Submitted:
18 December 2023
Posted:
19 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Review of credit management policies
3. Formal modeling of the credit business model
- -
- mean E(L) and standard deviation ;
- -
- mean E(N) and standard deviation ;
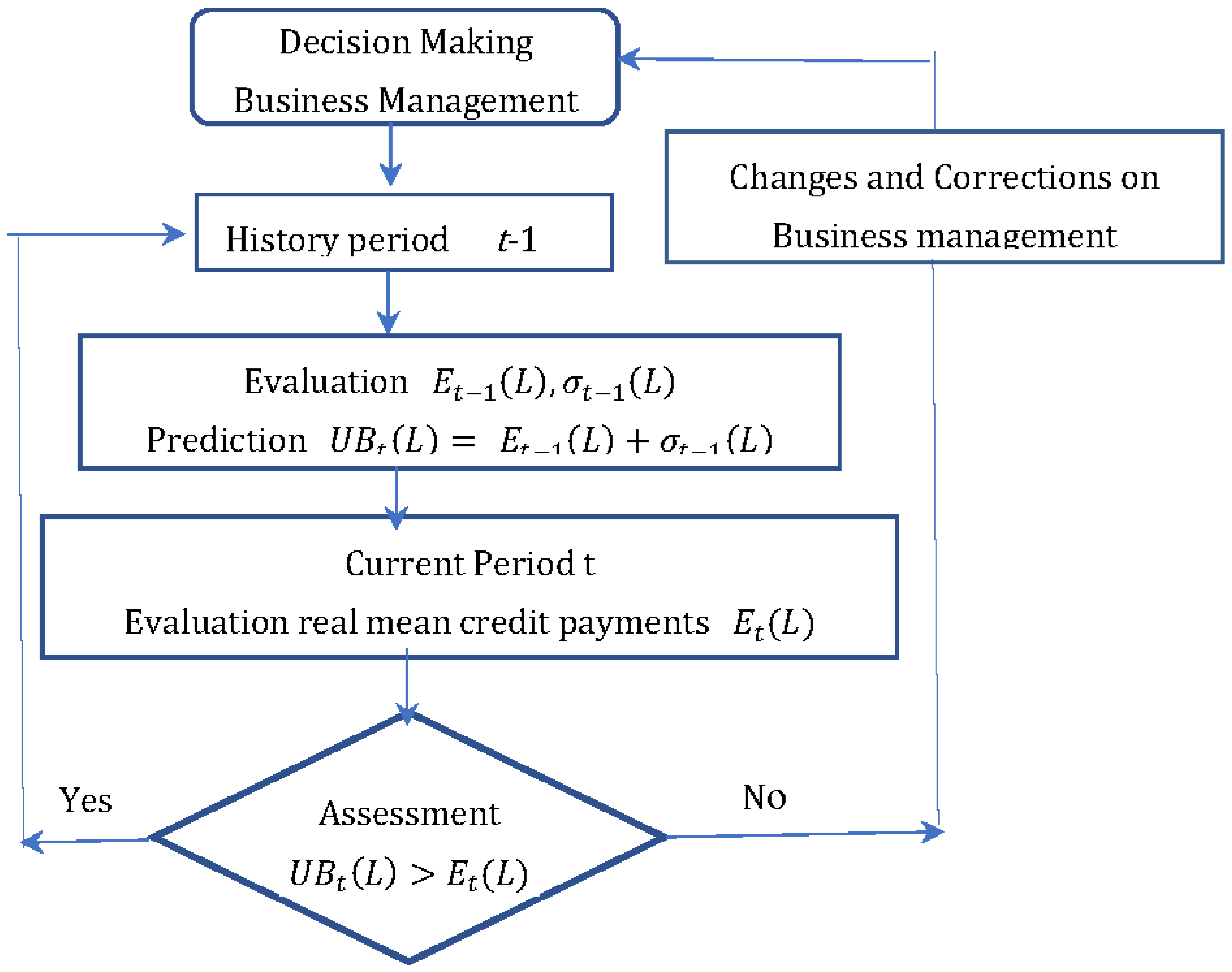
4. Analysis of the farm’s credit policy
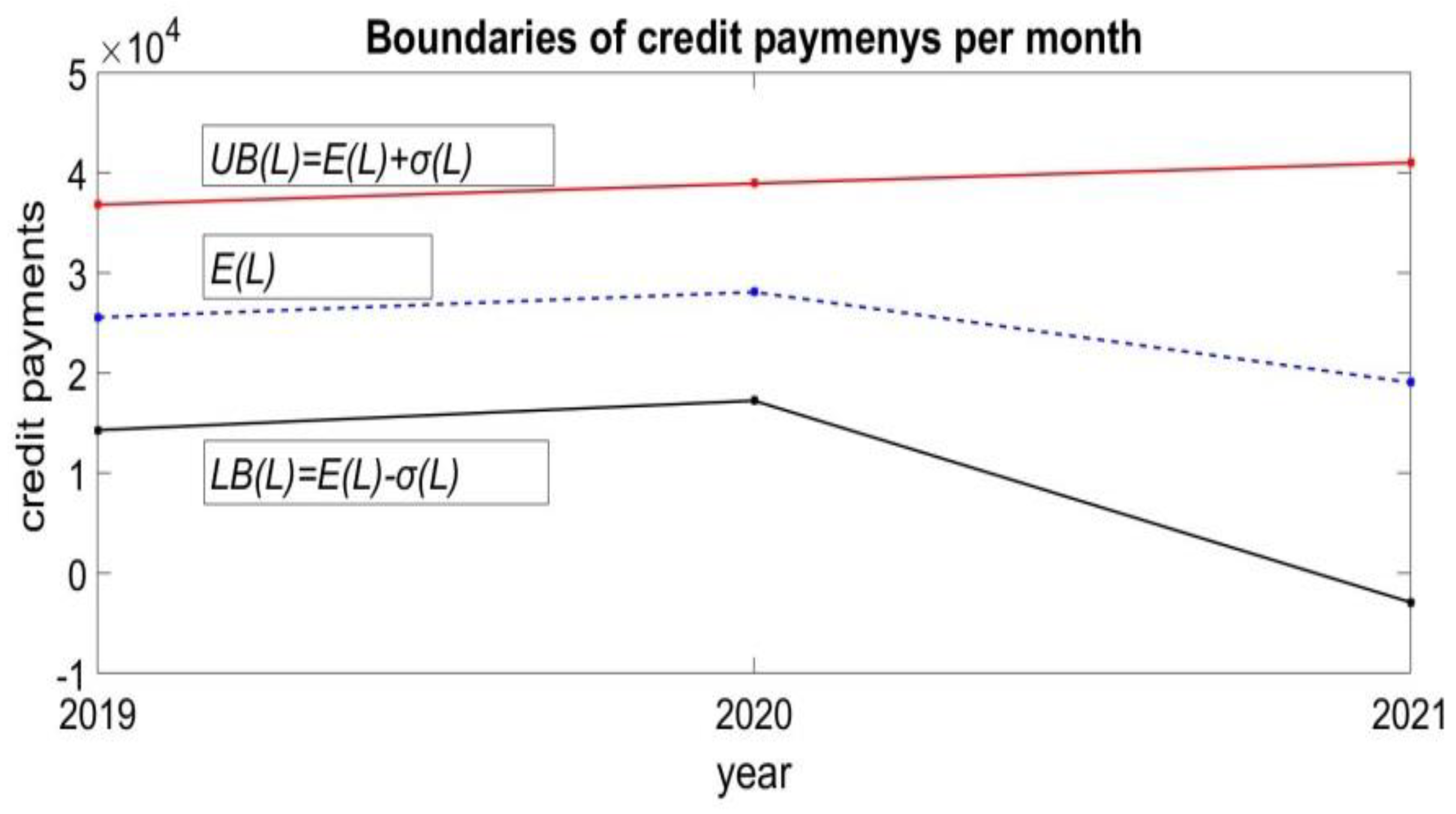
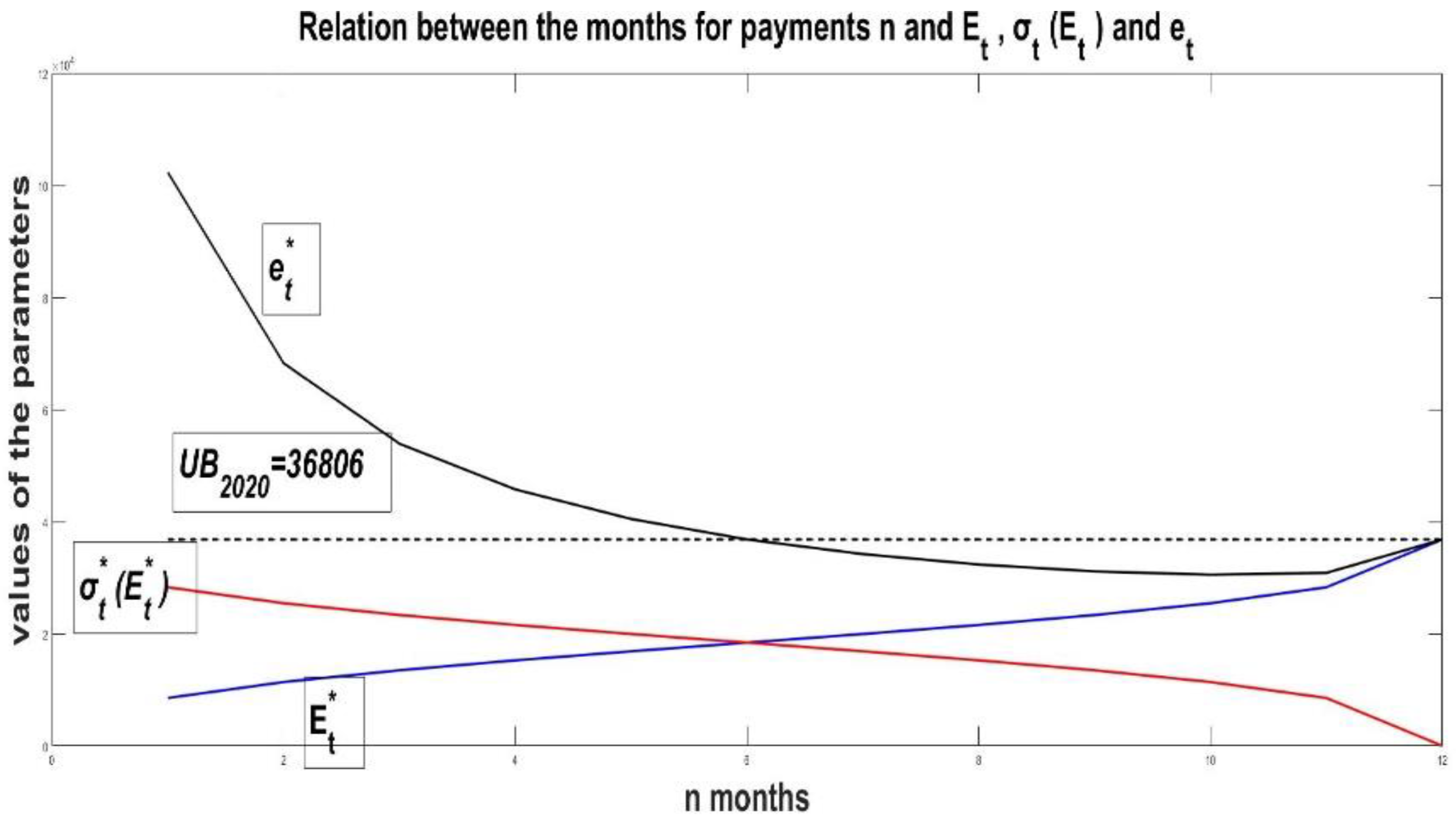
- Estimation of average E(L) and for the previous historical period of credit payments. For the case of 2019 this gives and .
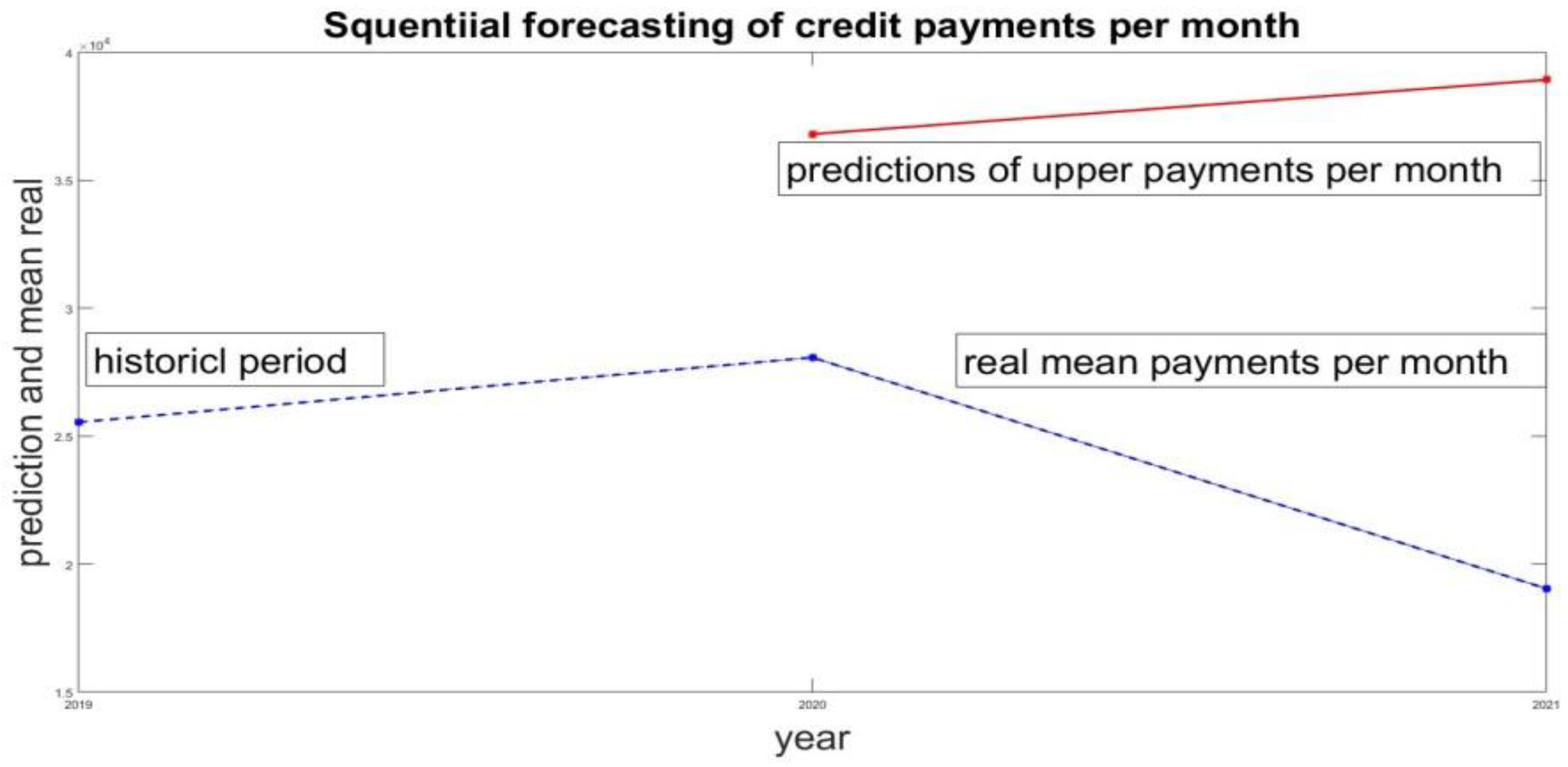
- Estimate the upper bound for this historical period. For the case of 2019 this gives . The value of is taken as the forecast of the monthly credit payments for 2020. Accordingly, this gives limits on the new credits that can be taken. This is the maximum amount of credit that can be used in 2020.
- Evaluation of the forecast. At the end of 2020, average payments payments are estimated. It is a measure of the real values of credit payments L. The comparison between the forecast of the upper limit of the forecast volume of new credits and the actual average payments gives the estimate
5. Assessment of the total credit volumes per year
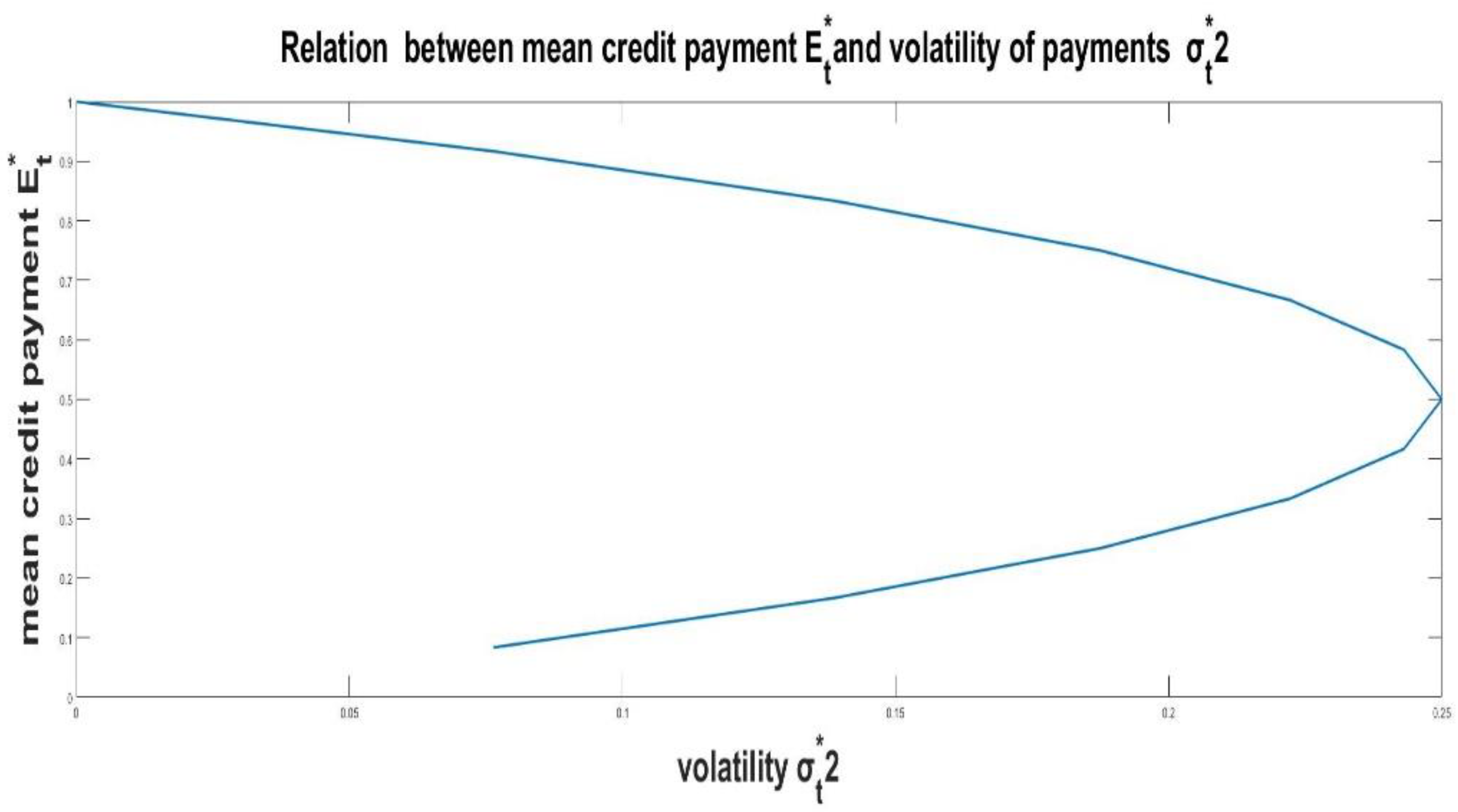
6. Assessment of characteristics for individual credit
7. Potential solution for business management correction
8. Discussions
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kipronoh, P.; Mweta, T. Overview of Working Capital Management: Effective Measures in Managing Working Capital Components to Entrepreneurs. European Journal of Business and Management, 2018, 10(8), 83-86. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327435910_Overview_of_Working_Capital_Management_Effective_Measures_in_Managing_Working_Capital_Components_to_Entrepreneurs (Accessed on 09.12.2023).
- Tiwary, D.; Paul S. Role of Bank Credit and External Commercial Borrowings in Working Capital Financing: Evidence from Indian Manufacturing Firms. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 2023, 16(11) 468. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/1911-8074/16/11/468 (Accessed on 09.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Ismail, R. Working Capital – An Effective Business Management Tool. International Journal of Humanities and Social Science Invention, 2017, 6(3), 12-23. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315445011_Working_Capital_-_An_Effective_Business_Management_Tool (Accessed on 09.12.2023).
- Pakdel, M.; Ashrafi, M. Relationship between Working Capital Management and the Performance of Firm in Different Business Cycles. Dutch Journal of Finance and Management, 2019, 3(1), 1-7. Available online: https://www.djfm-journal.com/article/relationship-between-working-capital-management-and-the-performance-of-firm-in-different-business-5874 (Accessed on 09.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Samithamby, S. Working Capital Management. SSRN Electronic Journal, 2020, 1-22. 10.2139/ssrn.3578141. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3578141 (Accessed on 09.12.2023). http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3578141.
- Fatema, H.; Feysal, M.; Nobanee, H. Working Capital Management of Johnson and Johnson, 2022. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358021457_Working_Capital_Management_of_Johnson_and_Johnson (Accessed on 11.12.2023).
- Herdinata, C. Credit Policy Planning in Medium Scale Business. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 2017 8(1), 14-19. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/313786341_Credit_Policy_Planning_in_Medium_Scale_Business (Accessed on 11.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Reyad H.M.; Zariyawati M.A.; Ong T.S.; Muhamad H. The Impact of Macroeconomic Risk Factors, the Adoption of Financial Derivatives on Working Capital Management, and Firm Performance. Sustainability. 2022, 14(21), 14447. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/21/14447 (Accessed on 11.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Ntiamoah, E. B.; Egyiri, P. O.; Fiaklou, D.; Kwamega, M. An Assessment of Credit Management Practices on Loan Performance. International Journal of Marketing, Strategy, Operations Research and Organizational Behavior, 2014, 30(20), 1127-1131, Available online: https://www.academia.edu/7871974/An_Assessment_of_Credit_Management_Practices_on_Loan_Performance?email_work_card=view-paper (Accessed on 11.12.2023).
- Liu, Wenjuan. Enterprise Credit Risk Management Using Multicriteria Decision-Making. J. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 1-10. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/mpe/2021/6191167/ (Accessed on 11.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, M.; Tarca, S. Regulatory Capital Modelling for Credit Risk. International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Finance, 2015, 18(5). Available online: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/abs/10.1142/S021902491550034X (Accessed on 11.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Madaan, M.; Kumar, A.; Keshri, C.; Jain, R.; Nagrath, P. Loan default prediction using decision trees and random forest: A comparative study. IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 1022 012042, IOP Publishing. Available online: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1757-899X/1022/1/012042 (Accessed on 12.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Bhanu, L. U.; Narayana, S. Customer Loan Prediction Using Supervised Learning Technique. International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications (IJSRP), 2021 11(6), 403-407. Available online: https://www.ijsrp.org/research-paper-0621/ijsrp-p11453.pdf (Accessed on 12.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Swapnesh, D.; Nayak, D. S. K.; Tripti, S. Loan eligibility prediction using machine learning: a comparative approach. Global Journal of Modeling and Intelligent Computing, 2023, 3(1), 48-54, ISSN: 2767-1917, Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/372656643_LOAN_ELIGIBILITY_PREDICTION_USING_MACHINE_LEARNING_A_COMPARATIVE_APPROACH (Accessed on 12.12.2023).
- Wu, W. Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Loan Default. J. Intelligent Information Management, 2022, 14, 157-164. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/pdf/iim_2022092709434339.pdf (Accessed on 12.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Aslam, U.; Aziz, H. I. T.; Sohail, A.; Batcha, N.K. An Empirical Study on Loan Default Prediction Models. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience, 2019, 16(8), 3483-3488. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335966806_An_Empirical_Study_on_Loan_Default_Prediction_Models (Accessed on 12.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Qiu, D.; Ergu,D.; Ying, C.; Liu, K. A study on predicting loan default based on the random forest algorithm, Procedia Computer Science, 2019, 162, 503-513, ISSN 1877-0509 Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1877050919320277 (Accessed on 12.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Nalawade, S.; Andhe, S.; Parab, S.; Sankhe, A. Loan Approval Prediction. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 2022, 09(04), 669-673, ISSN: 2395 Available online: https://www.academia.edu/85429526/Loan_Approval_Prediction?email_work_card=view-paper (Accessed on 12.12.2023).
- Orlova, E. Mechanism and Model for Decision-Making in Credit Risk Management. Conference: Proceedings of the Fourth Workshop on Computer Modelling in Decision Making (CMDM 2019), 2019. Available online: https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/cmdm-19/125925611 (Accessed on 12.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Olabamiji, O.; Michael, O. Credit Management Practices and Bank Performance: Evidence from First Bank. South Asian Journal of Social Studies and Economics, 2018, 1(1), 1-10. Available online: https://journalsajsse.com/index.php/SAJSSE/article/view/502 (Accessed on 12.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Mburu, I.; Mwangi, L.; Muathe, S. Credit Management Practices and Loan Performance: Empirical Evidence from Commercial Banks in Kenya. International Journal of Current Aspects in Finance, Banking and Accounting, 2020, 2(1), 51-63. ISSN 2707-8035 Available online: https://journals.ijcab.org/journals/index.php/IJCFA/article/view/105 (Accessed on 12.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Herdinata, C. Credit Policy Planning in Medium Scale Business. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 2017, 8(1), 14-19. Available online: https://dspace.uc.ac.id/bitstream/handle/123456789/961/Paper961.pdf?sequence=6&isAllowed=y (Accessed on 14.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Farhan, N.H.S.; Almaqtari, F.A.; Al-Matari, E.M.; SENAN, N.A.M.; Alahdal, W.M.; Hazaea S.A. Working Capital Management Policies in Indian Listed Firms: A State-Wise Analysis, Sustainability, 2021, 13(8), 4516. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/13/8/4516 (Accessed on 14.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Olabisi, J.; Oladejo, D. A.; Adegoke, J. F.; Abioro, M. Credit management policy and firms’ profitability: evidence from infant manufacturing firms in southwest Nigeria. The Journal Contemporary Economy, 2019, 4(4), 59-69, ISSN 2537–4222. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338423067_CREDIT_MANAGEMENT_POLICY_AND_FIRMS'_PROFITABILITY_EVIDENCE_FROM_INFANT_MANUFACTURING_FIRMS_IN_SOUTHWEST_NIGERIA (Accessed on 14.12.2023).
- Otto, W. Management of trade credit by small and medium-sized enterprises. Journal of Economic and Financial Sciences, 2018, 11(1), 1-8. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/324361630_Management_of_trade_credit_by_small_and_medium-sized_enterprises (Accessed on 14.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Poot, M. Credit and Collection Management Practices, Credit Risk Management, and Financial Performance of Private Higher Educational Institutions (HEIs) in the Philippines: Basis for Continuous Improvement. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Entrepreneurship and Business Management (ICEBM 2019), Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research, 2020, 14, 288-295. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/342778867_Credit_and_Collection_Management_Practices_Credit_Risk_Management_and_Financial_Performance_of_Private_Higher_Educational_Institutions_HEIs_in_the_Philippines_Basis_for_Continuous_Improvement (Accessed on 14.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Kipronoh, P.; Mweta, T. Overview of Working Capital Management: Effective Measures in Managing Working Capital Components to Entrepreneurs. European Journal of Business and Management, 2018, 10(8), 83-86, ISSN 2222-1905, Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327435910_Overview_of_Working_Capital_Management_Effective_Measures_in_Managing_Working_Capital_Components_to_Entrepreneurs (Accessed on 14.12.2023).
- Zimon, G. Working Capital. Encyclopedia, 2021, 1(3), 764-772. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2673-8392/1/3/58 (Accessed on 14.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Pakdel, M.; Ashrafi, M. Relationship between Working Capital Management and the Performance of Firm in Different Business Cycles. Dutch Journal of Finance and Management, 2019, 3(1), 1-7. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/335204064_Relationship_between_Working_Capital_Management_and_the_Performance_of_Firm_in_Different_Business_Cycles (Accessed on 14.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Demiraj, R.; Dsouza, S.; Abiad, M. Working Capital Management Impact on Profitability: Pre-Pandemic and Pandemic Evidence from the European Automotive Industry. Risks, 2022, 10(12):236. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9091/10/12/236 (Accessed on 14.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Ngugi, D. Quantitative Methods For Business Management. 2018; p. 420. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329031752_Quantitative_Methods_For_Business_Management (Accessed on 14.12.2023).
- Lariviere, M. A.; Porteus, E.L. Stalking information: Bayesian inventory management with unobserved lost sales. Management Science, 1999, 45(3), 346–363. Available online: https://pubsonline.informs.org/doi/10.1287/mnsc.45.3.346 (Accessed on 14.12.2023). [CrossRef]
- Standard Normal Distribution Showing Standard Deviations. Digital image. Statistics How To, 2016. Available online: https://www.statisticshowto.com/probability-and-statistics/ (Accessed on 14.12.2023).
| Month | 2019 li [BGN] |
2019 ni [BGN] |
2020 li [BGN] |
2020 ni [BGN] |
2021 li [BGN] |
2021 ni [BGN] |
| I | 7690 | 1 | 45802 | 3 | 4750 | 1 |
| II | 6000 | 1 | 34297 | 2 | 19523 | 4 |
| III | 25195 | 3 | 11505 | 1 | 18447 | 4 |
| IV | 25195 | 3 | 45802 | 5 | 20598 | 6 |
| V | 25195 | 3 | 22463 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| VI | 25195 | 3 | 22463 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| VII | 25195 | 3 | 22463 | 3 | 58569 | 4 |
| VIII | 25195 | 3 | 38614 | 5 | 14824 | 3 |
| IX | 25195 | 3 | 26665 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| X | 25195 | 3 | 27760 | 5 | 19824 | 4 |
| XI | 45802 | 3 | 19523 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| XII | 45802 | 3 | 19523 | 3 | 63315 | 6 |
| Year | σ(L) | σ(N) | ||
| 2019 | 25542 | 11264 | 2.67 | 0.78 |
| 2020 | 28074 | 10853 | 3.5 | 1.31 |
| 2021 | 19041 | 21965 | 2.67 | 2.35 |
| Year |
min |
max |
min |
max |
| 2019 | 14278 | 36806 | 1.89 | 3.45 |
| 2020 | 17221 | 38927 | 2.19 | 4.81 |
| 2021 | -2924 | 41006 | 0.35 | 5.02 |
| Historical period | Prediction of maximal credit for 2020 | Real mean value of payments 2020 | Historical period | Prediction of maximal credit for 2021 | Real mean value of payments 2021 |
| 2019 | 36 806 | 28 074 | 2020 | 38 027 | 19 041 |
| Year | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| 306 510 | 336 880 | 228 497 | |
| 39 021 | 37 596 | 76 089 | |
| 345 531 | 374 476 | 304 586 |
| Historical period | 2020 maximum credit forecast | Real average payments 2020 | Historical period | 2021 maximum credit forecast | Real average payments 2021 |
| 2019 | 345 531 | 336 880 | 2020 | 374 476 | 228 497 |
| Year | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
| 9578 | 8021 | 7140 | |
| 5170 | 1379 | 8687 | |
| 14 748 | 9400 | 15 828 |
| Historical period | 2020 maximum credit forecast | Real average payments 2020 | Historical period | 2021 maximum credit forecast | Real average payments 2021 |
| 2019 | 14 748 | 8021 | 2020 | 9400 | 7140 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





