1. Introduction
Topographic variations supports a various patterns
and processes in climatology, hydrology, and ecology, among other disciplines
and is key to understanding the variation of the earth’s phenomena (Amatulli,
et al. 2018). The Topographic Ruggedness Index (TRI) continue to be utilized
by experts in various fields of study as the measurement has often known for
providing a relatively accurate view of the vertical change taking place in the
terrain model from cell to cell (Esri, 2020). TRI is a measurement developed to
express the amount elevation difference between adjacent cells of a digital
elevation grid (Riley et al. 1999), proving data on the relative change in
height of the hill slope (Esri, 2020). The index has been utilized in this
study with the raster function generating the visual representation of the TRI
for Nyanga District of Zimbabwe. This study seeks to add to the body of knowledge
the application of GIS and remote sensing in determining topographic
ruggedness, and its relationship with drainage density.
2. Literature Review
Topographic Ruggedness
Various researches have shown the significance of
TRI in analyzing topographic characteristics. Riley et al. (1999) note that the
measurement is commonly used in species distribution studies to account for the
heterogeneity of topography or terrain, and if the value is larger it means the
area is more rugged. The index has also been used to quantify landscape
ruggedness for animal habitat analysis using Geographic Information Systems
(GIS) (Sapping et al. 2010). On a similar note, TRI has also been used to
determine the quantitative analysis of topographic ruggedness in reindeer
winter grounds for two regions in Norway (Nellemann & Fry, 1995).
Topographic ruggedness was found to be significantly higher in high use areas,
while indices of topographic ruggedness reflecting fine scale features (10 – 20
meters) matched well with the availability of potential feeding sites. Thus
topographic structure should be considered a useful habitat attribute for
planning on reindeer winter habitats, as the measurement provides a simple
technique for quantifying differences in fine scale ruggedness between
habitats.
In another study, Konkathi et al. (2019) developed
a static fire risk index with topographic ruggedness as one of the parameters
influencing forest fires. MODIS land cover type yearly L3 global 500m SIN grid
(MCD 12 Q1) was used to compute fuel type based on historical fire data and
STRM DEM was used to compute slope index, elevation index, aspect index, and
TRI. The study exhibited 32.38% fire risk zone.
TRI has also been used as one of the
macro-topographic factors in enhancing planning of timber harvesting in
Zalesina, Croatia (Duka, et al. 2015). Unevenness of topographic was determined
based on the TRI which showed moderately to very high rugged topographic on
60.1% of the study area, where vehicle mobility could be difficult.
3. Study Area, Materials and Methodology
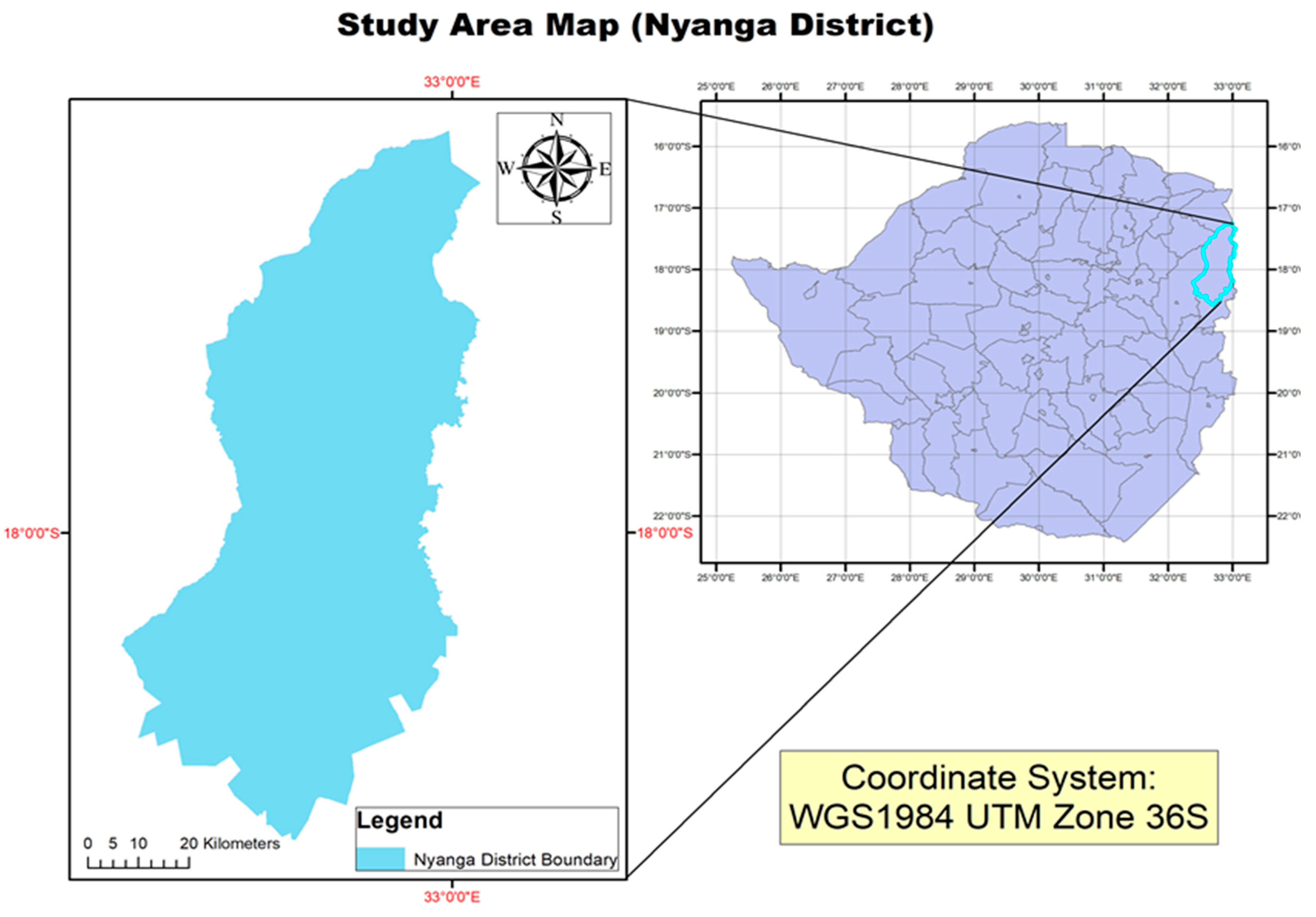
Nyanga District is located in Manicaland Province
of Zimbabwe, and lies along the international border with Mozambique. The
latitude of Nyanga is -18.220079, and the longitude is 32.746369. The district
has an average yearly temperature of 20.22°C, and typically receives about
138.47 millimeters of precipitation, and has 122.71 rainy days annually.
Materials
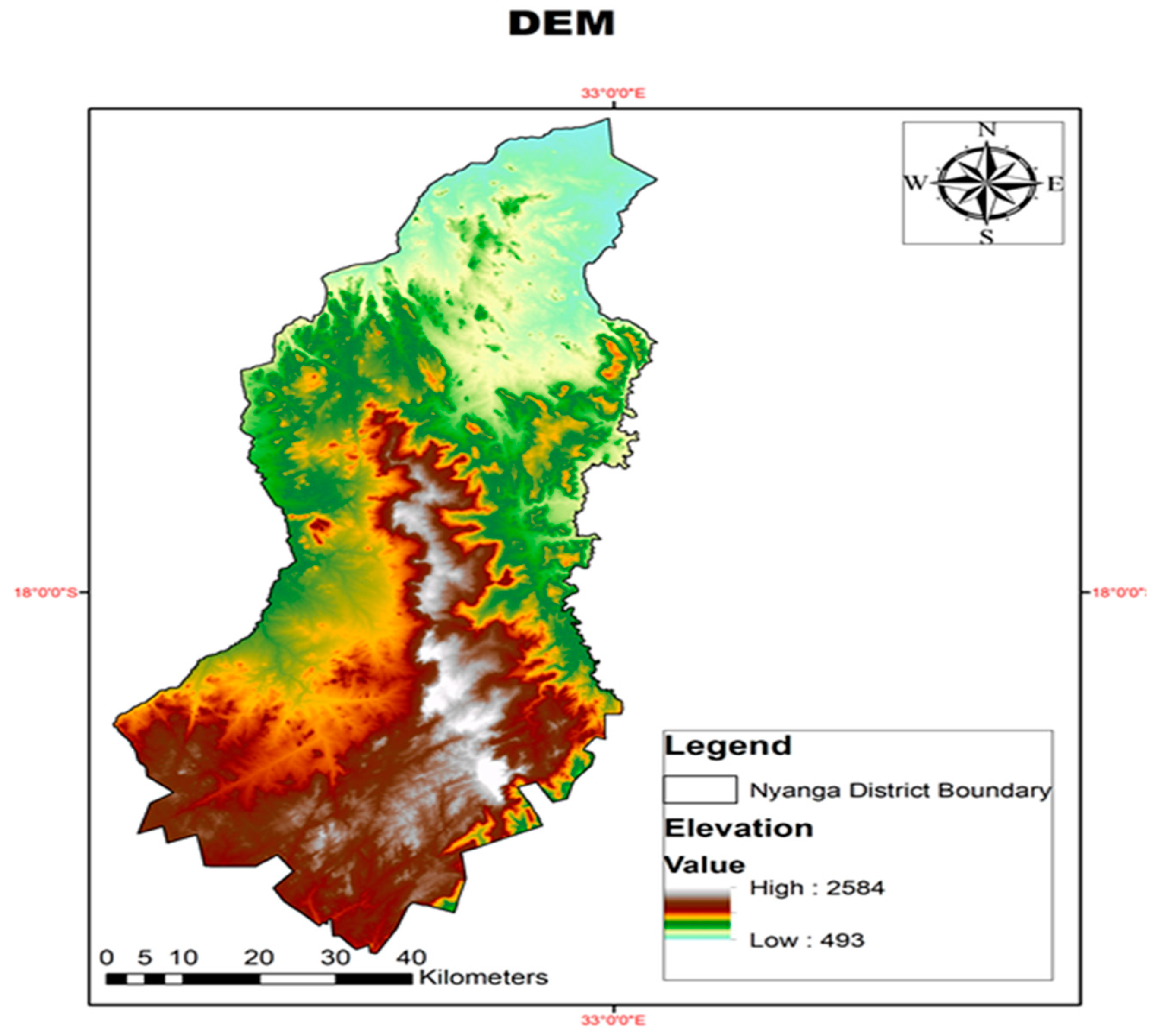
The study utilized DEM for Nyanga District
downloaded from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Shuttle Radar
Topography Mission (SRTM) at 1 Arc Second Global (30m) resolution (Figure 1). Spatial Analyst tool in ArcMap10.8
was used to perform topographic analysis from DEM. Topographic algorithms and
focal statistics were used to determine topographic ruggedness index (TRI) for
the study area.
Figure 1.
Location of Study Area.
Figure 1.
Location of Study Area.
Figure 2.
Elevation map for the study area downloaded from USGS.
Figure 2.
Elevation map for the study area downloaded from USGS.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Calculating Topographic Ruggedness Index (TRI)
TRI for the study was generated to express the
amount of elevation difference between adjacent cells of a DEM, and the
following calculations were performed on DEM using focal statistics Focal
Statistics in ArcMap for the original grid and for its square;
3.2. Focal Statistics Calculations in ArcGIS
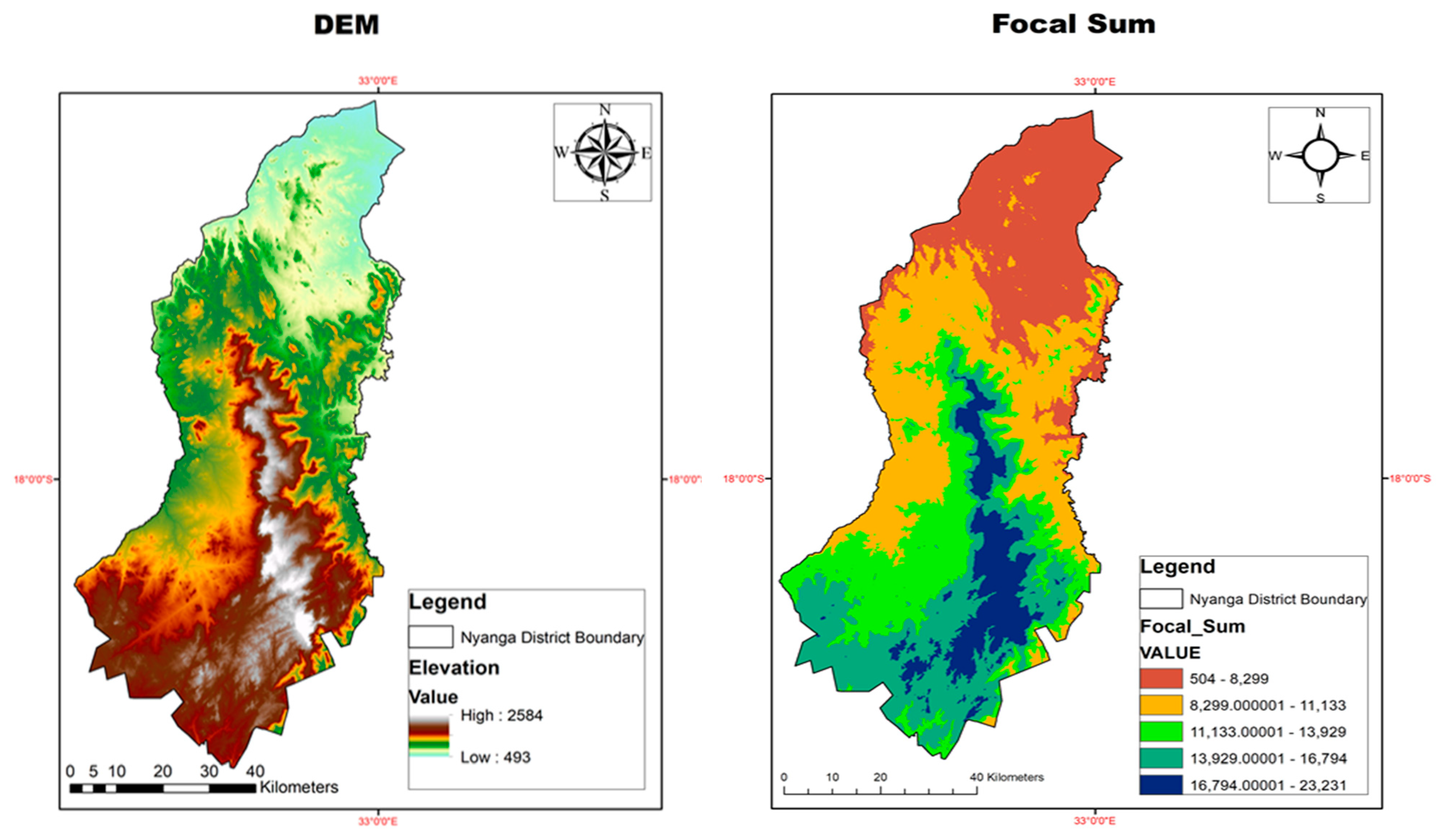
The significance of Focal Statistics is a statistic
function performed on DEM such as the mean, maximum, minimum or sum of all
values in the neighbourhood. This study considers rectangle neighbourhood which
is specified by providing a width and a height in either cells or map units,
and only the cells with centers which fall within the defined object are
processed as part of the rectangle neighbourhood (Esri, 2023). The Focal
Statistics calculations are as follows;
3.2.1. Focal Sum of DEM
Given a DEM, Focal statistics was used to;
Figure 3.
DEM and Focal Sum of DEM.
Figure 3.
DEM and Focal Sum of DEM.
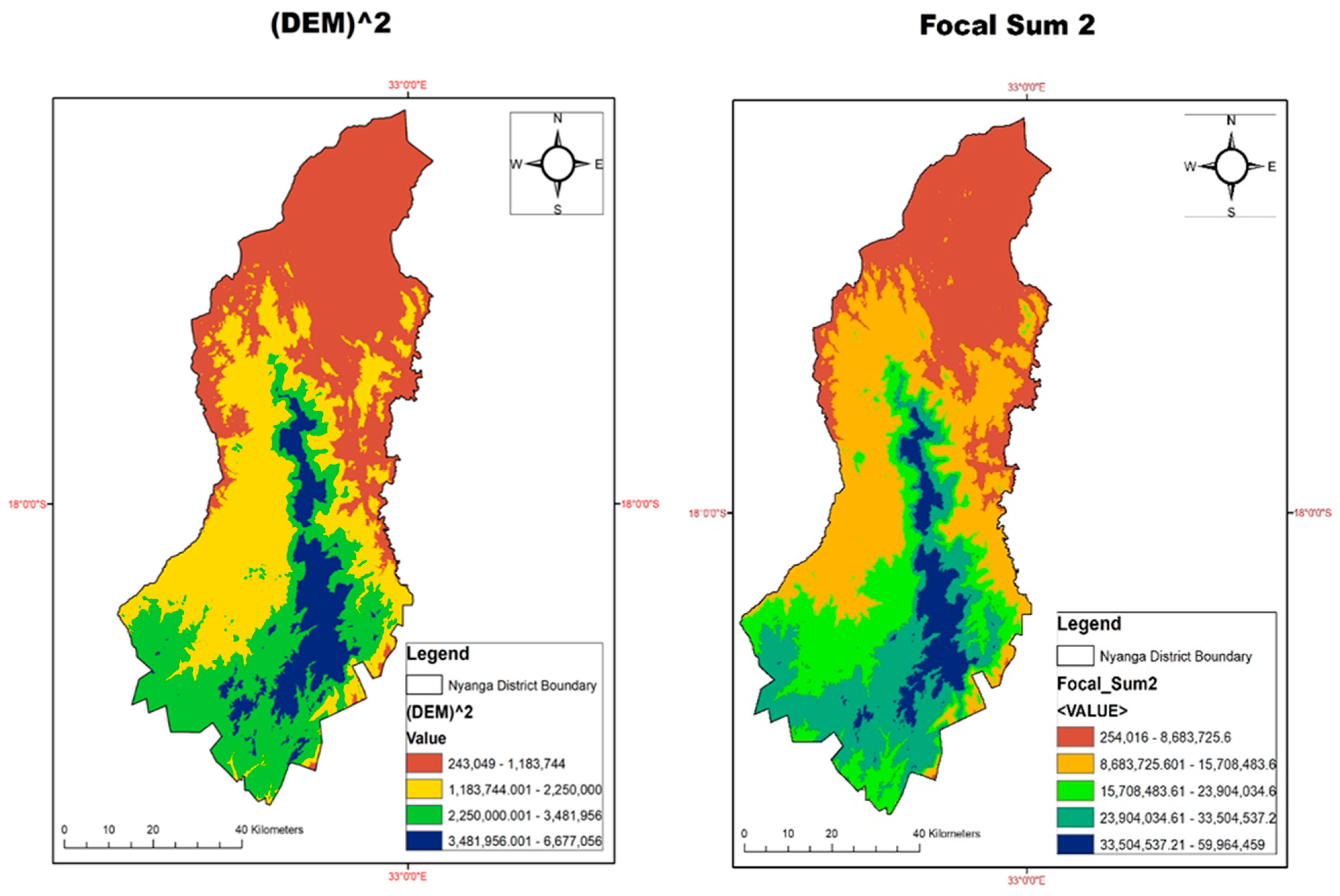
2.2.2. Focal Sum of DEM ²
Given a DEM, Focal statistics was used to calculate (DEM) ² using Math Algebra (Raster Calculator) in spatial analyst toolbox as:
Focal sum of (DEM) ² was computed as;
Figure 4.
Representation of DEM ² and Focal Sum of DEM ².
Figure 4.
Representation of DEM ² and Focal Sum of DEM ².
3.3. TRI Calculations
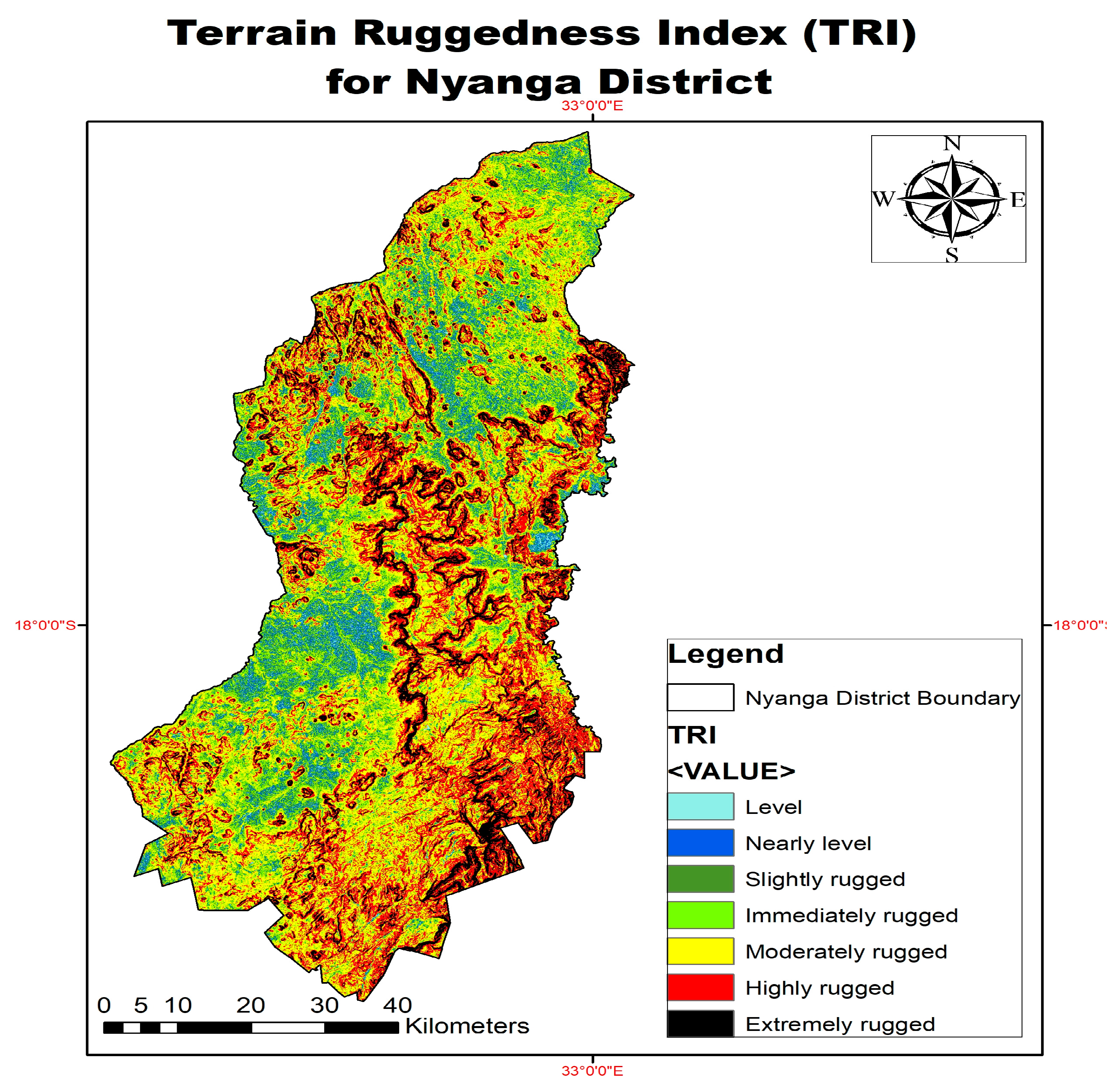
Raster Calculator in Math Algebra was used to calculate the TRI (r) and a TRI map for the study area was generated. The representation of TRI is shown in
Figure 5 below. TRI calculates the room mean square deviation (RMSD) for each cell grid in a DEM, calculating residuals or elevation differences between a grid cell and its eight neighbours.
Method
Given that x be the value in the central square; xi, i = 1 …..., 8 index the values in the neighboring squares; and r be the topographic ruggedness index, such that r² equals the sum of (xi - x) ². Two algebra are computed as follows
-
i.
The sum of the values in the neighborhood, equal to s = Sum {xi} + x; and
-
ii.
The sum of squares of the values, equal to t = Sum {(xi) ² + x².
Expanding the squares;
r² = Sum {(xi - x) ²}
r²= Sum {xi² + x² - 2*x*xi}
r²= Sum {xi²} + 8*x² - 2*x*Sum {xi}
r²= [Sum {xi²} + x²] + 7*x² - 2*x*[Sum {xi} + x - x]
r²= t + 7*x² - 2*x*[Sum {xi} + x] + 2*x²
r²= t + 9*x² - 2*x*s.
This study employed Focal Statistics and Math Algebra in ArcMap to generate TRI for the study area as follows:
4. Conclusion
The ruggedness zones derived from TRI calculations are namely; level, nearly level, slightly rugged, immediately rugged, moderately rugged, highly rugged and extremely rugged zones. The higher the TRI, the higher the ruggedness, while areas with low TRI resemble flat areas. Though the TRI strongly depends on a local scale slope derived from an average adjacent neighbor slope algorithm, and selection of different lag distances in the computation of spatial variability, the model is suitable for calculating ruggedness index for habitat area analysis, where sources of error in DEMs will not entirely affect biological interpretations of data. The algorithm presented could also be used for smaller areas with high quality data and corrected DEMs. This study supports views by Dilts et al. (2023) that despite widespread adoption, ruggedness metrics require thorough testing using both artificial landscapes and real world applications. Therefore, further studies may focus on machine learning models to generate accurate TRI.
Author Declaration
I acknowledge that this piece of work is my own and has not yet been published anywhere.
Funding
No funding availed to conduct the research.
Acknowledgement
The author wish to thank colleagues at the University of Zimbabwe for their contribution in making this research a success.
Potential Competing Interest
No potential competing interests to declare.
References
- ESRI (2020). TopographicRuggedness Index (TRI). Living Atlas of the World. Available on: https://livingatlas_dcdev.opendata.arcgis.com/content/28360713391948af9303c0aeabb45afd/about. [Accessed on 03 July 2023].
- Rahmati O, Kalantari Z, Samadi M, Uuemaa E, Moghaddam DD, Nalivan OA, Destouni G, Tien Bui D. GIS-Based Site Selection for Check Dams in Watersheds: Considering Geomorphometric and Topo-Hydrological Factors. Sustainability. 2019; 11(20):5639. [CrossRef]
- Sappington, J. M. , Longshore, K.M., Thompson D.B., (2010). Quantifying Landscape Ruggedness for Animal Habitat Analysis: A Case Study Using Bighorn Sheep in the Mojave Desert. Journal of Wildlife Management. [CrossRef]
- Stojilković, B. (2022). Towards Transferable Use of TopographicRuggedness Component in the Geo-diversity Index. Resources 11(2):22. [CrossRef]
- Konkathi, P. , Shetty, A., Kolluru, V., Yathish P. H., and Pruthviraj, U. (2019)."Static Fire Risk Index for the Forest Resources of Karnataka." IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 2019, pp. 6716-6719. [CrossRef]
- Dilts, T.E. , Blum, M.E., Shoemaker, K.T. et al. (2023). Improved topographic ruggedness indices more accurately model fine-scale ecological patterns. Landsc Ecol 38, 1395–1410. [CrossRef]
- Duka, A. , Porsinsky, T., & Vusic, D. (2015). DTM Models to enhance the planning of timber harvesting. [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.J. , De Gloria, S.D., Elliot, R., (1999). A Topographicruggedness Index that Quantifies Topographic Heterogeneity. Intermountain Journal of Sciences, vol. 5 (1–4): 23–27.
- Esri (2021). ArcMap 10.8 Help Archive: Curvature Function. Available on: https://desktop.arcgis.com/en/arcmap/latest/manage-data/raster-and-images/curvature-function. [Accessed on 30 November 2023].
- Geospatial Analysis 6th Edition of 2021 Update (2021). Profiles and Curvature. Available on: https://www.spatialanalysisonline.com/HTML/?profiles_and_curvature.htm. [Accessed on 20 October 2023].
- Amatulli, G. , Domisch, S., Tuanmu, M.-N., Parmentier, B., Ranipeta, A., Malczyk, J., and Jetz, W. (2018) A suite of global, cross-scale topographic variables for environmental and biodiversity modeling. Scientific Data volume 5, Article number: 180040. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).