Introduction
The development of drug resistance is one of several clinical challenges causing anti-cancer drugs limited efficacy or failure. The identification of resistance mechanisms to therapies helps to design novel therapeutics [
1,
2]. Over the past ten years, evidences have shown that abnormalities in apoptosis signaling pathways, such as the activation of anti-apoptotic proteins were highly associated with immune and drug resistance [
3].
Among these proteins, c-FLIP (Cellular FLICE Inhibitory Protein) is a major anti-apoptotic and resistance protein, restraining apoptosis induced by the TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor) superfamily members, including TRAIL (TNF-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand), Fas-L or TNFα, as well as apoptosis stimulated by chemotherapeutic drugs in cancer cells [
4]. c-FLIP is overexpressed in many different types of human cancers such as ovarian carcinomas [
5], colorectal carcinomas [
6], gastric adenocarcinomas [
7], prostate carcinomas [
8]. An upregulated level of c-FLIP has also been detected in primary tissues from patients with lung adenocarcinomas [
9], hepatocellular carcinomas [
10], melanomas [
11], B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia [
12] and Hodgkin’s lymphomas [
13].
c-FLIP has 13 distinct variants, but only three of them are expressed as proteins in human cells. These are known as c-FLIP (L), c-FLIP (s) and c-FLIP(R) [
14]. The long form c-FLIP (L) with a 55 kDa molecular weight (MW) is similar to procaspase-8, containing two
N-terminal tandem “Death effector domains” = DED1 and DED2, and a
C-terminal caspase-like domain, lacking the catalytic cysteine residue responsible for the proteolytic activity of caspases. The short form c-FLIP (s) (26 kDa MW) is composed only of two DEDs (DED1 and DED2) without a caspase-Like domain and a short
C-terminus [
15]. Another short form of the protein called c-FLIP (R) (27 kDa) is specifically expressed in a number of T and B cells such as Raji cells as well as in human primary T cells. It also contains
N-terminal DEDs ( DED1 and DED2), but a short
C-terminus composed of a stretch of residues playing a key role in the ubiquitination of c-FLIP proteins (Chang et al., 2006; Golks et al., 2005)
c-FLIP is considered as being a key inhibitory molecule in the extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway, preventing the homodimerization and autoactivation of procaspase-8/10, the initiator caspases of apoptosis. This extrinsic pathway, also called death receptor pathway, is induced by different ligands of the TNF superfamily (TRAIL, Fas-L, TNFα) binding to their respective death receptors DRs (TRAIL- R1/R2, Fas, TNF receptor). These ligands’ bindings induce the trimerization of the respective DRs which in turn recruit the adaptor protein FADD [
17]. Once FADD is recruited to the DRs, procaspase-8/10 binds by its DED2 domain to the DED domain of FADD, leading to DISC (Death Inducing Signaling Complex) formation and the activation of downstream caspases and subsequent apoptosis [
18]. However, this apoptotic signaling pathway can be attenuated or totally inhibited by c-FLIP. First, it was suggested that c-FLIP binds by its DED2 to DED of FADD and impedes the recruitment of procaspase-8 to the DISC, thereby precluding its activation [
19]. Then, Scaffidi and coworkers have contradicted this hypothesis and demonstrated that caspase-8 is always recruited to the DISC at the same time as c-FLIP(s/L) proteins (Scaffidi et al., 1999). Procaspase-8 forms a heterodimeric complex with c-FLIP(L), resulting in an incomplete cleavage and limited activation of caspase-8, due to the lack of c-FLIP(L) enzymatic activity. This heterodimerization prevents further apoptotic signal transduction. By competition, c-FLIP(s) over-expression can also inhibit the processing of caspase-8 at the DISC, thus blocking the activation of the apoptotic cascade. These findings reflect different functional roles of c-FLIP(L) and c-FLIP(s) in inhibiting apoptosis [
21].
TRAIL, also called APO-2L, is a member of TNF family and is mainly expressed by immune cells. It is a type II transmembrane protein with a C-terminal extracellular domain, which can be cleaved by a cysteine protease resulting in a soluble form [
22]. TRAIL can bind to five distinct receptors. TRAIL-R1 (DR4) and TRAIL-R2 (DR5), are classical death receptors and can trigger apoptosis with their functional cytoplasmic death domain (DD). TRAIL-R3 (DcR1), TRAIL-R4 (DcR2) also known as decoy receptors, as well the circulating receptor Osteoprotegerin (OPG) are not able to propagate a death signal due to a lack of a functional cytoplasmic death domain [
23]. TRAIL expressed on cytotoxic T cells and NK cells is a potent anti-tumor molecule since it has been proven to preferentially kill cancer cells in a wide variety of tumors and does not exhibit any toxicity in a majority of normal cells. However, a large number of cancers evade TRAIL-induced apoptosis and become TRAIL resistant through different mechanisms including the over expression of c-FLIP [
24]. Selective knock-down of c-FLIP(L) sensitizes tumor cells to TRAIL-induced cell death in human lung cancer cell lines [
25]. It has also been demonstrated that Withanolide E, a steroidal lactone derived from
Physalis peruviana, can highly sensitize renal carcinoma cells and other human cancer cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through rapid destabilization, aggregation and proteasomal degradation of c-FLIP proteins, confirming the key role of c-FLIP in protecting cells from death ligands mediated apoptosis [
26].
So far, except siRNAs approaches, c-FLIP inhibitors that have been studied act indirectly on c-FLIP, such as Cisplatin which induces p53-dependent FLIP ubiquitination and degradation in ovarian cancer cells [27], or Actinomycin D which downregulates FLIP(L) and FLIP(s) expression in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia [28]. Thus, the identification of molecules directly targeting c-FLIP and which are more stable than siRNA represents a new promising strategy to overcome therapy resistance. c-FLIP is structurally similar to caspase-8. Each DED of c-FLIP shares ∼25%
similarity with DEDs of caspase-8, and the C-terminus (270 amino acids) of c-FLIP is also ∼25% identical to the C-terminus of caspase-8 [
29]. Thus, due to this homology, the identification of
new compounds that selectively bind to c-FLIP versus caspase-8 and prevent its recruitment to the DISC is challenging.
Based on this rational, molecular modeling and docking experiments were set up to construct c-FLIP and caspase-8 homology models in order to find selective inhibitors targeting unique sequences of c-FLIP and not caspase-8. In vitro assays using recombinant c-FLIP(s) and FADD, coupled with in cellulo assays demonstrated the inhibitory role of these new compounds, restoring TRAIL-mediated apoptosis and selectively preventing c-FLIP/FADD interactions. Our findings suggest that blocking c-FLIP recruitment into the DISC by specific inhibitors decreases tumor resistance to death receptors mediated apoptosis and represent a new avenue for cancer treatment.
Materials and methods
Molecular modeling
- 1)
Homology modeling of DED2 domains
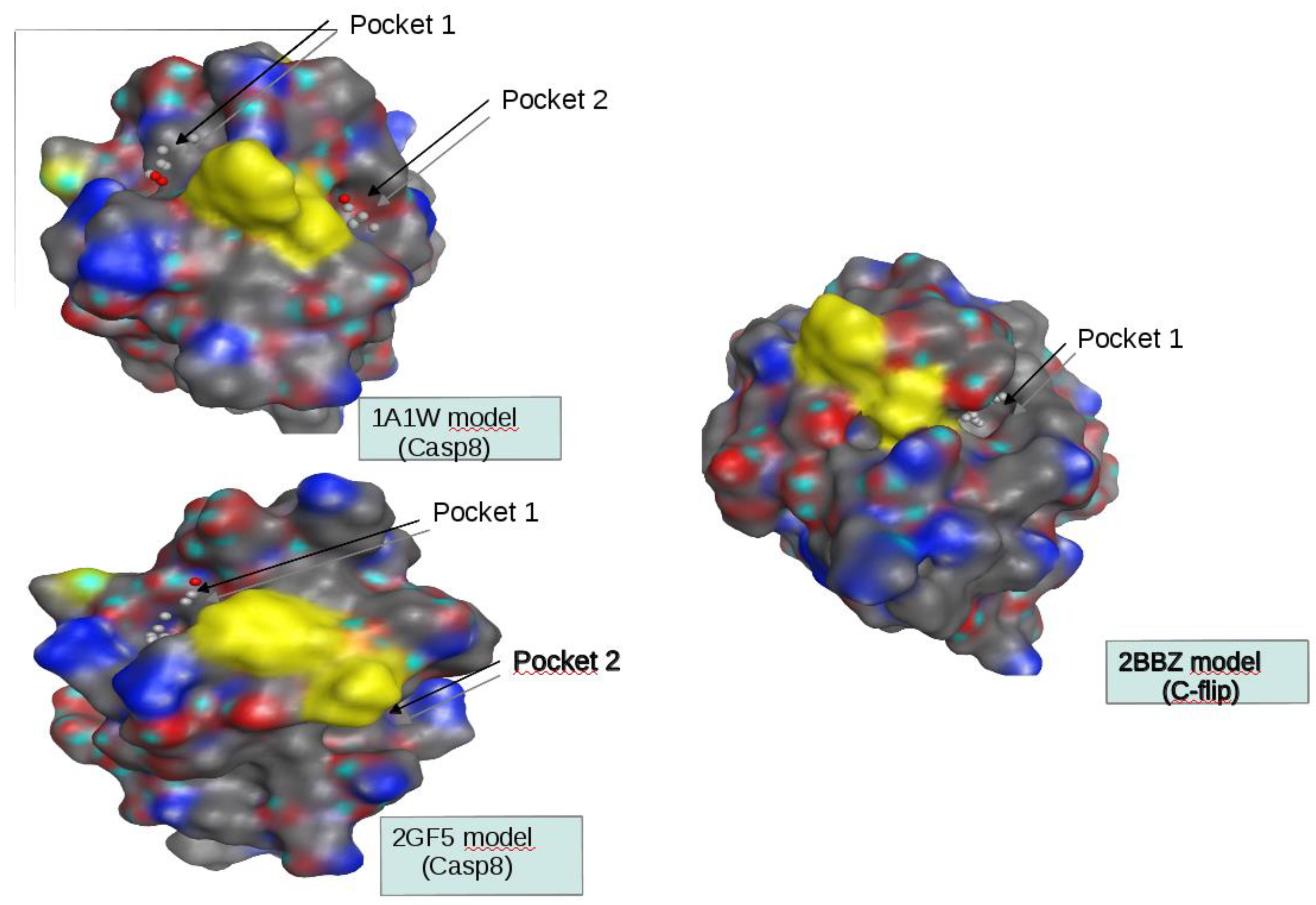
Homology models were built using MOE software (Molecular Operating Environment). First, sequences of the DED2 domains of c-FLIP and of CASP8 were extracted from the Uniprot database and used to find homolog structures in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) using the BLAST software. Three sequences showed a significant percentage of identity with the target sequences (around 30%) to perform homology modeling. Three structures of the FADD DED domain (PDB.ID 1A1W, 1A1Z, 2GF5) and three structures of two v-FLIP DED2 domains (PDB.ID 2BBR, 2BBZ, 3CL3) were identified as suitable templates for modeling the DED2 domains of CASP8 and c-FLIP respectively.
- 2)
Identification of the binding site
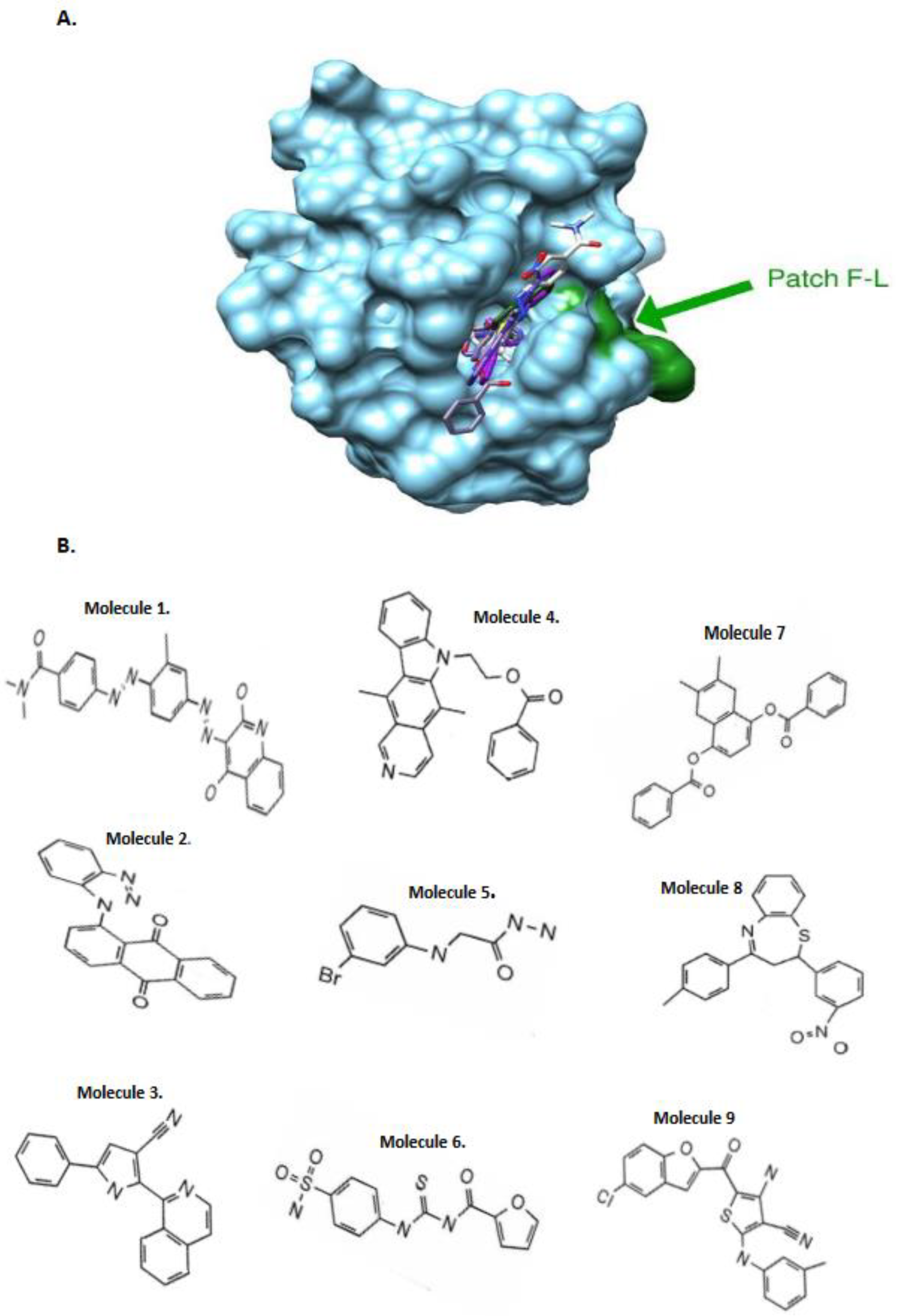
SiteFinder module of the MOE software was used to identify druggable pockets at the surface of our models and only the homology models which present such pockets at the vicinity of the F-L hydrophobic patch were retained. Two models of the CASP8 DED2 domain and one model of the c-FLIP DED2 were kept based on the PDB.ID 1A1W, 2GF5 and 2BBZ structure templates respectively.
- 3)
Docking of chemical libraries
The 1880 molecules from the NCI DiversitySet3 and extracted from the ZINC database were virtually screened on the three models (2 for CASP8 DED2 and one for c-FLIP DED2) using two docking software, AutoDock and Glide. The ZINC database provides ready-to-dock sets of purchasable molecules. The results of these two virtual screenings were combined using a consensus scoring method and a root mean square deviation (RMSD) filter.
- 4)
Consensus scoring function
In addition to the Glide and AutoDock scoring functions, the MOE GBVI/WS dG function was selected to rescore all poses of the docked ligands. Therefore, the binding modes of each docked ligand with Glide and AutoDock were assessed using four score values. The score values were normalized using the Z-score following formula:
where μ is the mean and σ is the standard deviation of the scores.
The four normalized scores were then summed up and ranked by decreasing order, the best score being the lowest ones. To keep only ligands presenting similar poses with the two docking methods, we calculated the RMSD (Root Mean Square Deviation) between the poses obtained by the two methods. The ligands which present a RMSD value higher than 2 Å were removed from the ranking.
- 5)
Hit selection
The goal of this docking study was to identify ligands that selectively bind to c-FLIP and not to CASP8. For this purpose, the best 20 screened molecules obtained on the c-FLIP target domain were compared with the best 20 molecules obtained on each CASP8 model. Molecules present in the top 20 for c-FLIP and absent in the top 20 for CASP8 models were considered selective ligands.
Cell culture
H1703 (Human non-small lung cancer cell line), mock transfected or overexpressing c-FLIP(L) cells were grown in RPMI 1640 (LONZA) culture media supplemented with 10 % fetal bovine serum and puromycin (2 µg/ml) from Sigma-Aldrich. The cells were kept in a humidified atmosphere in an incubator at 37°C and 5 % CO₂. H1703 were a kind gift from O. Micheau (INSERM, DIJON FRANCE).
Reagents and antibodies
KillerTRAIL (human recombinant) were purchased from Alexis Biochemicals. The nine most highly selective molecules targeting cFLIP were obtained from NCI–DS&CB (National Cancer Institute-Drug Synthesis and Chemistry Branch, USA). For western blotting (WB) experiments, we used the following antibodies: anti-FLIP antibodies DAVE2 and NF6 (ADIPOGEN), caspase-3 (8G10; OZYME), PARP (Asp214, 19F4; OZYME), caspase-8 (1C12; OZYME), anti-MBP (New England Biolabs), anti-His (C-ter) (INVITROGEN). Anti-His(ab81663) was used to immuno-precipitate the DISC complex, and the following antibodies: anti-Flip (DAVE II, Adipogen), anti-FADD (556402,BD), anti-casp8 (5F7,EnzoLife), anti-DR4 (1139, ProSci), anti-DR5 (3696, Cell Signaling were used for WB analysis. Anti-rabbit and anti-mouse HRP linked secondary antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), β-actin (Sigma Aldrich) were also used.
Flow cytometry analysis
Apoptotic cell death was confirmed by flow cytometry (cytoFLEX, Beckman Coulter) using Annexin V-PE Kit, according to the manufacturer’s instructions (BD Biosciences). In brief, H1703 cells were seeded at a density of 2 x 10⁵ cells/well in 24 well plates and incubated for 24 hours. Cells were then treated, as indicated in figure legends, for 18 hours. Thereafter, cells were collected, washed and re-suspended in 1X Annexin-V binding buffer. Annexin-V- PE was added to the cells and left 20 mins at room temperature in the dark. 7-AAD dye was added and Flow cytometric analysis was performed in the final step.
Recombinant protein production and purification
Full-length c-FLIP(s) and FADD were synthesized (Genscript, USA), and subcloned respectively into pET24b(+) (Novagen) and pMAL-C2X (New England Biolabs) expression vectors. The resulting constructs enabled the fusion of the corresponding protein with a C-terminal polyhistidine peptide, or a N-terminal Maltose Binding Protein (MBP).
All proteins were expressed in 1 mM IPTG-induced Rosetta transformed bacterial cells with the expression vectors. After 18 hours of induction at 37°C, cells were harvested and pellets were resuspended in a lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM NaCl, pH 8, 0.1% Triton) in addition to 0,1 mg/ml lysozyme and 1mM PMSF (Phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride) and incubated for 20 minutes at 4°C. Cells were then lyzed by freeze-thaw cycles, followed by sonification. Lysate was centrifuged at 34000 g for 20 minutes at 4°C, and supernatant was loaded on chromatographic media. HisPurTM Ni-NTA Chromatography Cartridge 1 mL (Thermo Scientific) or MBPTrapTM HP 1 mL (GE Healthcare) were respectively used for purification of c-FLIP(s) or FADD, following columns manufacturer procedures. Protein purity was assessed by SDS-PAGE analysis and concentrations were qualified using the Bio-Rad protein assay based on the Bradford dye-binding method.
Pull-Down binding assay
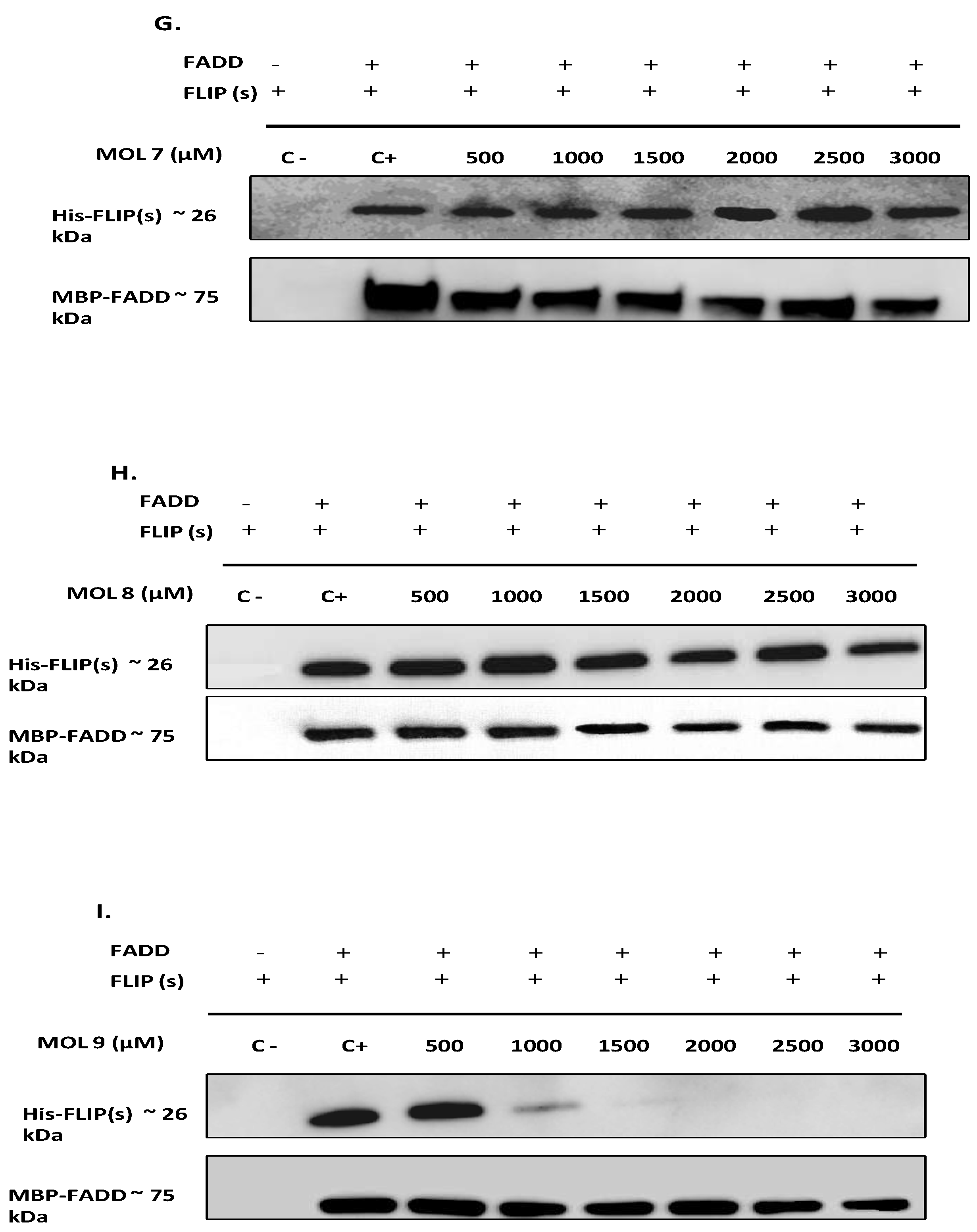
The purified proteins were mixed at a ratio of 1:7 for FADD:FLIP(s), equivalent to 0,7 mg/ml for FADD and 6,8 mg/ml for FLIP (26µM and 261 µM respectively) and incubated for 18 hours at 4°C with 0-3000 µM concentration range of each inhibitor. Then, the incubation mix was loaded on a MBPTrap chromatography cartridge and purified using 10 mM maltose as eluent. Negative controls were also performed without FADD. Unbound and eluted samples were used for Western Blot analysis.
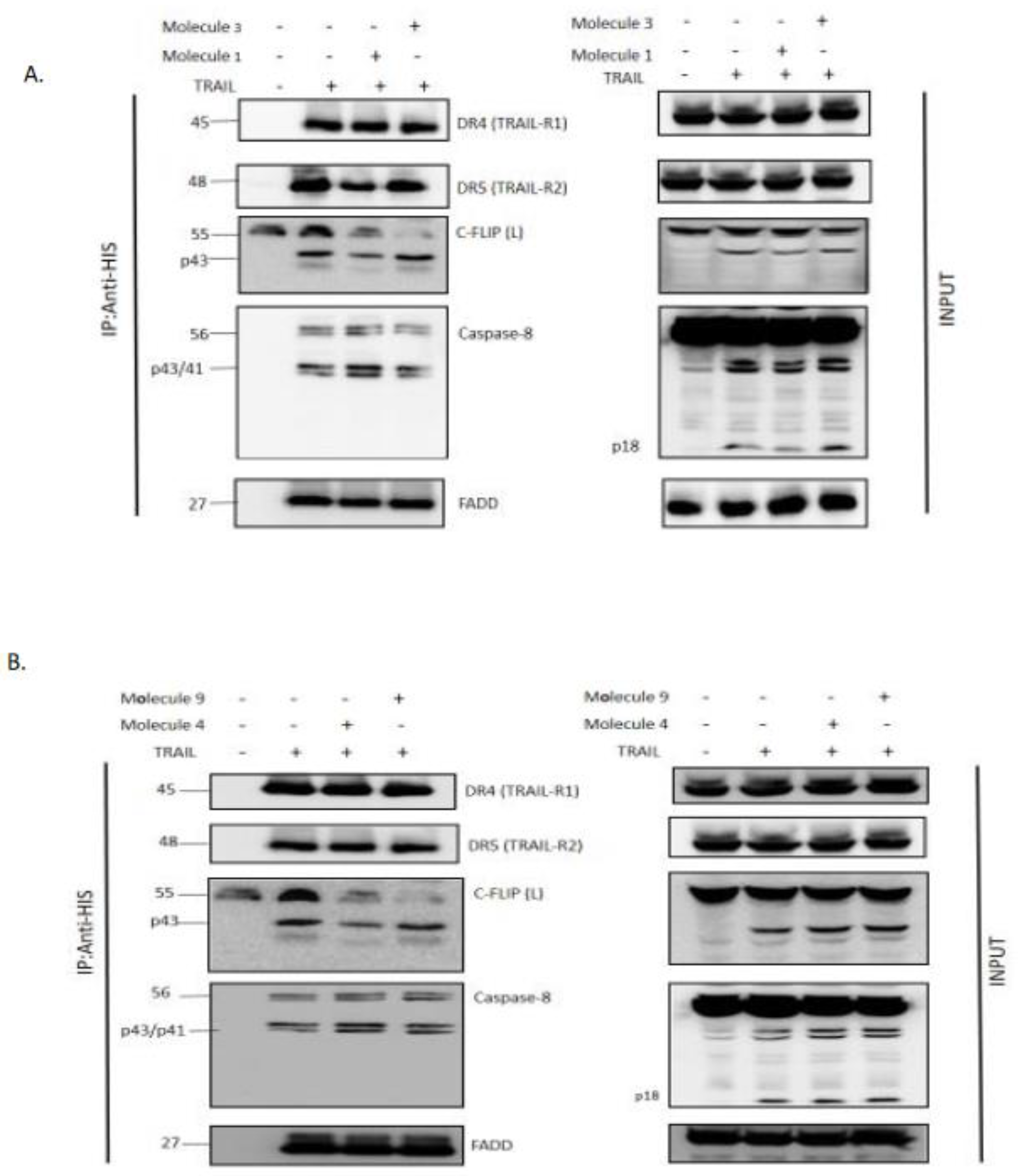
DISC Immunoprecipitation
For DISC Immunoprecipitation, 50.10⁶ H1703-FLIP(L) cells seeded in F175 Flasks were incubated overnight. The next day, cells were collected in 10 ml of media, pre-treated with seletected Molecules 1,3,4 or 9 (500 µM) for 2 hours and then stimulated with 1 µg/mL His-TRAIL for 20 minutes. Reaction was blocked with cold PBS, and cells were lysed in 1 mL of IP-Lysis Buffer (1% NP40, 20 mM TRIS HCL Ph 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 10 % Glycerol) containing COMPLETE Inhibitor of Proteases cocktail (Roche), for 30 mins on ice. Lysates were cleared by centrifugation at 15000 RPM, 20 minutes at 4°C. All supernatants were pre-cleared with 50 µL of Sepharose 6B (Sigma 6B100) for 1.5 hour at 4°C on a wheel, and then centrifugated at 1500 RPM at 4°C for 15 seconds. To analyze the DISC complex, supernatants were collected and incubated overnight at 4°C with 50 µL Protein G beads and coupled with 3 µg anti-His tag antibody (abcam ab81663) supplemented with 1 µM of caspase inhibitor Z-VAD. After immunoprecipitation (IP), beads were washed 4 times with IP-lysis buffer (without inhibitor of proteases) and eluted with 120 µL of LDS buffer with DTT. Samples were left 30 minutes at room temperature, then heated 5 minutes at 95°C before WB analysis.
Western blot analysis
Pull-down eluted samples were heated 5 minutes at 99°C with Laemmli Buffer and then passed on 4%-12% gradient SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membrane (GE Healthcare). To evaluate enzymatic activity, treated cells were lysed in RIPA buffer at 4°C and centrifuged at 15 000 rpm for 20 minutes. Protein concentration was then determined using Bradford assay. Equal amounts of proteins (50µg) were boiled for 5 minutes with 1X LDS sample buffer and then loaded on a 4%-12% SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. Membranes were blocked by 5% non-fat milk in PBS-TWEEN 20 (0.1%) for one hour at room temperature and then incubated with different primary antibodies for one to two hours at room temperature. Membranes were then washed by PBS-TWEEN and incubated for 1 hour with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies. Proteins bands were visualized by chemoluminescence protocol ECL (Thermo Scientific).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with the Student t test.
Discussion
TRAIL’s ability to specifically kill tumor cells
in vitro and
in vivo makes this death ligand or its death receptors promising anticancer agent or target which exhibited potent anticancer activity in several preclinical studies [
41]. However, a number of primary cancer cells are resistant to TRAIL monotherapy. This resistance can occur at the death receptor level via the upregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein c-FLIP [
42]. c-FLIP is also a potent resistance factor against other TNFα superfamily members and chemotherapeutic drug-mediated apoptosis [
43]. c-FLIP has been found to be overexpressed in many types of malignancies, and its overexpression is associated with poor prognosis and tumor progression due to its involvement in the inhibition of the apoptotic process [
44]. The three known variants of c-FLIP are able to interfere with the FADD/caspase-8 interaction, thus inhibiting caspase-8 recruitment into the DISC and blocking its activation which ultimately lead to inhibition of apoptosis [
14]. Because c-FLIP upregulation prevents the apoptotic machinery and leads to cancer promotion, its silencing has been shown to restore apoptosis. Therefore c-FLIP is considered as an important promising target in cancer therapies. In this context, we aimed to identify new inhibitory molecules specifically targeting c-FLIP and combine them with TRAIL in order to restore apoptosis in cancer cells. It was indeed previously reported in several studies that a combination of targeted anti-cancer therapies with TRAIL sensitizes resistant cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis [
45,
46].
Because of the high structural homology to caspase-8 [
14], c-FLIP is a difficult molecule to target since small molecules able to block its recruitment into the DISC may also inhibit caspase-8 recruitment, thereby preventing apoptosis. Therefore, small molecules selectively targeting c-FLIP without affecting caspase-8 functions are required. The challenge of our work was to identify new molecules that can selectively bind to c-FLIP and inhibit its interaction with FADD within the DISC, without affecting caspase-8 binding. We aimed to construct
in silico DED2 domains of c-FLIP and caspase-8 based on homology models as their human crystallographic structures were not established. Searching for similar target sequences, Yang and collaborators [
47] showed that v-FLIP DED2 and FADD DED were structurally similar to DED2 of c-FLIP and caspase-8 respectively. After having successfully generated a 3D-model homology domain of c-FLIP and caspase-8 DED2 and identify a potential unique druggable pocket in c-FLIP (
Figure 1, 2), we initiated
in silico screening and docking experiments of 1880 compounds from the NCI database targeting the homology model structures of c-FLIP and caspase-8 . This large set of chemical molecules led us to select compounds that only bound to c-FLIP and not caspase-8. These molecules selectively target and bind to DED2 of c-FLIP and not caspase-8.
Among the DED2-c-FLIP binding molecules, we selected nine compounds exhibiting the most potent binding affinity toward DED2 of c-FLIP versus DED2 of caspase-8. Further analyses were required to assess whether these new molecules were able to inhibit DED-FADD/DED2-cFLIP interaction. FADD is considered as the nucleus of the DISC assembly and responsible for initial caspase-8/-10 and c-FLIP recruitment through homotypic DEDs interactions [
48]. FADD is composed of two distinct domains: DD (Death Domain) responsible for receptor engagement, and DED domain which contains a face-exposed hydrophobic patch, conserved in all other DEDs proteins, and thought to be crucial for DED-DED interactions with caspase-8 and c-FLIP [
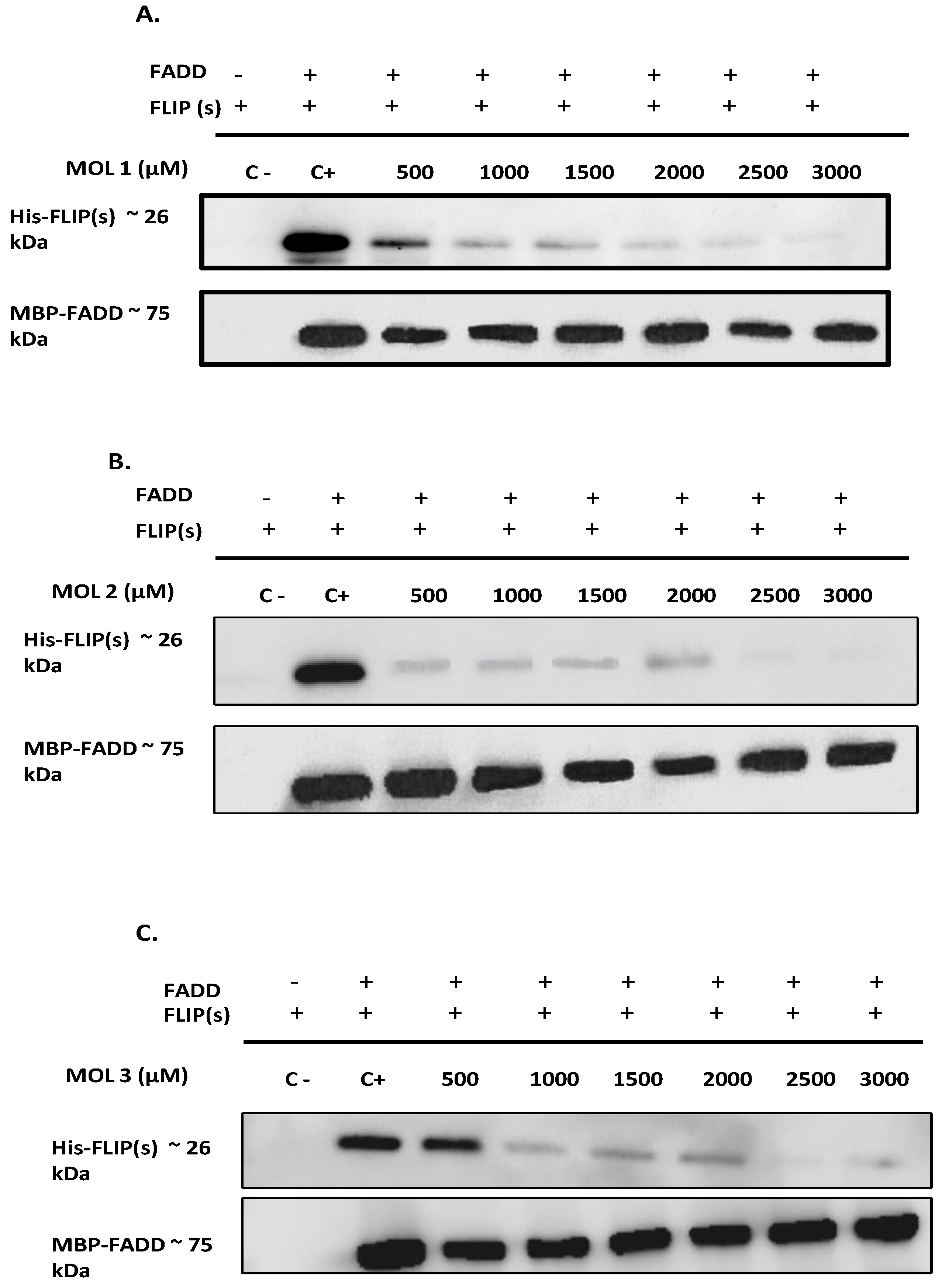
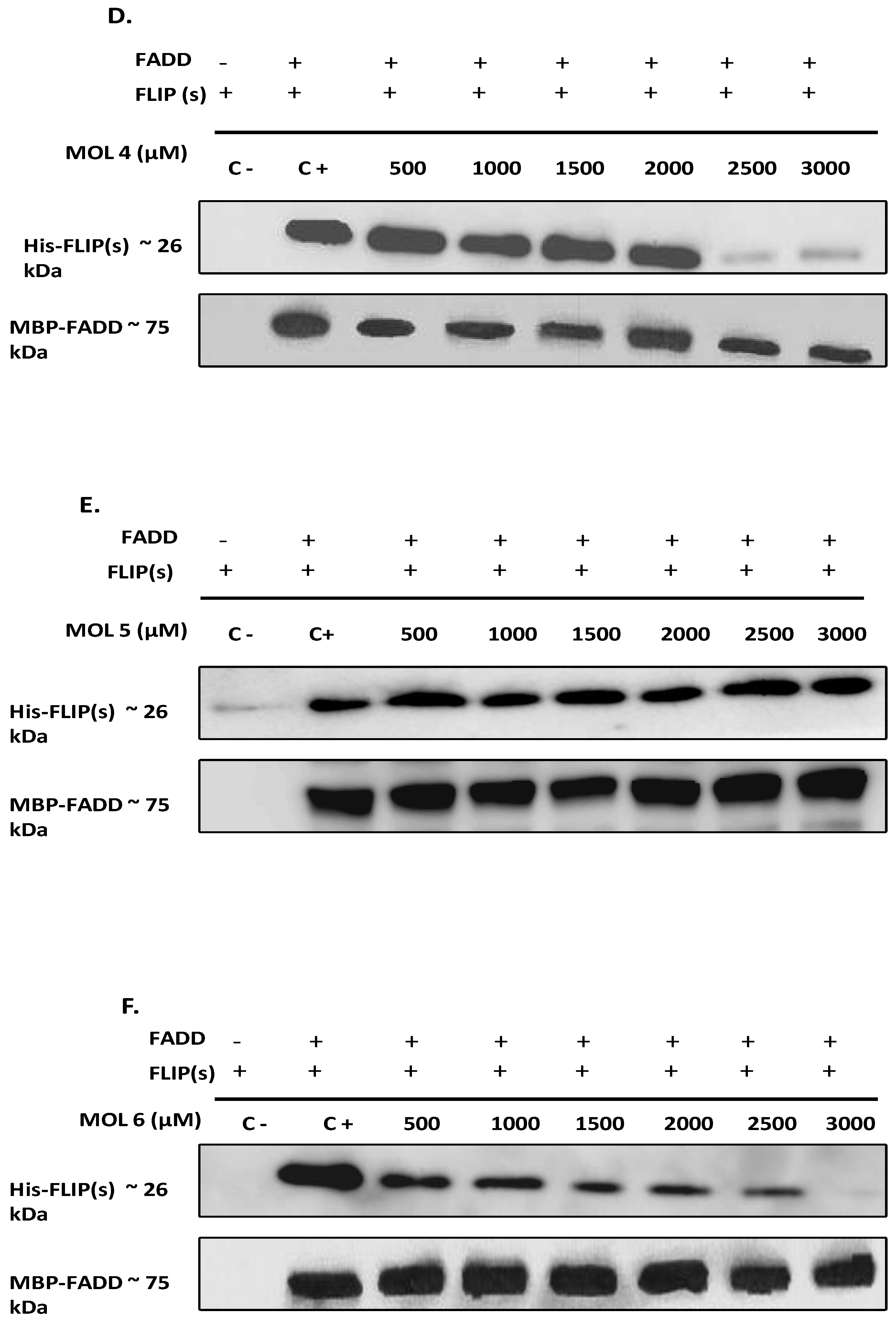
49]. Therefore, to elucidate the effect of the nine selected molecules, we investigated the interactions between the recombinant human FADD and c-FLIP(S) full length. The long form c-FLIP (L) was indeed impossible to produce and purify due to its rapid precipitation and low stability. Here we showed that Molecules 1, 2, 3, 4 and 9 were able to inhibit FADD-c-FLIP (S) interaction in a pull down assay (
Figure 3 A-D and I). In addition, molecules 1, 3, 4 and 9 were able to prevent FLIP recruitment into the DISC using the Immunoprecipitation assay, confirming our previous results.
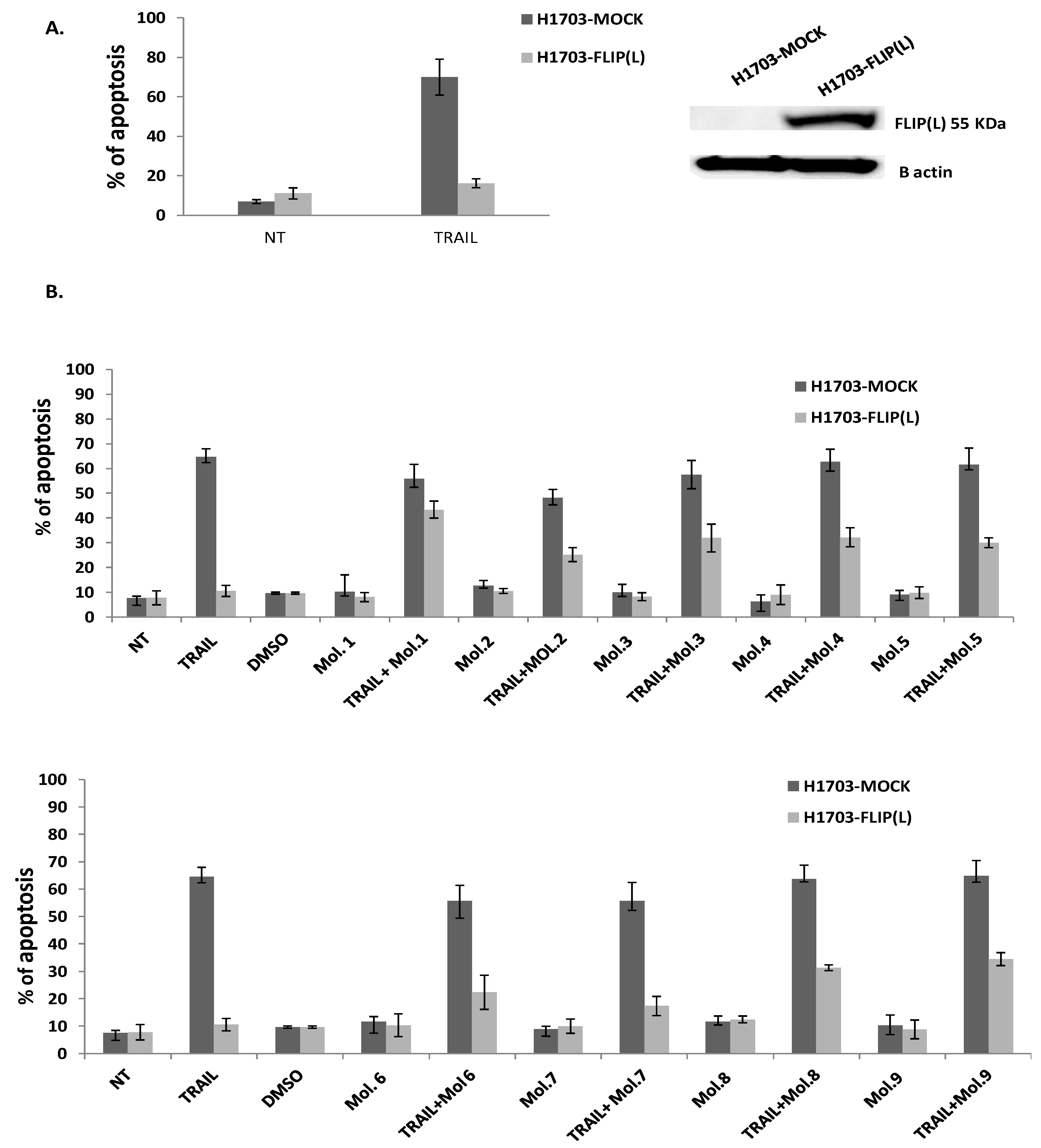
We further assessed whether these 9 chemicals could inhibit c-FLIP binding to FADD in a cellular model. It has been reported that c-FLIP is highly expressed in Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) where its high cytoplasmic expression correlates with poor prognosis. Moreover, c-FLIP inhibits anticancer drug-induced apoptosis in preclinical models of NSCLC [
50]. Thus, we overexpressed the long form of c-FLIP (L) protein in H1703 cancer cells (NSCLC) and we treated these cells first with TRAIL alone. As observed in
Figure 5A, an ectopic expression of c-FLIP (L) inhibits TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. In contrast, when c-FLIP (L) is absent, cancer cells were sensitive to TRAIL, confirming the primary function of c-FLIP as an inhibitor of apoptosis and a possible biomarker of tumor resistance. As the activity of TRAIL is prevented by c-FLIP overexpression, targeting c-FLIP by our new molecules may restore TRAIL function, as it is broadly referenced in several studies showing that c-FLIP silencing sensitizes tumor cells to death ligands induced apoptosis [
51]. To evaluate the efficiency of our new selected molecules in inhibiting c-FLIP function, a combination of them with TRAIL was assessed and showed a remarkable enhancement of the apoptotic level in c-FLIP-overexpressing cells; while the same molecules exhibit no significant cell death when administered alone compared to non-treated cells (
Figure 5B). These findings revealed that the new identified molecules are distinctly efficient against c-FLIP and help to restore apoptosis in TRAIL-resistant cells, while they are not cytotoxic alone.
Molecules 1, 3, 4 and 9 are able to restore apoptosis when combined with TRAIL (
Figure 5B), confirming their binding affinity to c-FLIP (
Figure 3) and their role in preventing c-FLIP recruitment into the DISC (
Figure 4).These molecules are poorly used in other studies but some results showed that they target and inhibit the following enzymes: Protein-tyrosine phosphatase (by molecule 1), MAP kinase ( by molecule 3 and 4), and matrix metalloproteinase (by molecule 9). In contrast, while molecules 2 and 6 showed an inhibitory role of FADD/c-FLIP interaction in the molecular assay (
Figure 3B, F), they were poorly restoring apoptosis in resistant cancer cells overexpressing c-FLIP (
Figure 5). Such results indicate that these two molecules may lose their binding potential to c-FLIP within the cell and they might require further chemical and structural modifications in order to enhance their binding affinity to c-FLIP. Surprisingly, we found that molecules 5, 7 and 8 could not prevent FADD/c-FLIP interaction in the pull-down assay (
Figure 3E, G, H). In contrast they were able to sensitize resistant cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis, especially molecule 8 which enhanced apoptosis by more than 30%, with no cytotoxicity by itself. This evidence led us to conclude that these three molecules are not selective to c-FLIP and they may target other signaling pathways contributing to cell death.
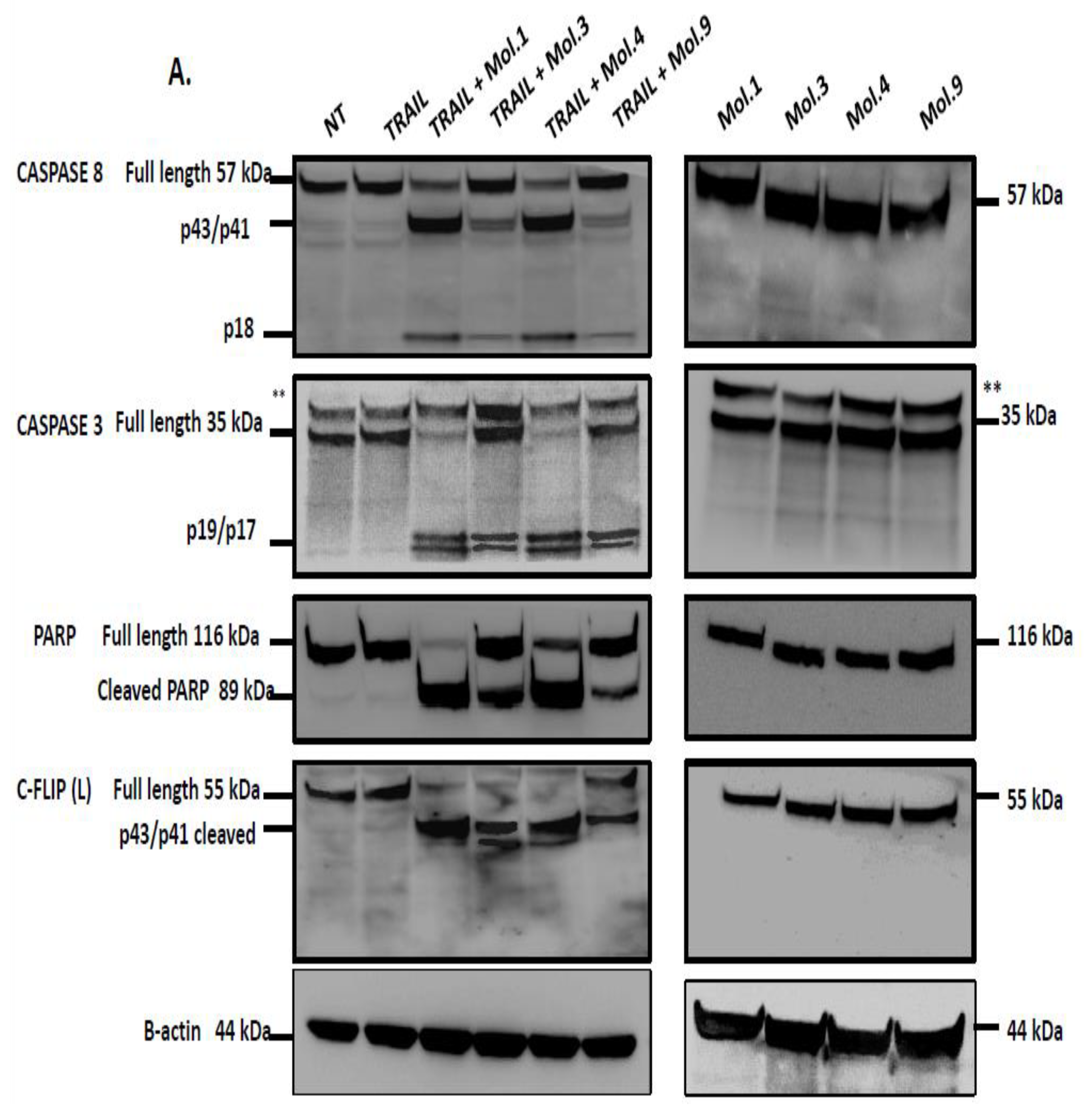
c-FLIP competes with caspase-8 recruitment into the DISC and prevents its activation, thereby blocking downstream caspases activation and apoptotic pathway [
52]. Downregulation of c-FLIP using siRNAs sensitizes cells to caspases-dependent apoptosis [
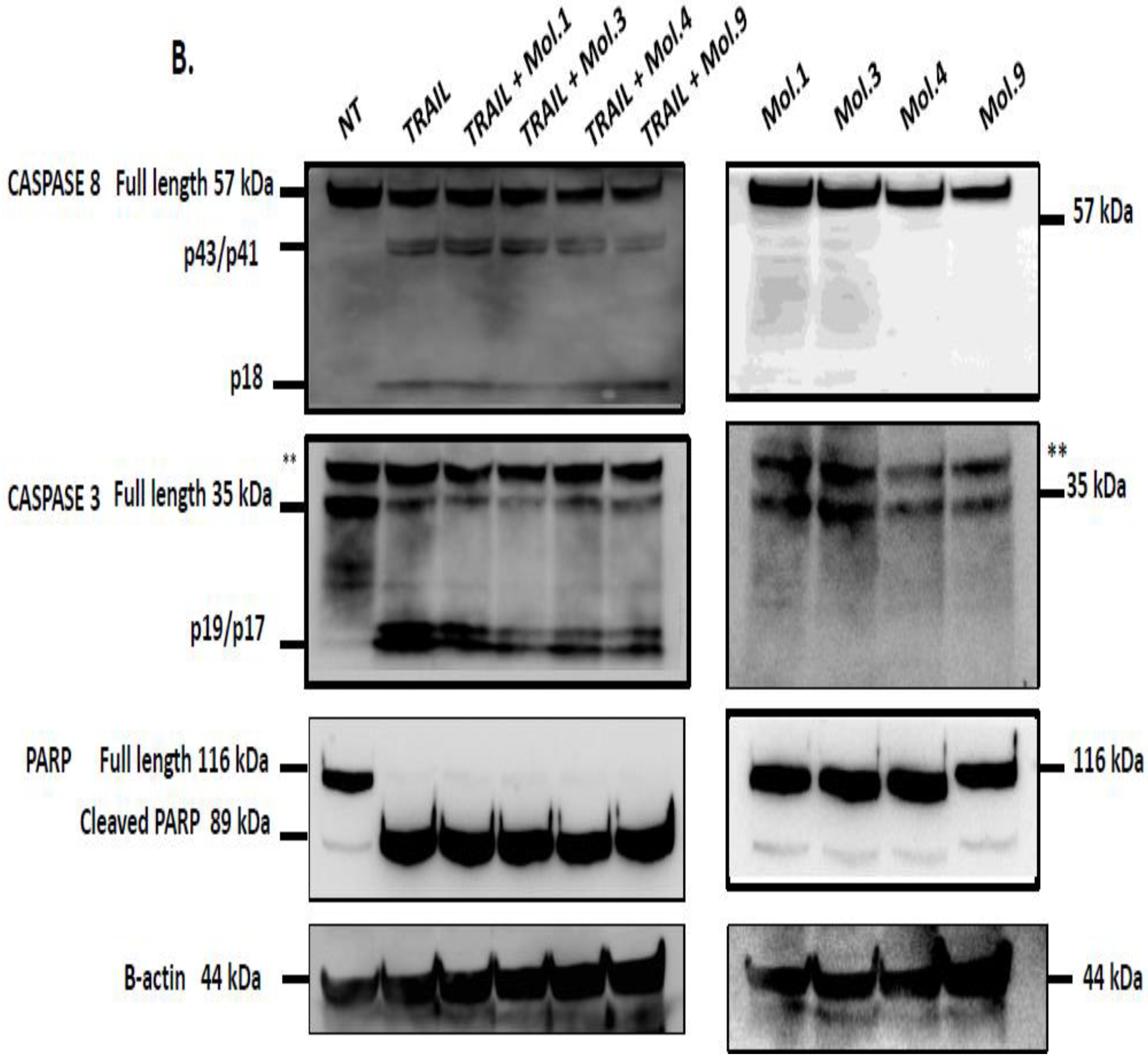
53]. In this study, we investigated caspases activity after combination of TRAIL with c-FLIP-inhibitory molecules to evaluate the restoration of extrinsic apoptosis. Our data indicates that caspase activity is blocked when c-FLIP is active and recruited into the DISC (
Figure 6A). However, inhibiting c-FLIP function with these new molecules enhances caspases-8, -3 and PARP cleavages and promotes TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Moreover, when cells overexpressing c-FLIP are treated with the molecules alone, no caspases activation and PARP cleavage have been observed indicating that the administration of these compounds is safe and does not induce any cytotoxicity. Similarly, when cells lacking c-FLIP (L) were treated with these compounds alone, we did not observe any caspase cleavage, suggesting that these molecules exhibit no side effect on cells with no expression of c-FLIP.
In conclusion, we report that c-FLIP expression is a relevant biomarker of cancer resistance in general and for the anticancer agent TRAIL. In this current study, we have demonstrated that c-FLIP function can be inhibited by new small molecules while caspase-8 remains unaffected. Inhibition of c-FLIP interaction with FADD precludes c-FLIP from its recruitment into the DISC and allows caspase-8 binding to FADD, promoting TRAIL-induced apoptosis in resistant cancer cells. This combination therapy of TRAIL with these c-FLIP targeted new agents could be a promising approach to eradicate tumors with c-FLIP upregulation. However, maximizing the binding affinity of the most efficient molecules by structural modifications are needed in order to restore a higher level of apoptosis in tumor cells.