1. Introduction
According to the Rome IV criteria, functional dyspepsia (FD) is a complex of symptoms (postprandial fullness, early satiation epigastric pain and epigastric burning) for the last 3 months with symptom onset at least 6 months before diagnosis with no evidence of organic, systemic, or metabolic disease that would explain the symptoms on routine investigations [
1,
2]. According to the results of large-scale studies, the prevalence of FD worldwide ranges from 10 to 30%. Patients with FD have a reduced quality of life, which is associated with the severity of symptoms and concomitant depression, the need for high medical costs and reduced ability to work [
1,
3]. The pathogenesis of FD development is not fully understood [
1,
2,
3,
4].
The prevalence of Helicobacter pylori among patients with FD ranges from 20 to 60%. [
5]. Eradication therapy in these patients led to a decrease in the symptom severity in some patients but it is not always effective [
1,
6,
7]. To increase еradication therapy efficacy, several methods have been proposed, including addition probiotics and mucosal protective agents such as rebamipide to standard eradication therapy. This complementation showed a positive effect [
6,
7,
8,
9].
The Lactobacillus reuteri (the new name is Limosilactobacillus reuteri) strain DSM 17648 was selected as a highly specific H. pylori antagonist binding these bacteria in artificial gastric juice, reducing their mobility and adhesion ability. L. reuteri strain DSM 17648 co-aggregates different types and species of Helicobacter (H. pylori type I and II, H. heilmannii type I and II, H. canis), but not bacterial representatives of normal oral or intestinal microbiota [
10]. It has been suggested that not only live bacteria, but also inactivated bacteria, containing their metabolic products (postbiotics, also called metabiotics, ghostbiotics or paraprobiotics) can have a positive effect [
11,
12]. Postbiotics are safer for consumers, faster in action, and less demanding to storage conditions than probiotics because they do not contain live bacteria. Postbiotic based on L. reuteri DSM 17648 with a trade name Pylopass™ showed ability to reduce activity of H. pylori, and exerted a preventive effect of secondary diseases and related symptoms due to H. pylori infection. Moreover, the preventive effect was carried over well after the supplementation itself, at least for the six month period [
10,
13,
14]. However, there was no placebo-controlled randomized study that directly showed its ability to increase the effectiveness of eradication therapy in adults. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of postbiotic based on L. reuteri DSM 17648 as supplementation for the H. pylori eradication therapy in patients with functional dyspepsia is the aim of this study.
2. Materials and Methods
This randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled, multicenter, parallel study was approved by the Local ethics committee of Sechenov University (protocol № 10-19 dated 17.07.2019) in accordance with the Helsinki declaration and registered in the ISRCTN registry (ISRCTN20716052). The study was conducted in 6 independent centers in Russia from September 2019 to June 2023.
The randomization lists was created using the blockrand package (version 1.3) of the Microsoft R Open statistical software with the following parameters:
two blinded groups with equal distribution into groups;
six uniformly created randomization lists - one for each center
randomization sequences (seed) were 4037 (Center 1), 3031 (Center 2), 3739 (Center 3), 3034 (Center 4), 3259 (Center 5), and 3125 (Center 6).
variable block length (2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18 or 20), total number of blocks were 18 for Center 1, 17 for Center 2, 16 for Center 3, 16 for Center 4, 20 for Center 5, and 18 for Center 6.
2.1. Patients
All patients who visited the clinics of the centers with characteristic complaints of functional dyspepsia were screened for participation in the study.
The inclusion criteria were:
male or female aged 18-65;
for a woman of childbearing age: mandatory use of contraceptive methods;
confirmed diagnosis of functional dyspepsia according to the Rome IV criteria [
1];
presence of H. pylori infection according to 13C UBT [
6,
7];
no history of previous eradication therapy at least a year before the screening;
ability to understand and willingness to follow all protocol details;
signed informed consent.
The exclusion criteria were:
erosive, ulcerative, or cicatricial changes in the stomach and/or duodenum;
history of eradication therapy less than 1 year prior to screening;
use of antibiotics and/or bismuth trication dicitrate and/or H2 secretion blockers and/or proton pump inhibitors 30 days before and during the study;
use of macrolide antibiotics less than 1 year prior to screening;
any severe, decompensated, or unstable medical condition that could affect the clinical evaluation of the investigational product or put the patient at risk;
pregnancy, lactation;
known sensitivity to any components of the study product and any of the drugs prescribed in this study;
history of surgical treatment of the stomach, resection of the small intestine or operations on the pancreas;
a positive blood test result for HIV and/or syphilis and/or HbsAg and/or HCVAb;
chronic diarrhea of various etiologies, except for functional diarrhea or irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea;
participation in another clinical study 30 days before and during the study;
use of probiotics, symbiotics, prebiotics for the treatment of H. pylori infections and for other reasons within 30 days prior to study entry;
refusal to continue the study, including the refusal of visits 3 and / or 4 and the investigations on these visits (other than taking blood for analyses);
development of a clinical condition that is associated with safety and, in the opinion of the investigator, requires termination of participation in the clinical study;
failure to comply with the minimum duration of eradication therapy (10 days, compliance less than 75%);
use during the treatment and follow-up period of antibiotics, probiotics, prebiotics, postbiotics, antisecretory or bismuth drugs, sucralfate, drugs with a pronounced hepato- and nephrotoxic effect, with the exception of drugs that were used in the tested eradication therapy regimens.
Initially, based on study by Zagari et al. [
15], it was assumed for sample size estimation that the eradication rate would be 75% in the control group and 90% in the postbiotic group, which at significance level of 95%, power of 80%, and randomization rate 1:1 gave the required number of patients included in 172 persons. However, the development of the COVID-19 pandemic has slowed patient enrollment and we have revised our calculations based on more recent work by De Francesco et al. [
16], estimating that that the eradication rate would be 79% in the control group and 94% in the postbiotic group). Based on these data the STATISTICA 10 software (StatSoft Inc., Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA) calculated required number of patients as 64 for each group which corresponds to 128 included patients.
2.2. Intervention
Patients were randomized 1:1 to the postbiotic and placebo groups. Out-patients in the postbiotic group simultaneously with standard eradication therapy (esomeprazole 20 mg bid 15-30 min before meals + amoxicillin 1000 mg bid after meal+ clarithromycin 500 mg bid after meal for 14 days) received 1 capsule with 324 mg Helinorm™ containing 200 mg Pylopass™ (2 x 1010 spray-dried L. reuteri DSM 17648 cells) bid with meals for 14 days and another 14 days after completion of eradication therapy.
2.3. Controls
Out-patients in the placebo (control) group simultaneously with standard eradication therapy (esomeprazole 20 mg bid 15-30 min before meal + amoxicillin 1000 mg bid after meal+ clarithromycin 500 mg bid after meal for 14 days) received the placebo at a dose of 324 mg bid with meals for 14 days and another 14 days after completion of eradication therapy. Visually, the placebo capsules and their jars did not differ from the postbiotic capsules and jars. Neither the patients nor the medical staff working with them knew whether it was postbiotic or placebo.
2.4. Outcomes
The primary outcome was successful eradication of H. pylori, defined as a negative 13С- UBT 28 days after the end of the postbiotic/placebo administration (42 days after the end of eradication therapy). The period of eradication therapy (14+/-2 days) was defined as the treatment period, and the period after the end of eradication therapy until the repeated breath test for H. pylori (42+/-3 days) was defined as the follow-up period.
13C-UBT was carried out according to the same methodology at the inclusion of the study and at its end. It was performed in the morning on an empty stomach using the Helicarb kit (Isocarb Limited, Moscow, Russia). The patient drank 200 ml of orange juice included in this kit and 5 minutes after it he/she exhaled air into the Urease test bag 1. Then he/she was given a 50 ml aqueous solution containing 50 mg 13C-urea. During the next 30 minutes, the patient did not eat, rested and did not smoke, and subsequently a new sample of exhaled air was taken from him/her in the Urease test bag 2. Both bags were delivered to the laboratory on the same day or in the morning of the next day, where their contents were analyzed by infrared isotope analyzer IRIS-Doc (Kibion AB; Sweden) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. The presence of H. pylori infection was assessed by an increase in 13C-carbon dioxide between the samples UBT 2 and UBT 1, which these bacteria produce from the 13C-urea with the urease enzyme in the stomach .
Secondary outcomes included:
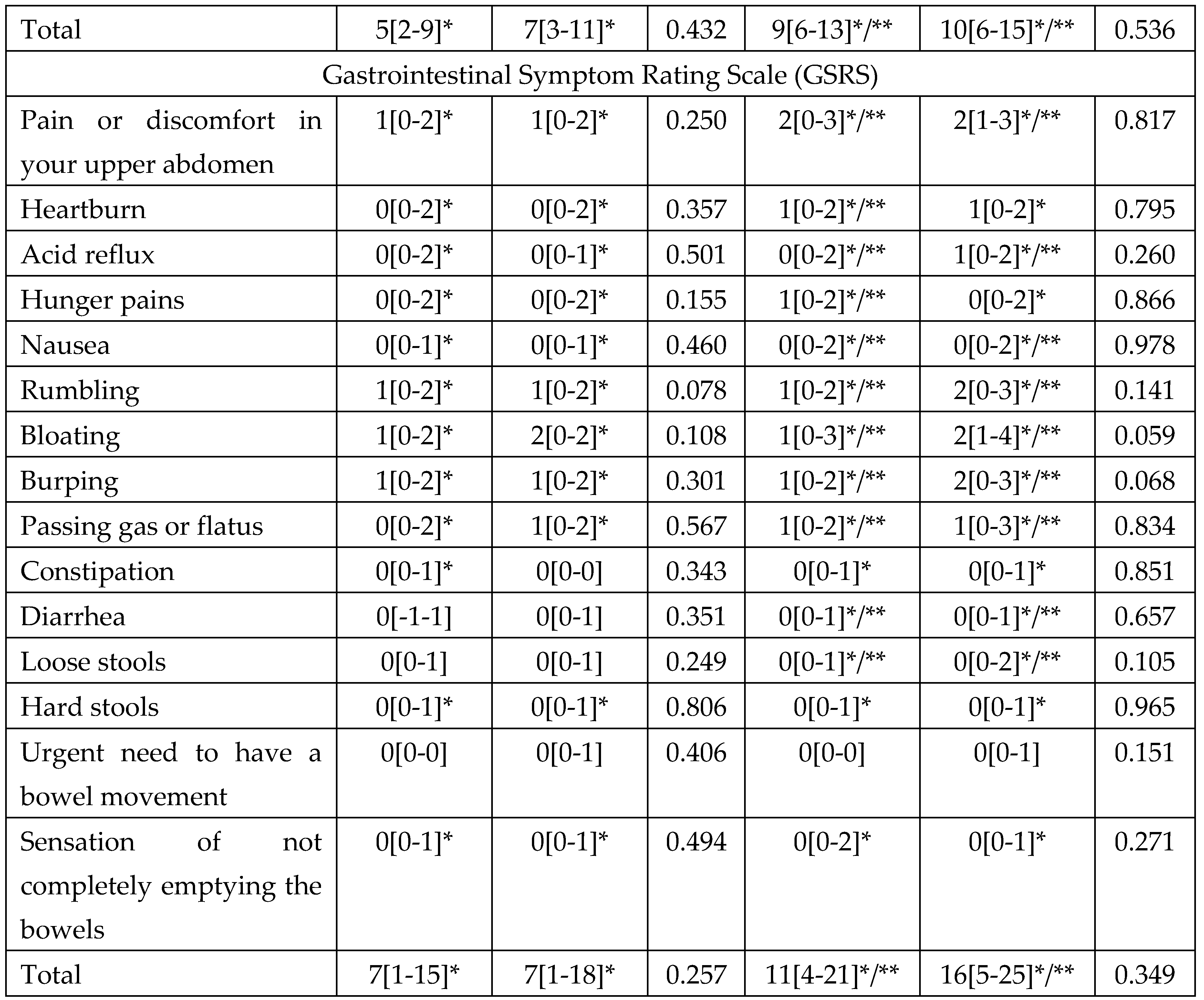
1) a change in the severity of digestive symptoms, defined as a change in the 7x7 [
17] and Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) [
18] questionnaire scores ;
2) a change in the quality of life, defined as change in the SF-36 [
19] questionnaire scores;
3) a change in the value of the main parameters of a complete blood count (hemoglobin, white blood cell and platelet count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate) and a biochemical blood test (the serum levels of total protein, total bilirubin, creatinine, amylase, alkaline phosphatase, ALT, and AST);
4) frequency and severity of adverse effects of therapy;
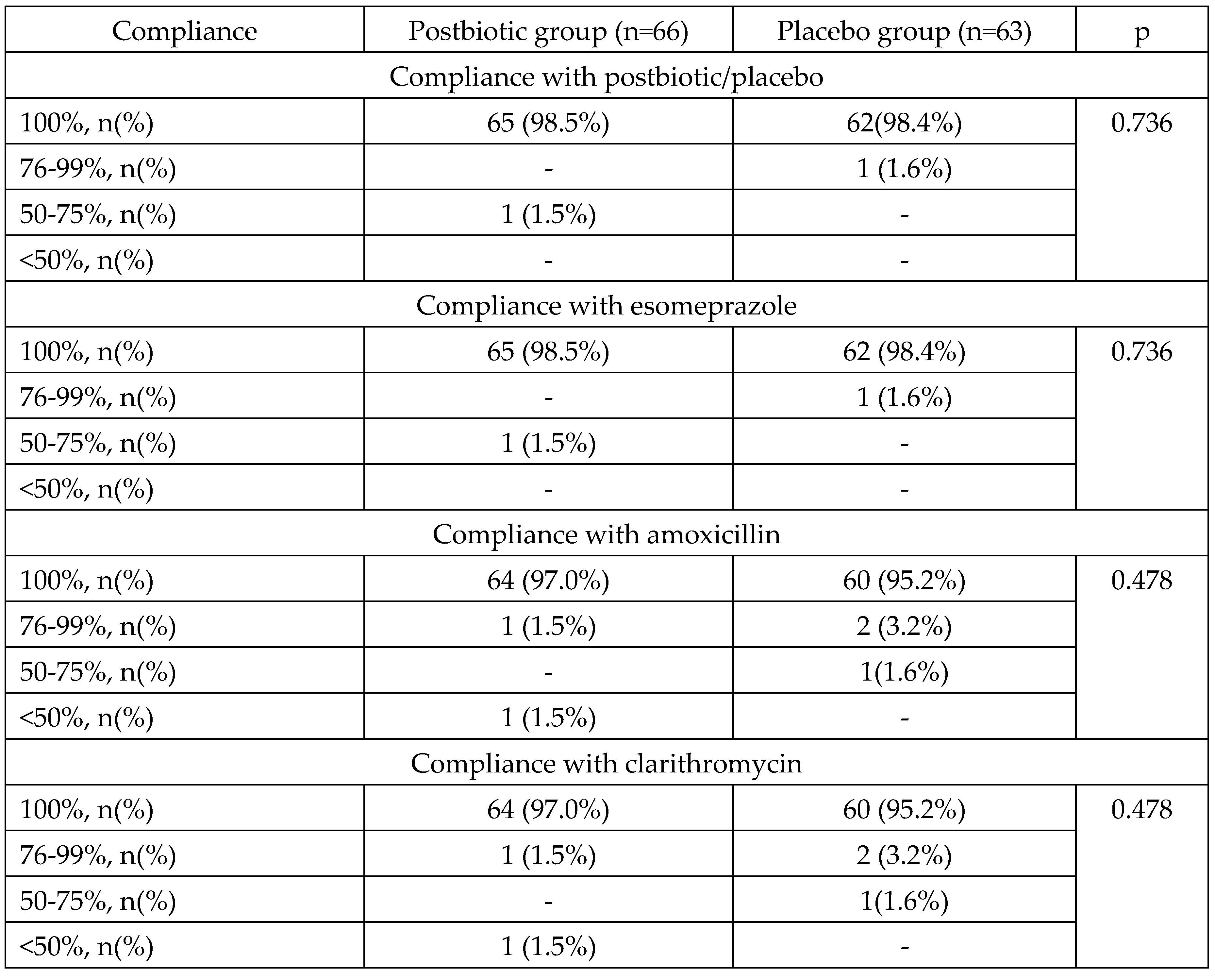
5) therapy compliance, defined as the ratio of the number of used drugs to those that should be used. The number of used drugs was estimated by the number of empty places in the drug blisters, which patients returned by the end of eradication therapy.
The study scheme is presented in
Table 1.
2.5. Statistics
Quantitative parameters were presented as a median [interquartile range]. Comparison of categorical data was carried out by Fisher’s exact test; comparison of quantitative and semi-quantitative data was evaluated by the Mann-Whitney method. Changes in the values of extended and semi-quantitative parameters were assessed by the Wilcoxon test. Significance criterion was p<0.05. Statistical data processing was carried out using the STATISTICA 10 software (StatSoft Inc., Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA). The effectiveness of therapy was assessed according to the per-protocol analysis; safety and compliance were assessed according to the intention-to-treat analysis.
3. Results
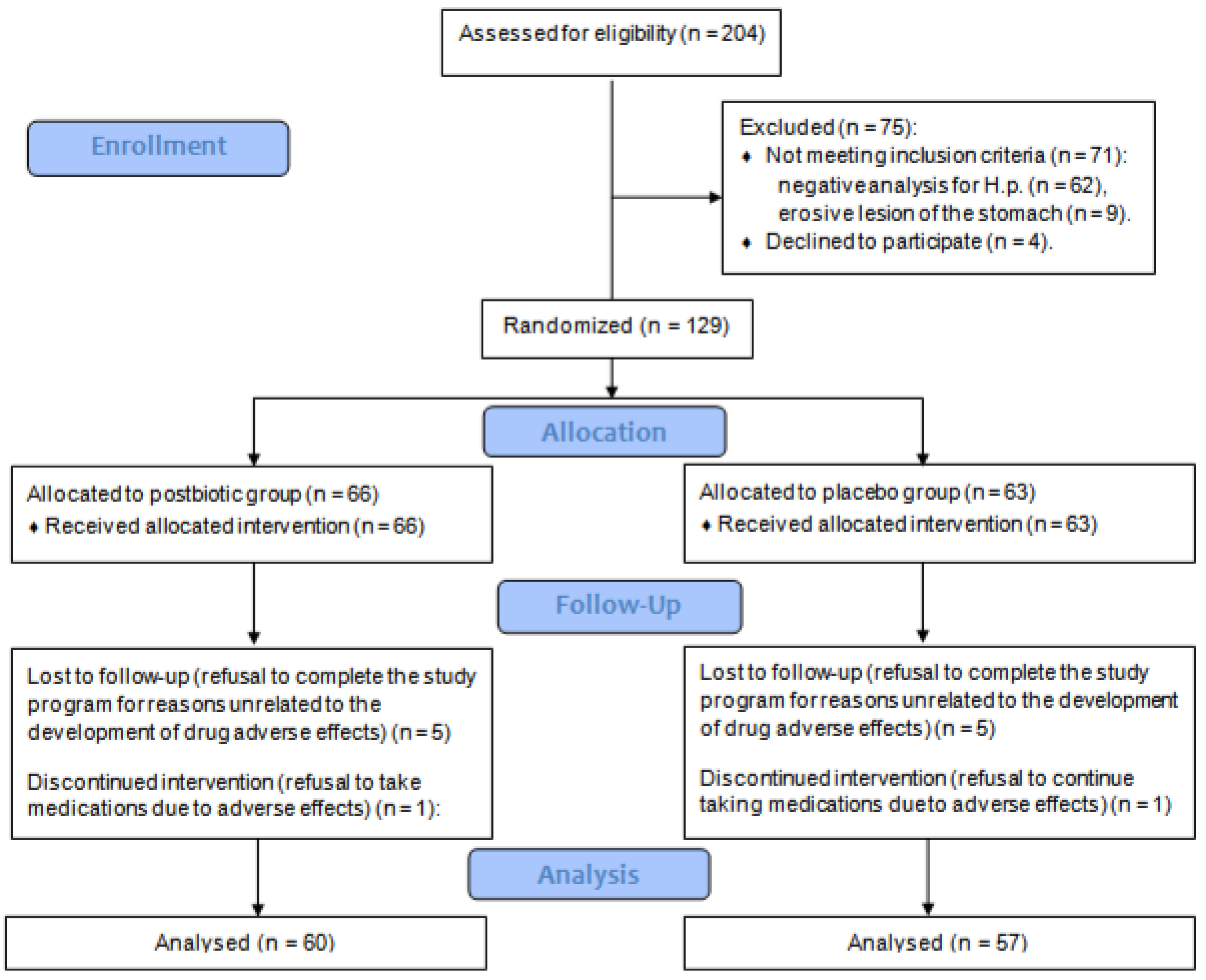
Of the 204 screened patients, 129 met the criteria and were included in the study. Among them, 66 were randomized to the postbiotic group and 63 did to the placebo group. Five patients in each group refused to visit the centers again (visits 3 and/or 4) to evaluate the results of therapy. One patient in each group developed adverse effects that led to the termination of eradication therapy before the minimum time (10 days), so they were also excluded from the analysis. In total, data from 60 patients in the postbiotic group and 57 patients in the placebo group were analyzed (
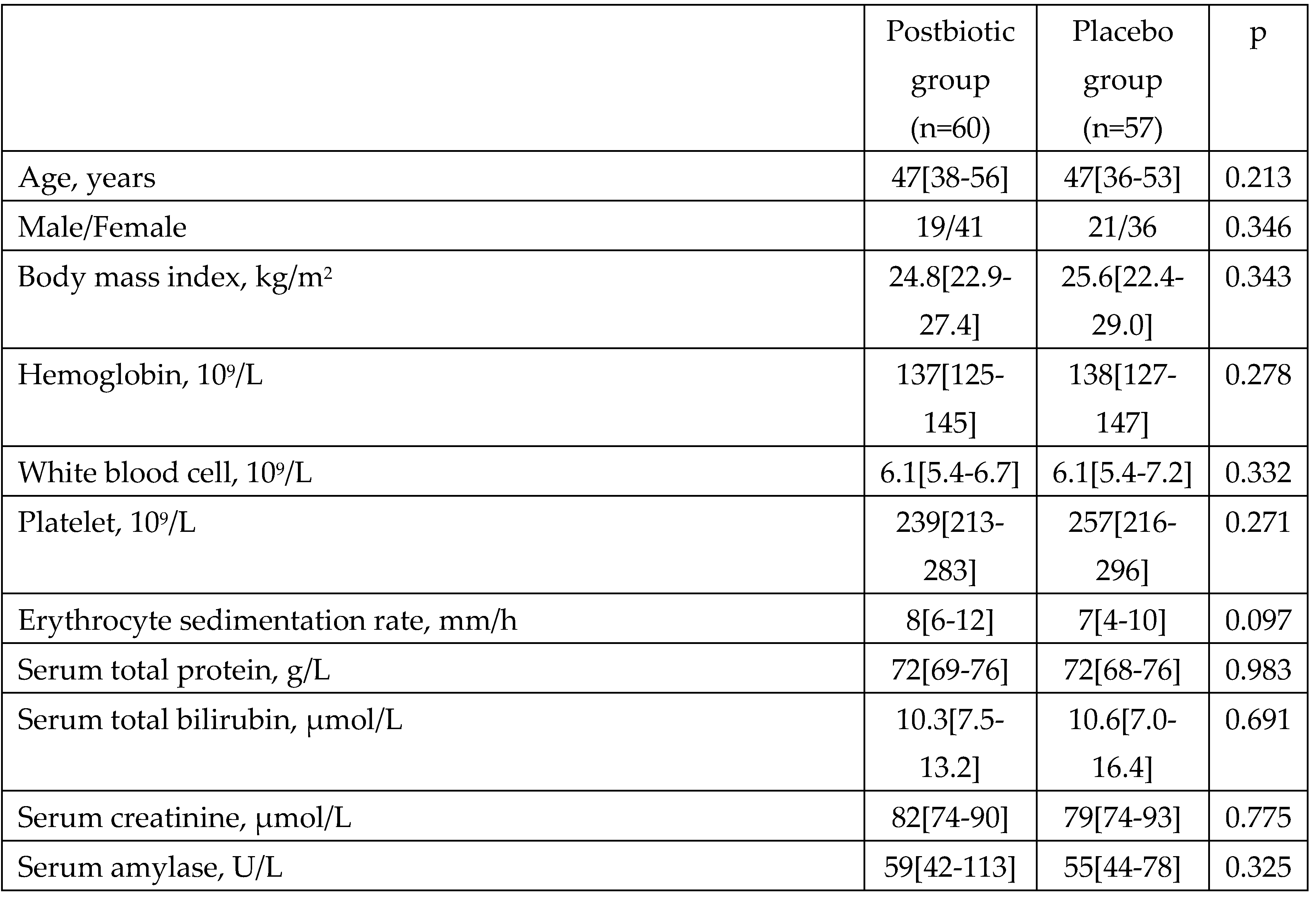
Figure 1). There was no significant difference in baseline parameters between groups (
Table 2). There was no significant difference between groups in the incidence of comorbidities and the use of medication to treat them (
Supplementary Table S1).
At the end of the follow-up period, 2 (3.3%) patients in the postbiotic group and 8 (14.0%) patients in the placebo group had a positive 13C-UBT for H. pylori. The eradication efficiency was 96.7% for the postbiotic group and 86.0% for the placebo group (p = 0.039;
Table 3).
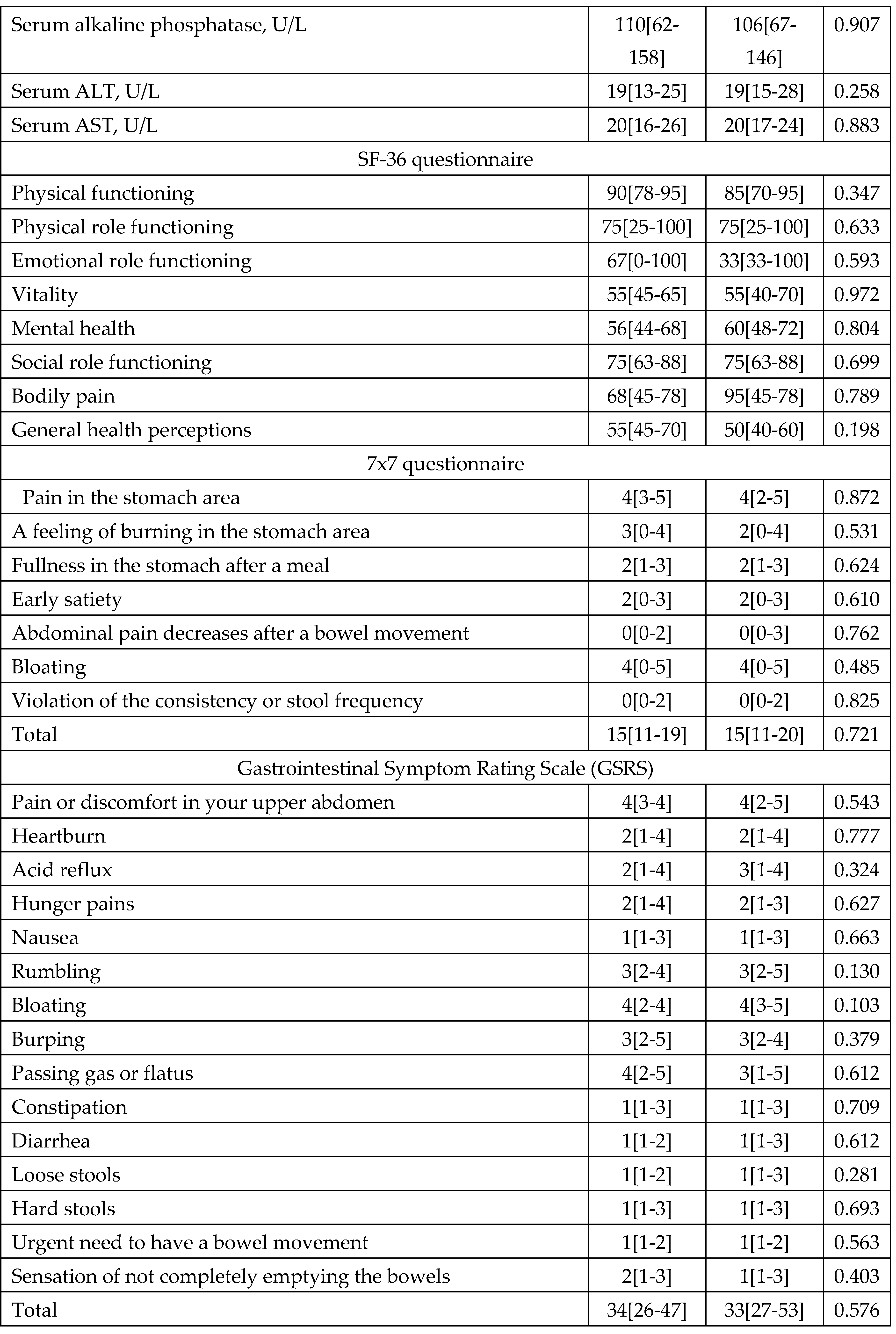
By the end of the follow-up period, both groups showed significant improvements in quality of life according to all sections of the SF-36 scale with no significant differences between groups (
Table 4).
At the end of eradication therapy (Day 14) in both groups, there were significant improvements compared to baseline in most digestive symptoms, including symptoms of functional dyspepsia (pain in the stomach area, a feeling of burning in the stomach area, fullness in the stomach after a meal, early satiety, and bloating), which became even more significant by the end of the follow-up period (
Table 4). There was no significant difference in the change in the severity of digestive symptoms neither at the end of eradication therapy nor at the end of the follow-up period between the groups (
Table 4).
There was no significant change in any of the tested laboratory parameters from baseline to the end of eradication therapy and there were also no differences in these parameters between the groups (
Supplementary Table S2).
Compliance with the postbiotic was 100% in 98.5% of patients and did not significantly differ from the compliance with placebo. Compliance with standard eradication therapy was 100% in 97.0% of patients in the postbiotic group and did not differ significantly from that in the placebo group (
Table 5).
Adverse effects developed in 30.8% of patients in the postbiotic group and in 38.0% of patients in the placebo group. Most of them were mild. Only in 1.5% of patients in the postbiotic group and in 3.2% of patients in the placebo group, the development of adverse effects required discontinuation of drugs (pain in the lumbar region in one patient in the postbiotic group; severe nausea with bitter taste in the mouth in one patient in the placebo group; moderate diarrhea in another patient in the placebo group). Serious adverse effects were not registered. The postbiotic regimen tended to cause diarrhea less frequently than regime without it, but this difference did not reach the level of significance (10.6% vs 15.9%; P=0.267). The overall number of digestive adverse effects in the postbiotic group was lower than in the placebo group. The incidence of non-digestive and specific digestive adverse effects also did not significantly differ between the groups (
Table 6).
4. Discussion
H. pylori infection is one of the most common human infections in the world. This bacterium is recognized as the etiological agent of most forms of chronic gastritis and peptic ulcer, and is also involved in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer and MALT-lymphoma [
6]. It has also been suggested that it is responsible for the development of some cases of functional dyspepsia. The eradication therapy in such patients can lead to a regression of symptoms [
6], which coincides with the results of our study.
Therefore, the eradication of H. pylori becomes an important target. Several drug regimens have been proposed, among which those with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) + amoxicillin + clarithromycin is one of the first line regimen in countries with low resistance of H. pylori to claritromycin (Russia is one of them) [
6]. Recent studies have shown the benefit of longer therapy (14 days versus 10 and 7 days [
6]). However, even in this case, the effectiveness of eradication therapy was about 80-90% [
6,
15,
16,
20,
21]. To further increase it, several methods have been proposed, including the use of probiotics [
22]. Among several microorganisms tested for this purpose, one of the most interesting is L. reuteri that survives in the gastric acid environment colonizes the gastric mucosa and inhibits the growth of several pathogenic bacteria, including H. pylori [
23]. Various live strains of this bacterium have shown the ability to reduce the load of H. pylori (decrease in 13C-UBT values) [
24,
25]. The use of this probiotic together with PPI led to the eradication of H. pylori in a number of patients [
24,
25]. However, despite the fact that the efficacy of 10-14-day first-line eradication therapy combined with this probiotic in many studies tended to be higher than without it [
27,
28,
29,
30]., this difference reached significance only in the most recent study from Malaysia [
31].
The efficacy of non-viable L. reuteri (postbiotic/metabiotic) for this purpose was also analyzed. After long-term screening, the DSM 17648, a strain with maximum anti-Helicobacter activity in artificial gastric juice, was selected. Its mechanism of action is to bind to H. pylori that leads to reducing mobility and adhesion ability of these pathogenic bacteria [
10]. Postbiotic based on this strain has been marketed under the trade name Pylopass™. It showed the ability to reduce H. pylori load in the stomach according to the urease breath test [
10,
13,
14] and its efficacy for H. pylori eradication in combination with IPP was as effective as standard eradication therapy [
32]. Our study is the first multicenter placebo-controlled study to confirm the efficacy of non-viable L. reuteri DSM 17648 (Pylopass™) as an enhancer of standard 14-day first-line bismuth-free eradication therapy in adults.
However, our study conflicts with a recently published work from China that did not show this effect. [
33]. The difference between our and the Chinese therapy regimens was that the Chinese colleagues used co-treatment (eradication therapy + L. reuteri DSM 17648) with a 14-day pre-treatment with L. reuteri DSM 17648, but we used a 14-day post-treatment with this co-treatment. In addition, our Chinese colleagues used a half our dose of drug (1 x 1010 dead L. reuteri DSM 17648 cells vs. 2 x 1010 ones). All this could lead to an insufficient effect of this therapy. Further RCTs comparing these regimens are required to verify our hypothesis. Another reason for these differences may be the ethnic genetic specifics of patients and H. pylori strain differences. Studies in other countries are required to verify this hypothesis.
Although we did not obtain a significant reduction in the frequency of specific adverse effects of therapy as a result of the addition of L. reuteri DSM 17648 to the eradication therapy, the overall number of digestive adverse effects in the group of patients receiving it was significantly lower (p=0.049). Yang et al. [
33] observed a significant effect from L. reuteri supplementation on the reduction of the incidence of eradication therapy-induced diarrhea (p=0.022) and abdominal distention (p=0.022), which may be due to the larger number of patients (n=200) included in that study or ethnic genetic specifics of these patients.
The strength of the present study is its design (multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled), which is gold standard of clinical research. It is the first study showing that addition of inactivated L. reuteri DSM 17648-to 14-day first-line eradication therapy significantly increases eradication efficacy.
One limitation of this study is the lack of a complete placebo group, that should have consisted of patients who received placebo instead of eradication therapy. This does not allow a correct assessment of the effect of the eradication therapy itself on the symptoms of FD. A further large study comparing live and non-viable L. reuteri DSM 17648 would answer the question of what is more effective in H. pylori eradication, a probiotic or a postbiotic. It would also be promising to evaluate how the addition of L. reuteri affects the efficacy of bismuth eradication quadruple therapy, which is another aim for future research.
5. Conclusions
The postbiotic (metabiotic) based on Lactobacillus reuteri DSM17648 significantly improves the efficacy of H. pylori eradication therapy in functional dyspepsia and decreases overall number of digestive adverse effects of this therapy.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Research idea - Vladimir Ivashkin. Study design - Vladimir Ivashkin, Igor Maev, Elena Poluektova, Alexander Sinitsa. Research and data analysis - all authors. Draft writing - Roman Maslennikov. Draft editing - all authors.
Funding
The study was sponsored by Novozymes A/S (Denmark) and Parusin (Germany). The sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Local ethics committee of Sechenov University (protocol № 10-19 dated 17.07.2019) in accordance with the Helsinki declaration.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The study was sponsored by Novozymes A/S (Denmark) and Parusin (Germany). The sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Stanghellini V, Chan FCL, Hasler WL, et al. Gastroduodenal disorders. Gastroenterology 2016; 150:1380-92. [CrossRef]
- Ivashkin VT, Mayev IV, Sheptulin AA, Lapina TL, Trukhmanov AS, Kartavenko IM, Kiprianis VA, Okhlobystina OZ Diagnosis and treatment of the functional dyspepsia: clinical guidelines of the Russian Gastroenterological Association. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2017;27(1):50-61. [CrossRef]
- Talley, N. Talley N. Functional Dyspepsia: Advances in Diagnosis and Therapy. Gut liver. 2017; 11(3): 349–357. [CrossRef]
- Madisch A, Andresen V, Enck P, Labenz J, Frieling T, Schemann M: The diagnosis and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Dtsch Arztebl Int 2018; 115: 222–32. [CrossRef]
- Diaconu S, Predescu A, Moldoveanu A, Pop CS, Fierbineanu-Braticevici C. Helicobacter pylori infection: old and new. J Med Life. 2017; 10(2): 112–117.
- Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, Rokkas T, Gisbert JP, Liou JM, Schulz C, et al. Management of Helicobacter pylori infection: the Maastricht VI/Florence consensus report. Gut. 2022:gutjnl-2022-327745. [CrossRef]
- Ivashkin VT, Lapina TL, Maev IV, Drapkina OM, Kozlov RS, Sheptulin AA, et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines of Russian Gastroenterological Association, Scientific Society for the Clinical Study of Human Microbiome, Russian Society for the Prevention of Non-Communicable Diseases, Interregional Association for Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobial Chemotherapy for H. pylori Diagnostics and Treatment in Adults. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2022;32(6):72-93. [CrossRef]
- Ivashkin VT, Maev IV, Abdulganieva DI, Alekseenko SA, Gorelov AV, et al. Practical Recommendations of Scientific Society for the Study of Human Microbiome and the Russian Gastroenterological Association on Use of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics and Functional Foods in Treatment and Prevention of Gastroenterological Diseases in Children and Adults. Russian Journal of Gastroenterology, Hepatology, Coloproctology. 2021;31(2):65-91. [CrossRef]
- Lv Z, Wang B, Zhou X, et al. Efficacy and safety of probiotics as adjuvant agents for Helicobacter pylori infection: a meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med. 2015; 9:707-16. [CrossRef]
- Holz C, Busjahn A, Mehling H, Arya S, Boettner M, Habibi H, Lang C. Significant Reduction in Helicobacter pylori Load in Humans with Non-viable Lactobacillus reuteri DSM17648: A Pilot Study. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2015;7(2):91-100. [CrossRef]
- Shenderov, BA; Sinitsa, AV; Zakharchenko MM.; Lang C. 2020. Metabiotics: present state, challenges and perspectives. Springer International Publishing. [CrossRef]
- Liang B, Xing D. The Current and Future Perspectives of Postbiotics. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2023 Feb 10:1–18. [CrossRef]
- Mehling H, Busjahn A. Non-Viable Lactobacillus reuteri DSMZ 17648 (Pylopass™) as a New Approach to Helicobacter pylori Control in Humans. Nutrients 2013;5:3062-3073. [CrossRef]
- Buckley M, Lacey S, Doolan A, Goodbody E, Seamans K. The effect of Lactobacillus reuteri supplementation in Helicobacter pylori infection: a placebo-controlled, single-blind study. BMC Nutrition 2018;4:48. [CrossRef]
- Zagari RM, Bianchi-Porro G, Fiocca R, Gasbarrini G, Roda E, Bazzoli F. Comparison of 1 and 2 weeks of omeprazole, amoxicillin and clarithromycin treatment for Helicobacter pylori eradication: the HYPER Study. Gut. 2007;56(4):475-9. [CrossRef]
- De Francesco V, Ridola L, Hassan C, Bellesia A, Alvaro D, Vaira D, Zullo A. Two-week Triple Therapy with either Standard or High-dose Esomeprazole for First-line H. pylori Eradication. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2016;25(2):147-50. [CrossRef]
- Ivashkin V, Sheptulin A, Shifrin O, Poluektova E, Pavlov C, Ivashkin K, Drozdova A, Lyashenko O, Korolev A. Clinical validation of the “7 × 7” questionnaire for patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;34(6):1042-1048. [CrossRef]
- Revicki DA, Wood M, Wiklund I, Crawley J. Reliability and validity of the gastrointestinal symptom rating scale in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Qual Life Res. 1997;7(1):75–83. [CrossRef]
- Weinberger M, Samsa GP, Hanlon JT, Schmader K, Doyle ME, Cowper PA, Uttech KM, Cohen HJ, Feussner JR. An evaluation of a brief health status measure in elderly veterans. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1991;39(7):691-4. [CrossRef]
- Nyssen OP, Bordin D, Tepes B, Pérez-Aisa Á, Vaira D, Caldas M, et al. European Registry on Helicobacter pylori management (Hp-EuReg): patterns and trends in first-line empirical eradication prescription and outcomes of 5 years and 21 533 patients. Gut. 2021;70(1):40-54. [CrossRef]
- Bordin DS, Embutnieks YV, Vologzhanina LG, Il’chishina TA, Voinovan IN, Sarsenbaeva AS, et al. European Registry on the management of Helicobacter pylori infection (Hp-EuReg): analysis of 2360 patients receiving first-line therapy in Russia. Ter Arkh. 2018;90(2):35-42. [CrossRef]
- Zhang M, Zhang C, Zhao J, Zhang H, Zhai Q, Chen W. Meta-analysis of the efficacy of probiotic-supplemented therapy on the eradication of H. pylori and incidence of therapy-associated side effects. Microb Pathog. 2020;147:104403. [CrossRef]
- Dargenio C, Dargenio VN, Bizzoco F, Indrio F, Francavilla R, Cristofori F. Limosilactobacillus reuteri Strains as Adjuvants in the Management of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(7):733. [CrossRef]
- Dore MP, Cuccu M, Pes GM, Manca A, Graham DY. Lactobacillus reuteri in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection. Intern Emerg Med. 2014;9(6):649-54. [CrossRef]
- Francavilla R, Lionetti E, Castellaneta SP, Magistà AM, Maurogiovanni G, et al. Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori infection in humans by Lactobacillus reuteri ATCC 55730 and effect on eradication therapy: a pilot study. Helicobacter. 2008;13(2):127-34. [CrossRef]
- Dore MP, Bibbò S, Pes GM, Francavilla R, Graham DY. Role of Probiotics in Helicobacter pylori Eradication: Lessons from a Study of Lactobacillus reuteri Strains DSM 17938 and ATCC PTA 6475 (Gastrus®) and a Proton-Pump Inhibitor. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2019;2019:3409820. [CrossRef]
- Emara MH, Mohamed SY, Abdel-Aziz HR. Lactobacillus reuteri in management of Helicobacter pylori infection in dyspeptic patients: a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2014;7(1):4-13. [CrossRef]
- Naghibzadeh N, Salmani F, Nomiri S, Tavakoli T. Investigating the effect of quadruple therapy with Saccharomyces boulardii or Lactobacillus reuteri strain (DSMZ 17648) supplements on eradication of Helicobacter pylori and treatments adverse effects: a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022;22(1):107. [CrossRef]
- Francavilla R, Polimeno L, Demichina A, Maurogiovanni G, Principi B, Scaccianoce G, Ierardi E, Russo F, Riezzo G, Di Leo A, Cavallo L, Francavilla A, Versalovic J. Lactobacillus reuteri strain combination in Helicobacter pylori infection: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;48(5):407-13. [CrossRef]
- Poonyam P, Chotivitayatarakorn P, Vilaichone RK. High Effective of 14-Day High-Dose PPI- Bismuth-Containing Quadruple Therapy with Probiotics Supplement for Helicobacter Pylori Eradication: A Double Blinded-Randomized Placebo-Controlled Study. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2019;20(9):2859-2864. [CrossRef]
- Ismail NI, Nawawi KNM, Hsin DCC, et al. Probiotic containing Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17648 as an adjunct treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Helicobacter. 2023; 00:e13017. [CrossRef]
- Muresan IAP, Pop LL, Dumitrascu DL. Lactobacillus reuteri versus triple therapy for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori in functional dyspepsia. Med Pharm Rep. 2019;92(4):352-355. [CrossRef]
- Yang C, Liang L, Lv P, Liu L, Wang S, Wang Z, Chen Y. Effects of non-viable Lactobacillus reuteri combining with 14-day standard triple therapy on Helicobacter pylori eradication: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Helicobacter. 2021;26(6):e12856. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).