1. Introduction
Environmental pollution remains an urgent global concern, demanding innovative strategies aligned with sustainability principles and cleaner production practices. Among the critical environmental challenges, the contamination of water resources by heavy metals and other hazardous substances such as organic dyes, pesticides, drugs, antibiotics, and phenols [
1,
2] stands as a transcendental threat to ecosystems and human well-being. In this context, the development of sustainable and eco-friendly methods for contaminant removal assumes paramount importance. In this context, it's crucial to highlight that the primary origins of heavy metals in the surroundings encompass electroplating, battery manufacturing, mining, pulp production, paint manufacturing, metal melting, pigment creation, ceramics, and related sectors [
3,
4,
5]. Metals such as mercury (Hg), lead (Pb), nickel (Ni), zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), , chromium (Cr), and Copper (Cu), are prevalent heavy metals, classified as perilous waste and acknowledged for their teratogenic and carcinogenic properties [
6,
7]. The pronounced contamination of aquatic ecosystems caused by heavy metal presence represents a crucial and pressing concern, underscoring the necessity to address this global challenge [
8,
9]. In this regard, various methodologies for water remediation have been reported, including ion exchange, electrochemical treatment, chemical precipitation, water dilution, adsorption and sediment neutralization through biological and catalytic methods [
10,
11,
12,
13]. Among these, the adsorption technique has gained significant recognition for its eco-friendly, convenient, and highly efficient attributes. Therefore, one promising avenue for addressing this challenge involves the application of adsorption-based removal systems, known for their effectiveness and environmental compatibility. In recent years, researchers have increasingly explored the utilization of green-synthesized nanoparticles in tandem with naturally occurring zeolites to create high-performance adsorbent materials [
14,
15]. This approach combines the unique properties of both components to achieve enhanced contaminant removal while minimizing the ecological footprint of the process.
On one aspect, Zeolites are aluminosilicates with crystalline microporous structures, extensively utilized as catalysts, adsorbents, and ion exchangers [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. They are classified as tectosilicate-type minerals and due to the specific pore sizes, the thermal stability, and the high disponibility, the zeolites offer an excellent alternative for water remediation.
On the other hand, silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) have been the focus of considerable interest due to their unique adsorption capabilities, superior conductivity, chemical stability, and antimicrobial properties, which are all vital for efficient water treatment. Additionally, their antibacterial properties make them highly effective against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including viruses, bacteria, and fungi. They are commercially applied in point-of-use water treatment as a post-treatment for filtrate water [
21,
22,
23,
24,
25]. However, traditional AgNPs synthesis methods often entail the use of harsh chemicals and energy-intensive processes, presenting substantial environmental concerns. In contrast, green synthesis methods leverage biogenic reducing agents derived from natural sources, aligning seamlessly with the principles of cleaner production and sustainable chemistry.
Recent research involves utilizing various parts of plants like leaves, roots, flowers, fruits, and rhizomes as effective reducing agents for synthesizing AgNPs [
26]. Plants such as guava, neem, aloe vera, Momordica charantia, Eclipta alba, lemon, hibiscus, Leptadenia reticulata, Clitoria ternatea, and tulasi have gained prominence in AgNP synthesis. Moreover, a considerable body of research focuses on investigating the antibacterial activity of these Ag nanoparticles [
27]. An important method for green synthesis entails employing an extract from Justicia Spicigera as a reducing agent to produce silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). This method not only mitigates the environmental impact associated with nanoparticle synthesis but also harnesses the intrinsic potential of bioactive compounds for sustainable materials development. In parallel, the incorporation of AgNPs into naturally abundant zeolites, readily available in regions such as Mexico, offers a unique opportunity to engineer high-performance adsorbent materials. Zeolites possess well-defined porous structures and ion-exchange capabilities, rendering them ideal candidates for adsorption-based contaminant removal applications [
28].
The primary objective of this study is to present a systematic investigation into the development and application of kinetic adsorption models for sustainable contaminant removal. We leverage the synergistic effects of green-synthesized AgNPs and Mexican zeolite to craft an efficient and eco-friendly adsorption system capable of removing hazardous contaminants from water resources. Likewise, in this work, we comprehensively address the synthesis, characterization, and experimental approach for contaminant elimination of the composite material. With respect to adsorption models, it’s crucial to highlight that both first and second order models, linear or non-linear, are routinely employed in adsorption kinetics studies. These models consider factors such as external mass transfer, intraparticle diffusion, and adsorption at specific sites. Linear models can often adequately fit experimental data, particularly when the adsorbate concentration is low. However, non-linear models may offer a superior fit in instances where the adsorbate concentration is high. As such, a comprehensive evaluation of all factors influencing the Cu adsorption process is necessary to accurately decipher the specific aspects of the Cu adsorption phenomenon in the Zeolite-Ag composite. This allows for the establishment of a specific adsorption mechanism for this Zeolite, Ag, and Cu²⁺ system, as proposed in this work. The results presented in this study unequivocally demonstrate the superior efficacy of the composite in degrading Cu²⁺ ions, outperforming conventional materials. In essence, this research represents a fusion of sustainable synthesis approaches with readily available materials, presenting a promising avenue to address the pressing requirement for sustainable contaminant removal technologies. Our findings make a significant contribution to the expanding realm of knowledge on cleaner production practices, offering a new and eco-friendly approach to water purification and environmental remediation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zeolite Preparation:
In this study, a zeolite sourced from Oaxaca was utilized as the primary adsorbent material. The zeolite underwent a series of preparatory steps to ensure its suitability for contaminant removal. Initially, the raw zeolite was mechanically milled and sieved to achieve a particle size of -120 +60 mesh (2 mm). To enhance its purity and remove impurities, a thorough washing treatment was conducted. The zeolite was subjected to magnetic stirring at 700 rpm for 60 minutes. Subsequently, the material was carefully dried at a controlled temperature of 30 °C for 24 hours.
2.2. Synthesis of Zeolite-Ag Composite:
The synthesis of the Zeolite-Ag composite involved a two-stage process, commencing with the green synthesis of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs).
2.2.1. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles:
A total of 5.0 grams of dried and milled Justicia Spicigera plant material was mixed with 30 mL of deionized water. This mixture was heated to 100 °C and maintained at this temperature for 20 minutes. Subsequently, the Justicia Spicigera solution was cooled to room temperature.
In parallel, a 50 mM solution of Silver Nitrate (AgNO3) of reagent grade with a purity of 99.98% was prepared in an aqueous medium. This chemical was sourced from Sigma-Aldrich (EE.UU). The solutions obtained from the previous steps were combined. After 1 hour of post-reaction, a noticeable color change from dark brown to dark gray signified the successful synthesis of Ag NPs.
2.2.2. Homogeneous nucleation of Ag Nanoparticles into Zeolite:
Initially, 10 mg of zeolite, which had been previously meshed to 200 mesh, washed and dried, was diluted in 30 mL of deionized water. The Ag nanoparticles, previously prepared, were introduced into the zeolite solution. The mixture underwent ultrasonic stirring for 15 minutes to facilitate the incorporation process. The resulting material was then dried at 30 °C until powders of the Zeolite Ag composite were obtained.
2.3. Adsorption Experiments:
To evaluate the adsorption capacity of both the zeolite and the Zeolite-Ag complex for Cu²⁺ ions, adsorbate (Cu²⁺) and adsorbent concentrations were set at 2.5 mg/L and 20 g/L, respectively. The adsorbate/adsorbent solutions were subjected to ultrasonication at 40 kHz and 100 W (pH=7). At defined time intervals (30 min), aliquots of the solutions were extracted and measured using Absorption Atomic Spectroscopy (AAS). The measurements were taken until the pollutant concentration reached its minimum value.
2.4. Kinetic Adsorption Models:
To comprehensively assess the adsorption behavior of Cu²⁺ ions by both the zeolite and the Zeolite-Ag complex, we employed both linear and non-linear kinetic adsorption models. These models allowed us to gain a thorough understanding of the interaction mechanisms governing the adsorption process between the adsorbent materials and the heavy metal ions. This robust experimental methodology facilitated the systematic investigation of contaminant removal using our synthesized materials, offering valuable insights into their performance and efficiency in the context of cleaner production and environmental sustainability.
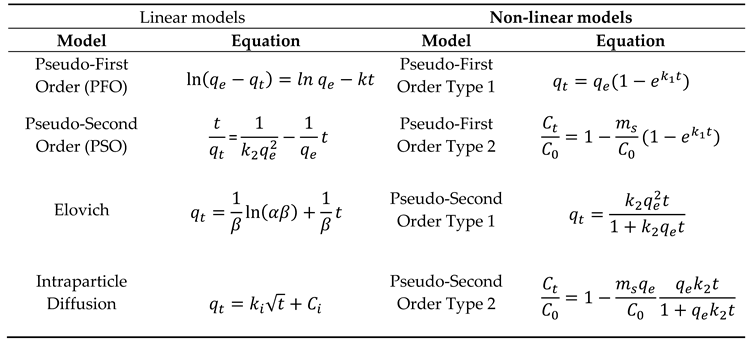
Table 1 show the kinetic adsorption models employed [
29,
30,
31,
32]:
The curve fitting of the experimental data to both linear and nonlinear theoretical models, as outlined in
Table 1, was executed using the software “Origin 9.2”. This software employs the least-squares algorithm, a method also known as chi-square minimization, to derive the curve fit. The primary objective of this method is to minimize the deviations between the theoretical curve(s) and the experimental points. The algorithm accomplishes this by selecting parameters that yield the smallest deviations.
The least-squares method is defined as follows:
Where xi′ is the row vector for the ith (i = 1, 2, … , n) observation.
Furthermore, the Levenberg-Marquardt (L-M) algorithm was employed to adjust the parameter values in the iterative procedure. The L-M algorithm is an iterative procedure that combines the Gauss-Newton method and the steepest descent method. It works well for most cases and has become the standard of nonlinear least square routines.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Materials Characterization
3.1.2. Scanning electron microscopy SEM
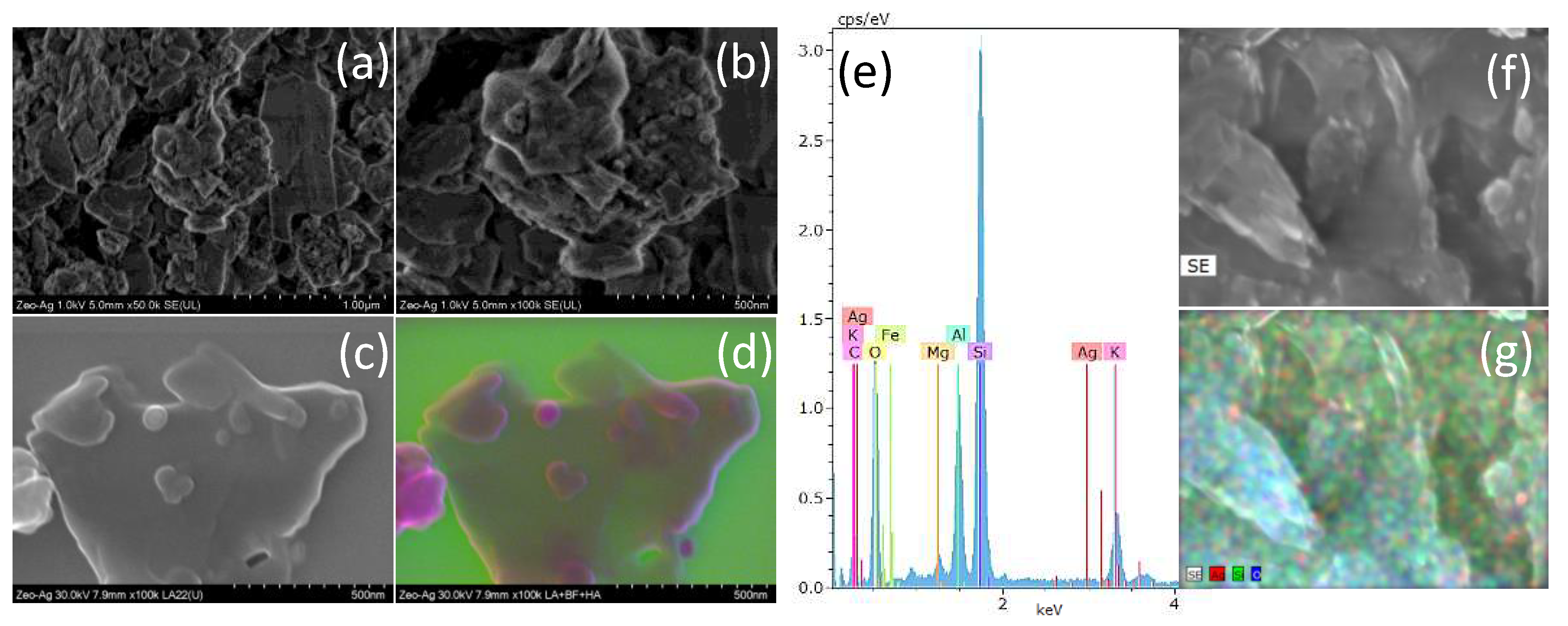
Figure 1 This figure showcases a series of scanning electron microscopy images that offer an in-depth visualization of the zeolite structure and the distribution of silver nanoparticles within it. Figures (a) and (b) are secondary electrons micrographs captured at low magnifications, which distinctly depict the coexistence of zeolite and silver nanoparticles. These micrographs reveal the presence of silver nanoparticles with dimensions smaller than 50 nm on the zeolite’s surface, signifying the successful implementation of the green synthesis method outlined in this study.
Figure 1(c) presents a low-angle (LA) image that provides a unique perspective of the Zeolite-Ag composite, while
Figure 1(d) is a composite representation with color enhancement to improve visual clarity. These images collectively demonstrate the successful integration of silver nanoparticles with zeolite, substantiating our assertion that the green synthesis route we proposed was effective in achieving this result. Finally,
Figure 1(e), (f), and (g) represent an Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS) of the Zeolite composite, a secondary electron image of the specific zone from which the EDS data was obtained, and an EDS mapping that provides a spatial distribution of elements within the Zeolite-Ag Composite, respectively. This EDS study confirms the concurrent presence of zeolite and silver nanoparticles, further emphasizing the successful implementation of the green synthesis method outlined in this study.
3.1.3. Transmission electron microscopy SEM
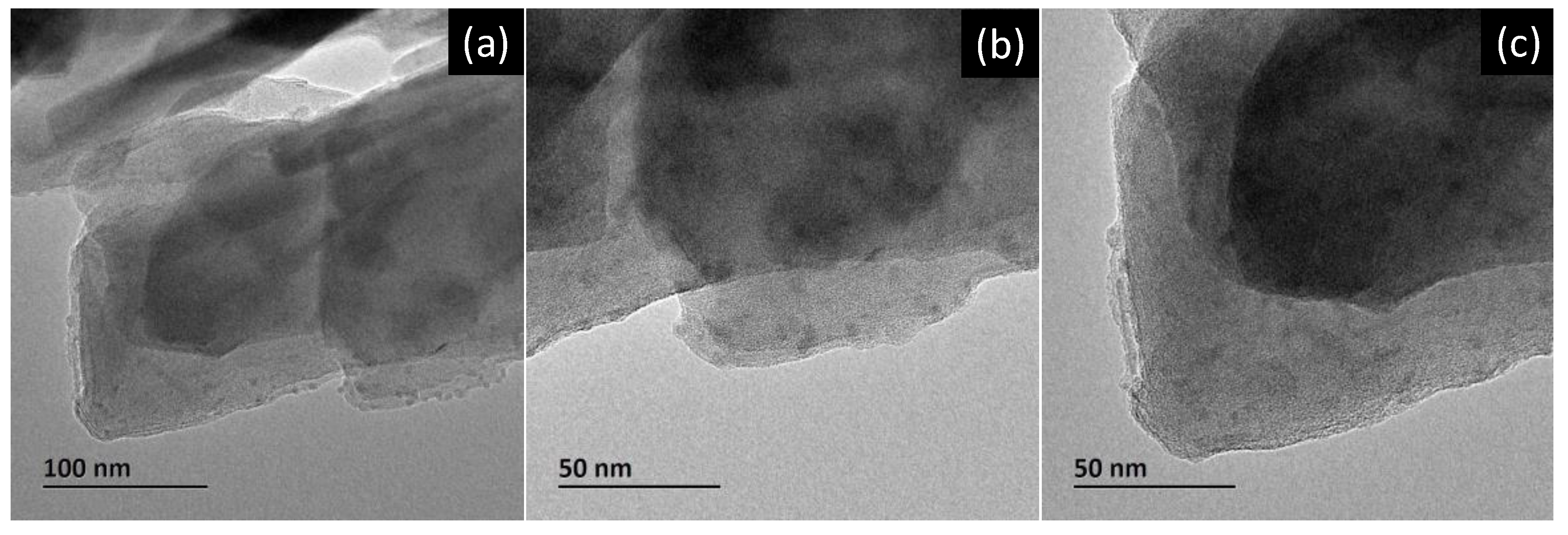
Figure 2 (a)-(c) shows bright field transmission electron microscopy (BF-TEM) images from the Zeolite-Ag composite, which illustrate the distribution of the Ag nanoparticles onto the zeolite structure, by these TEM images, is possible to determine and corroborate the Ag nanoparticles formation and their particle size, which is approximately of 5 nm. In this sense, is important to mention that the resolution of the TEM, allows for to resolution of minimal particle size of the AgNPs, on the other hand, and in comparative form, the SEM images did not reveal the smaller sizes of the AgNPs, therefore, presumably coexists two particle size distributions, the fist around 50 nm and the second of 5 nm approximately. Additionally, is essential to consider that the homogeneous porosity of the zeolite, and the pore size permit a selective interaction with different Ag particle sizes. Nevertheless, the behavior and Cu2+ adsorption efficiency is evaluated by taking a count of these factors, and by theoretical kinetic adsorption models incorporate and describe as principal variables the initials and final concentration of Cu2+ in solution, such as the adoption time. The parameter derived from these models describes in detail the adoption of Cu2+ behavior.
3.1.4. X-Ray diffraction analysis
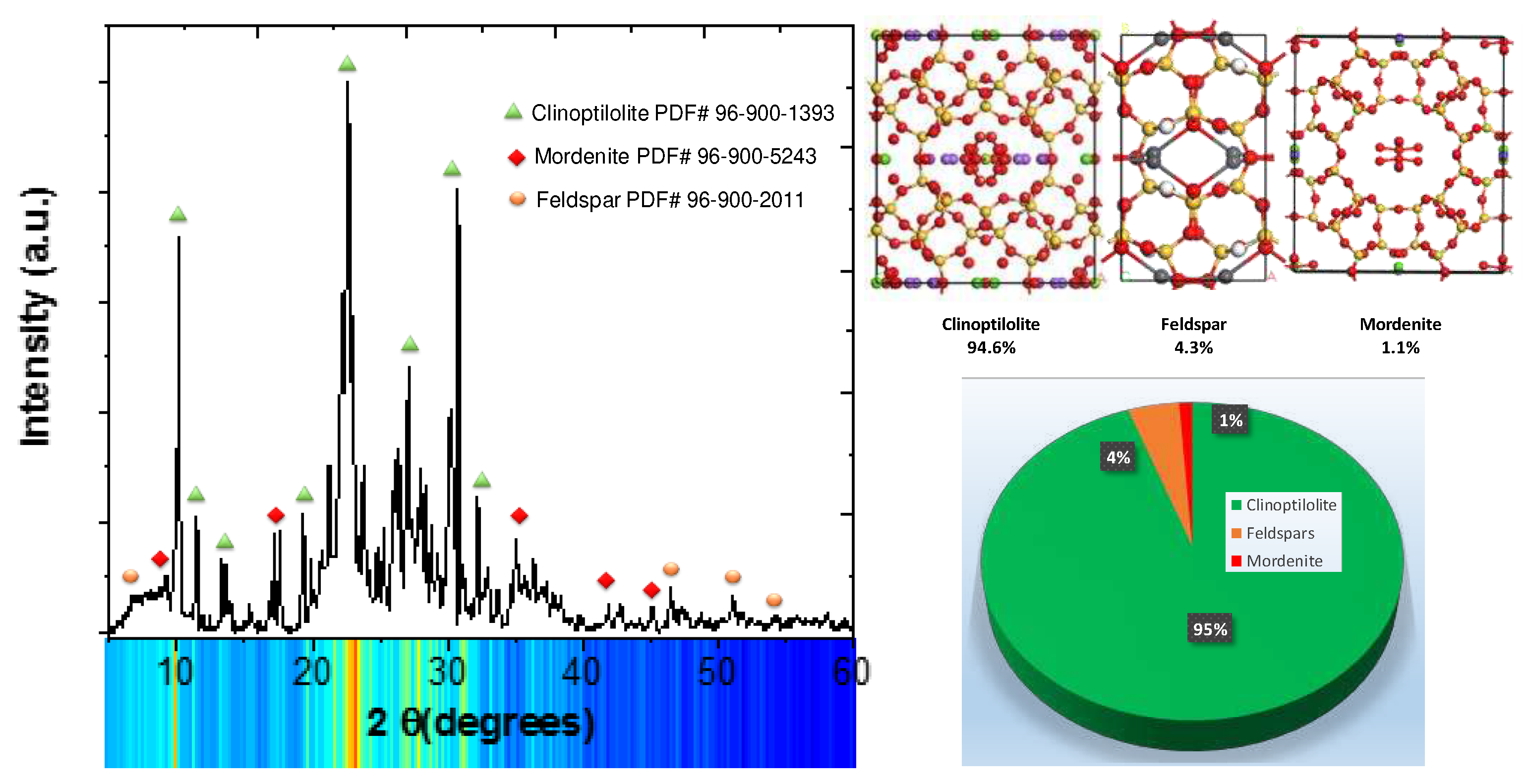
In
Figure 3, we present the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern resulting from the treatment of natural zeolite powders with deionized water. As illustrated in the figure, the XRD pattern distinctly showcases well-defined peaks corresponding to the characteristic clinoptilolite crystalline structure as main phase. Concurrently, the residual peaks observed in the XRD pattern can be attributed to the coexistence of mordenite and feldspar phases within the sample.
The clinoptilolite, possesses a monoclinic crystalline structure with the following lattice parameters: a = 17.65 Å, b = 17.92 Å, c = 7.403 Å, and β = 116.39°. This crystallographic arrangement corresponds to the C2/m space group (PDF# 96-900-1393). Additionally, Mordenite phase exhibits an orthorhombic crystalline structure characterized by lattice parameters of a = 18.16 Å, b = 20.45 Å, and c = 7.54 Å. This crystal structure aligns with the Cmc21 space group and is indexed under entry PDF#96-900-5243. Conversely, the feldspar phase is distinguished by a monoclinic crystal lattice, featuring lattice parameters of a = 8.544 Å, b = 12.99 Å, c = 7.181 Å, and β = 116.16°. This particular crystallographic configuration is classified under the C2/m space group and is annotated as entry PDF#96-900-2011. In order to substantiate the observed results, a quantitative phase analysis was conducted. As illustrated in
Figure 3, the analysis revealed a composition comprising 94.3 weight percent of the clinoptilolite phase, 4.3% of feldspar, and 1.1 % of the mordenite. These findings suggest that the adsorption properties inherent to the natural zeolite primarily emanate from the clinoptilolite structural component. Subsequent analyses included modeling of the clinoptilolite structure to further elucidate its properties and potential applications.
3.2. Adsorption Study of Cu2+ by Zeolite and Zeolite-Ag.
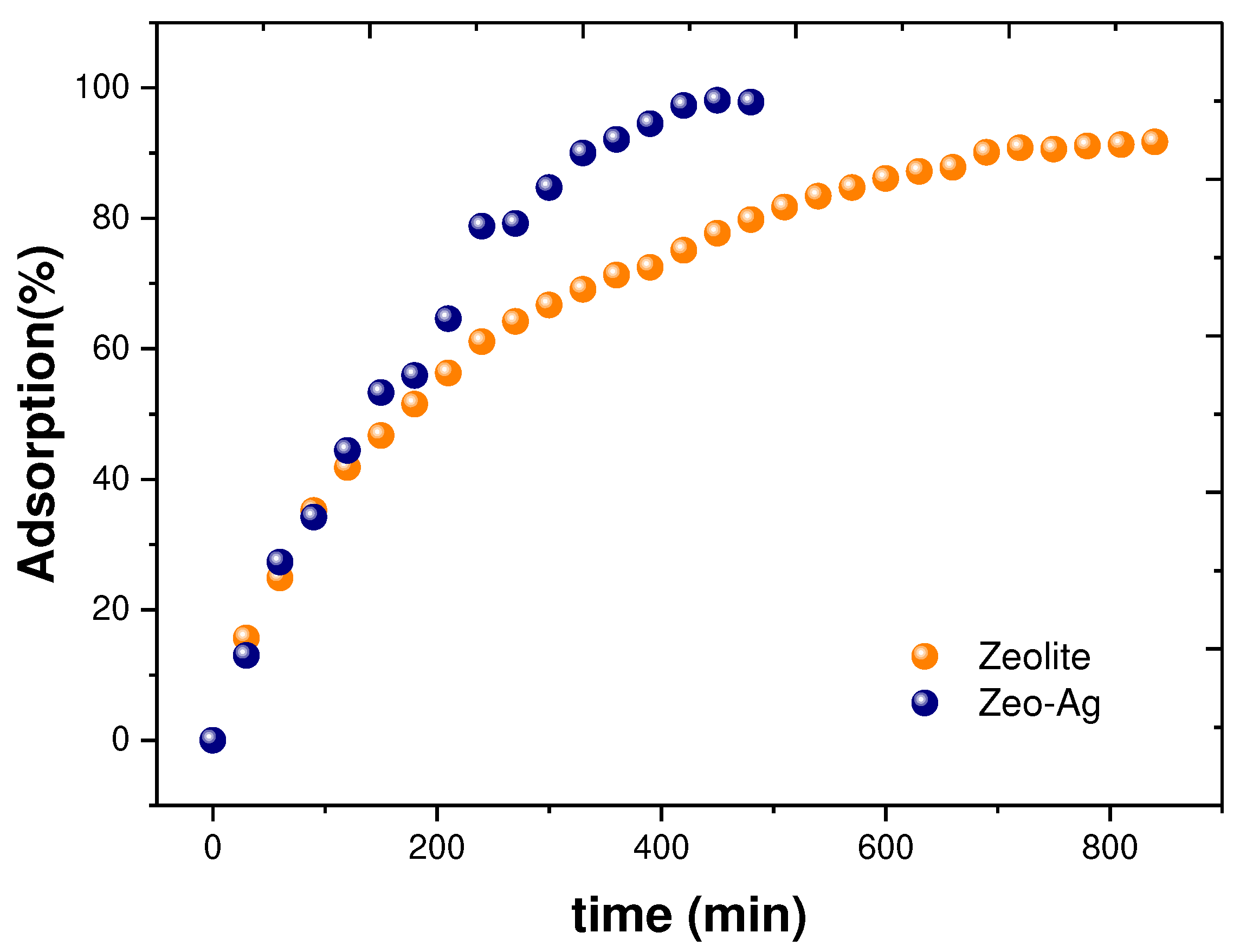
Concerning the adsorption of Cu
2+ onto the Zeolite and Zeolite-Ag composite materials,
Figure 4 presents experimental data obtained through Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) measurements. Notably, we observed maximum adsorption times of 840 minutes for Zeolite and 480 minutes for the Zeolite-Ag composite, representing a significant reduction of 360 minutes in the latter case, which can be attributed to the presence of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) on the Zeolite surface.
This observed phenomenon can be ascribed to the synergistic interaction between Zeolite and Ag NPs. Firstly, this synergy reduces the Cu adsorption time. Secondly, it enhances the Cu adsorption percentage, reaching 91% for pristine Zeolite and 98% for the Zeolite-Ag composite. This behavior can be explained by the intrinsic ionic exchange capacity of Zeolite and the Van der Waals attraction forces associated with the partial positive charges of the Ag NPs, as previously [
33]. In essence, this combined effect facilitates Cu adsorption, corroborated by the AAS measurements shown in
Figure 4.
3.3. Kinetic adsorption models.
3.3.1. Linear models adsorption models
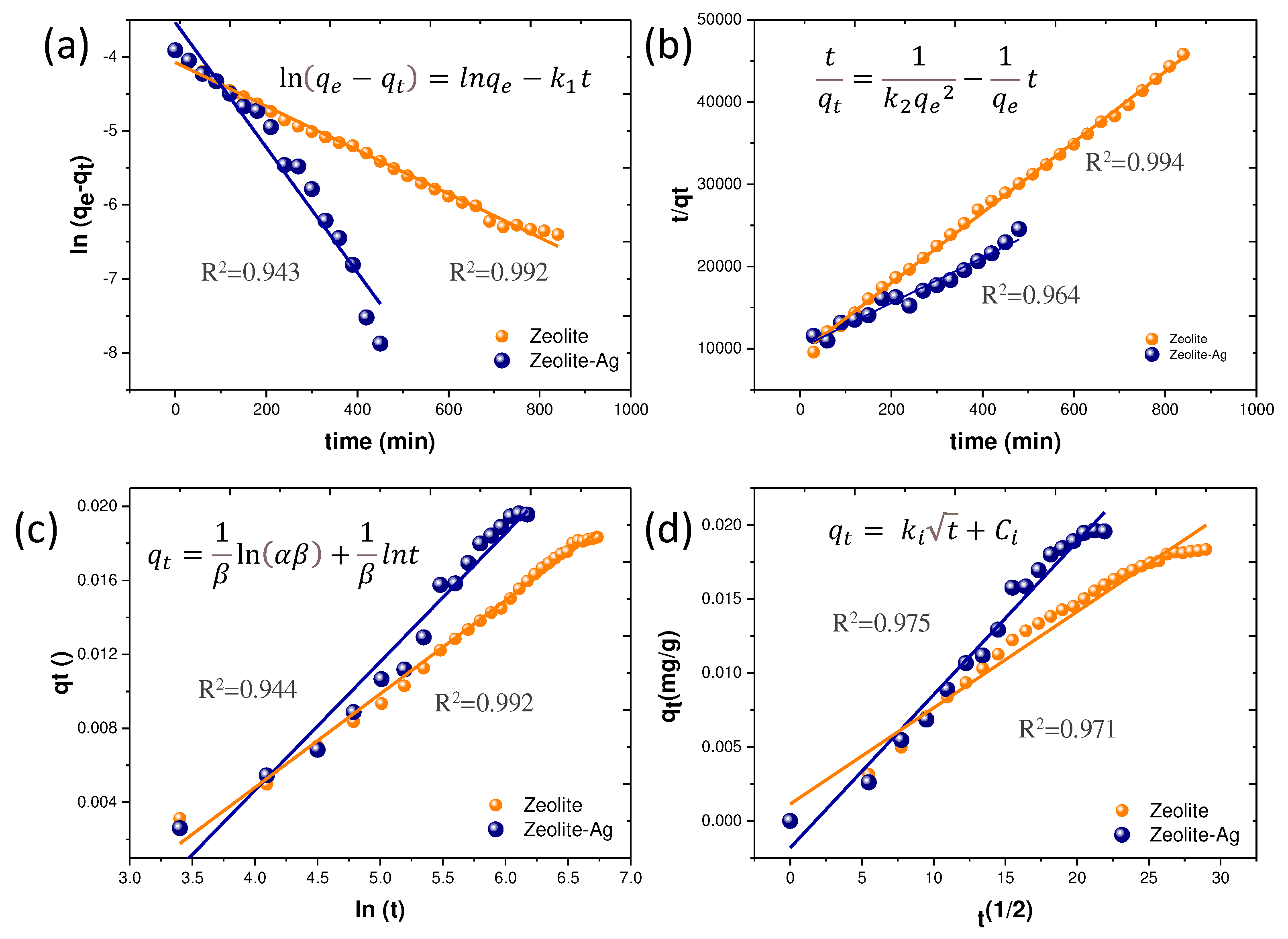
To determine the most suitable kinetic adsorption model for the experimental data from the Cu adsorption process, we evaluated the Pseudo-first order, Pseudo-second order, Elovich, and Intraparticle Diffusion Models, as depicted in
Figure 5(a)-(d). The equations corresponding to each kinetic adsorption model are included within their respective graphs. Impressively, the highest correlation coefficients (R
2) were observed for the Pseudo-second order model. The detailed kinetic parameters presented in
Table 2.
In this context, the Ho kinetic adsorption model, also known as the Pseudo-Second Order model, provides the best fit for describing the Cu2+ adsorption mechanism by both Zeolite and the Zeolite-Ag composite. The Pseudo-second order model signifies a reversible second-order reaction, particularly relevant under low sorbate-to-sorbent ratios. Consequently, the Cu adsorption process is governed by two primary factors: ionic exchange within the Zeolite and Van der Waals attraction forces arising from the partial positive charges of the Ag NPs.
3.3.2. Non-linear adsorption models
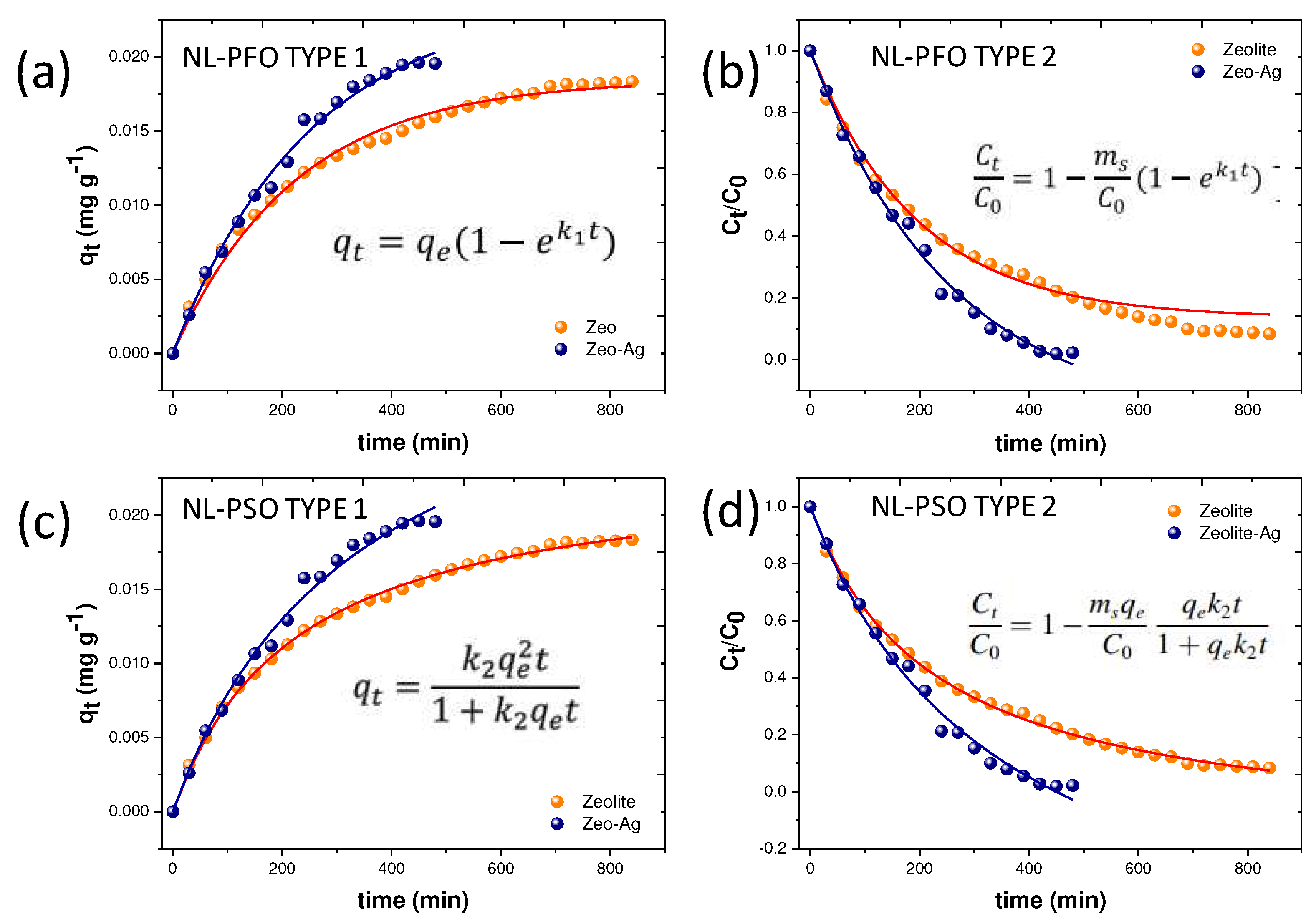
Non-linear adsorption models were employed in this study to compare their performance with linear models in the context of adsorption phenomena. Four distinct models were proposed, including two variations of the pseudo first-order model and two non-linear models corresponding to the pseudo second-order model presented in the experimental methodology [
31,
34,
35,
36].
In both cases, the parameters involved in these models serve to characterize the adsorption rates and the quantity of adsorbate and sorbate engaged in the process.
Figure 6 illustrates the application of these non-linear adsorption models to the Zeolite and Zeolite-Ag composite.
Based on the calculated correlation factors, the non-linear models offer a superior description of the Cu adsorption mechanism on the Zeolite-Ag composite (
Table 3) compared to the linear models presented earlier. It is noteworthy that the parameters used to derive the non-linear models, such as the initial and final absorbate concentrations, provide a highly precise depiction of the adsorption phenomena due to a more rigorous control of sorbate behavior.
In a broader context, both the linear and non-linear pseudo second-order models exhibit superior precision in describing the adsorption process compared to the pseudo first-order models. The nature of the pseudo second-order models suggests a reversible second-order reaction at low sorbate-to-sorbent ratios. Consequently, the Cu adsorption process is governed by two primary phenomena: the ionic exchange within the Zeolite and the Van der Waals attractive forces associated with the partial positive charges of the Ag nanoparticles. Previous research has indicated that the typical exchange capacity of the mineral and the reactivity of Ag nanoparticles can synergistically influence the Cu²⁺ adsorption process [
37,
38,
39]. Specifically, the polarization of the Zeolite in aqueous solutions and the electrostatic interactions of Ag nanoparticles contribute to the formation of negative potentials within the metal-oxygen bonds associated with the zeolite [
40,
41].
This comprehensive analysis underscores the effectiveness of non-linear adsorption models, particularly the pseudo second-order models, in elucidating the Cu2+ adsorption mechanism on the Zeolite-Ag composite, providing valuable insights into the complex interplay of adsorption processes and contributing to the understanding of adsorption phenomena in environmental remediation.
3.4. Non-Linear Langmuir and Freundlich adsorptions isotherms.
According to the results obtained from non-linear PFO and PSO models, is possible to affirm that the pseudo second order model describe in best form the adsorption Cu2+ by the Zeolite and Zeolite-Ag complex.
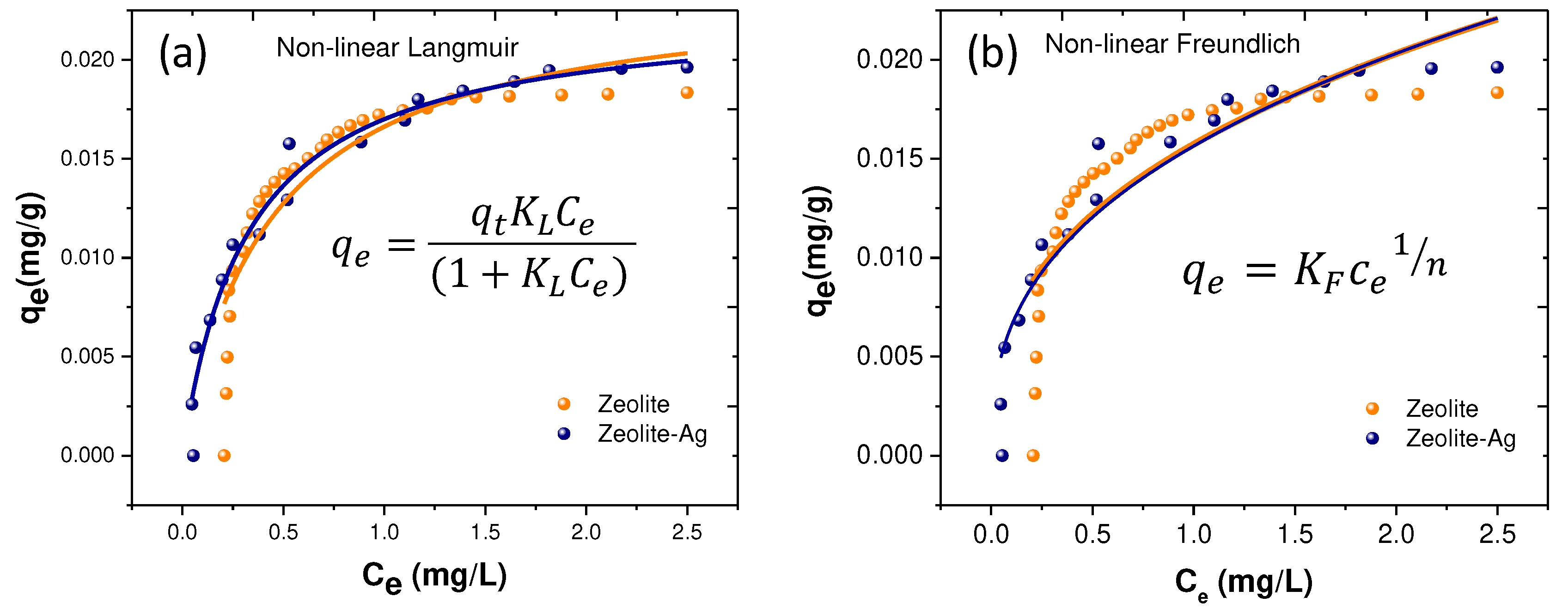
Nonetheless, a thorough investigation into the adsorption of Cu2+ utilizing Zeolites and Zeolite-Ag is crucial. In this regard, non-linear models for Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms were developed, illustrated in
Figure 7 (a) and (b), respectively. The objective was to accurately depict the uniformity of Cu
2+ adsorption on the material surfaces. The Langmuir isotherm, a theoretical model portraying substance adsorption forming a monolayer on a solid surface, was examined. The proposed model offers a more precise description, considering saturation effects and cooperativity among adsorbed molecules. The non-linear Langmuir equation defines the relationship between the quantity of substance adsorbed on the surface (qe) and the concentration in solution (Ce). This model presupposes a finite number of adsorption sites on the surface. Furthermore, a non-linear model for the Freundlich equation was developed, a more general model than Langmuir, capable of representing multilayer adsorption on the solid surface. The Freundlich model is characterized by its adsorption exponent (n), which signifies surface heterogeneity and adsorption intensity. The non-linear Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms are mathematically governed by the subsequent expressions.
Based on the results obtained for the rate constants KL and Kf, as well as the correlation factors R2, it is affirmed that the non-linear models of PFO and PSO exhibit notably high correlation factors, thereby providing a more accurate description of the Cu2+ adsorption phenomenon. Notably, the R2 values for the non-linear Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms were 0.96 and 0.90, respectively, for the Zeolite-Ag sample. In contrast, for the pristine zeolite, these values were relatively lower (0.81 and 0.68). However, this outcome reveals significant information regarding monolayer formation on the surface of the Zeolite and Zeolite-Ag samples. In essence, the surface of the Zeolite and Zeolite-Ag samples behaves heterogeneously, resulting in the adsorption of Cu2+ ions described by a physisorption phenomenon, presumably due to electrostatic forces' interactions between the adsorbent and adsorbate. Furthermore, it can be asserted that the incorporation of Ag nanoparticles enables the creation of a more homogeneous adsorption surface on zeolite. This could be associated with enhanced stability of electrostatic charges and an increased number of exchange sites within the Zeolite-Ag sample.
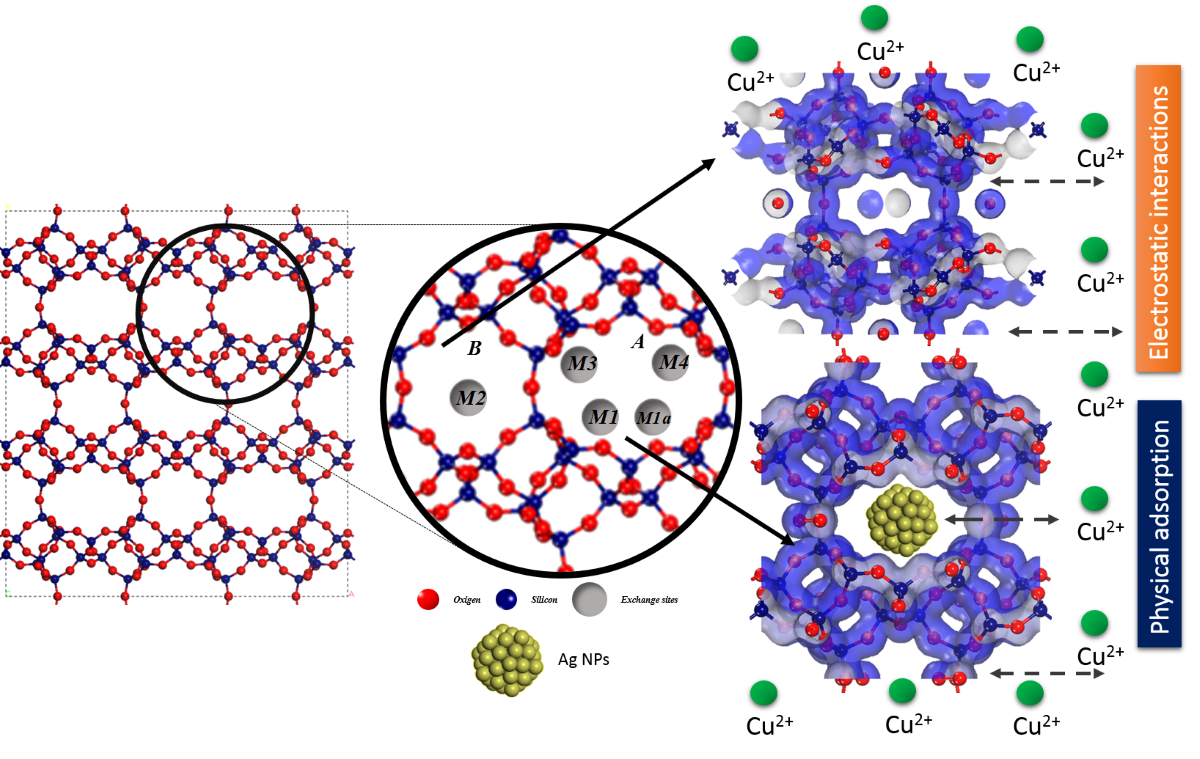
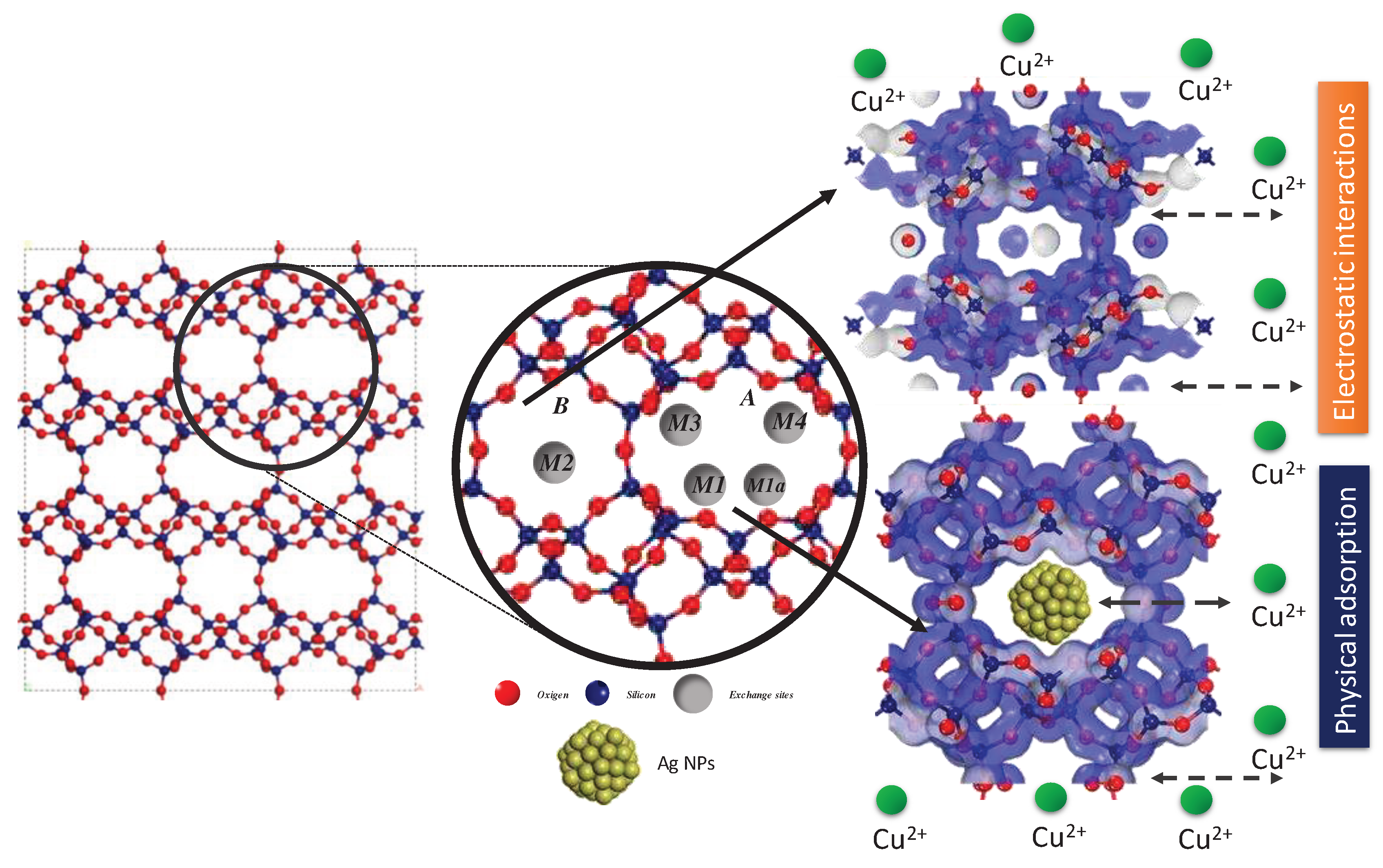
In order to comprehensively describe and discuss the obtained results,
Figure 8 presents the structure of clinoptilolite-type zeolite viewed along the c-vector. This view showcases the primary channels A and B, along with the extraframework cation sites and their nucleophilic and electrophilic positions. It also illustrates their interaction with adsorbed Cu2+ ions. In this context, the figure delineates the structural characteristics of clinoptilolite, which adopts a monoclinic crystal structure, belonging to the C2/m space group. Its structural framework consists of four- and five-membered rings, while the channel system is defined by eight- and ten-membered rings [
42,
43]. Within this structure, three principal cationic sites exist, hosting alkali and alkaline-earth cations. Two of these sites, labeled as M1 and M3, are located within channel A and are coordinated with oxygen atoms from the 8-membered lateral ring. The third crucial site, M2, is positioned within channel B. Additionally, a fourth site, M4, with significantly lower occupancy, was identified for hydrated cations of small size at the center of channel A. Notably, there is a distinction between sites M1 and M3, where the latter is more confined within the 8-membered lateral ring and less exposed to the channel. Sites M1 and M1a are shifted towards the center of the channel, with M1a weakly coordinated by atoms from the lateral ring, albeit closer to the T1-O4-T2 and T1-O6-T5 bonds of the 10-membered ring within the channel.
4. Conclusions
In summary, the present research describes and analyzes the removal of copper ions (Cu²⁺) carried out by natural zeolite and the Zeolite-Ag composite, which represents promising applications in water purification and environmental remediation. As a discussion, it can be stated that the mechanism of Cu²+ adsorption is mainly described by a physisorption process and electrostatic interactions between the zeolite doped with Ag nanoparticles and the Cu2+ ions. The following key factors substantiate and reinforce the presented results, on one hand, zeolites are characterized by their crystalline aluminosilicate framework, showcasing a well-defined three-dimensional network of channels and cavities. These channels accommodate exchangeable cations, primarily sodium (Na⁺) or potassium (K⁺), replaceable by other cations through ion-exchange mechanisms. In the context of copper ion removal, zeolite-Ag NPs effectively leverage this ion-exchange property. Conversely, the integration of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) into the zeolite structure significantly amplifies its capacity for copper ion removal. Ag NPs serve as highly efficient adsorption sites for copper ions, benefiting from their expansive surface area and strong affinity for heavy metal ions like Cu²⁺. This synergistic effect combines the ion-exchange capacity of zeolite with the adsorption prowess of Ag NPs. Moreover, the efficacy of copper ion removal by zeolite-Ag NPs stems from the selectivity and affinity of the zeolite framework and Ag NPs for Cu²+ ions. Copper ions demonstrate a noteworthy affinity for both the negatively charged sites within the zeolite structure and the Ag NPs, driven by electrostatic interactions and coordination chemistry. Consequently, Cu²⁺ ions preferentially adsorb onto the surface of zeolite-Ag NPs. The removal of copper ions by zeolite-Ag NPs follows distinct kinetic and equilibrium processes. Initially, a rapid adsorption of Cu²⁺ ions occurs on the surface of zeolite-Ag NPs, followed by a slower diffusion of ions into the internal channels of the zeolite structure. Upon reaching equilibrium, the concentration of copper ions in the solution minimizes, indicating successful removal. In conclusion, the effective removal of copper ions by zeolite-Ag nanoparticles is a complex interplay of ion-exchange processes, surface interactions, and the unique properties of both the zeolite framework and the incorporated Ag NPs. This approach offers a promising avenue for mitigating copper ion contamination in water and environmental systems, addressing a critical issue in water quality management and pollution control.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.D.JR.B. and RP.; methodology, A.D.J.R.B. and SYRL.; software, A.D.J.R.B.; validation, A.D.J.R.B., S.Y.R.L. and R.P.; formal analysis, A.D.J.R.B; investigation, A.D.J.R.B. and S.Y.R.L.; resources, A.D.J.R.B. and N.M.L.; data curation, A.D.J.RB. and N.M.L; writing—original draft preparation, A.D.J.R.B..; writing—review and editing, A.D.J.R.B. and R.P..; visualization, A.D.J.R.B., N.M.L, R.P. and S.Y.R.L.; supervision, A.D.J.R.B.; project administration, A.D.J.R.B.; funding acquisition, A.D.J.R.B. and N.M.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
National Council for Humanities, Science, and Technology (CONAHCYT, Mexico) through the “Investigadoras e Investigadores por México-CONAHCYT” program.
Acknowledgments
Álvaro de Jesús Ruíz-Baltazar expresses deep appreciation for the invaluable support extended by the National Council for Humanities, Science, and Technology (CONAHCYT, Mexico), in conjunction with the Center of Applied Physics and Advanced Technology (CFATA-UNAM), through the "Investigadoras e Investigadores por México-CONAHCYT" program. Furthermore, our heartfelt gratitude goes to the National Materials Characterization Laboratory (LaNCaM) under the auspices of CFATA-UNAM, and the "Instituto de Ciencias Biomédicas de la UACJ," for their unwavering support during the sabbatical period.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fu, H.; Ding, N.; Ma, D.; Xu, Q.; Lin, B.; Qiu, B.; Lin, Z.; Guo, L. Green Synthesis of Three-Dimensional Au Nanorods@TiO2 Nanocomposites as Self-Cleaning SERS Substrate for Sensitive, Recyclable, and In Situ Sensing Environmental Pollutants. Biosensors 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Ma, C.; Wang, Y. Functional Nucleic Acid Probes Based on Two-Photon for Biosensing. Biosensors 2023, 13, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, E. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Plasmonic Biosensors. Biosensors 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Štukovnik, Z.; Fuchs-godec, R. Nanomaterials and Their Recent Applications in Impedimetric Biosensing. 2023, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Yin, S.J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, F.Q. Nanoporous ZIF-8 Microparticles as Acetylcholinesterase and Alkaline Phosphatase Mimics for the Selective and Sensitive Detection of Ascorbic Acid Oxidase and Copper Ions. Biosensors 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhan, L.; Xue, Z.; Yusef, K.K.; Hu, H.; Wu, M. Adsorption of Cu (II) and Cd (II) from Wastewater by Sodium Alginate Modified Materials. J. Chem. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunecki, P.; Wdowin, M.; Hanc, E. Fly Ash-Derived Zeolites and Their Sorption Abilities in Relation to Elemental Mercury in a Simulated Gas Stream. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 391, 136181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, C.; Lucini, P.; Mancinelli, M.; Abdolrahimi, M.; Martucci, A.; Peddis, D.; Maraschi, F.; Cavalcante, F.; Sturini, M. Lead, Zinc, Nickel and Chromium Ions Removal from Polluted Waters Using Zeolite Formed from Bauxite, Obsidian and Their Combination with Red Mud: Behaviour and Mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fan, M.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, M. One-Pot Synthesis of Lamellar Fe-Cu Bimetal-Decorated Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Enhanced Removal of Cr(VI) from Water. Nanomaterials 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Wang, K.; Ma, E.; Wang, H. Multifunctional Biotemplated Micromotors for In Situ Decontamination of Antibiotics and Heavy Metals in Soil and Groundwater. Nanomaterials 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segneanu, A.-E.; Trusca, R.; Cepan, C.; Mihailescu, M.; Muntean, C.; Herea, D.D.; Grozescu, I.; Salifoglou, A. Innovative Low-Cost Composite Nanoadsorbents Based on Eggshell Waste for Nickel Removal from Aqueous Media. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.C.; Wu, G.; Xu, G.; Song, J.H.; Choi, N.J. Synthesis of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Coal Fly Ash Hybrid Nano-Fiber Membranes for Adsorption of Heavy Metals in Diesel Fuel. Nanomaterials 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsuki, J.; Natsuki, T. Silver Nanoparticle/Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Nanocomposites: One-Step Green Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, A.; Pérez, R. Kinetic Adsorption Study of Silver Nanoparticles on Natural Zeolite: Experimental and Theoretical Models. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, A.; Esparza, R.; Gonzalez, M.; Rosas, G.; Pérez, R. Preparation and Characterization of Natural Zeolite Modified with Iron Nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahos, F.A.; Sainz-Vidal, A.; Sánchez-Pérez, C.; Saniger, J.M.; Gràcia, I.; Saniger-Alba, M.M.; Matatagui, D. ZIF Nanocrystal-Based Surface Acousticwave (SAW) Electronic Nose to Detect Diabetes in Human Breath. Biosensors 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Pi, F.; Liu, L. A Competitive “On-Off-Enhanced On” AIE Fluorescence Switch for Detecting Biothiols Based on Hg2+ Ions and Gold Nanoclusters. Biosensors 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Chang, Y.; Liu, M. An Electrochemical Aptasensor Integrating Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework for Highly Selective Detection of Bioaerosols. Biosensors 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Zhou, R.; Hao, G.; Tang, X.; Liu, X.; Bi, J.; Dai, H.; Shen, Y. Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 Composite-Based Enzyme-Linked Aptamer Assay for the Sensitive Detection of Deoxynivalenol. Biosensors 2023, 13, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonova, E.A.; Kuznetsov, A.B.; Svetlichnyi, V.A.; Kononova, N.G.; Shevchenko, V.S.; Nigmatulina, E.N.; Kolesnichenko, M. V.; Kokh, K.A.; Rashchenko, S. V.; Kokh, A.E. Nd3+ and Pr3+ Doped Anti-Zeolite Matrix-LiBa12(BO3)7F4: Crystal Structures, Luminescence Properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 247, 122612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese Alex, K.; Tamil Pavai, P.; Rugmini, R.; Shiva Prasad, M.; Kamakshi, K.; Sekhar, K.C. Green Synthesized Ag Nanoparticles for Bio-Sensing and Photocatalytic Applications. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 13123–13129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakakhel, M.A.; Sajjad, W.; Wu, F.; Bibi, N.; Shah, K.; Yali, Z.; Wang, W. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Their Shortcomings, Animal Blood a Potential Source for Silver Nanoparticles: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2021, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.-J.; Xie, Y.-M.; Chen, X.-Y.; Xi, C.; Zhang, F.-F.; Wang, M.; Shang, L.; Huang, Y.; Du, X.-W.; Kulinich, S.A. Ag-Doped Cu Nanosheet Arrays for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 6533–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan Afandy, H.; Sabir, D.K.; Aziz, S.B. Antibacterial Activity of the Green Synthesized Plasmonic Silver Nanoparticles with Crystalline Structure against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria. Nanomaterials 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, I.; Thakur, A.; Kumar, G.; Long, Q.; Zhang, K.; Sidu, R.K.; Thakur, S.; Sarkar, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Iyaswamy, A.; et al. Delivery of Apoplastic Extracellular Vesicles Encapsulating Green-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles to Treat Citrus Canker. Nanomaterials 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekmezci, M.; Ozturk, H.; Akin, M.; Bayat, R.; Sen, F.; Darabi, R.; Karimi-Maleh, H. Bimetallic Biogenic Pt-Ag Nanoparticle and Their Application for Electrochemical Dopamine Sensor. Biosensors 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Bao, L.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; He, B.; Hou, X. Reporter Molecules Embedded Au@Ag Core-Shell Nanospheres as SERS Nanotags for Cardiac Troponin I Detection. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, A.; Reyes-López, S.Y.; Tellez-Vasquez, O.; Esparza, R.; Rosas, G.; Pérez, R. Analysis for the Sorption Kinetics of Ag Nanoparticles on Natural Clinoptilolite. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, H.; Dong, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, W.; Shi, Y. The Effective Adsorption of Tetracycline onto MoS2@Zeolite-5: Adsorption Behavior and Interfacial Mechanism. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Pan, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, P.; Zou, G.; Du, L.; Guo, X. Micro- and Nano-Plastics Play Different Roles in Oxytetracycline Adsorption on Natural Zeolite: Additional Adsorbent and Competitive Adsorbate. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, Á. de J. Environmentally Friendly Alternative for Heavy Metal Adsorption Based on Doped Diatoms with Au Nanoparticles: A Novel Approach in Green Synthesis of Adsorbents and Kinetic Adsorption Study. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2022, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Chirino, J.; Dáder Jiménez, A.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Hybrid Na-A Zeolite/Oxycut Residue Thin Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane for Cr (III) Removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-Baltazar, Á. de J.; Reyes-López, S.Y.; Zamora Antuñano, M.A.; Pérez, R. Application of Modified Silicates with Gold Nanoparticles on Environmental Remediation: Study of Non-Linear Kinetic Adsorption Models Focused on Heavy Metals. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmi, F.A.; Ngadi, N.; Wong, S.; Inuwa, I.M.; Opotu, L.A. Kinetics, Thermodynamics, Isotherm and Regeneration Analysis of Chitosan Modified Pandan Adsorbent. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Cheng, Z.; Tian, Y.; Qiu, F.; Chang, H.; Li, S.; Cai, Y.; Quan, X. Adsorption of Ni(II) on Detoxified Chromite Ore Processing Residue Using Citrus Peel as Reductive Mediator: Adsorbent Preparation, Kinetics, Isotherm, and Thermodynamics Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Lin, X.; Luo, L.; Yang, J.; Luo, J.; Liao, X.; Cheng, H. Biosorption of Copper Ions through Microalgae from Piggery Digestate: Optimization, Kinetic, Isotherm and Mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Zha, J.; Tian, G.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Liang, J. Synthesis of Zeolites by In-Situ Conversion of Geopolymers and Their Performance of Heavy Metal Ion Removal in Wastewater:A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 349, 131441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, B.; Zhu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. In-Situ Synthesis of Zeolite X in Foam Geopolymer as a CO2 Adsorbent. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlalveni, C.; Lallianrawna, S.; Biswas, A.; Selvaraj, M.; Changmai, B.; Rokhum, S.L. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Plant Extracts and Their Antimicrobial Activities: A Review of Recent Literature. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 2804–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiraroj, D.; Tungasmita, S.; Tungasmita, D.N. Silver Ions and Silver Nanoparticles in Zeolite A Composites for Antibacterial Activity. Powder Technol. 2014, 264, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Botella, E.; Valencia, S.; Rey, F. Zeolites in Adsorption Processes: State of the Art and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17647–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunova, E.L.; Mikosch, H. Cation Site Preference in Zeolite Clinoptilolite: A Density Functional Study. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 177, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, L.; Gao, M.; Bai, H.; Nagasaka, T. Synthesis of Zeolite-Geopolymer Composites with High Zeolite Content for Pb(II) Removal by a Simple Two-Step Method Using Fly Ash and Metakaolin. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).