1. Introduction
The digital orthophoto is a remote sensing image that has undergone geometric correction, possessing both map geometric accuracy and image characteristics. It accurately portrays the terrain and landforms of a scene and can be utilized for measuring real distances. It plays a crucial role in various fields such as land surveying, urban planning, resource management, and emergency response. It aids in monitoring urban development and changes, tracking alterations in land cover and land use. Additionally, it enables rescue personnel to gain more effective insights into disaster areas, enhancing efficiency in responding to emergencies.
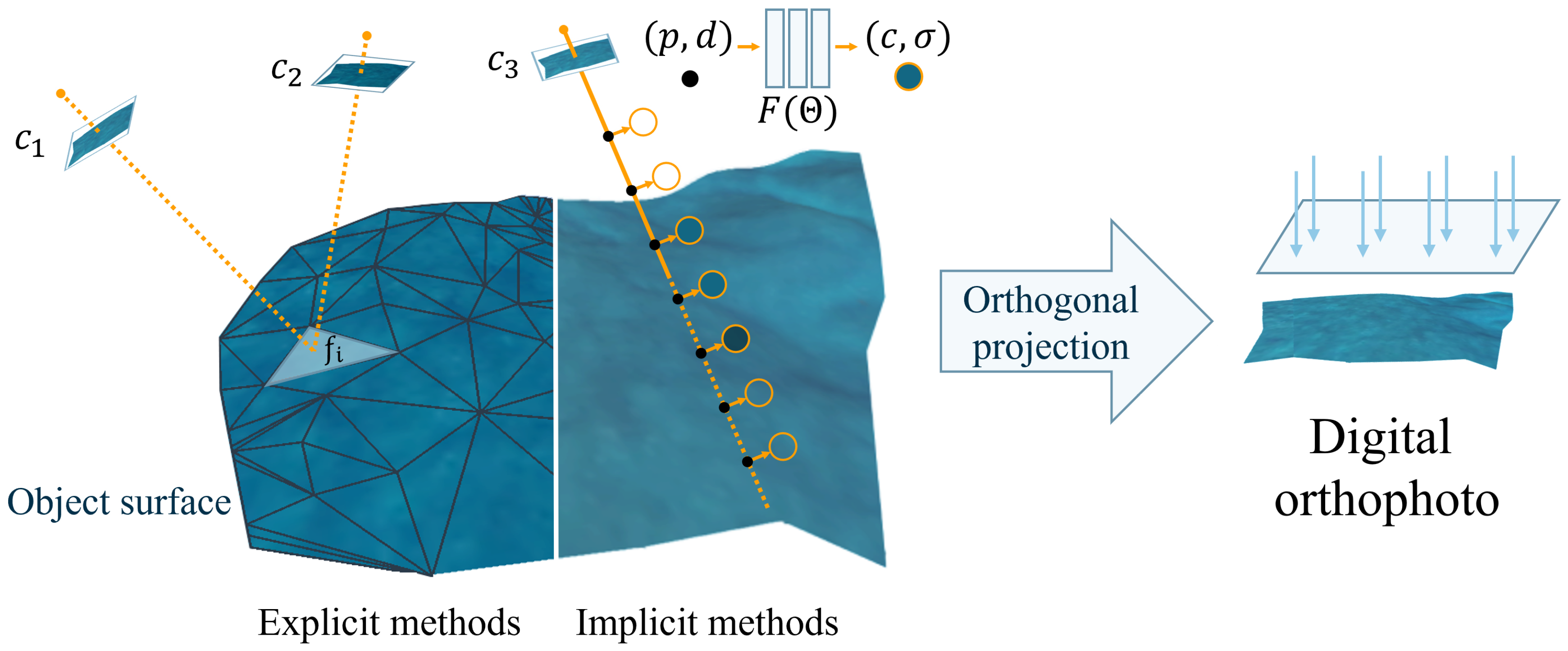
The core of digital orthophoto generation lies in obtaining elevation and texture information of objects within the spatial scene. In order to obtain the elevation and texture of the spatial objects’s surface as shown in
Figure 1, the traditional method of generating digital orthophoto mainly draws inspiration from the concept of MVS. It involves reprojecting three-dimensional objects onto different images using the camera’s intrinsic and extrinsic parameters. By extracting two image patches centered around the reprojection point, this method then infers the likelihood of the object being at the current elevation based on a quantitative assessment of the similarity between these scenes. Consequently, it reconstructs the necessary spatial structural information of the scene and the final result are obtained through top view projection. We define such algorithms that utilize traditional geometry-based approaches to acquire explicit three-dimensional spatial structures and subsequently generate digital orthophoto as explicit methods.
As a rapidly advancing emerging neural rendering method for novel view synthesis, NeRF[
1] has gained significant attention in recent years due to its remarkable rendering quality. Therefore, we specifically focused on the feasibility of NeRF in digital orthophoto generation. As shown in
Figure 1, NeRF initiates the rendering process by sampling a series of points along targeted rays (represented by the black dots), then estimates the volume density and radiance at specific viewpoints (represented by the circles with an orange outline) for these sample points with neural networks
, finally it applies volume rendering to produce the pixel values. As a specific viewpoint of the scene, the digital orthophoto can be rendered using NeRF by employing a set of parallel rays that are orthogonal to the ground. In this paper, we define the digital orthophoto generation methods based on neural rendering, which do not rely on traditional three-dimensional reconstruction, as implicit methods.
In this paper, we will compare the algorithmic processes and performance of explicit and implicit methods in digital orthophoto generation. Within the explicit methods, we selected the TDM algorithm[
2], known for its exceptional speed performance. To unleash its potential, we conducted CUDA version porting and optimization modifications, significantly enhancing the generation efficiency. For implicit methods, we implemented orthographic view rendering based on NeRF, and selected the speed-optimized Instant NGP[
3] as a representative experiment. The experimental results reveal that the explicit method demonstrates notably high efficiency in generation speed. Both explicit and implicit methods yield acceptable levels of measurement accuracy and exhibit comparable rendering quality.
2. Related Work
Digital Orthophoto Generation Methods
In digital photogrammetry, a mature workflow of digital orthophoto generation is presented in [
4]. A general approach of digital orthophoto generation often relies on 3D reconstruction[
5,
6], involves performing sparse and dense reconstructions on a sequence of images, and then orthogonally projecting the reconstructed 3D model onto a horizontal plane to obtain the digital orthophoto. A digital orthophoto generation method with the assistance of Pix4D is proposed in [
7], they also proposing post-processing methods based on Pix4D for digital orthophoto generation. Many efforts are being made to accelerate digital orthophoto generation, but these works are usually focused on specific scenarios. Some works have optimized digital orthophoto generation in structured scenes. For instance, Wang et.al[
8] extracted and matched lines from the original images, then transformed these matched lines into the 3D model, reducing the computational cost of pixel-by-pixel matching in dense reconstruction. Li et.al[
9] used deep learning methods to obtain a topological graph in the of the scenes, enhancing the accuracy at the edges of buildings. Lin et.al[
10] arranged ground control points at the edges of buildings to ensure the accuracy of these edges. Some studies have made improvements for more specialized scenes. For instance, Lin et al.[
11] focused on agricultural surveying scenarios, utilizing the spectral characteristics of vegetation to determine its location, thereby achieving fast digital orthophoto generation in agricultural mapping contexts. Zhao et al.[
12] assumed the target scene to be a plane, employing simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) for real-time camera pose estimation and projecting the original images onto the imaging plane of the digital orthophoto. These methods speed up the digital orthophoto generation by sacrificing the generality of the algorithms. Some methods[
13,
14] utilize DEM (Digital Elevation Model) to accelerate the digital orthophoto generation,but this approach is constrained by the acquisition speed of the DEM.
Zhao et al.[
2] were the first to propose a process for digital orthophoto generation directly using sparse point clouds. This approach eliminates the redundant computations that occur in the dense reconstruction phase of the standard 3D reconstruction-based digital orthophoto generation methods, significantly increasing the speed of generation.
NeRF with Sparse Parametric Encodings
In recent years, methods for novel view images synthesis on neural rendering have rapidly evolved. Mildenhall et al.[
1] introduced Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), which represents a scene as a continuous neural radiance field. NeRF optimizes a fully-connected deep network as an implicit function to approximate the volume density and view-dependent emitted radiance from 5D coordinates
, with
representing the volume density at a spatial point. To render an image from a specific novel viewpoint, NeRF initially: (1) generates camera rays traversing the scene and samples a set of 3D points along these rays, (2) inputs the sampled points and viewing directions into the neural network to obtain a collection of densities rgb values, and (3) employs differentiable volume rendering to synthesize a 2D image.
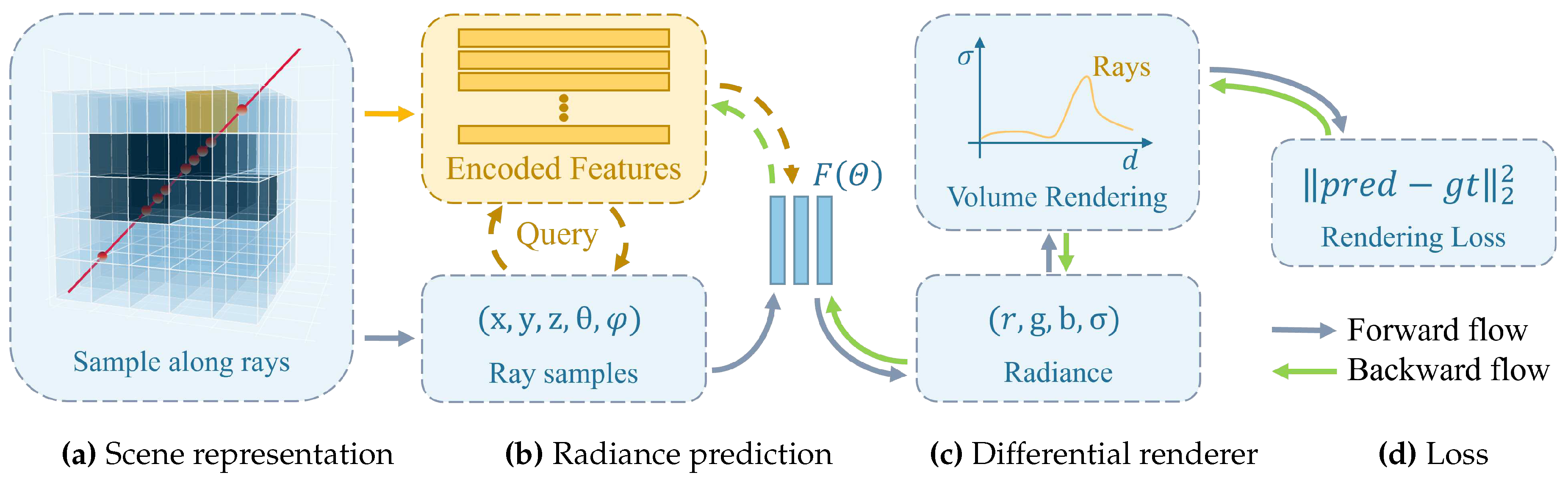
Many recent works have incorporated sparse parametric encoding into NeRF for enhancement, generally aiming to pre-construct a series of auxiliary data structures with encoded features within the scene. We summarizes these NeRF with sparse parametric encoding into four stages in
Figure 2: (1) Scene representation, (2) Radiance prediction, (3) Differentiable renderer, and (4) Loss function. For the first stage in
Figure 2, numerous sparse parametric encoding techniques have been proposed, such as dense and multi-resolution grids[
3,
15,
16], plannar factorization[
17,
18,
19], point clouds[
20], and other formats[
21,
22]. The central concept behind these methods is to decouple local features of the scene from the MLP, thereby enabling the use of more flexible network architectures. Typically represented by a grid in the
Figure 2, resulting in the local encoding feature lookup table shown in the orange part. For the second stage in
Figure 2, a coarse-fine strategy is often used to sample along rays, and a cascaded MLP is typically used to predict volume density and view-dependent emitted radiance. Several studies have attempted to enhance rendering quality by improving sampling methods[
19,
23,
24]; some have employed occupancy grids to achieve sampling acceleration[
25]; others have focused on adjusting the MLP structure to facilitate easier network training[
26]. For the third stage in
Figure 2, the figure exemplifies the most commonly used volume rendering, but other differentiable rendering methods are also employed[
27], with Nvdiffrast[
28] providing efficient implementations of various differentiable renderers. For the fourth stage in
Figure 2, the figure presents the most commonly used mean squared error loss between rendered and ground truth images, with some works introducing additional supervision, such as methods incorporating depth supervision[
29,
30]. With different scene representation, various loss functions are incorporated to constrain the network.
3. Method
We choose our proposed TDM algorithm as the explicit method for digital orthophoto generation and Instant NGP as the implicit method. Both methods rely on the sparse reconstruction results from Structure from Motion (SfM). To generate digital orthophoto, both methods require prior information of accurate ground normal vectors. By using Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) information as a prior for sparse reconstruction, we can obtain accurate ground normal vectors while also recovering the correct scale of scene.
3.1. Explicit Method — TDM
The TDM algorithm, when generating digital orthophoto, essentially processes information for each pixel, equivalent to raster data processing. To achieve the final rendering, the key lies in accurately estimating the elevation values and corresponding textures for each raster. The following will introduce the algorithm flow of our CUDA-adapted and optimized version for the TDM algorithm in this paper.
Raster Attribute Initialization: by specifying the spatial resolution
, the raster image G to be generated is obtained with dimensions
, where each raster represents a pixel in the final digital orthophoto image. Each raster cell possesses four attributes: 1) raster color
. 2) raster elevation
. 3) raster normal vector
. 4) Confidence score of raster elevation
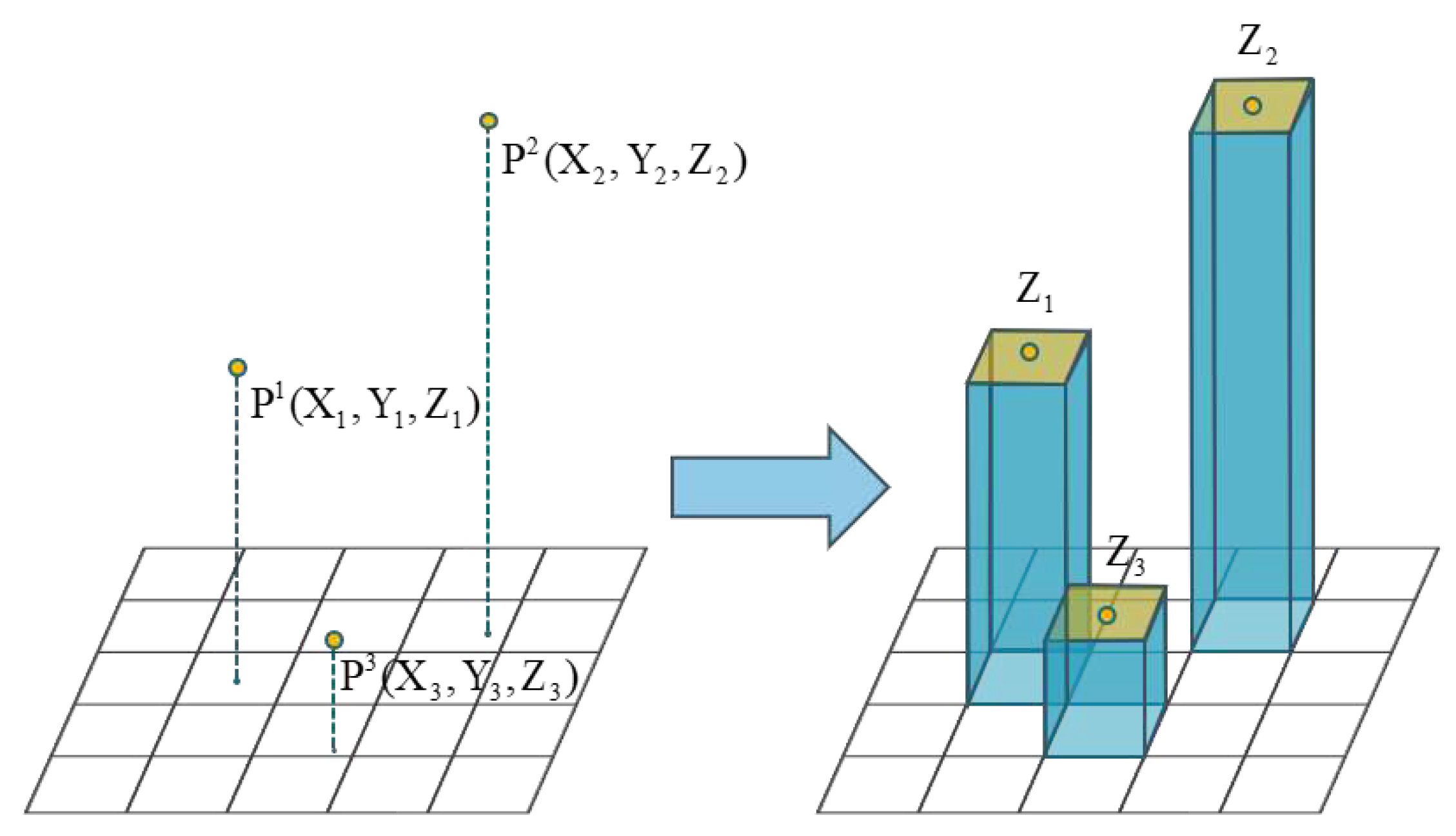
. As shown in
Figure 3, the algorithm traverses through all three-dimensional point clouds, performs orthographic projection to obtain the raster cell
corresponding to a certain three-dimensional point
. Subsequently, the elevation
of that raster is initialized.
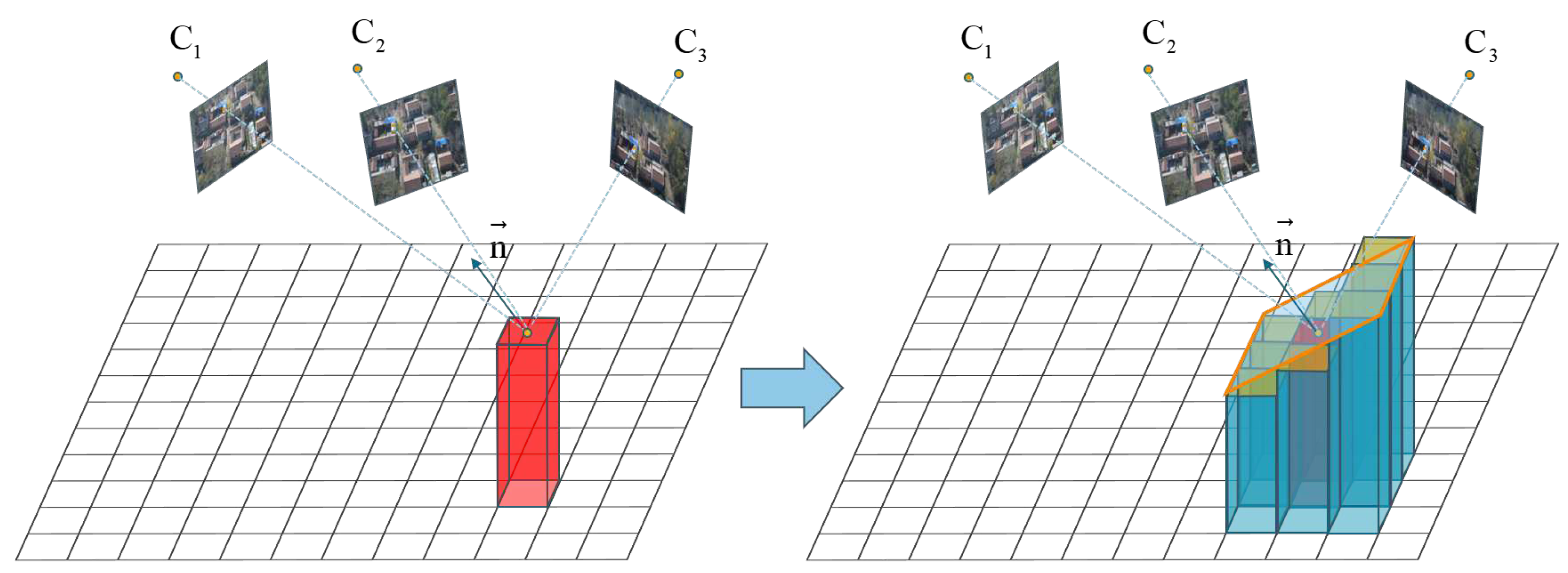
Elevation Propagation: given rasters with known elevation considered as seed units
, the propagation starts iteratively from these seed units. Each iteration propagates the elevation information
Z from the seed raster unit to all raster units within a patch. Subsequently, the adjustment of
occurs by random initialization of the normal vector
as shown in
Figure 4. The confidence measure for the plane uses the matching score [
2]
:
Furthermore, we can evaluate the reasonableness of depth information through color consistency. Once the computed
exceeds the confidence threshold
, the current depth information is considered reasonable. Then update the
,
and
of all raster units within the patch. During an iteration, there will be multiple random initialization of
. If the matching score remains below
, elevation information will not be propagated.
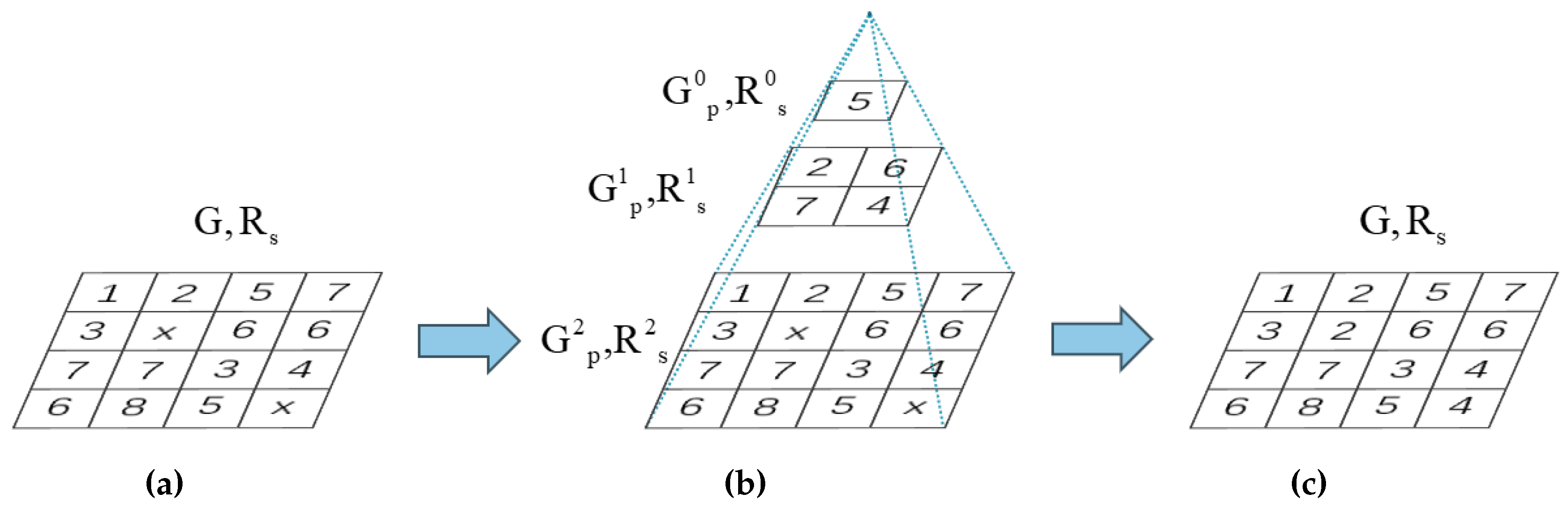
Multi-resolution Interpolation-based Elevation Filling: the original algorithm gradually reduces
after each iteration until the elevation propagation is complete. This will result in subsequently obtaining a lower confidence score for
and wasting a considerable amount of time. To efficiently reduce iteration time, we propose a multi-resolution interpolation-based elevation filling algorithm to acquire elevations of raster units with low confidence scores. When the initial value of
is
, it gradually decreases with the increase in iteration count until it equals
. At this stage, we utilize the proposed algorithm to assign values to raster units
without elevations as shown in
Figure 5.
After the elevation propagation, the initial seed
for this filling algorithm is derived from raster units
within the raster image
G, where the confidence measure
exceeds
. The spatial resolution
of the filling raster image
for the i-th layer of this multi-resolution grid is as follows:
where
and
are the maximum values of the X- and Y-coordinates in this area, likewise,
and
are the minimum values. When multiple
fall into the same raster unit
of
, we set the average of these points as the elevation value for that raster unit. If no points fall within a specific raster unit, we will retrieve the elevation value corresponding to the raster position from multi-resolution interpolation raster image
and set it as the elevation value for
. If
, the process is repeated, continuously constructing
as described above. Eventually, there are some raster units that have not been assigned elevation values in
G. We will then search for the elevation values corresponding to the raster positions in the highest resolution interpolation raster image
and assign them accordingly.
Texture Mapping: in each image, certain objects might be occluded by other objects, leading to erroneous texture mappings. Occlusion detection is necessary in such cases. Subsequently, texture mapping is performed based on and the corresponding projection relationship with the respective camera, obtaining color information for the raster cell. Finally, the generation of the final digital orthophoto is completed.
3.2. Implicit Method
We will use the most representative Instant NGP[
3] as an example to illustrate the process of digital orthophoto generation using NeRF. As a neural radiance field utilizing sparse parametric encodings, Instant NGP introduces multi-resolution hash encoding to address the
parameter complexity associated with dense voxel grids. In practice, Instant NGP divides the scene into voxel grids with
L levels of resolution. For each level of resolution grid, a compact spatial hash table
of a fixed size
T is used to store the
F-dimensional feature vectors on that resolution level’s grid.
When querying the feature vector of a spatial coordinate
x in Instant NGP, the process first identifies grid corners spatially close to
x on each resolution layer. Then, the feature vectors of adjacent grid corners are looked up in
. Next, linear interpolation is performed to obtain the feature vector of the spatial coordinate
x at that resolution level. This process is executed across all
L resolution levels. Subsequently, these feature vectors from different resolution layers are concatenated with auxiliary inputs
, forming the final MLP embedding input
. Finally, Instant NGP uses a Tiny MLP
to obtain the radiance
for the spatial coordinate
x. This process also aligns with the generalized description of neural radiance fields based on sparse parametric encoding as shown in
Figure 2. Instant NGP can achieve a balance between performance, storage, and efficiency by selecting appropriate hash table sizes
T.
As mentioned in
Section 1, digital orthophoto can be rendered with neural approaches. In contrast to the typical pinhole camera imaging model, digital orthophoto are rendered using a set of parallel light rays perpendicular to the ground as shown in
Figure 1. To ensure that Instant NGP achieves a rendering quality comparable to explicit methods, we adopted the largest scale model recommended in the paper.
4. Experiments And Analysis
The data utilized in this study were all obtained from the unmanned aerial vehicle. The camera’s center position was acquired through DGPS. We select the TDM algorithm as the representative explicit method for digital orthophoto generation. Similarly, we use Instant NGP as the representative implicit method for digital orthophoto generation.The commercial software Pix4D is widely used and performs exceptionally well in digital orthophoto generation. Therefore, we have chosen its generated results as the benchmark for measuring accuracy. Pix4D, being an explicit method, requires the full process of traditional 3D reconstruction during digital orthophoto generation. Hence, for the time comparison test, we have selected the TDM algorithm, which eliminates redundant computations during the dense reconstruction.
In this section, we initially conducted digital orthophoto generation tests on three common scenes: buildings, roads, and rivers. The objective was to demonstrate the image generation quality and algorithm robustness of both explicit and implicit methods across various scenes. Subsequently, for assessing the accuracy of the two methods, comparisons were made with the commercial software Pix4D regarding measurement precision. Finally, to evaluate the efficiency of both methods, we measured the time required for generating scenes of different sizes.
4.1. Test on Various Scenes
The
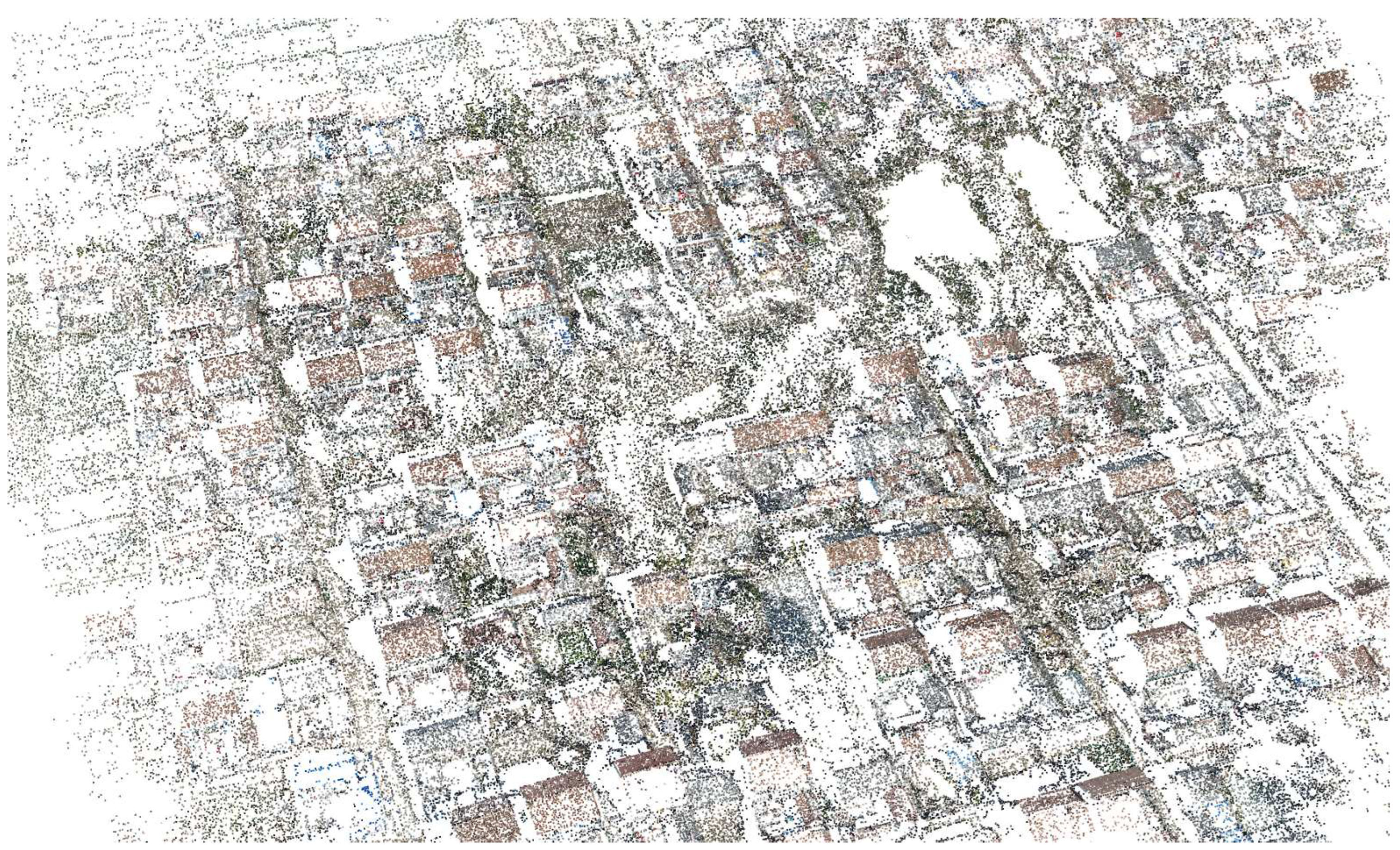
Figure 6 shows a set of original village photo data used for testing, including numerous scenes of slanted roofs of houses, trees, and other objects.We performed sparse reconstruction in conjunction with the camera’s DGPS information, enabling the recovery of accurate scale information and spatial relationships. The resultant 3D sparse point cloud as shown in
Figure 7 and camera poses served as prior information for subsequent explicit and implicit methods in digital orthophoto generation.After the final processing through the explicit and implicit methods, respectively, the resulting digital orthophoto are shown in the
Figure 8.
In the
Figure 9, we conducted digital orthophoto generation tests for various scenes using both explicit and implicit methods. We observed that the digital orthophoto generated by both explicit and implicit methods are similar and can be generated successfully across multiple scene tests.
4.2. Evaluation of Accuracy
To validate the measurement accuracy of different digital orthophoto generation methods, we will select a specific area within the city for subsequent testing scenes. We’ll utilize explicit methods (TDM), implicit methods (Instant NGP), and commercial software (Pix4D) to generate digital orthophoto, followed by comparing length measurements as shown in
Figure 10.
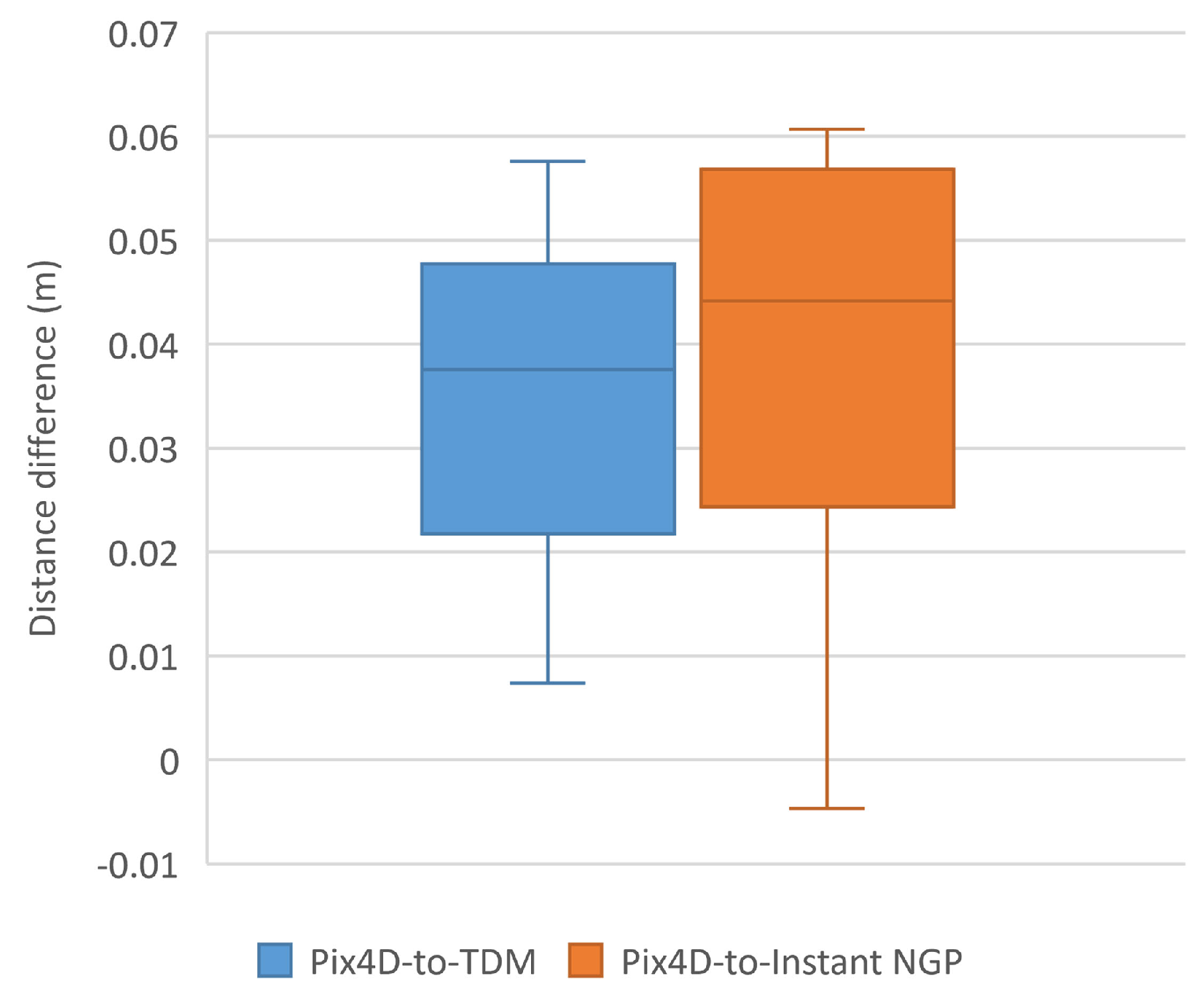
As can be seen from
Figure 11, the box-plot displays the differences in distance measurements in digital orthophoto. The median of the box plot generated from Pix4D-to-TDM is 0.03755m, while the other median from Pix4D-to-Instant NGP is 0.04415m, both around 0.04m. In comparison with Pix4D, this study concludes that both the explicit method (TDM) and the implicit method (Instant NGP) for digital orthophoto generation meet the requirements for mapping purposes.
4.3. Evaluation of Efficiency
To verify the generation efficiency between explicit and implicit methods, in this section, we will conduct tests on the generation time of digital orthophoto in five different size scenes. These two types of methods were run on a personal computer with an Intel(R) Core(TM) i7 - 12700 CPU @ 4.90 GHz and an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090.
Table 1 illustrates the time consumption for digital orthophoto generation using TDM and Instant NGP at different scene sizes. For TDM, the time measurement ranges from obtaining sparse reconstruction results to the generation of digital orthophoto. For Instant NGP, it starts from acquiring sparse reconstruction results, proceeds through model training, and culminates in rendering digital orthophoto. Across five different scene sizes, the TDM algorithm exhibits superior speed performance compared to Instant NGP, with its runtime reduced by two orders of magnitude. Therefore, explicit method currently hold a significant advantage over implicit method in terms of efficiency in digital orthophoto generation.
5. Conclusion
In this paper, we categorized the methods for digital orthophoto generation into explicit and implicit methods, exploring the potential of using NeRF for implicit digital orthophoto generation. We selected the most representative fast algorithms from the two categories: the TDM algorithm and Instant NGP. Additionally, we adapted and optimized TDM algorithm to a CUDA version, significantly enhancing the efficiency of digital orthophoto generation.
In both explicit and implicit methods, an initial step involves sparse reconstruction to obtain camera poses, point clouds, and other prior information. The former employs a elevation propagation process that explicitly integrates local color consistency of images with multi-view geometry theories to acquire scene elevation information and corresponding textures. Conversely, in NeRF, the loss function is designed as the color difference between rendered and real images. Throughout the training process, the neural network gradually fits to the real scene, implicitly capturing the surfaces and textures of scene objects, and synthesize novel view images through differentiable rendering. Finally, both methods complete the entire process to generate digital orthophoto.
We conducted tests on explicit and implicit methods for digital orthophoto generation in various scenes, measuring the generation efficiency and result quality. And we employed the commercial software Pix4D as a standard for assessing measurement accuracy and reliability, evaluating both methods. The results indicate that currently, explicit methods exhibit higher efficiency in generation compared to implicit methods, achieving a similar level of quality in generated output. Moreover, both methods meet the requirements for measurement accuracy. In our future work, we aim to further explore the development of implicit methods for digital orthophoto, leveraging the characteristics of orthographic perspectives to consider the potential implementation of fast implicit generation algorithms.
References
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Communications of the ACM 2021, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Jiang, G.; Li, Y. A Novel Method for Digital Orthophoto Generation from Top View Constrained Dense Matching. Remote Sensing 2022, 15, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Evans, A.; Schied, C.; Keller, A. Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG) 2022, 41, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, B.A.; Wolf, P.R. Elements of Photogrammetry (with Applications in GIS); McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2000.
- Schonberger, J.L.; Frahm, J.M. Structure-from-motion revisited. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016, pp. 4104–4113.
- Shen, S. Accurate multiple view 3d reconstruction using patch-based stereo for large-scale scenes. IEEE transactions on image processing 2013, 22, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Ai, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, Y. Generating a high-precision true digital orthophoto map based on UAV images. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 2018, 7, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, L.; Sun, Y.; Cui, X.; Mortimer, H.; Li, Y. True orthophoto generation using line segment matches. The Photogrammetric Record 2018, 33, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wegner, J.D.; Lucchi, A. Topological map extraction from overhead images. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019, pp. 1715–1724.
- Lin, T.Y.; Lin, H.L.; Hou, C.W. Research on the production of 3D image cadastral map. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Applied System Invention (ICASI). IEEE, 2018, pp. 259–262.
- Lin, Y.C.; Zhou, T.; Wang, T.; Crawford, M.; Habib, A. New orthophoto generation strategies from UAV and ground remote sensing platforms for high-throughput phenotyping. Remote Sensing 2021, 13, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Bu, S.; Jiang, H.; Han, P.; Li, K.; Wan, G. Real-time orthophoto mosaicing on mobile devices for sequential aerial images with low overlap. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, J.; Ladner, L.; Champion, R. Image processing techniques for digital orthophotoquad production. Photogrammetric engineering and remote sensing 1989, 55, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J. DOM generation from aerial images based on airborne position and orientation system. 2010 6th International Conference on Wireless Communications Networking and Mobile Computing (WiCOM). IEEE, 2010, pp. 1–4.
- Sun, C.; Sun, M.; Chen, H.T. Direct voxel grid optimization: Super-fast convergence for radiance fields reconstruction. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 5459–5469.
- Fridovich-Keil, S.; Yu, A.; Tancik, M.; Chen, Q.; Recht, B.; Kanazawa, A. Plenoxels: Radiance fields without neural networks. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 5501–5510.
- Chen, A.; Xu, Z.; Geiger, A.; Yu, J.; Su, H. Tensorf: Tensorial radiance fields. European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2022, pp. 333–350.
- Fridovich-Keil, S.; Meanti, G.; Warburg, F.R.; Recht, B.; Kanazawa, A. K-planes: Explicit radiance fields in space, time, and appearance. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2023, pp. 12479–12488.
- Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, B.; Gao, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y. Tri-miprf: Tri-mip representation for efficient anti-aliasing neural radiance fields. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 19774–19783.
- Xu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Philip, J.; Bi, S.; Shu, Z.; Sunkavalli, K.; Neumann, U. Point-nerf: Point-based neural radiance fields. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 5438–5448.
- Yu, A.; Li, R.; Tancik, M.; Li, H.; Ng, R.; Kanazawa, A. Plenoctrees for real-time rendering of neural radiance fields. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2021, pp. 5752–5761.
- Kulhanek, J.; Sattler, T. Tetra-NeRF: Representing Neural Radiance Fields Using Tetrahedra. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.09987 2023.
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Tancik, M.; Hedman, P.; Martin-Brualla, R.; Srinivasan, P.P. Mip-nerf: A multiscale representation for anti-aliasing neural radiance fields. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2021, pp. 5855–5864.
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Verbin, D.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Hedman, P. Mip-nerf 360: Unbounded anti-aliased neural radiance fields. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 5470–5479.
- Li, R.; Tancik, M.; Kanazawa, A. Nerfacc: A general nerf acceleration toolbox. arXiv preprint arXiv:2210.04847 2022.
- Zhang, K.; Riegler, G.; Snavely, N.; Koltun, V. Nerf++: Analyzing and improving neural radiance fields. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.07492 2020.
- Kerbl, B.; Kopanas, G.; Leimkühler, T.; Drettakis, G. 3d gaussian splatting for real-time radiance field rendering. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG) 2023, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, S.; Hellsten, J.; Karras, T.; Seol, Y.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Modular Primitives for High-Performance Differentiable Rendering. ACM Transactions on Graphics 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessle, B.; Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Nießner, M. Dense depth priors for neural radiance fields from sparse input views. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 12892–12901.
- Deng, K.; Liu, A.; Zhu, J.Y.; Ramanan, D. Depth-supervised nerf: Fewer views and faster training for free. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022, pp. 12882–12891.
Figure 1.
We categorize digital orthophoto generation methods into two types: explicit methods and implicit methods. The typical workflow of explicit methods involves obtaining the geometric structure with explicit parameters like mesh. The implicit methods are based on neural rendering, approximating the geometric structure with implicit neural networks. Both of them generate digital orthophoto through orthogonal projection.
Figure 1.
We categorize digital orthophoto generation methods into two types: explicit methods and implicit methods. The typical workflow of explicit methods involves obtaining the geometric structure with explicit parameters like mesh. The implicit methods are based on neural rendering, approximating the geometric structure with implicit neural networks. Both of them generate digital orthophoto through orthogonal projection.
Figure 2.
A schematic representation of NeRF with sparse parametric encoding. The process is divided into four stages: (a) Scene representation, primarily defining auxiliary data structures for scene’s sparse parametric encoding; (b) Radiance prediction, where sampling points are represented as feature embeddings, and the radiance at these points is obtained through the function ; (c) Differentiable rendering, rendering meaningful pixel RGB values based on the radiance of sampling points; (d) Loss computation, calculating the loss based on the rendering results, followed by backpropagation to optimize network parameters.
Figure 2.
A schematic representation of NeRF with sparse parametric encoding. The process is divided into four stages: (a) Scene representation, primarily defining auxiliary data structures for scene’s sparse parametric encoding; (b) Radiance prediction, where sampling points are represented as feature embeddings, and the radiance at these points is obtained through the function ; (c) Differentiable rendering, rendering meaningful pixel RGB values based on the radiance of sampling points; (d) Loss computation, calculating the loss based on the rendering results, followed by backpropagation to optimize network parameters.
Figure 3.
The figure illustrates the process of raster elevation initialization. In the initial stage, there are some points in three-dimensional space. Following the initialization process, rectangular raster cells are obtained. The height of the vertical column represents the elevation values of each cell.
Figure 3.
The figure illustrates the process of raster elevation initialization. In the initial stage, there are some points in three-dimensional space. Following the initialization process, rectangular raster cells are obtained. The height of the vertical column represents the elevation values of each cell.
Figure 4.
The figure demonstrates the elevation propagation process. The red rectangular raster represents the seed unit. A plane composed of the seed unit and eight neighboring units with unknown elevation calculates matching score based on color consistency. If the score meets the threshold, the elevations of other raster units will be initialized based on the normal vector of the seed raster unit.
Figure 4.
The figure demonstrates the elevation propagation process. The red rectangular raster represents the seed unit. A plane composed of the seed unit and eight neighboring units with unknown elevation calculates matching score based on color consistency. If the score meets the threshold, the elevations of other raster units will be initialized based on the normal vector of the seed raster unit.
Figure 5.
The figures illustrates the Multi-resolution interpolation-based elevation filling process. (a) The raster image obtained after elevation propagation contains raster units with unknown elevations. (b) The process of generating the multi-resolution interpolation raster images. (c) The resulting raster image after elevation filling using the multi-resolution interpolation raster images.
Figure 5.
The figures illustrates the Multi-resolution interpolation-based elevation filling process. (a) The raster image obtained after elevation propagation contains raster units with unknown elevations. (b) The process of generating the multi-resolution interpolation raster images. (c) The resulting raster image after elevation filling using the multi-resolution interpolation raster images.
Figure 6.
The original images of some village scenes captured by unmanned aerial vehicle.
Figure 6.
The original images of some village scenes captured by unmanned aerial vehicle.
Figure 7.
The point cloud of the village scenery obtained after sparse reconstruction.
Figure 7.
The point cloud of the village scenery obtained after sparse reconstruction.
Figure 8.
The figure illustrates the digital orthophoto generation results from two methods within the same village scene. (a) depict the output derived from the explicit method. (b) depict the output obtained from implicit method
Figure 8.
The figure illustrates the digital orthophoto generation results from two methods within the same village scene. (a) depict the output derived from the explicit method. (b) depict the output obtained from implicit method
Figure 9.
The figure shows digital orthophoto of houses, bridges, and rivers in the same scenes generated by two different methods. The left column (a, c, e, g) is generated by an explicit method (TDM), while the right column (b, d, f, h) is generated by an implicit method (Instant NGP).
Figure 9.
The figure shows digital orthophoto of houses, bridges, and rivers in the same scenes generated by two different methods. The left column (a, c, e, g) is generated by an explicit method (TDM), while the right column (b, d, f, h) is generated by an implicit method (Instant NGP).
Figure 10.
Digital orthophoto generated respectively by TDM, Instant NGP and Pix4D.The segments with consistent colors and corresponding values represent identical distances measured across the three results.
Figure 10.
Digital orthophoto generated respectively by TDM, Instant NGP and Pix4D.The segments with consistent colors and corresponding values represent identical distances measured across the three results.
Figure 11.
The box-plot shows the differences in distance measurements between the explicit method (TDM) and the implicit method (Instant NGP) compared to Pix4D in the same scene as depicted in
Figure 10.
Figure 11.
The box-plot shows the differences in distance measurements between the explicit method (TDM) and the implicit method (Instant NGP) compared to Pix4D in the same scene as depicted in
Figure 10.
Table 1.
Efficiency comparison of three methods of various scene sizes.
Table 1.
Efficiency comparison of three methods of various scene sizes.
| Scene size(m) |
Method |
| @images |
TDM |
Instant NGP |
|
36 s |
s |
|
60 s |
s |
|
88 s |
s |
|
103 s |
s |
|
129 s |
s |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).