Submitted:
19 December 2023
Posted:
19 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Approaches Used to Calculate the Parameters of the Runaway Electron Beam in High-Voltage Gas Discharges
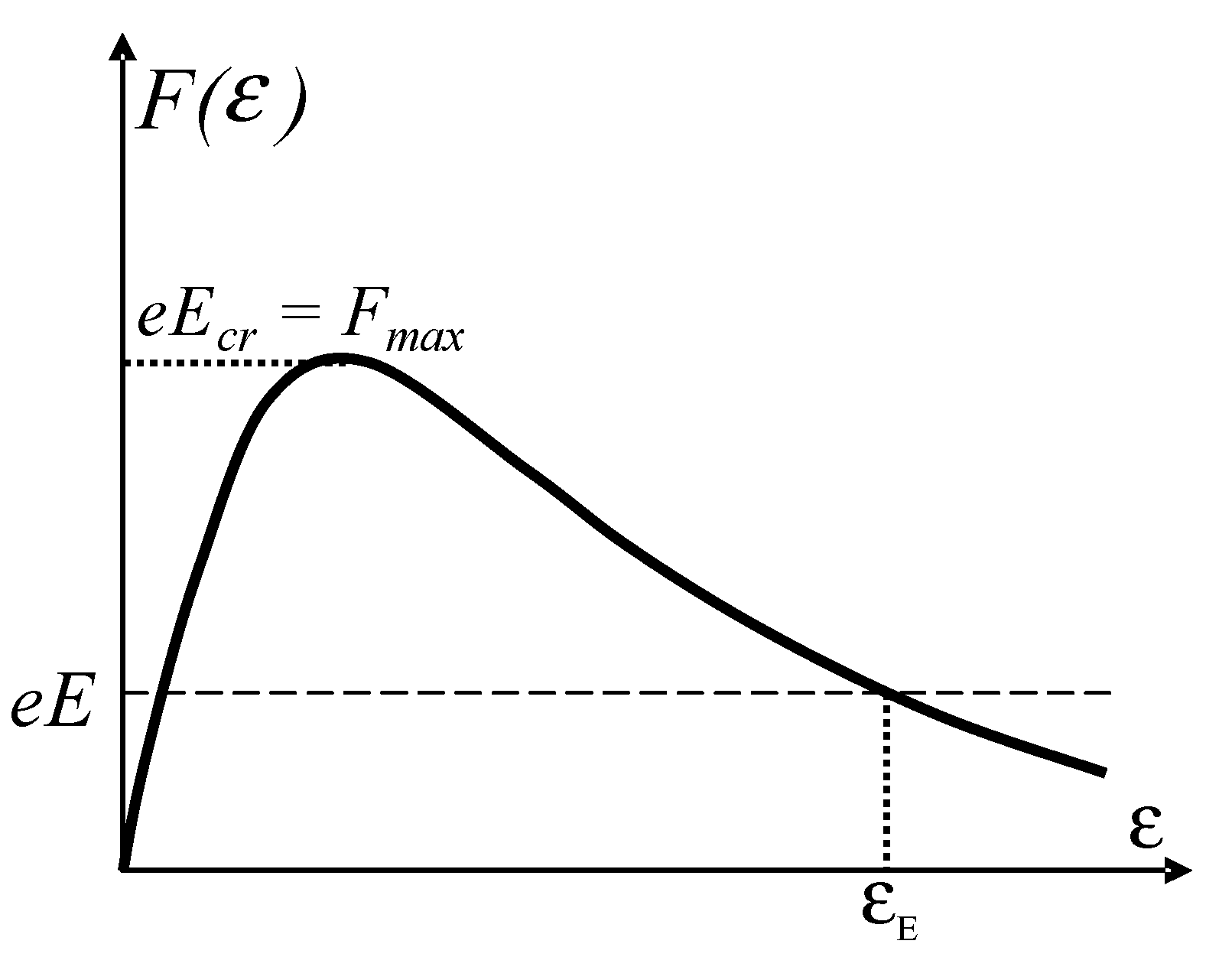
2.1. Critical electric field strength
2.2. Kinetic model of the runaway electron effect
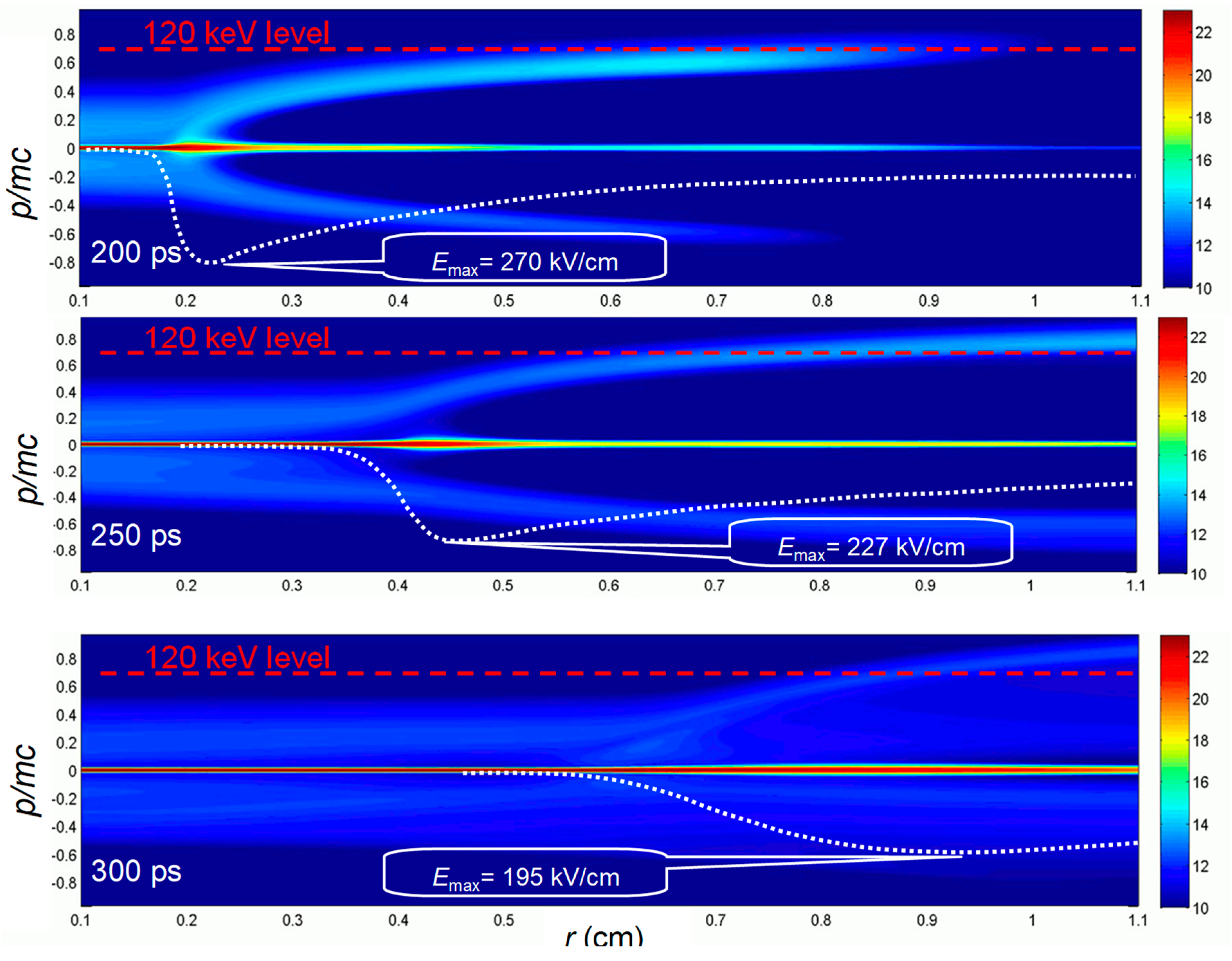
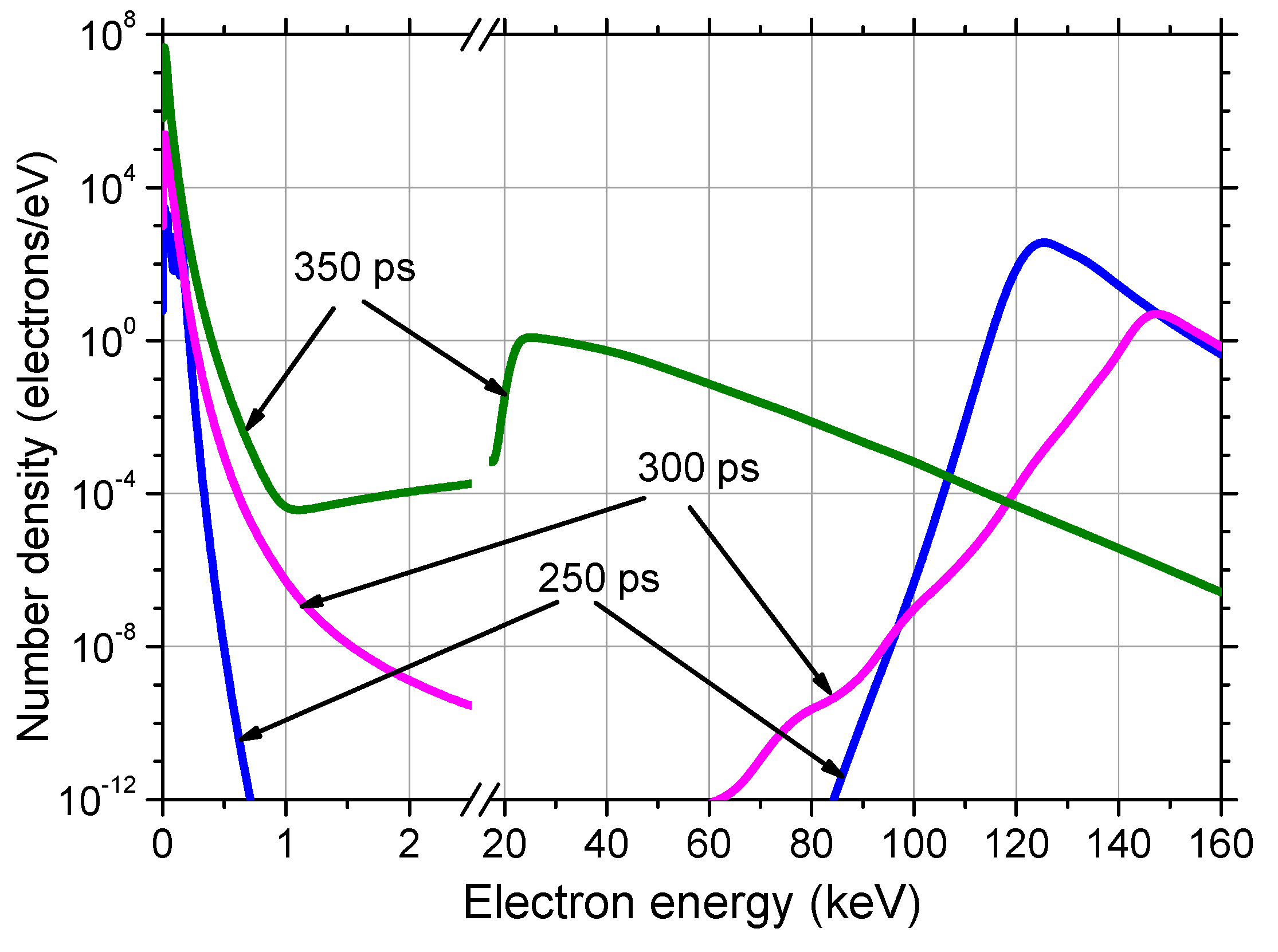
3. Results of modeling
4. Experimental installations and measurement procedures
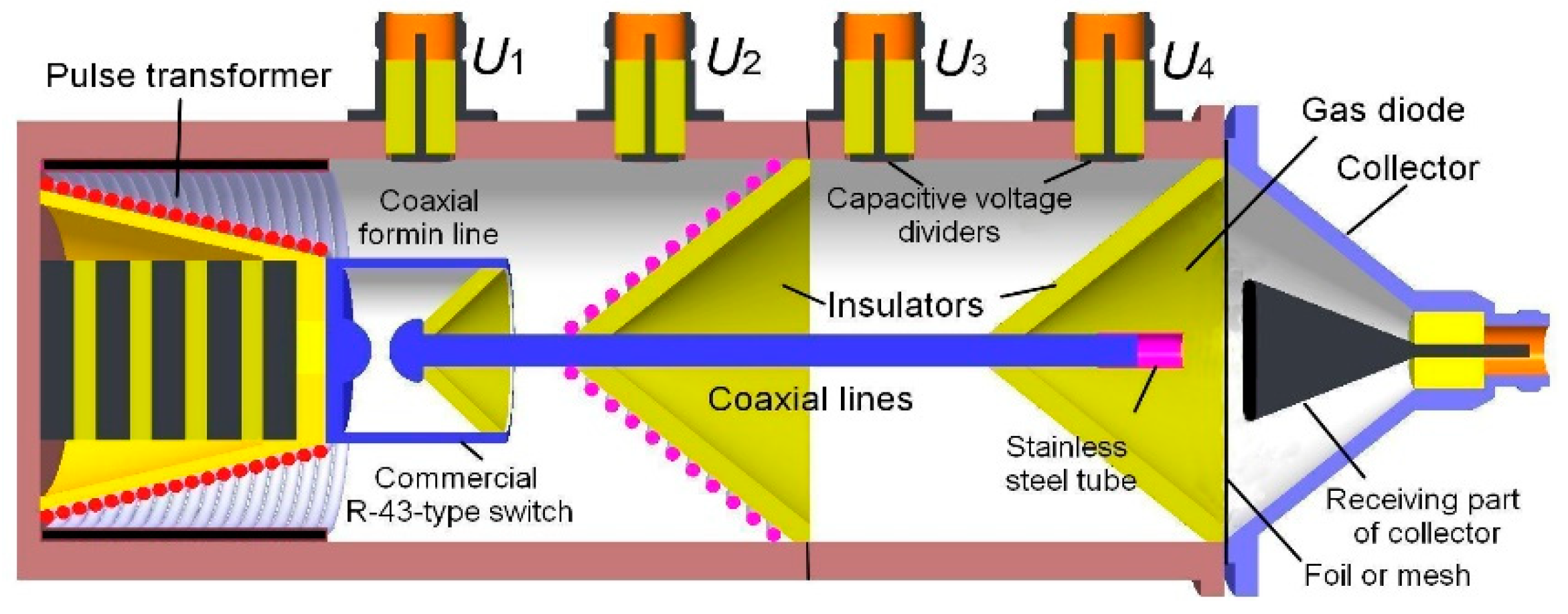
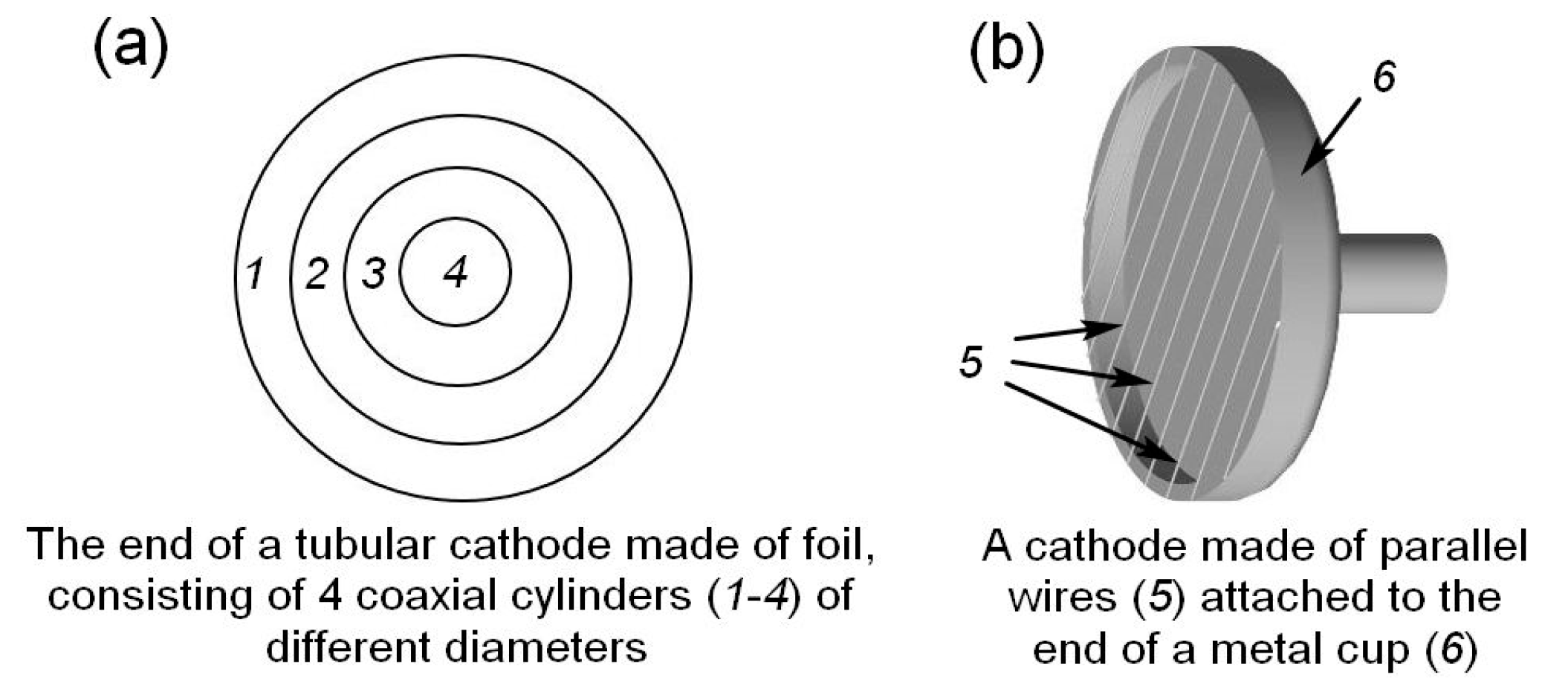
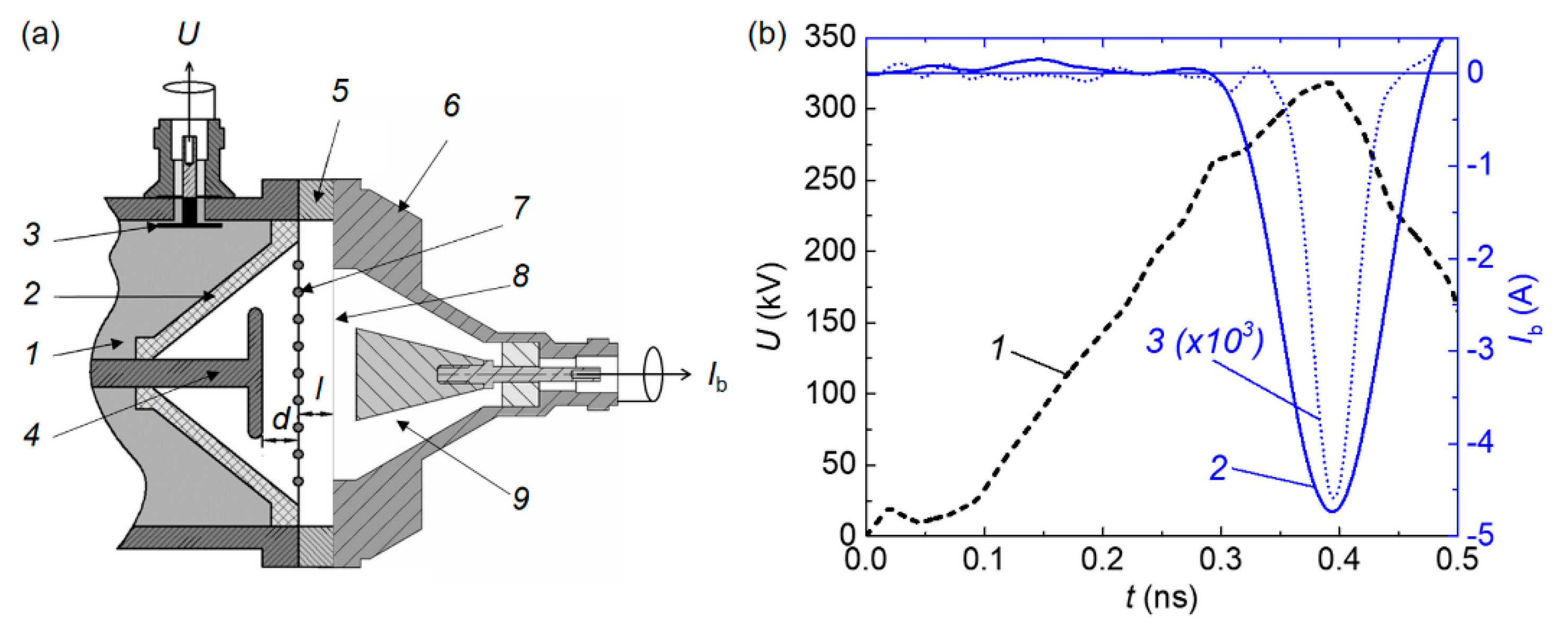
4.1. Generators, cathodes, and collectors for forming and measuring the RAEB
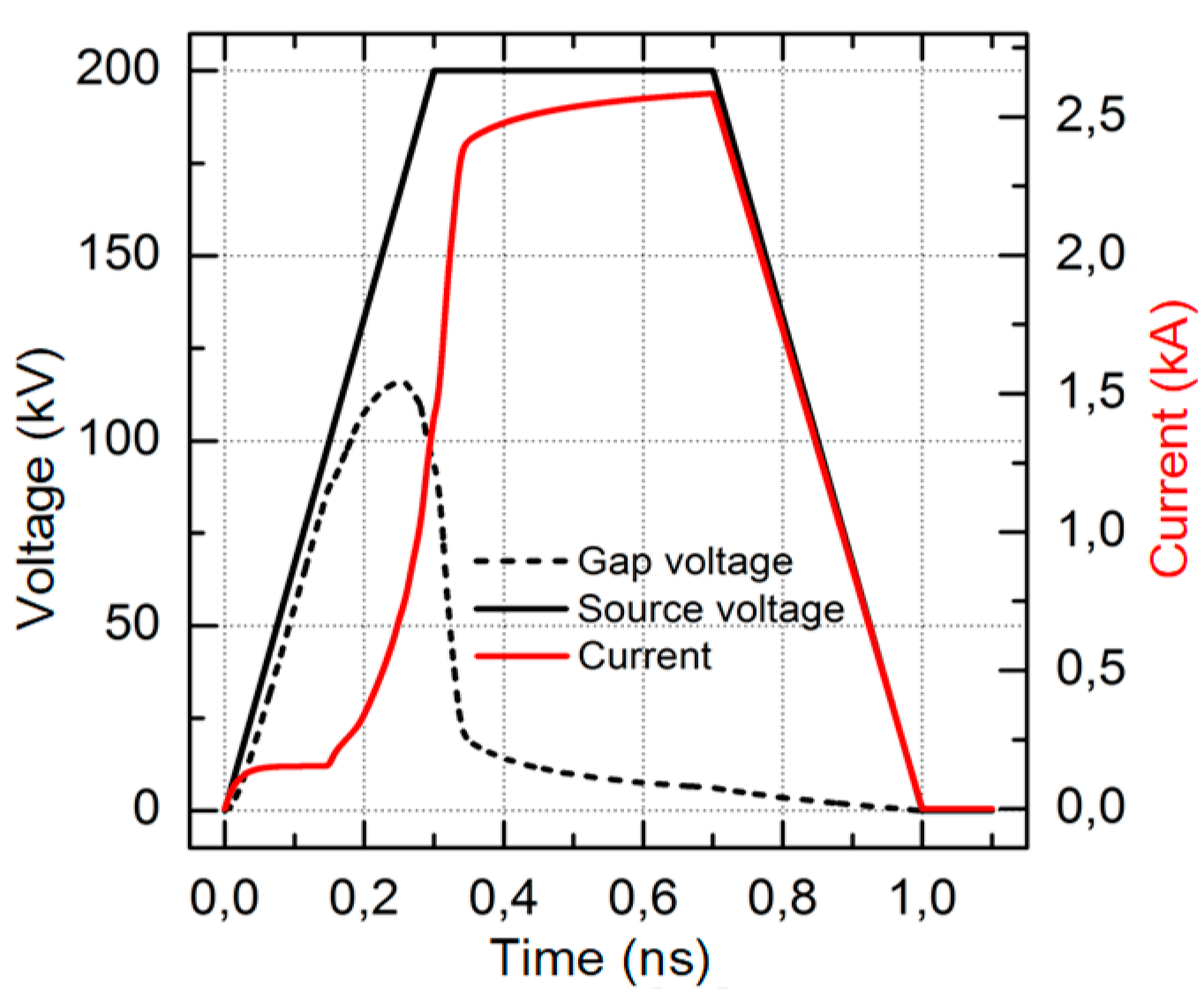
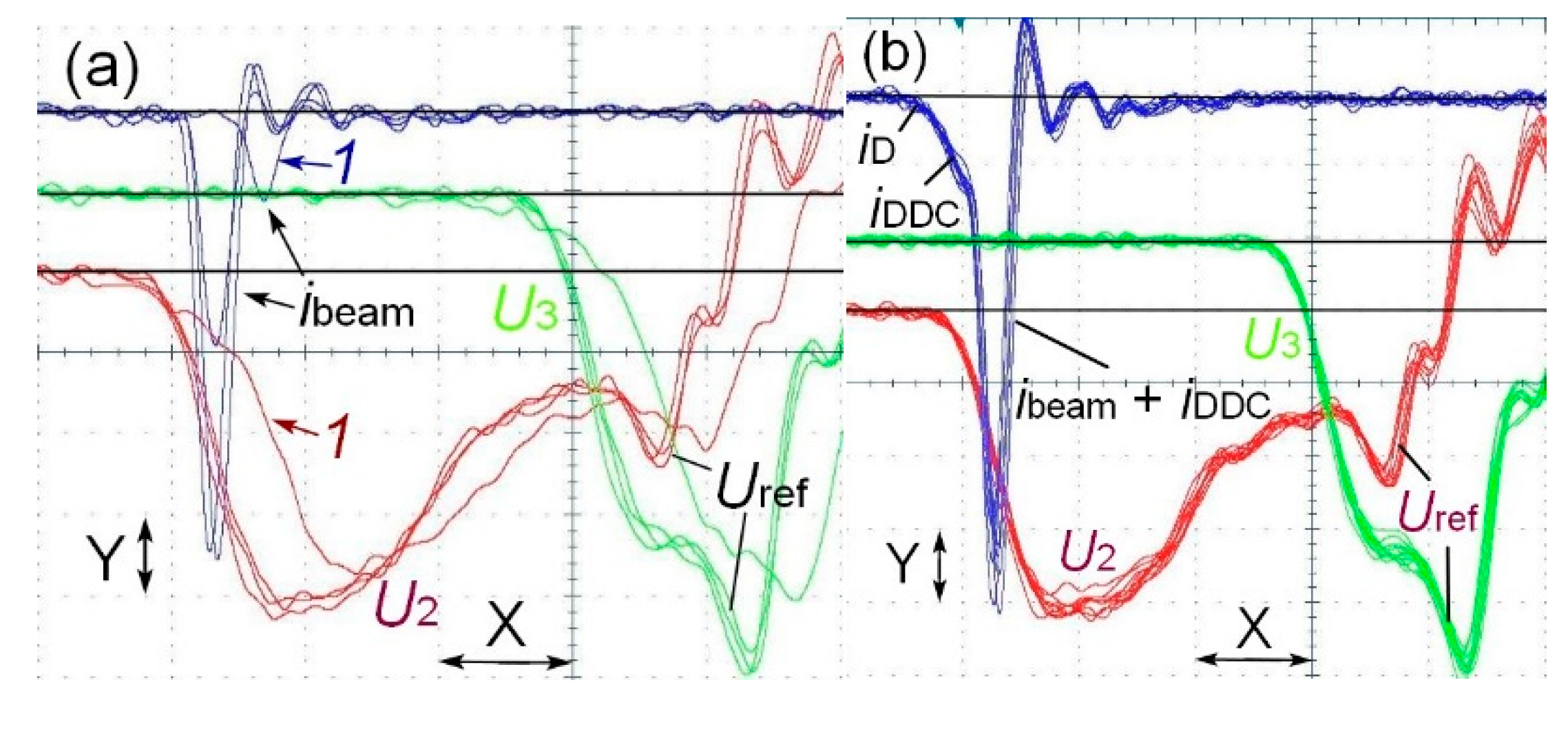
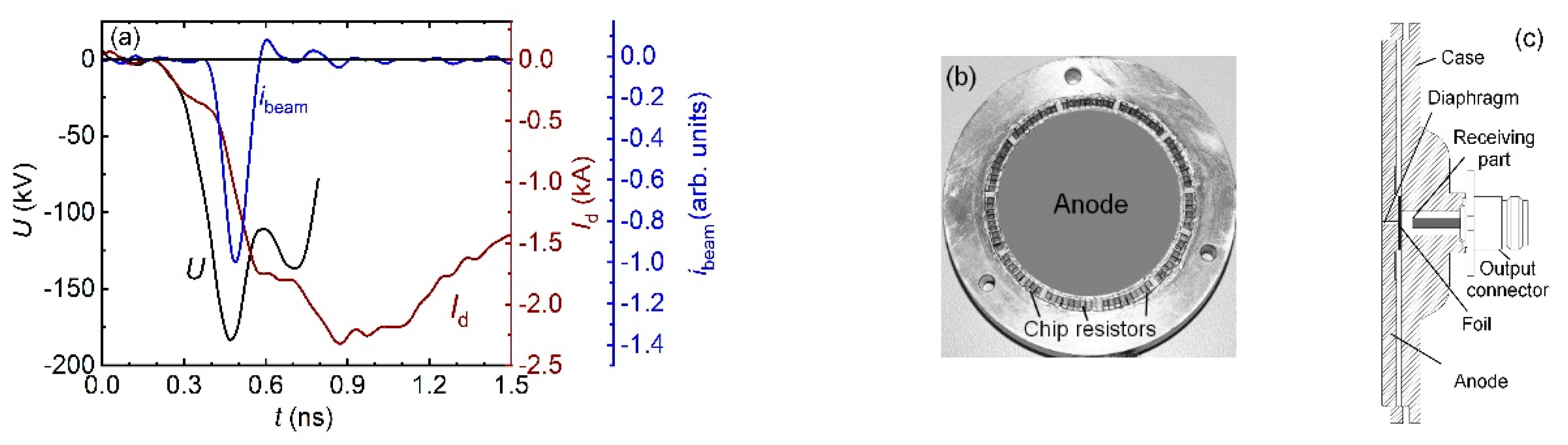
4.2. Measurement of the parameters of the voltage pulses, discharge currents, and SAEB
5. Experimental data
5.1. Influence of various factors on the SAEB parameters
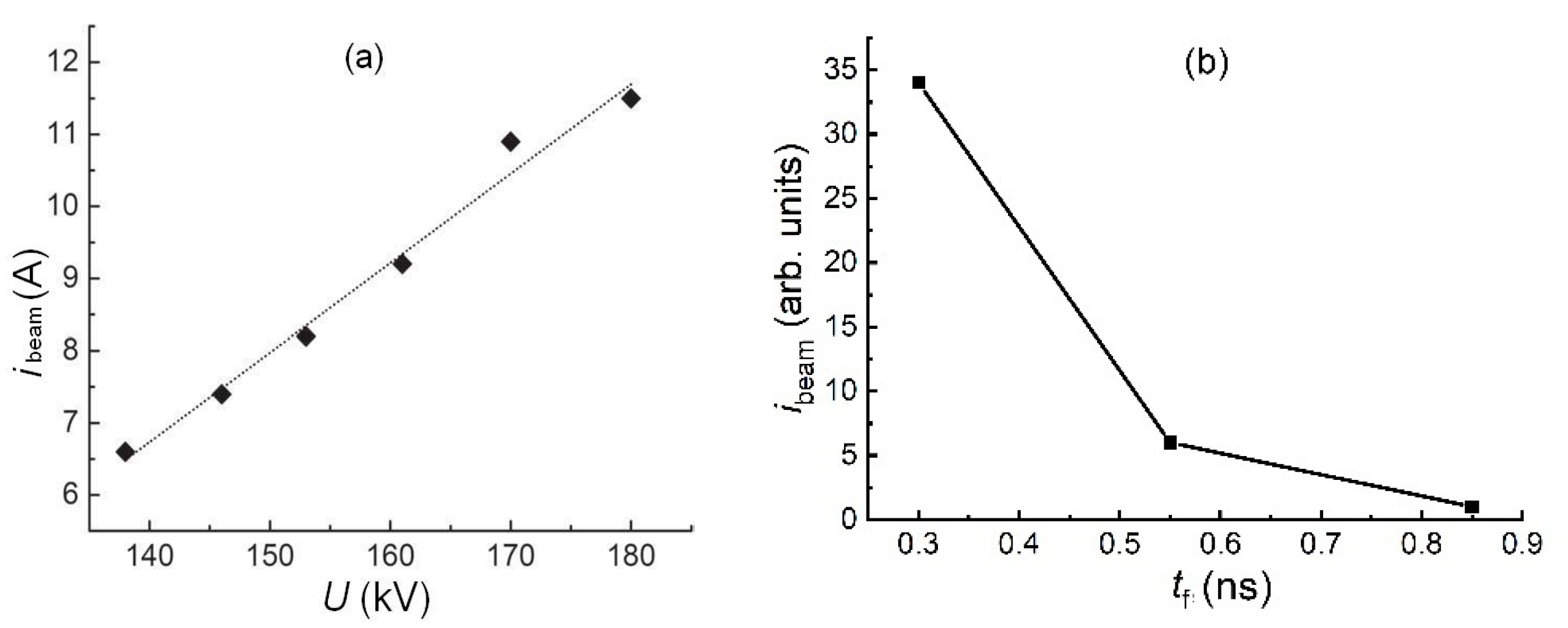
5.1.1. Influence of the pulse amplitude and front duration on the voltage pulse
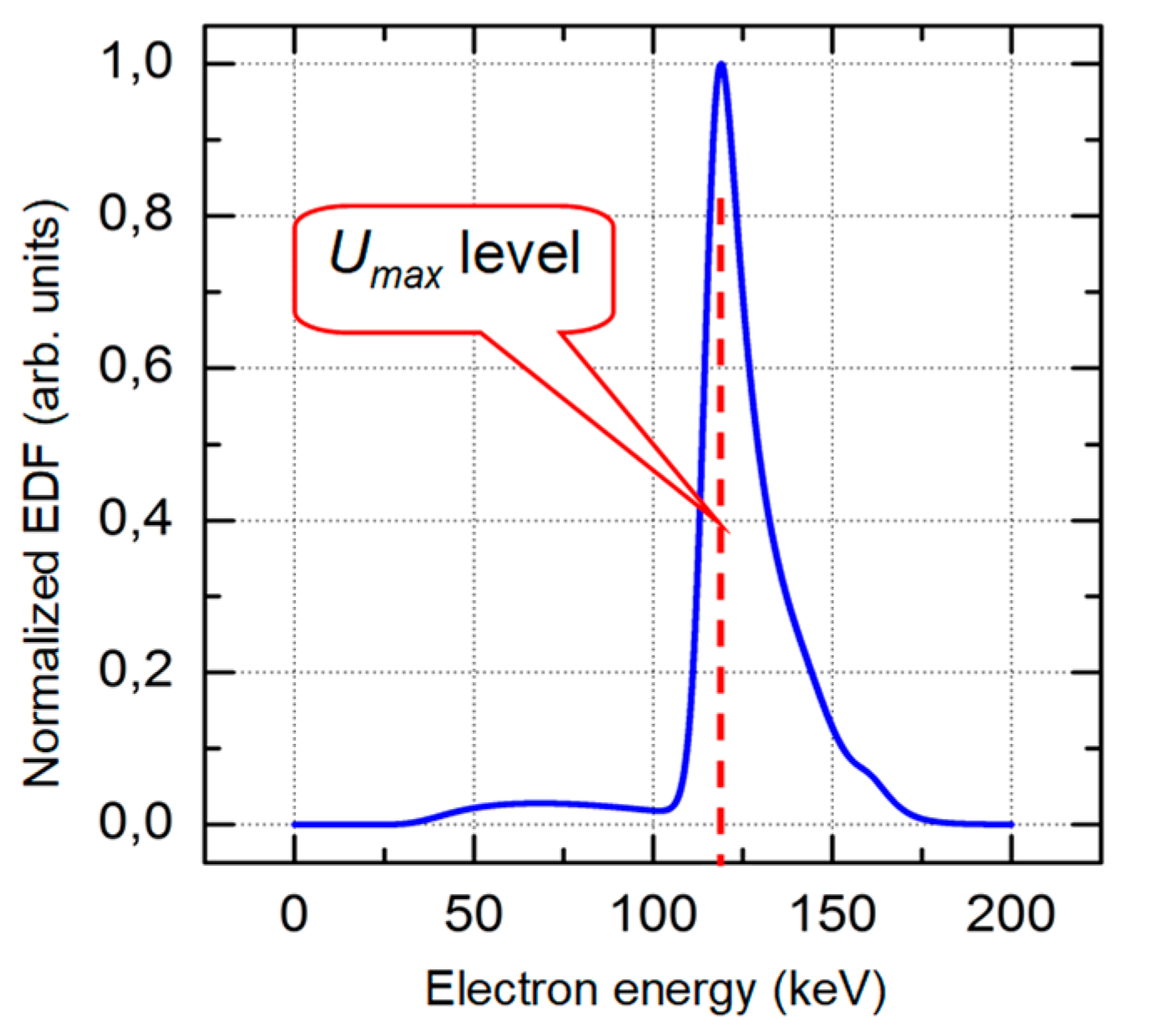
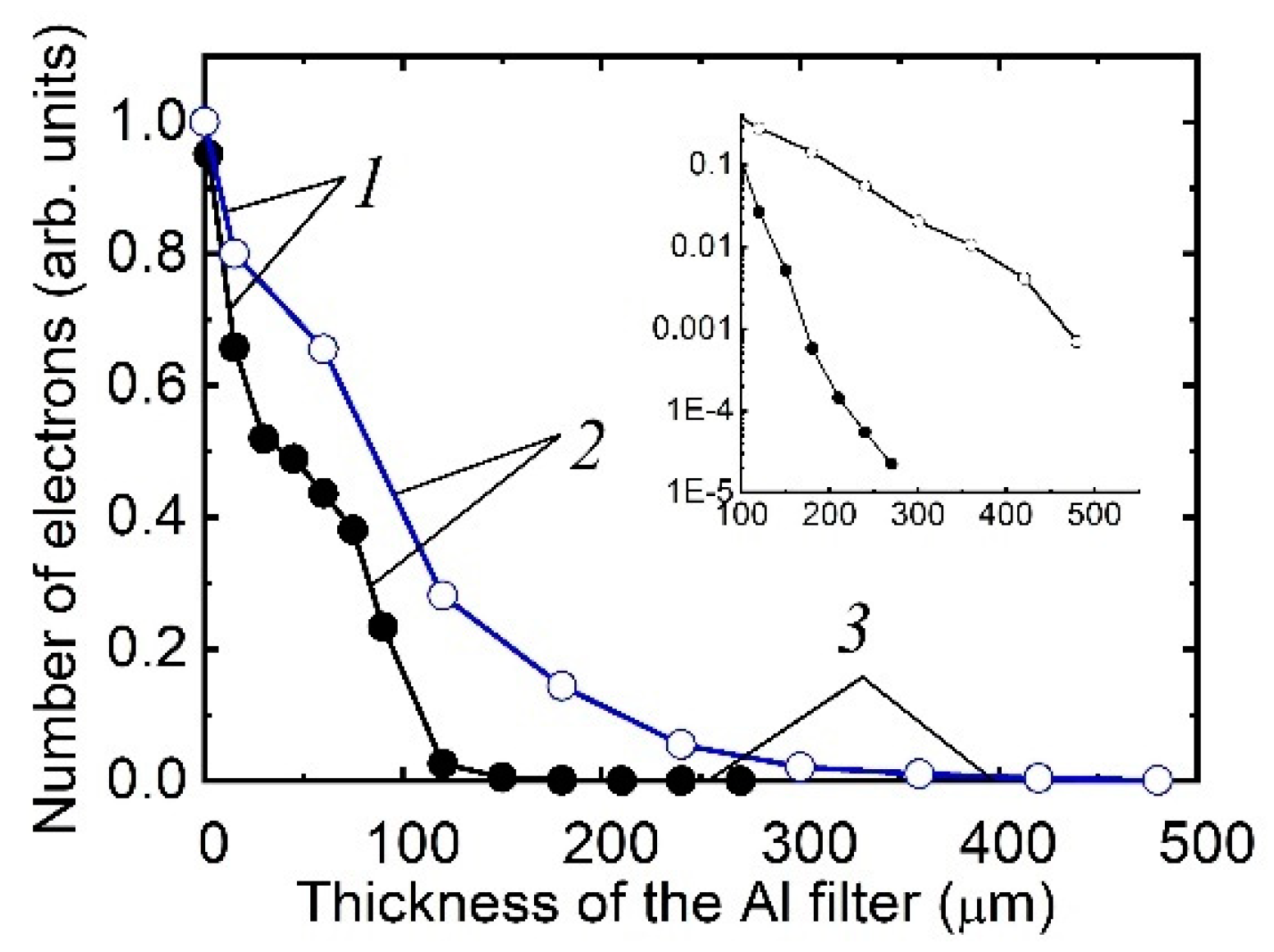
5.1.2. Runaway electron energy distribution
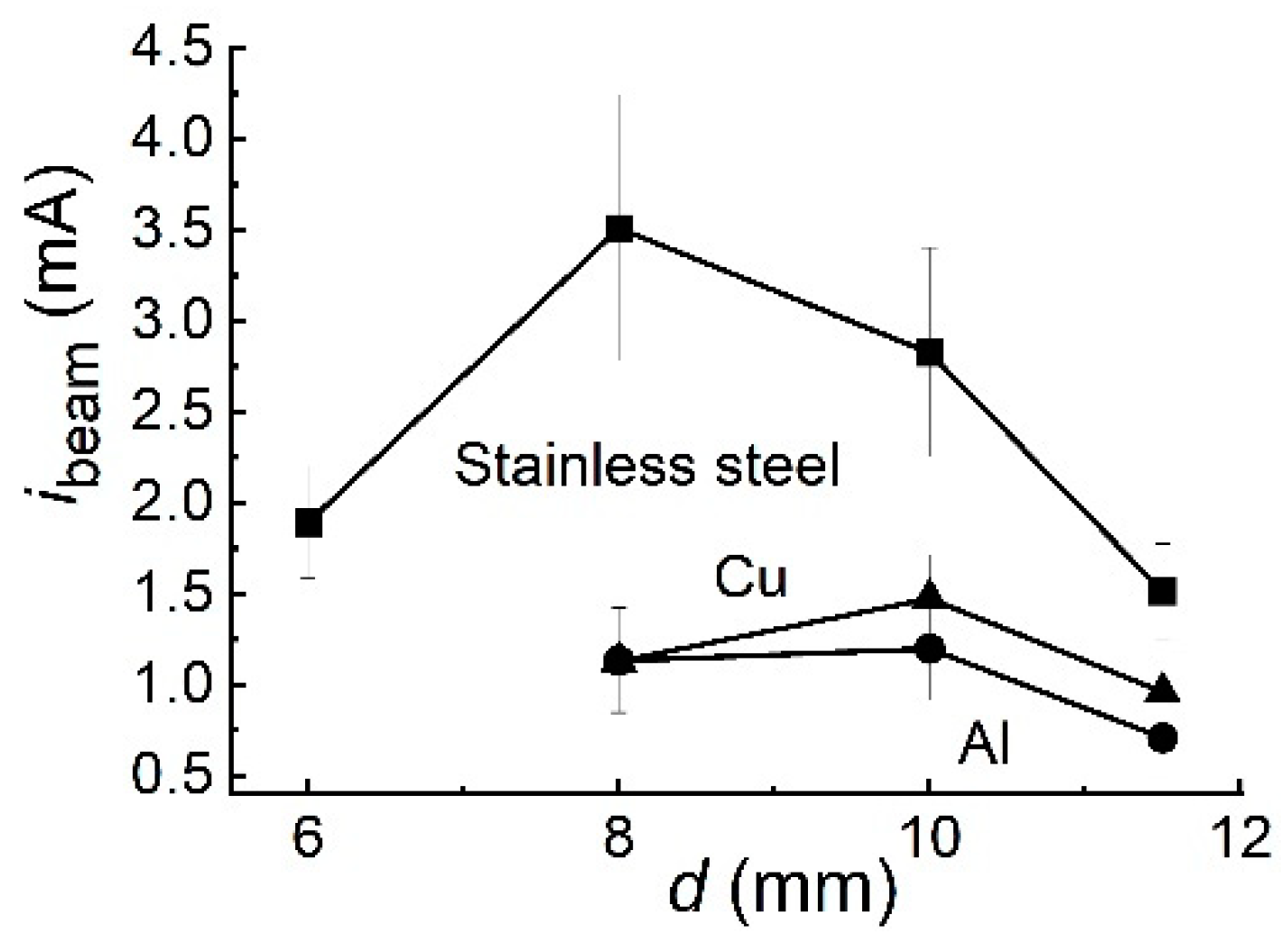
5.1.3. Influence of the cathode material and shape on the SAEB parameters
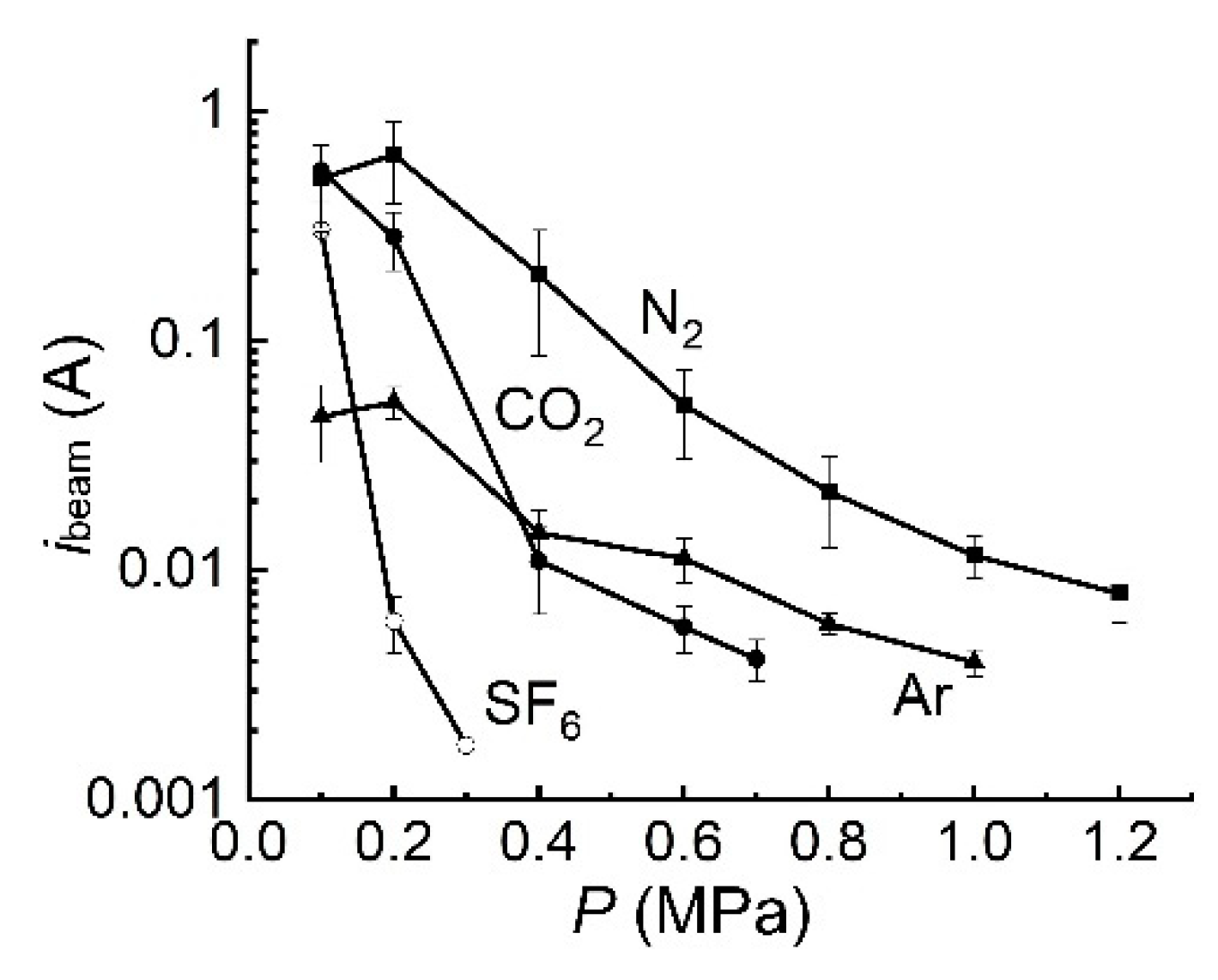
5.1.4. Influence of the gas pressure and type on the SAEB parameters
5.1.5. Generation of an RE beam in the direction opposite to the anode
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, C.T.R. The acceleration of β-particles in strong electric fields such as those of thunderclouds. Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 1925, 22, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.J. XLII. Ionization by moving electrified particles. Phil. Mag. S. 1912, 23, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanelli, R.G. XVII. Electron energies resulting from an electric field in a highly ionized gas. Phil. Mag. S. 1949, 40, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreicer, H. Electron and ion runaway in a fully ionized gas. I. Phys. Rev. 1959, 115, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreicer, H. Electron and ion runaway in a fully ionized gas. II. Phys. Rev. 1960, 117, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.V. On the theory of runaway electrons. Sov. Phys. JETP 1961, 12, 904–912. [Google Scholar]
- Gurevich, A.V.; Zybin, K.P. Runaway breakdown and electric discharges in thunderstorms. Phys.-Usp. 2001, 44, 1119–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askar’yan, G.A. Acceleration of particles by the edge field of a moving plasma point that intensifies an electric field. Sov. JETP Lett. 1965, 1, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Askar’yan, G.A. Self-acceleration of ionizing particles in an electric field of a polarizing ionization loop. Sov. JETP Lett. 1965, 2, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Frankel, S.; Highland, V.; Sloan, T.; Van Dyck, O.; Wales, W. Observation of X-rays from spark discharges in spark chamber. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1966, 44, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankevich, Yu.L.; Kalinin, V.G. Fast electrons and X-ray radiation in the initial stage of impulse spark discharge development in the air. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 1967, 177, 72–73. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Noggle, R.C.; Krider, E.P.; Wayland, J.R. A search for X rays from helium and air discharges at atmospheric pressure. J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 4746–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasova, L.V.; Khudyakova, L.N. X-ray at pulsed discharges in air. J. Tech. Phys. 1969, 39, 1530–1533. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Tarasova, L.V.; Khudyakova, L.N.; Loiko, T.V.; Tsukerman, V.A. Runaway electrons and X rays of nanosecond discharges in gases at pressures 0.1-760 Torr. J. Tech. Phys. 1974, 44, 564–568. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Babich, L.P.; Loiko, T.V.; Tsukerman, V.A. High-voltage nanosecond discharge in a dense gas at a high overvoltage with runaway electrons. Sov. Phys. Usp. 1990, 3, 521–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, L.P. High-energy phenomena in electric discharges in dense gases: Theory, experiment and natural phenomena; Futurepast: Arlington, VA, USA, 2003; p. 358. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlovskii, A.I.; Bosamykin, V.S.; Karelin, V.I.; Nikolskii, V.S. Electric-discharge laser with firing in the active volume. Kvantovaya Elektronika Moscow 1976, 3, 601–604. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Bosamykin, V.S.; Karelin, V.I.; Pavlovskii, A.I.; Repin, P.B. X ray radiation of microseconds duration in phase of formation of spark channels. Sov. Tech. Phys. Lett. 1980, 6, 885–888. [Google Scholar]
- Byszewski, W.W.; Reinhold, G. X–ray diagnostics of runaway electrons in fast gas discharges. Phys. Rev. A 1982, 26, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparro, J.E.; Justis, W.; Krompholz, H.G.; Hatfield, L.L.; Neuber, A.A. Breakdown delay times for subnanosecond gas discharges at pressures below one atmosphere. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2008, 36, 2505–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rep’ev, A.G.; Repin, P.B. Spatiotemporal parameters of the x-ray radiation from a diffuse atmospheric-pressure discharge. Tech. Phys. 2008, 53, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shao, T.; Yu, Y.; Niu, Z.; Yan, P.; Zhou, Y. Detection of x-ray emission in a nanosecond discharge in air at atmospheric pressure. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2010, 81, 123501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buranov, S.N.; Gorokhov, V.V.; Karelin, V.I.; Pavlovskii, A.I.; Repin, P.B. Wide-aperture source of x-ray radiation for preionization of the large-volume electric-discharge lasers. Sov. J. Quantum Electron. 1991, 21, 891–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.T.R. The electric field of a thundercloud and some of its effects. Proc. Phys. Soc. London 1924, 37, 32D–37D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseev, S.B.; Orlovskii, V.M.; Tarasenko, V.F. Electron beams formed in a diode filled with air or nitrogen at atmospheric pressure. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2003, 29, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseev, S.B.; Gubanov, V.P.; Orlovskii, V.M.; Stepchenko, A.S.; Tarasenko, V.F. Measuring the parameters of an electron beam. Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2003, 46, 505–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F.; Yakovlenko, S.I. The electron runaway mechanism in dense gases and the production of high-power subnanosecond electron beams. Phys.-Usp. 2004, 47, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F.; Baksht, E.Kh.; Burachenko, A.G.; Kostyrya, I.D.; Lomaev, M.I.; Rybka, D.V. Generation of supershort avalanche electron beams and formation of diffuse discharges in different gases at high pressure. Plasma Devices Oper. 2008, 16, 267–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levko, D.; Krasik, Y.E.; Tarasenko, V.F. Present status of runaway electron generation in pressurized gases during nanosecond discharges. Int. Rev. Phys. 2012, 6, 165–194. [Google Scholar]
- Naidis, G.V.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Babaeva, N.Y.; Lomaev, M.I. Subnanosecond breakdown in high-pressure gases. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2018, 27, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F. Runaway electrons in diffuse gas discharges. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2020, 29, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F. (Ed.) Runaway electrons preionized diffuse discharges; Nova Science Publishers: New York, USA, 2014; p. 598. [Google Scholar]
- Mesyats, G.A.; Korovin, S.D.; Sharypov, K.A.; Shpak, V.G.; Shunailov, S.A.; Yalandin, M.I. Dynamics of subnanosecond electron beam formation in gas-filled and vacuum diodes. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2006, 32, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesyats, G.A.; Yalandin, M.I.; Reutova, A.G.; Sharypov, K.A.; Shpak, V.G.; Shunailov, S.A. Picosecond runaway electron beams in air. Plasma Phys. Rep. 2012, 38, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F.; Shpak, V.G.; Shunailov, S.A.; Yalandin, M.I.; Orlovskii, V.M.; Alekseev, S.B. Subnanosecond electron beams formed in a gas-filled diode. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2003, 29, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F.; Shunailov, S.A.; Shpak, V.G.; Kostyrya, I.D. Supershort electron beam from air filled diode at atmospheric pressure. Laser Part. Beams 2005, 23, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F.; Lyubutin, S.K.; Rukin, S.N.; Slovikovskii, B.G.; Kostyrya, I.D.; Orlovskii, V.M. Generation of X-ray radiation with a high pulse repetition rate by means of a volume discharge in an open gas diode. Tech. Phys. 2005, 50, 1462–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, N.M.; Kozhevnikov, V.Yu.; Kozyrev, A.V.; Mesyats, G.A.; Semeniuk, N.S.; Sharypov, K.A.; Shunailov, S.A.; Yalandin, M.I. Mechanism and dynamics of picosecond radial breakdown of a gas-filled coaxial line. Plasma Sources Sci. Tech. 2020, 29, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesyats, G.; Rostov, V.; Sharypov, K.; Shpak, V.; Shunailov, S.; Yalandin, M.; Zubarev, N. Emission features and structure of an electron beam versus gas pressure and magnetic field in a cold-cathode coaxial diode. Electronics 2022, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesyats, G.A.; Osipenko, E.A.; Sharypov, K.A.; Shpak, V.G.; Shunailov, S.A.; Yalandin, M.I.; Zubarev, N.M. An ultra-short dense paraxial bunch of sub-relativistic runaway electrons. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2022, 43, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Huang, B.; Shao, T. Reconstruction of energy spectrum of runaway electrons in nanosecond-pulse discharges in atmospheric air. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 064011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Yan, P. Atmospheric-pressure pulsed discharges and plasmas: Mechanism, characteristics and applications. High Voltage 2018, 3, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Zhang, C.; Niu, Z.; Yan, P.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Baksht, E.K.; Burahenko, A.G.; Shut’ko, Y.V. Diffuse discharge, runaway electron, and x-ray in atmospheric pressure air in an inhomogeneous electrical field in repetitive pulsed modes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 021503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Zhang, C.; Burachenko, A.G.; Rybka, D.V.; Kostyrya, I.D.; Lomaev, M.I.; Baksht, E.K.; Yan, P. Application of dynamic displacement current for diagnostics of subnanosecond breakdowns in an inhomogeneous electric field. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2013, 84, 053506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Shao, T.; Baksht, E.K.; Burachenko, A.G.; Yan, P. Effect of cathode materials on the generation of runaway electron beams and X-rays in atmospheric pressure air. Laser Part. Beams 2013, 31, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F.; Zhang, C.; Baksht, E.K.; Burachenko, A.G.; Shao, T.; Beloplotov, D.V.; Lomaev, M.I.; Yan, P.; Kozyrev, A.V.; Semeniuk, N.S. Review of supershort avalanche electron beam during nanosecond-pulse discharges in some gases. Matter Radiat. Extremes 2017, 2, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloplotov, D.V.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Sorokin, D.; Zhang, C.; Shao, T. Positive and negative streamers in air and nitrogen in a sharply inhomogeneous electric field under conditions of runaway electron generation. High Volt. 2023, 8, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovskii, A.I.; Babich, L.P.; Loiko, T.V.; Tarasova, L.V. Runaway of electrons in gas discharges and the origin of the minimum of U(Pd). Sov. Phys. Dokl. 1985, 20, 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Babich, L.P.; Loiko, T.V. Runaway electrons at high voltage nanosecond discharges in sulfur hexafluoride at pressure of 1 atm. Tech. Phys. 1991, 61, 153–155. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Babich, L.P.; Kutsyk, I.M. Numerical simulation of a nanosecond discharge in helium at atmospheric pressure, developing in the regime of runaway of electrons. TVT 1995, 33, 191–199. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Babich, L.P.; Loiko, T.V. Subnanosecond pulses of runaway electrons generated in atmosphere by high-voltage pulses of microsecond duration. Dokl. Phys. 2009, 54, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, L.P.; Loiko, T.V. Peculiarities of detecting pulses of runaway electrons and X-rays generated by high-voltage nanosecond discharges in open atmosphere. Plas. Phys. Rep. 2010, 36, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolev, Y.D.; Mesyats, G.A. Physics of Pulsed Breakdown in Gases; UD RAS: Yekaterinburg, Russia, 1998; p. 274. [Google Scholar]
- Kozyrev, A.V.; Korolev, Yu.D.; Mesyats, G.A.; Novoselov, Yu.N. Proc. of Abstracts of the Sixth All-Union Conference on Low-Temperature Plasma: Leningrad, 1983, vol. 2, pp. 228–230.
- Tkachev, A.N.; Yakovlenko, S.I. On the mechanism of the runaway of electrons in a gas: The upper branch of the self-sustained discharge ignition curve. JETP Lett. 2003, 77, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachev, A.N.; Yakovlenko, S.I. The mechanism of electron runaway in a gas and a criterion of the self-sustained discharge initiation. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2003, 29, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boichenko, A.M.; Tkachev, A.N.; Yakovlenko, S.I. The Townsend coefficient and runaway of electrons in electronegative gas. JETP Lett. 2003, 78, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yatsui, K.; Orlovskii, V.M.; Tarasenko, V.F. Numerical simulation of sub-nanosecond electron beam extraction from gas-filled diode. Proceedings of Int. Conf. on High-Power Part. Beams, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2004; IEEE: 2005; 174-177.
- Levko, D.; Yatom, S.; Vekselman, V.; Gleizer, J.Z.; Gurovich, V.T.; Krasik, Y.E. Numerical simulations of runaway electron generation in pressurized gases. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 013303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisenkov, V.V.; Shklyaev, V.A. Numerical study of the generation of runaway electrons in a gas diode with a hot channel. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 113507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreshkin, E.V.; Barengolts, S.A.; Chaikovsky, S.A.; Oreshkin, V.I. Simulation of a runaway electron avalanche developing in an atmospheric pressure air discharge. Phys. Plasmas, 2015, 22, 123505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gu, J.; Wang, R.; Ma, H.; Yan, P.; Shao, T. Simulation of runaway electron inception and breakdown in nanosecond pulse gas discharges. Laser Part. Beams 2016, 34, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikov, V.Yu.; Kozyrev, A.V.; Semeniuk, N.S. Modeling of space charge effects in intense electron beams: Kinetic equation method versus PIC method. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2017, 45, 2762–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belomyttsev, S.Y.; Grishkov, A.A.; Shklyaev, V.A.; Ryzhov, V.V. Current in a pulsed gas breakdown at a highly inhomogeneous electric field. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 123, 043309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeva, N.Yu.; Naidis, G.V.; Tereshonok, D.V.; Son, E.E. Development of nanosecond discharges in atmospheric pressure air: Two competing mechanisms of precursor electrons production. J Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 434002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikov, V.Yu.; Kozyrev, A.V.; Semeniuk, N.S. Physical Kinetics of Electrons in a High-Voltage Pulsed High-Pressure Discharge with Cylindrical Geometry. Rus. Phys. J. 2017, 60, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, N.M.; Ivanov, S.N. Mechanism of runaway electron generation at gas pressures from a few atmospheres to several tens of atmospheres. Plas. Phys. Rep. 2018, 44, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhevnikov, V.Yu.; Kozyrev, A.V.; Semeniuk, N.S. Why do Electrons with “Anomalous Energies” appear in High-Pressure Gas Discharges? EPJ Web Conf. 2018, 167, 01005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkov, E.I.; Babich, L.P.; Kutsyk, I.M. Dependence of the Generation Rate of High-Energy Electrons in Helium on the Electron Angular Scattering Model. Plas. Phys. Rep. 2021, 47, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starikovskiy, A.Yu.; Aleksandrov, N.L.; Shneider, M.N. Simulation of decelerating streamers in inhomogeneous atmosphere with implications for runaway electron generation. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 063301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breizman, B.N.; Aleynikov, P.; Hollmann, E.M.; Lehnen, M. Physics of runaway electrons in tokamaks. Nucl. Fusion 2019, 59, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, M.; Ekmark, I.; Berger, E.; Fülöp, T. Runaway electron generation during tokamak start-up. J. Plasma Phys. 2022, 88, 905880317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.J. Energy distribution of lost high-energy runaway electrons based on their bremsstrahlung emission in the EAST tokamak. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 107, 045204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtinen, N.G.; Inan, U.S.; Bell, T.F. Effects of thunderstorm-driven runaway electrons in the conjugate hemisphere: Purple sprites, ionization enhancements, and gamma rays. J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 2001, 106, 28841–28856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, G.J.; Bhat, P.N.; Mallozzi, R.; Horack, J.M.; Koshut, T.; Kouveliotou, C.; Pendleton, G.N.; Meegan, C.A.; Wilson, R.B.; Paciesas, W.S.; Goodman, S.J. Discovery of intense gamma-ray flashes of atmospheric origin. Science 1994, 264, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaerdinov, N.S.; Lidvansky, A.A.; Petkov, V.B. Cosmic rays and the electric field of thunderclouds: Evidence for acceleration of particles (runaway electrons). Atmos. Res. 2005, 76, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.E.; Lehtinen, N.G.; Inan, U.S. Runaway relativistic electron avalanche seeding in the Earth’s atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res.: Space Phys. 2008, 113, A10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, G.; Wada, Y.; Ohira, Y.; Nakazawa, K.; Enoto, T. Atmospheric electron spatial range extended by thundercloud electric field below the relativistic runaway electron avalanche threshold. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD035958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilingarian, A. Thunderstorm Ground Enhancements Measured on Aragats and Progress of High-Energy Physics in the Atmosphere. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, J.R.; Saleh, Z.; Rassoul, H.K.; Concha, D.; Rahman, M.; Cooray, V.; Jerauld, J.; Uman, M.A.; Rakov, V.A. A study of X-ray emission from laboratory sparks in air at atmospheric pressure. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmospheres 2008, 113, D23207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, V.; Montanyà, J. Influence of the voltage-time derivative in x-ray emission from laboratory sparks. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 37, L044543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkin, P.O.; Van Deursen, A.P.; Ebert, U. Experimental study on hard x-rays emitted from metre-scale negative discharges in air. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 025205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkin, P.O.; Köhn, C.; Ebert, U.; Van Deursen, A.P. Analyzing x-ray emissions from meter-scale negative discharges in ambient air. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2016, 25, 044002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Cooray, V.; Ahmad, N.A.; Nyberg, J.; Rakov, V.A.; Sharma, S. X rays from 80-cm long sparks in air. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L06805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.V.; Van Deursen, A.P.J.; Elbert, U.M. Multiple x-ray bursts from long discharges in air. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 234012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhan, P.A.; Sorokin, A.R. Open discharge generating an electron beam-Mechanism, properties, and applications for pumping lasers at moderate pressures. Sov. Phys. Tech. Phys. 1985, 30, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Bokhan, P.A.; Zakrevsky, Dm.E.; Gugin, P.P. Generation of high-current electron beam in a wide-aperture open discharge. Phys. Plasmas 2011, 18, 103112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, A.R. Legend about photoemission discharge. Phys.-Usp. 2018, 61, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhan, P.A. On physical processes in an open discharge. Phys.-Usp. 2018, 61, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Zhang, C.; Ren, C.; Shao, T. Guiding effect of runaway electrons in atmospheric pressure nanosecond pulsed discharge: Mode transition from diffuse discharge to streamer. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2022, 31, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, P.; Luo, H.; Zou, X.; Wang, X. Observation of electron runaway in a tip-plane air gap under negative nanosecond pulse voltage by PIC/MCC simulation. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2022, 31, 045027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levko, D.; Raja, L.L. Kinetics of the fast ionization waves with runaway electrons. Phys. Plasmas 2023, 30, 073502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zou, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y. A numerical investigation on electron runaway threshold at the initial stage of atmospheric streamer development. Phys. Plasmas 2023, 30, 073501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Z.; Fan, S.; Ren, S.; Qiu, A. Numerical investigation of runaway electrons during the breakdown of homogeneous electric field air gaps under nanosecond pulse voltage. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2023, 51, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloplotov, D.V.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Sorokin, D.A. Runaway electrons at the formation of a positive ionization wave in nitrogen and air. JETP Lett. 2022, 116, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Huang, B.D.; Zhang, C.; Qi, B.; Chen, W.; Shao, T. The critical effect of electron acceleration under enhanced electric field near the cathode on the formation of runaway electrons and diffuse discharge in atmosphere. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2023, 32, 085013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobanov, L.N.; Mesyats, G.A.; Osipenko, E.A.; Sharypov, K.A.; Shpak, V.G.; Shunailov, S.A.; Yalandin, M.I.; Zubarev, N.M. Disk-shaped bunch of runaway electrons formed in a magnetized air diode. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2023, 44, 1748–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, M.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Qiu, A. The effects of pulse voltage rise time on the nanosecond pulsed breakdown of nitrogen spark switch at atmospheric pressure with 3D PIC-MCC model. Phys. Plasmas 2023, 30, 043901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Molin, A.; Nocente, M.; Dalla Rosa, M.; Panontin, E.; Rigamonti, D.; Tardocchi, M.; Shevelev, A.; Khilkevitch, E.; Iliasova, M.; Giacomelli, L.; et al. A new hard x-ray spectrometer for runaway electron measurements in tokamaks. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 085501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhan, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhong, W. Development of hard X-ray spectrometer with full digital data acquisition for runaway electron studies at HL-2M. J. Inst. 2023, 18, T02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadnichuk, E.; Svechnikova, E. The criterion for self-sustaining production of relativistic runaway electron avalanches by the positron feedback in thunderstorms. Atmos. Res. 2022, 277, 106329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Vidal, L.; da Silva, C.L.; Sonnenfeld, R.G. Production of runaway electrons and x-rays during streamer inception phase. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 56, 055201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDevitt, C. A physics-informed deep learning model of the hot tail runaway electron seed. arXiv preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasko, V.P.; Celestin, S.; Bourdon, A.; Janalizadeh, R.; Jansky, J. Conditions for inception of relativistic runaway discharges in air. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2022GL102710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breizman, B.N.; Kiramov, D.I. Marginal stability constraint on runaway electron distribution. Phys. Plasmas 2023, 30, 022301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Zhang, C. (Eds.) , Pulsed Discharge Plasmas: Characteristics and Applications. Springer Nature. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethe, H. Zur Theorie des Durchgangs schneller Korpuskularstrahlen durch Materie. Ann. Phys. 1930, 397, 325–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. Quantum Mechanics: Non-Relativistic Theory, 3rd ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, England, 1977; p. 691. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasenko, V.F. (Ed.) Generation of runaway electron beams and X-rays in high pressure gases, Volume 2: Processes and Applications; Nova Science Publishers: New York, USA, 2016; p. 315. [Google Scholar]
- Itikawa, Y. Cross sections for electron collisions with nitrogen molecules. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2006, 35, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, T.; Ito, R. A generalized empirical equation for the transmission coefficient of electrons. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1975, 127, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F. (Ed.) Generation of runaway electron beams and X-rays in high pressure gases, Volume 1: Techniques and Measurements; Nova Science Publishers: New York, USA, 2016; p. 405. [Google Scholar]
- Yalandin, M.I.; Shpak, V.G. Compact high-power subnanosecond repetitive-pulse generators (review). Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2001, 44, 285–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesyats, G.A.; Yalandin, M.I.; Sharypov, K.A.; Shpak, V.G.; Shunailov, S.A. Generation of a picosecond runaway electron beam in a gas gap with a nonuniform field. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2008, 36, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesyats, G.A. Pulsed power; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, USA, 2007; p. 568. [Google Scholar]
- Mesyats, G.A.; Pedos, M.S.; Rukin, S.N.; Rostov, V.V.; Romanchenko, I.V.; Sadykova, A.G.; Sharypov, K.A.; Shpak, V.G.; Shunailov, S.A.; Ul’masculov, M.R.; Yalandin, M.I. Formation of 1.4 MeV runaway electron flows in air using a solid-state generator with 10 MV/ns voltage rise rate. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 163501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baksht, E.Kh.; Burachenko, A.G.; Kozhevnikov, V.Yu.; Kozyrev, A.V.; Kostyrya, I.D.; Tarasenko, V.F. Spectrum of fast electrons in a subnanosecond breakdown of air-filled diodes at atmospheric pressure. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 305201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efanov, V.M.; Efanov, M.V.; Komashko, A.V.; Kriklenko, A.V.; Yarin, P.M.; Zazoulin, S.V. High-Voltage and High-PRF FID Pulse Generators. In Ultra-Wideband, Short Pulse Electromagnetics 9; Sabath, F., Giri, D.V., Rachidi, F., Kaelin, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasenko, V.F.; Baksht, E.K.; Beloplotov, D.V.; Burachenko, A.G.; Sorokin, D.A.; Lomaev, M.I. Generation and registration of runaway electron beams during the breakdown of highly overvoltaged gaps filled with dense gases. J. of Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 424001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F.; Beloplotov, D.V.; Sorokin, D.A. Duration of the runaway electron beam at a subnanosecond leading edge of the voltage pulse. Tech. Phys. 2022, 67, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, L.P.; Becker, K.H.; Loiko, T.V. Luminescence from minerals excited by subnanosecond pulses of runaway electrons generated in an atmospheric-pressure high-voltage discharge in air. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2009, 37, 2261–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babich, L.P.; Loiko, T.V. Energy-spectra and time parameters of runaway electrons in nanosecond breakdown of dense gases. Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 1985, 55, 956–958. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Babich, L.P.; Loiko, T.V.; Rodigin, A.V. Calibration of Detectors of Ionizing Emissions by Means of a Subnanosecond Runaway Electron Beam Generated by Discharge in Open Atmosphere at High Overvoltages. Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2014, 57, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesyats, G.A.; Reutova, A.G.; Sharypov, K.A.; Shpak, V.G.; Shunailov, S.A.; Yalandin, M.I. On the observed energy of runaway electron beams in air. Laser and Particle Beams. 2011, 29, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesyats, G.A. Explosive Electron Emission; URO-Press: Ekaterinburg, Russia, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin, D.A.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Beloplotov, D.V.; Lomaev, M.I. Features of streamer formation in a sharply non-uniform electric field. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 143301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, D.A.; Beloplotov, D.V.; Tarasenko, V.F.; Baksht, E.K. Main modes of runaway electron generation during a breakdown of high-pressure gases in an inhomogeneous electric field. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 224101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolev, Yu.D.; Mesyats, G.A. Field-Emission and Explosive Processes in Gas Discharges; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1982; p. 255. [Google Scholar]
- Nefedtsev, E.V.; Onischenko, S.A. Modification of the cathode material around the explosive electron emission centers in the spark stage of vacuum breakdown. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2022, 48, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, V.F.; Beloplotov, D.V.; Panchenko, A.N.; Sorokin, D.A. Thin luminous tracks of particles released from electrodes with a small radius of curvature in pulsed nanosecond discharges in air and argon. Surfaces 2023, 6, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunhardt, E.E.; Byszewski, W.W. Development of overvoltage breakdown at high gas pressure. Physical Review A 1980, 21, 2069–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




