Submitted:
06 December 2023
Posted:
07 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Primary Brain Tumors
2.1. Benign Tumors
2.2. Malignant Tumors
3. Gangliosides in Brain Metastases
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schnaar, R.L. Gangliosides of the vertebrate nervous system. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 3325–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasques, J.F.; de Jesus Gonçalves, R.G.; da Silva-Junior, A.J.; Martins, R.S.; Gubert, F.; Mendez-Otero, R. Gangliosides in nervous system development, regeneration, and pathologies. Neural Regen Res. 2023, 18, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunghi, G.; Fazzari, M.; Di Biase, E.; Mauri, L.; Chiricozzi, E.; Sonnino, S. The structure of gangliosides hides a code for determining neuronal functions. FEBS Open Bio. 2021, 12, 3193–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilcaes, A.A.; Garbarino-Pico, E.; Torres Demichelis, V.; Daniotti, J.L. Ganglioside synthesis by plasma membrane-associated sialyltransferase in macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komura, N.; Suzuki, K.G.; Ando, H.; Konishi, M.; Koikeda, M.; Imamura, A.; Chadda, R.; Fujiwara, T.K.; Tsuboi, H.; Sheng, R.; Cho, W.; Furukawa, K.; Furukawa, K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Ishida, H.; Kusumi, A.; Kiso, M. Raft-based interactions of gangliosides with a GPI-anchored receptor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolter, T. Ganglioside biochemistry. ISRN Biochem. 2012, 2012, 506160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiricozzi, E.; Lunghi, G.; Di Biase, E.; Fazzari, M.; Sonnino, S.; Mauri, L. GM1 ganglioside is a key factor in maintaining the mammalian neuronal functions avoiding neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Haar Àvila, I.; Windhouwer, B.; van Vliet, S.J. Current state-of-the-art on ganglioside-mediated immune modulation in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023, 42, 941–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakomori Si, S.I. The glycosynapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002, 99, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, N.; Toyoda, M.; Ishiwata, T. Gangliosides as signaling regulators in cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzaki, K. Aβ-ganglioside interactions in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuverink, M.; Barbieri, J.T. Protein toxins that utilize gangliosides as host receptors. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 156, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavdarli, S.; Groux-Degroote, S.; Delannoy, P. Gangliosides: the double-edge sword of neuro-ectodermal derived tumors. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitan, F.; Robu, A.C.; Popescu, L.; Flangea, C.; Vukelić, Ž.; Zamfir, A.D. B subunit monomers of cholera toxin bind G1 ganglioside class as revealed by chip-nanoelectrospray multistage mass spectrometry. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2015, 34, 388–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfir, A.D. Neurological analyses: focus on gangliosides and mass spectrometry. Adv Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 806, 153–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sipione, S.; Monyror, J.; Galleguillos, D.; Steinberg, N.; Kadam, V. Gangliosides in the brain: physiology, pathophysiology and therapeutic applications. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 572965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledeen, R.; Chowdhury, S. Gangliosides in neurodegenerative diseases. Adv. Neurobiol. 2023, 29, 391–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z. Ganglioside GM1 and the central nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ica, R.; Mlinac-Jerkovic, K.; Ilic, K.; Sajko, T.; Munteanu, C.V.A.; Zamfir, A.D.; Kalanj-Bognar, S. Gangliosidome of a human hippocampus in temporal lobe epilepsy resolved by high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry. Molecules 2022, 27, 4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.G.N.; Ando, H.; Komura, N.; Konishi, M.; Imamura, A.; Ishida, H.; Kiso, M.; Fujiwara, T.K.; Kusumi, A. Revealing the raft domain organization in the plasma membrane by single-molecule imaging of fluorescent ganglioside analogs. Methods Enzymol. 2018, 598, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.X.; Ingólfsson, H.I.; de Vries, A.H.; Marrink, S.J.; Tieleman, D.P. Ganglioside-lipid and ganglioside-protein interactions revealed by coarse-grained and atomistic molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2017, 121, 3262–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, T.; Hua, Y.J.; Dahlgren, M.W.; Livingston, M.; Johansson-Lindbom, B.; Yrlid, U. Direct interaction between cholera toxin and dendritic cells is required for oral adjuvant activity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worstell, N.C.; Krishnan, P.; Weatherston, J.D.; Wu, H.-J. Binding cooperativity matters: a GM1- like ganglioside-cholera toxin B subunit binding study using a nanocube-based lipid bilayer array. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hgge, H.; Peter-Katalinić, J.; Reuter, G.; Schauer, R.; Ghidoni, R.; Sonnino, S.; Tettamanti, G. Analysis of gangliosides using fast atom bombardment mass spectrometry. Chem. Phys. Lipids 1985, 37, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metelmann, W.; Vukelić, Z.; Peter-Katalinić, J. Nanoelectrospray ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of gangliosides from human brain tissue. J. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 36, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, A.; Suzuki, M.; Ito, E.; Nitta, T.; Inokuchi, J.I. Mass spectrometry of gangliosides. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1804, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Han, J.; Xiong, S.; Yong, W.; Zhao, Z. Combination of ESI and MALDI mass spectrometry for qualitative, semi-quantitative and in situ analysis of gangliosides in brain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamfir, A.; Vukelić, Ž.; Bindila, L.; Peter-Katalinić, J.; Almeida, R.; Sterling, A.; Allen, M. Fully-automated chip-based nanoelectrospray tandem mass spectrometry of gangliosides from human cerebellum. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 15, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamfir, A.D.; Lion, N.; Vukelić, Ž.; Bindila, L.; Rossier, J.; Girault, H.H.; Peter-Katalinić, J. Thin chip microsprayer system coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer for glycoconjugate analysis. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flangea, C.; Serb. A.; Sisu, E.; Zamfir, A.D. Chip-based nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry of brain gangliosides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011, 1811, 513–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, M.; Ica, R.; Zamfir, A.D. Developments and applications of separation and microfluidics methods coupled to electrospray mass spectrometry in glycomics of nervous system gangliosides. Electrophoresis 2021, 42, 429–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukelić, Ž.; Zamfir, A.D.; Bindila, L.; Froesch, M.; Peter-Katalinić, J.; Usuki, S.; Yu, R.K. Screening and sequencing of complex sialylated and sulfated glycosphingolipid mixtures by negative ion electrospray Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, M.A.; Marshall, A.G.; Hendrickson, C.L.; Nilsson, C.L.; Fredman, P.; Månsson, J.E. Structural characterization of the GM1 ganglioside by infrared multiphoton dissociation, electron capture dissociation, and electron detachment dissociation electrospray ionization FT-ICR MS/MS. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ica, R.; Munteanu, C.V.; Vukelić, Ž.; Zamfir, A.D. High-resolution mass spectrometry reveals a complex ganglioside pattern and novel polysialylated structures associated with the human motor cortex. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. (Chichester). 2021, 27, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbu, M.; Ica, R.; Petrut, A.; Vukelić, Ž.; Munteanu, C.V.A.; Petrescu, A.J.; Zamfir, A.D. Gangliosidome of human anencephaly: a high resolution multistage mass spectrometry study. Biochimie 2019, 163, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbu, M.; Robu, A.C.; Ghiulai, R.M.; Vukelić, Ž.; Clemmer, D.E.; Zamfir, A.D. Electrospray ionization ion mobility mass spectrometry of human brain gangliosides. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5166–5178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, M.; Vukelić, Ž.; Clemmer, D.E.; Zamfir, A.D. Ion mobility mass spectrometry provides novel insights into the expression and structure of gangliosides in the normal adult human hippocampus. Analyst 2018, 143, 5234–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Bailey, L.S.; Gao, T.; Jiang, W.; Yu, L.; Bennett, D.A.; Zhao, J.; Basso, K.B.; Guo, Z. Analysis and Comparison of mouse and human brain gangliosides via two-stage matching of MS/MS spectra. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 6403–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minyan, L.; Bingjia, H.; Zhen, X.; Limin, W.; Yan, C.; Xiangjiao, L.; Shuang, S.; Ning, S. Prenatal ultrasound evaluation of fetal cutaneous hemangioma and related complications. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2023, 36, 2157257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, K.; Kunimoto, Y.; Inaba, N.; Mikita, C.; Kaminaka, N.; Kanazawa, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; . Kakimoto, T.; Suenaga, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Suzuki, N.; Baba, M.J. Distribution analysis of infantile hemangioma or capillary malformation on the head and face in Japanese patients. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mespreuve, M.; Vanhoenacker, F.; Lemmerling, M. Familial Multiple Cavernous Malformation Syndrome: MR Features in This Uncommon but Silent Threat. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2016, 100, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickison, P.; Christou, E.; Wargon, O. A prospective study of infantile hemangiomas with a focus on incidence and risk factors. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2011, 28, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idiculla, P.S.; Gurala, D.; Philipose, J.; Rajdev, K.; Patibandla, P. Cerebral Cavernous Malformations, Developmental Venous Anomaly, and Its Coexistence. Eur. Neurol. 2020, 83, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.; Brown, Z.J.; Baghdadi, A.; Kamel, I.R.; Pawlik, T.M. A Comprehensive Review of Hepatic Hemangioma Management. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2022, 26, 1998–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, B.; Moosa, S.; Rajagopal, R. Cavernous hemangioma of the conjunctiva. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 67, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, I.A.; Polster, S.P. Cavernous angiomas: deconstructing a neurosurgical disease. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 131, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caton, M.T.; Shenoy, V.S. Cerebral Cavernous Malformations; StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcanti, D.D.; Kalani, M.Y.; Martirosyan, N.L.; Eales, J.; Spetzler, R.F.; Preul, M.C. Cerebral cavernous malformations: from genes to proteins to disease. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 116, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Zalvide, J.; Faurobert, E.; Albiges-Rizo, C.; Tournier-Lasserve, E. Cerebral cavernous malformations: from CCM genes to endothelial cell homeostasis. Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeen, R.; Wu, G. Gangliosides of the Nervous System. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1804, 19–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Pang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Du, G. Ganglioside GD3 synthase (GD3S), a novel cancer drug target. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2018, 8, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiopu, C.; Flangea, C.; Capitan, F.; Serb, A.; Vukelić, Ž.; Kalanj-Bognar, S.; Zamfir, A.D. Determination of ganglioside composition and structure in human brain hemangioma by chip-based nanoelectrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 2465–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, R.; Mosoarca, C.; Chirita, M.; Udrescu, V.; Dinca, N.; Vukelić, Z.; Allen, M.; Zamfir, A.D. Coupling of fully automated chip-based electrospray ionization to high-capacity ion trap mass spectrometer for ganglioside analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 378, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serb, A.; Schiopu, C.; Flangea, C.; Vukelić, Ž.; Sisu, E.; Dinca, N.; Zagrean, L.; Zamfir, A.D. High-throughput analysis of gangliosides in defined regions of fetal brain by fully automated chip-based nanoelectrospray ionization multi-stage mass spectrometry. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 15, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfir, A.D.; Vukelić, Ž.; Schneider, A.; Sisu, E.; Dinca, N.; Ingendoh, A. A novel approach for ganglioside structural analysis based on electrospray multiple-stage mass spectrometry. J. Biomol. Tech. 2007, 18, 188–193. [Google Scholar]
- Sarbu, M.; Dehelean, L.; Munteanu, C.V.; Vukelić, Ž.; Zamfir, A.D. Assessment of ganglioside age-related and topographic specificity in human brain by Orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 521, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ica, R.; Simulescu, A.; Sarbu, M.; Munteanu, C.V. A.; Vukelić, Ž.; Zamfir, A.D. High resolution mass spectrometry provides novel insights into the ganglioside pattern of brain cavernous hemangioma. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 609, 113976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galleguillos, D.; Wang, Q.; Steinberg, N.; Zaidi, A.; Shrivastava, G.; Dhami, K.; Daskhan, G.C.; Schmidt, E.N.; Dworsky-Fried, Z.; Giuliani, F.; Churchward, M.; Power, C.; Todd, K.; Taylor, A.; Macauley, M.S.; Sipione, S.J. Anti-inflammatory role of GM1 and other gangliosides on microglia. J. Neuroinflammation 2022, 19, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaesung, L.; Heehong, H.; Sung Joong, L. Distinct roles of GT1b and CSF-1 in microglia activation in nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain. 2021, 17448069211020918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netsky, M.G.; Lapresle, J. The first account of a meningioma. Bull Hist. Med. 1956, 30, 465–468. [Google Scholar]
- Salari, N.; Ghasemi, H.; Fatahian, R.; Mansouri, K.; Dokaneheifard, S.; Shiri, M.H.; Hemmati, M.; Mohammadi, M. The global prevalence of primary central nervous system tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Information. Available online: https://www.giiresearch.com/report/imarc1362800-meningioma-market-epidemiology-industry-trends.html (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Neff, K.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2016-2020. Neuro. Oncol. 2023, 25, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marosi, C.; Hassler, M.; Roessler, K.; Reni, M.; Sant, M.; Mazza, E.; Vecht, C. Meningioma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2008, 67, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, A.R.; Roelcke, U. Meningioma. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofela, A.A.; McGavinc, L.; Whitfield, P.C.; Hanemann, C.O. Biomarkers for differentiating grade II meningiomas from grade I: a systematic review. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 35, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritsch, S.; Batchelor, T.T.; Gonzalez Castro, L.N. Diagnostic, therapeutic, and prognostic implications of the 2021 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system. Cancer 2021, 128, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbritti, R.V.; Polito, F.; Cucinotta, M.; Lo Giudice, C.; Caffo, M.; Tomasello, C.; Germanò, A.; Aguennouz, M. Meningiomas and proteomics: focus on new potential biomarkers and molecular pathways. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 2016, 13, 369–380. [Google Scholar]
- Fahlström, A.; Dwivedi, S.; Drummond, K. Multiple meningiomas: Epidemiology, management, and outcomes. Neurooncol. Adv. 2023, 5, 3–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamszus, K. Meningioma pathology, genetics, and biology. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawloski, J.A.; Fadel, H.A.; Huang, Y.W.; Lee, I.Y. Genomic biomarkers of meningioma: A focused review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alruwaili, A.A.; De Jesus, O. Meningioma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publisher: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nazem, A.A.; Ruzevick, J.; Ferreira, M.J. Advances in meningioma genomics, proteomics, and epigenetics: insights into biomarker identification and targeted therapies. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 4544–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhoudarian, G.; Whitelegge, J.P.; Kelly, D.F.; Simonian, M. Proteomics analysis of brain meningiomas in pursuit of novel biomarkers of the aggressive behavior. J. Proteomics Bioinform. 2016, 9, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; Soffietti, R.; von Deimling, A.; Ellison, D.W. The 2021 WHO classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torp, S.H.; Solheim, O.; Skjulsvik, A.J. The WHO 2021 classification of central nervous system tumours: a practical update on what neurosurgeons need to know-a minireview. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Han, L.; Zhao, H. DNA methylation meningioma biomarkers: attributes and limitations. Front. Mol. Neurisci. 2023, 16, 1182759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennel, H.D.; Bosslet, K.; Geisseli, H.; Bauer, B.L. I mmunohistochemically visualized localisation of gangliosides G1ac2 (GD3) and Gtri2 (GD2) in cells of human intracranial tumors. Exp. Toxic Pathol. 2000, 52, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidsson, P.; Fredman, P.; Collins, V.P.; von Holst, H.; Miinsson, J.E.; Svennerholm, L. Ganglioside composition in human meningiomas. J. Neurochem. 1989, 53, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berra, B.; Papi, L.; Bigozzi, U.; Serino, D.; Morichi, R.; Mennonna, P.; Rapelli, S.; Cogliati, T.; Montali, E. Correlation Between cytogenetic data and ganglioside pattern in human meningiomas. Int. J. Cancer 1991, 47, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radić, B.; Vukelić, Ž.; Bognar, S.K. Serum gangliosides in patients with brain tumors. Coll. Antropol. 2008, 32, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Schiopu, C.; Vukelic, Z.; Capitan, F.; Kalanj-Bognar, S.; Sisu, E.; Zamfir, A.D. Chip-nanoelectrospray quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry of meningioma gangliosides: A preliminary study. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 1778–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domon, B.; Costello, C.E. A systematic nomenclature of carbohydrate fragmentation in FAB-MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconjugate J. 1988, 5, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, Q.; Adams, J. Structure determination of ceramide and neutral glycosphingolipids by collisional activation of [M+Li]+ ions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1992, 3, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirtz, A.; Rech, F.; Dubois-Pot-Schneider, H.; Dumond, H. Astrocytoma: a hormone-sensitive tumor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Wang, X. Immunological classification of gliomas based on immunogenomic profiling. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, A.; Wesseling, P. Histologic classification of gliomas. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 134, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Bauchet, L.; Davis, F.G.; Deltour, I.; Fisher, J.L.; Langer, C.E.; Pekmezci, M.; Schwartzbaum, J.A.; Turner, M.C.; Walsh, K.M.; Wrensch, M.R.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: a "state of the science" review. Neuro. Oncol. 2014, 16, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesfin, F.B.; Al-Dhahir, M.A. Gliomas. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publisher: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fyllingen, E.H.; Bø, L.E.; Reinertsen. I.; Jakola, A.S.; Sagberg, L.M.; Berntsen, E.M.; Salvesen, Ø.; Solheim, O. Survival of glioblastoma in relation to tumor location: a statistical tumor atlas of a population-based cohort. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2021, 163, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, D.; Turcan, S. Origin of gliomas. Semin Neurol. 2018, 38, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Smith-Cohn, M.; Cohen, A.L.; Colman, H. Glioma subclassifications and their clinical significance. Neurotherapeutics 2017, 14, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesseling, P.; Capper, D. WHO 2016 classification of gliomas. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 44, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, A. Brain tumor classification in magnetic resonance images using deep learning and wavelet transform. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Dinesan, M.; Ajayakumar, T. Survival and quality of life analysis in glioblastoma multiforme with adjuvant chemoradiotherapy: a retrospective study. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2022, 27, 1026–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, M.; Gupta, V. Astrocytoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publisher: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, D.G.; Kaye, A.H. Diagnosis and management of astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas and mixed gliomas: a review. Australas. Radiol. 2001, 45, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet. A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, L.J.; Davies, P.; Herbert, C.; Kurian, K.M. Pre-diagnostic blood biomarkers for adult glioma. Front Oncol. 2023, 13, 1163289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, E.; Butler, H.J.; Board, R.; Brennan, P.M.; Chalmers, A.J.; Dawson, T.; Goodden, J.; Hamilton, W.; Hegarty, M.G.; James, A.; Jenkinson, M.D.; Kernick, D.; Lekka, E.; Livermore, L.J.; Mills, S.J.; O’Neill, K.; Palmer, D.S.; Vaqas, B.; Baker, M.J. Health economic evaluation of a serum-based blood test for brain tumour diagnosis: exploration of two clinical scenarios. B.M.J. Open. 2018, 8, e017593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandner, S.; Jaunmuktane, Z. IDH mutant astrocytoma: biomarkers for prognostic stratification and the next frontiers. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2019, 45, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesileanu, C.M.S.; Vallentgoed, W.R.; French, P.J.; van den Bent, M.J. Molecular markers related to patient outcome in patients with IDH-mutant astrocytomas grade 2 to 4: A systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 175, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, A.; Avery, L.M.; Sohaei, D.; Soosaipillai, A.; Richer, M.; Horbinski, C.; McCortney, K.; Xu, W.; Diamandis, E.P.; Prassas, I. Discovery of novel glioma serum biomarkers by proximity extension assay. Clin. Proteomics 2023, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pienkowski, T.; Kowalczyk, T.; Kretowski, A.; Ciborowski, M. A review of gliomas-related proteins. Characteristics of potential biomarkers. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 3425–3444. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Rashid, K.; Ibrahim, K.; Wong, J.H.D.; Mohd Ramli, N. Lipid alterations in glioma: A systematic review. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Huang, Z.; Wei, B.; Li, M. Comprehensive metabolomics study on the pathogenesis of anaplastic astrocytoma via UPLC-Q/TOF-MS. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022, 101, e29594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkblom, B.; Wibom, C.; Eriksson, M.; Bergenheim, A.T.; Sjöberg, R.L.; Jonsson, P.; Brännström, T.; Antti, H.; Sandström, M.; Melin, B. Distinct metabolic hallmarks of WHO classified adult glioma subtypes. Neuro. Oncol. 2022, 24, 1454–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Semreen, A.M.; El-Huneidi, W.; Bustanji, Y.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Alqudah, M.A.Y.; Alhusban, A.; Shara, M.; Abuhelwa, A.Y.; Soares, N.C.; Semreen, M.H.; Alzoubi, K.H. Preclinical and clinical applications of metabolomics and proteomics in glioblastoma research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraco, P.; Bacci, A.; Ferrazza, P.; van den Hauwe, L.; Pertile, R.; Girlando, S.; Barbareschi, M.; Gagliardo, C.; Morganti, A.G.; Petralia, B. Magnetic resonance imaging derived biomarkers of IDH mutation status and overall survival in grade III astrocytomas. Diagnostics (Basel) 2020, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortin Ensign, S.P.; Jenkins, R.B.; Giannini, C.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Galanis, E.; Kizilbash, S.H. Translational significance of CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion in isocitrate dehydrogenase-mutant astrocytoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2023, 25, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohba, S.; Kuwahara, K.; Yamada, S.; Abe, M.; Hirose, Y. Correlation between IDH, ATRX, and TERT promoter mutations in glioma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2020, 37, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Gerges, N.; Korshunov, A.; Sabha, N.; Khuong-Quang, D.A.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Fleming, A.; Hadjadj, D.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Majewski, J.; Dong, Z.; Siegel, P.; Albrecht, S.; Croul, S.; Jones, D.T.; Kool, M.; Tonjes, M.; Reifenberger, G.; Faury, D.; Zadeh, G.; Pfister, S.; Jabado, N. Frequent ATRX mutations and loss of expression in adult diffuse astrocytic tumors carrying IDH1/IDH2 and TP53 mutations. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shi, L.; Su, Y. Aquaporin-4 as a new potential molecular biomarker for prognosis of low-grade glioma: comprehensive analysis based on online platforms. World Neurosurg. 2023, 175, e713–e722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, Z.; Wu, S.; Huang, Y.; Song, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Fa, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Q.; Cao, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Yang, T. GlioMarker: An integrated database for knowledge exploration of diagnostic biomarkers in gliomas. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 792055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traylor, T.D.; Hogan, E.L. Gangliosides of human cerebral astrocytomas. J. Neurochem. 1980, 34, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.S.; Hogan, E.L.; Koontz, D.A.; Traylor, T.D. Serum gangliosides in cerebral astrocytoma. Ann. Neurol. 1980, 8, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladisch, S.; Chang, F.; Li, R.; Cogen, P.; Johnson, D. Detection of medulloblastoma and astrocytoma-associated ganglioside GD3 in cerebrospinal fluid. Cancer Lett. 1997, 120, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleurence, J.; Cochonneau, D.; Fougeray, S.; Oliver, L.; Geraldo, F.; Terme, M.; Dorvillius, M.; Loussouarn, D.; Vallette, F.; Paris, F.; Birklé, S. Targeting and killing glioblastoma with monoclonal antibody to O-acetyl GD2 ganglioside. Oncotarget. 2016, 7, 41172–41185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperzyk, J.L.; El-Abbadi, M.M.; Hauser, E.C.; D’Azzo, A.; Platt, F.M.; Seyfried, T.N. N-butyldeoxygalactonojirimycin reduces neonatal brain ganglioside content in a mouse model of GM1 gangliosidosis. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, K.; Aixinjueluo, W.; Kasama, T.; Ohkawa, Y.; Yoshihara, M.; Ohmi, Y.; Tajima, O.; Suzumura, A.; Kittaka, D.; Furukawa, K. Disruption of GM2/GD2 synthase gene resulted in overt expression of 9-O-acetyl GD3 irrespective of Tis21. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, R.; Kobbe, B.; Stoffel, W. Quantification of gangliosides by microbore high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zamfir, A.D.; Fabris, D.; Capitan, F.; Munteanu, C.; Vukelić, Ž.; Flangea, C. Profiling and sequence analysis of gangliosides in human astrocytoma by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7321–7335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartik, P.; Maglott, A.; Entlicher, G.; Vestweber, D.; Takeda, K.; Martin, S.; Dontenwill, M. Detection of a hypersialylated beta1 integrin endogenously expressed in the human astrocytoma cell line A172. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Best, M.G.; Sol, N.; Zijl, S.; Reijneveld, J.C.; Wesseling, P.; Wurdinger, T. Liquid biopsies in patients with diffuse glioma. Acta Neuropathol. 2015, 129, 849–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groux-Degroote, S.; Delannoy, P. Cancer-associated glycosphingolipids as tumor markers and targets for cancer immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukelić, Ž.; Kalanj-Bognar, S.; Froesch, M.; Bîndila, L.; Radić, B.; Allen, M.; Peter-Katalinić, J.; Zamfir, A.D. Human gliosarcoma-associated ganglioside composition is complex and distinctive as evidenced by high-performance mass spectrometric determination and structural characterization. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, W.; Maira, M.; Roychoudhury, R.; Galan, A.; Brahimi, F.; Gilbert, M.; Cunningham, A.M.; Josephy, S.; Pirvulescu, I.; Moffett, S.; Saragovi, H.U. Vaccination with tumor-ganglioside glycomimetics activates a selective immunity that affords cancer therapy. Cell. Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berois, N.; Pittini, A.; Osinaga, E. Targeting Tumor glycans for cancer therapy: successes, limitations, and perspectives. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavdarli, S.; Delannoy, P.; Groux-Degroote, S. O-acetylated gangliosides as targets for cancer immunotherapy. Cells 2020, 9, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navid, F.; Santana, V.M.; Barfield, R.C. Anti-GD2 antibody therapy for GD2-expressing tumors. Curr. Cancer Drug Targ. 2010, 10, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasawa, T.; Zhang, P.; Ohkawa, Y.; Momota, H.; Wakabayashi, T.; Ohmi, Y.; Bhuiyan, R.H.; Furukawa, K.; Furukawa, K. Enhancement of malignant properties of Human glioma cells by ganglioside GD3/GD2. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, C.C.; Pearl, D.K.; Coons, S.W.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Johnson, P.C.; Zheng, M.; Yates, A.J. Correlation of ganglioside patterns of primary brain tumors with survival. Cancer 1995, 75, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.C.; Wang, P.Y.; Lou, Y.W.; Khoo, K.H.; Hsiao, M.; Hsu, T.L.; Wong, C.H. Glycolipid GD3 and GD3 synthase are key drivers for glioblastoma stem cells and tumorigenicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2016, 113, 5592–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabris, D.; Rožman, M.; Sajko, T.; Vukelić, Ž. Aberrant ganglioside composition in glioblastoma multiforme and peritumoral tissue: A mass spectrometry characterization. Biochimie 2017, 137, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, M.; Vukelić, Ž.; Clemmer, D.E.; Zamfir, A.D. electrospray ionization ion mobility mass spectrometry provides novel insights into the pattern and activity of fetal hippocampus gangliosides. Biochimie 2017, 139, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, M.; Raab, S.; Henderson, L.; Fabris, D.; Vukelić, Ž.; Clemmer, D.E.; Zamfir, A.D. Cerebrospinal fluid: profiling and fragmentation of gangliosides by ion mobility mass spectrometry. Biochimie 2020, 170, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, M.; Clemmer, D.E.; Zamfir, A.D. Ion mobility mass spectrometry of human melanoma gangliosides. Biochimie 2020, 177, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbu, M.; Petrica, L.; Clemmer, D.E.; Vukelić, Ž.; Zamfir, A.D. Gangliosides of human glioblastoma multiforme: a comprehensive mapping and structural analysis by ion mobility tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 32, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamasaki, H.; Aoyagi, M.; Kasama, T.; Handa, S.; Hirakawa, K.; Taki, T. GT1b in human metastatic brain tumors: GT1b as a brain metastasis-associated ganglioside. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1437, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, K.C.; Liapis, E.; Harris, B.T.; Perlin, D.S.; Carter, C.L. Mass spectrometry imaging discriminates glioblastoma tumor cell subpopulations and different microvascular formations based on their lipid profiles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermini, L.; Morganti, E.; Post, A.; Yeganeh, B.; Caniggia, I.; Leadley, M.; Faria, C.C.; Rutka, J.T.; Post, M. Imaging mass spectrometry identifies prognostic ganglioside species in rodent intracranial transplants of glioma and medulloblastoma. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0176254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza-Kallee, N.; Bergès, R.; Hein, V.; Cabaret, S.; Garcia, J.; Gros, A.; Tabouret, E.; Tchoghandjian, A.; Colin, C.; Figarella-Branger, D. Deciphering the Action of Neuraminidase in Glioblastoma Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahlavi, A.; Rayman, P.; Richmond, A.L.; Biswas, K.; Zhang, R.; Vogelbaum, M.; Tannenbaum, C.; Barnett, G.; Finke, J.H. Glioblastomas induce T-lymphocyte death by two distinct pathways involving gangliosides and CD70. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5428–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morantz, R.A.; Feigin, I.; Ransohoff 3rd, J. Clinical and pathological study of 24 cases of gliosarcoma. J. Neurosurg. 1976, 45, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanis, E.; Buckner, J.C.; Dinapoli, R.P.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Jenkins, R.B.; Wang, C.H.; O’Fallon, J.R.; Farr Jr., G. Clinical outcome of gliosarcoma compared with glioblastoma multiforme: north central cancer treatment group results. J. Neurosurg. 1998, 89, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frandsen, S.; Broholm, H.; Larsen, V.A.; Grunnet, K.; Møller, S.; Poulsen, H.S.; Michaelsen, S.R. Clinical characteristics of gliosarcoma and outcomes from standardized treatment relative to conventional glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, N.U.; Ishtiaq, H.; Rahim, S.; Abdul-Ghafar, J.; Ahmad, Z. Gliosarcoma in patients under 20 years of age. A clinicopathologic study of 11 cases and detailed review of the literature. BMC. Pediatr. 2021, 21, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Higaki, K.; Furuta, T.; Moritsubo, M.; Yoshitake, H.; Nagata, Y.; Hashikawa, T.; Sakai, H.; Nakagawa, S.; Takahashi, K.; Sugita, Y. Gliosarcoma with unusual glial components: Two case reports. Neuropathology 2022, 42, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.G.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.S.; Suh, S.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, D.G. Primary gliosarcoma with extracranial metastasis. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2020, 8, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardis, C.; Donner, D.; Sanai, N.; Xiu, J.; Mittal, S.; Michelhaugh, S.K.; Pandey, M.; Kesari, S.; Heimberger, A.B.; Gatalica, Z.; Korn, M.W.; Sumrall, A.L.; Phuphanich, S. Gliosarcoma vs. glioblastoma: a retrospective case series using molecular profiling. B.M.C. Neurol. 2021, 21, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, G.S.; Krag, D.N. Selective delivery of therapeutic agents for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2006, 6, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, A.W.; Patel, A.J. Review of Current Principles of the Diagnosis and Management of Brain Metastases. Front Oncol. 2022, 12, 857622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, M.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, M.; Suh, S.H.; Chang, Y.S.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, J.M. Brain Metastases From Lung Adenocarcinoma May Preferentially Involve the Distal Middle Cerebral Artery Territory and Cerebellum. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G., 2nd; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of radiosurgery alone vs radiosurgery with whole brain radiation therapy on cognitive function in patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.I.; Bustos, M.A.; Wu, J.; Jones, P.; Chang, S.C.; Kiyohara, E.; Tran, K.; Zhang, X.; Stern, S.L.; Izraely, S.; Sagi-Assif, O.; Witz, I.P.; Davies, M.A.; Mills, G.B.; Kelly, D.F.; Irie, R.F.; Hoon, D.S.B. Upregulation of cell surface GD3 ganglioside phenotype is associated with human melanoma brain metastasis. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 8, 1760–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, Y.; Zhang, P.; Momota, H.; Kato, A.; Hashimoto, N.; Ohmi, Y.; Bhuiyan, R.H.; Farhana, Y.; Natsume, A.; Wakabayashi, T.; Furukawa, K.; Furukawa, K. Lack of GD3 synthase (St8sia1) attenuates malignant properties of gliomas in genetically engineered mouse model. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3756–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobowski, M.; Cazet, A.; Steenackers, A.; Delannoy, P. Role of Complex Gangliosides in Cancer Progression. Carbohydr. Chem. 2012, 37, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeersch, S.; Vanbeselaere, J.; Delannoy, C.P.; Drolez, A.; Mysiorek, C.; Guérardel, Y.; Delannoy, P.; Julien, S. Accumulation of GD1α Ganglioside in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells Expressing ST6GalNAc V. Molecules 2015, 20, 6913–6924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmi, Y.; Kambe, M.; Ohkawa, Y.; Hamamura, K.; Tajima, O.; Takeuchi, R.; Furukawa, K.; Furukawa, K. Differential roles of gangliosides in malignant properties of melanomas. PLoS One. 2018, 13, e0206881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimaki, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yagasaki, H.; Masuda, S. Multiple immunofluorescence imaging analysis reveals differential expression of disialogangliosides GD3 and GD2 in neuroblastomas. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2021, 25, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, T.N.; Mukherjee, P. Ganglioside GM3 Is Antiangiogenic in Malignant Brain Cancer. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 961243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, P.D.; Zhang, X.H.; Nadal, C.; Shu, W.; Gomis, R.R.; Nguyen, D.X.; Minn, A.J.; van de Vijver, M.J.; Gerald, W.L.; Foekens, J.A.; Massagué, J. Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Nature 2009, 459, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamfir, A.D.; Serb, A.; Vukelic, Ž.; Flangea, C.; Schiopu, C.; Fabris, D.; Kalanj-Bognar, S.; Capitan, F.; Sisu, E. Assessment of the molecular expression and structure of gangliosides in brain metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by an advanced approach based on fully automated chip-nanoelectrospray mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, Y.; Momota, H.; Kato, A.; Hashimoto, N.; Tsuda, Y.; Kotani, N.; Honke, K.; Suzumura, A.; Furukawa, K.; Ohmi, Y.; Natsume, A.; Wakabayashi, T.; Furukawa, K. Ganglioside GD3 enhances invasiveness of gliomas by forming a complex with platelet-derived growth factor receptor α and yes kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 16043–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
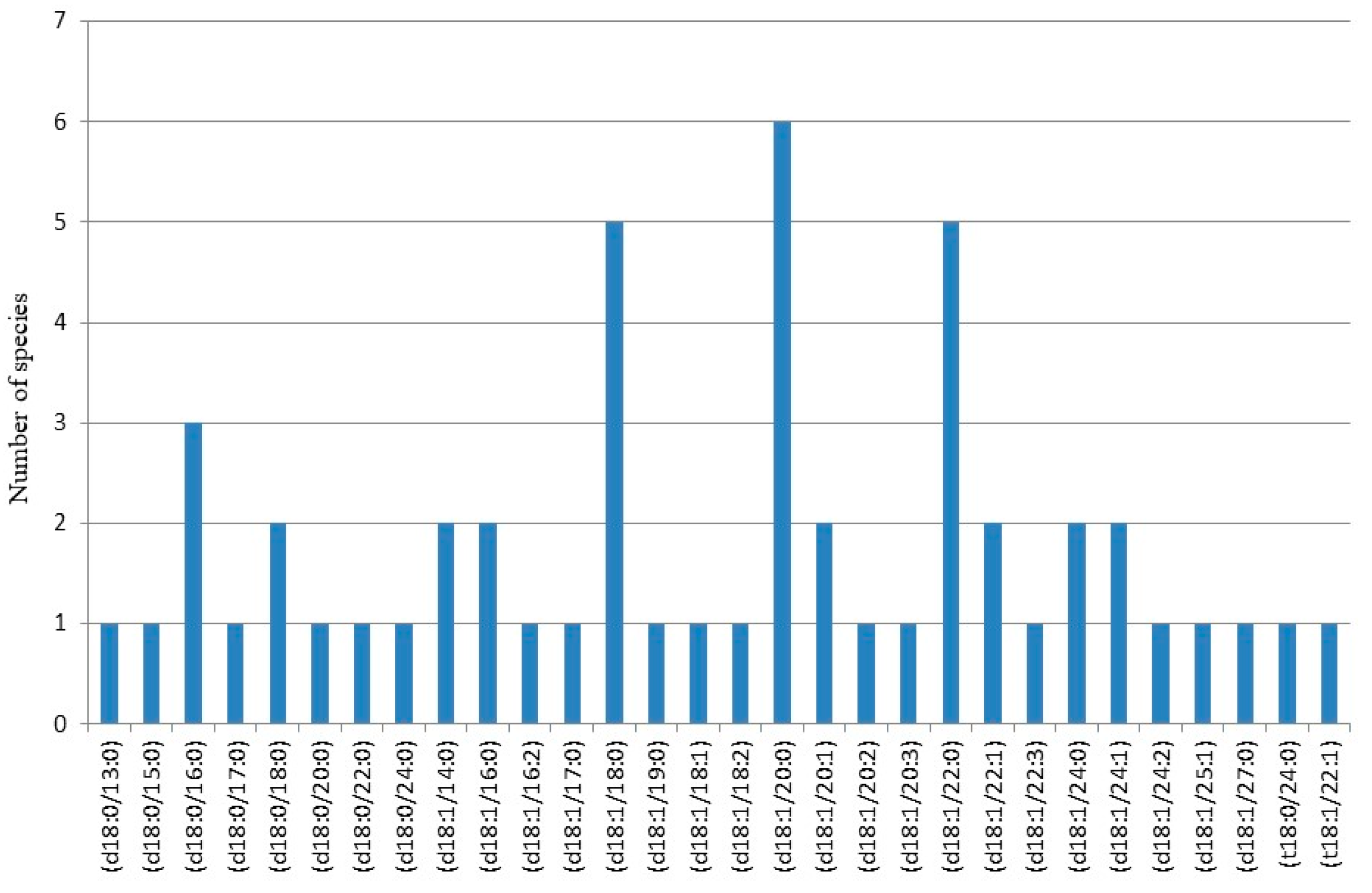
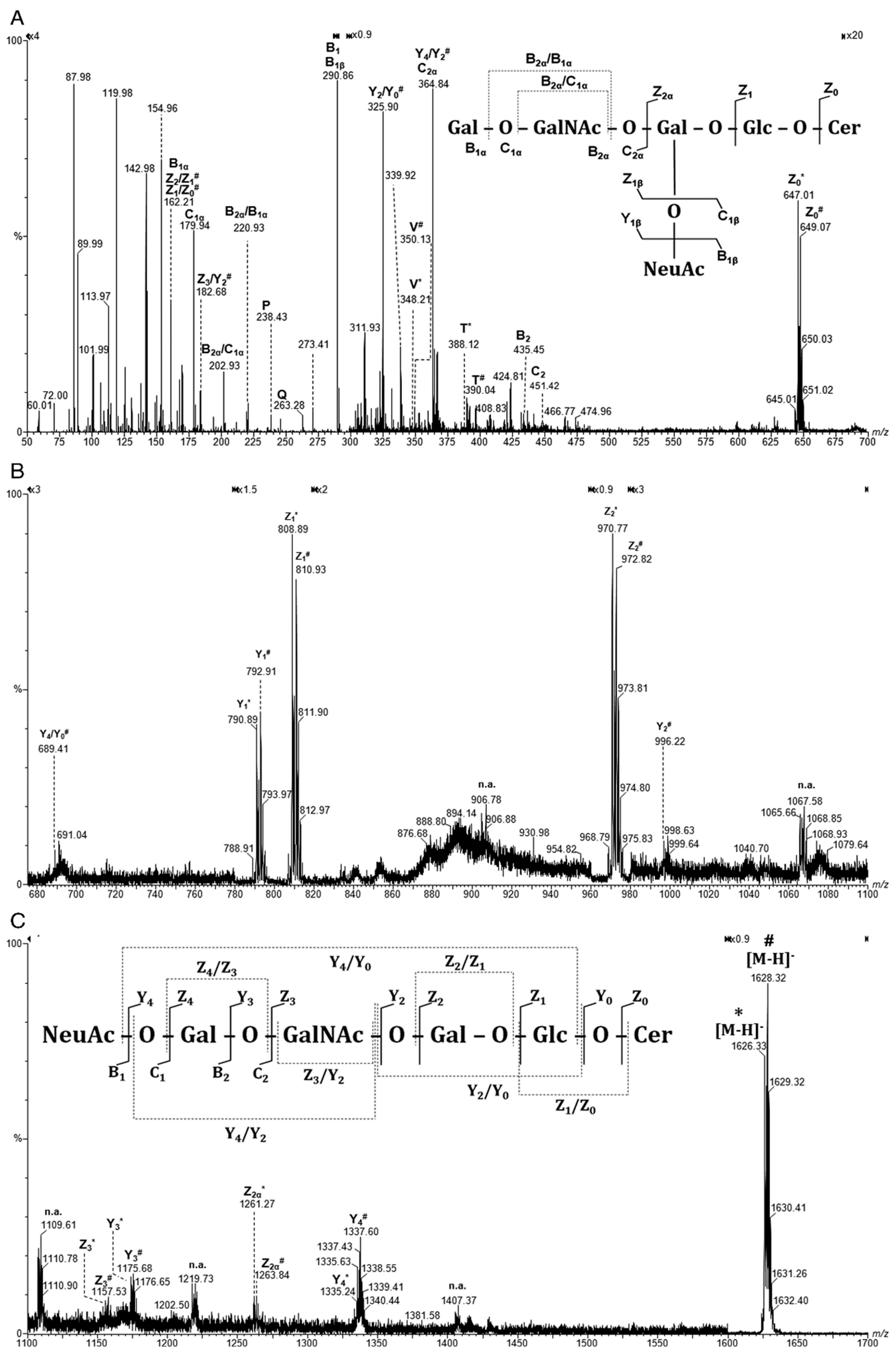
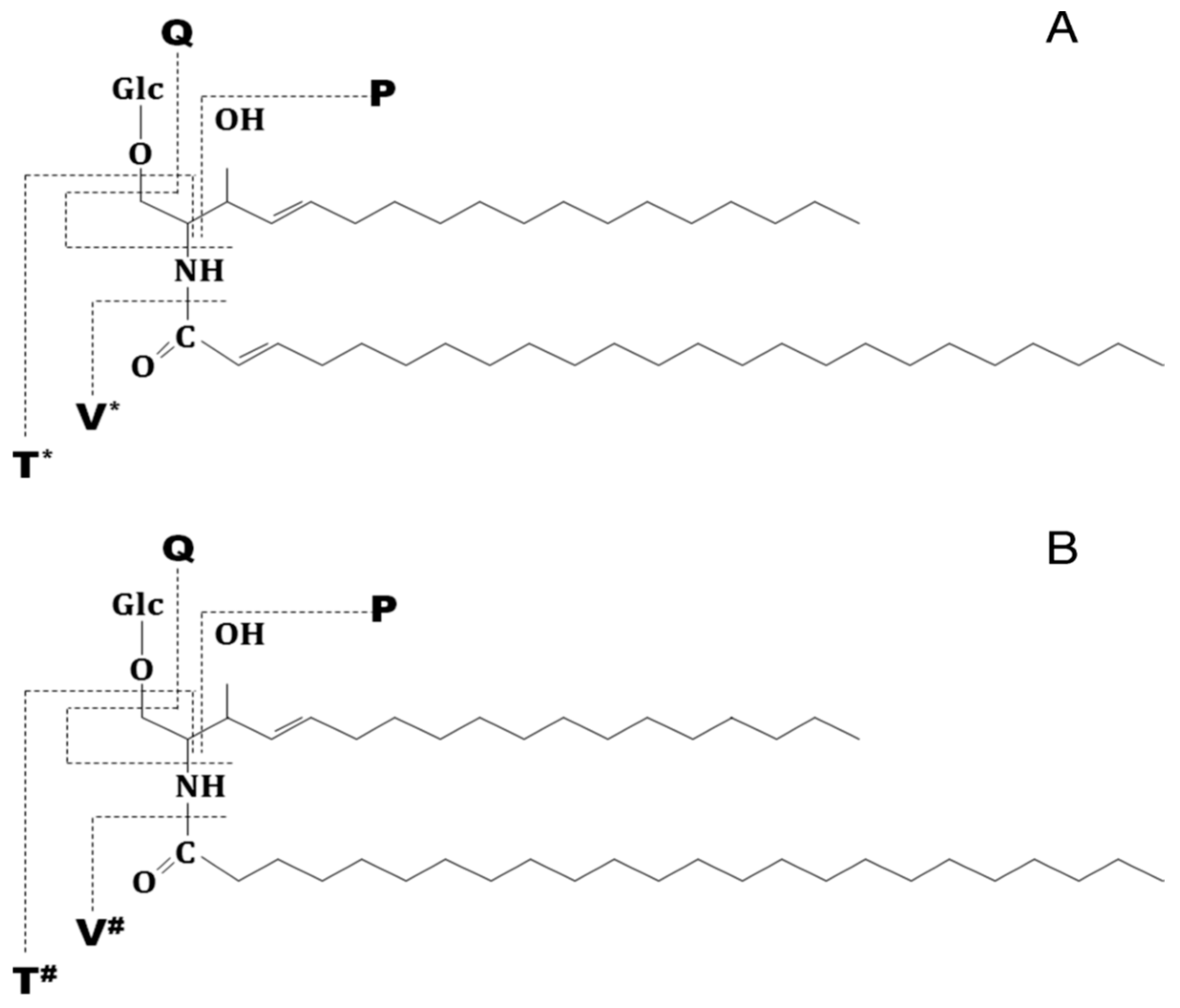
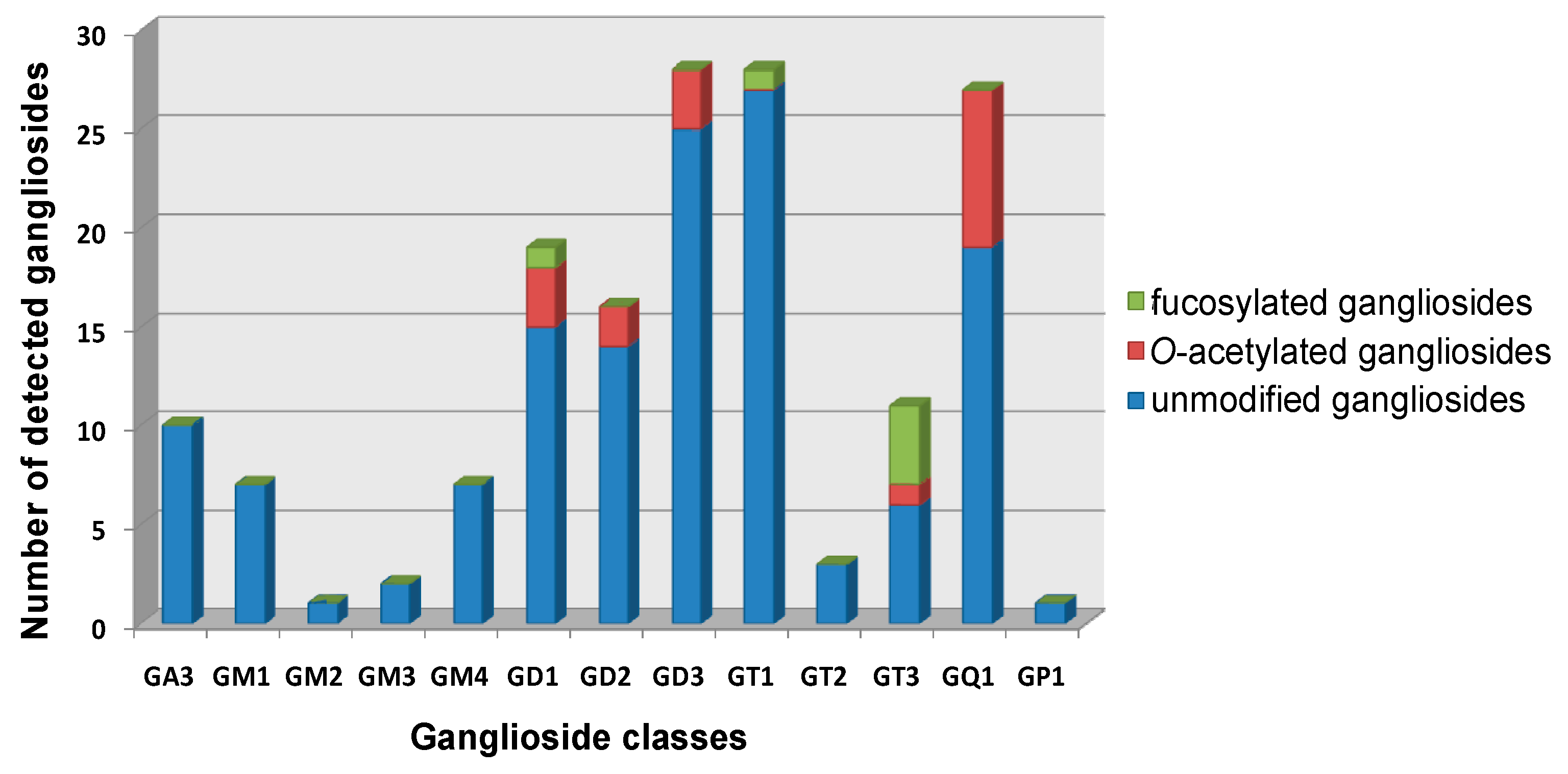
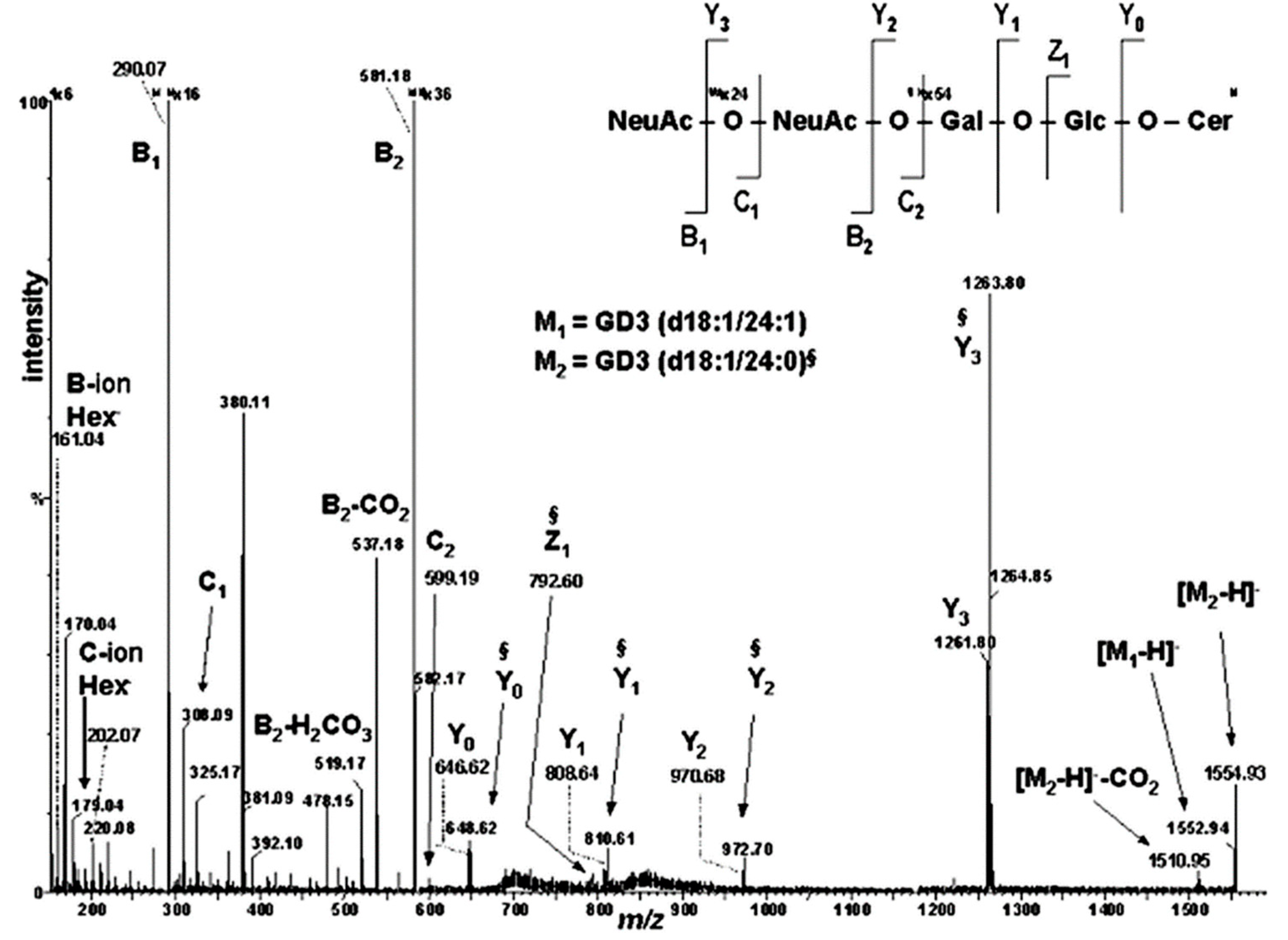
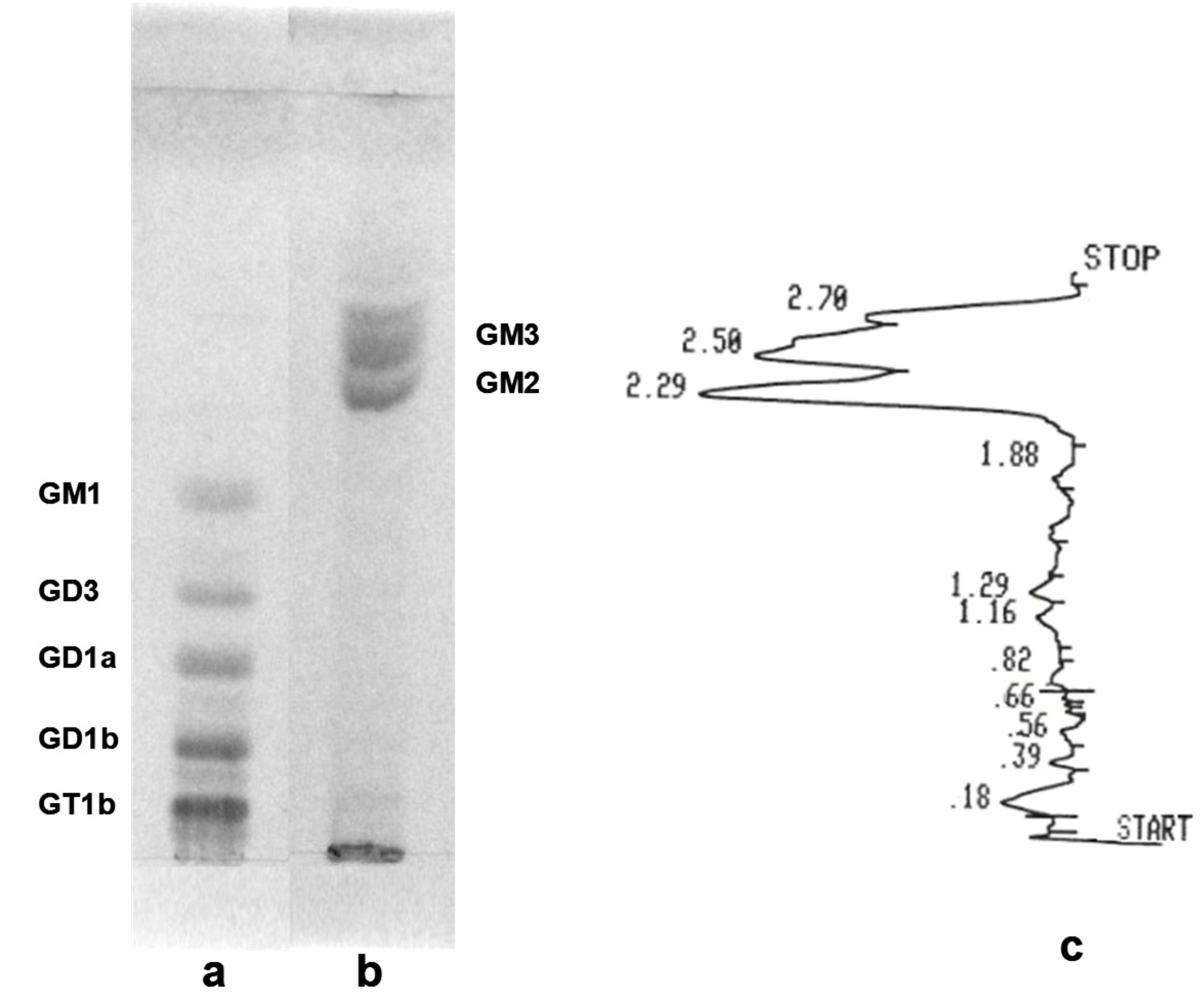
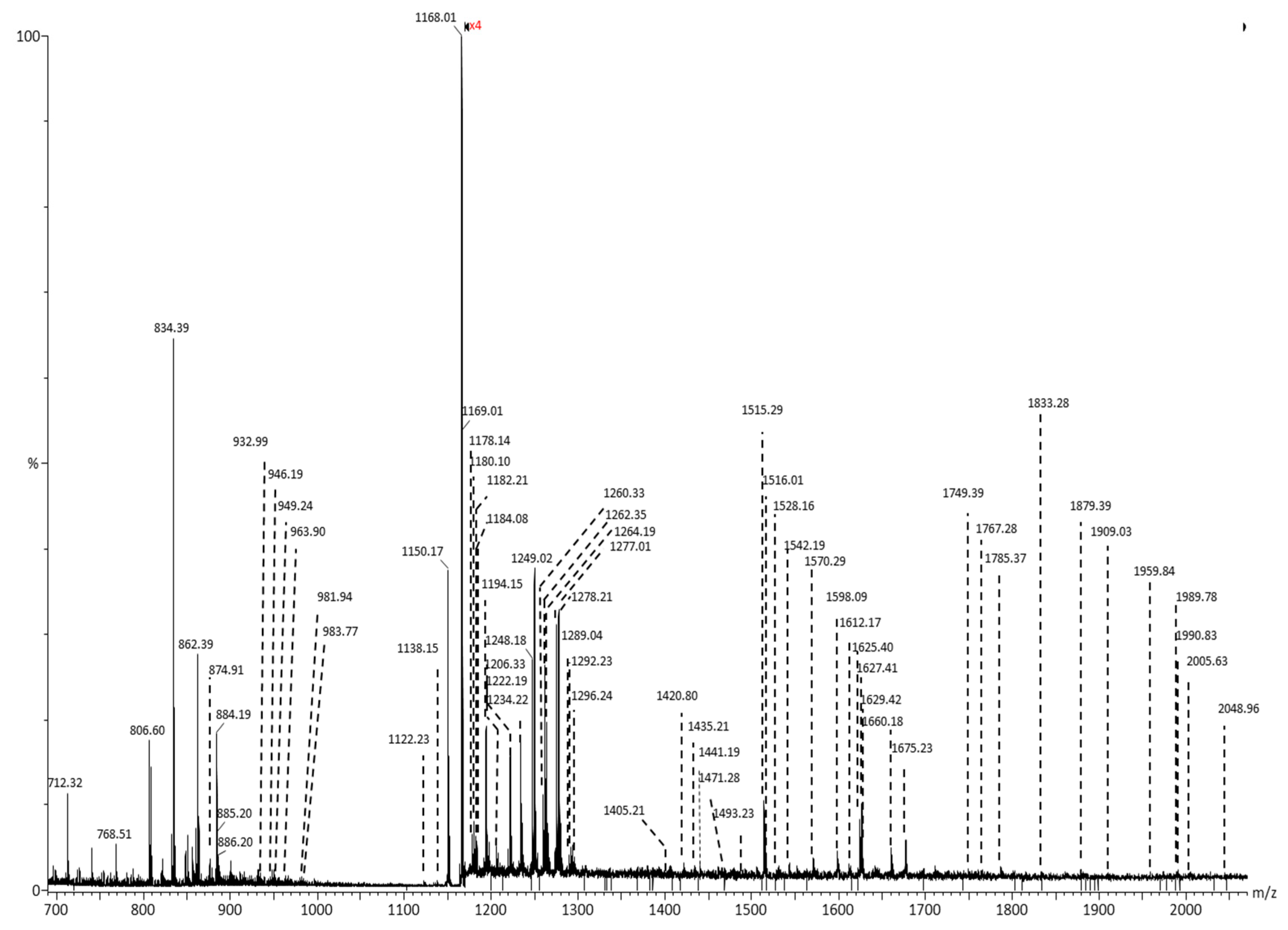
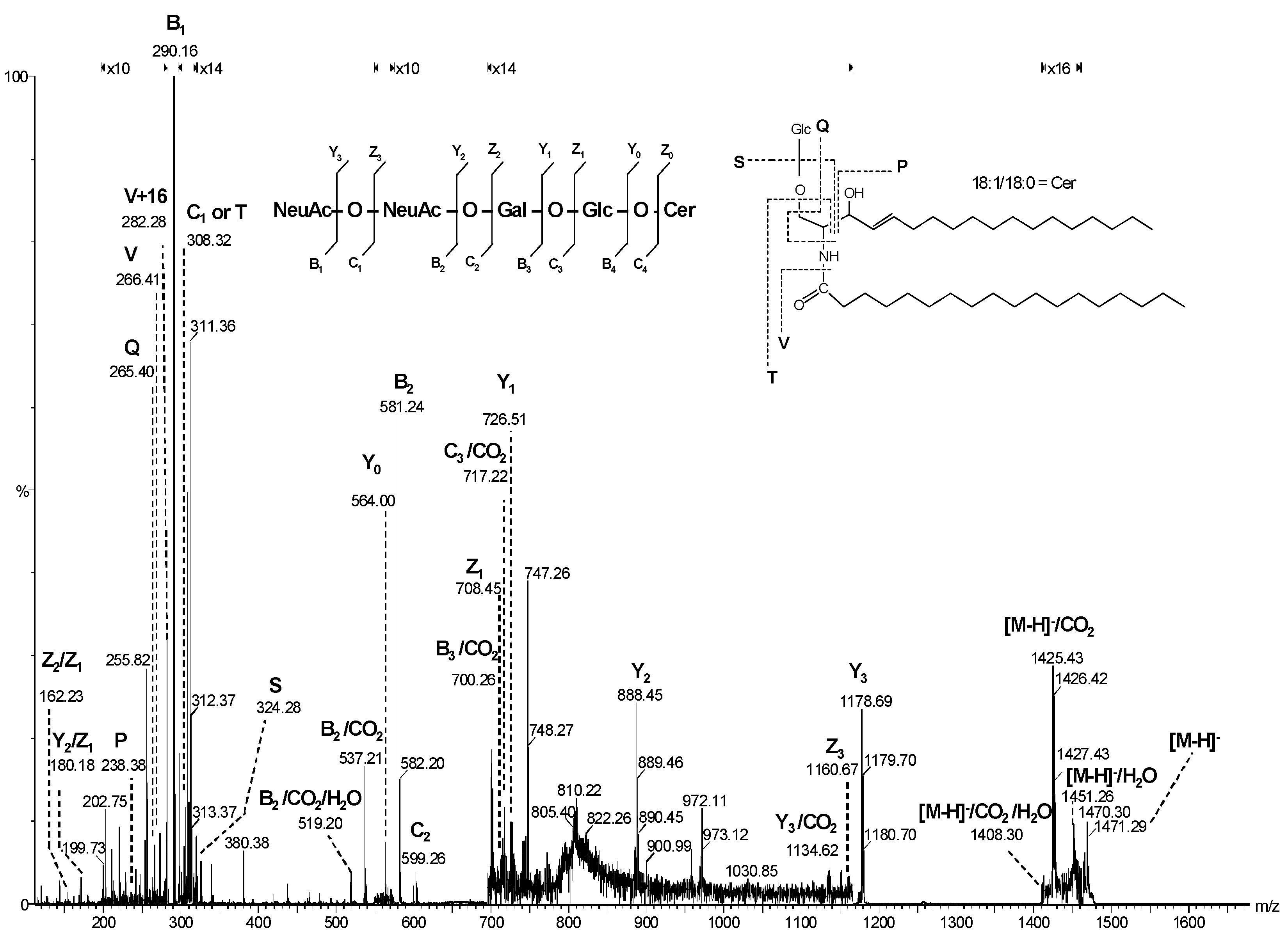
| Nr. crt. | Proposed structure | m/ztheor. | m/zexp. | Molecular Ion | Mass accuracy (ppm) | Relative abundance % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GM3(d18:0/24:0) | 645.3958 | 645.3930 | [M-4H++2Na+-H2O]2- | 4.3 | 35.03 |
| 2 | GM3(t18:0/24:0) | 662.3986 | 662.3960 | [M-4H++2Na+]2- | 3.9 | 18.51 |
| 3 | GT1(d18:1/18:0) | 708.3479 | 708.3472 | [M-3H+]3- | 0.9 | 28.77 |
| 4 | GD3(d18:0/16:0) | 712.8989 | 712.9012 | [M−2H+-H2O]2− | -3.2 | 30.83 |
| 5 | GD3(d18:1/16:0) | 720.8964 | 720.8964 | [M-2H+]2- | 0 | 34.05 |
| 6 | GT1(d18:1/20:0) | 717.6917 | 717.6918 | [M-3H+]3- | -0.1 | 31.83 |
| 7 | GT1(d18:1/22:0) | 727.0355 | 727.0339 | [M-3H+]3- | 2.2 | 29.41 |
| 8 | GT1(t18:1/22:1) | 731.6952 | 731.6950 | [M-3H+]3- | 0.2 | 28.77 |
| 9 | GM2(d18:1/24:0) | 732.9452 | 732.9510 | [M–2H+]2− | -7.9 | 33.55 |
| 10 | GD3(d18:1/18:1) | 733.9121 | 733.9118 | [M–2H+]2− | 0.4 | 78.73 |
| 11 | GD3(d18:1/18:0) | 734.9121 | 734.9122 | [M-2H+]2- | -0.1 | 59.21 |
| 12 | O-Ac-GT1(d18:0/22:0) | 735.7073 | 735.7051 | [M-3H+-H2O]3- | 2.9 | 52.67 |
| 13 | GD3(d18:1/20:0) | 748.9277 | 748.9276 | [M-2H+]2- | 0.1 | 42.85 |
| 14 | GM1(d18:1/14:0) | 754.8901 | 754.8914 | [M-3H+ +Na +]2- | -1.7 | 35.78 |
| 15 | GM1(d18:0/16:0) | 758.9226 | 758.9269 | [M-2H+]2- | -5.6 | 28.66 |
| 16 | GD3(d18:1/22:1) | 761.9356 | 761.9365 | [M-2H+]2- | -1.1 | 32.73 |
| 17 | GD3(d18:1/22:0) | 762.9434 | 762.9432 | [M-2H+]2- | 0.2 | 42.90 |
| 18 | GM1(d18:1/18:2) | 769.9148 | 769.9210 | [M-2H+]2- | -8.0 | 59.21 |
| 19 | GD3(d18:1/24:2) | 774.9434 | 774.9432 | [M-2H+]2- | 0.2 | 47.93 |
| 20 | GD3(d18:1/24:1) | 775.9512 | 775.9512 | [M-2H+]2- | 0.012 | 59.21 |
| 21 | GD3(d18:1/24:0) | 776.9590 | 776.9592 | [M-2H+]2- | -0.2 | 47.93 |
| 22 | GM1(d18:0/18:0) | 783.9292 | 783.9283 | [M-3H++Na+]2- | 1.1 | 35.78 |
| 23 | GD2(d18:0/13:0) | 793.4598 | 793.4618 | [M−2H+-H2O]2− | -2.5 | 51.73 |
| 24 | GM1(d18:0/18:0) | 794.9202 | 794.9232 | [M-4H++2Na+]2- | -3.7 | 41.82 |
| 25 | GM1(d18:1/20:0) | 796.9371 | 796.9384 | [M-3H++Na+]2- | -1.6 | 47.12 |
| 26 | GM1(d18:0/20:0) | 808.9359 | 808.9434 | [M-4H++2Na+]2- | -9.2 | 26.78 |
| 27 | GM1(d18:0/20:0) | 809.9437 | 809.9441 | [M-4H++2Na+]2- | -0.4 | 30.60 |
| 28 | GQ1(d18:1/20:0) | 814.7235 | 814.7252 | [M-3H+]3- | -2.0 | 24.76 |
| 29 | GD3(d18:1/28:0) | 815.9813 | 815.9850 | [M−3H++Na]2− | -4.5 | 29.53 |
| 30 | GD2(d18:1/18:0) | 827.4464 | 827.4387 | [M−2H+ -H2O]2 | 9.3 | 30.19 |
| 31 | GD2(d18:1/18:0) | 836.4517 | 836.4515 | [M-2H+]2- | 0.2 | 55.21 |
| 32 | GD2(d18:1/20:0) | 850.4674 | 850.4671 | [M-2H+]2- | 0.3 | 41.82 |
| 33 | Fuc-GM1(d18:1/18:3) | 863.918 | 863.9180 | [M-4H++2Na+]2- | 0 | 87.86 |
| 34 | GD1(d18:1/18:0) | 917.4781 | 917.4782 | [M-2H+]2- | -0.1 | 94.38 |
| 35 | GD1(d18:1/20:0) | 922.4885 | 922.4835 | [M−2H+-H2O]2− | 5.4 | 36.29 |
| 36 | GT3(d18:1/25:1) | 928.5067 | 928.5061 | [M−2H+]2− | 0.6 | 32.64 |
| 37 | GD1(d18:1/20:0) | 931.4938 | 931.4938 | [M-2H+]2- | 0 | 100 |
| 38 | GD1(d18:1/22:0) | 945.5094 | 945.5081 | [M-2H+]2- | 1.3 | 38.41 |
| 39 | O-Ac- GD1(d18:1/20:1) | 951.4912 | 951.4899 | [M-2H+]2- | 1.3 | 66.04 |
| 40 | GD1(d18:1/24:1) | 958.5173 | 958.5155 | [M-2H+]2- | 1.8 | 17.46 |
| 41 | Fuc-GT3(d18:1/20:2) | 965.4888 | 965.4874 | [M−2H+]2− | 1.4 | 12.38 |
| 42 | Fuc GT3(d18:1/20:1) | 966.4966 | 966.4971 | [M-2H+]2- | -0.5 | 24.90 |
| O-Ac GD1(d18:1/22:0) | 966.5068 | 966.4971 | [M-2H+]2- | 10.0 | 12.85 | |
| 43 | Fuc GD1(d18:0/18:0) | 991.5149 | 991.5089 | [M-2H+]2- | 6.0 | 12.38 |
| 44 | O-Ac-GM4(d18:1/16:0) | 1031.6628 | 1031.6579 | [M-H+]- | 4.7 | 79.67 |
| 45 | GT1(d18:1/14:0) | 1034.995 | 1034.9885 | [M-2H+]2- | 6.2 | 65.37 |
| 46 | GT1(d18:1/18:0) | 1063.0258 | 1063.0255 | [M-2H+]2- | 0.2 | 59.92 |
| 47 | GT1(d18:1/20:3) | 1074.0181 | 1074.0160 | [M−2H+]2− | 1.9 | 86.69 |
| GT1(d18:1/18:0) | 1074.0168 | 1074.0160 | [M-3H++Na+]2- | 0.7 | 86.69 | |
| 48 | GT1(d18:1/20:0) | 1077.0414 | 1077.0427 | [M-2H+]2- | -1.2 | 62.77 |
| 49 | GT1(d18:1/22:3) | 1088.0337 | 1088.0338 | [M-2H+]2- | -0.09 | 73.38 |
| GT1(d18:1/20:0) | 1088.0325 | 1088.0338 | [M-3H++Na+]2- | -1.1 | 73.38 | |
| 50 | GT1(d18:1/22:0) | 1091.0571 | 1091.0479 | [M-2H+]2- | 8.4 | 54.37 |
| 51 | GT1(d18:1/24:1) | 1115.0559 | 1115.0584 | [M-3H++Na+]2- | -2.2 | 68.90 |
| 52 | GM3(d18:0/16:0) | 1151.7052 | 1151.7036 | [M-H+]- | 1.3 | 62.77 |
| 53 | (CH3COO-) GalNAc GT1(d18:1/16:2) | 1179.049 | 1179.0457 | [M--H+]2- | 2.7 | 59.92 |
| 54 | GA1(d18:1/18:0) | 1235.7626 | 1235.7589 | [M-H+ -H2O]- | 2.9 | 49.90 |
| 55 | GM3(d18:1/27:0) | 1305.8774 | 1305.8889 | [M-H+]- | -8.8 | 28.66 |
| 56 | GM3(d18:1/27:0) | 1327.859 | 1327.8499 | [M-2H++Na+]- | 6.8 | 78.90 |
| 57 | GD3(d18:1/16:0) | 1442.801 | 1442.8043 | [M-H+]- | -2.2 | 64.76 |
| 58 | GM1(d18:1/14:0) | 1488.806 | 1488.8092 | [M-H+]- | -2.1 | 58.46 |
| 59 | GM1(d18:1/22:0) | 1600.9312 | 1600.9337 | [M-H+]- | -1.5 | 62.07 |
| 60 | GD2(d18:1/17:0) | 1659.8955 | 1659.8918 | [M-H+]- | 2.2 | 78.90 |
| 61 | GalNAc-GM1 (d18:1/8:1) |
1745.9323 | 1745.9223 | [M-H+]- | 5.7 | 58.08 |
| 62 | GD1(d18:1/16:0) | 1807.9327 | 1807.9201 | [M-H+]- | 6.9 | 58.45 |
|
m/z (monoisotopic) experimental |
m/z (monoisotopic) theoretical |
Mass accuracy (ppm) |
Molecular ion |
Proposed structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 917.47 | 917.48 | 10.90 | [M-2H]2- | GD1, nLD1 or LD1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 931.33 | 931.34 | 10.74 | [M-2H]2- | GD1, nLD1 or LD1 (d18:1/20:0) |
| 947.33 | 947.34 | 10.55 | [M-H]- | LacCer (d18:0/22:0) |
| 980.19 | 980.21 | 20.40 | [M+Na-2H]- | GM4 (d18:1/14:2) |
| 1019.78 | 1019.80 | 19.60 | [M-2H]2- | GT2 (d18:1/22:2) |
| 1063.31 | 1063.33 | 18.81 | [M-2H]2- | GT1(d18:1/18:0) or GT1(d18:0/18:1) |
| 1074.00 | 1074.02 | 18.62 | [M+ Na-3H]2- | GT1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1098.18 | 1098.20 | 18.21 | [M-2H]2- | GT1(d18:1/23:0) or GT1(d18:0/23:1) |
| 1127.42 | 1127.45 | 26.61 | [M+Na-2H]- | GM3 (d18:1/13:2) |
| 1179.71 | 1179.74 | 25.42 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/18:0) |
| 1224.33 | 1224.36 | 24.50 | [M-H]- | Fuc-GM3 (d18:1/12:0) |
| 1231.01 | 1231.04 | 24.37 | [M+2Na-4H]2- | GQ1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1268.66 | 1268.69 | 23.64 | [M-H]- | GM2 (d18:1/10:0) |
| 1382.78 | 1382.82 | 28.92 | [M-H]- | GM2 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1408.81 | 1408.85 | 28.38 | [M-H]- | GM2 (d18:1/20:1) |
| 1440.74 | 1440.78 | 27.75 | [M-H]- | GD3 (d18:1/16:1) |
| 1470.99 | 1471.03 | 27.19 | [M-H]- | GD3 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1518.82 | 1518.86 | 26.33 | [M-H]- | GM1(d18:0/16:0) |
| 1544.78 | 1544.83 | 32.36 | [M-H]- | GM1, nLM1 or LM1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1572.80 | 1572.85 | 31.78 | [M-H]- | GM1, nLM1 or LM1 (d18:1/20:0) |
| 1600.86 | 1600.92 | 37.47 | [M-H]- | GM1,nLM1or LM1 (d18:1/22:0) |
| 1700.83 | 1700.89 | 35.27 | [M+2Na-3H]- | GM1(d18:1/26:0) |
| 1830.33 | 1830.40 | 38.25 | [M-H]- | GT3 (d18:1/23:1) |
| 1835.87 | 1835.94 | 38.12 | [M-H]- | GD1,nLD1or LD1(d18:1/18:0) |
| 1857.88 | 1857.95 | 37.67 | [M+Na-2H]- | GD1, nLD1 or LD1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1885.92 | 1885.99 | 37.11 | [M+Na-2H]- | GD1(d18:1/20:0) |
| 1916.85 | 1916.92 | 36.51 | [M-H]- | GD1 (d18:1/24:2) |
| 1965.95 | 1966.02 | 35.60 | [M-H]- | GT2(d18:1/18:1) or GT2(d18:0/18:2) |
| 1992.46 | 1992.53 | 35.12 | [M-H]- | Hex-HexNAc-nLM1(d18:1/24:1) |
| 1996.89 | 1996.96 | 35.05 | [M-H]- | GD2–lactone (d18:1/22:2) |
| 2052.52 | 2052.60 | 38.96 | [M-H]- | GT2 (d18:0/24:0) |
| 2098.16 | 2098.24 | 38.13 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GD1(d18:1/34:2) |
| 2124.12 | 2124.20 | 37.66 | [M-H]- | GT1(d18:1/18:2) or GT1(d18:0/18:3) |
| 2385.13 | 2385.22 | 37.73 | [M+3Na-4H]- | GT1(18:1/32:2) |
| 2524.14 | 2524.24 | 39.61 | [M+Na-2H]- | GQ1(d18:1/24:0) |
| 2622.46 | 2622.56 | 38.12 | [M+Na-2H]- | GQ1(d18:1/31:0) |
| 2827.26 | 2827.37 | 38.91 | [M-H]-(-H2O) | GP1(d18:1/28:2) |
|
m/z (monoisotopic) experimental |
m/z (monoisotopic) theoretical |
Mass accuracy (ppm) |
Molecular ion |
Proposed structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 872.37 | 872.38 | 11.46 | [M-2H]2- | O-Ac-GD2 or (d18:1/20:0) |
| 911.30 | 911.31 | 10.97 | [M-2H]2- | GD1, nLD1 or LD1 (d18:1/18:3) |
| 1063.31 | 1063.33 | 18.81 | [M-2H]2- | GT1(d18:1/18:0) or GT1(d18:0/18:1) |
| 1175.94 | 1175.96 | 17.00 | [M-H]- | GM3 (d18:1/18:2) |
| 1197.77 | 1197.80 | 25.04 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:0/19:0) |
| 1235.78 | 1235.81 | 24.29 | [M-H]- | GM3 (d18:1/22:0) |
| 1306.03 | 1306.06 | 22.97 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/27:0) |
| 1510.80 | 1510.84 | 26.47 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GD3 (d18:1/18:1) |
| 1644.27 | 1644.31 | 24.33 | [M-H]- | GM1 (d18:0/25:0) |
| 1662.18 | 1662.22 | 24.06 | [M-H]- | GM1 (d18 : 1 / 29 : 2) |
| 1684.78 | 1684.82 | 23.73 | [M-H]- | GD2(d18:1/19:2) or GD2(d18:0/19:3) |
| 1847.38 | 1847.42 | 21.65 | [M-H]- | GT3(d18:0/24:0) |
| 1879.05 | 1879.09 1879.10 |
21.28 26.60 |
[M-H]-(-H2O) [M+Na-2H]- | Fuc-GT3(d18:0/17:0) or O-Ac-GT3 (d18:1/22:2) |
| 2024.17 | 2024.23 | 29.64 | [M+2Na-3H]- | GD1 (d18:0/28:0) |
| 2050.55 | 2050.60 | 24.37 | [M-H]- | GT2(d18:1/24:0) or GT2(d18:0/24:1) |
| 2072.15 | 2072.21 | 28.95 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GD1(d18:1/32:1) |
| 2076.13 | 2076.19 | 28.90 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GD1(d18:0/32:0) |
| 2102.20 | 2102.26 | 28.54 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GD1(d18:1/34:0) |
| 2112.02 | 2112.09 | 33.14 | [M-H]- | GT1(d18:1/17:2) or GT1(d18:0/17:3) |
| 2123.90 | 2123.97 | 32.95 | [M-H]- | GT1(d18:1/18:2) |
| 2175.73 | 2175.80 | 32.16 | [M-H]- | GT2 (d18:1/33:0) |
| 2186.52 | 2186.60 | 36.57 | [M-H]- | GT1(d18:0/22:0) |
| 2237.08 | 2237.16 | 35.76 | [M-H]- | GT1(d18:1/26:1) |
| 2246.90 | 2246.98 | 35.60 | [M-H]- | Fuc-GT1(d18:0/16:0) |
| 2287.72 | 2287.80 | 34.96 | [M-H]- | Fuc-GT1 (d18:0/20:0) |
| 2346.00 | 2346.09 | 38.36 | [M-H]-(-H2O) | GQ1(d18:1/13:1) |
| 2385.13 | 2385.22 | 37.73 | [M+3Na-4H]- | GT1(18:1/32:2) |
| 2472.12 | 2472.21 | 36.40 | [M-H]- | GQ1(d18:1/22:1) |
| 2582.46 | 2582.56 | 38.71 | [M-H]-(-H2O) | GQ1(d18:1/31:0) |
| 2618.41 | 2618.51 | 38.18 | [M+2Na-3H]- | GQ1(d18:0/29:0) |
| 2642.52 | 2642.62 | 37.83 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GQ1(d18:1/31:0) |
| 2673.42 | 2673.52 | 37.41 | [M-H]- | GP2(d18:1/27:0) |
| 2906.39 | 2906.50 | 37.85 | [M-H]- | Fuc-GP1(d18:1/23:1) |
|
m/z (monoisotopic) experimental |
m/z (monoisotopic) theoretical |
Mass accuracy (ppm) |
Molecular ion |
Proposed structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 917.47 | 917.48 | 10.90 | [M-2H]2- | GD1, nLD1 or LD1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 931.33 | 931.34 | 10.74 | [M-2H]2- | GD1, nLD1 or LD1 (d18:1/20:0) |
| 947.33 | 947.34 | 10.55 | [M-H]- | LacCer (d18:0/22:0) |
| 980.19 | 980.21 | 20.40 | [M+Na-2H]- | GM4 (d18:1/14:2) |
| 1019.78 | 1019.80 | 19.60 | [M-2H]2- | GT2 (d18:1/22:2) |
| 1063.31 | 1063.33 | 18.81 | [M-2H]2- | GT1(d18:1/18:0) or GT1(d18:0/18:1) |
| 1074.00 | 1074.02 | 18.62 | [M+ Na-3H]2- | GT1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1098.18 | 1098.20 | 18.21 | [M-2H]2- | GT1(d18:1/23:0) or GT1(d18:0/23:1) |
| 1127.42 | 1127.45 | 26.61 | [M+Na-2H]- | GM3 (d18:1/13:2) |
| 1179.71 | 1179.74 | 25.42 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/18:0) |
| 1224.33 | 1224.36 | 24.50 | [M-H]- | Fuc-GM3 (d18:1/12:0) |
| 1231.01 | 1231.04 | 24.37 | [M+2Na-4H]2- | GQ1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1268.66 | 1268.69 | 23.64 | [M-H]- | GM2 (d18:1/10:0) |
| 1382.78 | 1382.82 | 28.92 | [M-H]- | GM2 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1408.81 | 1408.85 | 28.38 | [M-H]- | GM2 (d18:1/20:1) |
| 1440.74 | 1440.78 | 27.75 | [M-H]- | GD3 (d18:1/16:1) |
| 1470.99 | 1471.03 | 27.19 | [M-H]- | GD3 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1518.82 | 1518.86 | 26.33 | [M-H]- | GM1(d18:0/16:0) |
| 1544.78 | 1544.83 | 32.36 | [M-H]- | GM1, nLM1 or LM1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1572.80 | 1572.85 | 31.78 | [M-H]- | GM1, nLM1 or LM1 (d18:1/20:0) |
| 1600.86 | 1600.92 | 37.47 | [M-H]- | GM1,nLM1or LM1 (d18:1/22:0) |
| 1700.83 | 1700.89 | 35.27 | [M+2Na-3H]- | GM1(d18:1/26:0) |
| 1830.33 | 1830.40 | 38.25 | [M-H]- | GT3 (d18:1/23:1) |
| 1835.87 | 1835.94 | 38.12 | [M-H]- | GD1,nLD1or LD1(d18:1/18:0) |
| 1857.88 | 1857.95 | 37.67 | [M+Na-2H]- | GD1, nLD1 or LD1 (d18:1/18:0) |
| 1885.92 | 1885.99 | 37.11 | [M+Na-2H]- | GD1(d18:1/20:0) |
| 1916.85 | 1916.92 | 36.51 | [M-H]- | GD1 (d18:1/24:2) |
| 1965.95 | 1966.02 | 35.60 | [M-H]- | GT2(d18:1/18:1) or GT2(d18:0/18:2) |
| 1992.46 | 1992.53 | 35.12 | [M-H]- | Hex-HexNAc-nLM1(d18:1/24:1) |
| 1996.89 | 1996.96 | 35.05 | [M-H]- | GD2–lactone (d18:1/22:2) |
| 2052.52 | 2052.60 | 38.96 | [M-H]- | GT2 (d18:0/24:0) |
| 2098.16 | 2098.24 | 38.13 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GD1(d18:1/34:2) |
| 2124.12 | 2124.20 | 37.66 | [M-H]- | GT1(d18:1/18:2) or GT1(d18:0/18:3) |
| 2385.13 | 2385.22 | 37.73 | [M+3Na-4H]- | GT1(18:1/32:2) |
| 2524.14 | 2524.24 | 39.61 | [M+Na-2H]- | GQ1(d18:1/24:0) |
| 2622.46 | 2622.56 | 38.12 | [M+Na-2H]- | GQ1(d18:1/31:0) |
| 2827.26 | 2827.37 | 38.91 | [M-H]-(-H2O) | GP1(d18:1/28:2) |
| m/z (monoisotopic) theoretical | m/z (monoisotopic) experimental | Mass accuracy (ppm) |
Molecular ion | Proposed structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 875.19 | 874.91 | 33 | [M-H]- | LacCer(d18:1/17:0) |
| 933.31 | 932.99 | 35 | [M-H]- | LacCer(d18:0/21:0) |
| 947.34 | 947.19 | 16 | [M-H]- | LacCer(d18:0/22:0) |
| 949.22 | 949.24 | 21 | [M+2Na-3H]- | LacCer(d18:0/19:0) |
| 964.24 | 963.90 | 35 | [M-H]- | GM4(d18:0/14:0) |
| 982.19 | 981.94 | 25 | [M+Na-2H]- | GM4(d18:1/14:1) |
| 984.21 | 983.87 | 34 | [M+Na-2H]- | GM4(d18:1/14:0) or GM4(d18:0/14:1) |
| 1122.48 | 1122.23 | 22 | [M-H]- | GA2(d18:0/20:0) |
| 1138.44 1138.48 |
1138.15 | 25 29 |
[M-H]- | Fuc-GM4(d18:0/16:0) GA2(t18:0/20:0) |
| 1150.49 1150.40 |
1150.17 | 28 20 |
[M-H]- [M-H]- |
GA2(d18:1/21:0) GM3(d18:1/16:1) |
| 1168.42 | 1168.01 | 35 | [M-H]- | GM3(t18:0/16:0) |
| 1178.46 | 1178.14 | 27 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/18:1) |
| 1179.74 | 1180.10 | 30 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/18:0) |
| 1182.49 | 1182.21 | 24 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:0/18:0) |
| 1184.37 | 1184.08 | 24 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GA1(d18:1/10:0) |
| 1194.50 | 1194.15 | 29 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/19:0) or GM3(d18:0/19:1) |
| 1206.51 1206.64 |
1206.33 | 15 26 |
[M-H]- [M-H]- |
GM3(d18:1/20:1) GA2(d18:0/26:0) |
| 1222.51 1222.55 |
1222.19 | 26 29 |
[M-H]- [M-H]- |
O-Ac-GM3(d18:1/18:0) GM3(d18:0/21:1) or GM3(d18:1/21:0) |
| 1234.56 1234.52 |
1234.22 | 27 24 |
[M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/22:1) O-Ac-GM3(d18:1/19:1) |
| 1248.55 1248.59 |
1248.18 | 33 30 |
[M-H]- |
O-Ac-GM3(d18:1/20:1) GM3(d18:1/23:1) |
| 1248.59 | 1249.02 | 34 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/23:0) |
| 1260.60 | 1260.33 | 21 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/24:2) |
| 1262.62 | 1262.35 | 21 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/24:1) |
| 1264.63 | 1264.19 | 35 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/24:0) |
| 1276.61 1276.64 1276.69 |
1277.01 | 31 29 25 |
[M-H]- [M-H]- [M-H]-(-H2O) |
O-Ac-GM3(d18:1/22:0) GM3(d20:1/23:1) GM3(d18:0/26:0) |
| 1278.66 1278.61 |
1278.21 | 35 31 |
[M-H]- [M-H]- |
GM3(d20:1/23:0) O-Ac-GM3(d18:1/22:0) or O-Ac-GM3(d18:0/22:1) |
| 1288.67 1288.67 |
1289. 04 | 29 29 |
[M-H]- [M-H]- |
GM3(d18:1/26:2) or GM3(d18:2/26:1) GM3(d20:1/24:2) |
| 1292.68 | 1292.23 | 35 | [M-H]- | GM3(d18:1/26:0) or GM3(d18:0/26:1) |
| 1296.54 1296.59 1296.61 |
1296.24 | 23 27 28 |
[M-H]- [M-H]- [M-H]- |
Fuc-GM3(d18:1/16:1) O-Ac-GA1(d18:1/18:0) GA1(d18:0/21:0) or GA1(d18:0/21:0) |
| 1405.65 | 1405.21 | 31 | [M+Na-2H]- | GM2(d18:1/18:0) |
| 1420.68 | 1420.80 | 8 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GM2(d18:2/18:2) |
| 1435.59 | 1435.21 | 26 | [M+Na-2H]- | GD3(d18:1/14:1) or GD3(d18:0/14:2) or GD3(d18:2/14:0) |
| 1441.66 | 1441.19 | 33 | [M-H]- | GD3(d18:1/16:1) or GD3(d18:0/16:2) or GD3(d18:2/16:0) |
| 1471.73 | 1471.28 | 31 | [M-H]- | GD3(d18:1/18:0) |
| 1493.71 | 1493.23 | 32 | [M+Na-2H]- | GD3(d18:1/18:0) |
| 1515.69 1515.74 1515.78 |
1515.29 | 26 30 32 |
[M+2Na-3H]- [M-H]- [M-H]- |
GD3(d18:1/18:0) or GD3(d18:0/18:1) GM1(d18:1/16:1) or GM1(d18:0/16:2) or GM1(d18:2/16:0) O-Ac-GD3(d18:0/18:0) |
| 1515.71 1515.75 |
1516.01 | 20 17 |
[M+Na-2H]- [M-H]- |
GD3(d18:1/20:2) or GD3(d18:0/20:3) or GD3(d18:2/20:1) GM1(d18:2/16:0) or GM1(d18:1/16:1) or GM1(d18:0/16:2) |
| 1527.83 | 1528. 16 | 22 | [M-H]- | GD3(d18:0/22:0) |
| 1541.79 | 1542. 19 | 26 | [M-H]- | GM1(d18:1/18:2) or GM1(d18:2/18:1) or GM1(d18:0/18:3) |
| 1569.78 1569.83 1569.77 |
1570.29 | 32 29 33 |
[M+2Na-3H]- [M-H]- [M+Na-2H]- |
GD3(d18:1/22:0) or GD3(d18:0/22:1) GM1(d18:1/20:1) or GM1(d18:0/20:2) or GM1(d18:2/20:0) GD3(d18:0/24:2) or GD3(d18:1/24:1) or GD3(d18:2/24:0) |
| 1597.88 | 1598.09 | 13 | [M-H]- | GM1(d18:0/22:2) or GM1(d18:1/22:1) or GM1(d18:2/22:0) |
| 1611.77 | 1612.17 | 25 | [M+2Na-3H]- | GM1(d18:1/20:2) |
| 1625.89 1625.92 |
1625.40 | 30 30 |
[M+2Na-3H]- [M-H]- |
GD3(d18:1/26:1) or GD3(d18:0/26:2) or GD3(d18:2/26:0) GM1(d18:1/24:2) |
| 1627.90 1626.93 |
1627.41 | 30 29 |
[M+2Na-3H]- [M-H]- |
GD3(d18:0/26:1) or GD3(d18:1/26:0) GM1(d18:0/24:2) or GM1(d18:1/24:1) or GM1(d18:2/24:0) |
| 1629.92 1628.94 |
1629.42 | 31 29 |
[M-H]- [M-H]- |
GM1(d18:0/24:1) or GM1(d18:1/24:0) di-O-Ac-GM1(d18:1/18:0) |
| 1659.79 | 1660.18 | 23 | [M+3Na-4H]- | GM1(d18:1/22:3) or GM1(d18:0/22:4) or GM1(d18:2/22:2) |
| 1674.87 | 1675.23 | 21 | [M+Na-2H]- (-H2O) | GD2 (d18:1/18:2) |
| 1748.97 | 1749.39 | 24 | [M+Na-2H]- | GD2 (d18:1/22:1) |
| 1766.97 | 1767.28 | 18 | [M-H]- (-H2O) | GT3 (d18:1/20:1) |
| 1785.07 | 1785.37 | 17 | [M-H]- | O-Ac-GD2(d18:1/23:0) or O-Ac-GD2(d18:0/23:1) |
| 1833.81 1833.07 |
1833.28 | 29 11 |
[M-H]- [M-H]- |
GT3(d18:0/23:0) O-Ac-GT3 (d18:0/20:0) |
| 1861.12 1861.12 |
1861.24 | 6 6 |
[M-H]- [M-H] (-H2O) |
O-Ac-GT3-lactone(d18:0/22:0) O-Ac-GT3(d18:0/22:0) |
| 1879.09 1879.10 1879.99 |
1879.39 | 16 15 32 |
[M+Na-2H]- [M-H]-(-H2O) [M-H]- |
O-Ac-GT3 (d18:2/22:1) Fuc-GT3(d18:0/17:0) GT2(d18:1/12:1) or GT2(d18:2/12:0) |
| 1909.16 | 1909.03 | 7 | [M-H]- | GD1 (d18:1/22:0) |
| 1960.21 1960.12 |
1959.84 | 19 14 |
[M-H]- (-2H2O) [M-H]- |
GT2(d18:0/20:0) GT2(d18:1/18:3) or GT2(d18:2/18:2) |
| 1990.17 1990.19 |
1989.78 | 20 21 |
[M+Na-2H]- [M-H]- |
GT2(d18:0/18:0) GT2(d18:0/20:3) or GT2(d18:1/20:2) or GT2(d18:2/20:1) |
| 1990.19 | 1990.83 | 32 | [M-H]- | GT2(d18:1/20:1) or GT2(d18:0/20:2) or GT2(d18:2/20:0) |
| 2005.20 2006.19 |
2005.63 | 21 28 |
[M-H]- | Fuc-GD1(d18:1/20:2) O-Ac-GT2(d18:1/18:1) |
| 2048.23 2048.10 |
2048.80 | 28 34 |
[M-H]- [M-H]-(-H2O) |
di-O-Ac-GT2(d18:0/18:0) GT1(d18:2/14:2) or GT1(d18:3/14:1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




