Submitted:
25 December 2023
Posted:
26 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
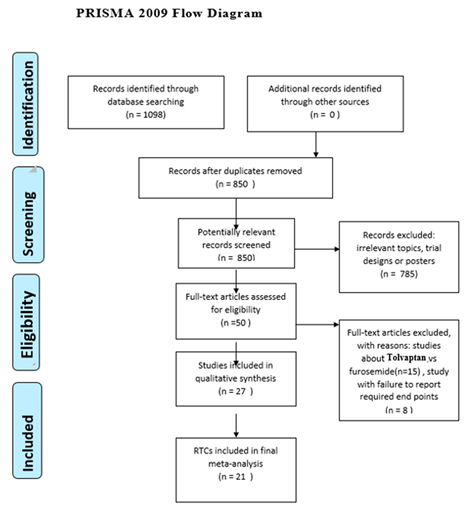
Study selection
Inclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria
Data extraction
Assessment of risk of bias
Statistical analysis
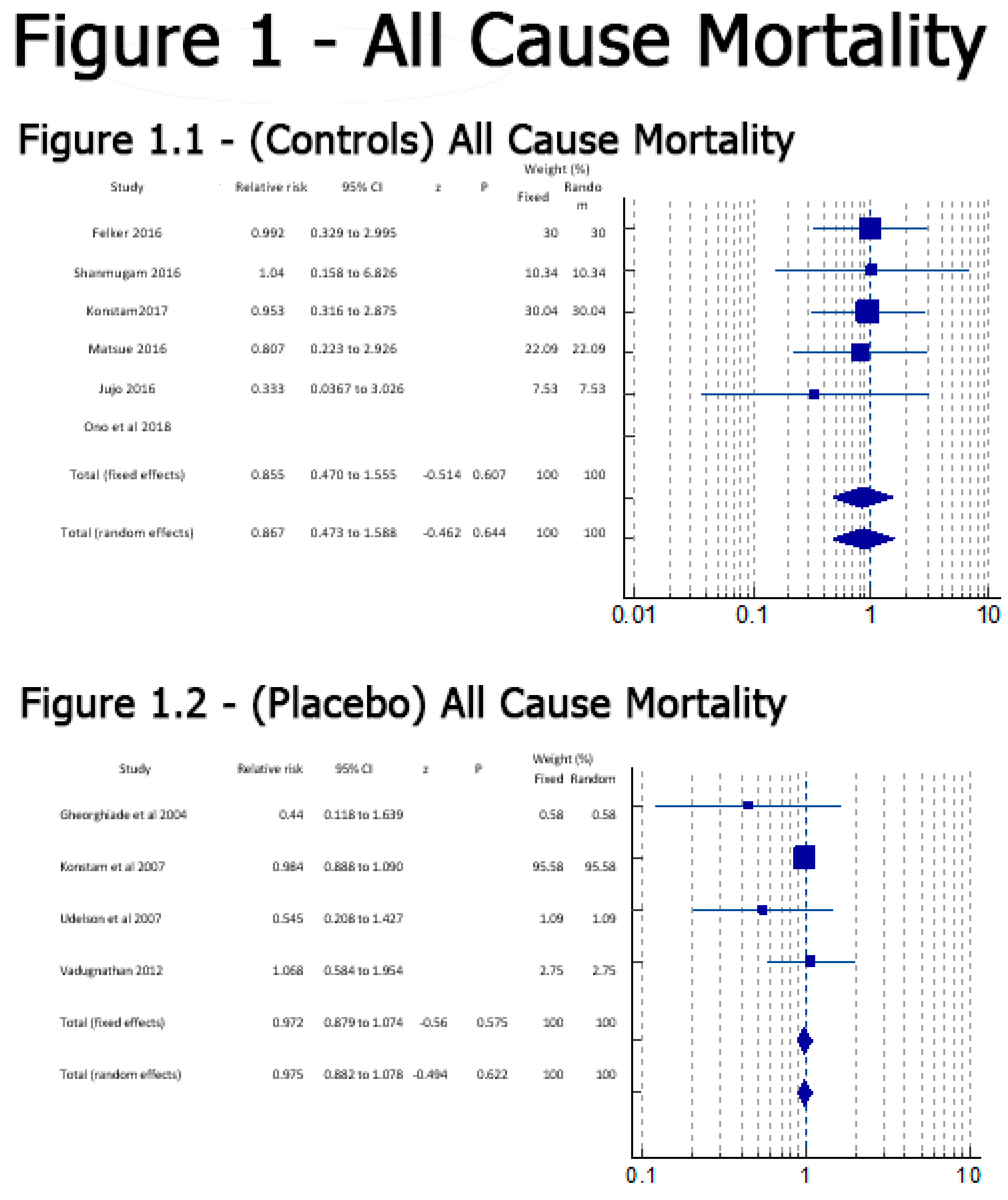
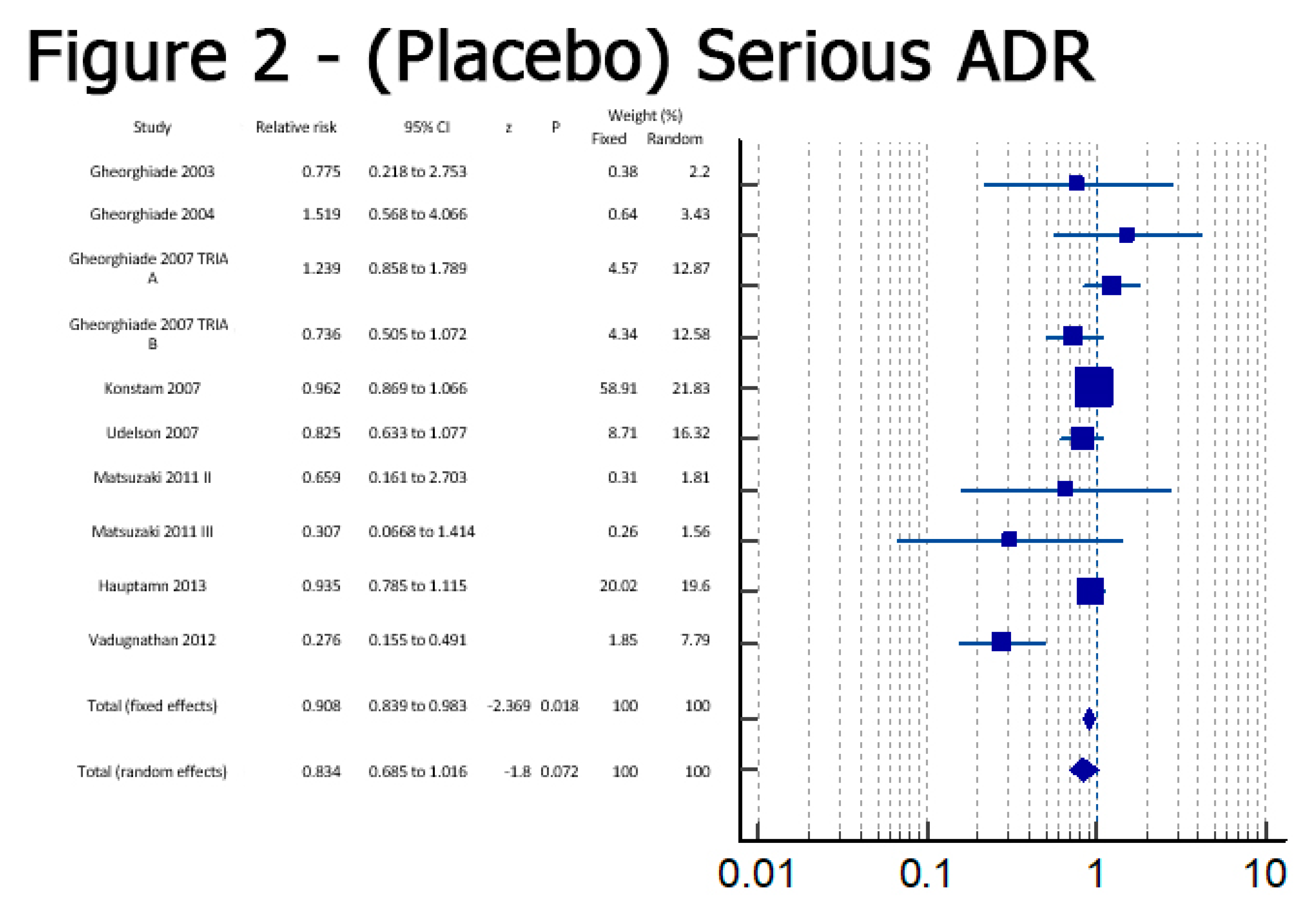
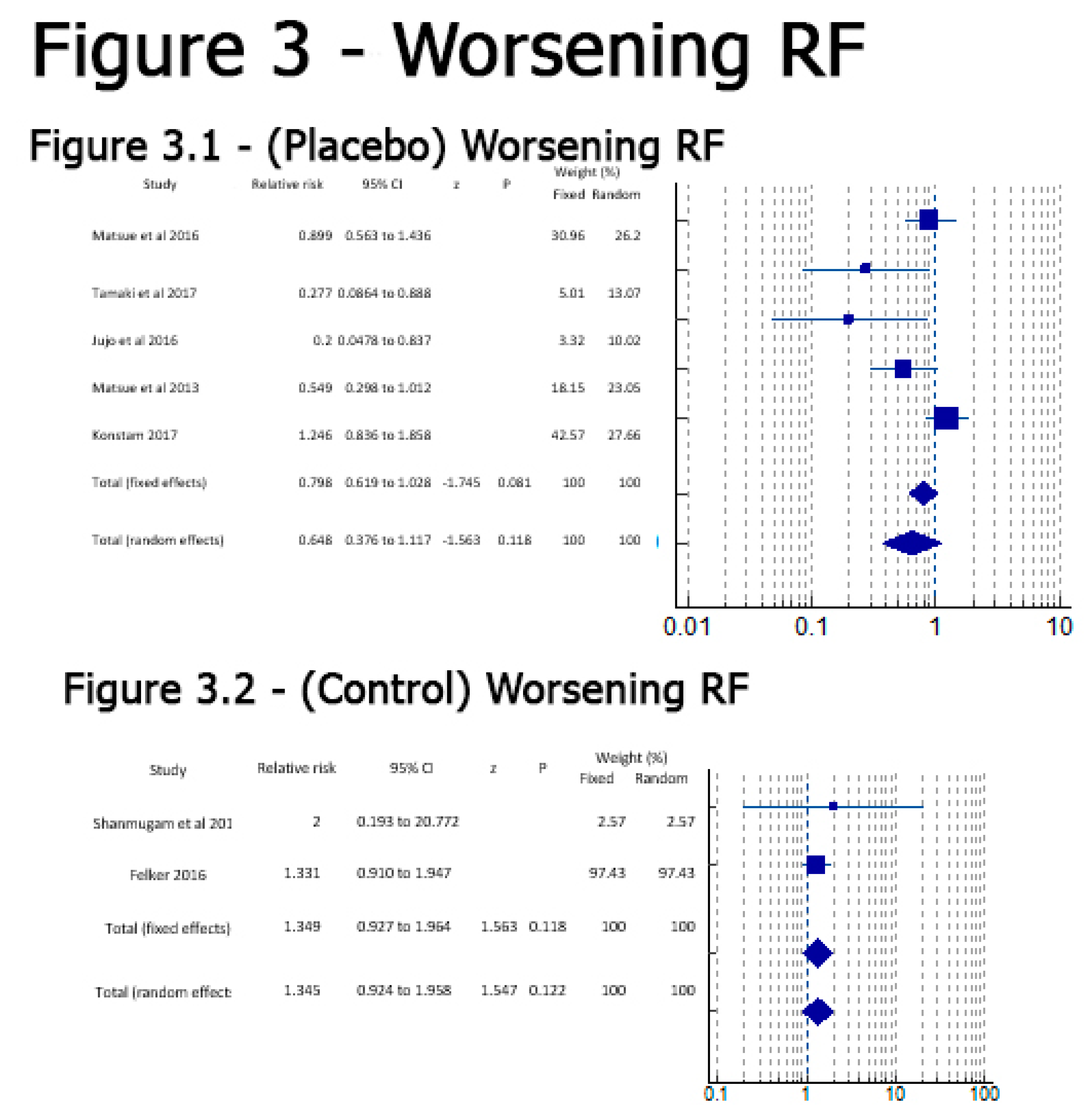
Results
Discussion
| No | Study | Quality | Type of Study | Year of publishing | Place of research | Sample Size | Time Period of Data Collection | Intervention | Follow Up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Felker 2016 [19] | Good | RCT | 2017 | USA | 257 | at 0,24,48 hours of giving medication | Tolvaptan/Control | 48 hours after administration |
| 2 | Gheorghiade 2007 TRIALA [22] | Good | RCT | 2007 | USA and Europe | 2048 | from Oct 7 2003 to Feb3 2006 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 7 days |
| 3 | Gheorghiade 2007 TRIALB [22] | Good | RCT | 2007 | USA and Europe | 2058 | from Oct 7 2003 to Feb3 2006 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 7 days |
| 4 | Gheorghiade et al 2003 [10] | Good | RCT | 2003 | USA | 254 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 25 days | |
| 5 | Gheorghiade et al 2004 [15] | Good | RCT | 2004 | USA and Argentina | 319 | 60 days | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 60 days |
| 6 | Haught et al 2008 [23] | Good | RCT | 2008 | USA | 181 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | ||
| 7 | Hauptamn 2013 [24] | Good | RCT | 2013 | USA | Tolvaptan/Placebo | |||
| 8 | Jujo et al 2016 [14] | Good | RCT | 2016 | Japan | 60 | Tolvaptan/Control | 5days | |
| 9 | Konstam et al 2007 [8] | Good | RCT | 2007 | USA | 4133 | from Oct 7 2003 to Feb3 2006 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | long term |
| 10 | Konstam et al 2008 [23] | Good | Tolvaptan/Placebo | ||||||
| 11 | Konstam et al 2017 [20] | Good | RCT | 2017 | USA | 250 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 3 days | |
| 12 | Li ling et al 2011 [12] | Good | RCT | 2011 | China | 65 | 0,4,7 days | Tolvaptan/13Placeb14o | 7 days |
| 13 | Matsue et al 2016 [25] | Good | RCT | 2016 | Japan | 217 | Tolvaptan/Control | 2 days | |
| 14 | Matsue et al 2013 [26] | Good | Observational study | 2013 | Japan | 114 | 0,24,48 hrs | Tolvaptan/Control | 2 days |
| 15 | Matsuzaki et al 2011 [11] | Good | RCT | 2011 | Japan | 117 | 7 days | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 7 days |
| 16 | Ono et al 2018 [21] | Good | Observational study | 2018 | Japan | 58 | Tolvaptan/Control | 6 months | |
| 17 | Shanmugam et al 2016 [17] | Good | RCT | 2016 | India | 51 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 4 days | |
| 18 | Suzuki 2013 [27] | Good | RCT | 2013 | Japan | 109 | Tolvaptan/Control | ||
| 19 | Tamaki et al 2017 [16] | Good | RCT | 2017 | Japan | 50 | Tolvaptan/Control | 2 days | |
| 20 | Udelson et al 2007 [13] | Good | RCT | 2008 | USA | 181 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 1 day | |
| 21 | Udelson et al 2011 [9] | Good | RCT | 2011 | USA | 83 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 2 days | |
| 22 | Vadugnathan 2012 [18] | Good | RCT | 2012 | USA | 759 | Tolvaptan/Placebo | 7 days |
Conclusion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- E Alskaf AT, A Al-Mohammad,. Tolvaptan for Heart Failure, Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Trials 2016 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27159621/.
- Izumi Y MK, Iwao H,. Therapeutic Potential of Vasopressin-Receptor Antagonists in Heart Failure 2014 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24401675/.
- Steven R Goldsmith MG. Vasopressin antagonism in heart failure 2005 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16286160/. 1628.
- Takanori Yamazaki YI, Yasuhiro Nakamura, Naoto Yamashita, Hiroyuki Fujiki, Mayuko Osada-Oka, et al. Tolvaptan improves left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction in rats 2012 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22984091/.
- Chunbin Wang BX, Lin Cai. Effects of Tolvaptan in patients with acute heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis 2017 [Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12872-017-0598-y. [CrossRef]
- Punniyakoti T Veeraveedu SSP, Ken'ichi Yamaguchi, Yutaka Komai, Rajarajan A Thandavarayan, Vijayakumar Sukumaran, et al. Arginine vasopressin receptor antagonists (vaptans): pharmacological tools and potential therapeutic agents 2010 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20708094/.
- Xiong B HY, Tan J, Yao Y, Wang C, Qian J, et al. The short-term and long-term effects of tolvaptan in patients with heart failure: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials 2015 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26334632/#affiliation-1.
- Marvin A Konstam MG, John C Burnett Jr, Liliana Grinfeld, Aldo P Maggioni, Karl Swedberg, et al. Effects of oral tolvaptan in patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure: the EVEREST Outcome Trial 2007 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17384437/.
- James E Udelson MB, Paul J Hauptman, Rafael Sequeira, Ignatius Thomas, Terrence O'Brien, et al. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of tolvaptan monotherapy compared to furosemide and the combination of tolvaptan and furosemide in patients with heart failure and systolic dysfunction 2011 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22123358/.
- Mihai Gheorghiade IN, John Ouyang, Frank Czerwiec, Jun-ichi Kambayashi, Manuela Zampino, et al. Vasopressin V2-receptor blockade with tolvaptan in patients with chronic heart failure: results from a double-blind, randomized trial 2003 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12742979/.
- Masunori Matsuzaki MH, Tohru Izumi, Masatake Fukunami,. Efficacy and safety of tolvaptan in heart failure patients with volume overload despite the standard treatment with conventional diuretics: a phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (QUEST study) 2011 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22120092/. [CrossRef]
- Li Ling ZW, Bai Hua,. The efficacy and safety of tolvaptan on treating congestive heart failure patients with hyponatremia 2011 [Available from: https://heart.bmj.com/content/97/Suppl_3/A127.1.
- James E Udelson FAM, Enrique Flores, Hassan Ibrahim, Stewart Katz, Gregory Koshkarian, et al. Multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study on the effect of oral tolvaptan on left ventricular dilation and function in patients with heart failure and systolic dysfunction 2007 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17543634/.
- Kentaro Jujo KS, Issei Ishida, Yuho Furuki, Ahsung Kim, Yuki Suzuki, et al. Randomized pilot trial comparing tolvaptan with furosemide on renal and neurohumoral effects in acute heart failure 2016 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27818782/.
- Mihai Gheorghiade WAG, Christopher M O'Connor, Kirkwood F Adams Jr, Uri Elkayam, Alejandro Barbagelata, et al. Effects of tolvaptan, a vasopressin antagonist, in patients hospitalized with worsening heart failure: a randomized controlled trial 2004 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15113814/.
- Shunsuke Tamaki YS, Takahisa Yamada,Takashi Morita,Yoshio Furukawa,Yusuke Iwasaki, et al. Tolvaptan Reduces the Risk of Worsening Renal Function in Patients With Acute Decompensated Heart Failure and Preserved Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction - Prospective Randomized Controlled Study 2017 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28202885/.
- Elangovan Shanmugam CRMPD, Melvin George, Amrita Jena, Muthukumar Rajaram, Balaji Ramaraj, et al. Effect of tolvaptan on acute heart failure with hyponatremia – A randomized, double blind, controlled clinical trial 2016 [Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0019483215002394.
- Muthiah Vaduganathan MG, Peter S Pang, Marvin A Konstam, Faiez Zannad, Karl Swedberg, et al. Efficacy of oral tolvaptan in acute heart failure patients with hypotension and renal impairment 2012 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22673023/.
- G Michael Felker RJM, Robert T Cole, Kirkwood F Adams, Gregory F Egnaczyk, Mona Fiuzat, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Tolvaptan in Patients Hospitalized With Acute Heart Failure 2017 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27654854/.
- Marvin A Konstam MK, Arthur Chandler, Ravi Dhingra, Freny Vaghaiwalla Mody, Howard Eisen, et al. Short-Term Effects of Tolvaptan in Patients With Acute Heart Failure and Volume Overload 2017 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28302292/.
- Yohei Ono HT, Masahiro Inoue, Yukio Mabuchi, Tetsuya Ueda, Tadashi Suzuki, et al. Clinical effect of long-term administration of tolvaptan in patients with heart failure and chronic kidney disease 2018 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29998996/.
- Mihai Gheorghiade MAK, John C Burnett Jr, Liliana Grinfeld, Aldo P Maggioni, Karl Swedberg, et al. Short-term clinical effects of tolvaptan, an oral vasopressin antagonist, in patients hospitalized for heart failure: the EVEREST Clinical Status Trials 2007 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17384438/. [CrossRef]
- James E Udelson CO, John Ouyang, Holly Krasa, Christopher A Zimmer, Geir Frivold, et al. Acute hemodynamic effects of tolvaptan, a vasopressin V2 receptor blocker, in patients with symptomatic heart failure and systolic dysfunction: an international, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled trial 2008 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19007589/.
- Paul J Hauptman JB, Mihai Gheorghiade, Liliana Grinfeld, Marvin A Konstam, Dusan Kostic, et al. Clinical course of patients with hyponatremia and decompensated systolic heart failure and the effect of vasopressin receptor antagonism with tolvaptan 2013 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23743487/.
- Yuya Matsue MS, Sho Torii,Satoshi Yamaguchi,Seiji Fukamizu,Yuichi Ono, et al. Clinical Effectiveness of Tolvaptan in Patients With Acute Heart Failure and Renal Dysfunction 2016 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26915749/.
- Yuya Matsue MS, Mie Seya, Ryota Iwatsuka, Akira Mizukami, Wataru Nagahori, et al. Tolvaptan reduces the risk of worsening renal function in patients with acute decompensated heart failure in high-risk population 2013 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23159210/.
- Satoshi Suzuki AY, Takayoshi Yamaki, Koichi Sugimoto, Hiroyuki Kunii, Kazuhiko Nakazato, et al. Acute heart failure volume control multicenter randomized (AVCMA) trial: comparison of tolvaptan and carperitide 2013 [Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24142853/.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





