1. Introduction
The Swiss Personalized Health Network (SPHN) [
1] is a research infrastructure initiative focused on establishing an enabling framework to support the sharing of health-related data in accordance with the FAIR principles [
2]. At the heart of this initiative is the SPHN Semantic Interoperability Framework, a comprehensive system that provides semantic artifacts for the representation, validation, and statistical analysis of health data. Additionally, a tool stack is in place to support researchers and hospitals in effectively utilizing this technology. Built on the Semantic Web stack, the framework leverages Resource Description Framework (RDF), Web Ontology Language (OWL), Shape Constraints Language (SHACL), and SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language (SPARQL) for its formalization. This foundation ensures a seamless and standardized approach to handling health-related information.
The 2023.2 release of the SPHN RDF Schema facilitates the semantic representation of clinical data such as diagnoses, routine clinical measurements, and standard lab tests [
3] and already provided partial coverage for clinical omics data tailored to a restricted set of specific use-cases. For instance, genomic information is addressed through overarching concepts designed for representing basic genomic variations, including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Additionally, it incorporates simple concepts for representing a chromosome, genes, transcripts, and proteins. However, these existing concepts only cover a fraction of the vast genomic, and more broadly the omics landscape. To comprehensively address the diverse needs of SPHN National Data Streams [
4], particularly in domains such as oncology, pediatric care, and infectious diseases, there is a necessity to expand the SPHN RDF Schema. This expansion will be a key focus in the upcoming 2024.1 release (which will be released in Jan 2024), ensuring that the SPHN RDF Schema aligns with the evolving demands in this critical area.
Data models for capturing (gen)omics data, for instance those of nucleotide repositories such as European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) [
5], European Genome-Phenome Archive (EGA) [
6] and Genomic Data Commons [
7], are already well known, but have their own drawbacks. They are either simple catch-all data models with little semantics, too application-centric, or more focussed on study and attribution metadata. Ontologies such as the Ontology for Biomedical investigations (OBI) [
8] and Semanticscience Integrated Ontology (SIO) [
9] offer high expressivity and ontological rigor. However, they leave room for different ways of representing information and require a solid ontology engineering background. FAIR Genomes [
10] broadly fits our use case, but it is too specific for genomics, tailored more towards the data capture side than the optimal data structure, and designed to fit a broad range of data capture applications thereby staying generic.
Here, we present a genomics concept model that covers all aspects of the (clinical) NGS workflow and metadata. This model builds upon the existing SPHN RDF Schema and follows a generalized design to allow for extension to other omics fields. It aligns with existing ontologies and vocabularies, and mirrors the design of common domain data models where applicable.
2. Methods
First, a workshop was organized to capture the needs and requirements of stakeholders and map the (gen)omics data domain. Participants from 12 institutions including clinicians, researchers, bioinformaticians, data managers, and leadership, from Swiss university hospitals, technology institutes, and the genome center, collaboratively identified the most relevant concepts, relations, and attributes, as well as the process flow for omics experiments with a focus on genomics. This served as input for follow-up interviews with each national data stream, where stakeholders clarified their use cases and domain, and presented example data for each use case. All acquired information about the data domain and (gen)omics workflows was compiled into a ‘statements document’, i.e., a document that lists what was assumed to be true about the domain as simple statements, organized per topic. Stakeholders iteratively provided refinements until consensus was reached.
A review was performed of common (gen)omics data models from nucleotide repositories and platforms, as well as biomedical ontologies and vocabularies, to evaluate whether these could be (partly) reused for intended use cases, requirements, and data.
The final model was validated at a second workshop where participants scrutinized it by applying it to example data of their use cases.
The concept set was formalized using the SPHN Dataset template [
11]; SPHN Schema Forge [
12] was used to validate the resulting dataset, as well as to generate the corresponding RDF Schema, SHACL validation rules, and SPARQL queries [
7].
2. Results
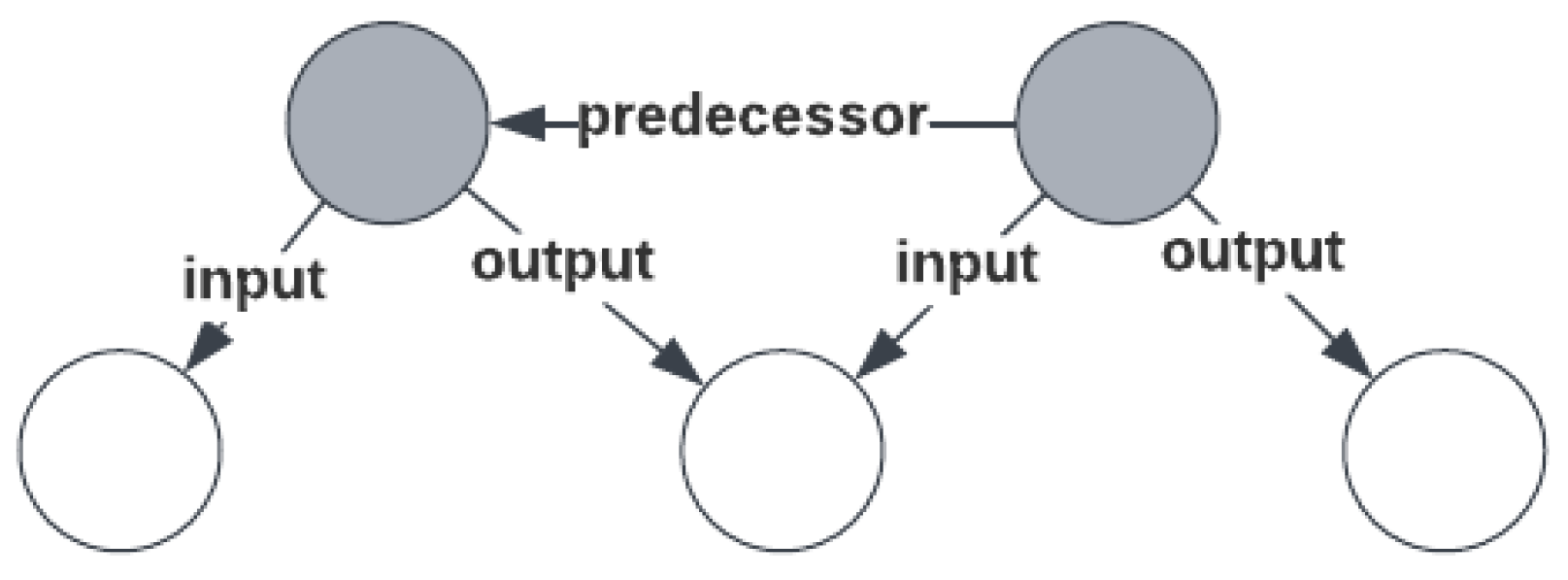
From literature research and the initial workflow that was created in the first workshop, it became clear that omics research could be modeled as a series of consecutive steps, where the output of one step may serve as the input of another. For example, a sample or data may be input for sample or data processing steps. In
Figure 1, the order of individual steps is indicated by relating steps that directly precede each other with a ‘predecessor’ relation, forming a chain or sequence of steps. The material or data that is produced and subsequently produced between preceding steps is indicated using an output or input relation, respectively, but is optional, since this information is not always available or relevant (it is implied). This pattern forms the backbone of the model.
Each step in the omics workflow is a process concept that is composed of essential metadata concepts about that process. The three top-level concepts for representing the omics workflow are ‘Sample Processing’, ‘Assay’, and ‘Data Processing’. Here, the name ‘Assay’ was favored over ‘Experiment’ since the latter has ambiguous interpretation, and is used differently in several data models in the same domain. The ‘Sample Processing’ concept is composed of zero or more input and/or output ‘Sample’ concepts, while the ‘Data Processing’ concept is composed of zero or more input and/or output ‘Data File’ concepts. The ‘Assay’ concept is composed of zero or more input ‘Sample’ concepts and zero or more output ‘Data File’ concepts. Note that both top level concepts ‘Sample Processing’ and ‘Data Processing’ and their descendants may be repeated to express a sequence of processing steps. The documents describing these concepts are available at the SPHN Interoperability Framework Gitlab repository [
13].
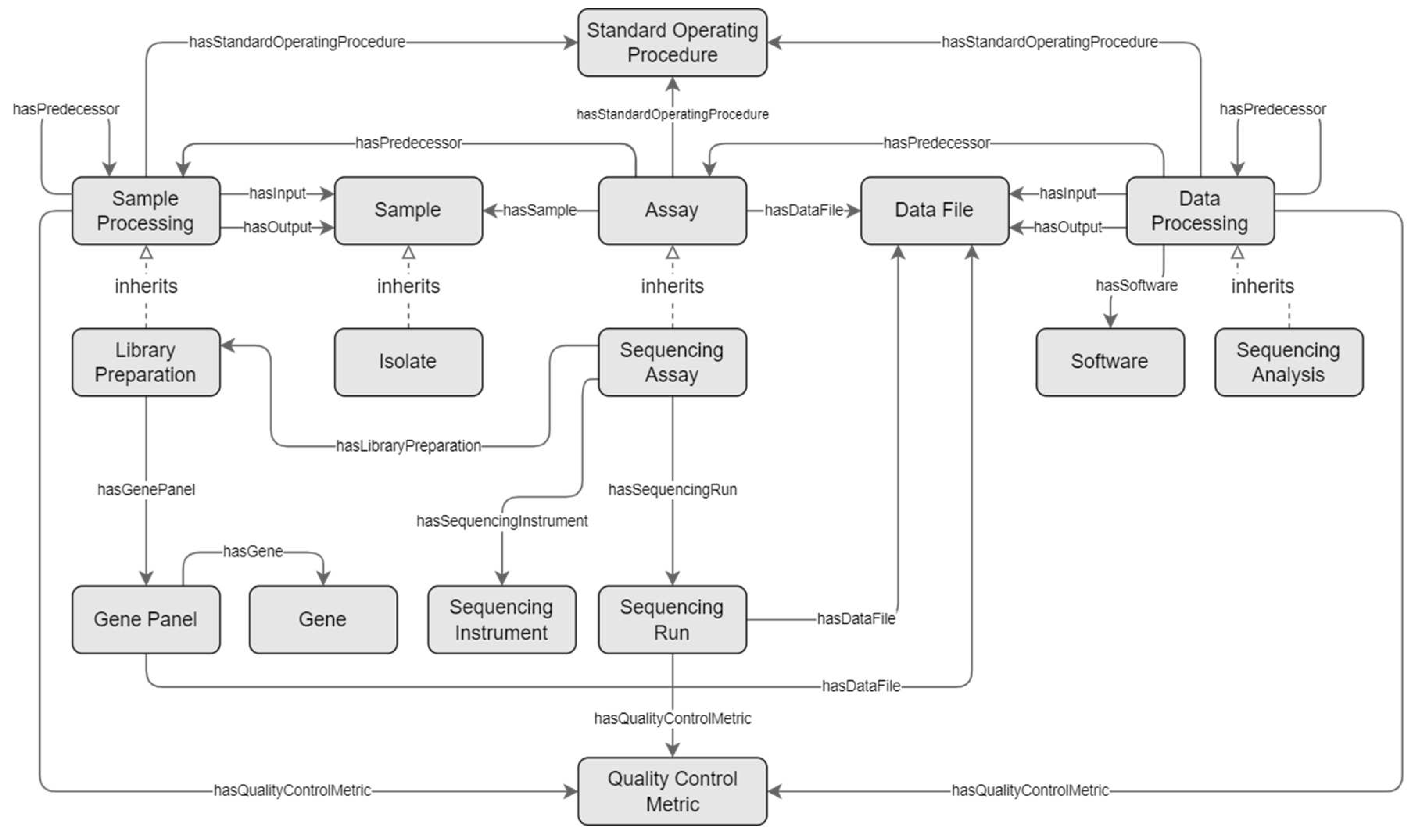
For the genomics field, special concepts are introduced that derive from these generic concepts: ‘Library Preparation’ derives from ‘Sample Processing’, ‘Sequencing Assay’ from ‘Assay’, and ‘Sequencing Analysis’ from ‘Data Processing’. Derived concepts inherit every ‘composedOf’ from their more generic counterpart, and may be consecutively repeated in a similar manner. The excerpt of the schema is presented as a diagram in
Figure 2 and described in the paragraphs below.
Central to the genomics workflow is the sequencing assay. The ‘Sequencing Assay’ concept is composed of essential metadata concepts, representing the sequencer (‘Sequencing Instrument’), library preparation (‘Library Preparation’), intended read length and depth, and zero or more runs (‘Sequencing Run’). The ‘Sequencing Run’ concept represents the actual execution of the assay, and holds information that may vary per run, such as read count, average insert size, average read length, and optional quality control metrics (represented via the ‘Quality Control Metric’ concept).
The ‘Library Preparation’ concept is a special type of ‘Sample Processing’ that is part of a ‘Sequencing Assay’. It holds information on the library preparation kit, target enrichment kit, and intended insert size, and, in case a gene panel kit is used as target enrichment, information on the gene panel’s focus genes. Any other processing steps that precede an assay’s library preparation may be registered using the ‘Sample Processing’ concept.
Following the sequencing assay, there are one or more data processing steps that manipulate the output of the assay. These are represented by the ‘Sequencing Analysis’ concept, a specialization of ‘Data Processing’, that is composed of an optional reference genome.
The model further provides utility concepts with general applicability. For instance, ‘Standard Operating Procedure’ concept was created to provide information about the prescribed step-by-step procedure that was followed to conduct experimental procedures such as sample processing, assays, and data processing. In addition, the ‘Quality Control Metric’ concept holds information about the value of certain quality control metrics that are relevant for these processes, such as the ‘Phred quality score’ for DNA sequencing.
The ‘Isolate’ concept is a specialization of the ‘Sample’, with a property to indicate the isolated organism, which is relevant for pathogen surveillance research.
Where applicable, concepts are aligned to terms and classes from common public domain terminologies, such as SNOMED CT and OBI, thereby facilitating semantic interoperability. For instance, the ‘Assay’ concept has a meaning binding to OBI’s ‘assay’ class (OBI:0000070), while ‘Isolate’ has a meaning binding to SNOMED CT’s ‘Microbial isolate specimen (specimen)’ concept (SNOMED:119303007). In addition, selected subsets or branches from common public terminologies are imposed as value sets for most nominal attributes. For instance, the type of sequence analysis is indicated by descendants of EDAM’s [
14] ‘Analysis’ operation, or similar.
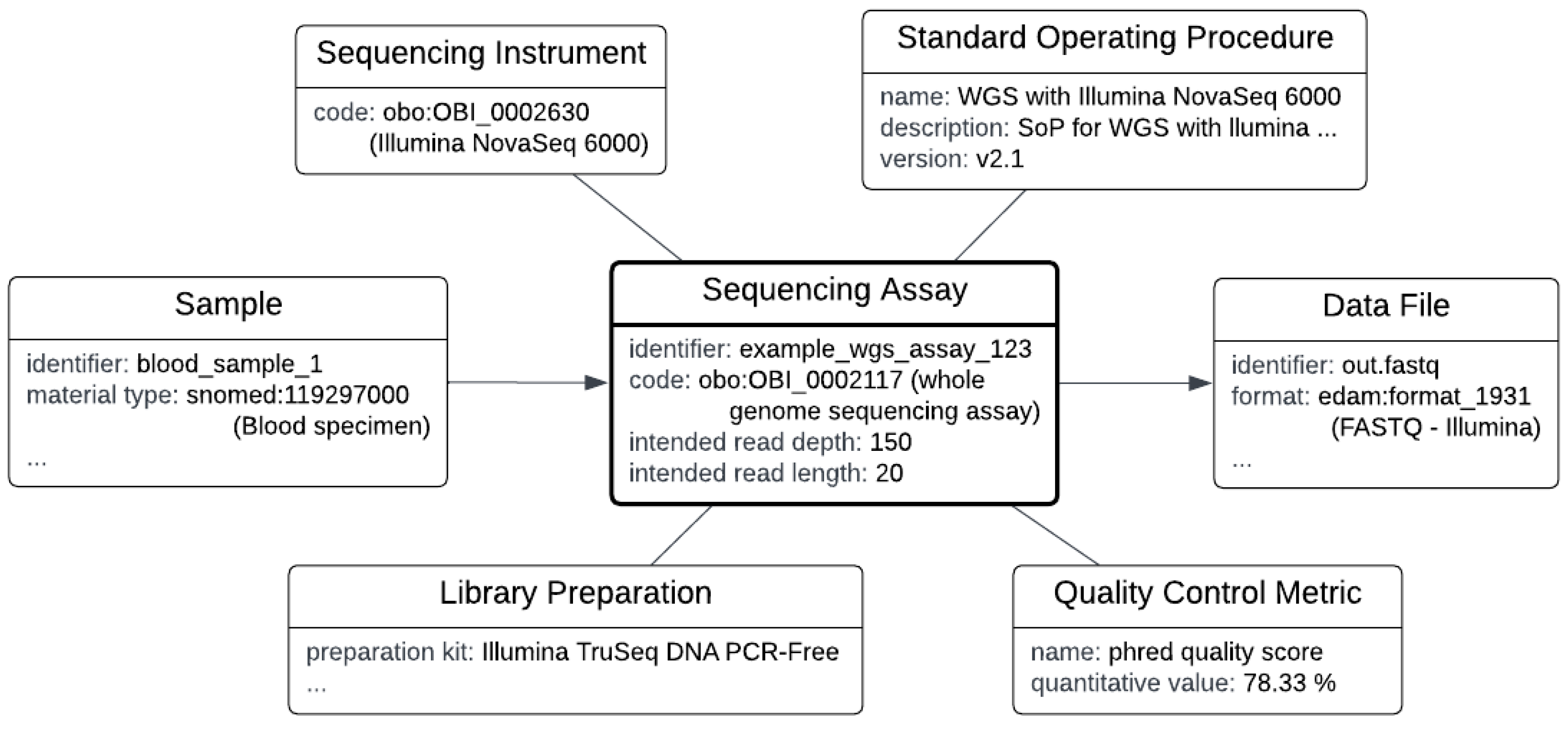
The diagram in
Figure 3 visualizes an example instance of a sequencing assay and related metadata. Listing 1 gives an RDF representation of the same example; the full RDF in Turtle syntax is available at [
15]. Note that, as with other procedure concepts, many of the composite concepts are optional and may be omitted in case this data is not known or not relevant. For instance, a ‘Standard Operating Procedure’ may not be known or shared, or may be trivial (
i.e., the operating instructions by the vendor of a platform). Note that each run produces its own data file(s), which may be selected or discarded as input for data analysis, based on quality metrics of the run.
|
Listing 1. Example instantiation in RDF of a whole genome sequencing assay and related metadata. |
  
|
An example of how to express the genomics workflow as a sequence of processes is visualized in
Figure 3, with the corresponding RDF representation in Listing 2. Some properties have been left out for brevity. While this example represents a typical genomics workflow, the same pattern is applied for other omics experiments.
The genomics extension, including corresponding SPHN RDF Schema, SHACL shapes, and SPARQL queries, is distributed as part of the 2024.1 release, and is available for download at the SPHN Interoperability Framework Gitlab repository [
13].
3. Discussion
A genomics semantic data model was developed that builds on the SPHN schema and follows a design that makes it applicable to other omics domains. The model covers clinical use cases from the SPHN National Data Streams including omics data from oncology, pediatric care, and pathogen surveillance and others at Swiss University Hospitals and research institutions. It aligns with common biomedical terminologies such as SNOMED CT, OBI, and GENEPIO, and mirrors the structure of existing domain models such as FAIR Genomes where possible. For instance, the pattern of expressing the investigative workflow as a sequence of processes, where material or data produced by one process serves as input for the next process, is similar to that of OBI and SIO. Also, the intended use of the genomics concepts mirrors that of FAIR Genomes, where FAIR Genomes’ ‘Sample Preparation’ module broadly corresponds to the ‘Library Preparation’ concept, the ‘Sequencing’ module with the ‘Sequencing Assay’ concept, and the ‘Analysis’ module with the ‘Sequencing Analysis’ concept, respectively. The SPHN omics extension also reuses the value set for library kits from FAIR Genomes. In contrast to FAIR Genomes, we aimed for more normalization, for instance by introducing a separate ‘Standard Operating Procedure’ concept and reference it, while this information is part of the ‘Material’ and ‘Analysis’ modules as protocol attributes in the FAIR Genomes model. The ‘Run’ concept also served to factor out run-specific information, and keep all information that is the same for every run in a sequencing experiment within the ‘Sequencing Assay’ concept. In addition, we aim to use concept references over text or string attributes, such as with the ‘Standard Operating Procedure’, ‘Software’ (algorithm), or ‘Quality Control Metric’ concepts, all of which are expressed as text attributes in FAIR Genomes. Lastly, the SPHN omics extension for the SPHN RDF Schema offers several utility concepts, such as ‘Isolate’ and ‘Gene Panel’, that may be seamlessly combined with other concepts to express the clinical case metadata, has extension points to add additional concepts for any step in the omics workflow, and allows material or data processing concepts to be chained which allows for more fine grained expression of the experimental processing. Note that these differences are not shortcomings, but reflect the differences in application: where FAIR Genomes provides a generic content model for data capture applications for clinical NGS, the SPHN (gen)omics extension mainly focuses on semantic data exchange with a common framework to fit a broader range of omics fields. Besides, data expressed using the SPHN RDF Schema may easily be transformed to the FAIR Genomes model, whereas the inverse is harder.
The model allows to describe metadata on the process, and, in combination with other SPHN concepts, the outcome of the genomics workflow. Also bulk transcriptomics and, to a lesser extent, omics research in general can be represented with the model that is presented in this paper. Since the model is purely meant for exchange of experimental metadata and data, catalog-level metadata, such as study, funding, or attribution, was left out. Although there are some general purpose high-level concepts such as ‘Sample Processing’, ‘Assay’, and ‘Data Processing’, we refrained from introducing a complete concept hierarchy; only concepts that have direct applicability were introduced. Also, while it would be useful to allow for partonomy, for instance by allowing sample or data processing concepts to be composed of arbitrary part processes, it was not introduced to restrict to only one way to apply the concepts.
The 2023.2 SPHN RDF Schema release incorporated various external terminologies to enhance data description. For genomics, the following terminologies are provided on the DCC Terminology Service [
16] Genotype Ontology (GENO), HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC), and Sequence Ontology (SO) for comprehensive variant representation and human gene naming. In the 2024.1 release, as genomics concepts expanded, additional terminologies such as EMBRACE Data and Methods (EDAM) ontology, Experimental Factor Ontology (EFO), Genomic Epidemiology Ontology (GENEPIO), and Ontology for Biomedical Investigations (OBI) will be integrated.
4. Conclusion
We developed a genomics extension of the SPHN RDF Schema, in close collaboration with stakeholders of the SPHN, to facilitate their data sharing use cases. This omics extension aligns with common biomedical ontologies and offers extension points for other omics research. This set of concepts forms the basis for the further concepts developed in the NDSs for other omics data, driving the vision of holistic view on the personalized health data in one single knowledge graph.
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank Aitana Neves, Alexander Leichtle, Andre Kahles, Andrea Agostini, Assaf Sternberg, Cédric Howald, Cyril Matthey-Doret, Daniel Damian, Daphné Chopard, Dylan Lawless, Gaëtan De Frapoint, Irene Keller, Jossena Lype, Katrin Männik, Leonardus Bosch, Lorenzo Cerutti, Manuel Schweighofer, Marc Zimmerli, Michael P. Schmid, Natalia Chicherova, Nicolas Edouard Martin Freundler, Nicolas Freundler, Nora Toussaint, Oksana Riba Grognuz, Patrick Buhlman, Patrick Hirschi, Patrick Pedrioli, Peter Fritsch, Phil Cheng, Reinhard A. Dietrich, Ruben Casanova, Stefan Neuenschwander, Stefan Nicolet, Sylvain Pradervand, Tess Brody, Thomas Müller-Focke, Tural Yarahmadov, Vito Zanotelli and Walid Gharib for their participation to the Omics data modeling workshops and their contributions to this extension of the SPHN RDF Schema. This work was funded by the Swiss State Secretariat for Education, Research and Innovation (SERI) through the SPHN initiative.
References
- V. Touré, P. Kraus, K. Gnodtke, J. Buchhorn, D. Unni, P. Horki, J. L. Raisaro, K. Kalt, D. Teixeira, K. Crameri, S. Österle, FAIRification of health-related data using semantic web technologies in the Swiss Personalized Health Network. Scientific Data 10.1 (2023) 127. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Wilkinson et al., The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Scientific Data 3.1 (2016) 160018. [CrossRef]
- SPHN Interoperability Framework version 2023-2 release, 2023. URL: https://git.dcc.sib.swiss/sphn-semantic-framework/sphn-schema/-/releases/2023-2.
- SPHN National Data Streams. URL: https://sphn.ch/services/funding_old/nds/.
- D. Yuan et al., The European Nucleotide Archive in 2023, Nucleic Acids Research (2023) gkad1067. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Freeberg et al., The European Genome-phenome Archive in 2021, Nucleic Acids Research 50, D1 (2022) D980–D987. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Jensen, V. Ferretti, R. L. Grossman, L. M. Staudt, The NCI Genomic Data Commons as an engine for precision medicine, Blood 130.4 (2017) 453–459. [CrossRef]
- Bandrowski et al., The Ontology for Biomedical Investigations, PLOS ONE 11.4 (2016), e0154556. [CrossRef]
- M. Dumontier et al., The Semanticscience Integrated Ontology (SIO) for biomedical research and knowledge discovery, Journal of Biomedical Semantics 5.1 (2014), 14. [CrossRef]
- K. J. van der Velde et al., FAIR Genomes metadata schema promoting Next Generation Sequencing data reuse in Dutch healthcare and research. Scientific Data 9.1 (2022) 169. [CrossRef]
- SPHN Interoperability Framework dataset template, 2023. URL: https://git.dcc.sib.swiss/sphn-semantic-framework/sphn-schema/-/tree/master/templates/dataset_template. Accessed: 2023-11-28.
- SPHN Schema Forge - SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, 2023, URL https://schemaforge.dcc.sib.swiss/. Accessed: 2023-11-27.
- SPHN Interoperability Framework Release-candidate-2024-1, 2023. URL: https://git.dcc.sib.swiss/sphn-semantic-framework/sphn-schema/-/tree/release-candidate-2024-1.
- J. Ison, M. Kalas, I. Jonassen, D. Bolser, M. Uludag, H. McWilliam, J. Malone, R. Lopez, S. Pettifer, P. Rice, EDAM: an ontology of bioinformatics operations, types of data and identifiers, topics and formats, Bioinformatics 29, 10 (2013). [CrossRef]
- Example instantiation of genomic concepts from SPHN RDF Schema 2024.1. URL: https://gist.github.com/deepakunni3/1a1324fcddb82fb0c1064f8025be5852.
- P. Krauss, V. Touré, K. Gnodtke, K. Crameri, S. Österle, DCC Terminology Service—An Automated CI/CD Pipeline for Converting Clinical and Biomedical Terminologies in Graph Format for the Swiss Personalized Health Network, Applied Sciences 11.23 (2021) 11311. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).