Submitted:
20 December 2023
Posted:
20 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Physiological background of myocardial fluid filtration
2.1. Starling forces and microvascular fluid filtration
| JV =LPS[(PC-PI)-σ(ΠC-ΠG)] |
| LPS: ~ 0.35 ml min-1 mmHg-1 100 g-1 [34,35] |
| S: 500 cm2 g-1 [35,36] |
| PC: end-diastolic 20 - 30 mmHg [37,38] |
| PI: ~120 mmHg during systole, 15 mmHg during diastole [39,40] |
| σ: 0.51 - 0.67 for plasma proteins; 0.41 - 0.59 for albumin [39,41,42] |
| ΠC: 21 - 24 mmHg [39,43,44] |
| ΠG: 13-20 mmHg [45] |
2.2. The glycocalyx as key regulator of the endothelial barrier
3. Pathophysiology
3.1. Glycocalyx disintegration
3.2. Intercellular junctions and key signalling processes
3.3. Inflammation and myocardial oedema
3.4. Detection of myocardial oedema and myocarditis
3.5. SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Myocarditis in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Arrhythmias in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Glycocalyx changes and inflammation in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Immunothrombosis in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Possible long-term effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection
3.6. Cardiotrophic viruses and myocarditis
| Virus | Glycocalyx components | Literature reference |
|---|---|---|
| Parvovirus B19 | heparan sulphate, sialic acid | [381] |
| Human herpesvirus 1, 6 | heparan sulphate, syndecan-1 | [382,383] |
| Epstein–Barr virus | glycoproteins, hyaluronan synthesis | [384,385] |
| Human cytomegalovirus | heparan sulphate | [386,387] |
| Enteroviruses | heparan sulphate, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1, sialylated glycan | [388,389,390] |
| Adenovirus | heparan sulphate, sialic acid | [391,392,393] |
| Hepatitis C virus | heparan sulphate, syndecan-1 | [394,395] |
| SARS-CoV-2 | heparan sulphate proteoglycans | [223,396] |
| Influenza virus | sialic acids, hyaluronan synthesis | [391,397] |
4. Clinical implications and treatment options
4.1. Myocardial oedema and myocarditis
4.2. Endothelial damage and glycocalyx disintegration
4.3. Thrombosis
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasques-Nóvoa F, Angélico-Gonçalves A, Alvarenga JMG, et al. Myocardial oedema: pathophysiological basis and implications for the failing heart. ESC Hear Fail. 2022;9(2):958-976. [CrossRef]
- Mehlhorn U, Geissler HJ, Laine GA, Allen SJ. Myocardial fluid balance. Eur J Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2001;20(6):1220-1230. [CrossRef]
- Laine GA, Allen SJ. Left ventricular myocardial edema. Lymph flow, interstitial fibrosis, and cardiac function. Circ Res. 1991;68(6):1713-1721. [CrossRef]
- Desai K, V. , Laine GA, Stewart RH, et al. Mechanics of the left ventricular myocardial interstitium: effects of acute and chronic myocardial edema. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008;294(6):H2428-34. [CrossRef]
- Rubboli A, Sobotka PA, Euler DE. Effect of acute edema on left ventricular function and coronary vascular resistance in the isolated rat heart. Am J Physiol - Hear Circ Physiol. 1994;267(3 36-3). [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto M, McClure DE, Schertel ER, et al. Effects of hypoproteinemia-induced myocardial edema on left ventricular function. Am J Physiol. 1998;274(3):H937-44. [CrossRef]
- Karolle BL, Carlson RE, Aisen AM, Buda AJ. Transmural distribution of myocardial edema by NMR relaxometry following myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Am Heart J. 1991;122(3 Pt 1):655-664. [CrossRef]
- Röttgen R, Christiani R, Freyhardt P, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging findings in acute myocarditis and correlation with immunohistological parameters. Eur Radiol. 2011;21(6):1259-1266. [CrossRef]
- Friedrich MG, Strohm O, Schulz-Menger J, Marciniak H, Luft FC, Dietz R. Contrast media-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging visualizes myocardial changes in the course of viral myocarditis. Circulation. 1998;97(18):1802-1809. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Dorado D, Andres-Villarreal M, Ruiz-Meana M, Inserte J, Barba I. Myocardial edema: A translational view. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012;52(5):931-939. [CrossRef]
- Duncker DJ, Bache RJ. Regulation of coronary blood flow during exercise. Physiol Rev. 2008;88(3):1009-1086. [CrossRef]
- Bassenge E, Heusch G. Endothelial and neuro-humoral control of coronary blood flow in health and disease. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1990;116:77-165. [CrossRef]
- Ziegler WH, Goresky CA. Transcapillary exchange in the working left ventricle of the dog. Circ Res. 1971;29(2):181-207. [CrossRef]
- Li L, Zhao Q, Kong W. Extracellular matrix remodeling and cardiac fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 2018;68-69:490-506. [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, NG. The Extracellular Matrix in Ischemic and Nonischemic Heart Failure. Circ Res. 2019;125(1):117-146. [CrossRef]
- Weber, KT. Cardiac interstitium in health and disease: the fibrillar collagen network. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989;13(7):1637-1652. [CrossRef]
- Valiente-Alandi I, Schafer AE, Blaxall BC. Extracellular matrix-mediated cellular communication in the heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2016;91:228. [CrossRef]
- Al-Kofahi M, Omura S, Tsunoda I, et al. IL-1β reduces cardiac lymphatic muscle contraction via COX-2 and PGE2 induction: Potential role in myocarditis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:1591-1600. [CrossRef]
- Abassi Z, Khoury EE, Karram T, Aronson D. Edema formation in congestive heart failure and the underlying mechanisms. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:2720.
- Davis KL, Laine GA, Geissler HJ, Mehlhorn U, Brennan M, Allen SJ. Effects of myocardial edema on the development of myocardial interstitial fibrosis. Microcirculation. 2000;7(4):269-280. [CrossRef]
- Van Heerebeek L, Hamdani N, Handoko ML, et al. Diastolic stiffness of the failing diabetic heart: importance of fibrosis, advanced glycation end products, and myocyte resting tension. Circulation. 2008;117(1):43-51. [CrossRef]
- Van Heerebeek L, Borbély A, Niessen HWM, et al. Myocardial Structure and Function Differ in Systolic and Diastolic Heart Failure. Circulation. 2006;113(16):1966-1973. [CrossRef]
- Fraser DD, Patterson EK, Slessarev M, et al. Endothelial Injury and Glycocalyx Degradation in Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: Implications for Microvascular Platelet Aggregation. Crit care Explor. 2020;2(9):e0194. [CrossRef]
- Rapkiewicz A, V. , Mai X, Carsons SE, et al. Megakaryocytes and platelet-fibrin thrombi characterize multi-organ thrombosis at autopsy in COVID-19: A case series. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;24:100434. [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Paz L, Capodanno D, Montalescot G, Angiolillo DJ. Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Thrombosis and Coagulopathy: Review of the Pathophysiological Characteristics and Implications for Antithrombotic Management. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(3):1-24. [CrossRef]
- Varga Z, Flammer AJ, Steiger P, et al. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet (London, England). 2020;395(10234):1417-1418. [CrossRef]
- Zhang S, Liu Y, Wang X, et al. SARS-CoV-2 binds platelet ACE2 to enhance thrombosis in COVID-19. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13(1). [CrossRef]
- Panzer B, Kopp CW, Neumayer C, et al. Toll-like Receptors as Pro-Thrombotic Drivers in Viral Infections: A Narrative Review. Cells. 2023;12(14):1865. [CrossRef]
- Poledniczek M, Neumayer C, Kopp CW, et al. Micro- and Macrovascular Effects of Inflammation in Peripheral Artery Disease—Pathophysiology and Translational Therapeutic Approaches. Biomedicines. 2023;11(8). [CrossRef]
- Poledniczek M, Neumayer C, Kopp CW, et al. Micro- and Macrovascular Effects of Inflammation in Peripheral Artery Disease – Pathophysiology and Translational Therapeutic Approaches. Published online July 17, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Starling, EH. On the Absorption of Fluids from the Connective Tissue Spaces. J Physiol. 1896;19(4):312-326. [CrossRef]
- Levick JR, Michel CC. Microvascular fluid exchange and the revised Starling principle. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;87(2):198-210. [CrossRef]
- Staverman, AJ. The theory of measurement of osmotic pressure. Recl des Trav Chim des Pays-Bas. 1951;70(4):344-352. [CrossRef]
- MICHEL, CC. Fluid movements through capillary walls. In: Handbook of Physiology. The Cardiovascular System Microcirculation, Section 2. Vol 0. American Physiology Society; 1984:375-409.
- Chilian WM, Eastham CL, Layne SM, Marcus ML. Small vessel phenomena in the coronary microcirculation: phasic intramyocardial perfusion and coronary microvascular dynamics. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1988;31(1):17-38. [CrossRef]
- Bassingthwaighte, JB. A concurrent flow model for extraction during transcapillary passage. Circ Res. 1974;35(3):483-503. [CrossRef]
- Chilian, WM. Microvascular pressures and resistances in the left ventricular subepicardium and subendocardium. Circ Res. 1991;69(3):561-570. [CrossRef]
- Koyama T, Kikuchi Y, Kakiuchi Y, Nagashima C. An analysis of water movement between myocardial tissue and capillary blood during reactive hyperemia. Jpn J Physiol. 1979;29(1):1-13. [CrossRef]
- Laine GA, Granger HJ. Microvascular, interstitial, and lymphatic interactions in normal heart. Am J Physiol. 1985;249(4 Pt 2). [CrossRef]
- Stein PD, Marzilli M, Sabbah HN, Lee T. Systolic and diastolic pressure gradients within the left ventricular wall. Am J Physiol. 1980;238(5). [CrossRef]
- Pilati, CF. Macromolecular transport in canine coronary microvasculature. Am J Physiol. 1990;258(3 Pt 2). [CrossRef]
- Mehlhorn U, Davis KL, Laine GA, Geissler HJ, Allen SJ. Myocardial fluid balance in acute hypertension. Microcirculation. 1996;3(4):371-378. [CrossRef]
- Mehlhorn U, Allen SJ, Davis KL, Geissler HJ, Warters RD, Rainer de Vivie E. Increasing the colloid osmotic pressure of cardiopulmonary bypass prime and normothermic blood cardioplegia minimizes myocardial oedema and prevents cardiac dysfunction. Cardiovasc Surg. 1998;6(3):274-281. [CrossRef]
- Navar PD, Navar LG. Relationship between colloid osmotic pressure and plasma protein concentration in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1977;233(2). [CrossRef]
- Curry FE, Michel CC. The Colloid Osmotic Pressure Across the Glycocalyx: Role of Interstitial Fluid Sub-Compartments in Trans-Vascular Fluid Exchange in Skeletal Muscle. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9. [CrossRef]
- Mortimer PS, Levick JR. Chronic peripheral oedema: the critical role of the lymphatic system. Clin Med. 2004;4(5):448-453. [CrossRef]
- Reitsma S, Slaaf DW, Vink H, et al. The endothelial glycocalyx: Composition, functions, and visualization. Pflugers Arch Eur J Physiol. 2007;454(3):345-359. [CrossRef]
- Vink H, Duling BR. Capillary endothelial surface layer selectively reduces plasma solute distribution volume. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;278(1). [CrossRef]
- Ori A, Wilkinson MC, Fernig DG. A Systems Biology Approach for the Investigation of the Heparin/Heparan Sulfate Interactome. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(22):19892. [CrossRef]
- Wiig H, Swartz MA. Interstitial fluid and lymph formation and transport: physiological regulation and roles in inflammation and cancer. Physiol Rev. 2012;92(3):1005-1060. [CrossRef]
- Wearn, JT. THE EXTENT OF THE CAPILLARY BED OF THE HEART. J Exp Med. 1928;47(2):273-290. [CrossRef]
- Laine, GA. Microvascular changes in the heart during chronic arterial hypertension. Circ Res. 1988;62(5):953-960. [CrossRef]
- Verbrugge FH, Bertrand PB, Willems E, et al. Global myocardial oedema in advanced decompensated heart failure. Eur Hear journal Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;18(7):787-794. [CrossRef]
- Takegawa R, Kabata D, Shimizu K, et al. Serum albumin as a risk factor for death in patients with prolonged sepsis: An observational study. J Crit Care. 2019;51:139-144. [CrossRef]
- Boyd JH, Forbes J, Nakada TA, Walley KR, Russell JA. Fluid resuscitation in septic shock: a positive fluid balance and elevated central venous pressure are associated with increased mortality. Crit Care Med. 2011;39(2):259-265. [CrossRef]
- Wiig H, Rubin K, Reed RK. New and active role of the interstitium in control of interstitial fluid pressure: potential therapeutic consequences. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2003;47(2):111-121. [CrossRef]
- Weinbaum S, Tarbell JM, Damiano ER. The structure and function of the endothelial glycocalyx layer. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2007;9:121-167. [CrossRef]
- Squire JM, Chew M, Nneji G, Neal C, Barry J, Michel C. Quasi-periodic substructure in the microvessel endothelial glycocalyx: a possible explanation for molecular filtering? J Struct Biol. 2001;136(3):239-255. [CrossRef]
- Rostgaard J, Qvortrup K. Electron microscopic demonstrations of filamentous molecular sieve plugs in capillary fenestrae. Microvasc Res. 1997;53(1):1-13. [CrossRef]
- Tarbell JM, Cancel LM. The glycocalyx and its significance in human medicine. J Intern Med. 2016;280(1):97-113. [CrossRef]
- Pries AR, Secomb TW, Gaehtgens P. The endothelial surface layer. Pflugers Arch. 2000;440(5):653-666. [CrossRef]
- Lipowsky, HH. Microvascular rheology and hemodynamics. Microcirculation. 2005;12(1):5-15. [CrossRef]
- Vink H, Constantinescu AA, Spaan JAE. Oxidized lipoproteins degrade the endothelial surface layer : implications for platelet-endothelial cell adhesion. Circulation. 2000;101(13):1500-1502. [CrossRef]
- Mehta D, Malik AB. Signaling mechanisms regulating endothelial permeability. Physiol Rev. 2006;86(1):279-367. [CrossRef]
- Busch B, Ljungman C, Heldin CM, Waskson E, Öbrink B. Surface properties of cultured endothelial cells. Haemostasis. 1979;8(3-5):142-148. [CrossRef]
- Damiano, ER. The effect of the endothelial-cell glycocalyx on the motion of red blood cells through capillaries. Microvasc Res. 1998;55(1):77-91. [CrossRef]
- Adamson RH, Huxley VH, Curry FE. Single capillary permeability to proteins having similar size but different charge. Am J Physiol. 1988;254(2 Pt 2). [CrossRef]
- Henry CBS, Duling BR. Permeation of the luminal capillary glycocalyx is determined by hyaluronan. Am J Physiol. 1999;277(2). [CrossRef]
- Adamson, RH. Permeability of frog mesenteric capillaries after partial pronase digestion of the endothelial glycocalyx. J Physiol. 1990;428(1):1-13. [CrossRef]
- Powers MR, Blumenstock FA, Cooper JA, Malik AB. Role of albumin arginyl sites in albumin-induced reduction of endothelial hydraulic conductivity. J Cell Physiol. 1989;141(3):558-564. [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger EE, Hamelin M. Interaction of serum proteins with lung endothelial glycocalyx: its effect on endothelial permeability. Am J Physiol. 1984;247(2 Pt 2). [CrossRef]
- Turner MR, Clough G, Michel CC. The effects of cationised ferritin and native ferritin upon the filtration coefficient of single frog capillaries. Evidence that proteins in the endothelial cell coat influence permeability. Microvasc Res. 1983;25(2):205-222. [CrossRef]
- Levick JR, Michel CC. The effect of bovine albumin on the permeability of frog mesenteric capillaries. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1973;58(1):87-97. [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Quintero S, V. , Amaya R, Pahakis M, Tarbell JM. The endothelial glycocalyx mediates shear-induced changes in hydraulic conductivity. Am J Physiol Circ Physiol. 2009;296(5):H1451-H1456. [CrossRef]
- Jacob M, Rehm M, Loetsch M, et al. The endothelial glycocalyx prefers albumin for evoking shear stress-induced, nitric oxide-mediated coronary dilatation. J Vasc Res. 2007;44(6):435-443. [CrossRef]
- Li Q, Bolli R, Qiu Y, Tang XL, Murphree SS, French BA. Gene therapy with extracellular superoxide dismutase attenuates myocardial stunning in conscious rabbits. Circulation. 1998;98(14):1438-1448. [CrossRef]
- Shimada K, Kobayashi M, Kimura S, et al. Anticoagulant heparin-like glycosaminoglycans on endothelial cell surface. Jpn Circ J. 1991;55(10):1016-1021. [CrossRef]
- Tovar AMF, De Mattos DA, Stelling MP, Sarcinelli-Luz BSL, Nazareth RA, Mourão PAS. Dermatan sulfate is the predominant antithrombotic glycosaminoglycan in vessel walls: implications for a possible physiological function of heparin cofactor II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1740(1):45-53. [CrossRef]
- Patterson EK, Cepinskas G, Fraser DD. Endothelial Glycocalyx Degradation in Critical Illness and Injury. Front Med. 2022;9:898592. [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg BM, Vink H, Spaan JAE. The Endothelial Glycocalyx Protects Against Myocardial Edema. Circ Res. 2003;92(6):592-594. [CrossRef]
- Jacob M, Bruegger D, Rehm M, Welsch U, Conzen P, Becker BF. Contrasting effects of colloid and crystalloid resuscitation fluids on cardiac vascular permeability. Anesthesiology. 2006;104(6):1223-1231. [CrossRef]
- Bruegger D, Jacob M, Rehm M, et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide induces shedding of endothelial glycocalyx in coronary vascular bed of guinea pig hearts. Am J Physiol Circ Physiol. 2005;289(5):H1993-H1999. [CrossRef]
- van den Berg BM, Vink H, Spaan JAE. The Endothelial Glycocalyx Protects Against Myocardial Edema. Circ Res. 2003;92(6):592-594. [CrossRef]
- Malik AB, Siflinger-Birnboim A. Vascular Endothelial Barrier Function and Its Regulation. Published online 1993:231-267. [CrossRef]
- Adamson, RH. Permeability of frog mesenteric capillaries after partial pronase digestion of the endothelial glycocalyx. J Physiol. 1990;428(1):1-13. [CrossRef]
- Mann, GE. Alterations of myocardial capillary permeability by albumin in the isolated, perfused rabbit heart. J Physiol. 1981;319(1):311-323. [CrossRef]
- Wiesinger A, Peters W, Chappell D, et al. Nanomechanics of the Endothelial Glycocalyx in Experimental Sepsis. Sokolov I, ed. PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e80905. [CrossRef]
- Rienks M, Carai P, van Teeffelen J, et al. SPARC preserves endothelial glycocalyx integrity, and protects against adverse cardiac inflammation and injury during viral myocarditis. Matrix Biol. 2018;74:21-34. [CrossRef]
- Epstein FH, Parrillo JE. Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Septic Shock. 1993;328(20):1471-1477. [CrossRef]
- Tang THC, Alonso S, Ng LFP, et al. Increased Serum Hyaluronic Acid and Heparan Sulfate in Dengue Fever: Association with Plasma Leakage and Disease Severity. Sci Rep. 2017;7. [CrossRef]
- Puerta-Guardo H, Glasner DR, Harris E. Dengue Virus NS1 Disrupts the Endothelial Glycocalyx, Leading to Hyperpermeability. PLoS Pathog. 2016;12(7):e1005738. [CrossRef]
- Bansch P, Nelson A, Ohlsson T, Bentzer P. Effect of charge on microvascular permeability in early experimental sepsis in the rat. Microvasc Res. 2011;82(3):339-345. [CrossRef]
- Henry CBS, Duling BR. TNF-alpha increases entry of macromolecules into luminal endothelial cell glycocalyx. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;279(6):H2815-23. [CrossRef]
- Ley K, Tedder TF. Leukocyte interactions with vascular endothelium. New insights into selectin-mediated attachment and rolling. J Immunol. 1995;155(2):525-528. [CrossRef]
- Peterson MW, Stone P, Shasby DM. Cationic neutrophil proteins increase transendothelial albumin movement. J Appl Physiol. 1987;62(4):1521-1530. [CrossRef]
- Hoover RL, Briggs RT, Karnovsky MJ. The adhesive interaction between polymorphonuclear leukocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Cell. 1978;14(2):423-428. [CrossRef]
- Morita Y, Clemens MG, Miller LS, et al. Reactive oxidants mediate TNF-alpha-induced leukocyte adhesion to rat mesenteric venular endothelium. Am J Physiol. 1995;269(6 Pt 2). [CrossRef]
- Carden DL, Smith JK, Korthuis RJ. Neutrophil-mediated microvascular dysfunction in postischemic canine skeletal muscle. Role of granulocyte adherence. Circ Res. 1990;66(5):1436-1444. [CrossRef]
- Radeva MY, Waschke J. Mind the gap: mechanisms regulating the endothelial barrier. Acta Physiol. 2018;222(1):e12860. [CrossRef]
- Ward BJ, Donnelly JL. Hypoxia induced disruption of the cardiac endothelial glycocalyx: implications for capillary permeability. Cardiovasc Res. 1993;27(3):384-389. [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu AA, Vink H, Spaan JAE. Elevated capillary tube hematocrit reflects degradation of endothelial cell glycocalyx by oxidized LDL. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001;280(3):H1051-7. [CrossRef]
- Gardner G, Banka CL, Roberts KA, Mullick AE, Rutledge JC. Modified LDL–Mediated Increases in Endothelial Layer Permeability Are Attenuated With 17β-Estradiol. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999;19(4):854-861. [CrossRef]
- Rangaswamy S, Penn MS, Saidel GM, Chisolm GM. Exogenous Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Injures and Alters the Barrier Function of Endothelium in Rats In Vivo. Circ Res. 1997;80(1):37-44. [CrossRef]
- Lehr HA, Frei B, Olofsson AM, Carew TE, Arfors KE. Protection From Oxidized LDL–Induced Leukocyte Adhesion to Microvascular and Macrovascular Endothelium In Vivo by Vitamin C but Not by Vitamin E. Circulation. 1995;91(5):1525-1532. [CrossRef]
- Liao L, Harris NR, Granger DN. Oxidized low-density lipoproteins and microvascular responses to ischemia-reperfusion. 1996;271(6 40-6). [CrossRef]
- Lehr HA, Becker M, Marklund SL, et al. Superoxide-dependent stimulation of leukocyte adhesion by oxidatively modified LDL in vivo. Arterioscler Thromb A J Vasc Biol. 1992;12(7):824-829. [CrossRef]
- Beręsewicz A, Czarnowska E, Mączewski M. Ischemic preconditioning and superoxide dismutase protect against endothelial dysfunction and endothelium glycocalyx disruption in the postischemic guinea-pig hearts. Myocard Ischemia Reperfus. Published online 1998:87-97. [CrossRef]
- Mulivor AW, Lipowsky HH. Inflammation- and ischemia-induced shedding of venular glycocalyx. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286(5):H1672-80. [CrossRef]
- Kurzelewski M, Czarnowska E, Beresewicz A. Superoxide- and nitric oxide-derived species mediate endothelial dysfunction, endothelial glycocalyx disruption, and enhanced neutrophil adhesion in the post-ischemic guinea-pig heart. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2005;56(2):163-178. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. 1598.
- Yu H, Kalogeris T, Korthuis RJ. Reactive species-induced microvascular dysfunction in ischemia/reperfusion. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;135:182-197. [CrossRef]
- Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M, Korthuis RJ. Ischemia/Reperfusion. Compr Physiol. 2016;7(1):113-170. [CrossRef]
- Huang Y, Xu W, Zhou R. NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death. Cell Mol Immunol 2021 189. 2021;18(9):2114-2127. [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9(6):653-660. [CrossRef]
- Yancopoulos GD, Davis S, Gale NW, Rudge JS, Wiegand SJ, Holash J. Vascular-specific growth factors and blood vessel formation. Nature. 2000;407(6801):242-248. [CrossRef]
- Polverini, PJ. The pathophysiology of angiogenesis. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1995;6(3):230-247. [CrossRef]
- Zimna A, Kurpisz M. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 in Physiological and Pathophysiological Angiogenesis: Applications and Therapies. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015. [CrossRef]
- Eliceiri BP, Paul R, Schwartzberg PL, Hood JD, Leng J, Cheresh DA. Selective requirement for Src kinases during VEGF-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Mol Cell. 1999;4(6):915-924. [CrossRef]
- Nelson AR, Fingleton B, Rothenberg ML, Matrisian LM. Matrix metalloproteinases: biologic activity and clinical implications. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(5):1135-1149. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Yosef Y, Miller A, Shapiro S, Lahat N. Hypoxia of endothelial cells leads to MMP-2-dependent survival and death. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;289(5). [CrossRef]
- Sun J, Singh P, Shami A, et al. Spatial Transcriptional Mapping Reveals Site-Specific Pathways Underlying Human Atherosclerotic Plaque Rupture. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;81(23):2213-2227. [CrossRef]
- Goetze JP, Bruneau BG, Ramos HR, Ogawa T, de Bold MK, de Bold AJ. Cardiac natriuretic peptides. Nat Rev Cardiol 2020 1711. 2020;17(11):698-717. [CrossRef]
- Ando SI, Imaizumi T, Harada S, Hirooka Y, Takeshita A. Atrial natriuretic peptide increases human capillary filtration and venous distensibility. J Hypertens. 1992;10(5):451-457. [CrossRef]
- Huxley VH, Tucker VL, Verburg KM, Freeman RH. Increased capillary hydraulic conductivity induced by atrial natriuretic peptide. Circ Res. 1987;60(2):304-307. [CrossRef]
- Jacob M, Saller T, Chappell D, Rehm M, Welsch U, Becker BF. Physiological levels of A-, B- and C-type natriuretic peptide shed the endothelial glycocalyx and enhance vascular permeability. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013;108(3). [CrossRef]
- Oberleithner H, Peters W, Kusche-Vihrog K, et al. Salt overload damages the glycocalyx sodium barrier of vascular endothelium. Pflugers Arch. 2011;462(4):519-528. [CrossRef]
- Selcuk M, Keskin M, Cinar T, et al. Prognostic significance of N-Terminal Pro-BNP in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia without previous history of heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(Supplement_1). [CrossRef]
- Huelsmann M, Neuhold S, Resl M, et al. PONTIAC (NT-proBNP Selected PreventiOn of cardiac eveNts in a populaTion of dIabetic patients without A history of Cardiac disease): A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(15):1365-1372. [CrossRef]
- Hartsock A, Nelson WJ. Adherens and tight junctions: Structure, function and connections to the actin cytoskeleton. Biochim Biophys Acta - Biomembr. 2008;1778(3):660-669. [CrossRef]
- Yano T, Torisawa T, Oiwa K, Tsukita S. AMPK-dependent phosphorylation of cingulin reversibly regulates its binding to actin filaments and microtubules. Sci Reports 2018 81. 2018;8(1):1-10. [CrossRef]
- González-Mariscal L, Tapia R, Chamorro D. Crosstalk of tight junction components with signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778(3):729-756. [CrossRef]
- Dejana E, Tournier-Lasserve E, Weinstein BM. The control of vascular integrity by endothelial cell junctions: molecular basis and pathological implications. Dev Cell. 2009;16(2):209-221. [CrossRef]
- Furuse, M. Molecular basis of the core structure of tight junctions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2(1). [CrossRef]
- Guillemot L, Paschoud S, Pulimeno P, Foglia A, Citi S. The cytoplasmic plaque of tight junctions: a scaffolding and signalling center. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778(3):601-613. [CrossRef]
- Schossleitner K, Rauscher S, Gröger M, et al. Evidence That Cingulin Regulates Endothelial Barrier Function In Vitro and In Vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016;36(4):647-654. [CrossRef]
- Dejana E, Vestweber D. The role of VE-cadherin in vascular morphogenesis and permeability control. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;116:119-144. [CrossRef]
- Bravi L, Dejana E, Lampugnani MG. VE-cadherin at a glance. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;355(3):515-522. [CrossRef]
- Gavard, J. Endothelial permeability and VE-cadherin: a wacky comradeship. Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(2):158-164. [CrossRef]
- Waschke J, Curry FE, Adamson RH, Drenckhahn D. Regulation of actin dynamics is critical for endothelial barrier functions. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288(3). [CrossRef]
- Stevens T, Garcia JGN, Shasby DM, Bhattacharya J, Malik AB. Mechanisms regulating endothelial cell barrier function. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000;279(3). [CrossRef]
- Prasain N, Stevens T. The actin cytoskeleton in endothelial cell phenotypes. Microvasc Res. 2009;77(1):53-63. [CrossRef]
- Dudek SM, Garcia JGN. Cytoskeletal regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability. J Appl Physiol. 2001;91(4):1487-1500. [CrossRef]
- Shasby DM, Shasby SS, Sullivan JM, Peach MJ. Role of endothelial cell cytoskeleton in control of endothelial permeability. Circ Res. 1982;51(5):657-661. [CrossRef]
- García-Ponce A, Citalán-Madrid AF, Velázquez-Avila M, Vargas-Robles H, Schnoor M. The role of actin-binding proteins in the control of endothelial barrier integrity. Thromb Haemost. 2015;113(01):20-36. [CrossRef]
- Wang L, Dudek SM. Regulation of vascular permeability by sphingosine 1-phosphate. Microvasc Res. 2009;77(1):39-45. [CrossRef]
- Xu M, Waters CL, Hu C, Wysolmerski RB, Vincent PA, Minnear FL. Sphingosine 1-phosphate rapidly increases endothelial barrier function independently of VE-cadherin but requires cell spreading and Rho kinase. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;293(4). [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson BA, Argraves KM. The role of sphingosine-1-phosphate in endothelial barrier function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1841(10):1403-1412. [CrossRef]
- David S, Ghosh CC, Mukherjee A, Parikh SM. Angiopoietin-1 requires IQ domain GTPase-activating protein 1 to activate Rac1 and promote endothelial barrier defense. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31(11):2643-2652. [CrossRef]
- Frye M, Dierkes M, Küppers V, et al. Interfering with VE-PTP stabilizes endothelial junctions in vivo via Tie-2 in the absence of VE-cadherin. J Exp Med. 2015;212(13):2267-2287. [CrossRef]
- Zeng Y, Adamson RH, Curry FRE, Tarbell JM. Sphingosine-1-phosphate protects endothelial glycocalyx by inhibiting syndecan-1 shedding. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014;306(3). [CrossRef]
- Schlegel N, Waschke J. cAMP with other signaling cues converges on Rac1 to stabilize the endothelial barrier- a signaling pathway compromised in inflammation. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;355(3):587-596. [CrossRef]
- Lampugnani MG, Zanetti A, Breviario F, et al. VE-cadherin regulates endothelial actin activating Rac and increasing membrane association of Tiam. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(4):1175-1189. [CrossRef]
- Kopperud RK, Rygh CB, Karlsen T V., et al. Increased microvascular permeability in mice lacking Epac1 (Rapgef3). Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2017;219(2):441-452. [CrossRef]
- Cullere X, Shaw SK, Andersson L, Hirahashi J, Luscinskas FW, Mayadas TN. Regulation of vascular endothelial barrier function by Epac, a cAMP-activated exchange factor for Rap GTPase. Blood. 2005;105(5):1950-1955. [CrossRef]
- Michel CC, Curry FE. Microvascular permeability. Physiol Rev. 1999;79(3):703-761. [CrossRef]
- Curry FRE, Adamson RH. Tonic regulation of vascular permeability. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2013;207(4):628-649. [CrossRef]
- Schlegel N, Baumer Y, Drenckhahn D, Waschke J. Lipopolysaccharide-induced endothelial barrier breakdown is cyclic adenosine monophosphate dependent in vivo and in vitro. Crit Care Med. 2009;37(5):1735-1743. [CrossRef]
- Schlegel N, Waschke J. Impaired cAMP and Rac 1 signaling contribute to TNF-alpha-induced endothelial barrier breakdown in microvascular endothelium. Microcirculation. 2009;16(6):521-533. [CrossRef]
- Baumer Y, Spindler V, Werthmann RC, Bünemann M, Waschke J. Role of Rac 1 and cAMP in endothelial barrier stabilization and thrombin-induced barrier breakdown. J Cell Physiol. 2009;220(3):716-726. [CrossRef]
- Aslam M, Tanislav C, Troidl C, Schulz R, Hamm C, Gündüz D. cAMP controls the restoration of endothelial barrier function after thrombin-induced hyperpermeability via Rac1 activation. Physiol Rep. 2014;2(10). [CrossRef]
- Dejana E, Orsenigo F. Endothelial adherens junctions at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2013;126(Pt 12):2545-2549. [CrossRef]
- Küppers V, Vockel M, Nottebaum AF, Vestweber D. Phosphatases and kinases as regulators of the endothelial barrier function. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;355(3):577-586. [CrossRef]
- Spindler V, Schlegel N, Waschke J. Role of GTPases in control of microvascular permeability. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;87(2):243-253. [CrossRef]
- Wojciak-Stothard B, Ridley AJ. Rho GTPases and the regulation of endothelial permeability. Vascul Pharmacol. 2002;39(4-5):187-199. [CrossRef]
- Flemming S, Burkard N, Renschler M, et al. Soluble VE-cadherin is involved in endothelial barrier breakdown in systemic inflammation and sepsis. Cardiovasc Res. 2015;107(1):32-44. [CrossRef]
- Orsenigo F, Giampietro C, Ferrari A, et al. Phosphorylation of VE-cadherin is modulated by haemodynamic forces and contributes to the regulation of vascular permeability in vivo. Nat Commun. 2012;3. [CrossRef]
- Garatti L, Wu MA, Ammirati E, Sacco A. Systemic leak capillary syndrome with myocardial involvement and cardiogenic shock: a case report. Eur Hear J - Case Reports. 2022;6(7). [CrossRef]
- Yacoub S, Wertheim H, Simmons CP, Screaton G, Wills B. Cardiovascular manifestations of the emerging dengue pandemic. Nat Rev Cardiol 2014 116. 2014;11(6):335-345. [CrossRef]
- Biering SB, Gomes de Sousa FT, Tjang L V., et al. SARS-CoV-2 Spike triggers barrier dysfunction and vascular leak via integrins and TGF-β signaling. Nat Commun 2022 131. 2022;13(1):1-19. [CrossRef]
- Dongaonkar RM, Stewart RH, Quick CM, Uray KL, Cox CS, Laine GA. Award article: Microcirculatory Society Award for Excellence in Lymphatic Research: time course of myocardial interstitial edema resolution and associated left ventricular dysfunction. Microcirculation. 2012;19(8):714-722. [CrossRef]
- Pratt JW, Schertel ER, Schaefer SL, et al. Acute transient coronary sinus hypertension impairs left ventricular function and induces myocardial edema. Am J Physiol. 1996;271(3 Pt 2):H834-41. [CrossRef]
- Dongaonkar RM, Stewart RH, Geissler HJ, Laine GA. Myocardial microvascular permeability, interstitial oedema, and compromised cardiac function. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;87(2):331-339. [CrossRef]
- Taherzadeh M, Das AK, Warren JB. Nifedipine increases microvascular permeability via a direct local effect on postcapillary venules. Am J Physiol. 1998;275(4). [CrossRef]
- Monmeneu J V, Bodí V, Sanchis J, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance evaluation of edema after ST-elevation acute myocardial infarction. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2009;62(8):858-866. [CrossRef]
- Fehrmann A, Treutlein M, Rudolph T, et al. Myocardial T1 and T2 mapping in severe aortic stenosis: Potential novel insights into the pathophysiology of myocardial remodelling. Eur J Radiol. 2018;107:76-83. [CrossRef]
- Alabed S, Saunders L, Garg P, et al. Myocardial T1-mapping and extracellular volume in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Magn Reson Imaging. 2021;79:66-75. [CrossRef]
- Spieker M, Haberkorn S, Gastl M, et al. Abnormal T2 mapping cardiovascular magnetic resonance correlates with adverse clinical outcome in patients with suspected acute myocarditis. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2017;19(1). [CrossRef]
- Gräni C, Eichhorn C, Bière L, et al. Prognostic Value of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Tissue Characterization in Risk Stratifying Patients With Suspected Myocarditis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(16):1964. [CrossRef]
- Stevenson LW, Tillisch JH. Maintenance of cardiac output with normal filling pressures in patients with dilated heart failure. Circulation. 1986;74(6):1303-1308. [CrossRef]
- Laine GA, Allen SJ, Katz J, Gabel JC, Drake RE. Effect of systemic venous pressure elevation on lymph flow and lung edema formation. J Appl Physiol. 1986;61(5):1634-1638. [CrossRef]
- Robinson AD, Ramanathan KB, McGee JE, Newman KP, Weber KT. Oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte necrosis with elevated serum troponins: pathophysiologic mechanisms. Am J Med Sci. 2011;342(2):129-134. [CrossRef]
- Colombo PC, Onat D, Harxhi A, et al. Peripheral venous congestion causes inflammation, neurohormonal, and endothelial cell activation. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(7):448-454. [CrossRef]
- Libby P, Lüscher T. COVID-19 is, in the end, an endothelial disease. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(32):3038-3044. [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. The Heart in COVID-19: Primary Target or Secondary Bystander? JACC Basic to Transl Sci. 2020;5(5):537-542. [CrossRef]
- Folco EJ, Mawson TL, Vromman A, et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induce Endothelial Cell Activation and Tissue Factor Production Through Interleukin-1α and Cathepsin G. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018;38(8):1901-1912. [CrossRef]
- Marcus AJ, Broekman MJ, Drosopoulos JHF, et al. The endothelial cell ecto-ADPase responsible for inhibition of platelet function is CD39. J Clin Invest. 1997;99(6):1351-1360. [CrossRef]
- Roy C, Tabiasco J, Caillon A, et al. Loss of vascular expression of nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1/CD39 in hypertension. Purinergic Signal. 2018;14(1):73-82. [CrossRef]
- Robson SC, Kaczmarek E, Siegel JB, et al. Loss of ATP diphosphohydrolase activity with endothelial cell activation. J Exp Med. 1997;185(1):153-163. [CrossRef]
- Wei LH, Kuo ML, Chen CA, et al. Interleukin-6 promotes cervical tumor growth by VEGF-dependent angiogenesis via a STAT3 pathway. Oncogene. 2003;22(10):1517-1527. [CrossRef]
- Ishii K, Sasaki T, Iguchi K, et al. Interleukin-6 induces VEGF secretion from prostate cancer cells in a manner independent of androgen receptor activation. Prostate. 2018;78(11):849-856. [CrossRef]
- Soga N, Namba N, McAllister S, et al. Rho family GTPases regulate VEGF-stimulated endothelial cell motility. Exp Cell Res. 2001;269(1):73-87. [CrossRef]
- Pober JS, Sessa WC. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(10):803-815. [CrossRef]
- Busse R, Fleming I. Vascular endothelium and blood flow. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;176(PART2):43-78.
- Moncada S, Higgs EA. Nitric oxide and the vascular endothelium. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006;176(PART1):213-254.
- McDONALD DM, THURSTON G, BALUK P. Endothelial Gaps as Sites for Plasma Leakage in Inflammation. Microcirculation. 1999;6(1):7-22. [CrossRef]
- Siao CJ, Lorentz CU, Kermani P, et al. ProNGF, a cytokine induced after myocardial infarction in humans, targets pericytes to promote microvascular damage and activation. J Exp Med. 2012;209(12):2291-2305. [CrossRef]
- Armulik A, Genové G, Betsholtz C. Pericytes: Developmental, Physiological, and Pathological Perspectives, Problems, and Promises. Dev Cell. 2011;21(2):193-215. [CrossRef]
- Wang S, Cao C, Chen Z, et al. Pericytes Regulate Vascular Basement Membrane Remodeling and Govern Neutrophil Extravasation during Inflammation. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45499. [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Flores L, Gutiérrez R, Madrid JF, et al. Pericytes. Morphofunction, interactions and pathology in a quiescent and activated mesenchymal cell niche. Histol Histopathol. 2009;24(7):909-969. [CrossRef]
- Peppiatt CM, Howarth C, Mobbs P, Attwell D. Bidirectional control of CNS capillary diameter by pericytes. Nat 2006 4437112. 2006;443(7112):700-704. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Li X, Chen M, Feng Y, Xiong C. The ACE2 expression in human heart indicates new potential mechanism of heart injury among patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(6):1097-1100. [CrossRef]
- Johnsson C, Hällgren R, Elvin A, Gerdin B, Tufveson G. Hyaluronidase ameliorates rejection-induced edema. Transpl Int. 1999;12(4):235-243. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, DG. Leucocyte Trafficking via the Lymphatic Vasculature- Mechanisms and Consequences. Front Immunol. 2019;10(MAR). [CrossRef]
- Schwager S, Detmar M. Inflammation and Lymphatic Function. Front Immunol. 2019;10. [CrossRef]
- Pfister F, Feng Y, Hagen F Vom, et al. Pericyte MigrationA Novel Mechanism of Pericyte Loss in Experimental Diabetic Retinopathy. Diabetes. 2008;57(9):2495-2502. [CrossRef]
- Curry FRE. Atrial natriuretic peptide: an essential physiological regulator of transvascular fluid, protein transport, and plasma volume. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(6):1458-1461. [CrossRef]
- Chappell D, Bruegger D, Potzel J, et al. Hypervolemia increases release of atrial natriuretic peptide and shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx. Crit Care. 2014;18(5):538. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira VM, Schulz-Menger J, Holmvang G, et al. Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Nonischemic Myocardial Inflammation: Expert Recommendations. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(24):3158-3176. [CrossRef]
- Iles LM, Ellims AH, Llewellyn H, et al. Histological validation of cardiac magnetic resonance analysis of regional and diffuse interstitial myocardial fibrosis. Eur Hear journal Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;16(1):14-22. [CrossRef]
- Palmisano A, Benedetti G, Faletti R, et al. Early T1 Myocardial MRI Mapping: Value in Detecting Myocardial Hyperemia in Acute Myocarditis. Radiology. 2020;295(2):316-325. [CrossRef]
- Beijnink CWH, van der Hoeven NW, Konijnenberg LSF, et al. Cardiac MRI to Visualize Myocardial Damage after ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Review of Its Histologic Validation. Radiology. 2021;301(1):4-18. [CrossRef]
- Masci PG, Pavon AG, Muller O, et al. Relationship between CMR-derived parameters of ischemia/reperfusion injury and the timing of CMR after reperfused ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2018;20(1). [CrossRef]
- Gutberlet M, Spors B, Thoma T, et al. Suspected chronic myocarditis at cardiac MR: diagnostic accuracy and association with immunohistologically detected inflammation and viral persistence. Radiology. 2008;246(2):401-409. [CrossRef]
- Luo Y, Liu BT, Yuan WF, Zhao CX. Frontiers of COVID-19-related myocarditis as assessed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. World J Clin Cases. 2022;10(20):6784. [CrossRef]
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(36):3599-3726. [CrossRef]
- Caforio ALP, Pankuweit S, Arbustini E, et al. Current state of knowledge on aetiology, diagnosis, management, and therapy of myocarditis: a position statement of the European Society of Cardiology Working Group on Myocardial and Pericardial Diseases. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(33):2636-2648. [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Piechota-Polańczyk A, Andreas M, Kopp CW. Cardiovascular Disease Management in the Context of Global Crisis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;20(1):689. [CrossRef]
- Siripanthong B, Asatryan B, Hanff TC, et al. The Pathogenesis and Long-Term Consequences of COVID-19 Cardiac Injury. JACC Basic to Transl Sci. 2022;7(3):294-308. [CrossRef]
- Liu PP, Blet A, Smyth D, Li H. The Science Underlying COVID-19: Implications for the Cardiovascular System. Circulation. 2020;142(1):68-78. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181(2):271-280.e8. [CrossRef]
- Prasad K, AlOmar SY, Almuqri EA, Rudayni HA, Kumar V. Genomics-guided identification of potential modulators of SARS-CoV-2 entry proteases, TMPRSS2 and Cathepsins B/L. PLoS One. 2021;16(8). [CrossRef]
- Amraei R, Yin W, Napoleon MA, et al. CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN Act as Receptors for SARS-CoV-2. ACS Cent Sci. 2021;7(7):1156-1165. [CrossRef]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri L, Ojha R, Pedro LD, et al. Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity. Science. 2020;370(6518). [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Jambrina M, Eder J, Kaptein TM, et al. Infection and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 depend on heparan sulfate proteoglycans. EMBO J. 2021;40(20). [CrossRef]
- Dai J, Wang Y, Wang H, et al. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2-Induced Innate Immune Responses and the Potential Application Value of Toll-Like Receptor Immunomodulators in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:948770.
- Capone C, Faraco G, Park L, Cao X, Davisson RL, Iadecola C. The cerebrovascular dysfunction induced by slow pressor doses of angiotensin II precedes the development of hypertension. Am J Physiol - Hear Circ Physiol. 2011;300(1):397-407.
- Kawamura H, Kobayashi M, Li Q, et al. Effects of angiotensin II on the pericyte-containing microvasculature of the rat retina. J Physiol. 2004;561(Pt 3):671-683. [CrossRef]
- Tilton RG, Kilo C, Williamson JR, Murch DW. Differences in pericyte contractile function in rat cardiac and skeletal muscle microvasculatures. Microvasc Res. 1979;18(3):336-352. [CrossRef]
- Bertram S, Heurich A, Lavender H, et al. Influenza and SARS-Coronavirus Activating Proteases TMPRSS2 and HAT Are Expressed at Multiple Sites in Human Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Tracts. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35876. [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto A, Kawakami R, Kawai K, et al. ACE2 (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2) and TMPRSS2 (Transmembrane Serine Protease 2) Expression and Localization of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Human Heart. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021;41(1):542-544. [CrossRef]
- Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, et al. Pulmonary Vascular Endothelialitis, Thrombosis, and Angiogenesis in Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(2):120-128. [CrossRef]
- Carsana L, Sonzogni A, Nasr A, et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a series of COVID-19 cases from northern Italy: a two-centre descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(10):1135-1140. [CrossRef]
- Tavazzi G, Pellegrini C, Maurelli M, et al. Myocardial localization of coronavirus in COVID-19 cardiogenic shock. 2020;22(5):911-915. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura Y, Katano H, Nakajima N, et al. SARS-CoV-2 is localized in cardiomyocytes: a postmortem biopsy case. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;111:43. [CrossRef]
- Kim YH, Nijst P, Kiefer K, Tang WHW. Endothelial Glycocalyx as Biomarker for Cardiovascular Diseases: Mechanistic and Clinical Implications. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2017;14(2):117-126. [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Hülsmann M, Schörgenhofer C, et al. Sublingual functional capillary rarefaction in chronic heart failure. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018;48(2):e12869. [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Steinlechner B, Zimpfer D, et al. Functional capillary impairment in patients with ventricular assist devices. Sci Reports 2019 91. 2019;9(1):1-8. [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Schörgenhofer C, Rieder T, et al. Microvascular rarefaction in patients with cerebrovascular events. Microvasc Res. 2022;140. [CrossRef]
- Xu J, Xiao W, Liang X, et al. A meta-analysis on the risk factors adjusted association between cardiovascular disease and COVID-19 severity. BMC Public Health. 2021;21(1):1533. [CrossRef]
- Gerotziafas GT, Catalano M, Colgan MP, et al. Guidance for the Management of Patients with Vascular Disease or Cardiovascular Risk Factors and COVID-19: Position Paper from VAS-European Independent Foundation in Angiology/Vascular Medicine. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120(12):1597-1628. [CrossRef]
- Ronco C, Reis T, Husain-Syed F. Management of acute kidney injury in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(7):738-742. [CrossRef]
- Ullah W, Saeed R, Sarwar U, Patel R, Fischman DL. COVID-19 Complicated by Acute Pulmonary Embolism and Right-Sided Heart Failure. JACC Case reports. 2020;2(9):1379-1382. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Liu L, Zhang D, et al. SARS-CoV-2 and viral sepsis: observations and hypotheses. Lancet (London, England). 2020;395(10235):1517-1520. [CrossRef]
- Siripanthong B, Nazarian S, Muser D, et al. Recognizing COVID-19-related myocarditis: The possible pathophysiology and proposed guideline for diagnosis and management. Hear Rhythm. 2020;17(9):1463-1471. [CrossRef]
- Antzelevitch C, Burashnikov A. Overview of Basic Mechanisms of Cardiac Arrhythmia. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2011;3(1):23-45. [CrossRef]
- Avolio E, Madeddu P. Discovering cardiac pericyte biology: From physiopathological mechanisms to potential therapeutic applications in ischemic heart disease. Vascul Pharmacol. 2016;86:53-63. [CrossRef]
- Sweeney M, Foldes G. It Takes Two: Endothelial-Perivascular Cell Cross-Talk in Vascular Development and Disease. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018;5:413767.
- Bontekoe J, Lee J, Bansal V, et al. Biomarker Profiling in Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Identifies the Relationship between Angiopoietin-2 and Atrial Fibrillation. Clin Appl Thromb. 2018;24(9_suppl):269S-276S. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Yang Y, Ng CY, Zhang Z, Liu T, Li G. Association of Plasma Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Levels and the Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0155275. [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms of Atrial Fibrosis in Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2017;3(5):425-435. [CrossRef]
- Chang S-H, Yeh Y-H, Lee J-L, Hsu Y-J, Kuo C-T, Chen W-J. Transforming growth factor-β-mediated CD44/STAT3 signaling contributes to the development of atrial fibrosis and fibrillation. Basic Res Cardiol. 2017;112(5):58. [CrossRef]
- Qiao G, Xia D, Cheng Z, Zhang G. miR-132 in atrial fibrillation directly targets connective tissue growth factor. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(4):4143-4150. [CrossRef]
- Lee LL, Chintalgattu V. Pericytes in the Heart. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1122:187-210. [CrossRef]
- Li M, Yi X, Ma L, Zhou Y. Hepatocyte growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor regulate atrial fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart disease via the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2013;6(5):1121-1126. [CrossRef]
- Freestone B, Chong AY, Lim HS, Blann A, Lip GYH. Angiogenic factors in atrial fibrillation: a possible role in thrombogenesis? Ann Med. 2005;37(5):365-372. [CrossRef]
- Doubt TJ, Hogan PM. Effects of hydrostatic pressure on conduction and excitability in rabbit atria. J Appl Physiol. 1978;45(1):24-32. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Xue YM, Guo HM, et al. High hydrostatic pressure induces atrial electrical remodeling through upregulation of inflammatory cytokines. Life Sci. 2020;242. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Deng CY, Xue YM, et al. High hydrostatic pressure induces atrial electrical remodeling through angiotensin upregulation mediating FAK/Src pathway activation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020;140:10-21. [CrossRef]
- Granger DN, Rodrigues SF, Yildirim A, Senchenkova EY. Microvascular Responses to Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Microcirculation. 2010;17(3):192-205. [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Jilma B, Kopp CW, Ertl S, Gremmel T, Koppensteiner R. Glycocalyx as Possible Limiting Factor in COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2021;12:607306. [CrossRef]
- Huertas A, Montani D, Savale L, et al. Endothelial cell dysfunction: a major player in SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19)? Eur Respir J. 2020;56(1). [CrossRef]
- Huang KJ, Su IJ, Theron M, et al. An interferon-γ-related cytokine storm in SARS patients. J Med Virol. 2005;75(2):185-194. [CrossRef]
- Šoltés L, Mendichi R, Kogan G, Schiller J, Stankovská M, Arnhold J. Degradative action of reactive oxygen species on hyaluronan. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7(3):659-668. [CrossRef]
- Maciej-Hulme, ML. New Insights Into Human Hyaluronidase 4/Chondroitin Sulphate Hydrolase. Front cell Dev Biol. 2021;9. [CrossRef]
- Matzner Y, Bar-Ner M, Yahalom J, Ishai-Michaeli R, Fuks Z, Vlodavsky I. Degradation of heparan sulfate in the subendothelial extracellular matrix by a readily released heparanase from human neutrophils. Possible role in invasion through basement membranes. J Clin Invest. 1985;76(4):1306. [CrossRef]
- Endo K, Takino T, Miyamori H, et al. Cleavage of syndecan-1 by membrane type matrix metalloproteinase-1 stimulates cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(42):40764-40770. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, DD. The Weibel-Palade body: The storage granule for von Willebrand factor and P-selectin. Thromb Haemost. 1993;70(1):105-110. [CrossRef]
- Gupta RM, Libby P, Barton M. Linking regulation of nitric oxide to endothelin-1: The Yin and Yang of vascular tone in the atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis. 2020;292:201-203. [CrossRef]
- Ng H, Havervall S, Rosell A, et al. Circulating Markers of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Are of Prognostic Value in Patients With COVID-19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021;41(2):988-994. [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A. A NET-thrombosis axis in COVID-19. Blood. 2020;136(10):1118-1119. [CrossRef]
- Barmada A, Klein J, Ramaswamy A, et al. Cytokinopathy with aberrant cytotoxic lymphocytes and profibrotic myeloid response in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine–associated myocarditis. Sci Immunol. 2023;8(83). [CrossRef]
- Boehmer TK, Kompaniyets L, Lavery AM, et al. Association Between COVID-19 and Myocarditis Using Hospital-Based Administrative Data - United States, March 2020-January 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70(35):1228-1232. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Garcia J, Jaladanki S, Rivas-Lasarte M, et al. New Heart Failure Diagnoses Among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(17):2260-2262. [CrossRef]
- Puntmann VO, Carerj ML, Wieters I, et al. Outcomes of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients Recently Recovered From Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020;5(11):1265. [CrossRef]
- Li H, Zhu H, Yang Z, Tang D, Huang L, Xia L. Tissue Characterization by Mapping and Strain Cardiac MRI to Evaluate Myocardial Inflammation in Fulminant Myocarditis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020;52(3):930-938. [CrossRef]
- Hinojar R, Varma N, Child N, et al. T1 Mapping in Discrimination of Hypertrophic Phenotypes: Hypertensive Heart Disease and Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Findings From the International T1 Multicenter Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;8(12). [CrossRef]
- Wang H, Li R, Zhou Z, et al. Cardiac involvement in COVID-19 patients: mid-term follow up by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021;23(1):14. [CrossRef]
- Liu T, Wu D, Yan W, et al. Twelve-Month Systemic Consequences of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Patients Discharged From Hospital: A Prospective Cohort Study in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis An Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am. 2022;74(11):1953. [CrossRef]
- Seecheran R, Narayansingh R, Giddings S, et al. Atrial Arrhythmias in a Patient Presenting With Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) Infection. J Investig Med high impact case reports. 2020;8. [CrossRef]
- Guzik TJ, Mohiddin SA, Dimarco A, et al. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system: implications for risk assessment, diagnosis, and treatment options. Cardiovasc Res. 2020;116(10):1666-1687. [CrossRef]
- Inciardi RM, Adamo M, Lupi L, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 and cardiac disease in Northern Italy. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(19):1821-1829. [CrossRef]
- Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020;323(11):1061-1069. [CrossRef]
- Colon CM, Barrios JG, Chiles JW, et al. Atrial Arrhythmias in COVID-19 Patients. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;6(9):1189-1190. [CrossRef]
- Kim YM, Guzik TJ, Zhang YH, et al. A Myocardial Nox2 Containing NAD(P)H Oxidase Contributes to Oxidative Stress in Human Atrial Fibrillation. Circ Res. 2005;97(7):629-636. [CrossRef]
- Shang C, Liu Z, Zhu Y, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Causes Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitophagy Impairment. Front Microbiol. 2022;12. [CrossRef]
- Muszyński P, Bonda TA. Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Atrial Fibrillation—Mechanisms and Pharmacological Interventions. J Clin Med 2021, Vol 10, Page 2385. 2021;10(11):2385. [CrossRef]
- Oudit GY, Wang K, Viveiros A, Kellner MJ, Penninger JM. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2—at the heart of the COVID-19 pandemic. Cell. 2023;186(5):906-922. [CrossRef]
- Jakovac H, Ferenčić A, Stemberger C, Mohar Vitezić B, Cuculić D. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antigens in the AV-Node of a Cardiac Conduction System-A Case Report. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2022;7(3). [CrossRef]
- Ferreira AJ, Moraes PL, Foureaux G, Andrade AB, Santos RAS, Almeida AP. The angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis is expressed in sinoatrial node cells of rats. J Histochem Cytochem. 2011;59(8):761-768. [CrossRef]
- Nádasy GL, Balla A, Cojocaru E, Cojocaru C, Vlad C-E, Eva L. Role of the Renin-Angiotensin System in Long COVID’s Cardiovascular Injuries. Biomed 2023, Vol 11, Page 2004. 2023;11(7):2004. [CrossRef]
- Khazaal S, Harb J, Rima M, et al. The Pathophysiology of Long COVID throughout the Renin-Angiotensin System. Molecules. 2022;27(9). [CrossRef]
- Carpenter RM, Young MK, Petri WAO, et al. Repressed Ang 1-7 in COVID-19 Is Inversely Associated with Inflammation and Coagulation. mSphere. 2022;7(4). [CrossRef]
- Stone E, Kiat H, McLachlan CS. Atrial fibrillation in COVID-19: A review of possible mechanisms. FASEB J. 2020;34(9):11347-11354. [CrossRef]
- Disertori M, Rigoni M, Pace N, et al. Myocardial Fibrosis Assessment by LGE Is a Powerful Predictor of Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias in Ischemic and Nonischemic LV Dysfunction: A Meta-Analysis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016;9(9):1046-1055. [CrossRef]
- McGonagle D, O’Donnell JS, Sharif K, Emery P, Bridgewood C. Immune mechanisms of pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy in COVID-19 pneumonia. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2(7):e437-e445. [CrossRef]
- Levi M, Thachil J, Iba T, Levy JH. Coagulation abnormalities and thrombosis in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(6):e438-e440. [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Panzer B, Józkowicz A, et al. Microvascular Thrombosis as a Critical Factor in Severe COVID-19. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(3):2492. [CrossRef]
- Mehta P, Porter JC, Manson JJ, et al. Therapeutic blockade of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in COVID-19-associated hyperinflammation: challenges and opportunities. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(8):822-830. [CrossRef]
- Hojyo S, Uchida M, Tanaka K, et al. How COVID-19 induces cytokine storm with high mortality. Inflamm Regen. 2020;40(1). [CrossRef]
- Ye Q, Wang B, Mao J. The pathogenesis and treatment of the `Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19. J Infect. 2020;80(6):607-613. [CrossRef]
- Zizzo G, Cohen PL. Imperfect storm: is interleukin-33 the Achilles heel of COVID-19? Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2(12):e779-e790. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y, Wang J, Liu C, et al. IP-10 and MCP-1 as biomarkers associated with disease severity of COVID-19. Mol Med. 2020;26(1). [CrossRef]
- Xu ZS, Shu T, Kang L, et al. Temporal profiling of plasma cytokines, chemokines and growth factors from mild, severe and fatal COVID-19 patients. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1). [CrossRef]
- Del Valle DM, Kim-Schulze S, Huang HH, et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat Med. 2020;26(10):1636-1643. [CrossRef]
- Benest A, V. , Kruse K, Savant S, et al. Angiopoietin-2 is critical for cytokine-induced vascular leakage. PLoS One. 2013;8(8). [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, NG. Cardiac fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res. 2021;117(6):1450-1488. [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar P, Gupta S, Sarkar S, Sen S. Upregulation of lysyl oxidase and MMPs during cardiac remodeling in human dilated cardiomyopathy. Mol Cell Biochem. 2008;307(1-2):159-167. [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutte D, Van Almen GC, Van Aelst LNL, et al. Matricellular proteins and matrix metalloproteinases mark the inflammatory and fibrotic response in human cardiac allograft rejection. Eur Heart J. 2013;34(25):1930-1941. [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutte D, Schellings MWM, Götte M, et al. Increased expression of syndecan-1 protects against cardiac dilatation and dysfunction after myocardial infarction. Circulation. 2007;115(4):475-482. [CrossRef]
- Zhang D, Li L, Chen Y, et al. Syndecan-1, an indicator of endothelial glycocalyx degradation, predicts outcome of patients admitted to an ICU with COVID-19. Mol Med. 2021;27(1). [CrossRef]
- Rovas A, Osiaevi I, Buscher K, et al. Microvascular dysfunction in COVID-19: the MYSTIC study. Angiogenesis. 2021;24(1):145. [CrossRef]
- Goonewardena SN, Grushko OG, Wells J, et al. Immune-Mediated Glycocalyx Remodeling in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2023;37(2):307. [CrossRef]
- Queisser KA, Mellema RA, Middleton EA, et al. COVID-19 generates hyaluronan fragments that directly induce endothelial barrier dysfunction. JCI Insight. 2021;6(17). [CrossRef]
- Buijsers B, Yanginlar C, de Nooijer A, et al. Increased Plasma Heparanase Activity in COVID-19 Patients. Front Immunol. 2020;11. [CrossRef]
- Roshdy A, Zaher S, Fayed H, Coghlan JG. COVID-19 and the Heart: A Systematic Review of Cardiac Autopsies. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;7. [CrossRef]
- Godoy LC, Goligher EC, Lawler PR, Slutsky AS, Zarychanski R. Anticipating and managing coagulopathy and thrombotic manifestations of severe COVID-19. CMAJ. 2020;192(40):E1156-E1161. [CrossRef]
- Denorme F, Vanhoorelbeke K, De Meyer SF. von Willebrand Factor and Platelet Glycoprotein Ib: A Thromboinflammatory Axis in Stroke. Front Immunol. 2019;10:495067.
- Kalagara T, Moutsis T, Yang Y, et al. The endothelial glycocalyx anchors von Willebrand factor fibers to the vascular endothelium. Blood Adv. 2018;2(18):2347-2357. [CrossRef]
- Middleton EA, He X-Y, Denorme F, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to immunothrombosis in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. Blood. 2020;136(10):1169-1179. [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science. 2004;303(5663):1532-1535. [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V. Neutrophil extracellular traps in immunity and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18(2):134-147. [CrossRef]
- Aiyegbusi OL, Hughes SE, Turner G, et al. Symptoms, complications and management of long COVID: a review. J R Soc Med. 2021;114(9):428-442. [CrossRef]
- Logue JK, Franko NM, McCulloch DJ, et al. Sequelae in Adults at 6 Months After COVID-19 Infection. JAMA Netw open. 2021;4(2):e210830. [CrossRef]
- Puntmann VO, Martin S, Shchendrygina A, et al. Long-term cardiac pathology in individuals with mild initial COVID-19 illness. Nat Med. 2022;28(10):2117-2123. [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, L. SARS CoV-2 related microvascular damage and symptoms during and after COVID-19: Consequences of capillary transit-time changes, tissue hypoxia and inflammation. Physiol Rep. 2021;9(3):e14726. [CrossRef]
- Mantovani A, Morrone MC, Patrono C, et al. Long Covid: where we stand and challenges ahead. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(10):1891-1900. [CrossRef]
- Nunn AVW, Guy GW, Brysch W, Bell JD. Understanding Long COVID; Mitochondrial Health and Adaptation—Old Pathways, New Problems. Biomedicines. 2022;10(12). [CrossRef]
- Xian H, Watari K, Sanchez-Lopez E, et al. Oxidized DNA fragments exit mitochondria via mPTP- and VDAC-dependent channels to activate NLRP3 inflammasome and interferon signaling. Immunity. 2022;55(8):1370-1385.e8. [CrossRef]
- Leone O, Pieroni M, Rapezzi C, Olivotto I. The spectrum of myocarditis: from pathology to the clinics. Virchows Arch 2019 4753. 2019;475(3):279-301. [CrossRef]
- Andréoletti L, Lévêque N, Boulagnon C, Brasselet C, Fornes P. Viral causes of human myocarditis. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2009;102(6-7):559-568. [CrossRef]
- Kühl U, Pauschinger M, Seeberg B, et al. Viral Persistence in the Myocardium Is Associated With Progressive Cardiac Dysfunction. Circulation. 2005;112(13):1965-1970. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, LT. Myocarditis. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(15):1526-1538. [CrossRef]
- Jeserich M, Brunner E, Kandolf R, et al. Diagnosis of viral myocarditis by cardiac magnetic resonance and viral genome detection in peripheral blood. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;29(1):121-129. [CrossRef]
- Schultheiss H-P, Baumeier C, Aleshcheva G, Bock C-T, Escher F. Viral Myocarditis—From Pathophysiology to Treatment. J Clin Med. 2021;10(22):5240. [CrossRef]
- Verdonschot J, Hazebroek M, Merken J, et al. Relevance of cardiac parvovirus B19 in myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy: review of the literature. Eur J Heart Fail. 2016;18(12):1430-1441. [CrossRef]
- Escher F, Kühl U, Gross U, et al. Aggravation of left ventricular dysfunction in patients with biopsy-proven cardiac human herpesvirus A and B infection. J Clin Virol. 2015;63:1-5. [CrossRef]
- Bonavita CM, Cardin RD. Don’t Go Breaking My Heart: MCMV as a Model for HCMV-Associated Cardiovascular Diseases. Pathog (Basel, Switzerland). 2021;10(5). [CrossRef]
- Magno Palmeira M, Umemura Ribeiro HY, Garcia Lira Y, et al. Heart failure due to cytomegalovirus myocarditis in immunocompetent young adults: a case report. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9(1). [CrossRef]
- Roubille C, Brunel AS, Gahide G, Kovacsik HV, Le Quellec A. Cytomegalovirus (CMV) and acute myocarditis in an immunocompetent patient. Intern Med. 2010;49(2):131-133. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe M, Panetta GL, Piccirillo F, et al. Acute Epstein-Barr related myocarditis: An unusual but life-threatening disease in an immunocompetent patient. J Cardiol cases. 2019;21(4):137-140. [CrossRef]
- Schultheiss HP, Piper C, Sowade O, et al. Betaferon in chronic viral cardiomyopathy (BICC) trial: Effects of interferon-β treatment in patients with chronic viral cardiomyopathy. Clin Res Cardiol. 2016;105(9):763-773. [CrossRef]
- Pauschinger M, Bowles NE, Fuentes-Garcia FJ, et al. Detection of adenoviral genome in the myocardium of adult patients with idiopathic left ventricular dysfunction. Circulation. 1999;99(10):1348-1354. [CrossRef]
- Ilyas SZ, Tabassum R, Hamed H, Rehman SU, Qadri I. Hepatitis C Virus-Associated Extrahepatic Manifestations in Lung and Heart and Antiviral Therapy-Related Cardiopulmonary Toxicity. Viral Immunol. 2017;30(9):633-641. [CrossRef]
- Matsumori A, Matoba Y, Sasayama S. Dilated cardiomyopathy associated with hepatitis C virus infection. Circulation. 1995;92(9):2519-2525. [CrossRef]
- Matsumori A, Shimada T, Chapman NM, Tracy SM, Mason JW. Myocarditis and heart failure associated with hepatitis C virus infection. J Card Fail. 2006;12(4):293-298. [CrossRef]
- Mathez G, Cagno V. Viruses Like Sugars: How to Assess Glycan Involvement in Viral Attachment. Microorganisms. 2021;9(6). [CrossRef]
- Cagno V, Tseligka ED, Jones ST, Tapparel C. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Viral Attachment: True Receptors or Adaptation Bias? Viruses. 2019;11(7). [CrossRef]
- Pickles RJ, Fahrner JA, Petrella JM, Boucher RC, Bergelson JM. Retargeting the coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor to the apical surface of polarized epithelial cells reveals the glycocalyx as a barrier to adenovirus-mediated gene transfer. J Virol. 2000;74(13):6050-6057. [CrossRef]
- Targosz-Korecka M, Kubisiak A, Kloska D, Kopacz A, Grochot-Przeczek A, Szymonski M. Endothelial glycocalyx shields the interaction of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with ACE2 receptors. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1). [CrossRef]
- Zhou R, Liu L, Wang Y. Viral proteins recognized by different TLRs. J Med Virol. 2021;93(11):6116-6123. [CrossRef]
- Choudhury A, Mukherjee S. In silico studies on the comparative characterization of the interactions of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein with ACE-2 receptor homologs and human TLRs. J Med Virol. 2020;92(10):2105-2113. [CrossRef]
- Katare PB, Nizami HL, Paramesha B, Dinda AK, Banerjee SK. Activation of toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis through SIRT2 dependent p53 deacetylation. Sci Reports 2020 101. 2020;10(1):1-15. [CrossRef]
- Garmaroudi FS, Marchant D, Hendry R, et al. Coxsackievirus B3 replication and pathogenesis. Future Microbiol. 2015;10(4):629-653. [CrossRef]
- Hsu TC, Wu WJ, Chen MC, Tsay GJ. Human parvovirus B19 non-structural protein (NS1) induces apoptosis through mitochondria cell death pathway in COS-7 cells. Scand J Infect Dis. 2004;36(8):570-577. [CrossRef]
- Bachelier K, Biehl S, Schwarz V, et al. Parvovirus B19-induced vascular damage in the heart is associated with elevated circulating endothelial microparticles. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0176311. [CrossRef]
- Vallbracht KB, Schwimmbeck PL, Kühl U, Seeberg B, Schultheiss HP. Endothelium-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of systemic arteries is impaired in patients with myocardial virus persistence. Circulation. 2004;110(18):2938-2945. [CrossRef]
- Belkin MN, Uriel N. Heart health in the age of highly active antiretroviral therapy: A review of HIV cardiomyopathy. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2018;33(3):317-324. [CrossRef]
- Matsumori A, Yamada T, Suzuki H, Matoba Y, Sasayama S. Increased circulating cytokines in patients with myocarditis and cardiomyopathy. Heart. 1994;72(6):561-566. [CrossRef]
- Kawai, C. From Myocarditis to Cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms of Inflammation and Cell Death. Circulation. 1999;99(8):1091-1100. [CrossRef]
- Neu C, Thiele Y, Horr F, et al. DAMPs Released from Proinflammatory Macrophages Induce Inflammation in Cardiomyocytes via Activation of TLR4 and TNFR. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(24). [CrossRef]
- Lavine KJ, Pinto AR, Epelman S, et al. The Macrophage in Cardiac Homeostasis and Disease: JACC Macrophage in CVD Series. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72(18):2213. [CrossRef]
- Magnani JW, Suk Danik HJ, Dec GW, DiSalvo TG. Survival in biopsy-proven myocarditis: A long-term retrospective analysis of the histopathologic, clinical, and hemodynamic predictors. Am Heart J. 2006;151(2):463-470. [CrossRef]
- Feldman AM, McNamara D. Myocarditis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(19):1388-1398. [CrossRef]
- Zaragoza C, Ocampo C, Saura M, et al. The role of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the host response to Coxsackievirus myocarditis. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1998;95(5):2469-2474. [CrossRef]
- Kühl U, Lassner D, Pauschinger M, et al. Prevalence of erythrovirus genotypes in the myocardium of patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. J Med Virol. 2008;80(7):1243-1251. [CrossRef]
- Kühl U, Pauschinger M, Noutsias M, et al. High prevalence of viral genomes and multiple viral infections in the myocardium of adults with “idiopathic” left ventricular dysfunction. Circulation. 2005;111(7):887-893. [CrossRef]
- Kühl U, Lassner D, Von Schlippenbach J, Poller W, Schultheiss HP. Interferon-Beta improves survival in enterovirus-associated cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(14):1295-1296. [CrossRef]
- Pauschinger M, Doerner A, Kuehl U, et al. Enteroviral RNA replication in the myocardium of patients with left ventricular dysfunction and clinically suspected myocarditis. Circulation. 1999;99(7):889-895. [CrossRef]
- Pietsch H, Escher F, Aleshcheva G, Lassner D, Bock CT, Schultheiss HP. Detection of parvovirus mRNAs as markers for viral activity in endomyocardial biopsy-based diagnosis of patients with unexplained heart failure. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1). [CrossRef]
- Kuhl U, Lassner D, Dorner A, et al. A distinct subgroup of cardiomyopathy patients characterized by transcriptionally active cardiotropic erythrovirus and altered cardiac gene expression. Basic Res Cardiol. 2013;108(5). [CrossRef]
- Fairweather DL, Frisancho-Kiss S, Rose NR. Viruses as adjuvants for autoimmunity: evidence from Coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis. Rev Med Virol. 2005;15(1):17-27. [CrossRef]
- Esfandiarei M, McManus BM. Molecular biology and pathogenesis of viral myocarditis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2008;3:127-155. [CrossRef]
- Huber, S. Viral Myocarditis and Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Etiology and Pathogenesis. Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(4):408-426. [CrossRef]
- Rose, NR. Viral myocarditis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28(4):383-389. [CrossRef]
- Bracamonte-Baran W, Čiháková D. Cardiac Autoimmunity: Myocarditis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1003:187-221. [CrossRef]
- Kawai, C. From myocarditis to cardiomyopathy: mechanisms of inflammation and cell death: learning from the past for the future. Circulation. 1999;99(8):1091-1100. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, MW. T cell mimicry in inflammatory heart disease. Mol Immunol. 2004;40(14-15):1121-1127. [CrossRef]
- Elamm C, Fairweather DL, Cooper LT. Republished: pathogenesis and diagnosis of myocarditis. Postgrad Med J. 2012;88(1043):539-544. [CrossRef]
- Monda E, Palmiero G, Rubino M, et al. Molecular Basis of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Cardiomyopathies. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):1-14. [CrossRef]
- Heymans S, Eriksson U, Lehtonen J, Cooper LT. The Quest for New Approaches in Myocarditis and Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68(21):2348-2364. [CrossRef]
- Westermann D, Lindner D, Kasner M, et al. Cardiac inflammation contributes to changes in the extracellular matrix in patients with heart failure and normal ejection fraction. Circ Heart Fail. 2011;4(1):44-52. [CrossRef]
- Huang LY, Halder S, Agbandje-Mckenna M. Parvovirus glycan interactions. Curr Opin Virol. 2014;7(1):108-118. [CrossRef]
- Conti C, Cirone M, Sgro R, Altieri F, Zompetta C, Faggioni A. Early interactions of human herpesvirus 6 with lymphoid cells: role of membrane protein components and glycosaminoglycans in virus binding. J Med Virol. 2000;62(4):487-497. [CrossRef]
- Hadigal S, Koganti R, Yadavalli T, Agelidis A, Suryawanshi R, Shukla D. Heparanase-Regulated Syndecan-1 Shedding Facilitates Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Egress. J Virol. 2020;94(6). [CrossRef]
- Connolly SA, Jardetzky TS, Longnecker R. The structural basis of herpesvirus entry. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19(2):110. [CrossRef]
- Stuhlmeier, KM. Hyaluronan production in synoviocytes as a consequence of viral infections: HAS1 activation by Epstein-Barr virus and synthetic double- and single-stranded viral RNA analogs. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(24):16781-16789. [CrossRef]
- Mitra D, Hasan MH, Bates JT, et al. The degree of polymerization and sulfation patterns in heparan sulfate are critical determinants of cytomegalovirus entry into host cells. PLoS Pathog. 2021;17(8). [CrossRef]
- Compton T, Nowlin DM, Cooper NR. Initiation of human cytomegalovirus infection requires initial interaction with cell surface heparan sulfate. Virology. 1993;193(2):834-841. [CrossRef]
- McLeish NJ, Williams ÇH, Kaloudas D, Roivainen MM, Stanway G. Symmetry-related clustering of positive charges is a common mechanism for heparan sulfate binding in enteroviruses. J Virol. 2012;86(20):11163-11170. [CrossRef]
- Tan CW, Poh CL, Sam I-C, Chan YF. Enterovirus 71 uses cell surface heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan as an attachment receptor. J Virol. 2013;87(1):611-620. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi K, Koike S. Cellular receptors for enterovirus A71. J Biomed Sci. 2020;27(1). [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Martínez IE, Ramos-Martínez E, Segura-Velázquez RÁ, et al. Heparan Sulfate and Sialic Acid in Viral Attachment: Two Sides of the Same Coin? Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(17). [CrossRef]
- Schröer K, Alshawabkeh M, Schellhorn S, Bronder K, Zhang W, Ehrhardt A. Influence of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Factor X on species D Human Adenovirus Uptake and Transduction. Viruses. 2022;15(1). [CrossRef]
- Fender P, Schoehn G, Perron-Sierra F, Tucker GC, Lortat-Jacob H. Adenovirus dodecahedron cell attachment and entry are mediated by heparan sulfate and integrins and vary along the cell cycle. Virology. 2008;371(1):155-164. [CrossRef]
- Grigorov B, Reungoat E, Gentil dit Maurin A, et al. Hepatitis C virus infection propagates through interactions between Syndecan-1 and CD81 and impacts the hepatocyte glycocalyx. Cell Microbiol. 2017;19(5). [CrossRef]
- Zhang F, Sodroski C, Cha H, Li Q, Liang TJ. Infection of Hepatocytes With HCV Increases Cell Surface Levels of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans, Uptake of Cholesterol and Lipoprotein, and Virus Entry by Up-regulating SMAD6 and SMAD7. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(1):257-270.e7. [CrossRef]
- Cerezo-Magaña M, Bång-Rudenstam A, Belting M. Proteoglycans: a common portal for SARS-CoV-2 and extracellular vesicle uptake. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023;324(1):C76-C84. [CrossRef]
- Bell TJ, Brand OJ, Morgan DJ, et al. Defective lung function following influenza virus is due to prolonged, reversible hyaluronan synthesis. Matrix Biol. 2019;80:14-28. [CrossRef]
- Corrado D, Basso C, Thiene G. Sudden cardiac death in young people with apparently normal heart. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;50(2):399-408. [CrossRef]
- Tschöpe C, Ammirati E, Bozkurt B, et al. Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: current evidence and future directions. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2021;18(3):169-193. [CrossRef]
- Baksi AJ, Kanaganayagam GS, Prasad SK. Arrhythmias in viral myocarditis and pericarditis. Card Electrophysiol Clin. 2015;7(2):269-281. [CrossRef]
- Peretto G, Sala S, Rizzo S, et al. Ventricular Arrhythmias in Myocarditis: Characterization and Relationships With Myocardial Inflammation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75(9):1046-1057. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira VM, Piechnik SK, Dall’Armellina E, et al. Native T1-mapping detects the location, extent and patterns of acute myocarditis without the need for gadolinium contrast agents. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2014;16(1). [CrossRef]
- Ammirati E, Moroni F, Sormani P, et al. Quantitative changes in late gadolinium enhancement at cardiac magnetic resonance in the early phase of acute myocarditis. Int J Cardiol. 2017;231:216-221. [CrossRef]
- Harrison JL, Jensen HK, Peel SA, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance and electroanatomical mapping of acute and chronic atrial ablation injury: a histological validation study. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(22):1486-1495. [CrossRef]
- Dickfeld T, Tian J, Ahmad G, et al. MRI-Guided ventricular tachycardia ablation: integration of late gadolinium-enhanced 3D scar in patients with implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2011;4(2):172-184. [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Armenta J, Berruezo A, Andreu D, et al. Three-dimensional architecture of scar and conducting channels based on high resolution ce-CMR: insights for ventricular tachycardia ablation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2013;6(3):528-537. [CrossRef]
- Perez-David E, Arenal Á, Rubio-Guivernau JL, et al. Noninvasive identification of ventricular tachycardia-related conducting channels using contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in patients with chronic myocardial infarction: comparison of signal intensity scar mapping and endocardial voltage mappin. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57(2):184-194. [CrossRef]
- Zeppenfeld K, Tfelt-Hansen J, de Riva M, et al. 2022 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with ventricular arrhythmias and the prevention of sudden cardiac death Developed by the task force for the management of patients with death of the European Society of Cardiology ( ESC ) Endorsed by the. Eur Heart J. Published online 2022:1-130. [CrossRef]
- Nagai T, Inomata T, Kohno T, et al. JCS 2023 Guideline on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Myocarditis. Circ J. 2023;87(5):674-754. [CrossRef]
- Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(25):2982-3021. [CrossRef]
- Stolfo D, Collini V, Sinagra G. Advanced Heart Failure in Special Population: Cardiomyopathies and Myocarditis. Heart Fail Clin. 2021;17(4):661-672. [CrossRef]
- Pozzi M, Banfi C, Grinberg D, et al. Veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for cardiogenic shock due to myocarditis in adult patients. J Thorac Dis. 2016;8(7):E495. [CrossRef]
- Combes A, Price S, Slutsky AS, Brodie D. Temporary circulatory support for cardiogenic shock. Lancet. 2020;396(10245):199-212. [CrossRef]
- Means, RT. The anaemia of infection. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2000;13(2):151-162. [CrossRef]
- Bellmann-Weiler R, Lanser L, Barket R, et al. Prevalence and Predictive Value of Anemia and Dysregulated Iron Homeostasis in Patients with COVID-19 Infection. J Clin Med. 2020;9(8):1-11. [CrossRef]
- Giustino G, Kirtane AJ, Baber U, et al. Impact of Anemia on Platelet Reactivity and Ischemic and Bleeding Risk: From the Assessment of Dual Antiplatelet Therapy With Drug-Eluting Stents Study. Am J Cardiol. 2016;117(12):1877-1883. [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Kopp CW, Koppensteiner R, et al. Decreased platelet inhibition by P2Y12 receptor blockers in anaemia. Eur J Clin Invest. 2018;48(1):e12861. [CrossRef]
- Ammirati E, Bizzi E, Veronese G, et al. Immunomodulating Therapies in Acute Myocarditis and Recurrent/Acute Pericarditis. Front Med. 2022;9:838564.
- Schultheiss HP, Khl U, Cooper LT. The management of myocarditis. Eur Heart J. 2011;32(21):2616-2625. [CrossRef]
- Lampejo T, Durkin SM, Bhatt N, Guttmann O. Acute myocarditis: aetiology, diagnosis and management. Clin Med (Northfield Il). 2021;21(5):e505. [CrossRef]
- Bang V, Ganatra S, Shah SP, et al. Management of Patients With Giant Cell Myocarditis: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77(8):1122-1134. [CrossRef]
- Cremer PC, Sheng CC, Sahoo D, et al. Double-blind randomized proof-of-concept trial of canakinumab in patients with COVID-19 associated cardiac injury and heightened inflammation. Eur Hear J Open. 2021;1(1). [CrossRef]
- Xu J, Zhou Z, Zheng Y, Yang S, Huang K, Li H. Roles of inflammasomes in viral myocarditis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023;13:1149911.
- van de Veerdonk FL, Giamarellos-Bourboulis E, Pickkers P, et al. A guide to immunotherapy for COVID-19. Nat Med 2022 281. 2022;28(1):39-50. [CrossRef]
- Ammirati E, Frigerio M, Adler ED, et al. Management of Acute Myocarditis and Chronic Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy: An Expert Consensus Document. Circ Heart Fail. 2020;13(11):e007405. [CrossRef]
- Merken J, Hazebroek M, Van Paassen P, et al. Immunosuppressive Therapy Improves Both Short- and Long-Term Prognosis in Patients With Virus-Negative Nonfulminant Inflammatory Cardiomyopathy. Circ Heart Fail. 2018;11(2):e004228. [CrossRef]
- Peretto G, Sala S, Luca G De, et al. Immunosuppressive Therapy and Risk Stratification of Patients With Myocarditis Presenting With Ventricular Arrhythmias. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2020;6(10):1221-1234. [CrossRef]
- Abernethy A, Raza S, Sun JL, et al. Pro-Inflammatory Biomarkers in Stable Versus Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. J Am Hear Assoc Cardiovasc Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018;7(8). [CrossRef]
- Wijk SS-V, Empel V Van, Davarzani N, et al. Circulating biomarkers of distinct pathophysiological pathways in heart failure with preserved vs. reduced left ventricular ejection fraction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015;17(10):1006-1014. [CrossRef]
- Hanna A, Frangogiannis NG. Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines as Therapeutic Targets in Heart Failure. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2020;34(6):849. [CrossRef]
- Bajaj NS, Gupta K, Gharpure N, et al. Effect of immunomodulation on cardiac remodelling and outcomes in heart failure: a quantitative synthesis of the literature. ESC Hear Fail. 2020;7(3):1319-1330. [CrossRef]
- Mann DL, McMurray JJV, Packer M, et al. Targeted Anticytokine Therapy in Patients With Chronic Heart Failure. Circulation. 2004;109(13):1594-1602. [CrossRef]
- Chung ES, Packer M, Lo KH, Fasanmade AA, Willerson JT. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, pilot trial of infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in patients with moderate-to-severe heart failure: results of the anti-TNF Therapy Against Congestive Heart Failure (AT. Circulation. 2003;107(25):3133-3140. [CrossRef]
- Paulus WJ, Zile MR. FROM SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATION TO MYOCARDIAL FIBROSIS: THE HFPEF PARADIGM REVISITED. Circ Res. 2021;128(10):1451. [CrossRef]
- Ning N, Guo HH, Iagaru A, Mittra E, Fowler M, Witteles R. Serial Cardiac FDG-PET for the Diagnosis and Therapeutic Guidance of Patients With Cardiac Sarcoidosis. J Card Fail. 2019;25(4):307-311. [CrossRef]
- Shelke AB, Aurangabadkar HU, Bradfield JS, Ali Z, Kumar KS, Narasimhan C. Serial FDG-PET scans help to identify steroid resistance in cardiac sarcoidosis. Int J Cardiol. 2017;228:717-722. [CrossRef]
- Terasaki F, Azuma A, Anzai T, et al. JCS 2016 Guideline on Diagnosis and Treatment of Cardiac Sarcoidosis - Digest Version. Circ J. 2019;83(11):2329-2388. [CrossRef]
- Birnie DH, Sauer WH, Bogun F, et al. HRS expert consensus statement on the diagnosis and management of arrhythmias associated with cardiac sarcoidosis. Hear Rhythm. 2014;11(7):1304-1323. [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2022;145(18):E876-E894. [CrossRef]
- McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. 2023 Focused Update of the 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(37). [CrossRef]
- Zeng S, Delic D, Chu C, et al. Antifibrotic effects of low dose SGLT2 Inhibition with empagliflozin in comparison to Ang II receptor blockade with telmisartan in 5/6 nephrectomised rats on high salt diet. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;146:112606. [CrossRef]
- Li C, Zhang J, Xue M, et al. SGLT2 inhibition with empagliflozin attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and fibrosis in diabetic mice heart. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18(1):1-13.
- Kosiborod MN, Esterline R, Furtado RHM, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with cardiometabolic risk factors hospitalised with COVID-19 (DARE-19): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(9):586-594. [CrossRef]
- SGLT2 inhibitors not linked with improved survival in hospitalised COVID-19 patients. Accessed December 3, 2023. https://www.escardio.org/The-ESC/Press-Office/Press-releases/SGLT2-inhibitors-notlinked-with-improved-survival-in-hospitalised-COVID-19-patients.
- Abani O, Abbas A, Abbas F, et al. Empagliflozin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023;11(12):905-914. [CrossRef]
- Pitt B, Agarwal R, Anker SD, et al. Association of Finerenone Use With Reduction in Treatment-Emergent Pneumonia and COVID-19 Adverse Events Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A FIDELITY Pooled Secondary Analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(10):e2236123-e2236123. [CrossRef]
- Henri O, Pouehe C, Houssari M, et al. Selective Stimulation of Cardiac Lymphangiogenesis Reduces Myocardial Edema and Fibrosis Leading to Improved Cardiac Function Following Myocardial Infarction. Circulation. 2016;133(15):1484-1497. [CrossRef]
- Schultheiss HP, Bock CT, Aleshcheva G, Baumeier C, Poller W, Escher F. Interferon-β Suppresses Transcriptionally Active Parvovirus B19 Infection in Viral Cardiomyopathy: A Subgroup Analysis of the BICC-Trial. Viruses. 2022;14(2). [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Lucke C, Spillmann F, Bock T, et al. Interferon beta modulates endothelial damage in patients with cardiac persistence of human parvovirus b19 infection. J Infect Dis. 2010;201(6):936-945. [CrossRef]
- Anzai A, Mindur JE, Halle L, et al. Self-reactive CD4+ IL-3+ T cells amplify autoimmune inflammation in myocarditis by inciting monocyte chemotaxis. J Exp Med. 2019;216(2):369. [CrossRef]
- Ammirati E, Varrenti M, Veronese G, et al. Prevalence and outcome of patients with acute myocarditis and positive viral search on nasopharyngeal swab. Eur J Heart Fail. 2021;23(7):1242-1245. [CrossRef]
- Gil-Cruz C, Perez-Shibayama C, de Martin A, et al. Microbiota-derived peptide mimics drive lethal inflammatory cardiomyopathy. Science. 2019;366(6467):881-886. [CrossRef]
- Amdani SM, Kim HS, Orvedahl A, John AO, Said A, Simpson K. Successful treatment of fulminant neonatal enteroviral myocarditis in monochorionic diamniotic twins with cardiopulmonary support, intravenous immunoglobulin and pocapavir. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;2018. [CrossRef]
- Abzug MJ, Michaels MG, Wald E, et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Pleconaril for the Treatment of Neonates With Enterovirus Sepsis. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2016;5(1):53-62. [CrossRef]
- Yen MH, Huang YC, Chen MC, et al. Effect of intravenous immunoglobulin for neonates with severe enteroviral infections with emphasis on the timing of administration. J Clin Virol. 2015;64:92-96. [CrossRef]
- Kühl U, Lassner D, Wallaschek N, et al. Chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6 in heart failure: prevalence and treatment. Eur J Heart Fail. 2015;17(1):9-19. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez MJ, Bergasa N V. Hepatitis C associated cardiomyopathy: potential pathogenic mechanisms and clinical implications. Med Sci Monit. 2008;14(5):RA55-63. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih. 1844.
- Baik SH, Jeong HS, Kim SJ, Yoon YK, Sohn JW, Kim MJ. A Case of Influenza Associated Fulminant Myocarditis Successfully Treated with Intravenous Peramivir. Infect Chemother. 2015;47(4):272-277. [CrossRef]
- Ito N, Sato M, Momoi N, et al. Influenza A H1N1 pdm09-associated myocarditis during zanamivir therapy. Pediatr Int. 2015;57(6):1172-1174. [CrossRef]
- Manaresi E, Gallinella G. Advances in the Development of Antiviral Strategies against Parvovirus B19. Viruses. 2019;11(7). [CrossRef]
- Düngen HD, Dordevic A, Felix SB, et al. β1-Adrenoreceptor Autoantibodies in Heart Failure: Physiology and Therapeutic Implications. Circ Heart Fail. 2020;13(1). [CrossRef]
- Li G, Hilgenfeld R, Whitley R, Clercq E De. Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023;22(6):449. [CrossRef]
- Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1824-1836. [CrossRef]
- Zhou D, Dai SM, Tong Q. COVID-19: a recommendation to examine the effect of hydroxychloroquine in preventing infection and progression. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(7):1667-1670. [CrossRef]
- Rout A, Tantry US, Novakovic M, Sukhi A, Gurbel PA. Targeted pharmacotherapy for ischemia reperfusion injury in acute myocardial infarction. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020;21(15):1851-1865. [CrossRef]
- Hentia C, Rizzato A, Camporesi E, et al. An overview of protective strategies against ischemia/reperfusion injury: The role of hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning. Brain Behav. 2018;8(5):e00959. [CrossRef]
- Heusch, G. Myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020;17(12):773-789. [CrossRef]
- Bruegger D, Rehm M, Jacob M, et al. Exogenous nitric oxide requires an endothelial glycocalyx to prevent postischemic coronary vascular leak in guinea pig hearts. Crit Care. 2008;12(3). [CrossRef]
- Koch E, Malek FA. Standardized Extracts from Hawthorn Leaves and Flowers in the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disorders – Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Planta Med. 2011;77(11):1123-1128. [CrossRef]
- Ebong EE, Lopez-Quintero S V., Rizzo V, Spray DC, Tarbell JM. Shear-induced endothelial NOS activation and remodeling via heparan sulfate, glypican-1, and syndecan-1. Integr Biol. 2014;6(3):338-347. [CrossRef]
- Peters W, Drueppel V, Kusche-Vihrog K, Schubert C, Oberleithner H. Nanomechanics and Sodium Permeability of Endothelial Surface Layer Modulated by Hawthorn Extract WS 1442. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29972. [CrossRef]
- Andreas M, Schmid AI, Keilani M, et al. Effect of ischemic preconditioning in skeletal muscle measured by functional magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy: a randomized crossover trial. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2011;13(1):32. [CrossRef]
- Broekhuizen LN, Lemkes BA, Mooij HL, et al. Effect of sulodexide on endothelial glycocalyx and vascular permeability in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2010;53(12):2646-2655. [CrossRef]
- Illien-Junger S, Grosjean F, Laudier DM, Vlassara H, Striker GE, Iatridis JC. Combined anti-inflammatory and anti-AGE drug treatments have a protective effect on intervertebral discs in mice with diabetes. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e64302. [CrossRef]
- Salmon AHJ, Ferguson JK, Burford JL, et al. Loss of the endothelial glycocalyx links albuminuria and vascular dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2012;23(8):1339-1350. [CrossRef]
- Harada N, Maeda M. Chemical structure of antithrombin-active rhamnan sulfate from monostrom nitidum. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1998;62(9):1647-1652. [CrossRef]
- Giantsos-Adams K, Lopez-Quintero V, Kopeckova P, Kopecek J, Tarbell JM, Dull R. Study of the therapeutic benefit of cationic copolymer administration to vascular endothelium under mechanical stress. Biomaterials. 2011;32(1):288-294. [CrossRef]
- Masola V, Zaza G, Onisto M, Lupo A, Gambaro G. Glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans and sulodexide and the endothelium: biological roles and pharmacological effects. Int Angiol. 2014;33(3):243-254. Accessed August 30, 2023. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24936533/.
- Frati Munari, AC. [Medical significance of endothelial glycocalyx. Part 2: Its role in vascular diseases and in diabetic complications]. Arch Cardiol Mex. 2014;84(2):110-116. [CrossRef]
- Taneja, R. Current status of oral pentosan polysulphate in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int Urogynecol J. 2021;32(5):1107-1115. [CrossRef]
- Cancel LM, Tarbell JM. Rhamnan sulfate enhances the endothelial glycocalyx and decreases the LDL permeability of human coronary artery endothelial cells in vitro. FASEB J. 2013;27(S1):896.3-896.3. [CrossRef]
- Merchant SH, Gurule DM, Larson RS. Amelioration of ischemia-reperfusion injury with cyclic peptide blockade of ICAM-1. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;284(4):H1260-8. [CrossRef]
- Kozar RA, Peng Z, Zhang R, et al. Plasma restoration of endothelial glycocalyx in a rodent model of hemorrhagic shock. Anesth Analg. 2011;112(6):1289-1295. [CrossRef]
- Suarez JI, Martin RH, Calvillo E, Bershad EM, Venkatasubba Rao CP. Effect of human albumin on TCD vasospasm, DCI, and cerebral infarction in subarachnoid hemorrhage: the ALISAH study. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2015;120:287-290. [CrossRef]
- Curry F-RE, Adamson RH. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and the “albumin effect” on rat venular microvessels. FASEB J. 2013;27(S1):896.2-896.2. [CrossRef]
- Bonaventura A, Vecchié A, Dagna L, et al. Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21(5):319-329. [CrossRef]
- Conway EM, Mackman N, Warren RQ, et al. Understanding COVID-19-associated coagulopathy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2022;22(10):639-649. [CrossRef]
- Carnevale R, Cammisotto V, Bartimoccia S, et al. Toll-Like Receptor 4-Dependent Platelet-Related Thrombosis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Circ Res. 2023;132(3):290-305. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H, Lao Q, Zhang J, Zhu J. Coagulopathy in COVID-19 and anticoagulation clinical trials. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2022;35(3):101377. [CrossRef]
- Chandra A, Chakraborty U, Ghosh S, Dasgupta S. Anticoagulation in COVID-19: current concepts and controversies. Postgrad Med J. 2022;98(1159):395-402. [CrossRef]
- Yadav P, Kumar D, Meena DS, et al. Post-Discharge Prophylactic Anticoagulation in COVID-19 Patients: A Clinical Dilemma. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(3):206-209. [CrossRef]
- Stone GW, Farkouh ME, Lala A, et al. Randomized Trial of Anticoagulation Strategies for Noncritically Ill Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;81(18):1747. [CrossRef]
- He, B. Viruses, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and interferon responses. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13(3):393-403. [CrossRef]
- Hur, S. Double-Stranded RNA Sensors and Modulators in Innate Immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2019;37:349-375. [CrossRef]
- Liddell, JR. Are Astrocytes the Predominant Cell Type for Activation of Nrf2 in Aging and Neurodegeneration? Antioxidants 2017, Vol 6, Page 65. 2017;6(3):65. [CrossRef]
- Vivarini áislan de C, Calegari-Silva TC, Saliba AM, et al. Systems approach reveals nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/protein kinase r crosstalk in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Front Immunol. 2017;8(SEP):283936.
- Andreas M, Schmid AI, Doberer D, et al. Heme arginate improves reperfusion patterns after ischemia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial in healthy male subjects. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2012;14(1). [CrossRef]
- Hangaishi M, Ishizaka N, Aizawa T, et al. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 can act protectively against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;279(2):582-588. [CrossRef]
- Li W, Zhang B, Wei X, Cui X, Kobayashi T. Effects of heme oxygenase 1 on brain edema and neurologic outcome after cardiopulmonary resuscitation in rats. Anesthesiology. 2008;109(2):260-268. [CrossRef]
- Ligi D, Lo Sasso B, Giglio RV, et al. Circulating histones contribute to monocyte and MDW alterations as common mediators in classical and COVID-19 sepsis. Crit Care. 2022;26(1). [CrossRef]
- Semeraro F, Ammollo CT, Morrissey JH, et al. Extracellular histones promote thrombin generation through platelet-dependent mechanisms: involvement of platelet TLR2 and TLR4. Blood. 2011;118(7):1952-1961. [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Eichelberger B, Kopp CW, et al. Disaggregation Following Agonist-Induced Platelet Activation in Patients on Dual Antiplatelet Therapy. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2017;10(4):359-367. [CrossRef]
- Panzer B, Wadowski PP, Huber K, Panzer S, Gremmel T. Protease-activated receptor-mediated platelet aggregation in patients with type 2 diabetes on potent P2Y12 inhibitors. Diabet Med. 2022;39(8). [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Pultar J, Weikert C, et al. Protease-activated receptor-mediated platelet aggregation in acute coronary syndrome patients on potent P2Y12 inhibitors. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2019;3(3):383-390. [CrossRef]
- Ofosu FA, Dewar L, Craven SJ, et al. Coordinate activation of human platelet protease-activated receptor-1 and -4 in response to subnanomolar alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(40):26886-26893. [CrossRef]
- Gremmel T, Michelson AD, Wadowski PP, et al. Sex-specific platelet activation through protease-activated receptor-1 in patients undergoing cardiac catheterization. Atherosclerosis. 2021;339:12-19. [CrossRef]
- Wadowski PP, Weikert C, Pultar J, et al. Ticagrelor Inhibits Toll-Like and Protease-Activated Receptor Mediated Platelet Activation in Acute Coronary Syndromes. Cardiovasc drugs Ther. 2020;34(1):53-63. [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heijden M, Van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Koolwijk P, Van Hinsbergh VWM, Groeneveld ABJ. Angiopoietin-2, permeability oedema, occurrence and severity of ALI/ARDS in septic and non-septic critically ill patients. Thorax. 2008;63(10):903-909. [CrossRef]
- Rau A, Schroeter N, Blazhenets G, et al. Widespread white matter oedema in subacute COVID-19 patients with neurological symptoms. Brain. 2022;145(9):3203-3213. [CrossRef]
- Bocci M, Oudenaarden C, Sàenz-sardà X, et al. Infection of brain pericytes underlying neuropathology of covid-19 patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11622.
- Stein SR, Ramelli SC, Grazioli A, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection and persistence in the human body and brain at autopsy. Nature. 2022;612(7941):758-763. [CrossRef]
- Davis HE, McCorkell L, Vogel JM, Topol EJ. Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat Rev Microbiol 2023 213. 2023;21(3):133-146. [CrossRef]
- Panagiotides NG, Zimprich F, Machold K, et al. A Case of Autoimmune Small Fiber Neuropathy as Possible Post COVID Sequelae. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(6). [CrossRef]
- Jones OY, Yeralan S. Is Long COVID a State of Systemic Pericyte Disarray? J Clin Med. 2022;11(3). [CrossRef]
- Abdi A, AlOtaiby S, Badarin F Al, Khraibi A, Hamdan H, Nader M. Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 with cardiomyocytes: Insight into the underlying molecular mechanisms of cardiac injury and pharmacotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;146:112518. [CrossRef]
- Delorey TM, Ziegler CGK, Heimberg G, et al. COVID-19 tissue atlases reveal SARS-CoV-2 pathology and cellulartargets. Nature. 2021;595(7865):107. [CrossRef]
- Katwa LC, Mendoza C, Clements M. CVD and COVID-19: Emerging Roles of Cardiac Fibroblasts and Myofibroblasts. Cells. 2022;11(8). [CrossRef]
- Daems M, Liesenborghs L, Boudewijns R, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection causes prolonged cardiomyocyte swelling and inhibition of HIF1α translocation in an animal model COVID-19. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:964512.
- Avolio E, Carrabba M, Milligan R, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein disrupts human cardiac pericytes function through CD147 receptor-mediated signalling: a potential non-infective mechanism of COVID-19 microvascular disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021;135(24):2667-2689. [CrossRef]
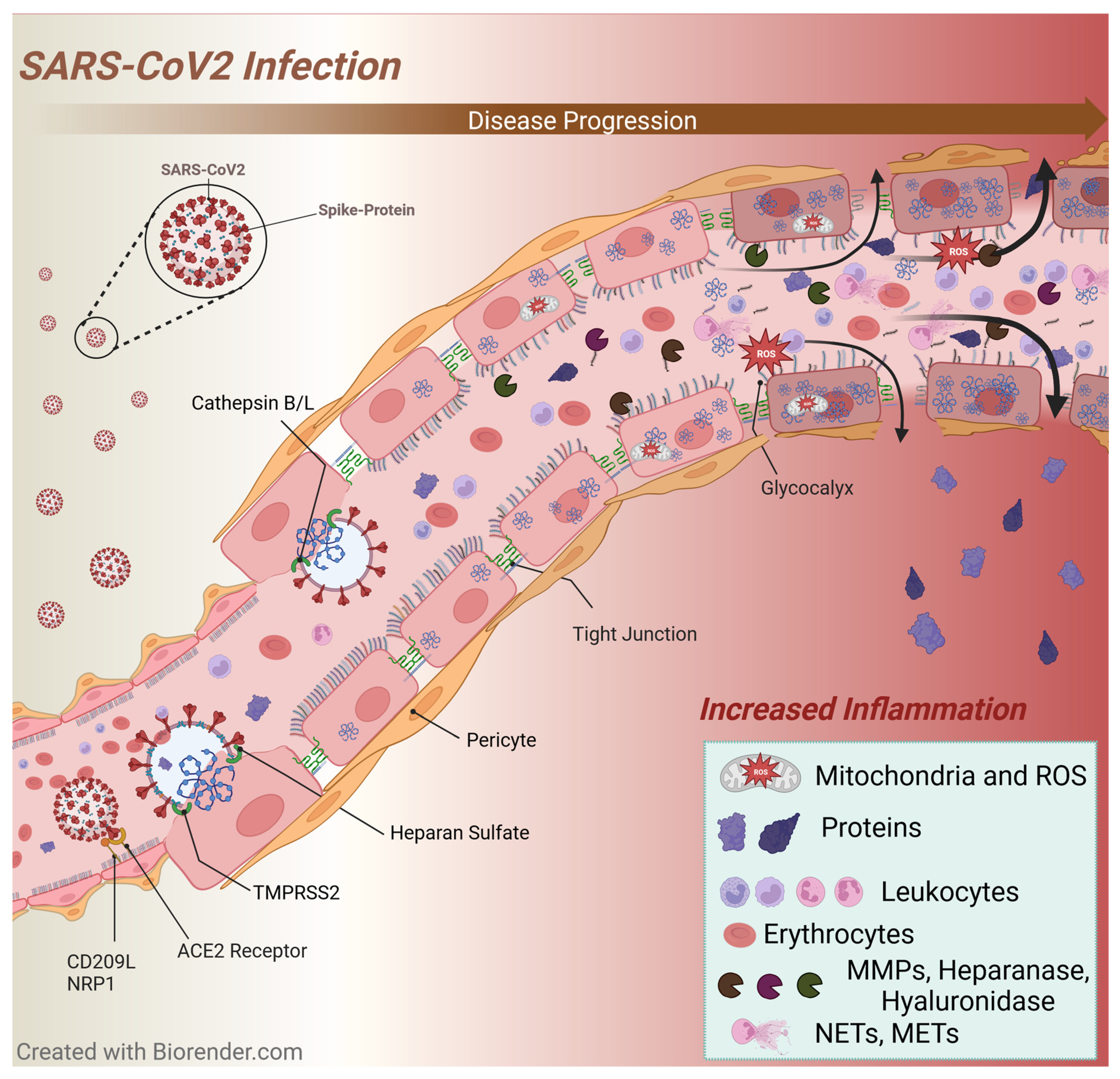
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





