1. Introduction
Schizophrenia comprises a group of severe mental disorders affecting about 1% of the population, with a substantial heritability factor of approximately 80% [
1]. Despite extensive research, a significant portion of the hereditary risk remains unidentified. Several susceptibility genes have already been found in brain signaling pathways, such as dopamine, glutamate, and D-amino acid; however, the etiology of schizophrenia is still mostly misunderstood. Susceptibility genes linked to neurotransmitter signaling pathways, including dopamine, glutamate, and D-amino acid, have been identified, yet the precise etiology of schizophrenia remains elusive. Emerging evidence underscores the crucial role of epigenetic alterations, specifically DNA methylation, in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, influencing gene expression [
2,
3].
DNA methylation, an epigenetic modification involving the addition of a methyl group to cytosine in CpG dinucleotides, regulates cell identity through gene expression [
4]. This process influences gene expression by either restricting access to promoter regions for transcription factors or affecting mRNA processing. However, DNA methylation profiles, generating epialleles (alleles differing solely by methylation), display significant heterogeneity and polymorphism due to the stochastic (as in transcription) or selective (as in gene imprinting) nature of CpG methylation [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12].
To address this complexity, we have developed a tool capable of identifying methylated CpGs under selection, forming a core or nucleus shared by several epialleles in linear DNA sequences [
13]. In simpler terms, this tool allows us to track and trace epialleles derived from a single precursor with common methylation traits in complex DNA sequence populations derived from cells in the brain and other organs during postnatal differentiation [
4,
13].
D-amino acids play crucial roles in various physiological processes, especially in the brain, and their dysregulation has been implicated in psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia [
14]. Notably, D-Serine and D-Aspartate serve as co-agonists at N-methyl-D-Aspartate receptors (NMDARs), governing diverse brain activities [
15,
16]. Altered levels of these D-amino acids have been observed in schizophrenia patients [
17,
18], with enzymes like D-Aspartate oxidase (DDO) [
19], serine racemase (SR), D-amino acid oxidase (DAO) and D-amino acid oxidase activator (DAOA) [
20] playing crucial roles in their production and degradation. Since DNA methylation patterns in the brain at CpG sites are essential for cellular identity during neurodevelopment [
21], we hypothesized that their alteration could contribute to the pathogenesis of schizophrenia through a spatiotemporal alteration of these genes in the human brain.
Our study, utilizing targeted bisulfite sequencing in post-mortem brains of individuals with schizophrenia, identified specific methyl-CpG signatures in genes associated with D-Aspartate and D-Serine metabolism in different brain areas, particularly the enzymes DDO, DAO, and DAOA.
Again, our methylation core analysis may identify brain locations within each individual and be connected to schizophrenia pathogenesis.
2. Results
2.1. Cerebellum and Hippocampus cells display specific methylation signatures in the D-Aspartate metabolizing gene, D-Aspartate oxidase (DDO).
D-Aspartate, an atypical amino acid abundant in the embryonic mammalian brain, stimulates glutamatergic NMDA and mGlu5 receptors at nanomolar concentrations [
22]. Free D-Aspartate levels are high in the embryonic brain of mammals and after birth, rapidly decrease [
23,
24] due to the onset of the D-Aspartate oxidase (DDO), which inactivates D-Aspartate by converting it into oxaloacetate [
25,
26].
Increased D-Aspartate levels have been associated with schizophrenia-like phenotypes in rodents, characterized by frontal-hippocampal hyper-connectivity and reduced activity of neurons exposed to phencyclidine [
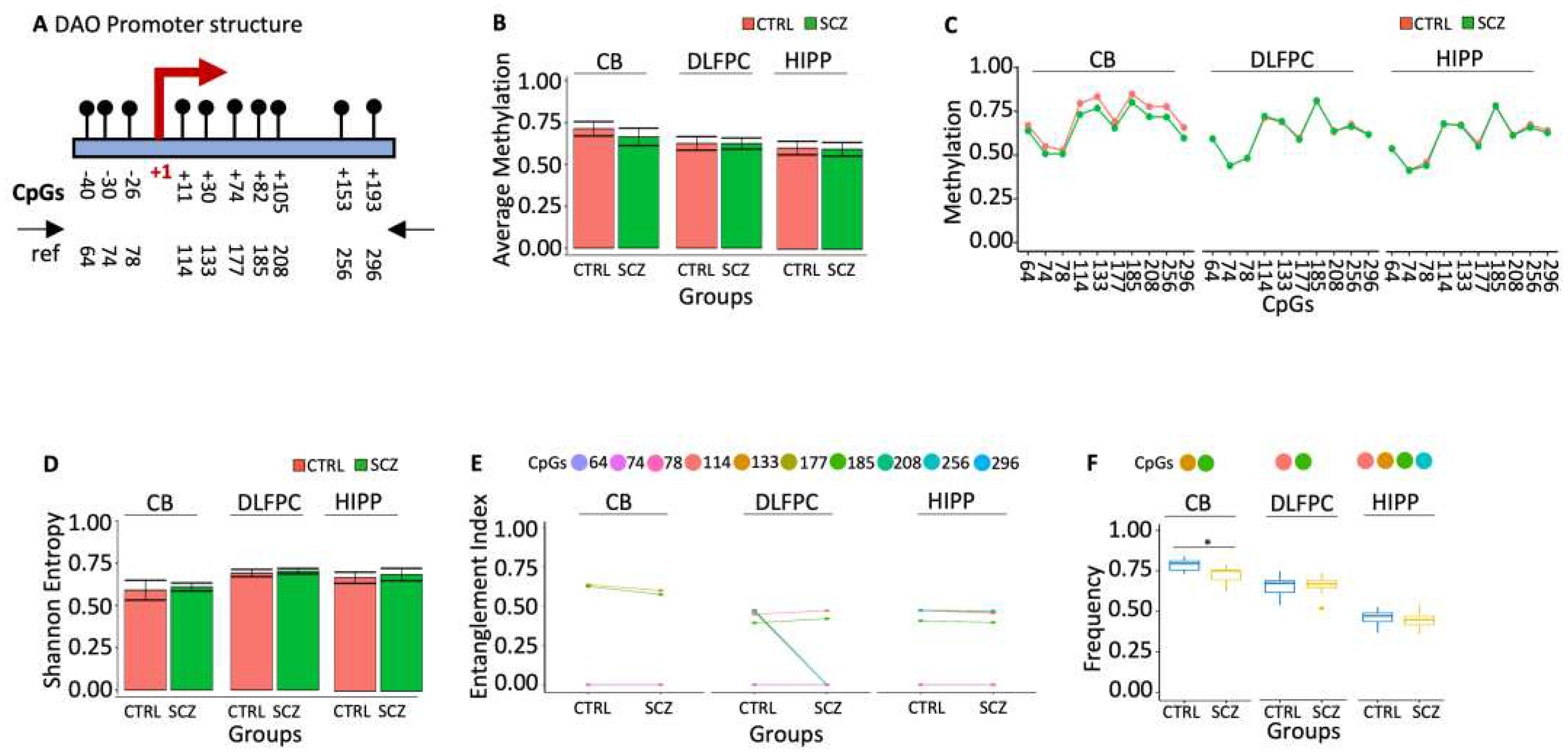
22]. The association between schizophrenia phenotypes and brain D-Aspartate levels may be mediated by epigenetic modifications of the DDO gene in specific brain areas that reduce its expression, leading to high D-Aspartate levels in specific brain areas. To test this association, we have defined the methylation profiles of DDO promoter and the transcription start site (TSS) (
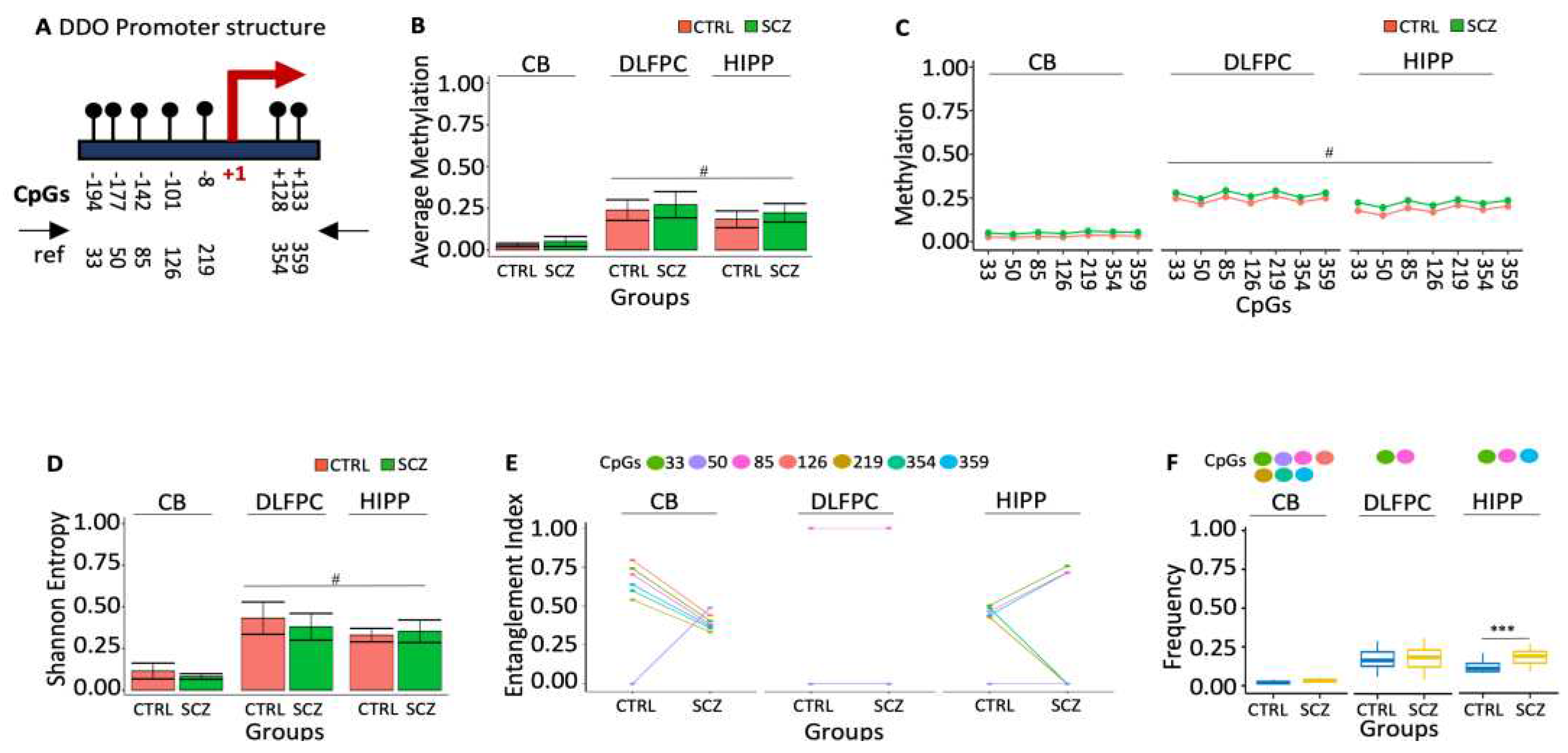
Figure 1A) in the three specific post-mortem brain areas of control (CTRL, n=20) and schizophrenic (SCZ, n=20): cerebellum (CB), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and hippocampus (HIPP). We found 25% of the molecules analyzed methylated in controls, DLPFC and HIPP, whereas in CB, the DDO promoter was poorly methylated (Figures 1B and C). The methylated sequences were highly polymorphic and heterogeneous (
Figure 1D). However, the methylation heterogeneity was apparent because sorting out the methyl-CpG (mCpG) combinations was statistically significant in the sequence populations we found in CB DDO promoter three methylated CpG cores. The abundance of these methylated CpGs in the DNA string changes dramatically compared to CTRL and SCZ. For example, i. the core with mCpGs 33-85-126-219-354-359 is abundant in CTRL CB. The structure of this core in the CB is peculiar because CpG 50, located at -177 from the TSS, is never methylated. In SCZ CB, this CpG is methylated and incorporated in the core (
Figure 1E, p<0.01); ii. the CpG core 33-85 is not informative because it is present in both CTRL and SCZ DLPFC at the same frequency; iii. the core 33-85-359 CpGs, on the other hand, marks SCZ HIPP (Figures 1E and 1F).
In conclusion, we have identified 2 methylation cores in the DDO promoter that characterize distinctively normal and SCZ discrete brain areas: 1. CpGs 33-85-126-219-354-359 in CB CTRL without CpG 50. This CpG is methylated only in SCZ (
Figure 1E); 2. the core with 33-85-359 CpGs, characterizes HIPP SCZ (
Figure 1F).
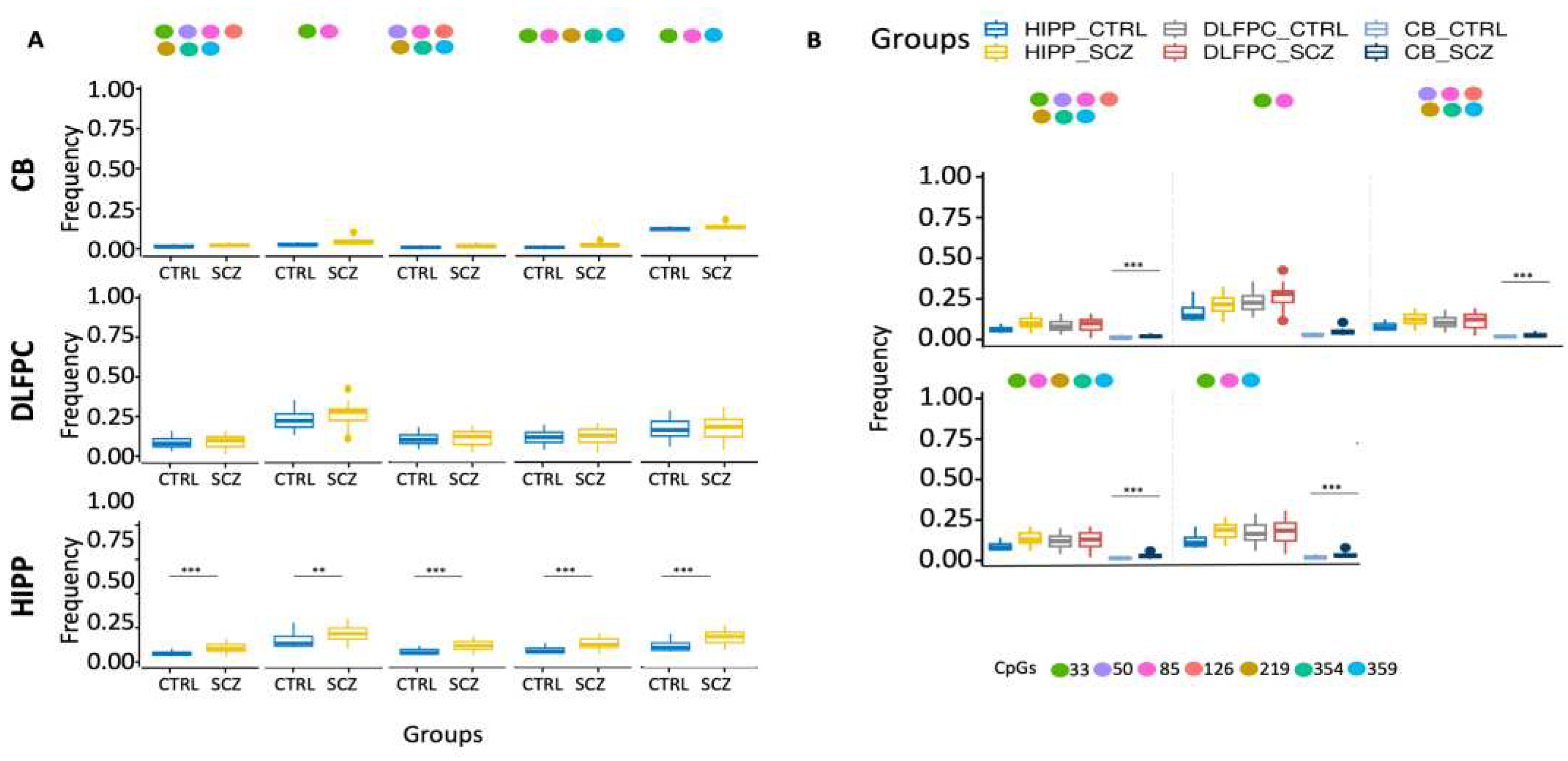
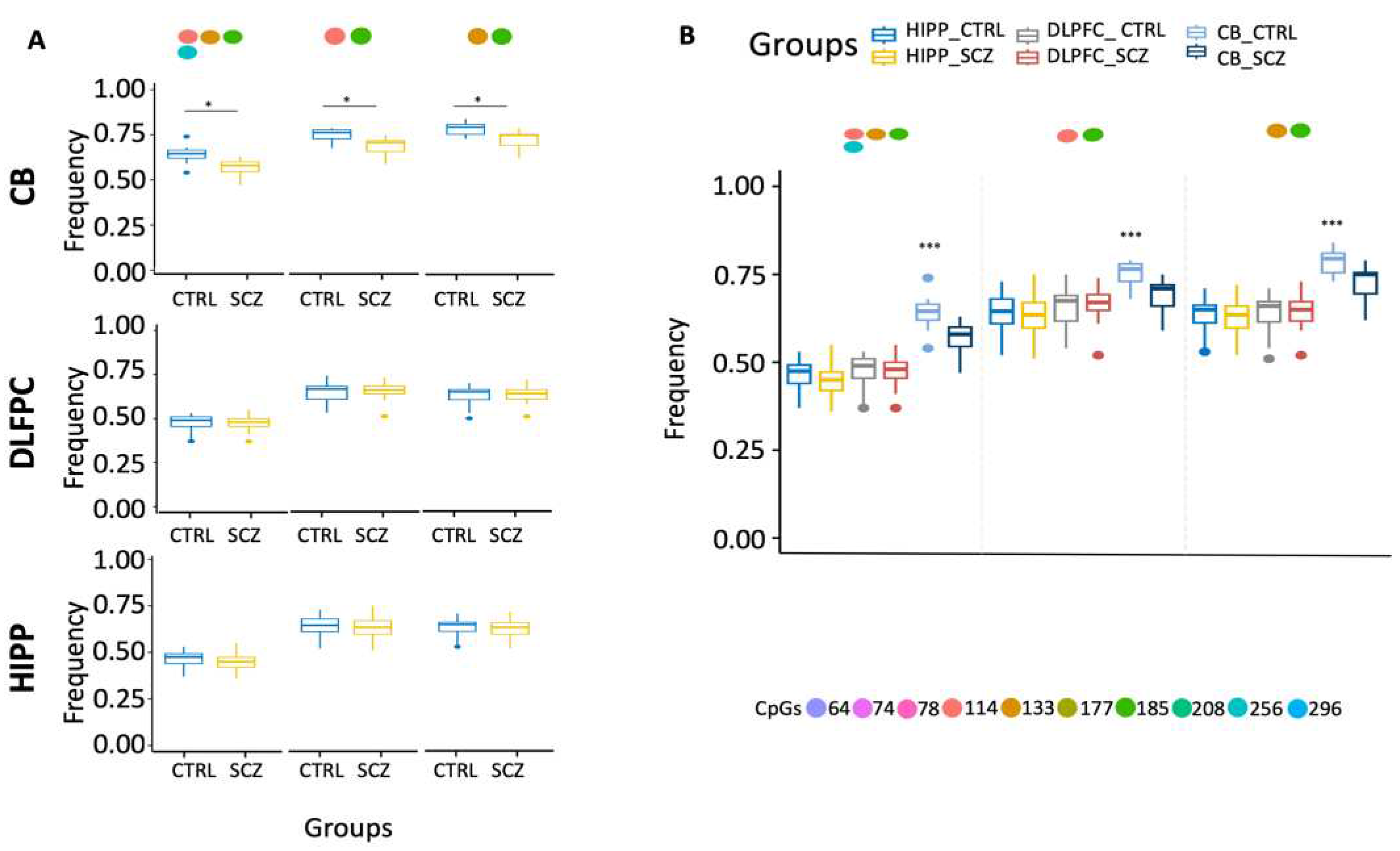
Moreover, ex-novo searches for the specific HIPP SCZ methylated core in all its configurations among analyzed areas showed that it increased only in HIPP SCZ (
Figure 2A). Furthermore, our results also showed that CB had lower levels of methylated cores in the DDO promoter than in analyzed areas (
Figure 2B).
2.2. Methylation signatures in D-Serine metabolizing genes in specific brain areas.
D-Serine is the primary co-agonist that stimulates N-methyl-D-Aspartate (NMDA) receptors in the forebrain and its levels, like D-Aspartate, in the brain are tightly regulated by several enzymes, such as serine racemase (SR) (conversion of L to D-Serine) or D amino-oxidase (DAO) or DAO activator (DAOA) (low D-Serine levels). Lower D-Serine levels have been reported in the brain of schizophrenic patients and higher D-Serine levels in the brain may be an important adjuvant to antipsychotic therapy to control schizophrenia phenotypes [
27]. To better understand the regulation of brain levels of D-Serine we looked for methylation signature(s) at the promoters and TSS of these genes in the three specific post-mortem brain areas of normal/control (CTRL, n=20) and schizophrenic (SCZ, n=20) human brain areas indicated above.
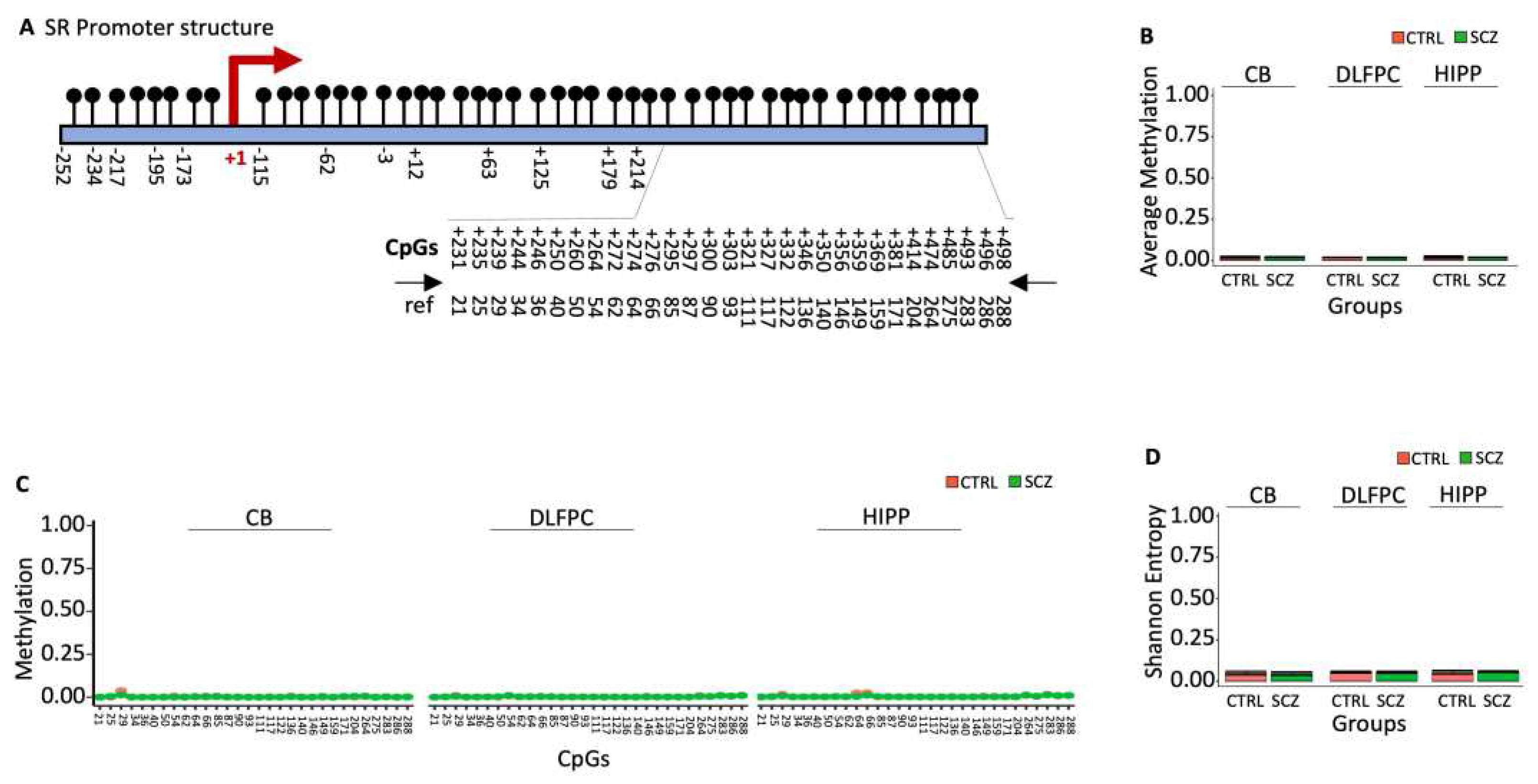
2.2.1. The Promoter and the TSS Serine Racemase (SR) are undermethylated both in normal and schizophrenic brain areas.
D-Serine is formed by the racemization of L-serine by the enzyme serine racemase, which under-expression has been shown to be associated with schizophrenia, especially with the paranoid subtype [
28]. The SR promoter is within a thick CpG island (
Figure 3A). Bisulfite sequencing analysis of the downstream region near TSS (
Figure 3A; nucleotides +209 to +522, with 30 CpG sites) revealed that the region was almost unmethylated with no difference in terms of average methylation, CpG methylation and Entropy (Figures 3B-3D) [
13].
2.2.2. Specific methylation signature in DAO gene promoter marks cerebellum in schizophrenic patients.
D-amino oxidase (DAO) is an oxidoreductase that oxidatively deaminates D-amino acids to the corresponding alpha-keto acid. Enhanced DAO activity has been reported as a potential cause of reduced D-Serine and thence impaired NMDAR functioning in schizophrenia [
29]. To confirm this hypothesis, we examined the methylation status of the DAO promoter (
Figure 4A) in three different areas derived from the post-mortem brains of SCZ and CTRL: cerebellum (CB), dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and hippocampus (HIPP). We found no difference in average methylation, cytosine methylation (
Figure 4B) and Entropy (
Figure 4D) in DLPFC, HIPP and CB. Using the tool above (MethCoresProfiler), we found three different cores marking the DAO gene regions: i. core 133–185 marked CB SCZ relative to the CB CTRL (
Figure 4F). ii. the original core 114-133-185-256 in DLPFC CTRL lost 133 and 256 mCpGs in SCZ. iii. the core 114-133-185-256 was stable in HIPP CTRL and SCZ (
Figure 4E).
Ex-novo searches for the SCZ methylated core per area showed a significant reduction of methylated core 133–185 only in the CB SCZ compared to controls (
Figure 4F). Moreover, ex-novo searches for the specific CB SCZ methylated core in all configurations in the various analyzed areas showed that it decreased specifications in the CB SCZ (
Figure 5A). Furthermore, our results also showed that CB CTRL had higher levels of methylated cores in the DAO promoter than other analyzed areas (
Figure 5B).
2.2.3. Qualitative DNA methylation configuration of the DAOA gene promoter mark schizophrenic patients.
The DAO activator (DAOA) gene product has been shown to affect DAO activity positively [
30] or negatively [
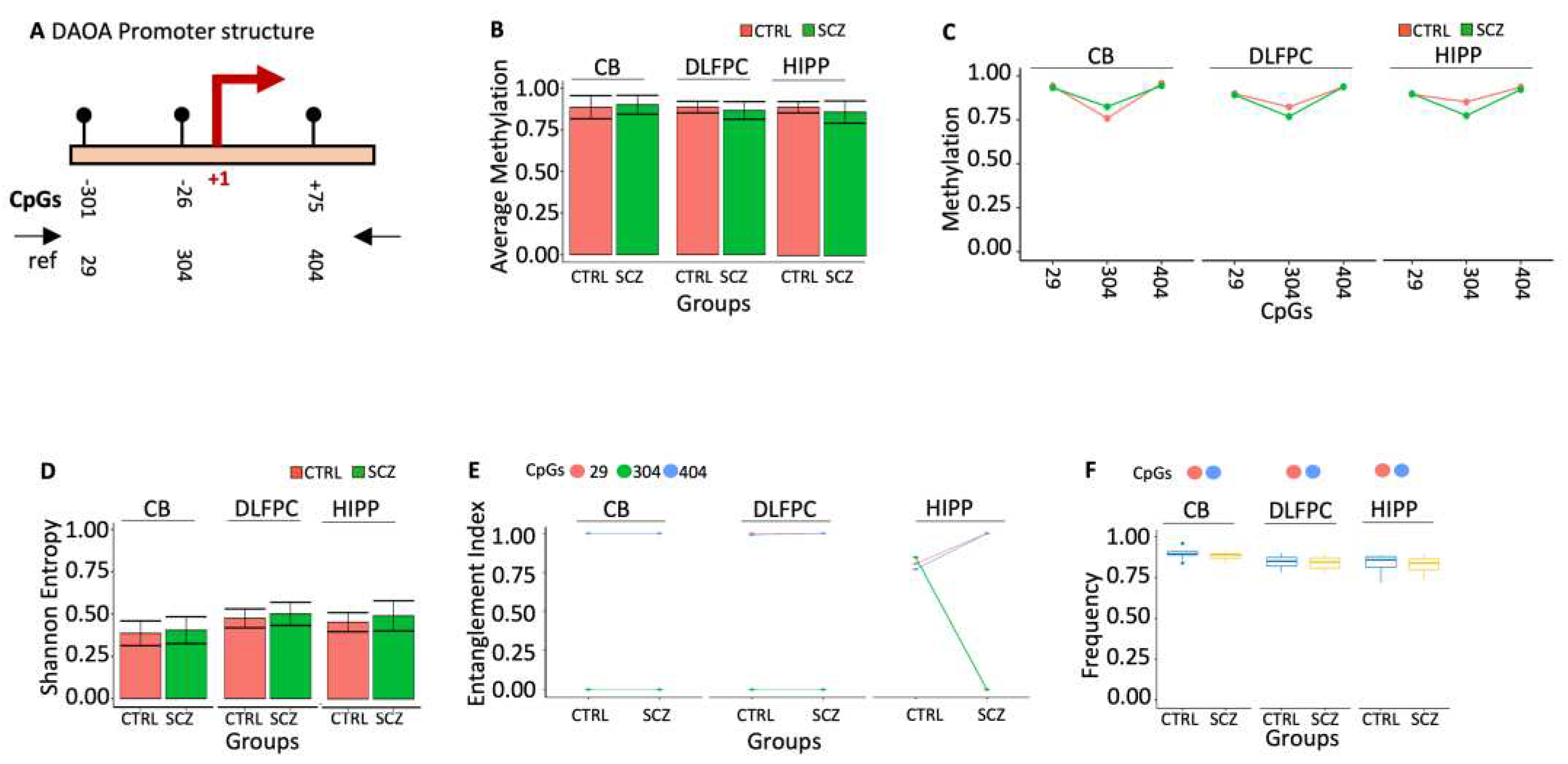
31]. The methylation analysis of the 434 bp (nucleotides -330 to +104) fragment spanning the DAOA promoter and the TSS shows only 3 CpGs (-301, -26, +75), which was examined for DNA methylation (
Figure 6A). We observed no significant alterations when we analyzed methylation status at single CpG sites between CTRL and SCZ in all brain regions (
Figure 6B). The DAOA promoter region has exceptionally high average CpG methylation in CTRL and SCZ groups across all studied brain regions. Data analysis of average methylation, like single CpGs, revealed no statistically significant variations between CTRL and SCZ in all brain regions (
Figure 6C) or Entropy (
Figure 6D).
Using the tool above (MethCoresProfiler), we identified two methylated cores in the DAOA promoter: i. the core 29-404 marked CB and DLFPC CTRL that was also stable in SCZ. ii. the core 29-304-404 marked HIPP CTRL that became 29-404 in HIPP SCZ with high frequency (
Figure 6E). However, this qualitative change of the CTRL HIPP core was insignificant in the areas analyzed for ex-scale research (
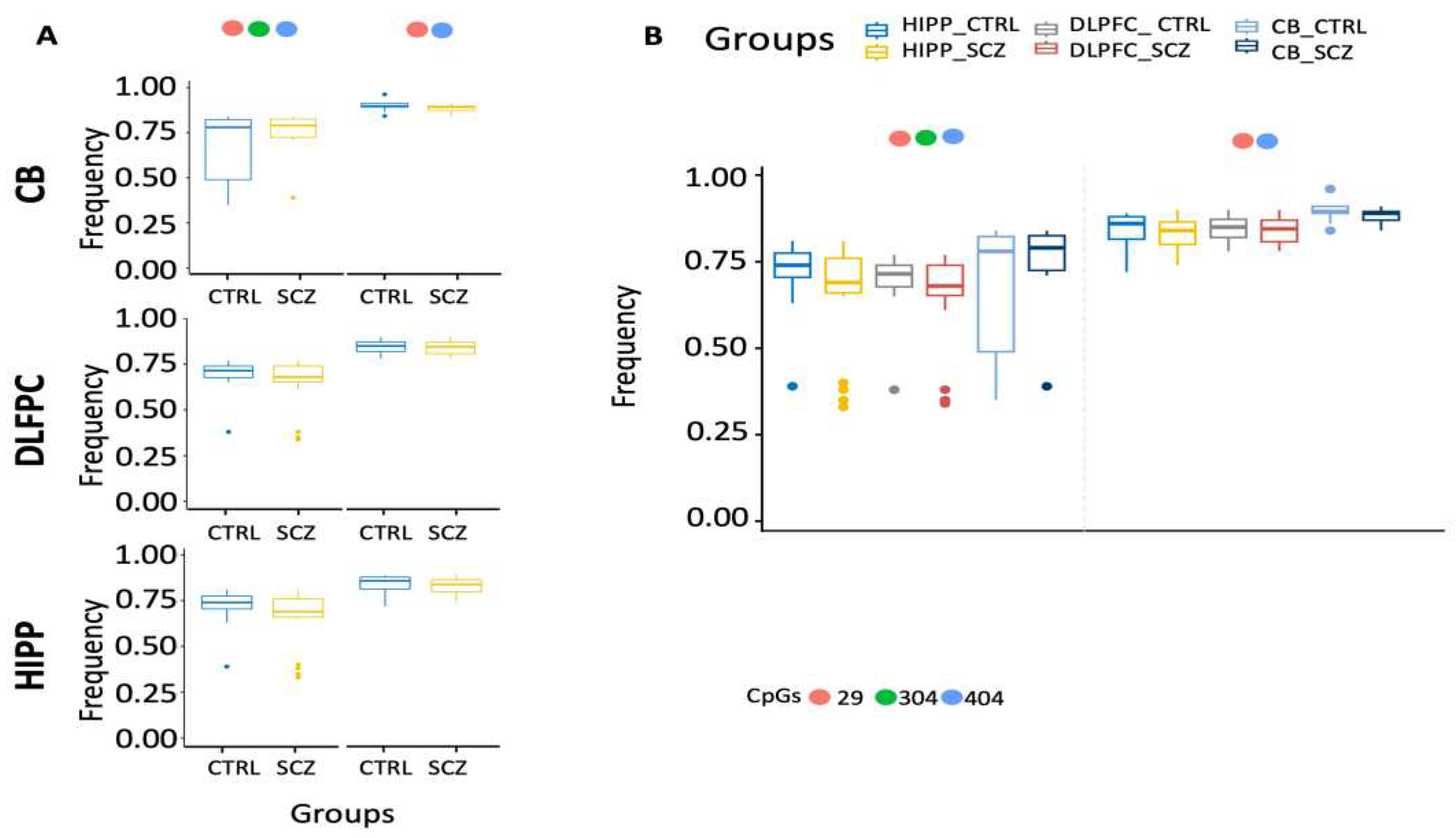
Figure 6F, 7A-B).
3. Discussion
The most extensively studied epigenetic modification, cytosine methylation in DNA, is intricately linked to gene transcription, nuclear architecture, and cell activity. Various factors, including transcription factor binding, can influence DNA methylation. Alterations in DNA methylation patterns are common in many human illnesses, making it a promising clinical diagnostic marker due to the physical stability of DNA and methylated DNA. Despite this, few DNA methylation-based markers, aside from some in cancer, have transitioned into clinical practice. Here, we present evidence supporting DNA methylation as a clinical marker for study and potential use in schizophrenia.
D-Aspartate and D-Serine, acting as NMDAR co-agonists and agonists, have been implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. Genetic investigations have identified specific SNPs within SR, DAO, and DAOA linked to schizophrenia [
32]. However, the relationship between the DNA methylation state of genes regulating D-Aspartate and D-Serine and schizophrenia has been minimally explored [
3]. This study employs a novel, ultradeep approach to comprehensively analyze the CpG methylation status of DDO, SR, DAO, and DAOA genes in post-mortem brain areas of patients with schizophrenia and non-psychiatric controls from different brain banks [
33,
34].
Despite no significant differences between diagnostic groups, our findings reveal brain area-specific methylation patterns that distinguish schizophrenia patients. The CpG methylation analysis of DDO and DAO genes, in particular, showcases the power of the proposed technique in detecting cell-to-cell methylation changes. The DDO promoter exhibited higher methylation levels in HIPP and DLPFC than CB, revealing tissue heterogeneity. However, distinct methylation patterns (methylated cores) were identified, differentiating CTRL and SCZ. The same approach on the DAO promoter showed qualitative and quantitative differences between CTRL and SCZ, marking distinct methylation nuclei in all explored regions.
Exploring the DAOA promoter, nearly complete methylation at few CpG sites was observed universally, explaining the gene's repression [
35]. However, HIPP exhibited qualitative changes between CTRL and SCZ. Analyzing SR, identified as a schizophrenia risk gene, revealed an entirely unmethylated CpG island in all analyzed areas, explaining the gene's activity [
36].
Our results demonstrate brain area-specific methylation signatures in DDO and DAO genes, suggesting a unique functional state in schizophrenia patients. The observed methylated cores in gene promoters between patients and controls may be associated with metabolic adaptation in response to persistent DNA damage reported in schizophrenic patients [
37,
38]. We propose a model linking high DDO methylation in SCZ HIPP to increased D-Aspartate levels stimulating NMDAR receptors. In contrast, low DAO methylation correlates with low D-Serine levels, potentially influencing metabolic pathways associated with schizophrenia [
39,
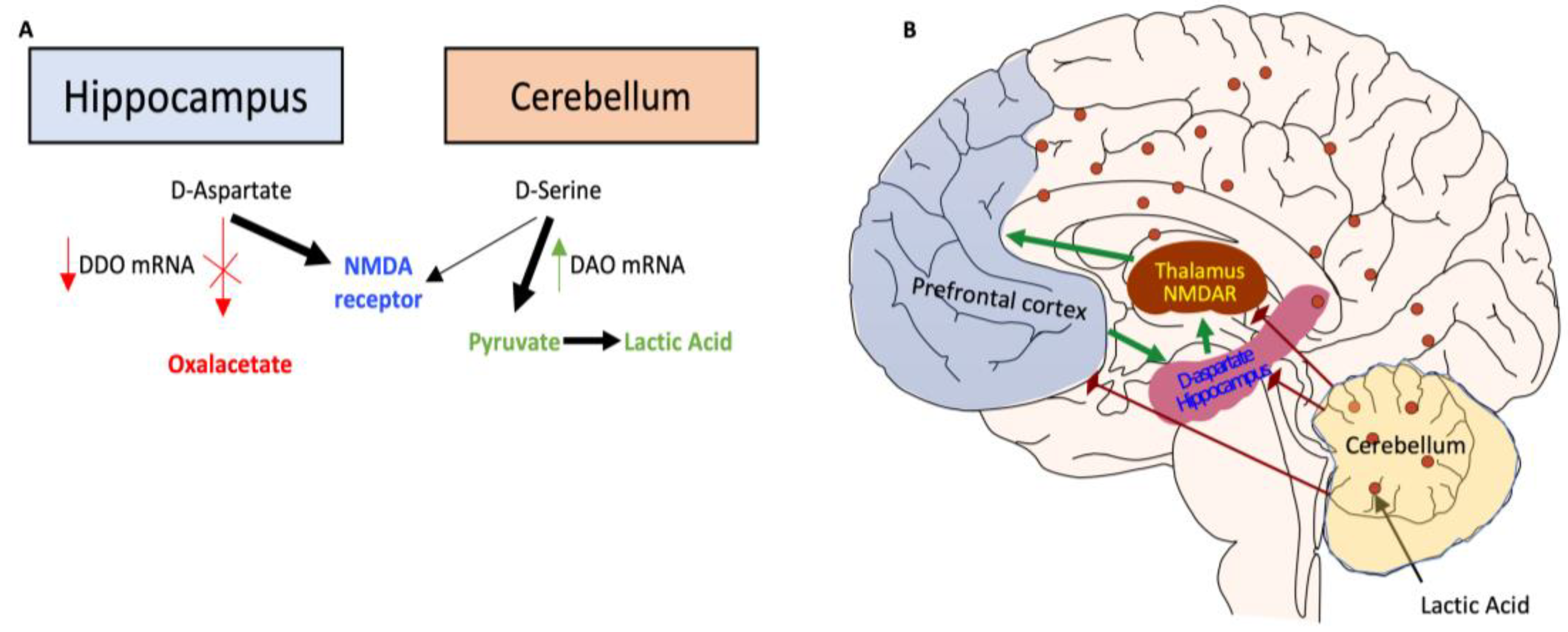
40]. This study underscores the role of altered brain bioenergetics in cognitive and functional deficits in schizophrenia.
Figure 8.
Proposed model of altered brain bioenergetics in schizophrenia.
Figure 8.
Proposed model of altered brain bioenergetics in schizophrenia.
Persistent DNA damage in schizophrenic individuals altered DNA methylation [
37,
38]. In the Hippocampus, hypermethylation of DDO promoter inhibits D-Aspartate metabolism, increasing D-Aspartate-stimulated NMDAR receptors. In contrast, in the Cerebellum, hypomethylation of DAO promoter increases D-Serine metabolism, potentially influencing metabolic pathways with the production of Pyruvate and Lactic Acid [
39]. Lactate levels in schizophrenia may be elevated due to increased anaerobic glycolysis, which might be caused by mitochondrial malfunction [
40].
4. Materials and Methods
The datasets used in this study were obtained from the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA). The public accession number is PRJEB24382. An overview of sample collection and DNA extraction is provided below. A detailed description of all the samples is reported in [
2,
3]. Following that, both homemade sequence management and methylation analysis are explained.
The human dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and hippocampus samples from post-mortem brains derived from the Human Brain and Spinal Fluid Resource Center, Los Angeles Healthcare Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA (Brain Bank 1, BB1, [
3],
DLFPC CTRL=20 and DLFPC SCZ=20; HIPP CTRL=20 and HIPP SCZ=20).
The human cerebellum samples from post-mortem brains derived from the MRC London Neurodegenerative Disease Brain Bank at King's College London's Institute of Psychiatry (Brain Bank 2, BB2, [
2],
CB CTRL=10 and CB SCZ=7). SCZ was clinically diagnosed using DSMIII-R criteria. For subsequent usage, frozen tissues were pulverized in liquid nitrogen and stored at 80 °C.
The Dneasy Blood & Tissue Kit was used to recover DNA from a portion of liquid nitrogen pulverized post-mortem brain tissues (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Using the EZ DNA Methylation Kit (Zymo Research), sodium bisulfite was used to converter the isolated genomic DNA. The PCR procedures were carried out using the bisulfite-specific primers described in [
3]. Following the PCR steps, AMPure purification magnetic beads (Beckman-Coulter, Brea, CA) were used to eliminate primer dimers. A library of bisulfite-treated amplicons was generated by pooling amplicons at an equimolar ratio. The amplicon library was sequenced using V3 reagent kits on an Illumina MiSeq system (Illumina).
Paired-end reads in FASTQ format from the ENA database (accession number: PRJEB24382) were merged using the PEAR (paired-end read merger) tool, setting a minimum of 40 nucleotides as the overlapping region. We retained only those reads with a mean quality score (Phred) >33 and a length between 400 and 500 nucleotides. The resulting reads were then converted in FASTA format using the PRINSEQ (preprocessing and information of sequence) tool. To extract methylated CpG configurations in single DNA molecules, reads in FASTA format were processed using ampliMethProfiler (available at
https://sourceforge.net/projects/amplimethprofiler/), applying several quality filters. We retained only reads characterized by (i) length ±50% compared with the reference length, (ii) at least 80% sequence similarity of the primer with the corresponding gene, (iii) at least 98% bisulfite efficiency, and (iv) alignment of at least 60% of their bases with the reference sequences. The methylation status of all cytosines in the CpG sequence context is coded as methylated (1) or unmethylated (0). Reads with ambiguous calls (including gaps or A or G) at the CpG dinucleotide were removed. The data, in binary formats, were successively analyzed with the MethCoresProfiler [
13].
Methylation average data are expressed as means ± standard deviation. Comparisons between 2 groups were performed using the unpaired Student t-test. Multiple comparisons were made using 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. A p-value ≤ 10^-10 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using JMP software (SAS, Cary, NC) and R software.
5. Conclusions
Evaluation of CpG combinations (methylated cores) may be more informative than classical methylation analyses. It may be effectively used in various applications, including in-depth determination of the epigenetic etiology of brain illnesses. Furthermore, if these analyses can be effectively transferred to peripheral cells, they can be used for diagnostic and clinical purposes.
Author Contributions
V.M., A.F. and T.I. performed bioinformatic analysis, analyzed the results, and prepared figures. M.C, A.Porcellini and A.Pezone supervised the experiments, analyzed the results, and provided scientific interpretations; A.Pezone wrote the paper. All authors discussed the results and provided input on the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partly financed as part of the program for the financing of the University research (FR) 2022 of the University of Naples Federico II [to A.Pezone], Fondazione Medicina Molecolare e Terapia Cellulare, Università Politecnica delle Marche [to A.Pezone], PON R&I 2014-2020 (E65F21002850007) [to A.Pezone].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in this study are freely accessible via the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA), accession no. PRJEB24382.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Enrico Vittorio Avvedimento for revising the manuscript and discussing the epigenetic dynamics and cell identity.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mortensen, P.B.; Pedersen, C.B.; Westergaard, T.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Ewald, H.; Mors, O.; Andersen, P.K.; Melbye, M. Effects of Family History and Place and Season of Birth on the Risk of Schizophrenia. New England Journal of Medicine 1999, 340, 603–608. [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, T.; Sacchi, S.; Errico, F.; Keller, S.; Palumbo, O.; Florio, E.; Punzo, D.; Napolitano, F.; Copetti, M.; Carella, M.; et al. Decreased Free D-Aspartate Levels Are Linked to Enhanced D-Aspartate Oxidase Activity in the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex of Schizophrenia Patients. npj Schizophrenia 2017, 3. [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.; Punzo, D.; Cuomo, M.; Affinito, O.; Coretti, L.; Sacchi, S.; Florio, E.; Lembo, F.; Carella, M.; Copetti, M.; et al. DNA Methylation Landscape of the Genes Regulating D-Serine and D-Aspartate Metabolism in Post-Mortem Brain from Controls and Subjects with Schizophrenia. Scientific Reports 2018, 8. [CrossRef]
- Improda, T.; Morgera, V.; Vitale, M.; Chiariotti, L.; Passaro, F.; Feola, A.; Porcellini, A.; Cuomo, M.; Pezone, A. Specific Methyl-CpG Configurations Define Cell Identity through Gene Expression Regulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 9951. [CrossRef]
- Jirtle, R.L.; Skinner, M.K. Environmental Epigenomics and Disease Susceptibility. Nature Reviews Genetics 2007, 8, 253–262. [CrossRef]
- Tramontano, A.; Boffo, F.L.; Russo, G.; De Rosa, M.; Iodice, I.; Pezone, A. Methylation of the Suppressor Gene P16INK4a: Mechanism and Consequences. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 446. [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.; Pezone, A.; Porcellini, A.; Muller, M.T.; Masternak, M.M. Non-Homologous End Joining Induced Alterations in DNA Methylation: A Source of Permanent Epigenetic Change. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 40359–40372. [CrossRef]
- Pezone, A.; Russo, G.; Tramontano, A.; Florio, E.; Scala, G.; Landi, R.; Zuchegna, C.; Romano, A.; Chiariotti, L.; Muller, M.T.; et al. High-Coverage Methylation Data of a Gene Model before and after DNA Damage and Homologous Repair. Scientific Data 2017, 4. [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Landi, R.; Pezone, A.; Morano, A.; Zuchegna, C.; Romano, A.; Muller, M.T.; Gottesman, M.E.; Porcellini, A.; Avvedimento, E.V. DNA Damage and Repair Modify DNA Methylation and Chromatin Domain of the Targeted Locus: Mechanism of Allele Methylation Polymorphism. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 33222. [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Tramontano, A.; Iodice, I.; Chiariotti, L.; Pezone, A. Epigenome Chaos: Stochastic and Deterministic DNA Methylation Events Drive Cancer Evolution. Cancers 2021, 13, 1800–1800. [CrossRef]
- Morano, A.; Angrisano, T.; Russo, G.; Landi, R.; Pezone, A.; Bartollino, S.; Zuchegna, C.; Babbio, F.; Bonapace, I.M.; Allen, B.; et al. Targeted DNA Methylation by Homology-Directed Repair in Mammalian Cells. Transcription Reshapes Methylation on the Repaired Gene. Nucleic Acids Research 2013, 42, 804–821. [CrossRef]
- Antonella Sarnataro; Giulia De Riso; Cocozza, S.; Pezone, A.; Majello, B.; Stefano Amente; Scala, G. A Novel Workflow for the Qualitative Analysis of DNA Methylation Data. Computational and structural biotechnology journal2022. [CrossRef]
- Pezone, A.; Tramontano, A.; Scala, G.; Cuomo, M.; Riccio, P.; De Nicola, S.; Porcellini, A.; Chiariotti, L.; Avvedimento, E. Tracing and Tracking Epiallele Families in Complex DNA Populations. NAR Genomics and Bioinformatics 2020, 2. [CrossRef]
- Nasyrova, R.F.; Khasanova, A.K.; Altynbekov, K.S.; Asadullin, A.R.; Markina, E.A.; Gayduk, A.J.; Shipulin, G.A.; Petrova, M.M.; Shnayder, N.A. The Role of D-Serine and D-Aspartate in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5142. [CrossRef]
- Errico, F.; Napolitano, F.; Nisticò, R.; Usiello, A. New Insights on the Role of Free D-Aspartate in the Mammalian Brain. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 1861–1871. [CrossRef]
- Mothet, J.-P.; Le Bail, M.; Billard, J.-M. Time and Space Profiling of NMDA Receptor Co-Agonist Functions. Journal of Neurochemistry 2015, 135, 210–225. [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Engberg, G.; Shimizu, E.; Nordin, C.; Lindström, L.H.; Iyo, M. Reduced D-Serine to Total Serine Ratio in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Drug Naive Schizophrenic Patients. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 2005, 29, 767–769. [CrossRef]
- Errico, F.; Napolitano, F.; Squillace, M.; Vitucci, D.; Blasi, G.; de Bartolomeis, A.; Bertolino, A.; D’Aniello, A.; Usiello, A. Decreased Levels of D-Aspartate and NMDA in the Prefrontal Cortex and Striatum of Patients with Schizophrenia. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2013, 47, 1432–1437. [CrossRef]
- Masumi Katane; Homma, H. D-Aspartate Oxidase: The Sole Catabolic Enzyme Acting on Free D-Aspartate in Mammals. Chem Biodivers. 2010, 7, 1435–1449. [CrossRef]
- Pollegioni, L.; Sacchi, S. Metabolism of the Neuromodulator D-Serine. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2010, 67, 2387–2404. [CrossRef]
- Petronis, A. Epigenetics as a Unifying Principle in the Aetiology of Complex Traits and Diseases. Nature 2010, 465, 721–727. [CrossRef]
- Errico, F.; Nuzzo, T.; Carella, M.; Bertolino, A.; Usiello, A. The Emerging Role of Altered D-Aspartate Metabolism in Schizophrenia: New Insights from Preclinical Models and Human Studies. Frontiers in Psychiatry 2018, 9. [CrossRef]
- Wolosker, H.; D’Aniello, A.; Snyder, S.H. D-Aspartate Disposition in Neuronal and Endocrine Tissues: Ontogeny, Biosynthesis and Release. Neuroscience 2000, 100, 183–189. [CrossRef]
- Koga, R.; Miyoshi, Y.; Hiroaki Sakaue; Kenji Hamase; Konno, R. Mouse D-Amino-Acid Oxidase: Distribution and Physiological Substrates. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences 2017, 4. [CrossRef]
- Van, P.P.; Brees, C.; Mannaerts, G.P. D-Aspartate Oxidase, a Peroxisomal Enzyme in Liver of Rat and Man. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 1991, 1073, 203–208. [CrossRef]
- Errico, F.; D’Argenio, V.; Sforazzini, F.; Iasevoli, F.; Squillace, M.; Guerri, G.; Napolitano, F.; Angrisano, T.; Anna Di Maio; Keller, S.; et al. A Role for D-Aspartate Oxidase in Schizophrenia and in Schizophrenia-Related Symptoms Induced by Phencyclidine in Mice. Transl Psychiatry. 2015, 5, e512–e512. [CrossRef]
- MacKay, M.-A.B.; Kravtsenyuk, M.; Thomas, R.; Mitchell, N.D.; Dursun, S.M.; Baker, G.B. D-Serine: Potential Therapeutic Agent And/or Biomarker in Schizophrenia and Depression? Frontiers in Psychiatry 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Morita, Y.; Ujike, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Otani, K.; Kishimoto, M.; Morio, A.; Kotaka, T.; Okahisa, Y.; Matsushita, M.; Morikawa, A.; et al. A Genetic Variant of the Serine Racemase Gene Is Associated with Schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 2007, 61, 1200–1203. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, G.; Coyle, J.T. GLUTAMATERGICMECHANISMS INSCHIZOPHRENIA. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 2002, 42, 165–179. [CrossRef]
- Chumakov, I.; Blumenfeld, M.; Guerassimenko, O.; Cavarec, L.; Palicio, M.; Abderrahim, H.; Bougueleret, L.; Barry, C.; Tanaka, H.; La Rosa, P.; et al. Genetic and Physiological Data Implicating the New Human Gene G72 and the Gene for D-Amino Acid Oxidase in Schizophrenia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2002, 99, 13675–13680. [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, S.; Bernasconi, M.; Martineau, M.; Mothet, J.-P.; Ruzzene, M.; Pilone, M.S.; Pollegioni, L.; Molla, G. PLG72 Modulates Intracellular D-Serine Levels through Its Interaction with D-Amino Acid Oxidase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2008, 283, 22244–22256. [CrossRef]
- Verrall, L.; Burnet, P.W.J.; Betts, J.F.; Harrison, P.J. The Neurobiology of D-Amino Acid Oxidase and Its Involvement in Schizophrenia. Molecular Psychiatry 2009, 15, 122–137. [CrossRef]
- Florio, E.; Keller, S.; Coretti, L.; Affinito, O.; Scala, G.; Errico, F.; Fico, A.; Boscia, F.; Maria Josè Sisalli; Mafalda Giovanna Reccia; et al. Tracking the Evolution of Epialleles during Neural Differentiation and Brain Development: D-Aspartate Oxidase as a Model Gene. Epigenetics 2016, 12, 41–54. [CrossRef]
- Qü, W.; Tatsuya Tsukahara; Nakamura, R.; Hideaki Yurino; Hashimoto, S.; Tsuji, S.; Takeda, H.; Morishita, S. Assessing Cell-To-Cell DNA Methylation Variability on Individual Long Reads. Scientific Reports 2016, 6. [CrossRef]
- Jagannath, V.; Marinova, Z.; Monoranu, C.-M.; Walitza, S.; Grünblatt, E. Expression of D-Amino Acid Oxidase (DAO/DAAO) and D-Amino Acid Oxidase Activator (DAOA/G72) during Development and Aging in the Human Post-Mortem Brain. Frontiers in Neuroanatomy 2017, 11. [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.J. Recent Genetic Findings in Schizophrenia and Their Therapeutic Relevance. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2014, 29, 85–96. [CrossRef]
- Raza, M.U.; Tufan, T.; Wang, Y.; Hill, C.; Zhu, M.-Y. DNA Damage in Major Psychiatric Diseases. Neurotoxicity research 2016, 30, 251–267. [CrossRef]
- Pezone, A.; Olivieri, F.; Maria Vittoria Napoli; Procopio, A.; Enrico Avvedimento; Gabrielli, A. Inflammation and DNA Damage: Cause, Effect or Both. Nature Reviews Rheumatology 2023, 19, 200–211. [CrossRef]
- Dogan, A.E.; Yuksel, C.; Du, F.; Chouinard, V.-A.; Öngür, D. Brain Lactate and PH in Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review of Findings from Magnetic Resonance Studies. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 1681–1690. [CrossRef]
- Rowland, L.M.; Pradhan, S.; Korenic, S.A.; S. Andrea Wijtenburg; L. Elliot Hong; Richard A.E. Edden; Barker, P.B. Elevated Brain Lactate in Schizophrenia: A 7 T Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study. Translational Psychiatry2016, 6, e967–e967. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Methylation of DDO promoter in control and schizophrenic individuals. (A) Structure of the DDO promoter. The black lines and circles on the diagram represent each CpG upstream of the transcription start site (TSS). (B) Average DNA methylation of the seven CpGs shown in (A). CpGs are shown as color-coded squares. (C) Average CpG methylation is shown in (A). (D) The methylated molecules’ Shannon entropy of the same samples. (E) The methylated cores’ composition and structure. A color code is used to identify each CpG on the upper side of the panel. (F) Frequency of the methylated core in the whole population. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 1.
Methylation of DDO promoter in control and schizophrenic individuals. (A) Structure of the DDO promoter. The black lines and circles on the diagram represent each CpG upstream of the transcription start site (TSS). (B) Average DNA methylation of the seven CpGs shown in (A). CpGs are shown as color-coded squares. (C) Average CpG methylation is shown in (A). (D) The methylated molecules’ Shannon entropy of the same samples. (E) The methylated cores’ composition and structure. A color code is used to identify each CpG on the upper side of the panel. (F) Frequency of the methylated core in the whole population. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 2.
Examination of distinct DDO methylation nuclei in different brain areas. (A) Search for distinct methylation cores in control and schizophrenic individuals. (B) Comparison of distinct methylation nuclei among different brain areas. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 2.
Examination of distinct DDO methylation nuclei in different brain areas. (A) Search for distinct methylation cores in control and schizophrenic individuals. (B) Comparison of distinct methylation nuclei among different brain areas. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 3.
Methylation of SR promoter in control and schizophrenic individuals. (A) Structure of the SR promoter. The black lines and circles on the diagram represent CpGs. (B) Average DNA methylation of the thirty CpGs shown in (A). CpGs are shown as color-coded squares. (C) Average CpG methylation is shown in (A). (D) The methylated molecules’ Shannon entropy of the same samples.
Figure 3.
Methylation of SR promoter in control and schizophrenic individuals. (A) Structure of the SR promoter. The black lines and circles on the diagram represent CpGs. (B) Average DNA methylation of the thirty CpGs shown in (A). CpGs are shown as color-coded squares. (C) Average CpG methylation is shown in (A). (D) The methylated molecules’ Shannon entropy of the same samples.
Figure 4.
Methylation of DAO promoter in control and schizophrenic individuals. (A) Structure of the DAO promoter. The black lines and circles on the diagram represent each CpG on the transcription start site (TSS). (B) Average DNA methylation of the ten CpGs shown in (A). CpGs are shown as color-coded squares. (C) Average CpG methylation is shown in (A). (D) The methylated molecules’ Shannon entropy of the same samples. (E) The methylated cores’ composition and structure. A color code is used to identify each CpG on the upper side of the panel. (F) Frequency of the methylated core in the whole population. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 4.
Methylation of DAO promoter in control and schizophrenic individuals. (A) Structure of the DAO promoter. The black lines and circles on the diagram represent each CpG on the transcription start site (TSS). (B) Average DNA methylation of the ten CpGs shown in (A). CpGs are shown as color-coded squares. (C) Average CpG methylation is shown in (A). (D) The methylated molecules’ Shannon entropy of the same samples. (E) The methylated cores’ composition and structure. A color code is used to identify each CpG on the upper side of the panel. (F) Frequency of the methylated core in the whole population. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 5.
Examination of distinct DAO methylation nuclei in different brain areas. (A) Search for distinct methylation cores in control and schizophrenic individuals. (B) Comparison of distinct methylation nuclei among different brain areas. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 5.
Examination of distinct DAO methylation nuclei in different brain areas. (A) Search for distinct methylation cores in control and schizophrenic individuals. (B) Comparison of distinct methylation nuclei among different brain areas. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 6.
Methylation of DAOA promoter in control and schizophrenic individuals. (A) Structure of the DAOA promoter. The black lines and circles on the diagram represent each CpG upstream of the transcription start site (TSS). (B) Average DNA methylation of the three CpGs shown in (A). CpGs are shown as color-coded squares. (C) Average CpG methylation is shown in (A). (D) The methylated molecules’ Shannon entropy of the same samples. (E) The methylated cores’ composition and structure. A color code is used to identify each CpG on the upper side of the panel. (F) Frequency of the methylated core in the whole population. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 6.
Methylation of DAOA promoter in control and schizophrenic individuals. (A) Structure of the DAOA promoter. The black lines and circles on the diagram represent each CpG upstream of the transcription start site (TSS). (B) Average DNA methylation of the three CpGs shown in (A). CpGs are shown as color-coded squares. (C) Average CpG methylation is shown in (A). (D) The methylated molecules’ Shannon entropy of the same samples. (E) The methylated cores’ composition and structure. A color code is used to identify each CpG on the upper side of the panel. (F) Frequency of the methylated core in the whole population. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 7.
Examination of distinct DAOA methylation nuclei in different brain areas. (A) Search for distinct methylation cores in control and schizophrenic individuals. (B) Comparison of distinct methylation nuclei among different brain areas. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
Figure 7.
Examination of distinct DAOA methylation nuclei in different brain areas. (A) Search for distinct methylation cores in control and schizophrenic individuals. (B) Comparison of distinct methylation nuclei among different brain areas. A pairwise comparison was performed with Student’s t-test: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, ***** p < 0.001 versus CTRL.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).