1. Introduction
Central mechanism in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), one of the serious aging-related diseases, are considered to be largely due to functional disruptions of gene products involved in insulin resistance [1-3]. Since compounds targeting for the gene products are expected to be useful for understanding of insulin resistance, efficient techniques and methods for compound identification are eagerly awaited [
4,
5].
In silico Structure-Based Drug Screening (SBDS), based on three-dimensional structural data of target proteins has been utilized in selection of compounds interacting to target protein [
6]. Here, we attempted to screen small compounds, affecting the negative regulatory function of the growth factor receptor-bound protein 14 (Grb14) toward insulin receptor (IR), with hierarchical
in silico SBDS.
Grb14, belongs to Grb7 family of adaptor proteins (Grb7/10/14) was initially cloned from human breast epithelial cell cDNA [
7]. Grb14 can associate with the intracellular kinase domain of IR, known as beta-subunit (IRβ), in response to insulin stimulation [
8]. The IRβ–Grb14 complex formation results in the inhibition of downstream signal transduction by preventing the activation of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) [3,
9,
10], and consequently glucose uptake is impaired. Currently, Grb14 has been believed to play a critical role in regulating insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis: (i) Grb14 knock-out mouse (
Grb14–/–) exhibited improved glucose tolerance, albeit lower circulating insulin levels [
11]; (ii) Grb14 mRNA levels were found to be increased in adipose tissue of
ob/ob, T2DM model mice [
12]; (iii) genome-wide association studies for South Asian region demonstrated a relevance of Grb14 to metabolic disorders especially insulin resistance [
13]. Grb14 has also been shown to regulate the function of the leptin receptor, which plays a critical role in regulating body weight and energy metabolism [
14].
In terms of structural feature, Grb7 family proteins are characterized by having four structural module [
8,
15,
16]: RA (Ras-associating) domain, PH (pleckstrin homology) domain, SH2 (Src homology 2) domain, and BPS (between the PH and SH2 domain) region. Among them, BPS region is a unique structural feature for Grb7 family proteins, and the Grb14(BPS) being primarily responsible for binding to activated IRβ [
8,
15]. In fact, the crystal structure of the complex of IRβ and part of the Grb14(BPS) (residues 373-409) was determined at 3.2 Å resolution by Depetris
et al. (PDBid: 2AUH) [
17]. One of the most important hallmark of the complex structure is the positioning of N-terminal portion of the Grb14(BPS) (
376LVAMDF) in the substrate binding groove of IRβ as pseudosubstrate. This observation indicates that the Grb14(BPS) is not only responsible for binding to the IR, but also functions as a competitive inhibitor for the tyrosine kinase activity of IRβ, i.e., the structural data was anticipated to provide valuable information for
in silico SBDS.
Considering the accumulating evidence for the pathogenicity of Grb14, together with the important role of the Grb14(BPS) in binding to IRβ, compounds that inhibit the complex formation between the Grb14(BPS) and IRβ are expected to have the potential to improve insulin sensitivity and duration of effect. Recently, Gondoin
et al. identified compound capable of inhibiting the protein–protein interaction (PPI) between Grb14 and IR [
18]. They experimentally validated 1,000 candidate compounds selected by virtual screening targeted to the whole structure of IRβ–Grb14(BPS) complex, and found one active compound called C8 by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer and co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) experiments. In the present study, small compound targeting the groove in IRβ for Grb14(BPS) binding were explored by highly efficient hierarchical
in silico SBDS strategy, composed of grid docking-based and genetic algorithm-based programs. Only ten top-ranked candidates were subjected to the experimental validation phase and action mechanism of one compound which showed promising activity was estimated by molecular dynamics (MD) simulation.
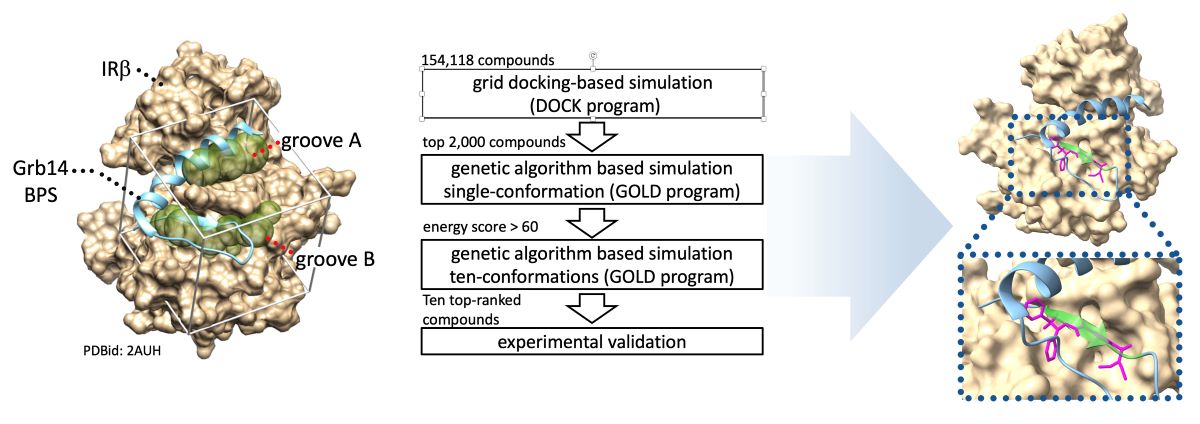
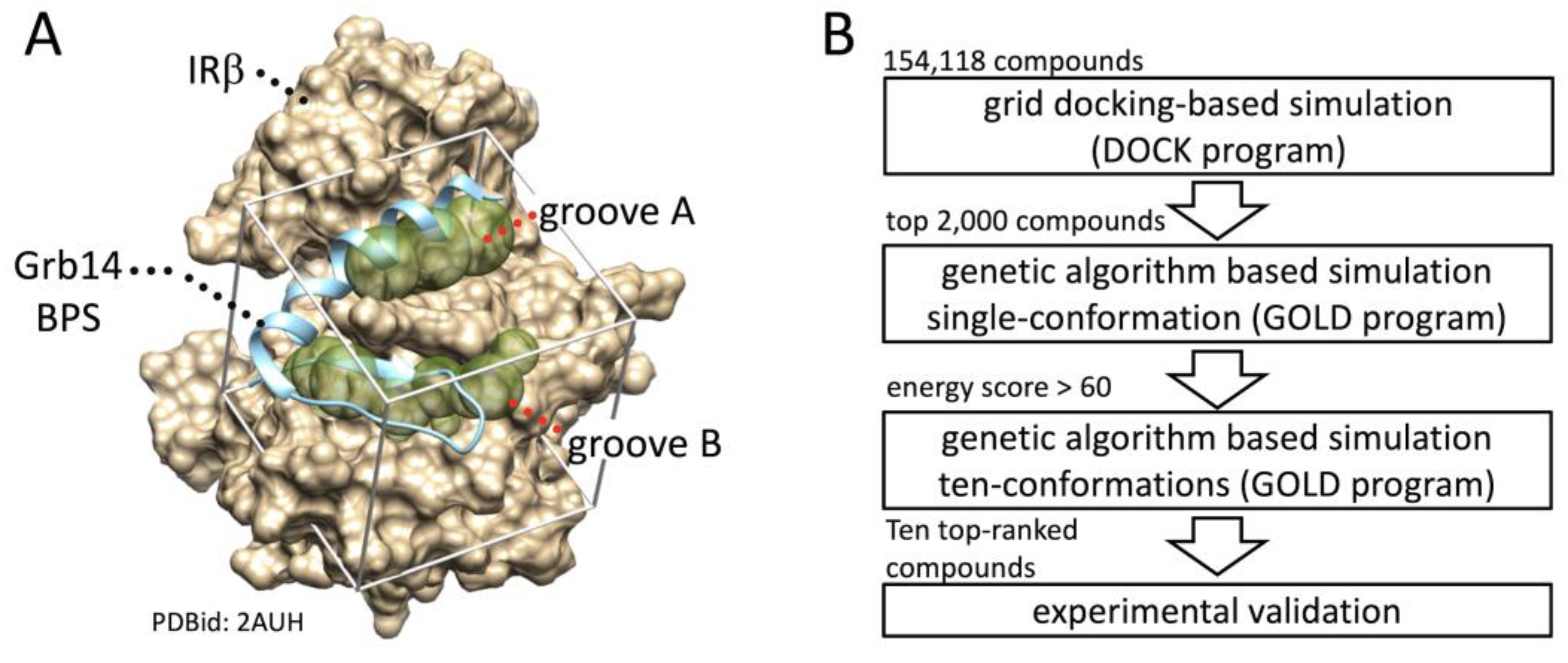
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of in silico SBDS. A, Binding pocket structures for in silico SBDS were prepared based on crystal structure of IRβ in complex with part of Grb14(BPS) (PDBid: 2AUH). The beige cloud represents van der Waals molecular surface of IRβ. The cyan ribbon diagram represents Grb14(BPS) (residues 373–409). The diaphanous spheres clusters, referred to as the binding groove A and B, were defined as the binding pockets for identification of novel inhibitor targeting PPI between IRβ and Grb14. B. Scheme of present in silico SBDS. Ten compounds were screened from the compound library through DOCK-GOLD programs combined screening.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of in silico SBDS. A, Binding pocket structures for in silico SBDS were prepared based on crystal structure of IRβ in complex with part of Grb14(BPS) (PDBid: 2AUH). The beige cloud represents van der Waals molecular surface of IRβ. The cyan ribbon diagram represents Grb14(BPS) (residues 373–409). The diaphanous spheres clusters, referred to as the binding groove A and B, were defined as the binding pockets for identification of novel inhibitor targeting PPI between IRβ and Grb14. B. Scheme of present in silico SBDS. Ten compounds were screened from the compound library through DOCK-GOLD programs combined screening.
2. Results
2.1. In silico identification of small compounds inhibiting Grb14-IRβ complex formation
In silico SBDS was performed to search for compounds that inhibit the PPI between IRβ and Grb14(BPS). In general, the removal of the inhibitor structure from the protein–inhibitor complex provides a favorable binding pocket when identify competitive inhibitors through
in silico SBDS [
19]. Herein, two binding pockets shown as groove A and B were identified after removal of the Grb14(BPS) structure from 2AUH (
Figure 1A). As shown in
Figure 1B, the hierarchical docking simulations were performed by high-throughput sorting based on grid docking (UCFS DOCK program), followed by genetic algorithm-based sorting (GOLD program) for single and multiple conformations. Ten compounds with an average GOLD score of 68.0 or higher were eventually selected and purchased (
Table S1). Hereafter, the selected compounds were referred to as compounds
1-
10.
2.2. Experimentally validation of the effect of selected compounds on IRS-1 activity
Grb14 has been reported to protect the phosphorylation status of the tyrosine residues in activation loop of IRβ from dephosphorylation by protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B [
9,
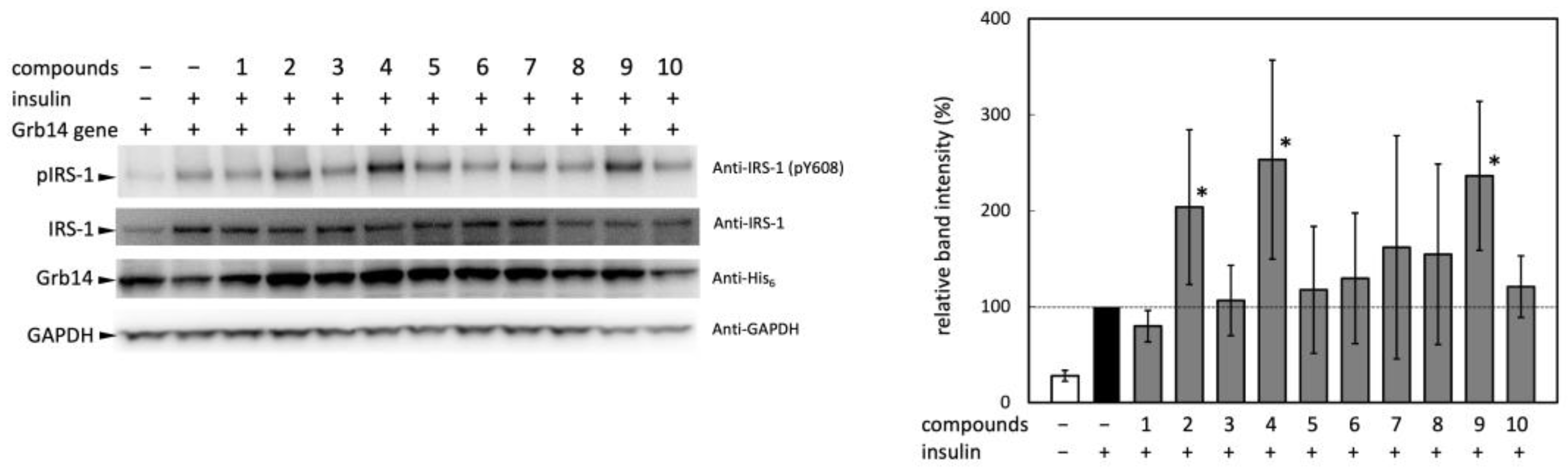
10]. In this context, there is a concern that the phosphorylation state of the activation loop of IRβ may not align with the intensity of insulin signaling. Hence, effect of the compounds on intracellular insulin signaling was assessed not by tyrosine phosphorylation in the activation loop but by that of IRS-1 which is located downstream of the receptor. The effect of the ten candidate compounds on IRS-1 activation in HEK293T cells was evaluated by phosphorylation at Tyr608 in IRS-1 (
Figure 2). As shown in a comparison of the band intensities represented in the right panel, insulin-induced phosphorylation was significantly enhanced by the pretreatment with compounds
2,
4, and
9. Due to considerable variability in band intensity, and an inability to identify significant differences except for the three compounds, these were selected for use in the subsequent animal experiment.
2.3. Effect of compounds 2, 4, and 9 on blood glucose levels
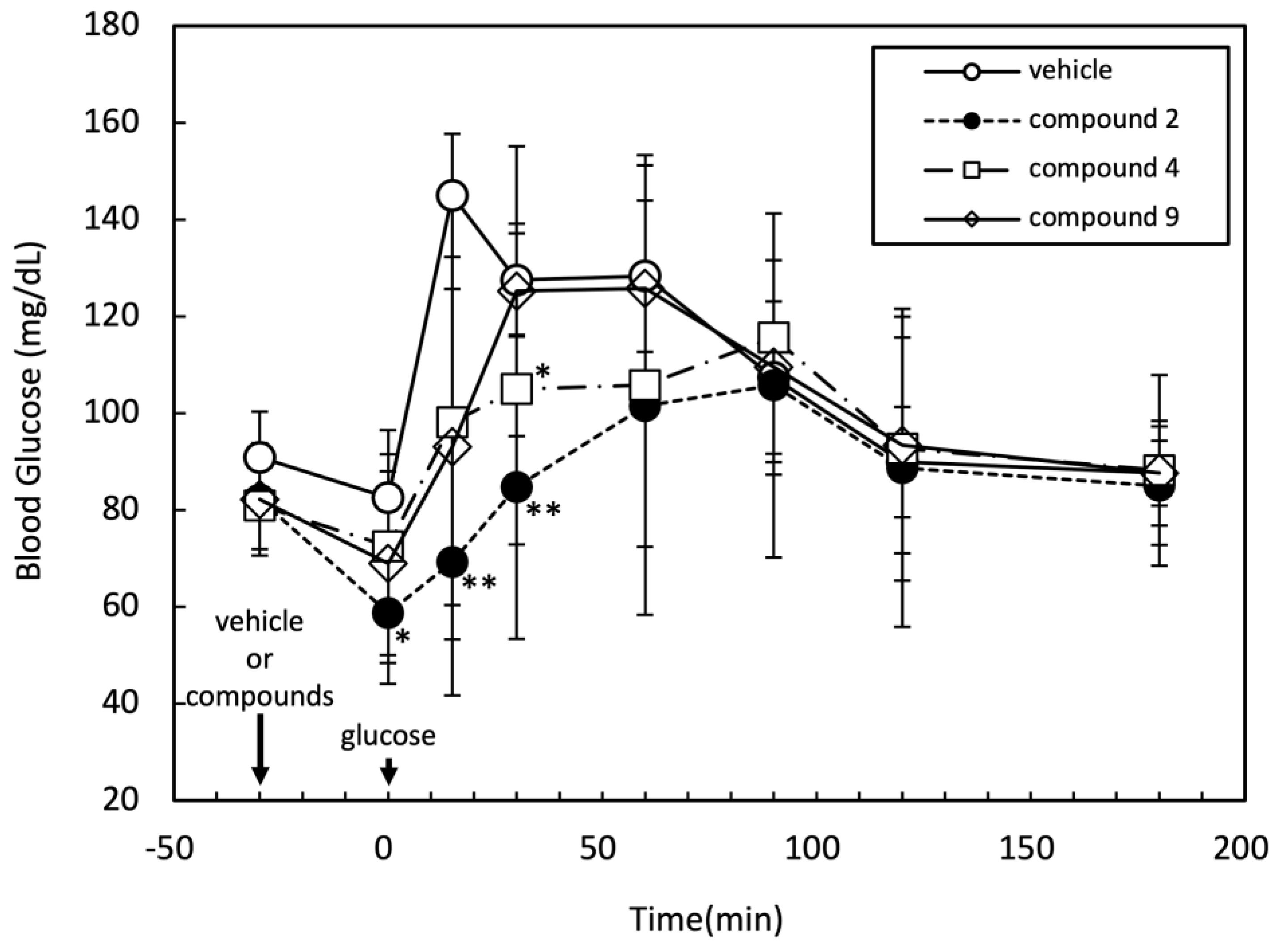
The effects of compounds
2,
4, and
9 on blood glucose levels in rat were assessed by oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). After intraperitoneal injection of the medication, glucose was administered orally 30 minutes thereafter. During the experiment, the time course of blood glucose level was monitored as shown in
Figure 3. Among the tested three compounds, compound
2 significantly suppressed the increase in blood glucose level at 0, 15, and 30 minutes after oral glucose administration. The compound
4 also showed moderate but significant reduction of blood glucose level at 30 minutes after oral glucose administration.
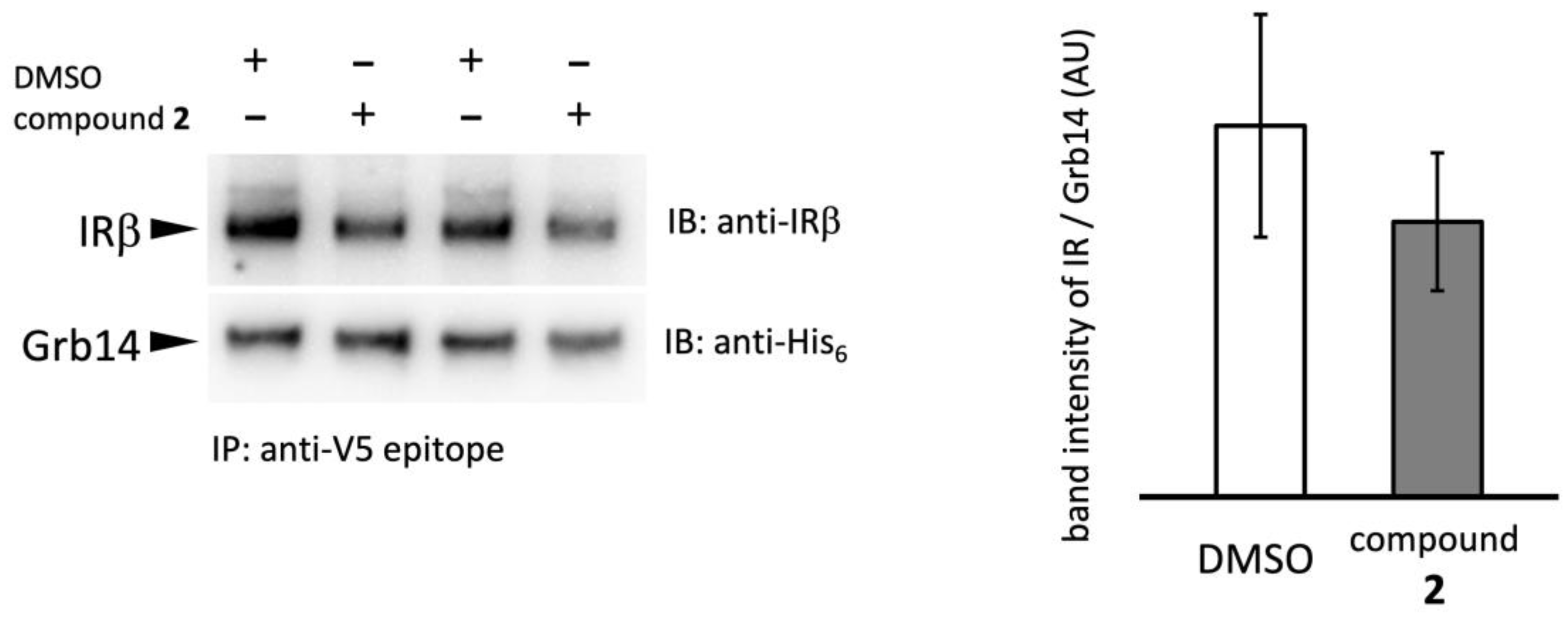
2.4. Effect of compound 2 on Grb14–IRβ complex formation
We next examined the effect of compound
2 on PPI between IRβ and Grb14 by Co-IP experiment (
Figure 4). Grb14 was immobilized on agarose beads via V5 epitope tag, then WGA purified IR was added with compound
2 or 2% DMSO [
18]. The IRβ–Grb14 complex formation was evaluated by band intensity ratio of coprecipitated IRβ and beads bound Grb14. The compound
2 slightly reduced the band intensity representing the formation of the IRβ–Grb14 complex at a concentration of 200 µg/ml; no significant difference was observed compared to the control, and complete inhibition of complex formation did not occur.
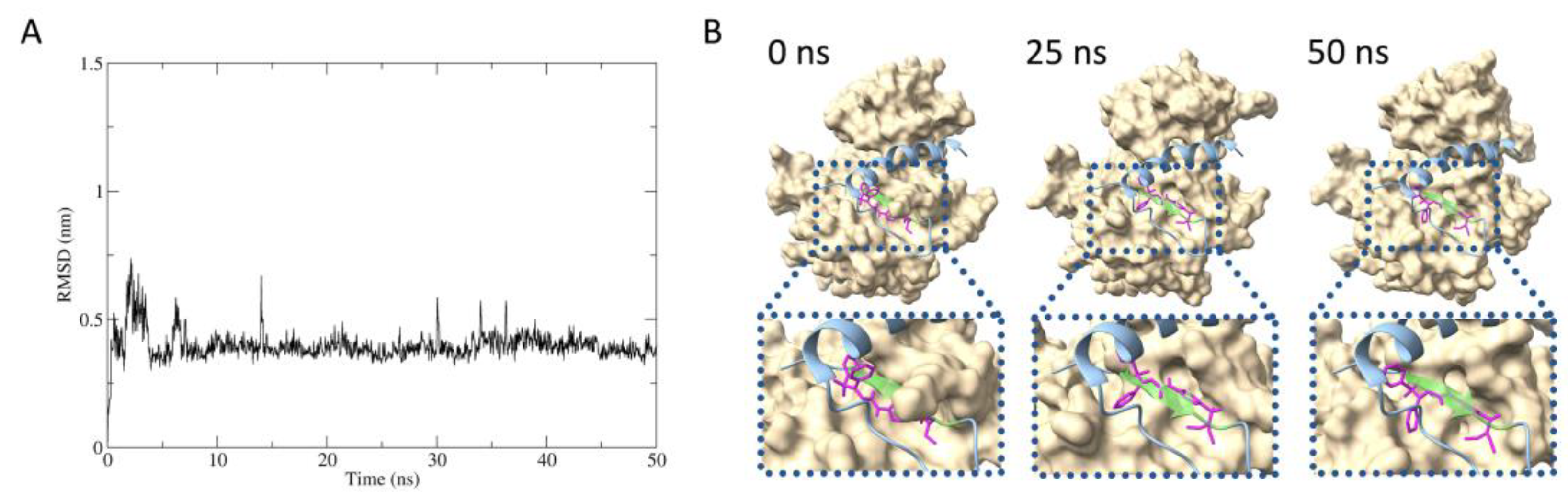
2.5. Predicted protein–inhibitor interaction by MD simulation
The stability of interaction between IRβ and compound
2 was estimated by molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. The root mean square deviation (RMSD) between compound
2 to IRβ maintained around 0.4 nm during the 50 nanosecond timescale, stable binding of compound
2 with IRβ was suggested (
Figure 5A). According to the molecular mechanics Poisson-Boltzmann surface area (MM-PBSA) analysis, the binding free energy was calculated to be -26.46 kcal/mol (data not show).
Figure 5B shows the estimated structures of IRβ in complex with compound
2 at 0, 25, and 50 nanoseconds in the MD simulation, overlaid with the Grb14(BPS). The compound
2 was suggested to bind to the same part of the tyrosine kinase pseudosubstrate region inside the BPS region (residues
376LVAMDF
381, represented in light green).
3. Discussion
Compounds that intervene at PPIs occurred in downstream of the insulin receptor have a mechanism of action distinct from existing drugs that modulate circulating insulin levels [
20]. Development of compounds that intervene at PPIs occurred in downstream of the insulin receptor would be beneficial in understanding of insulin resistance. In this context,
in silico SBDS has been anticipated as efficient technique. Since the Grb14-mediated insulin signal suppression is based on the PPI between Grb14(BPS) and IRβ, the structural data 2AUH was employed for virtual compound screening. In general, to screen for a competitive inhibitor through virtual screening, the utilization of apo-form structure is sometimes inappropriate. The structural data of IRβ in 2AUH was expected to provide preferable binding pocket or groove structures after removing of the Grb14(BPS) structure. The combination of high-throughput screening by grid docking (DOCK program) and precise evaluation of binding characteristics by genetic algorism (GOLD program) enables efficient compound screening as well as reducing computational costs. Among the three of ten compounds, selected from 154,118 compounds, were found to promote IRS-1 activation, and subsequent
in vivo experiments suggested that one of them (compound
2) inhibited the increase in blood glucose levels caused by glucose loading. The combined computational and experimental approach performed in this study has shown the potential to identify compounds that target PPIs without having to test a large number of compounds.
With respect to the structural data of 2AUH, Depetris
et al. observed that Leu376 in the pseudosubstrate within Grb14(BPS) occupies the kinase active site in IRβ, displacing a substrate tyrosine. Additionally, Val377, Met379, and Phe382 in the pseudosubstrate portion are involved in the interaction with Leu1171, Gly1169, and Gly1167 in IRβ, respectively [
17]. The MD simulations predict that compound
2 binds to IRβ competitively with the pseudosubstrate portion during 50 ns, and ligand interaction (LI) predictions indicate that compound
2 forms hydrogen bonds with Gly1166 and Leu1171, and cation–pi interaction with Gly1167 in IRβ (
Figure S1). In addition to these specific bindings, hydrophobic interactions toward the groove B were also predicted. Whereas, the present Co-IP analysis showed co-precipitation of IR was not effectively suppressed even at a high concentration of compound
2, suggesting compound
2 could not abolish the formation of the IRβ–Grb14 complex. In the design of molecularly targeted drugs, compound structures are designed for specific binding sites on the protein structure, such as substrate binding pockets. However, when targeting PPI, it appears necessary to target a broader area, such as the interaction surfaces [
21]. In addition, although the BPS region is known as the primary region responsible for binding to IRβ, the SH2 domain adjacent to the C-terminal side of the BPS region is also known to assist in the binding [
8,
15,
17]. From these perspectives, it would be difficult to eliminate the interaction between Grb14 and IRβ, which occurs on the surfaces of proteins and at multiple interaction sites with small molecules. Nonetheless, the possibility that compound
2 may exert its effects on a target distinct from the IRβ–Grb14 complex formation cannot be excluded; more detailed studies are needed to elucidate the mechanism of action of compound
2.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
Candidate compounds identified through SBDS were purchased from ChemBridge (San Diego, CA, USA). Gene constructs for expression of Grb14 (hGrb14/pcDNA3.1D/V5-His-TOPO) and IR (pFN21AE3464) in mammalian cells are reported previously [
22]. Rabbit anti-IRS-1 and anti-phospho-IRS-1 (Tyr608) mouse/(Tyr612) human antibodies were purchased from Merck (Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA). Horse radish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated Anti-His-tag monoclonal antibody was purchased from MLB (Nagoya, Japan). HRP-conjugated anti-IRβ mouse monoclonal antibody and goat HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA, USA). Other chemicals of reagent grade were obtained from Sigma, FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Industries (Osaka, Japan), and Nacalai Tesque (Kyoto, Japan).
4.2. In silico structure-based drug screening
Preparation of the virtual chemical library composed of 154,118 compounds was reported previously [
19]. Structural data of the IRβ in complex with the Grb14 BPS region (PDB-id: 2AUH) was used after removal of the BPS region structure. Protonation states and partial charges were adjusted at pH 7.0 using the Protonate 3D module the molecular operating environment (MOE) (Chemical Computing Group, Montreal, Canada). The screening system, constructed using UCSF DOCK (version 6.3) and CCDC GOLD suite (version 5.3), was employed to search for inhibitors targeting the IRβ–Grb14 complex formation. Throughout this study, these programs are referred to as the DOCK and GOLD programs, respectively. Initially, high-throughput screening was conducted using the DOCK program, based on grid docking, to estimate potential binding affinities. The top 2,000 compounds were selected based on this screening. Subsequently, compounds with a GOLD score greater than 60 for a single compound conformation were identified using the GOLD program. To generate diverse conformations for each compound, the Conformation Search module in MOE was utilized, resulting in ten distinct stable conformations for each compound. These conformations then underwent a rescreening process using the GOLD program. The obtained average GOLD scores for the selected compounds were then compared. Finally, the top ten compounds were purchased from ChemBridge and subjected to experimental validation. The precise molecular binding interactions between the compounds and the amino acids forming the IRβ substrate-binding cavity were inferred using the LI and PLIF modules within the MOE software.
4.3. Phosphorylation of IRS-1
HEK293T cells (105 cells/well) were seeded into 24-well plates 12 hours before cDNA transfection and were cultured in high-glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 µg/mL streptomycin, and 4 mM l-glutamine at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. The expression vectors for human IR (0.2 µg) and Grb14 vectors (0.8 µg) were co-transfected using X-tremeGENE 9 (Roche Diagnostics, Basel, Switzerland) transfection reagent. The cell culture was continued for 48 hours, then medium was replaced with serum-deprived DMEM. Incubation was continued for 3 hours after the addition of the test compounds (30 µg/mL), followed by treatment with 1 µM insulin for 10 minutes. The cultures were rinsed twice with DPBS and lysed with lysis buffer: 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 5 mM EDTA, 50 mM NaF, 1 mM orthovanadate, 30 mM sodium pyrophosphate, and cOmplete Ultra, Mini, EDTA-free (Roche Diagnostics). The cells were sonicated and centrifuged at 13,000 × g at 4°C for 20 minutes and the supernatants were subjected to immunoblot analysis. HRP was visualized by Chemi-Lumi One L (Nacalai tesque) and analyzed with LuminoGraph I (ATTO Corporation, Tokyo, Japan).
4.4. Oral glucose tolerance test
An OGTT was performed in 6-week-old male Fischer (F344/Jcl) rats purchased from CLEA Japan, Inc. (Tokyo, Japan). The rats were fasted for overnight followed by intraperitoneal injection of vehicle or Grb14 inhibitors dissolved in 50% DMSO. Thirty minutes after injection, rats were given glucose orally (2 g/kg BW). Blood glucose levels were measured from tail vein at 0, 15, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, and 210 minutes after the injection of vehicle or Grb14 inhibitors. The experiments were approved by the Animal Research Committee of Kurume University School of Medicine (Approval number: 2019-226).
4.5. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
The Co-IP experiment was conducted according to previously reported method with minor modifications [
22,
23]. In brief, Grb14 with V5 epitope and his-tags on C-terminal, and human IR and were separately overexpressed in COS-7 cell cultures. The cell cultures were maintained overnight in serum-free medium then stimulated with 1 µM insulin for 10 minutes. After rinsing with PBS, the cells were treated with the same lysis buffer used in the experiments evaluating IRS-1 phosphorylation. The supernatants containing IR or Grb14 were collected through brief sonication and centrifugation (13,000
× g at 4 °C for 20 minutes). The supernatant containing Grb14 was incubated with agarose-conjugated Anti-V5-Tag beads (FUJIFILM Wako) for 12 hours at 4°C. After washing the beads with the lysis buffer, IR, purified with the Glycoprotein Isolation Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was added together with 2% DMSO or compound
2 (200 µg/mL)
, then incubated at 4°C overnight. After washing the beads with the lysis buffer, proteins bound to the beads were analyzed by Western blotting as described above.
4.6. Molecular dynamics simulation
MD simulations were performed using the GROMACS package, with slight modifications to previously reported methods [
24]. The simulation system was prepared with the CHARMM-GUI web server, where TIP3P was used as a water molecule. The cutoff value of 1.2 nm was used as an interatomic distance for the van der Waals force and electrostatic interaction. The particle mesh Ewald method was used to calculate long-range electrostatic interactions. The LINCS constraint algorithm was used for the energy minimization, equilibration, and production MD calculations. Energy minimization calculations were conducted in up to 5,000 steps using the steepest descent algorithm. The equilibration calculations were conducted in one step under the NVT conditions (310.00 K), followed by two steps under NPT conditions (310.00 K, 1 bar). Finally, 50 ns production MD calculations were performed with a time step of 2 fs. MD trajectories were analyzed using g_rms in the GROMACS package.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
www.mdpi.com/xxx/s1, Table S1: Ten candidate compounds identified by
in silico SBDS; Figure S1: Ligand Interaction (LI) between IRβ and compound
2 complex formation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.M., S.A. and J.T.; methodology, T.M. and J.T.; software, S.A.; validation, T.M., Y.O., K.M. and J.T.; formal analysis, T.M., Y.O., K.M. and J.T.; investigation, T.M., K.I., Y.O., K.M. and J.T.; resources, T.M. and J.T.; data curation, T.M., K.I., Y.O. and J.T.; writing—original draft preparation, J.T.; writing—review and editing, T.M., K.I., Y.O., K.M., H.S., S.A. and J.T.; visualization, K.I., Y.O., K.M. and J.T.; supervision, J.T.; project administration, J.T.; funding acquisition, J.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Please add: This research was funded by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, grant number 23H04427 and 23K04964.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon the request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mr. Ko Suzuki for assistance of MD simulation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Norris, J.M.; Rich, S.S. Genetics of glucose homeostasis: implications for insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2012, 32, 2091–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.E.; Walker, M. Genetics of Insulin Resistance and the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr Cardiol Rep 2016, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusler, R.A.; McGraw, T.E.; Accili, D. Biochemical and cellular properties of insulin receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2018, 19, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artasensi, A.; Pedretti, A.; Vistoli, G.; Fumagalli, L. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Multi-Target Drugs. Molecules 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, S.; Nawroth, P.P.; Herzig, S.; Ekim Ustunel, B. Emerging Targets in Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Complications. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2021, 8, e2100275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bryant, S.H. Structure-based virtual screening for drug discovery: a problem-centric review. AAPS J 2012, 14, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, R.J.; Sanderson, G.M.; Janes, P.W.; Sutherland, R.L. Cloning and characterization of GRB14, a novel member of the GRB7 gene family. J Biol Chem 1996, 271, 12502–12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasus-Jacobi, A.; Perdereau, D.; Auzan, C.; Clauser, E.; Van Obberghen, E.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Girard, J.; Burnol, A.F. Identification of the rat adapter Grb14 as an inhibitor of insulin actions. J Biol Chem 1998, 273, 26026–26035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouaille, S.; Blanquart, C.; Zilberfarb, V.; Boute, N.; Perdereau, D.; Burnol, A.F.; Issad, T. Interaction between the insulin receptor and Grb14: a dynamic study in living cells using BRET. Biochem Pharmacol 2006, 72, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouaille, S.; Blanquart, C.; Zilberfarb, V.; Boute, N.; Perdereau, D.; Roix, J.; Burnol, A.F.; Issad, T. Interaction with Grb14 results in site-specific regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor. EMBO Rep 2006, 7, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, G.J.; Lyons, R.J.; Crew, A.J.; Jensen, T.E.; Molero, J.C.; Mitchell, C.J.; Biden, T.J.; Ormandy, C.J.; James, D.E.; Daly, R.J. Improved glucose homeostasis and enhanced insulin signalling in Grb14-deficient mice. Embo J 2004, 23, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cariou, B.; Capitaine, N.; Le Marcis, V.; Vega, N.; Bereziat, V.; Kergoat, M.; Laville, M.; Girard, J.; Vidal, H.; Burnol, A.F. Increased adipose tissue expression of Grb14 in several models of insulin resistance. Faseb J 2004, 18, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooner, J.S.; Saleheen, D.; Sim, X.; Sehmi, J.; Zhang, W.; Frossard, P.; Been, L.F.; Chia, K.S.; Dimas, A.S.; Hassanali, N.; et al. Genome-wide association study in individuals of South Asian ancestry identifies six new type 2 diabetes susceptibility loci. Nat Genet 2011, 43, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmioglu, N.; Macgregor, S.; Drong, A.W.; Hedman, Å.; Harris, H.R.; Randall, J.C.; Prokopenko, I.; Nyholt, D.R.; Morris, A.P.; Montgomery, G.W.; et al. Genome-wide enrichment analysis between endometriosis and obesity-related traits reveals novel susceptibility loci. Hum Mol Genet 2015, 24, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desbuquois, B.; Carre, N.; Burnol, A.F. Regulation of insulin and type 1 insulin-like growth factor signaling and action by the Grb10/14 and SH2B1/B2 adaptor proteins. Febs J 280, 794–816. [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Rose, D.W.; Olefsky, J.M.; Gustafson, T.A. Grb10 interacts differentially with the insulin receptor, insulin-like growth factor I receptor, and epidermal growth factor receptor via the Grb10 Src homology 2 (SH2) domain and a second novel domain located between the pleckstrin homology and SH2 domains. J Biol Chem 1998, 273, 6860–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depetris, R.S.; Hu, J.; Gimpelevich, I.; Holt, L.J.; Daly, R.J.; Hubbard, S.R. Structural basis for inhibition of the insulin receptor by the adaptor protein Grb14. Mol Cell 2005, 20, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondoin, A.; Hampe, C.; Eudes, R.; Fayolle, C.; Pierre-Eugene, C.; Miteva, M.; Villoutreix, B.O.; Charnay-Pouget, F.; Aitken, D.J.; Issad, T.; et al. Identification of insulin-sensitizing molecules acting by disrupting the interaction between the Insulin Receptor and Grb14. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 16901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, J.; Morita, K.; Kawashima, S.; Umei, T.; Baba, H.; Maruoka, T.; Komatsu, H.; Sakamoto, H.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Aoki, S. Identification of a novel class of small compounds with anti-tuberculosis activity by in silico structure-based drug screening. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2017, 70, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Bi, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, L. The Insulin Receptor: An Important Target for the Development of Novel Medicines and Pesticides. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkin, M.R.; Glicksman, M.A.; Fu, H.; Havel, J.J.; Du, Y. Inhibition of Protein-Protein Interactions: Non-Cellular Assay Formats. In Assay Guidance Manual; Markossian, S., Grossman, A., Brimacombe, K., Arkin, M., Auld, D., Austin, C., Baell, J., Chung, T.D.Y., Coussens, N.P., Dahlin, J.L., et al., Eds.; Bethesda (MD), 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Taira, J.; Higashimoto, Y. Phosphorylation of Grb14 BPS domain by GSK-3 correlates with complex forming of Grb14 and insulin receptor. J Biochem 2014, 155, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, J.; Kida, Y.; Inatomi, K.; Komatsu, H.; Higashimoto, Y.; Sakamoto, H. Phosphorylation of clustered serine residues in the N-terminus of BPS domain negatively regulates formation of the complex between human Grb14 and insulin receptor. J Biochem 2017, 162, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, J.; Murakami, K.; Monobe, K.; Kuriki, K.; Fujita, M.; Ochi, Y.; Sakamoto, H.; Aoki, S. Identification of novel inhibitors for mycobacterial polyketide synthase 13 via in silico drug screening assisted by the parallel compound screening with genetic algorithm-based programs. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 2022, 75, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).