Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
01 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasquale, E.B. The Eph Family of Receptors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.-Y.; Patel, O.; Janes, P.W.; Murphy, J.M.; Lucet, I.S. Eph Receptor Signalling: From Catalytic to Non-Catalytic Functions. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6567–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overman, R.C.; Debreczeni, J.E.; Truman, C.M.; McAlister, M.S.; Attwood, T.K. Biochemical and Biophysical Characterization of Four EphB Kinase Domains Reveals Contrasting Thermodynamic, Kinetic and Inhibition Profiles. Biosci. Rep. 2013, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surawska, H.; Ma, P.C.; Salgia, R. The Role of Ephrins and Eph Receptors in Cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004, 15, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.-K.; Kim, Y.-S.; Hwang, J.-W.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, S.-H.; Jeon, B.-T.; Park, P.-J. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Anticancer Peptide Derived from Ruditapes Philippinarum. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.A.A.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Kntayya, S.B.; Rukayadi, Y.; Hamid, H.A.; Razis, A.F.A. Moringa Oleifera Lam Targeting Chemoprevention. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 3675–3686. [Google Scholar]
- Sikder, K.; Sinha, M.; Das, N.; Das, D.K.R.; Datta, S.; Dey, S. Moringa Oleifera Leaf Extract Prevents in Vitro Oxidative DNA Damage. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Khalafalla, M.M.; Abdellatef, E.; Dafalla, H.M.; Nassrallah, A.A.; Aboul-Enein, K.M.; Lightfoot, D.A.; El-Deeb, F.E.; El-Shemy, H.A. Active Principle from Moringa Oleifera Lam Leaves Effective against Two Leukemias and a Hepatocarcinoma. African J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 8467–8471. [Google Scholar]
- Abdull Razis, A.F.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Kntayya, S.B. Health Benefits of Moringa Oleifera. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 8571–8576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, M.Z.; Kausar, F.; Hassan, M.; Javaid, S.; Malik, A. Anticancer Activities of Phenolic Compounds from Moringa Oleifera Leaves: In Vitro and in Silico Mechanistic Study. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2021, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asmari, A.K.; Albalawi, S.M.; Athar, M.T.; Khan, A.Q.; Al-Shahrani, H.; Islam, M. Moringa Oleifera as an Anti-Cancer Agent against Breast and Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0135814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Selvasekaran, P.; Kapoor, S.; Barbhai, M.D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Saurabh, V.; Potkule, J.; Changan, S.; ElKelish, A.; Selim, S.; et al. Moringa Oleifera Lam. Seed Proteins: Extraction, Preparation of Protein Hydrolysates, Bioactivities, Functional Food Properties, and Industrial Application. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Garza, N.G.; Chuc Koyoc, J.A.; Torres Castillo, J.A.; García Zambrano, E.A.; Betancur Ancona, D.; Chel Guerrero, L.; Sinagawa García, S.R. Biofunctional Properties of Bioactive Peptide Fractions from Protein Isolates of Moringa Seed (Moringa Oleifera). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 4268–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Cai, S.; Gao, M.; Chu, X.; Pan, X.; Gong, K.-K.; Xiao, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Purification of Antioxidant Peptides of Moringa Oleifera Seeds and Their Protective Effects on H2O2 Oxidative Damaged Chang Liver Cells. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés-Gaxiola, S.; León-Félix, J.; Jiménez-Nevárez, Y.B.; Angulo-Escalante, M.A.; Ramos-Payán, R.; Colado-Velázquez, J.; Heredia, J.B. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Novel Peptides from Moringa Oleifera Lam. Leaves. South African J. Bot. 2021, 141, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Santhanam, R.K.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Chen, H. Bioactive Peptide with Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities from Black Soybean [Glycine Max (L.) Merr.] Byproduct: Isolation, Identification and Molecular Docking Study. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, A.W.; Bartlett, P.F.; Lackmann, M. Therapeutic Targeting of EPH Receptors and Their Ligands. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, H.-Q.; Wu, X.-S.; Wei, B.; Chen, L. Eph Receptors and Ephrins as Targets for Cancer Therapy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 2894–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCall, J.L.; Gehring, D.; Clymer, B.K.; Fisher, K.W.; Das, B.; Kelly, D.L.; Kim, H.; White, M.A.; Lewis, R.E. KSR1 and EPHB4 Regulate Myc and PGC1β To Promote Survival of Human Colon Tumors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2016, 36, 2246–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spannuth, W.A.; Mangala, L.S.; Stone, R.L.; Carroll, A.R.; Nishimura, M.; Shahzad, M.M.K.; Lee, S.-J.; Moreno-Smith, M.; Nick, A.M.; Liu, R.; et al. Converging Evidence for Efficacy from Parallel EphB4-Targeted Approaches in Ovarian Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Kumar, S.R.; Stein, J.P.; Singh, J.; Krasnoperov, V.; Zhu, S.; Hassanieh, L.; Smith, D.L.; Buscarini, M.; Broek, D.; et al. EphB4 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Is Expressed in Bladder Cancer and Provides Signals for Cell Survival. Oncogene 2006, 25, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasina, R.; Mollberg, N.; Kawada, I.; Mutreja, K.; Kanade, G.; Yala, S.; Surati, M.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Critical Role for the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase EPHB4 in Esophageal Cancers. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liersch-Löhn, B.; Slavova, N.; Buhr, H.J.; Bennani-Baiti, I.M. Differential Protein Expression and Oncogenic Gene Network Link Tyrosine Kinase Ephrin B4 Receptor to Aggressive Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction Cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens-Walker, I.; Fernandini, B.C.; Maharaj, M.S.; Rockstroh, A.; Nelson, C.C.; Herington, A.C.; Stephenson, S.-A. The Tumour-Promoting Receptor Tyrosine Kinase, EphB4, Regulates Expression of Integrin-Β8 in Prostate Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abéngozar, M.A.; de Frutos, S.; Ferreiro, S.; Soriano, J.; Perez-Martinez, M.; Olmeda, D.; Marenchino, M.; Cañamero, M.; Ortega, S.; Megias, D.; et al. Blocking EphrinB2 with Highly Specific Antibodies Inhibits Angiogenesis, Lymphangiogenesis, and Tumor Growth. Blood 2012, 119, 4565–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, B.D.; Carol Tan, Y.-H.; Kanteti, R.S.; Liu, R.; Gayed, M.J.; Vokes, E.E.; Ferguson, M.K.; John Iafrate, A.; Gill, P.S.; Salgia, R. Novel EPHB4 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Mutations and Kinomic Pathway Analysis in Lung Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Solana, M.A.; Mejía-García, V.Y.; Téllez-Valencia, A.; García-Arenas, G.; Salas-Pacheco, J.; Alba-Romero, J.J.; Sierra-Campos, E. Nutritional Content and Elemental and Phytochemical Analyses of Moringa Oleifera Grown in Mexico. J. Chem. 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Islam, S.M.R.; Hossen, F.; Mahtab-ul-Islam, K.; Hasan, M.R.; Karim, R. Moringa Oleifera Is a Prominent Source of Nutrients with Potential Health Benefits. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaky, A.A.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Eun, J.-B.; Shim, J.-H.; Abd El-Aty, A.M. Bioactivities, Applications, Safety, and Health Benefits of Bioactive Peptides From Food and By-Products: A Review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM Virtual—A Novel Database of Food-Derived Peptides with In Silico-Predicted Biological Activity. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanen, J.-P.; Henkemeyer, M.; Nikolov, D.B. Crystal Structure of the Ligand-Binding Domain of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase EphB2. Nature 1998, 396, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burz, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Balacescu, O.; Irimie, A. Apoptosis in Cancer: Key Molecular Signaling Pathways and Therapy Targets. Acta Oncol. (Madr). 2009, 48, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornienko, A.; Mathieu, V.; Rastogi, S.K.; Lefranc, F.; Kiss, R. Therapeutic Agents Triggering Nonapoptotic Cancer Cell Death. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4823–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitvogel, L.; Galluzzi, L.; Smyth, M.J.; Kroemer, G. Mechanism of Action of Conventional and Targeted Anticancer Therapies: Reinstating Immunosurveillance. Immunity 2013, 39, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornesello, A.L.; Buonaguro, L.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M. The Role of Sensing Peptides in the Cross-Talk between Microbiota and Human Cancer Cells. Mini-Reviews Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Baby, D.; Rajguru, J.; Patil, P.; Thakkannavar, S.; Pujari, V. Inflammation and Cancer. Ann. Afr. Med. 2019, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.S.; Mahapatra, S. Das; R, S.; Sommano, S.R.; Prasad, S.K. Virtual Screening and Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship of Moringa Oleifera with Melanoma Antigen A (MAGE-A) Genes against the Therapeutics of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers (NSCLCs). Cancers (Basel). 2022, 14, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrov, I.; Bangov, I.; Flower, D.R.; Doytchinova, I. AllerTOP v.2—a Server for in Silico Prediction of Allergens. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Kapoor, P.; Gautam, A.; Chaudhary, K.; Kumar, R.; Chauhan, J.S.; Tyagi, A.; Raghava, G.P.S. Computational Approach for Designing Tumor Homing Peptides. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the Improved Discovery and Design of Functional Peptides: Common Features of Diverse Classes Permit Generalized Prediction of Bioactivity. PLoS One 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabuco, L.G.; Lise, S.; Petsalaki, E.; Russell, R.B. PepSite: Prediction of Peptide-Binding Sites from Protein Surfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W423–W427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.H.M.; Garg, A.; Keizer, D.; Pires, D.E. V.; Ascher, D.B. CSM-peptides: A Computational Approach to Rapid Identification of Therapeutic Peptides. Protein Sci. 2022, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cheong, H.H.; Siu, S.W.I. XDeep-AcPEP: Deep Learning Method for Anticancer Peptide Activity Prediction Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Multitask Learning. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3789–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riniker, S.; Landrum, G.A. Better Informed Distance Geometry: Using What We Know to Improve Conformation Generation. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 2562–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, J.; Ghidini, A.; Romano, A.; Gentilucci, L.; Musiani, F. PacDOCK: A Web Server for Positional Distance-Based and Interaction-Based Analysis of Docking Results. Molecules 2022, 27, 6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
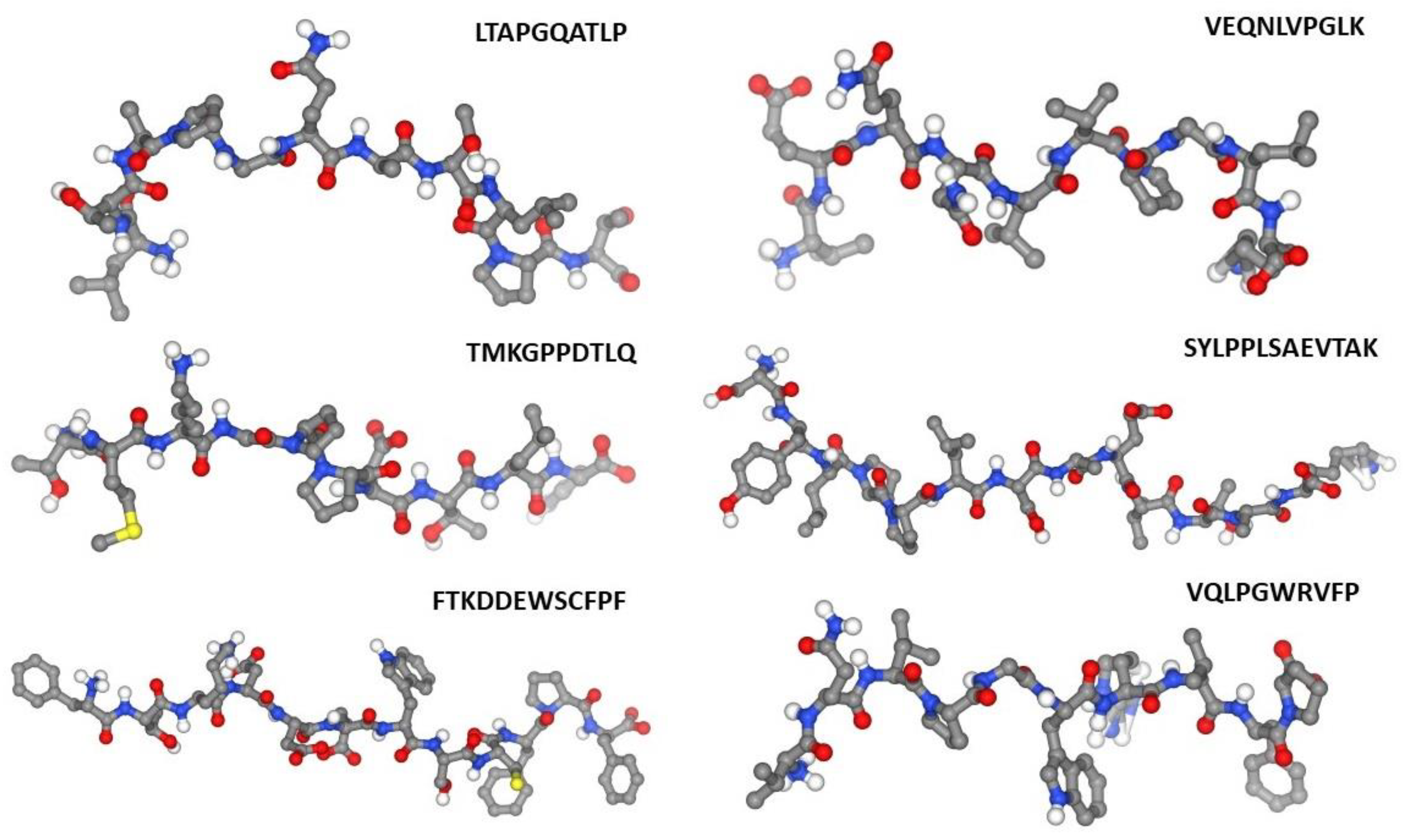
|
Peptide sequence |
Activity Prediction | |||||
| Anti-angiogenic | Anti-Bacterial | Anti-cancer | Anti-inflammatory | Anti-viral | Quorum Sensing | |
| VQLPGWRVFP | ---------- | --------- | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.52 | -------- |
| LTAPGQATLPT | ---------- | --------- | 0.52 | -------- | --------- | -------- |
| TMKGPPDTLQ | 0.51 | --------- | 0.57 | 0.71 | --------- | 0.92 |
| FTKDDEWSCFPF | ---------- | --------- | 0.54 | 0.54 | --------- | -------- |
| SYLPPLSAEVTAK | ---------- | --------- | 0.53 | 0.53 | --------- | -------- |
| VEQNLVPGLK | 0.57 | --------- | 0.79 | 0.77 | --------- | 0.97 |
|
Peptide sequence |
Multiple peptide servers | ||||||
| SCMTHP | ACPred | TumorHPD | Neptune | PR* | ToxinPred | AllerTop | |
| VQLPGWRVFP | THP (392.9) | ACP (0.91) | THP (0.33) | NON-THP (0.283) | 0.72 | Non-toxin | Allergen |
| LTAPGQATLPT | NON-THP (277.0) | NON-ACP (0.932) | NON-THP (-0.86) | NON-THP (0.097) | 0.18 | Non-toxin | Non- Allergen |
| TMKGPPDTLQ | THP (392.9) | NON-ACP (0.977) | NON-THP (-0.86) | NON-THP (0.368) | 0.14 | Non-toxin | Allergen |
| FTKDDEWSCFPF | THP (392.9) | NON-ACP (0.901) | THP (0.89) | NON-THP (0.063) | 0.80 | Non-toxin | Non- Allergen |
| SYLPPLSAEVTAK | THP (392.9) | NON-ACP (0.973) | NON-THP (-0.69) | THP (0.935) | 0.34 | Non-toxin | Non- Allergen |
| VEQNLVPGLK | NON-THP (209.3) | NON-ACP (0.986) | NON-THP (-0.1) | NON-THP (0.053) | 0.27 | Non-toxin | Non- Allergen |
|
Peptide sequence |
Activity Prediction | |||||
| Breast (μM) | Cervix (μM) | Colon (μM) | Lung (μM) | Prostate (μM) | Skin (μM) | |
| VQLPGWRVFP | 309.61 | 110.02 | 412.54 | 277.14 | 478.23 | 74.75 |
| LTAPGQATLPT | 551.05 | 408.95 | 490.98 | 822.35 | 301.11 | 503.92 |
| TMKGPPDTLQ | 520.78 | 163.37 | 617.55 | 684.13 | 386.68 | 372.89 |
| FTKDDEWSCFPF | 180.87 | 291.62 | 368.83 | 126.08 | 479.94 | 64.497 |
| SYLPPLSAEVTAK | 267.4 | 114.22 | 244.69 | 588.18 | 83.60 | 299.26 |
| VEQNLVPGLK | 474.14 | 109.63 | 557.37 | 457.76 | 315.45 | 297.65 |
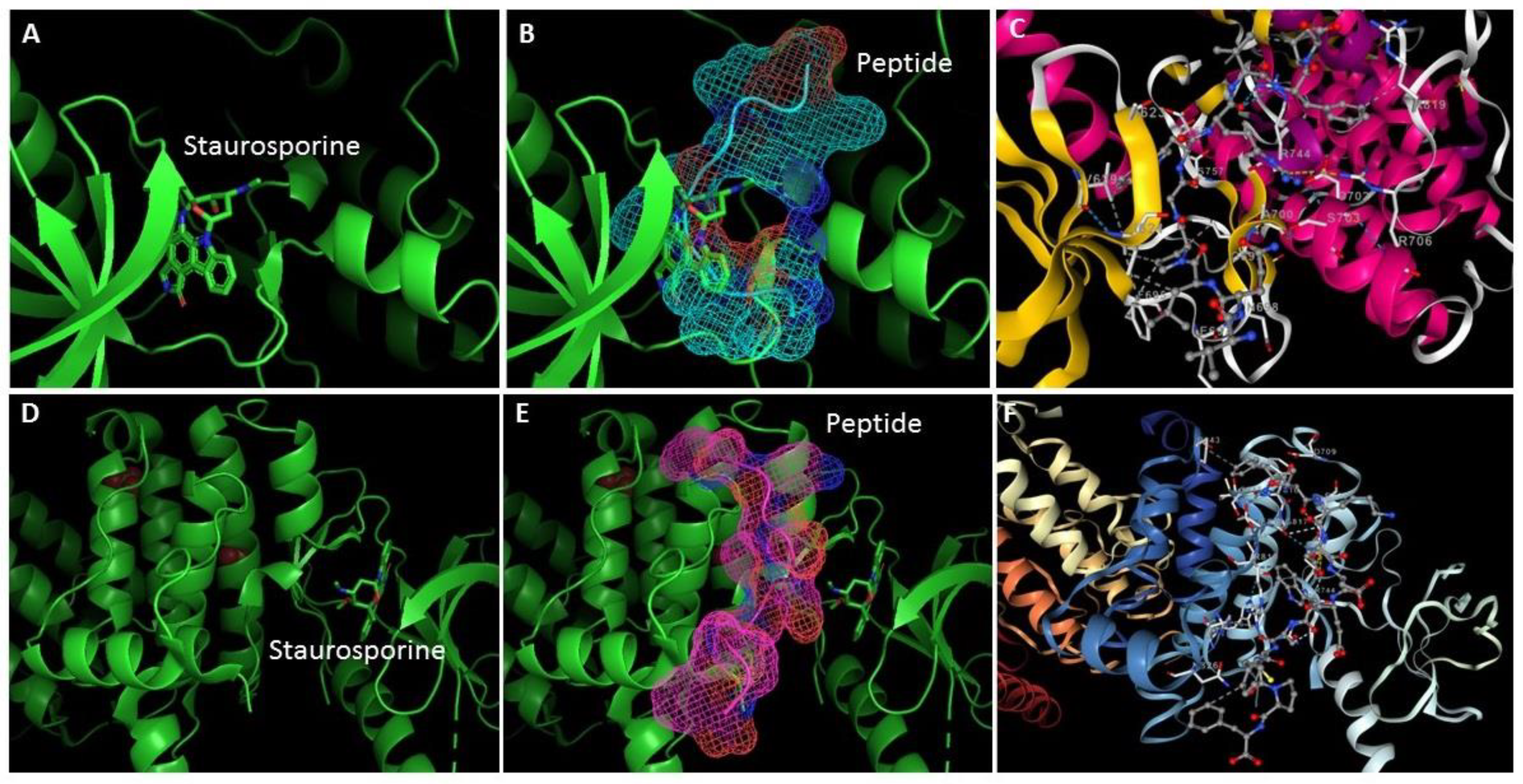
| Peptide sequence | PepSite2 p-value | ITScorePeP | HPEPDOCK 2.0 |
| VQLPGWRVFP | 0.0196 | -165.2 | -240.72 |
| LTAPGQATLPT | 0.0673 | -109.8 | -162.23 |
| TMKGPPDTLQ | 0.0078 | -120.2 | -149.67 |
| FTKDDEWSCFPF | 0.0720 | -217.1 | -201.74 |
| SYLPPLSAEVTAK | 0.0862 | -151.9 | -177.52 |
| VEQNLVPGLK | 0.0760 | -121.6 | -157.30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




