roles in Angiogenesis: Implications for Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. J Vasc Res 2008, 45, 2, 129-31. [CrossRef]
- Virgintino, D., F. Girolamo, M. Errede, C. Capobianco, D. Robertson, W. B. Stallcup, R. Perris, and L. Roncali. An Intimate Interplay between Precocious, Migrating Pericytes and Endothelial Cells Governs Human Fetal Brain Angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 2007, 10, 1, 35-45. [CrossRef]
- Girolamo, F., M. Errede, A. Bizzoca, D. Virgintino, and D. Ribatti. Central Nervous System Pericytes Contribute to Health and Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 10. [CrossRef]
- Sattiraju, A., and A. Mintz. Pericytes in Glioblastomas: Multifaceted Role within Tumor Microenvironments and Potential for Therapeutic Interventions. Adv Exp Med Biol 2019, 1147, 65-91. [CrossRef]
- Allsopp, G., and H. J. Gamble. An Electron Microscopic Study of the Pericytes of the Developing Capillaries in Human Fetal Brain and Muscle. J Anat 1979, 128, Pt 1, 155-68.
- ———. Light and Electron Microscopic Observations on the Development of the Blood Vascular System of the Human Brain. J Anat 1979, 128, Pt 3, 461-77.
- Gerhardt, H., and C. Betsholtz. Endothelial-Pericyte Interactions in Angiogenesis. Cell Tissue Res 2003, 314, 1, 15-23. [CrossRef]
- 17. Covas, Dimas T., Rodrigo A. Panepucci, Aparecida M. Fontes, Wilson A. Silva, Maristela D. Orellana, Marcela C. C. Freitas, Luciano Neder, Anemari R. D. Santos, Luiz C. Peres, Maria C. Jamur, and Marco A. Zago. Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Obtained from Diverse Human Tissues Share Functional Properties and Gene-Expression Profile with Cd146+ Perivascular Cells and Fibroblasts. Experimental Hematology 2008, 36, 5, 642-54. [CrossRef]
- Santos, G. S. P., L. A. V. Magno, M. A. Romano-Silva, A. Mintz, and A. Birbrair. Pericyte Plasticity in the Brain. Neurosci Bull 2019, 35, 3, 551-60. [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, M., J. J. Bara, C. M. Sprecher, U. Menzel, J. M. Jalowiec, R. Osinga, A. Scherberich, M. Alini, and S. Verrier. Pericyte Plasticity - Comparative Investigation of the Angiogenic and Multilineage Potential of Pericytes from Different Human Tissues. Eur Cell Mater 2016, 31, 236-49. [CrossRef]
- Huang, Hu. "Pericyte-Endothelial Interactions in the Retinal Microvasculature." International Journal of Molecular Sciences, no. 19 (2020). https://mdpi-res.com/d_attachment/ijms/ijms-21-07413/article_deploy/ijms-21-07413.pdf?version=1602149791.
- 21. Armulik, Annika, Alexandra Abramsson, and Christer Betsholtz. Endothelial/Pericyte Interactions. Circulation Research 2005, 97, 6, 512-23. [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D. Transgenic Mouse Models of Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 2008, 266, 1-35. [CrossRef]
- 23. Lee, Hye Shin, Jiyeon Han, Hyun-Jeong Bai, and Kyu-Won Kim. Brain Angiogenesis in Developmental and Pathological Processes: Regulation, Molecular and Cellular Communication at the Neurovascular Interface. The FEBS Journal 2009, 276, 17, 4622-35. [CrossRef]
- 24. Stapor, Peter C., Richard S. Sweat, Derek C. Dashti, Aline M. Betancourt, and Walter Lee Murfee. Pericyte Dynamics During Angiogenesis: New Insights from New Identities. J Vasc Res 2014, 51, 3, 163-74. [CrossRef]
- 25. Ahir, Bhavesh K., Herbert H. Engelhard, and Sajani S. Lakka. Tumor Development and Angiogenesis in Adult Brain Tumor: Glioblastoma. Molecular Neurobiology 2020, 57, 5, 2461-78. [CrossRef]
- Chertok, V. M., N. V. Zakharchuk, and A. G. Chertok. Cellular-Molecular Mechanisms of the Regulation of Angiogenesis in the Brain. Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology 2019, 49, 5, 544-54. [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, Domenico, Beatrice Nico, and Enrico Crivellato. Morphological and Molecular Aspects of Physiological Vascular Morphogenesis. Angiogenesis 2009, 12, 2, 101-11. [CrossRef]
- 28. Liu, Zhen-Ling, Huan-Huan Chen, Li-Li Zheng, Li-Ping Sun, and Lei Shi. Angiogenic Signaling Pathways and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy for Cancer. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2023, 8, 1, 198. [CrossRef]
- 29. Wälchli, Thomas, Jeroen Bisschop, Peter Carmeliet, Gelareh Zadeh, Philippe P. Monnier, Katrien De Bock, and Ivan Radovanovic. Shaping the Brain Vasculature in Development and Disease in the Single-Cell Era. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2023, 24, 5, 271-98. [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, M. R., F. Kuhnert, and C. J. Kuo. Developmental Angiogenesis of the Central Nervous System. Lymphat Res Biol 2008, 6, 3-4, 173-80. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D. R., Y. M. Wu, and S. F. Lin. The Protein Tyrosine Kinase Family of the Human Genome. Oncogene 2000, 19, 49, 5548-57. [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, K., and S. N. Savvides. Extracellular Assembly and Activation Principles of Oncogenic Class Iii Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Nat Rev Cancer 2012, 12, 11, 753-66. [CrossRef]
- Andrae, J., R. Gallini, and C. Betsholtz. Role of Platelet-Derived Growth Factors in Physiology and Medicine. Genes Dev 2008, 22, 10, 1276-312. [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, P., H. Gerhardt, S. Liebner, A. Abramsson, M. Enge, M. Hellstrom, G. Backstrom, S. Fredriksson, U. Landegren, H. C. Nystrom, G. Bergstrom, E. Dejana, A. Ostman, P. Lindahl, and C. Betsholtz. Endothelial Pdgf-B Retention Is Required for Proper Investment of Pericytes in the Microvessel Wall. Genes Dev 2003, 17, 15, 1835-40. [CrossRef]
- Mol, C. D., K. B. Lim, V. Sridhar, H. Zou, E. Y. Chien, B. C. Sang, J. Nowakowski, D. B. Kassel, C. N. Cronin, and D. E. McRee. Structure of a C-Kit Product Complex Reveals the Basis for Kinase Transactivation. J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 34, 31461-4. [CrossRef]
- 36. Matsui, Junji, Toshiaki Wakabayashi, Makoto Asada, Kentaro Yoshimatsu, and Masayuki Okada. Stem Cell Factor/C-Kit Signaling Promotes the Survival, Migration, and Capillary Tube Formation of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells*. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2004, 279, 18, 18600-07. [CrossRef]
- Errede, M., F. Girolamo, M. Rizzi, M. Bertossi, L. Roncali, and D. Virgintino. The Contribution of Cxcl12-Expressing Radial Glia Cells to Neuro-Vascular Patterning During Human Cerebral Cortex Development. Front Neurosci 2014, 8, 324. [CrossRef]
- Girolamo, F., A. Dallatomasina, M. Rizzi, M. Errede, T. Wälchli, M. T. Mucignat, K. Frei, L. Roncali, R. Perris, and D. Virgintino. Diversified Expression of Ng2/Cspg4 Isoforms in Glioblastoma and Human Foetal Brain Identifies Pericyte Subsets. PLoS One 2013, 8, 12, e84883. [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, H., H. Kubota, R. L. Lindberg, D. Leppert, S. M. Gloor, M. Errede, D. Virgintino, A. Fontana, Y. Yonekawa, and K. Frei. Endothelial Cell Barrier Impairment Induced by Glioblastomas and Transforming Growth Factor Beta2 Involves Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tight Junction Proteins. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2008, 67, 5, 435-48. [CrossRef]
- Virgintino, D., M. Errede, F. Girolamo, C. Capobianco, D. Robertson, A. Vimercati, G. Serio, A. Di Benedetto, Y. Yonekawa, K. Frei, and L. Roncali. Fetal Blood-Brain Barrier P-Glycoprotein Contributes to Brain Protection During Human Development. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2008, 67, 1, 50-61. [CrossRef]
- Virgintino, D., M. Errede, M. Rizzi, F. Girolamo, M. Strippoli, T. Wälchli, D. Robertson, K. Frei, and L. Roncali. The Cxcl12/Cxcr4/Cxcr7 Ligand-Receptor System Regulates Neuro-Glio-Vascular Interactions and Vessel Growth During Human Brain Development. J Inherit Metab Dis 2013, 36, 3, 455-66. [CrossRef]
- Virgintino, D., M. Rizzi, M. Errede, M. Strippoli, F. Girolamo, M. Bertossi, and L. Roncali. Plasma Membrane-Derived Microvesicles Released from Tip Endothelial Cells During Vascular Sprouting. Angiogenesis 2012, 15, 4, 761-9. [CrossRef]
- Amselgruber, W. M., M. Schäfer, and F. Sinowatz. Angiogenesis in the Bovine Corpus Luteum: An Immunocytochemical and Ultrastructural Study*. Anatomia, Histologia, Embryologia 1999, 28, 3, 157-66. [CrossRef]
- Blocki, A., Y. Wang, M. Koch, P. Peh, S. Beyer, P. Law, J. Hui, and M. Raghunath. Not All Mscs Can Act as Pericytes: Functional in Vitro Assays to Distinguish Pericytes from Other Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Angiogenesis. Stem Cells Dev 2013, 22, 17, 2347-55. [CrossRef]
- Manocha, E., A. Consonni, F. Baggi, E. Ciusani, V. Cocce, F. Paino, C. Tremolada, A. Caruso, and G. Alessandri. Cd146(+) Pericytes Subset Isolated from Human Micro-Fragmented Fat Tissue Display a Strong Interaction with Endothelial Cells: A Potential Cell Target for Therapeutic Angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 10. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J., Q. Chen, Y. Qiu, L. Chang, Z. Yu, Y. Li, S. J. Chang, Z. Chen, and X. Lin. Cd146(+) Mural Cells from Infantile Hemangioma Display Proangiogenic Ability and Adipogenesis Potential in Vitro and in Xenograft Models. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1063673. [CrossRef]
- Aye, M. T., S. Hashemi, B. Leclair, A. Zeibdawi, E. Trudel, M. Halpenny, V. Fuller, and G. Cheng. Expression of Stem Cell Factor and C-Kit Mrna in Cultured Endothelial Cells, Monocytes and Cloned Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells (Cfu-Rf). Experimental Hematology 1992, 20, 4, 523-27.
- 48. Koenig, Andrea, Elif Yakisan, Marlene Reuter, Muhan Huang, Karl-Walter Sykora, Selim Corbacioglu, and Karl Welte. Differential Regulation of Stem Cell Factor Mrna Expression in Human Endothelial Cells by Bacterial Pathogens: An in Vitro Model of Inflammation. Blood 1994, 83, 10, 2836-43. [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H., E. Ishii, S. Saito, K. Tashiro, I. Fujita, S. Yoshidomi, M. Ohtubo, K. Akazawa, and S. Miyazaki. Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Are an Important Source of C-Kit and Stem Cell Factor Which Regulate the Proliferation of Haemopoietic Progenitor Cells. Br J Haematol 1996, 94, 4, 606-11. [CrossRef]
- Fang, S., J. Wei, N. Pentinmikko, H. Leinonen, and P. Salven. Generation of Functional Blood Vessels from a Single C-Kit+ Adult Vascular Endothelial Stem Cell. PLoS Biol 2012, 10, 10, e1001407. [CrossRef]
- Shan, H. J., K. Jiang, M. Z. Zhao, W. J. Deng, W. H. Cao, J. J. Li, K. R. Li, C. She, W. F. Luo, J. Yao, X. Z. Zhou, D. Zhang, and C. Cao. Scf/C-Kit-Activated Signaling and Angiogenesis Require Gαi1 and Gαi3. Int J Biol Sci 2023, 19, 6, 1910-24. [CrossRef]
- Kim, K. L., Y. Meng, J. Y. Kim, E. J. Baek, and W. Suh. Direct and Differential Effects of Stem Cell Factor on the Neovascularization Activity of Endothelial Progenitor Cells. Cardiovasc Res 2011, 92, 1, 132-40. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, L. P., A. T. Grazul-Bilska, and D. A. Redmer. Angiogenesis in the Corpus Luteum. Endocrine 2000, 12, 1, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Virgintino, Daniela, Mariella Errede, David Robertson, Francesco Girolamo, Antonio Masciandaro, and Mirella Bertossi. Vegf Expression Is Developmentally Regulated During Human Brain Angiogenesis. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 2003, 119, 3, 227-32. [CrossRef]
- 55. Eilken, Hanna M., Rodrigo Diéguez-Hurtado, Inga Schmidt, Masanori Nakayama, Hyun-Woo Jeong, Hendrik Arf, Susanne Adams, Napoleone Ferrara, and Ralf H. Adams. Pericytes Regulate Vegf-Induced Endothelial Sprouting through Vegfr1. Nature Communications 2017, 8, 1, 1574. [CrossRef]
- 56. Franco, Marcela, Pernilla Roswall, Eliane Cortez, Douglas Hanahan, and Kristian Pietras. Pericytes Promote Endothelial Cell Survival through Induction of Autocrine Vegf-a Signaling and Bcl-W Expression. Blood 2011, 118, 10, 2906-17. [CrossRef]
- Al Ahmad, A., M. Gassmann, and O. O. Ogunshola. Maintaining Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity: Pericytes Perform Better Than Astrocytes During Prolonged Oxygen Deprivation. J Cell Physiol 2009, 218, 3, 612-22. [CrossRef]
- Mayo, J. N., and S. E. Bearden. Driving the Hypoxia-Inducible Pathway in Human Pericytes Promotes Vascular Density in an Exosome-Dependent Manner. Microcirculation 2015, 22, 8, 711-23. [CrossRef]
- 59. Venkatraman, Aparna, Meng Zhao, John Perry, Xi C. He, and Linheng Li. "Chapter 4 - Regulation of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Dynamics by Molecular Niche Signaling." In Biology and Engineering of Stem Cell Niches, edited by Ajaykumar Vishwakarma and Jeffrey M. Karp, 51-61. Boston: Academic Press, 2017.
- 60. Kim, Ji Yeon, Jun-Sub Choi, Sun-Hwa Song, Ji-Eun Im, Jung-Mo Kim, Kyungjong Kim, Soonboem Kwon, Hwa Kyoung Shin, Choun-Ki Joo, Byung Ho Lee, and Wonhee Suh. Stem Cell Factor Is a Potent Endothelial Permeability Factor. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 2014, 34, 7, 1459-67. [CrossRef]
- Sá da Bandeira, D., J. Casamitjana, and M. Crisan. Pericytes, Integral Components of Adult Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niches. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2017, 171, 104-13. [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, R., T. Takahashi, S. Nakamura, Y. Sekido, K. Nishida, M. Seto, T. Seito, T. Sugiura, Y. Ariyoshi, T. Takahashi, and et al. Expression of the C-Kit Protein in Human Solid Tumors and in Corresponding Fetal and Adult Normal Tissues. Am J Pathol 1993, 142, 1, 339-46.
- Carpenter, Graham. Nuclear Localization and Possible Functions of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2003, 15, 2, 143-48. [CrossRef]
- Song, S., K. M. Rosen, and G. Corfas. Biological Function of Nuclear Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Action. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2013, 5, 7. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Shiaw-Yih, Keishi Makino, Weiya Xia, Angabin Matin, Yong Wen, Ka Yin Kwong, Lilly Bourguignon, and Mien-Chie Hung. Nuclear Localization of Egf Receptor and Its Potential New Role as a Transcription Factor. Nature Cell Biology 2001, 3, 9, 802-08. [CrossRef]
- Schlessinger, Joseph. Cell Signaling by Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Cell 2000, 103, 2, 211-25. [CrossRef]
-
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. [CrossRef]
-
Journal of Biological Chemistry, 4344. [CrossRef]
- Shah, M., H. Kumar, S. Qiu, H. Li, M. Harris, J. He, A. Abraham, D. K. Crossman, A. Paterson, R. S. Welner, and R. Bhatia. Low C-Kit Expression Identifies Primitive, Therapy-Resistant Cml Stem Cells. JCI Insight 2023, 8, 1. [CrossRef]
- Xu, K., and O. Cleaver. Tubulogenesis During Blood Vessel Formation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2011, 22, 9, 993-1004. [CrossRef]
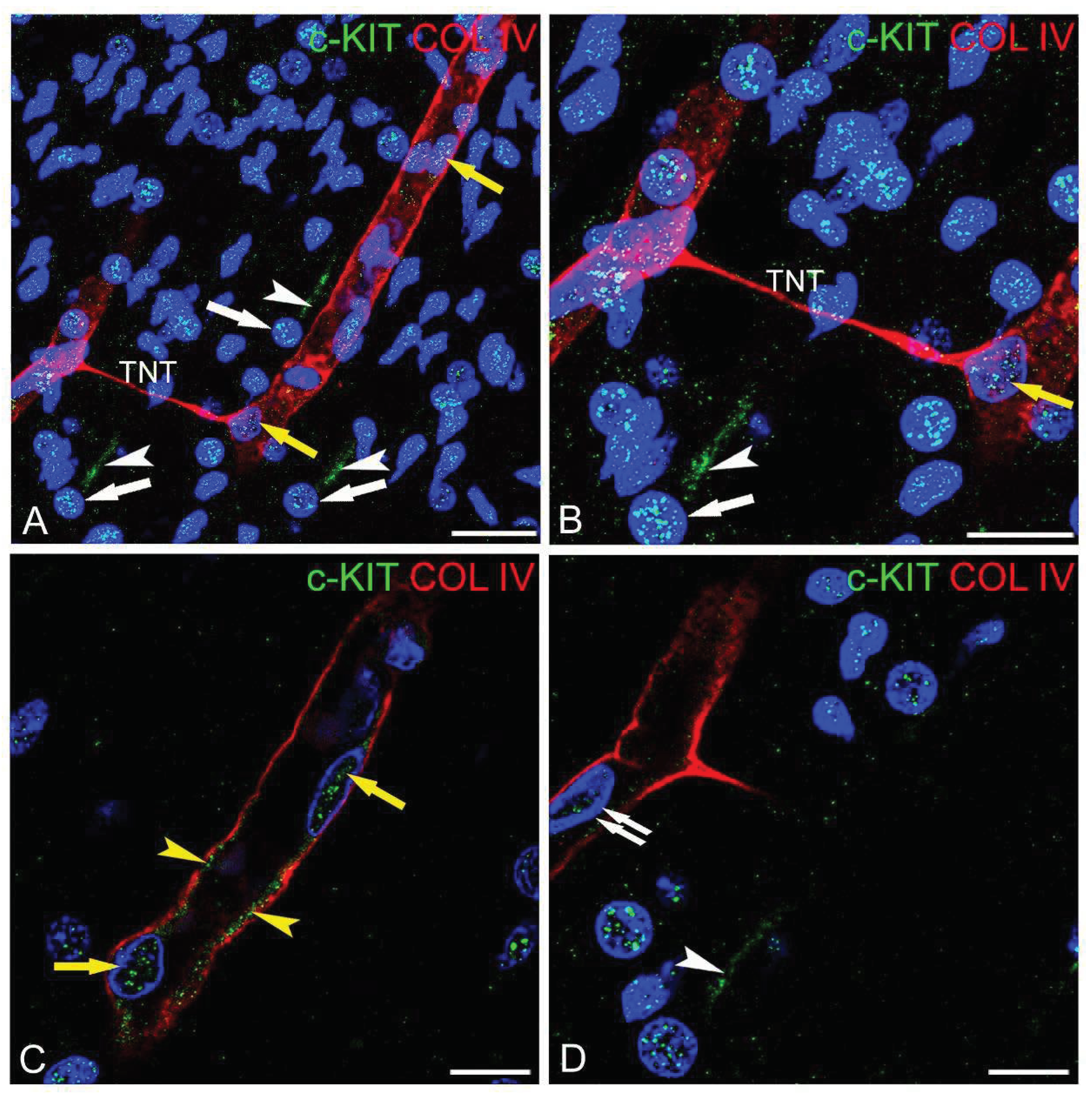
Figure 1.
(A-D) Representative confocal microscopy images of pericyte-TNTs in the human fetal brain, as shown by double staining with c-KIT and COL IV. Neuroblasts reveal a dual c-KIT staining, in the nucleus (white arrows) and on their leading process (arrowheads) (A, B, D). Two penetrating, radial vessels, whose profile is shown by COL IV, appear connected by a COL IV+ pericyte-TNT and show nuclear c-KIT staining on some of their endothelial cells (yellow arrows in A and B). (C, D) Subcellular details of endothelial c-KIT immunoreactivity are shown on the single optical planes from the z-stack depicted in (B); the dual c-KIT expression is recognizable on both the endothelial nucleus (yellow arrows) and the cell membrane (yellow arrowheads) in (C), whereas the purported receiving vessel shows a very low c-KIT nuclear labeling (D, double arrows). Nuclear counterstaining TOPRO-3. TNT, tunnelling nanotube. Bars A, 25 µm; B-D 15 µm.
Figure 1.
(A-D) Representative confocal microscopy images of pericyte-TNTs in the human fetal brain, as shown by double staining with c-KIT and COL IV. Neuroblasts reveal a dual c-KIT staining, in the nucleus (white arrows) and on their leading process (arrowheads) (A, B, D). Two penetrating, radial vessels, whose profile is shown by COL IV, appear connected by a COL IV+ pericyte-TNT and show nuclear c-KIT staining on some of their endothelial cells (yellow arrows in A and B). (C, D) Subcellular details of endothelial c-KIT immunoreactivity are shown on the single optical planes from the z-stack depicted in (B); the dual c-KIT expression is recognizable on both the endothelial nucleus (yellow arrows) and the cell membrane (yellow arrowheads) in (C), whereas the purported receiving vessel shows a very low c-KIT nuclear labeling (D, double arrows). Nuclear counterstaining TOPRO-3. TNT, tunnelling nanotube. Bars A, 25 µm; B-D 15 µm.
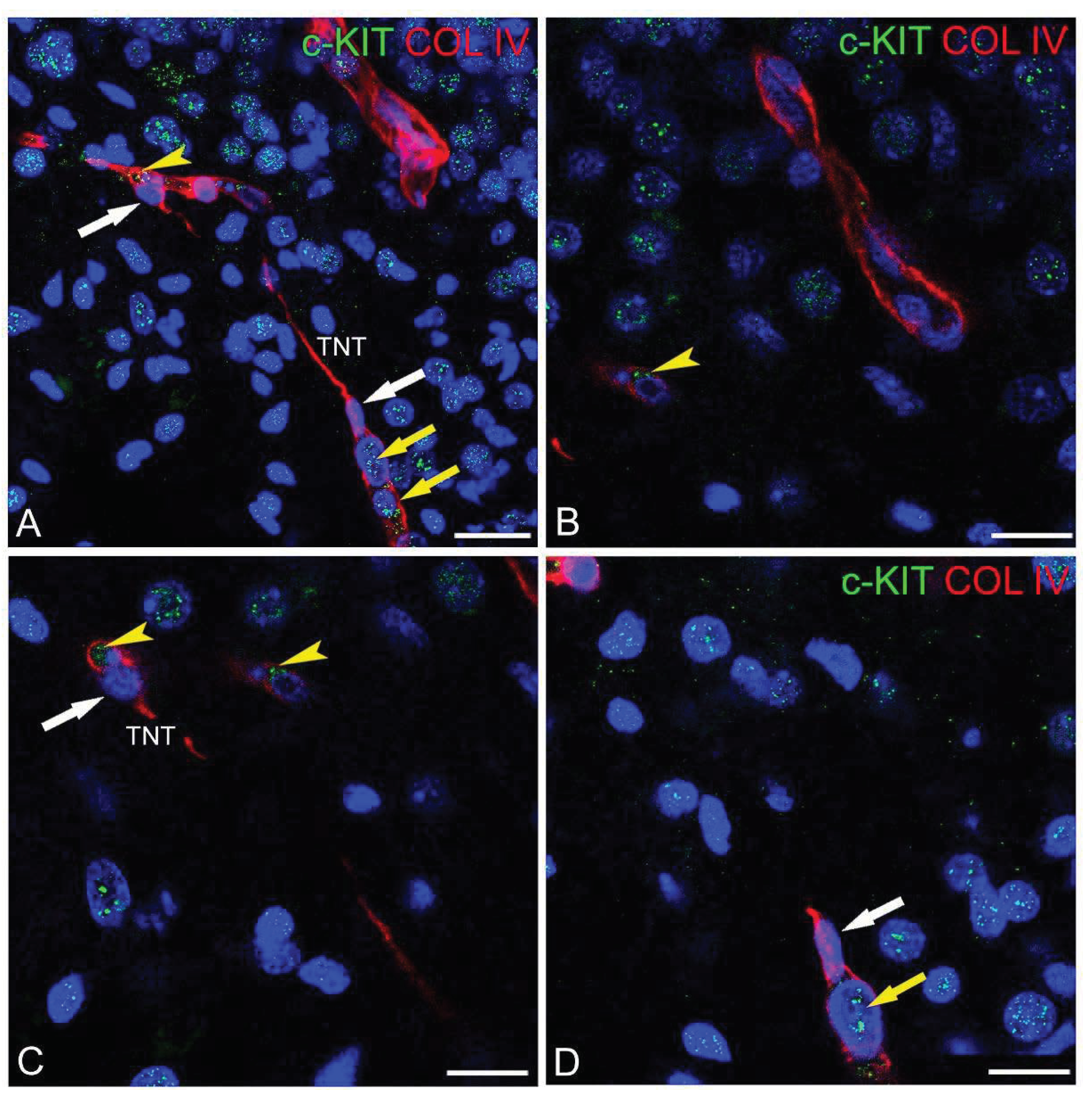
Figure 2.
(A-D) Representative confocal microscopy images of pericyte-TNTs in the human fetal brain, as shown by double staining with c-KIT and COL IV. (A, B) Two COL IV+ pericyte-TNTs bridging the gap between two capillaries; the leading pericytes are c-KIT-negative (white arrows), whereas the engaged endothelial cells show a nuclear (yellow arrows) and a membrane (yellow arrowhead) c-KIT immunolocalization: note in the upright corner a c-KIT unstained microvessels, better shown on the enlargement of a single optical plane in (B). (C, D) Enlargements of single optical planes from the z-stack depicted in (A) allow us to better recognize the c-KIT-negative leading pericyte (white arrow), the c-KIT-reactive nucleus of the engaged endothelial cells (D, yellow arrow), and the cell membrane endothelial staining (C, yellow arrowheads). Nuclear counterstaining TOPRO-3. TNT, tunnelling nanotube. Bars A, 25 µm; B-D 15 µm.
Figure 2.
(A-D) Representative confocal microscopy images of pericyte-TNTs in the human fetal brain, as shown by double staining with c-KIT and COL IV. (A, B) Two COL IV+ pericyte-TNTs bridging the gap between two capillaries; the leading pericytes are c-KIT-negative (white arrows), whereas the engaged endothelial cells show a nuclear (yellow arrows) and a membrane (yellow arrowhead) c-KIT immunolocalization: note in the upright corner a c-KIT unstained microvessels, better shown on the enlargement of a single optical plane in (B). (C, D) Enlargements of single optical planes from the z-stack depicted in (A) allow us to better recognize the c-KIT-negative leading pericyte (white arrow), the c-KIT-reactive nucleus of the engaged endothelial cells (D, yellow arrow), and the cell membrane endothelial staining (C, yellow arrowheads). Nuclear counterstaining TOPRO-3. TNT, tunnelling nanotube. Bars A, 25 µm; B-D 15 µm.
Figure 3.
(A-D) Representative confocal microscopy images of pericyte-TNTs in the human fetal brain, as shown by double staining with c-KIT and COL IV. (A, B) On a nuclear c-KIT+ background formed by fetal brain neuroblasts, COL IV+/c-KIT+ microvessels are recognizable and show a strong cell membrane c-KIT staining (A, yellow arrowhead), better demonstrated by the enlargement (B, (yellow arrowheads) of a single optical plane from (A). (C) A pericyte-TNT growing sprout showing the c-KIT unstained leading pericyte (white arrow) and the c-KIT+ nucleus of the engaged endothelial cell (yellow arrow). (D) The c-KIT+ nucleus of the engaged endothelial cell in (C) is better shown by the enlargement of a single optical plane (yellow arrow). Nuclear counterstaining TOPRO-3. TNT, tunnelling nanotube. Bars A-C 25 µm; D 15 µm.
Figure 3.
(A-D) Representative confocal microscopy images of pericyte-TNTs in the human fetal brain, as shown by double staining with c-KIT and COL IV. (A, B) On a nuclear c-KIT+ background formed by fetal brain neuroblasts, COL IV+/c-KIT+ microvessels are recognizable and show a strong cell membrane c-KIT staining (A, yellow arrowhead), better demonstrated by the enlargement (B, (yellow arrowheads) of a single optical plane from (A). (C) A pericyte-TNT growing sprout showing the c-KIT unstained leading pericyte (white arrow) and the c-KIT+ nucleus of the engaged endothelial cell (yellow arrow). (D) The c-KIT+ nucleus of the engaged endothelial cell in (C) is better shown by the enlargement of a single optical plane (yellow arrow). Nuclear counterstaining TOPRO-3. TNT, tunnelling nanotube. Bars A-C 25 µm; D 15 µm.
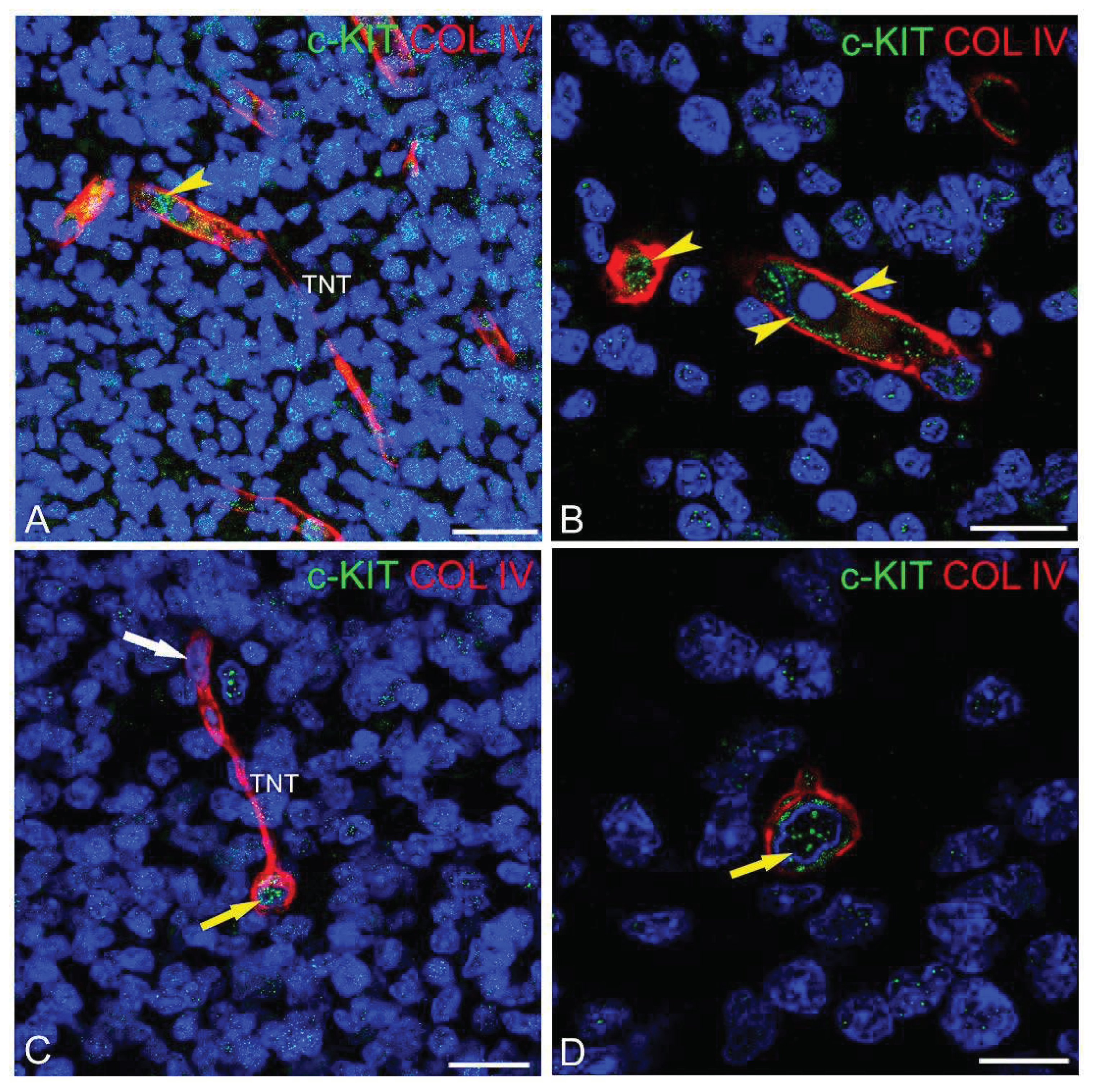
Figure 4.
(A-D) Representative confocal microscopy of human glioblastoma sections, as shown by double staining with c-KIT and COL IV. (A) Tumoral cells with c-KIT+ nuclei, a tumoral astrocyte-like cell with both nuclear and membrane c-KIT staining (asterisk), and COL IV+ tumoral vessels and pericyte-TNTs. (B-D) Details of the tumoral vessels show c-KIT unstained endothelial nuclei (double arrow) and weakly stained cell membranes (B, yellow arrowheads); c-KIT unstained nuclei are recognizable at the origin of the pericyte-TNTs (C, D; arrow); note in (B) and (D) the nuclear and cytoplasmic c-KIT staining of tumoral cells (white arrowheads). Nuclear counterstaining TOPRO-3. TNT, tunnelling nanotube. Bars A, 25 µm; B-D 15 µm.
Figure 4.
(A-D) Representative confocal microscopy of human glioblastoma sections, as shown by double staining with c-KIT and COL IV. (A) Tumoral cells with c-KIT+ nuclei, a tumoral astrocyte-like cell with both nuclear and membrane c-KIT staining (asterisk), and COL IV+ tumoral vessels and pericyte-TNTs. (B-D) Details of the tumoral vessels show c-KIT unstained endothelial nuclei (double arrow) and weakly stained cell membranes (B, yellow arrowheads); c-KIT unstained nuclei are recognizable at the origin of the pericyte-TNTs (C, D; arrow); note in (B) and (D) the nuclear and cytoplasmic c-KIT staining of tumoral cells (white arrowheads). Nuclear counterstaining TOPRO-3. TNT, tunnelling nanotube. Bars A, 25 µm; B-D 15 µm.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).