Submitted:
20 December 2023
Posted:
22 December 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction:
2. Systematic Literature Review:
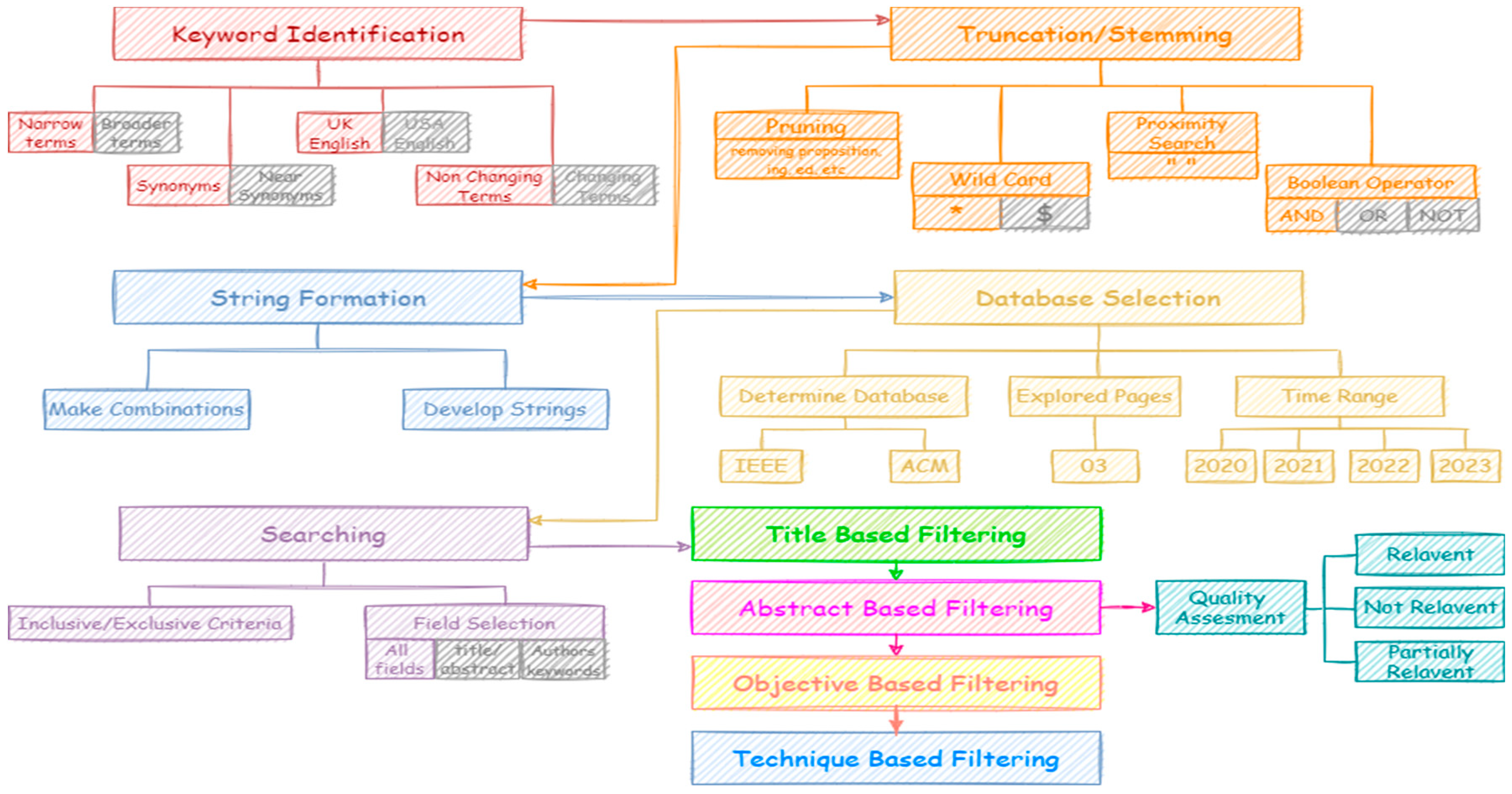
2.1. Keywords Identification:
2.1.1. Broader/Narrow Terms:
2.1.2. Synonyms/ Near Synonyms:
2.1.3. UK/US English:
2.1.4. Terminology change over Time:
2.2. Truncation/ Stemming:
2.2.1. Pruning:
2.2.2. Wild Card:
2.2.3. Proximity Search:
2.2.4. Boolean Operators:
2.3. String Development:
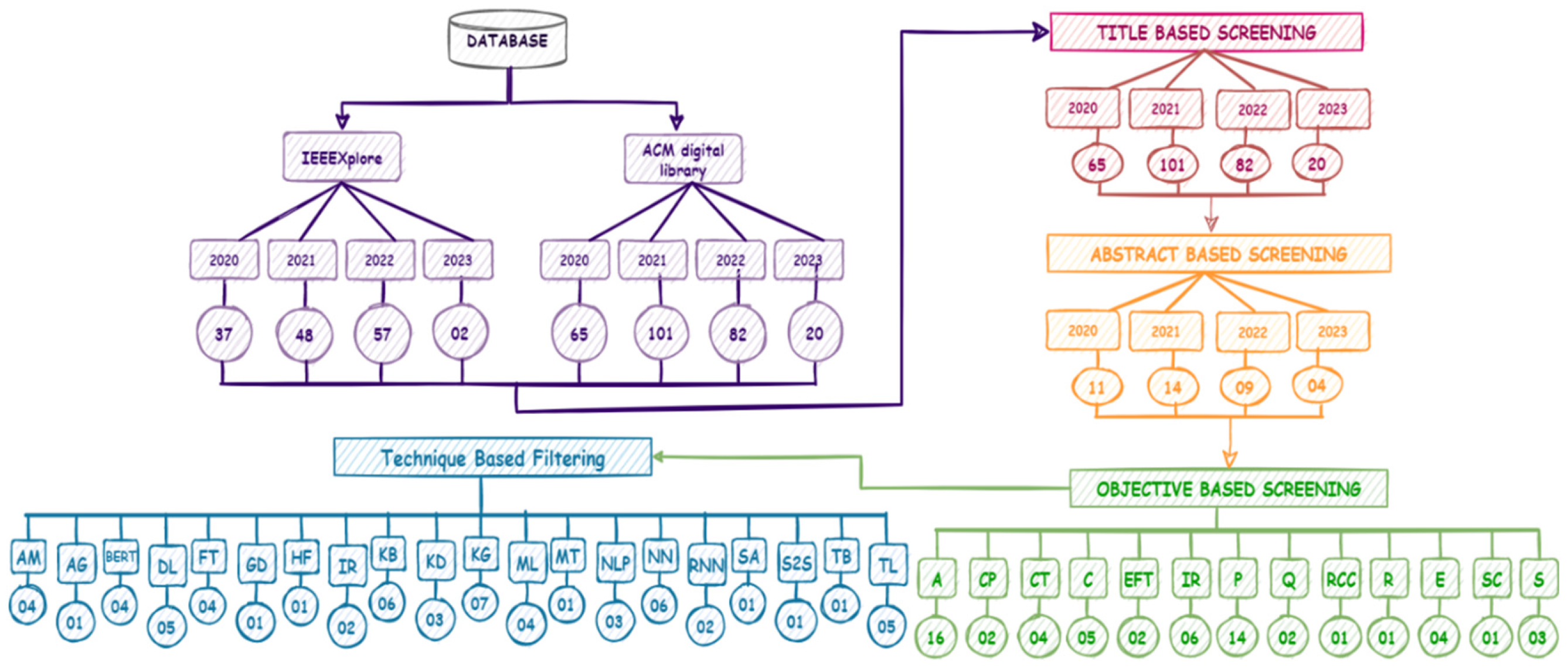
2.4. Database Selection:
2.4.1. Determine Databases:
2.4.2. Explored Pages:
2.4.3. Time Range
2.5. Searching:
2.5.1. Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria:
- Only those articles are downloaded those must have keywords of a string
- Articles published before 2020 are not considered
- The articles for which only citation is available are not considered.
2.5.2. Field Selection:
- All fields: You can use your search terms in any field. There will certainly be a large number of outcomes from this.
- Title/abstract: If the title and abstract contain search terms, the item is probably very relevant. It emphasizes the titles and abstracts with strong, descriptive writing.
- Keyword: Searches for what you entered in the list of terms that the author has provided.
2.6. Filtering:
2.6.1. Title Based Filtering:
2.6.2. Abstract Based Filtering:
2.6.3. Quality Assessment:
2.6.4. Objective Based Filtering:
2.6.5. Technique-based filtering:
| Ref. | TECHNIQUES | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AM | AG | BERT | DL | FT | GD | HF | IR | KB | KD | KG | ML | MT | NLP | NN | RNN | SA | S2S | TB | TL | |
| [1] | ✓ | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - |
| [2] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [3] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [4] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [5] | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [6] | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [7] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [8] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [9] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [10] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [11] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [12] | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| [13] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [14] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| [15] | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [16] | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | - |
| [17] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [18] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [19] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [20] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [21] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [22] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [23] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [24] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [25] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [26] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| [27] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [28] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [29] | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| [30] | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [31] | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| [32] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [33] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [34] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [35] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [36] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| [37] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [38] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
3. Datasets:
- The Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD) is a database of questions and responses derived from Wikipedia articles.
- MS MARCO (Microsoft MAchine Reading COmprehension): Contains sections from web documents and genuine user inquiries from Bing search.
- CoQA (Conversational Question Answering): Focusing on conversational question-answering utilizing short tales.
- QuAC (Question Answering in Context) is a tool for thinking through several phrases while answering questions in conversation.
- TriviaQA: Presents complex questions from various groups to test question-answering algorithms.
- Natural Questions: Queries generated from actual user inquiries from the internet with responses given in sections from Wikipedia.
- WikiQA: WikiQA is a dataset that emphasises the choice of answer sentences. It includes questions derived from web searches and offers a list of potential answers for each query, leaving it up to models to choose the most pertinent one.
4. Detailed Literature:
5. Critical Analysis:
| REF. PAPERS | TECHNIQUES | SHORTCOMINGS |
|---|---|---|
| [1,8,9,30] |
Attention Mechanism (AM) |
Quadratic Computational And Memory Requirements, Limited Context Capture, Sensitivity To Noise And Irrelevance, Neglecting Answer Impact On Question, Inadequate Selection From Complex Inputs. |
| [30] |
Attribute Graph Base Approach (AG) |
Data-intensive graph construction, sensitivity to noise and irrelevance, potential scalability issues with large datasets. |
| [18,20,25,34] |
BERT model (BERT) |
Dependency on high-quality and domain-specific training data for optimal performance. |
| [1,6,15,16,30] |
Deep Learning Approach (DL) |
The requirement for a lot of labelled data, the difficulty of interpretation, the cost of computing, and the danger of over-fitting, which require careful evaluation and consideration before deployment in real-world applications. |
| [12,29,31] |
Fine-Tuning (FT) |
Shallow changes to the language model, sensitivity to grammar mistakes, and the need for careful consideration during system development. |
| [18] |
Google Dialog-Flow (GD) |
The potential for misinterpretation of user queries and the need for ongoing maintenance and updates for accuracy and relevance. |
| [5] |
Human Feedback (HF) |
Challenges in obtaining high-quality feedback, potential biases in the feedback, and the associated cost of obtaining and processing it. |
| [6,10,17] |
Information Retrieval Techniques (IR) |
Performance dependency on the IR system, dataset limitations, insufficiency for complex questions, and computational expense of advanced techniques. |
| [7,11,21,22,23] |
Knowledge Base (KB) |
Lack of methods for verifying and validating the systems, time-consuming and expensive development and maintenance, and limited suitability for all types of questions and domains. |
| [12,14,35] |
Knowledge Distillation (KD) |
Potential ineffectiveness for all types of models or tasks, challenges in zero-shot transfer learning, limited effectiveness for noisy or error-prone data, potential limitations for specialized or complex architectures, and limitations for applications requiring high levels of accuracy or precision. |
| [3,8,9,19,24,32,33] |
Knowledge Graph (KG) |
Potential incompleteness or inaccuracy of knowledge graphs, challenges in mapping natural language questions to formal query representations, computational expense of multi-hop reasoning, and difficulties in matching entities in noisy or variable user queries to the knowledge graph. |
| [5,27,28,29,35] |
Machine Learning Approach (ML) |
The need for a lot of processing power and training data, as well as the importance of trained quality of information and question difficulty, and potential challenges in handling questions that require common sense reasoning or contextual understanding. |
| [37] |
Metamorphic Testing Theory (MT) |
Identifying and selecting metamorphic relations, especially for complex systems, and may not be suitable for all types of QA systems that lack clear metamorphic relations for testing. |
| [10,17] |
Natural Processing Languages (NLP) |
Feature engineering complexity, data quality, and context maintenance, understanding human nuances, semantic-based QA, and closed domain limitations. |
| [2,4,8,13,20,26] |
Neural Network Approach (NN) |
Limitations in feature extraction, data requirements, context understanding, and generating specific answers, but deep learning approaches help mitigate some of these challenges. |
| [1,6] |
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) |
Slow training and inference, limited representational power, difficulty in capturing long-term dependencies, and memory loss. |
| [16] |
Semantic Analysis Approach (SA) |
The limited application of existing systems, flaws in the models employed, and challenges in precise semantic tagging. |
| [1] |
Sequence-to-Sequence (Seq2Seq) |
Focused nature, weaknesses in the underlying models, and challenges in accurate semantic tagging. |
| [16] |
Template Based Approach (TB) |
Limitations in handling complex queries that require reasoning and inference. |
| [12,14,29,31] |
Transfer Learning (TL) |
Requires sufficient data and careful selection of pre-trained models for the target task. |
5. Performance Analysis:
| REF. PAPERS | OBJECTIVES | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | CP | CT | C | EFT | E | IR | P | Q | RCC | R | SC | S | |
| [1] | High | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [2] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [3] | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [4] | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [5] | High | - | Low | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [6] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [7] | High | - | - | Low | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - |
| [8] | - | - | Low | Low | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [9] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - |
| [10] | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [11] | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [12] | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - | High |
| [13] | - | - | Low | Low | - | High | - | - | High | - | - | - | - |
| [14] | High | - | - | - | - | - | High | High | - | - | - | - | High |
| [15] | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - |
| [16] | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [17] | - | - | Low | - | - | - | High | - | High | - | - | - | - |
| [18] | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [19] | High | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [20] | High | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [21] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [22] | High | - | - | Low | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [23] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | High | - | - | - | - |
| [24] | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High |
| [25] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [26] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [27] | High | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [28] | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [29] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [30] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [31] | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [32] | - | Low | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [33] | High | Low | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [34] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [35] | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [36] | - | - | - | Low | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
| [37] | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| [38] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | High | - | - | - | - | - |
6. Research Gaps & Solutions:
- Data scarcity: Deep learning-based systems for answering questions need an enormous amount of top-of-the training data that might be challenging to get in some fields or languages. One solution is to develop methods for generating synthetic training data, such as those based on data augmentation or generative adversarial networks[131].
- Lack of annotated data: Annotated data is essential for training deep learning models, but it can be difficult and expensive to obtain. One solution is to use transfer learning, where a pre-trained model is improved on a more restricted marked dataset [131].
- Limited ability to handle out-of-domain questions: Deep learning models are often trained on specific domains or datasets, which can limit their ability to answer questions outside of those domains. One solution is to use transfer learning or domain adaptation techniques, which can help the model generalize to new domains[131].
- Limited interpretability: It might be tricky to comprehend how deep learning models generate their results since they can be complicated to comprehend. Utilisation of attention mechanisms, which enable the model to concentrate on particular elements of the input when generating predictions, is one remedy.[132].
- Limited ability to handle low-resource languages: It might be difficult for low-resource languages to use deep learning models since they need a lot of metadata to function successfully. One solution is to use unsupervised or semi-supervised learning techniques, which can leverage unannotated data to improve performance[132].
- Limited generalization: The ability of deep learning models to generalize to new contexts or tasks to perform that are dissimilar from those they were trained on might be a challenge. One way is to employ multi-task learning that involves training a single model on a variety of related tasks. This can increase the generalizability of the mode[133].
- Lack of Explainability: Understanding the manner in which deep learning models generate their responses might be tricky since they can be tricky to evaluate. One solution is to use methods such as attention mechanisms or explainable AI, which can provide insights into how the model makes its predictions[133].
- Limited ability to handle noisy or ambiguous input: Natural language input can be noisy or ambiguous, which can make it challenging for deep learning models to accurately answer questions. One solution is to use models that can handle uncertainty, such as probabilistic models or fuzzy logic-based models[133].
- Lack of comprehensive evaluation: Many research papers evaluate their models on a limited set of metrics or datasets, which can make it difficult to compare different approaches. One solution is to use standardized benchmarks and evaluation metrics, which can facilitate fair comparisons between different models[134].
- Limited ability to handle multi-hop reasoning: Multi-hop reasoning involves answering questions that require multiple pieces of information to be combined. Deep learning models can struggle with this task, as they often rely on local context rather than global context. One solution is to use graph-based models, which can represent the relationships between different pieces of information[135].
- Limited ability to handle complex questions: Deep learning models can struggle with answering complex questions that require reasoning and inference. One solution is to use models that can perform logical reasoning, such as knowledge graph-based models or symbolic reasoning models[135].
- Limited ability to handle long documents: Deep learning models can struggle with long documents, as they may have difficulty retaining relevant information over long periods of time. One solution is to use memory-augmented models, which can store relevant information in an external memory and retrieve it when needed[136].
- Limited ability to handle multi-lingual questions: Deep learning models trained on one language may not perform well on questions in other languages. Cross-lingual transfer learning, which trains a model on many languages and is capable of transferring knowledge across them, is one remedy [137].
7. Conclusion:
References
- B. Afrae, B. A. Mohamed, and A. A. Boudhir, “A Question answering System with a sequence to sequence grammatical correction,” in Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Networking, Information Systems & Security, Marrakech Morocco: ACM, Mar. 2020, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Y. Deng, W. Zhang, and W. Lam, “Opinion-aware Answer Generation for Review-driven Question Answering in E-Commerce,” in Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Information & Knowledge Management, in CIKM ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Oct. 2020, pp. 255–264. [CrossRef]
- R. Gao and C. Li, “Knowledge Question-Answering System Based on Knowledge Graph of Traditional Chinese Medicine,” in 2020 IEEE 9th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Dec. 2020, pp. 27–31. [CrossRef]
- Z. Gao, X. Xia, D. Lo, and J. Grundy, “Technical Q8A Site Answer Recommendation via Question Boosting,” ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol., vol. 30, no. 1, p. 11:1-11:34, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- V. Gutta, N. B. Unnam, and P. K. Reddy, “An improved human-in-the-loop model for fine-grained object recognition with batch-based question answering,” in Proceedings of the 7th ACM IKDD CoDS and 25th COMAD, in CoDS COMAD 2020. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Jan. 2020, pp. 134–142. [CrossRef]
- C. Liu, T. He, Y. Xiong, H. Wang, and J. Chen, “A Novel Knowledge Base Question Answering Model Based on Knowledge Representation and Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network,” in 2020 International Conference on Service Science (ICSS), Aug. 2020, pp. 149–154. [CrossRef]
- X.-Y. Liu, Y. Zhang, Y. Liao, and L. Jiang, “Dynamic Updating of the Knowledge Base for a Large-Scale Question Answering System,” ACM Trans. Asian Low-Resour. Lang. Inf. Process., vol. 19, no. 3, p. 45:1-45:13, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Qiu, Y. Wang, X. Jin, and K. Zhang, “Stepwise Reasoning for Multi-Relation Question Answering over Knowledge Graph with Weak Supervision,” in Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, in WSDM ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Jan. 2020, pp. 474–482. [CrossRef]
- D. Wang, Y. Shen, and H.-T. Zheng, “Knowledge Enhanced Latent Relevance Mining for Question Answering,” in ICASSP 2020 - 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), May 2020, pp. 4282–4286. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang and Z. Wang, “Question Answering System based on Diease Knowledge Base,” in 2020 IEEE 11th International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), Oct. 2020, pp. 351–354. [CrossRef]
- Z. Wu, B. Kao, T.-H. Wu, P. Yin, and Q. Liu, “PERQ: Predicting, Explaining, and Rectifying Failed Questions in KB-QA Systems,” in Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, in WSDM ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Jan. 2020, pp. 663–671. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yang, L. Shou, M. Gong, W. Lin, and D. Jiang, “Model Compression with Two-stage Multi-teacher Knowledge Distillation for Web Question Answering System,” in Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, in WSDM ’20. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Jan. 2020, pp. 690–698. [CrossRef]
- H. Buzaaba and T. Amagasa, “A Scheme for Efficient Question Answering with Low Dimension Reconstructed Embeddings,” in The 23rd International Conference on Information Integration and Web Intelligence, in iiWAS2021. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Dec. 2022, pp. 303–310. [CrossRef]
- C. Chen, C. Wang, M. Qiu, D. Gao, L. Jin, and W. Li, “Cross-domain Knowledge Distillation for Retrieval-based Question Answering Systems,” in Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, in WWW ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Jun. 2021, pp. 2613–2623. [CrossRef]
- S. Jain, M. Khanna, and Ankita, “Context-Aware Deep Learning Approach for Answering Questions,” in 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Dec. 2021, pp. 26–31. [CrossRef]
- T. Jin and H.-J. Wang, “Research on the method of knowledge base question answering,” in 2021 3rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data and Business Intelligence (MLBDBI), Dec. 2021, pp. 527–530. [CrossRef]
- K. Jorgensen, Z. Zhao, H. Wang, M. Wang, and Z. He, “Context-Aware Question-Answer for Interactive Media Experiences,” in ACM International Conference on Interactive Media Experiences, in IMX ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Jun. 2021, pp. 156–166. [CrossRef]
- N. Kanodia, K. Ahmed, and Y. Miao, “Question Answering Model Based Conversational Chatbot using BERT Model and Google Dialogflow,” in 2021 31st International Telecommunication Networks and Applications Conference (ITNAC), Nov. 2021, pp. 19–22. [CrossRef]
- B. Liu, R. Yan, Y. Zuo, and Y. Tao, “A Knowledge-based Question-Answering Method for Military Critical Information Under Limited Corpus,” in 2021 2nd International Conference on Computer Engineering and Intelligent Control (ICCEIC), Nov. 2021, pp. 86–91. [CrossRef]
- Q. Liu, X. Geng, H. Huang, T. Qin, J. Lu, and D. Jiang, “MGRC: An End-to-End Multigranularity Reading Comprehension Model for Question Answering,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, pp. 1–12, 2021. [CrossRef]
- X. Liu et al., “Research and Application of Intelligent Question-Answer Algorithm Based on Multi-Channel Dilated Convolution,” in 2021 IEEE International Conference on Emergency Science and Information Technology (ICESIT), Nov. 2021, pp. 776–780. [CrossRef]
- F. Meng, W. Wang, and J. Wang, “Research on Short Text Similarity Calculation Method for Power Intelligent Question Answering,” in 2021 13th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Communication Networks (CICN), Sep. 2021, pp. 91–95. [CrossRef]
- T. Ploumis, I. Perikos, F. Grivokostopoulou, and I. Hatzilygeroudis, “A Factoid based Question Answering System based on Dependency Analysis and Wikidata,” in 2021 12th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems & Applications (IISA), Jul. 2021, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Y. Tang, H. Han, X. Yu, J. Zhao, G. Liu, and L. Wei, “An Intelligent Question Answering System based on Power Knowledge Graph,” in 2021 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Jul. 2021, pp. 01–05. [CrossRef]
- S. Xu, F. Liu, Z. Huang, Y. Peng, and D. Li, “A BERT-Based Semantic Matching Ranker for Open-Domain Question Answering,” in Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval, in NLPIR 2020. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Feb. 2021, pp. 31–36. [CrossRef]
- R. Zhao, S. Wu, Y. Mao, and N. Li, “A Multi-Level Semantic Fusion Algorithm Based on Historical Data in Question Answering,” in 2021 7th Annual International Conference on Network and Information Systems for Computers (ICNISC), Jul. 2021, pp. 950–956. [CrossRef]
- I. Annamoradnejad, “Requirements for Automating Moderation in Community Question-Answering Websites,” in 15th Innovations in Software Engineering Conference, in ISEC 2022. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Feb. 2022, pp. 1–4. [CrossRef]
- R. Butler, V. D. Duggirala, and F. Banaei-Kashani, “iLFQA: A Platform for Efficient and Accurate Long-Form Question Answering,” in Proceedings of the Fifteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, in WSDM ’22. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Feb. 2022, pp. 1565–1568. [CrossRef]
- C.-C. Kuo and K.-Y. Chen, “Toward Zero-Shot and Zero-Resource Multilingual Question Answering,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 99754–99761, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Li, X. Lu, and K. Shuang, “CypherQA: Question-answering method based on Attribute Knowledge Graph,” in 2021 The 9th International Conference on Information Technology: IoT and Smart City, in ICIT 2021. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Apr. 2022, pp. 243–247. [CrossRef]
- A. Malhar, P. Sawant, Y. Chhadva, and S. Kurhade, “Deep learning based Answering Questions using T5 and Structured Question Generation System’,” in 2022 6th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), May 2022, pp. 1544–1549. [CrossRef]
- E. Niazmand, “Enhancing Query Answer Completeness with Query Expansion based on Synonym Predicates,” in Companion Proceedings of the Web Conference 2022, in WWW ’22. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Aug. 2022, pp. 354–358. [CrossRef]
- J. Tian, B. Li, Y. Ji, and J. Wu, “Text-Enhanced Question Answering over Knowledge Graph,” in Proceedings of the 10th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Graphs, in IJCKG ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Jan. 2022, pp. 135–139. [CrossRef]
- C. Wang and X. Luo, “A Legal Question Answering System Based on BERT ,” in 2021 5th International Conference on Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence, in CSAI 2021. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Mar. 2022, pp. 278–283. [CrossRef]
- J. Cao, J. Cao, and Y. Wang, “Gentle Teaching Assistant Model For Improved Accuracy In Question-Answering,” in 2022 5th International Conference on Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing, in MLNLP2022. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Mar. 2023, pp. 353–359. [CrossRef]
- Y.-H. Chen, E. J.-L. Lu, and Y.-Y. Lin, “Efficient SPARQL Queries Generator for Question Answering Systems,” IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 99850–99860, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Z. Liu, Y. Feng, Y. Yin, J. Sun, Z. Chen, and B. Xu, “QATest: A Uniform Fuzzing Framework for Question Answering Systems,” in Proceedings of the 37th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering, in ASE ’22. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Jan. 2023, pp. 1–12. [CrossRef]
- J. Wu, T. Mu, J. Thiyagalingam, and J. Y. Goulermas, “Memory-Aware Attentive Control for Community Question Answering With Knowledge-Based Dual Refinement,” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, pp. 1–14, 2023. [CrossRef]
- “6879936.pdf.” Accessed: Apr. 25, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://web.stanford.edu/class/archive/cs/cs224n/cs224n.1184/reports/6879936.pdf.
- Y. Shen, E. M.-K. Lai, and M. Mohaghegh, “Effects of Similarity Score Functions in Attention Mechanisms on the Performance of Neural Question Answering Systems,” Neural Process Lett, vol. 54, no. 3, pp. 2283–2302, Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Bachrach et al., “An Attention Mechanism for Answer Selection Using a Combined Global and Local View.” arXiv, Sep. 20, 2017. Accessed: Apr. 25, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1707.01378.
- A. Osman and W. Samek, “DRAU: Dual Recurrent Attention Units for Visual Question Answering,” Computer Vision and Image Understanding, vol. 185, pp. 24–30, Aug. 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Zhao and Z. Jin, “Research Progress of Automatic Question Answering System Based on Deep Learning,” Open Access Library Journal, vol. 7, no. 6, Art. no. 6, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Brauwers and F. Frasincar, “A General Survey on Attention Mechanisms in Deep Learning,” IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., vol. 35, no. 4, pp. 3279–3298, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Varma, S. Shivam, S. Biswas, P. Saha, and K. Jalan, “Graph NLU enabled question answering system,” Heliyon, vol. 7, no. 9, p. e08035, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- “A knowledge graph based question answering method for medical domain - PMC.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8444078/ (accessed Apr. 25, 2023).
- P. Mital et al., Graph based Question Answering System. 2018.
- S. Vakulenko, J. D. F. Garcia, A. Polleres, M. de Rijke, and M. Cochez, “Message Passing for Complex Question Answering over Knowledge Graphs.” arXiv, Aug. 19, 2019. Accessed: Apr. 25, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/1908.06917.
- M. Shi, “Knowledge Graph Question and Answer System for Mechanical Intelligent Manufacturing Based on Deep Learning,” Mathematical Problems in Engineering, vol. 2021, p. e6627114, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- “BERT 101 - State Of The Art NLP Model Explained.” https://huggingface.co/blog/bert-101 (accessed Apr. 25, 2023).
- “How to Train A Question-Answering Machine Learning Model | Paperspace Blog.” https://blog.paperspace.com/how-to-train-question-answering-machine-learning-models/ (accessed Apr. 25, 2023).
- “How to build Question Answering system for online store with BERT,” Grid Dynamics Blog, Oct. 15, 2020. https://blog.griddynamics.com/question-answering-system-using-bert/ (accessed Apr. 25, 2023).
- “COBERT: COVID-19 Question Answering System Using BERT - PMC.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8220121/ (accessed Apr. 25, 2023).
- C. Zhang, Y. Lai, Y. Feng, and D. Zhao, “A review of deep learning in question answering over knowledge bases,” AI Open, vol. 2, pp. 205–215, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Mutabazi, J. Ni, G. Tang, and W. Cao, “A Review on Medical Textual Question Answering Systems Based on Deep Learning Approaches,” Applied Sciences, vol. 11, no. 12, Art. no. 12, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- “How to Train A Question-Answering Machine Learning Model,” Paperspace Blog, Dec. 14, 2020. https://blog.paperspace.com/how-to-train-question-answering-machine-learning-models/ (accessed Apr. 26, 2023).
- Y. Sharma and S. Gupta, “Deep Learning Approaches for Question Answering System,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 132, pp. 785–794, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. Alqifari, “Question Answering Systems Approaches and Challenges,” in Proceedings of the Student Research Workshop Associated with RANLP 2019, Varna, Bulgaria: INCOMA Ltd., Sep. 2019, pp. 69–75. [CrossRef]
- E. Stroh and P. Mathur, “Question Answering Using Deep Learning”.
- G. Shachaf, A. Brutzkus, and A. Globerson, “A Theoretical Analysis of Fine-tuning with Linear Teachers.” arXiv, Nov. 07, 2021. Accessed: Apr. 26, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2107.01641.
- “Building a QA System with BERT on Wikipedia,” NLP for Question Answering, May 19, 2020. https://qa.fastforwardlabs.com/pytorch/hugging%20face/wikipedia/bert/transformers/2020/05/19/Getting_Started_with_QA.html (accessed Apr. 26, 2023).
- “pdf.pdf.” Accessed: Apr. 26, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=ks4BvF7kpiP.
- D. Dimitriadis and G. Tsoumakas, “Artificial fine-tuning tasks for yes/no question answering,” Natural Language Engineering, pp. 1–23, Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Briggs, “How-to Fine-Tune a Q&A Transformer,” Medium, Sep. 02, 2021. https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-fine-tune-a-q-a-transformer-86f91ec92997 (accessed Apr. 26, 2023).
- “Solving internal search problems with Dialogflow,” Google Cloud Blog. https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/developers-practitioners/solving-internal-search-problems-dialogflow (accessed Apr. 26, 2023).
- “What is Google Dialogflow?” https://start-up.house/en/blog/articles/what-is-google-dialogflow (accessed Apr. 26, 2023).
- “Testing best practices (Dialogflow) | Dialogflow and legacy Actions SDK,” Google Developers. https://developers.google.com/assistant/df-asdk/dialogflow/testing-best-practices (accessed Apr. 26, 2023).
- “Dialogflow Review: Pricing, Pros, Cons & Features,” CompareCamp.com, Feb. 01, 2019. https://comparecamp.com/dialogflow-review-pricing-pros-cons-features/ (accessed Apr. 26, 2023).
- Z. Li, P. Sharma, X. H. Lu, J. Cheung, and S. Reddy, “Using Interactive Feedback to Improve the Accuracy and Explainability of Question Answering Systems Post-Deployment,” in Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2022, Dublin, Ireland: Association for Computational Linguistics, May 2022, pp. 926–937. [CrossRef]
- “send.pdf.” Accessed: Apr. 26, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://etd.ohiolink.edu/apexprod/rws_etd/send_file/send?accession=osu1609944750779603&disposition=inline.
- S. K. Dwivedi and V. Singh, “Research and Reviews in Question Answering System,” Procedia Technology, vol. 10, pp. 417–424, 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. A. Campos, K. Cho, A. Otegi, A. Soroa, E. Agirre, and G. Azkune, “Improving Conversational Question Answering Systems after Deployment using Feedback-Weighted Learning,” in Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain (Online): International Committee on Computational Linguistics, Dec. 2020, pp. 2561–2571. [CrossRef]
- Z. Li, P. Sharma, X. H. Lu, J. Cheung, and S. Reddy, “Using Interactive Feedback to Improve the Accuracy and Explainability of Question Answering Systems Post-Deployment,” in Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2022, Dublin, Ireland: Association for Computational Linguistics, May 2022, pp. 926–937. [CrossRef]
- “da8a13559cc19da8ab4eb8eb5f065e70019fd74c.pdf.” Accessed: Apr. 26, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://openreview.net/pdf/da8a13559cc19da8ab4eb8eb5f065e70019fd74c.pdf.
- “Evaluating QA: the Retriever & the Full QA System,” NLP for Question Answering, Jun. 30, 2020. https://qa.fastforwardlabs.com/elasticsearch/mean%20average%20precision/recall%20for%20irqa/qa%20system%20design/2020/06/30/Evaluating_the_Retriever_&_End_to_End_System.html (accessed Apr. 27, 2023).
- Á. Rodrigo, J. Pérez-Iglesias, A. Peñas, G. Garrido, and L. Araujo, A Question Answering System based on Information Retrieval and Validation. 2010.
- Z. Wang, V. X. Lin, and L. Mehr, “Deep Retriever: Information Retrieval for Multi-hop Question Answering”.
- “What is a Knowledge-based System? | Definition from TechTarget,” CIO. https://www.techtarget.com/searchcio/definition/knowledge-based-systems-KBS (accessed May 08, 2023).
- B. Zope, S. Mishra, K. Shaw, D. R. Vora, K. Kotecha, and R. V. Bidwe, “Question Answer System: A State-of-Art Representation of Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis,” Big Data and Cognitive Computing, vol. 6, no. 4, Art. no. 4, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- “(PDF) A Structured Testing Methodology for Knowledge-Based Systems.” https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221464216_A_Structured_Testing_Methodology_for_Knowledge-Based_Systems (accessed May 08, 2023).
- “Testing Knowledge Based Systems: A Case Study and Implications - ScienceDirect.” https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S147466701749447X (accessed May 08, 2023).
- D. Diefenbach, V. Lopez, K. Singh, and P. Maret, “Core techniques of question answering systems over knowledge bases: a survey,” Knowl Inf Syst, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 529–569, Jun. 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. Singh, I. Lytra, A. S. Radhakrishna, S. Shekarpour, M.-E. Vidal, and J. Lehmann, “No one is perfect: Analysing the performance of question answering components over the DBpedia knowledge graph,” Journal of Web Semantics, vol. 65, p. 100594, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- “Knowledge Distillation: Principles & Algorithms [+Applications].” https://www.v7labs.com/blog/knowledge-distillation-guide. https://www.v7labs.com/blog/knowledge-distillation-guide (accessed May 08, 2023).
- D. User, “Introduction to Knowledge Distillation,” Deci, Jun. 29, 2022. https://deci.ai/blog/knowledge-distillation-introduction/ (accessed May 08, 2023).
- C. Chen, C. Wang, M. Qiu, D. Gao, L. Jin, and W. Li, “Cross-domain Knowledge Distillation for Retrieval-based Question Answering Systems,” in Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, in WWW ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Jun. 2021, pp. 2613–2623. [CrossRef]
- “Improving Question Answering Performance Using Knowledge Distillation and Active Learning,” ar5iv. https://ar5iv.labs.arxiv.org/html/2109.12662 (accessed May 08, 2023).
- S. Soltan, H. Khan, and W. Hamza, “Limitations of Knowledge Distillation for Zero-shot Transfer Learning,” in Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Simple and Efficient Natural Language Processing, Virtual: Association for Computational Linguistics, Nov. 2021, pp. 22–31. [CrossRef]
- “Limitations of knowledge distillation for zero-shot transfer learning,” Amazon Science. https://www.amazon.science/publications/limitations-of-knowledge-distillation-for-zero-shot-transfer-learning (accessed May 08, 2023).
- “Question Answering based on Knowledge Graphs.” https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/question-answering-based-knowledge-graphs-andreas-blumauer (accessed May 08, 2023).
- Y. Zhang, H. Dai, Z. Kozareva, A. Smola, and L. Song, “Variational Reasoning for Question Answering With Knowledge Graph,” Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32, no. 1, Art. no. 1, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Yani and A. A. Krisnadhi, “Challenges, Techniques, and Trends of Simple Knowledge Graph Question Answering: A Survey,” Information, vol. 12, no. 7, Art. no. 7, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Liang, K. Stockinger, T. M. de Farias, M. Anisimova, and M. Gil, “Querying knowledge graphs in natural language,” Journal of Big Data, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 3, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- “How to Train A Question-Answering Machine Learning Model,” Paperspace Blog, Dec. 14, 2020. https://blog.paperspace.com/how-to-train-question-answering-machine-learning-models/ (accessed May 08, 2023).
- D. Marijan, A. Gotlieb, and M. Ahuja, Challenges of Testing Machine Learning Based Systems. 2019, p. 102. [CrossRef]
- S. Omri and C. Sinz, “Machine Learning Techniques for Software Quality Assurance: A Survey.” arXiv, Apr. 28, 2021. Accessed: May 08, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2104.14056.
- “QA Systems and Deep Learning Technologies – Part 1 - Alibaba Cloud Community.” https://www.alibabacloud.com/blog/qa-systems-and-deep-learning-technologies-part-1_71899 (accessed May 08, 2023).
- E. Altamimi, A. Elkawakjy, and C. Catal, “Metamorphic relation automation: Rationale, challenges, and solution directions,” Journal of Software: Evolution and Process, vol. 35, no. 1, p. e2509, 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Tu, M. Jiang, and Z. Ding, “A Metamorphic Testing Approach for Assessing Question Answering Systems,” Mathematics, vol. 9, no. 7, Art. no. 7, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Höhn, “Natural Language Question Answering Systems,” SEEBURGER Blog, Jan. 18, 2022. https://blog.seeburger.com/natural-language-question-answering-systems-get-quick-answers-to-concrete-questions/ (accessed May 08, 2023).
- “advanced-qa.pdf.” Accessed: May 08, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs474/2005fa/Handouts/advanced-qa.pdf.
- “Weights & Biases,” W&B. https://wandb.ai/mostafaibrahim17/ml-articles/reports/The-Answer-Key-Unlocking-the-Potential-of-Question-Answering-With-NLP--VmlldzozNTcxMDE3 (accessed May 08, 2023).
- “Question answering,” Wikipedia. May 06, 2023. Accessed: May 08, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Question_answering&oldid=1153385768.
- R. Alqifari, “Question Answering Systems Approaches and Challenges,” in Proceedings of the Student Research Workshop Associated with RANLP 2019, Varna, Bulgaria: INCOMA Ltd., Sep. 2019, pp. 69–75. [CrossRef]
- “Limitations of NLP in building Question/Answering systems - Proxzar.” https://www.proxzar.ai/blog/limitations-of-nlp-in-question-answering/ (accessed May 08, 2023).
- “TMLde1.pdf.” Accessed: May 08, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://upcommons.upc.edu/bitstream/handle/2117/118781/TMLde1.pdf.
- A. Team, “Intelligent QA Systems With NLP for Optimizing Customer Interactions,” AI Oodles, Jun. 05, 2020. https://artificialintelligence.oodles.io/blogs/qa-system-with-nlp/ (accessed May 08, 2023).
- R. Alqifari, “Question Answering Systems Approaches and Challenges,” in Proceedings of the Student Research Workshop Associated with RANLP 2019, Varna, Bulgaria: INCOMA Ltd., Sep. 2019, pp. 69–75. [CrossRef]
- L. Kodra, “A Review on Neural Network Question Answering Systems,” International Journal of Artificial Intelligence & Applications, vol. 8, pp. 59–74, Mar. 2017. [CrossRef]
- “Limitations of NLP in building Question/Answering systems,” Proxzar, Jul. 22, 2020. https://www.proxzar.ai/blog/limitations-of-nlp-in-question-answering/ (accessed May 08, 2023).
- “Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) Tutorial: Types and Examples [Updated] | Simplilearn,” Simplilearn.com. https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/deep-learning-tutorial/rnn (accessed May 16, 2023).
- A. Bansal, Z. Eberhart, L. Wu, and C. McMillan, “A Neural Question Answering System for Basic Questions about Subroutines.” arXiv, Jan. 11, 2021. Accessed: May 16, 2023. [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2101.03999.
- https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs224n/reports/final_summaries/summary215.html (Accessed May 16, 2023).
- M.-H. Wang, S. S. Yalaburg, and L. Shankarrao, “Question Answering System”.
- S. I. A. Saany, A. Mamat, A. Mustapha, L. S. Affendey, and M. N. A. Rahman, “Semantics question analysis model for question answering system,” ams, vol. 9, pp. 6491–6505, 2015. [CrossRef]
- S. S. Alanazi, N. Elfadil, M. Jarajreh, and S. Algarni, “Question Answering Systems: A Systematic Literature Review,” IJACSA, vol. 12, no. 3, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. N. Khin and K. M. Soe, “Question Answering based University Chatbot using Sequence to Sequence Model,” in 2020 23rd Conference of the Oriental COCOSDA International Committee for the Co-ordination and Standardisation of Speech Databases and Assessment Techniques (O-COCOSDA), Nov. 2020, pp. 55–59. [CrossRef]
- R. Agarwal, T. Jain, and K. Mehta, “Question Generation System using Seq2Seq”.
- “Question Answering (Part 4): Transformers | by Atul Singh, PhD | Medium.” https://atulsinghphd.medium.com/question-answering-part-4-transformers-6160a30fda62 (accessed May 16, 2023).
- W. Hou, “Seq2seq-Attention Question Answering Model”.
- S. S. Alanazi, N. Elfadil, M. Jarajreh, and S. Algarni, “Question Answering Systems: A Systematic Literature Review,” IJACSA, vol. 12, no. 3, 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Biermann, S. Walter, and P. Cimiano, “A Guided Template-Based Question Answering System over Knowledge Graphs”.
- “(PDF) SPARQL Template-Based Question Answering.” https://www.researchgate.net/publication/240615221_SPARQL_Template-Based_Question_Answering (accessed May 16, 2023).
- J. Gomes, R. C. de Mello, V. Ströele, and J. F. de Souza, “A Hereditary Attentive Template-based Approach for Complex Knowledge Base Question Answering Systems,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 205, p. 117725, Nov. 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Höffner et al., “User Interface for a Template Based Question Answering System,” in Knowledge Engineering and the Semantic Web, P. Klinov and D. Mouromtsev, Eds., in Communications in Computer and Information Science. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2013, pp. 258–264. [CrossRef]
- S. S. Alanazi, N. Elfadil, M. Jarajreh, and S. Algarni, “Question Answering Systems: A Systematic Literature Review,” IJACSA, vol. 12, no. 3, 2021. [CrossRef]
- “Question answering as a ‘lingua franca’ for transfer learning - Amazon Science.” https://www.amazon.science/blog/question-answering-as-a-lingua-franca-for-transfer-learning (accessed May 16, 2023).
- Y.-A. Chung, H.-Y. Lee, and J. Glass, “Supervised and Unsupervised Transfer Learning for Question Answering,” in Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers), New Orleans, Louisiana: Association for Computational Linguistics, Jun. 2018, pp. 1585–1594. [CrossRef]
- Y. Boreshban, S. M. Mirbostani, G. Ghassem-Sani, S. A. Mirroshandel, and S. Amiriparian, “Improving question answering performance using knowledge distillation and active learning,” Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 123, p. 106137, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- T. M. Lai, T. Bui, N. Lipka, and S. Li, “Supervised Transfer Learning for Product Information Question Answering,” in 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Dec. 2018, pp. 1109–1114. [CrossRef]
- E. Stroh and P. Mathur, “Question Answering Using Deep Learning”.
- C. Zhang, Y. Lai, Y. Feng, and D. Zhao, “A review of deep learning in question answering over knowledge bases,” AI Open, vol. 2, pp. 205–215, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Sharma and S. Gupta, “Deep Learning Approaches for Question Answering System,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 132, pp. 785–794, 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. Alanazi, N. Mohamed, M. Jarajreh, and S. Algarni, “Question Answering Systems: A Systematic Literature Review,” International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, vol. 12, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Haroon, Deep Learning Based Question Answering System: A Review. 2019. [CrossRef]
- L. Nie and J. Ye, “Question answering algorithm based on deep learning,” in Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering, in EITCE ’21. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, Dec. 2022, pp. 731–734. [CrossRef]
- H. Abdel-Nabi, A. Awajan, and M. Ali, “Deep learning-based question answering: a survey,” Knowledge and Information Systems, vol. 65, pp. 1–87, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, K., Hussain, S. J., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Humayun, M. (2019, April). SYN flood attack detection based on bayes estimator (SFADBE) for MANET. In 2019 International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCIS) (pp. 1-4). IEEE.
- Adeyemo Victor Elijah, Azween Abdullah, NZ JhanJhi, Mahadevan Supramaniam and Balogun Abdullateef O, “Ensemble and Deep-Learning Methods for Two-Class and Multi-Attack Anomaly Intrusion Detection: An Empirical Study” International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications(IJACSA), 10(9), 2019. [CrossRef]
- Lim, M., Abdullah, A., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2021). Performance optimization of criminal network hidden link prediction model with deep reinforcement learning. Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, 33(10), 1202-1210. [CrossRef]
- Gaur, L., Singh, G., Solanki, A., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Bhatia, U., Sharma, S., ... & Kim, W. (2021). Disposition of youth in predicting sustainable development goals using the neuro-fuzzy and random forest algorithms. Human-Centric Computing and Information Sciences, 11, NA.
- Kumar, T., Pandey, B., Mussavi, S. H. A., & Zaman, N. (2015). CTHS based energy efficient thermal aware image ALU design on FPGA. Wireless Personal Communications, 85, 671-696. [CrossRef]
- Nanglia, S., Ahmad, M., Khan, F. A., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2022). An enhanced Predictive heterogeneous ensemble model for breast cancer prediction. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 72, 103279. [CrossRef]
- Gaur, L., Afaq, A., Solanki, A., Singh, G., Sharma, S., Jhanjhi, N. Z., ... & Le, D. N. (2021). Capitalizing on big data and revolutionary 5G technology: Extracting and visualizing ratings and reviews of global chain hotels. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 95, 107374. [CrossRef]
- Diwaker, C., Tomar, P., Solanki, A., Nayyar, A., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Abdullah, A., & Supramaniam, M. (2019). A new model for predicting component-based software reliability using soft computing. IEEE Access, 7, 147191-147203. [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S. J., Ahmed, U., Liaquat, H., Mir, S., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Humayun, M. (2019, April). IMIAD: intelligent malware identification for android platform. In 2019 International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCIS) (pp. 1-6). IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Humayun, M., Alsaqer, M. S., & Jhanjhi, N. (2022). Energy optimization for smart cities using iot. Applied Artificial Intelligence, 36(1), 2037255. [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G., Verma, S., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Talib, M. N. (2020, December). Secure surveillance system using chaotic image encryption technique. In IOP conference series: materials science and engineering (Vol. 993, No. 1, p. 012062). IOP Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Almusaylim, Z. A., Zaman, N., & Jung, L. T. (2018, August). Proposing a data privacy aware protocol for roadside accident video reporting service using 5G in Vehicular Cloud Networks Environment. In 2018 4th International conference on computer and information sciences (ICCOINS) (pp. 1-5). IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Wassan, S., Chen, X., Shen, T., Waqar, M., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2021). Amazon product sentiment analysis using machine learning techniques. Revista Argentina de Clínica Psicológica, 30(1), 695.
- Shahid, H., Ashraf, H., Javed, H., Humayun, M., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & AlZain, M. A. (2021). Energy optimised security against wormhole attack in iot-based wireless sensor networks. Comput. Mater. Contin, 68(2), 1967-81. [CrossRef]
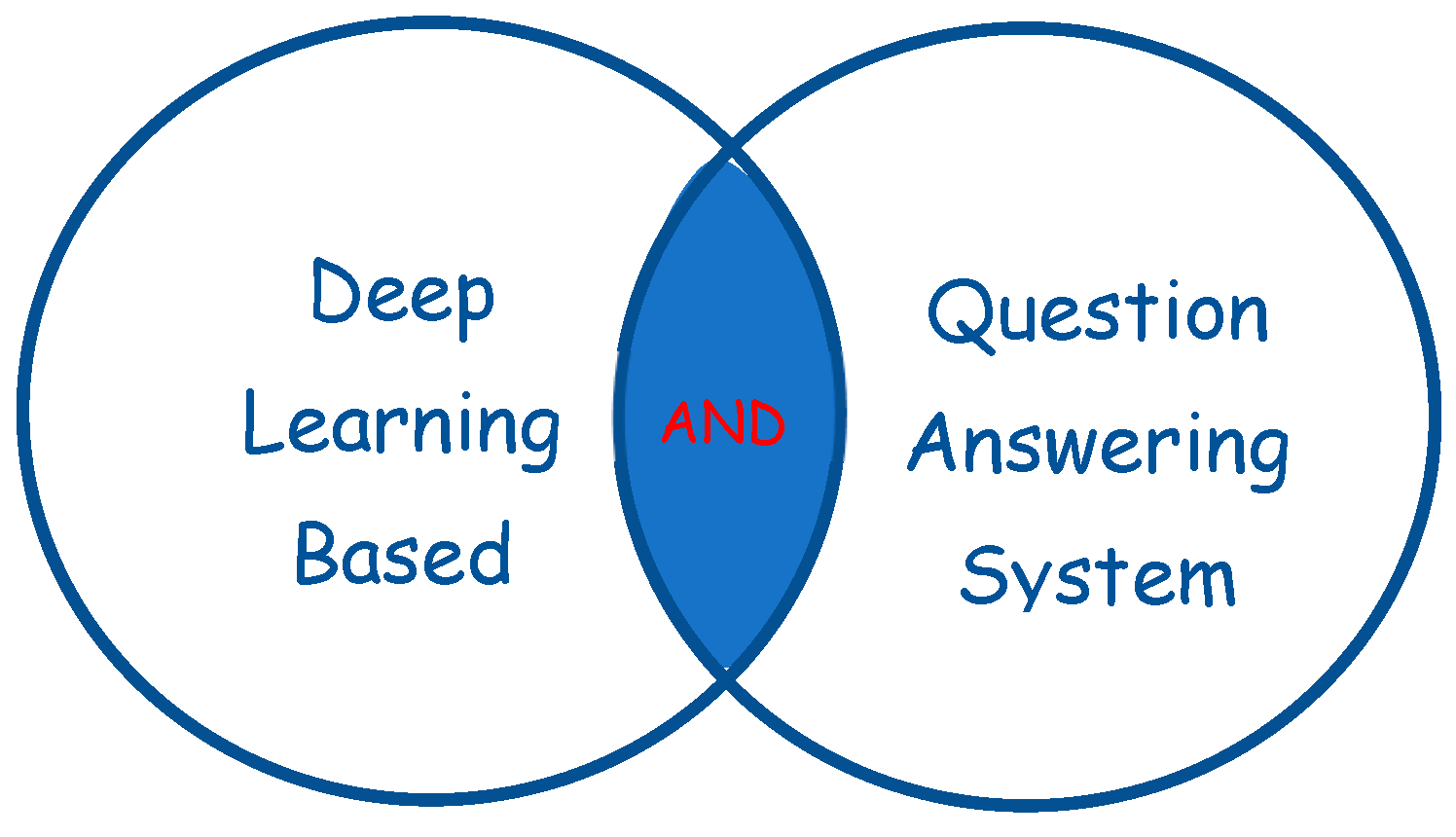

| Deep Learning | based | Question Answering System |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | - | Query Answering System |
| Context Aware | - | Automated Answering System |
| Deep Architectures | - | - |
| Deep Models | - | - |
| Deep Neural Network | - | - |
| Knowledge | - | - |
| Machine Learning | - | - |
| Deep Learning | Base | Question | Answer System |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLearning | Base | Question | Answer System |
| DeepLearning | Base* | Question | Answer* System |
| Deep Learning | Based | Question Answering System |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | Based | Question Answering System |
| Artificial Intelligence | Based | Query Answering System |
| Artificial Intelligence | Based | Automate Answering System |
| Context Aware | Based | Question Answering System |
| Context Aware | Based | Query Answering System |
| Context Aware | Based | Automate Answering System |
| Deep Architectures | Based | Question Answering System |
| Deep Architectures | Based | Query Answering System |
| Deep Architectures | Based | Automate Answering System |
| Deep Learning | Based | Question Answering System |
| Deep Learning | Based | Query Answering System |
| Deep Models | Based | Question Answering System |
| Deep Models | Based | Query Answering System |
| Deep Models | Based | Automate Answering System |
| Deep Neural Network | Based | Question Answering System |
| Deep Neural Network | Based | Query Answering System |
| Deep Neural Network | Based | Automate Answering System |
| Knowledge | Based | Question Answering System |
| Knowledge | Based | Query Answering System |
| Knowledge | Based | Automate Answering System |
| Machine Learning | Based | Question Answering System |
| Machine Learning | Based | Query Answering System |
| Machine Learning | Based | Automate Answering System |
| Year | Database | Pages Explored |
Available Articles (per page) |
Related Articles |
Total (415) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | IEEEXplore | 3 | 20 | 37 | 102 |
| ACM | 3 | 30 | 65 | ||
| 2021 | IEEEXplore | 3 | 20 | 48 | 149 |
| ACM | 3 | 30 | 101 | ||
| 2022 | IEEEXplore | 3 | 20 | 57 | 142 |
| ACM | 3 | 30 | 82 | ||
| 2023 | IEEEXplore | 3 | 20 | 02 | 22 |
| ACM | 3 | 30 | 20 |
| Title Based Filtering | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | Total |
| Relevant Papers | 66 | 102 | 94 | 16 | 278 |
| Abstract Based Filtering | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | Total |
| Relevant Papers | 11 | 14 | 09 | 04 | 38 |
| Quality Assessment | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Relevancy | Closely Relevant | Partially Relevant | Not Relevant |
| Papers | 38 | 77 | 146 |
| Notation | Abbreviation | Notation | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | A | Performance | P |
| Completeness | CP | Quality | Q |
| Computation Time | CT | Readability & Comprehend Context | RCC |
| Cost | C | ||
| Effectiveness | EFT | Relevancy | R |
| Efficiency | E | Scalability | SC |
| Improved Results | IR | Speed | S |
| REF. PAPERS TITLE | OBJECTIVES | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | CP | CT | C | EFT | E | IR | P | Q | RCC | R | SC | S | |
| A Question answering System with a sequence to sequence grammatical correction [1] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Opinion-aware Answer Generation for Review-driven Question Answering in E-Commerce [2] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| Knowledge Question-Answering System Based on Knowledge Graph of Traditional Chinese Medicine [3] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Technical Q8A Site Answer Recommendation via Question Boosting [4] | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| An improved human-in-the-loop model for fine-grained object recognition with batch-based question answering[5] | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| A Novel Knowledge Base Question Answering Model Based on Knowledge Representation and Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network [6] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| Dynamic Updating of the Knowledge Base for a Large-Scale Question Answering System [7] | ✓ | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - |
| Stepwise Reasoning for Multi-Relation Question Answering over Knowledge-Graph with Weak Supervision[8] | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Knowledge Enhanced Latent Relevance Mining for Question Answering[9] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - |
| Question Answering System based on Disease Knowledge Base[10] | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| PERQ: Predicting, Explaining, and Rectifying Failed Questions in KB-QA Systems[11] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Model Compression with Two-stage Multi-teacher Knowledge Distillation for Web Question Answering System[12] | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| A Scheme for Efficient Question Answering with Low Dimension Reconstructed Embedding’s [13] | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| Cross-domain Knowledge Distillation for Retrieval-based Question Answering Systems[14] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| Context-Aware Deep Learning Approach for Answering Questions[15] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - |
| Research on the method of knowledge base question answering[16] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Context-Aware Question-Answer for Interactive Media Experience [17] | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| Question Answering Model Based Conversational Chatbot using BERT Model and Google Dialogflow[18] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| A Knowledge-based Question-Answering Method for Military Critical Information Under Limited Corpus[19] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| MGRC: An End-to-End Multigranularity Reading Comprehension Model for Question Answering[20] | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Research and Application of Intelligent Question-Answer Algorithm Based on Multi-Channel Dilated Convolution[21] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| Research on Short Text Similarity Calculation Method for Power Intelligent Question Answering[22] | ✓ | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| A Factoid based Question Answering System based on Dependency Analysis and Wikidata[23] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - |
| An Intelligent Question Answering System based on Power Knowledge Graph [24] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ |
| A BERT-Based Semantic Matching Ranker for Open-Domain Question Answering[25] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| A Multi-Level Semantic Fusion Algorithm Based on Historical Data in Question Answering[26] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| Requirements for Automating Moderation in Community Question-Answering Websites[27] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| iLFQA: A Platform for Efficient and Accurate Long-Form Question Answering[28] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Toward Zero-Shot and Zero-Resource Multilingual Question Answering[29] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| CypherQA: Question-answering method based on Attribute Knowledge Graph[30] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| Deep learning based Answering Questions using T5 and Structured Question Generation System[31] | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Enhancing Query Answer Completeness with Query Expansion based on Synonym Predicates[32] | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Text-Enhanced Question Answering over Knowledge Graph[33] | ✓ | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| A Legal Question Answering System Based on BERT [34] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| Gentle Teaching Assistant Model For Improved Accuracy In Question-Answering [35] | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Efficient SPARQL Queries Generator for Question Answering Systems[36] | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| QATest: A Uniform Fuzzing Framework for Question Answering Systems[37] | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Memory-Aware Attentive Control for Community Question Answering With Knowledge-Based Dual Refinement [38] | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ✓ | - | - | - | - | - |
| Notation | Abbreviation | Notation | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Attention Mechanism | AM | Knowledge Graph | KG |
| Attribute Graph Base Approach | AG | Machine Learning Approach | ML |
| BERT model | BERT | Metamorphic Testing Theory | MT |
| Deep Learning Approach | DL | Natural Processing Languages | NLP |
| Fine-Tuning | FT | Neural Network Approach | NN |
| Google Dialog-Flow | GD | Recurrent Neural Network | RNN |
| Human Feedback | HF | Semantic Analysis Approach | SA |
| Information Retrieval Techniques | IR | Sequence-to-Sequence | Seq2Seq |
| Knowledge Base | KB | Template Based Approach | TB |
| Knowledge Distillation | KD | Transfer Learning | TL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





