Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
01 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
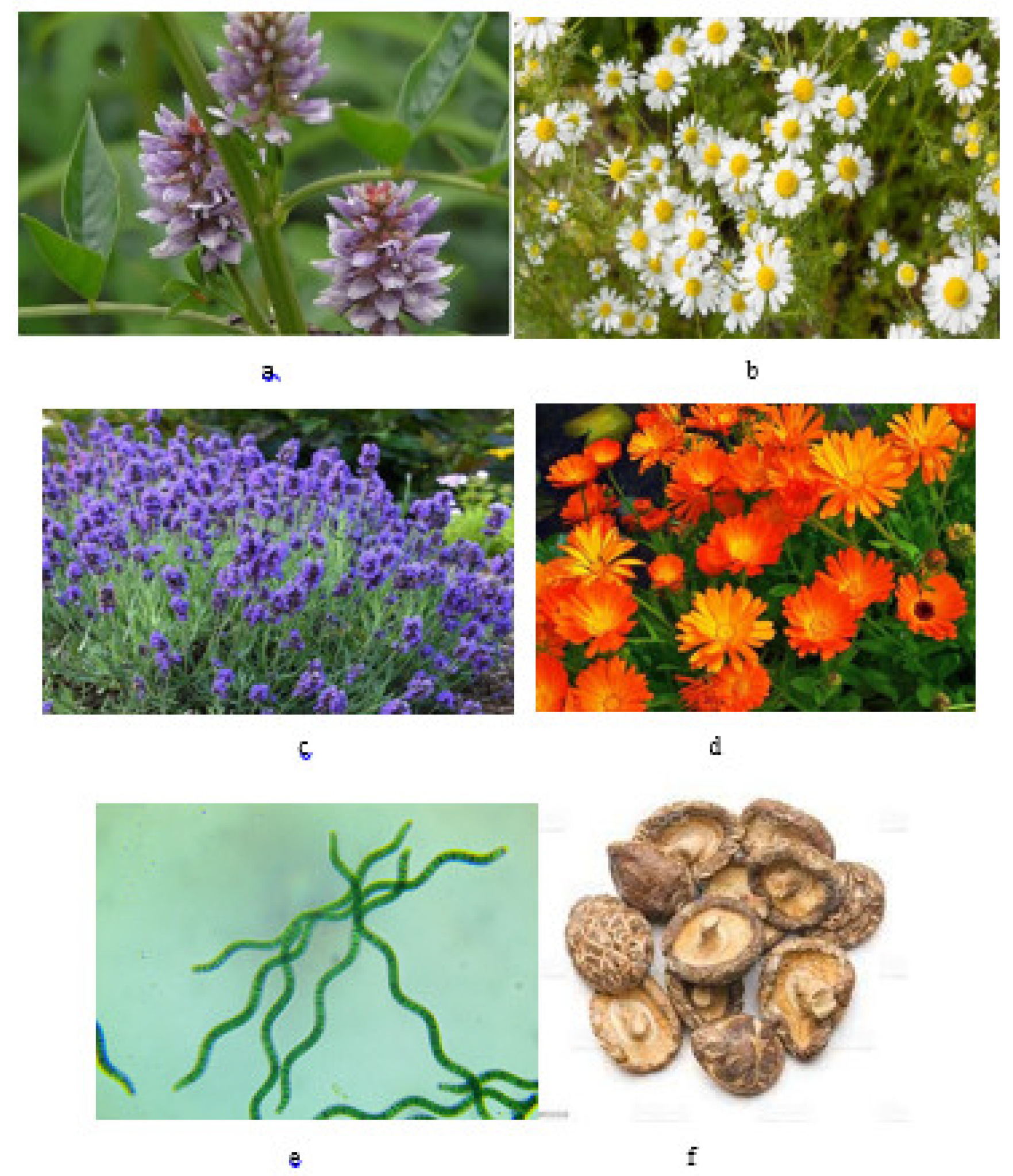
2.1. Choosing Medicinal Plants, Spirulina Algae, and Shiitake Mushrooms
2.2. Extraction and Production of Essential Oils from Studied Plants
2.3. Exosome Extraction Methods
2.4. Formulation for Creating Medicinal and Cosmetic Products
2.5. Designing Animal Experiments
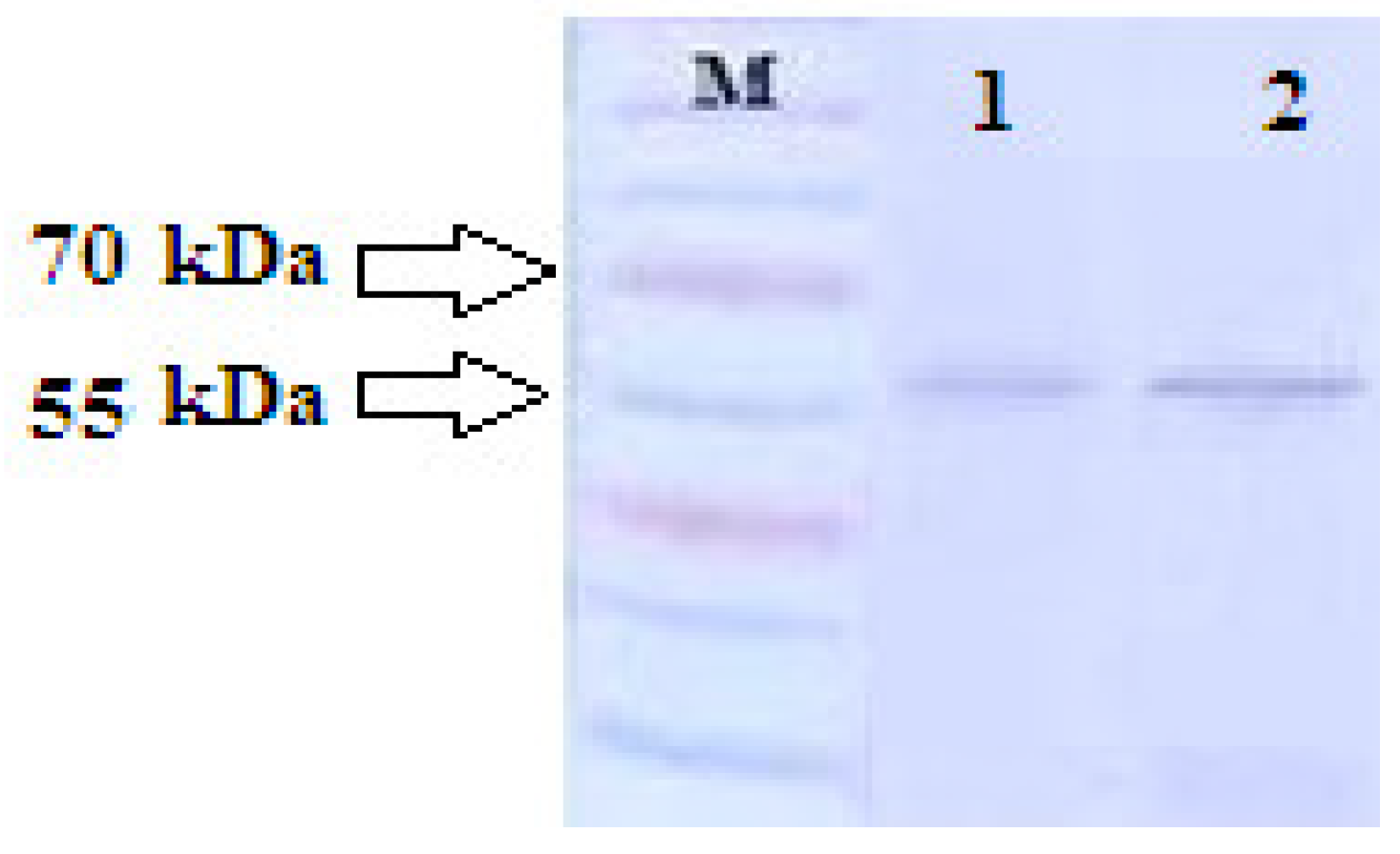
2.6. Measuring Exosome Uptake by Cells Using Spectrophotometric Method
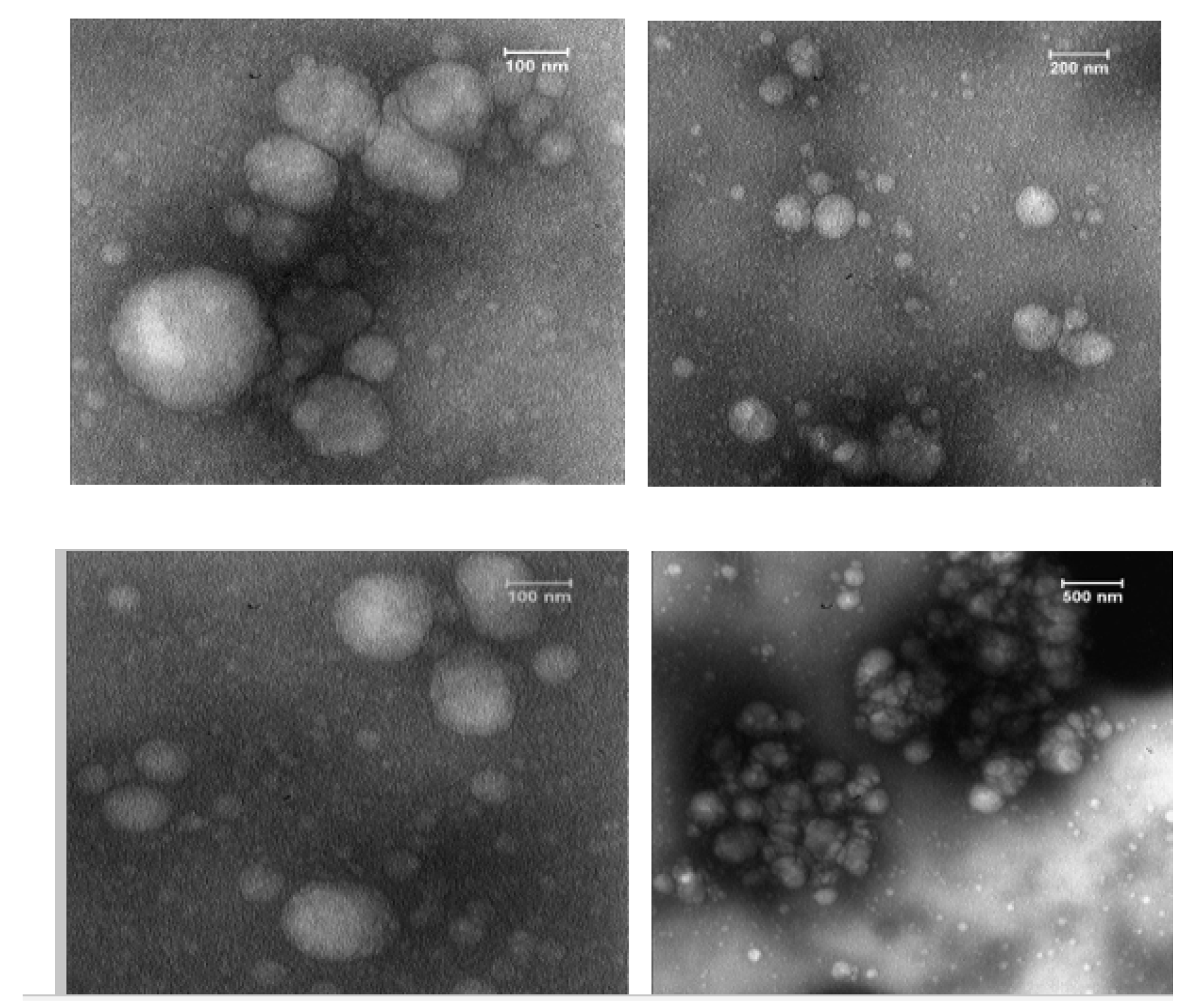
2.7. Quality and Structural Verification of Exosomes using Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
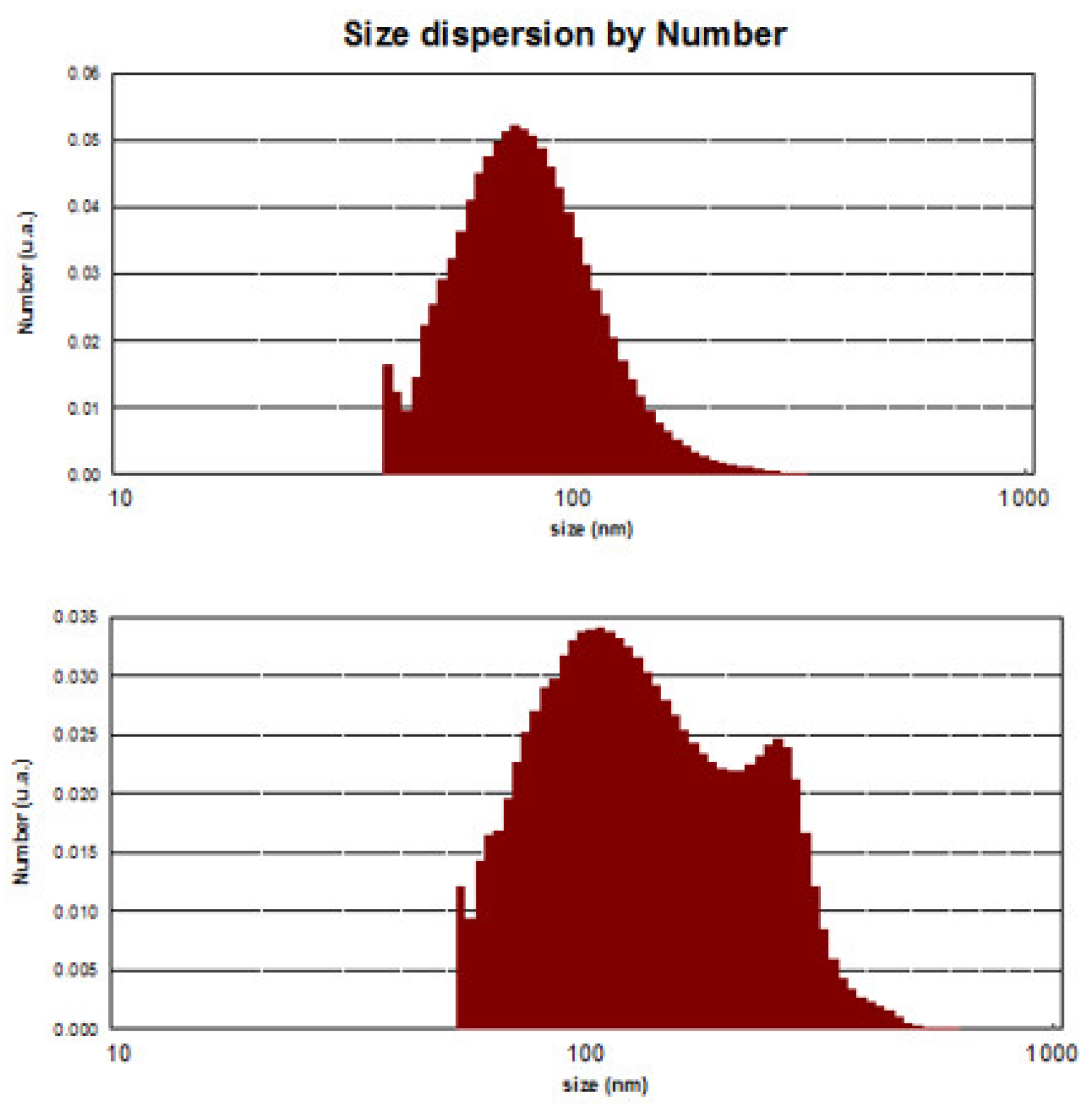
2.8. Measuring Exosome Size and Percentage Using Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
2.9. Evaluation of Toxic Properties and In Vitro Survival Rates of Extracted Exosomes
2.10. Conducting in Vivo Clinical and Molecular Trials
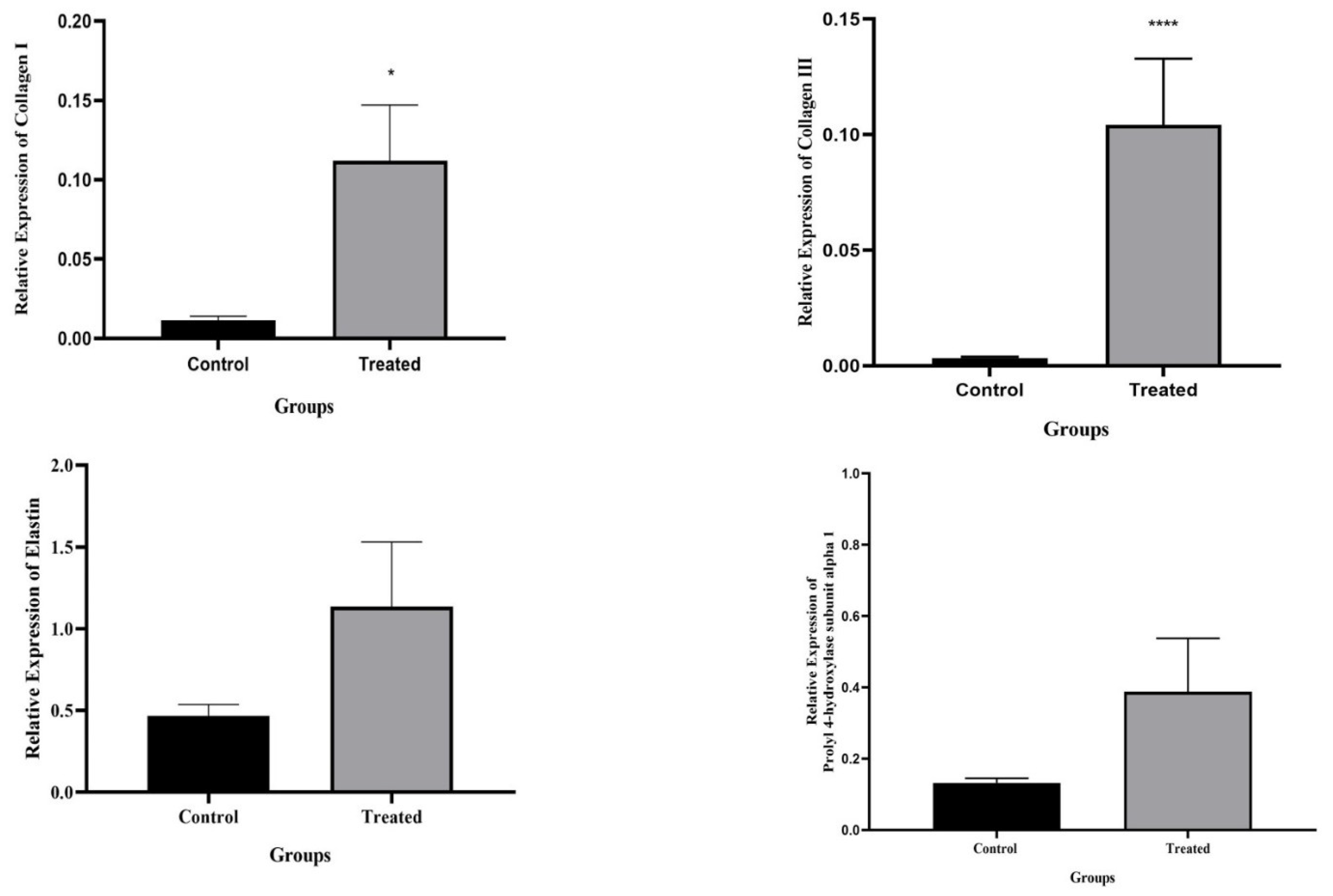
2.10.1. RNA Level Gene Expression Analysis and Real-time Tissue Testing
2.10.2. Exploring Tyrosinase Enzyme Expression
2.11. Conducting Clinical Trials on Human Subjects
3. Results
3.1. Spectrophotometric
3.2. TEM
3.3. DLS analyses
3.4. MTT
3.5. Real-time PCR
3.6. Tyrosinase Enzyme Expression
4. Discussion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- K. Wakamatsu, J.H. Zippin, S. Ito, Chemical and biochemical control of skin pigmentation with special emphasis on mixed melanogenesis, Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 34 (2021) 730–747. [CrossRef]
- F. Liu, L. Qu, H. Li, J. He, L. Wang, Y. Fang, X. Yan, Q. Yang, B. Peng, W. Wu, Advances in Biomedical Functions of Natural Whitening Substances in the Treatment of Skin Pigmentation Diseases, Pharmaceutics. 14 (2022) 2308. [CrossRef]
- H. Liu, J. Wang, J. Hu, L. Wang, Z. Guo, W. Fan, Y. Xu, D. Liu, Y. Zhang, M. Xie, Genome-wide association analysis reveal the genetic reasons affect melanin spot accumulation in beak skin of ducks, BMC Genomics. 23 (2022) 1–12. [CrossRef]
- H. Choi, J.-H. Yoon, K. Youn, M. Jun, Decursin prevents melanogenesis by suppressing MITF expression through the regulation of PKA/CREB, MAPKs, and PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β cascades, Biomed. Pharmacother. 147 (2022) 112651. [CrossRef]
- P.M. Ridzuan, N.M. Kummara, M.H. Islah, V. Jeyamathi, A.A. Nur-Alisyia, A.R. Ridzuan, Review on Aesthetic & Cosmetic Industries in Malaysia-A Way Forward, Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 11 (2021) 744–755. [CrossRef]
- V. González-Molina, A. Martí Pineda, N. González, Topical treatments for Melasma and their mechanism of action, J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 15 (2022) 19–28.
- S. Fonseca, M.N. Amaral, C.P. Reis, L. Custódio, Marine Natural Products as Innovative Cosmetic Ingredients, Mar. Drugs. 21 (2023) 170. [CrossRef]
- L.T. Kee, C.Y. Ng, M.E. Al-Masawa, J.B. Foo, C.W. How, M.H. Ng, J.X. Law, Extracellular Vesicles in Facial Aesthetics: A Review, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (2022) 6742. 6742. [CrossRef]
- S.J. Phang, S. Basak, H.X. Teh, G. Packirisamy, M.B. Fauzi, U.R. Kuppusamy, Y.P. Neo, M.L. Looi, Advancements in Extracellular Matrix-Based Biomaterials and Biofabrication of 3D Organotypic Skin Models, ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 8 (2022) 3220–3241. [CrossRef]
- K. Chinchulkar, S. Gajbhiye, ANTI-THERMAL SKIN AGING ACTIVITY OF AQUEOUS EXTRACT DERIVED FROM APPLE MINT (MENTHA SUAVEOLENS EHRH.), MUSHROOM EXTRACT (ALBATRELLUS OVINUS) AND OTHER HERBS, (2020).
- C. Stani, L. Vaccari, E. Mitri, G. Birarda, FTIR investigation of the secondary structure of type I collagen: New insight into the amide III band, Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 229 (2020) 118006. 118006. [CrossRef]
- L.T.N. Ngoc, J. Moon, Y. Lee, Antioxidants for improved skin appearance: Intracellular mechanism, challenges and future strategies, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. (2023). [CrossRef]
- M. Jacobs, Comparitive study on the combination of Nigella Sativa with micro-needling for post-acne scarring, (2020).
- C. Lian, X. Wang, X. Qiu, Z. Wu, B. Gao, L. Liu, G. Liang, H. Zhou, X. Yang, Y. Peng, Collagen type II suppresses articular chondrocyte hypertrophy and osteoarthritis progression by promoting integrin β1− SMAD1 interaction, Bone Res. 7 (2019) 8. [CrossRef]
- T.S. Martins, M. Vaz, A.G. Henriques, A review on comparative studies addressing exosome isolation methods from body fluids, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 415 (2023) 1239–1263. [CrossRef]
- R. Bano, F. Ahmad, M. Mohsin, A perspective on the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles from different biofluids, RSC Adv. 11 (2021) 19598–19615. [CrossRef]
- B. Michela, Liquid biopsy: a family of possible diagnostic tools, Diagnostics. 11 (2021) 1391. [CrossRef]
- J. Meldolesi, Exosomes and ectosomes in intercellular communication, Curr. Biol. 28 (2018) R435–R444. [CrossRef]
- D. Liu, Y. Gao, J. Liu, Y. Huang, J. Yin, Y. Feng, L. Shi, B.P. Meloni, C. Zhang, M. Zheng, Intercellular mitochondrial transfer as a means of tissue revitalization, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6 (2021) 65. [CrossRef]
- C. Caruso Bavisotto, F. Scalia, A. Marino Gammazza, D. Carlisi, F. Bucchieri, E. Conway de Macario, A.J.L. Macario, F. Cappello, C. Campanella, Extracellular vesicle-mediated cell–cell communication in the nervous system: Focus on neurological diseases, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20 (2019) 434. [CrossRef]
- A. Gorshkov, L. Purvinsh, A. Brodskaia, A. Vasin, Exosomes as natural nanocarriers for RNA-based therapy and prophylaxis, Nanomaterials. 12 (2022) 524. [CrossRef]
- G. Nam, Y. Choi, G.B. Kim, S. Kim, S.A. Kim, I. Kim, Emerging prospects of exosomes for cancer treatment: from conventional therapy to immunotherapy, Adv. Mater. 32 (2020) 2002440. [CrossRef]
- N. Khosravi, E. Pishavar, B. Baradaran, F. Oroojalian, A. Mokhtarzadeh, Stem cell membrane, stem cell-derived exosomes and hybrid stem cell camouflaged nanoparticles: A promising biomimetic nanoplatforms for cancer theranostics, J. Control. Release. 348 (2022) 706–722. [CrossRef]
- S.M. Patil, S.S. Sawant, N.K. Kunda, Exosomes as drug delivery systems: a brief overview and progress update, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 154 (2020) 259–269. [CrossRef]
- C. Gutierrez-Millan, C. Calvo Díaz, J.M. Lanao, C.I. Colino, Advances in exosomes-based drug delivery systems, Macromol. Biosci. 21 (2021) 2000269. [CrossRef]
- M. Pirisinu, T.C. Pham, D.X. Zhang, T.N. Hong, L.T. Nguyen, M.T.N. Le, Extracellular vesicles as natural therapeutic agents and innate drug delivery systems for cancer treatment: Recent advances, current obstacles, and challenges for clinical translation,: Semin. Cancer Biol., Elsevier, 2022: 340-355. [CrossRef]
- L. Dini, S. Tacconi, E. Carata, A.M. Tata, C. Vergallo, E. Panzarini, Microvesicles and exosomes in metabolic diseases and inflammation, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 51 (2020) 27–39. [CrossRef]
- A. Hassanzadeh, H.S. Rahman, A. Markov, J.J. Endjun, A.O. Zekiy, M.S. Chartrand, N. Beheshtkhoo, M.A.J. Kouhbanani, F. Marofi, M. Nikoo, Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-derived exosomes in regenerative medicine and cancer; overview of development, challenges, and opportunities, Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12 (2021) 1–22. [CrossRef]
- K. Asgarpour, Z. Shojaei, F. Amiri, J. Ai, M. Mahjoubin-Tehran, F. Ghasemi, R. ArefNezhad, M.R. Hamblin, H. Mirzaei, Exosomal microRNAs derived from mesenchymal stem cells: cell-to-cell messages, Cell Commun. Signal. 18 (2020) 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Raghav, P.A. Shiekh, A. Kumar, Transplantation of engineered exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate diabetic peripheral neuropathy under electrical stimulation, Bioact. Mater. 6 (2021) 2231–2249. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhao, J. Liu, S. Liu, P. Yang, Y. Liang, J. Ma, S. Mao, C. Sun, Y. Yang, Fibroblast exosomal TFAP2C induced by chitosan oligosaccharides promotes peripheral axon regeneration via the miR-132-5p/CAMKK1 axis, Bioact. Mater. 26 (2023) 249–263. [CrossRef]
- J.P. Bischoff, A. Schulz, H. Morrison, The role of exosomes in intercellular and inter-organ communication of the peripheral nervous system, FEBS Lett. 596 (2022) 655–664. [CrossRef]
- S. Galland, I. Stamenkovic, Mesenchymal stromal cells in cancer: a review of their immunomodulatory functions and dual effects on tumor progression, J. Pathol. 250 (2020) 555–572. [CrossRef]
- M. Arabpour, A. Saghazadeh, N. Rezaei, Anti-inflammatory and M2 macrophage polarization-promoting effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes, Int. Immunopharmacol. 97 (2021) 107823. [CrossRef]
- Y. Han, J. Yang, J. Fang, Y. Zhou, E. Candi, J. Wang, D. Hua, C. Shao, Y. Shi, The secretion profile of mesenchymal stem cells and potential applications in treating human diseases, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7 (2022) 92. [CrossRef]
- A. Ortega, O. Martinez-Arroyo, M.J. Forner, R. Cortes, Exosomes as drug delivery systems: endogenous nanovehicles for treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus, Pharmaceutics. 13 (2021) 3. [CrossRef]
- R. Heydari, F. Koohi, M. Rasouli, K. Rezaei, E. Abbasgholinejad, S. Bekeschus, M. Doroudian, Exosomes as Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnostic Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents, Vaccines. 11 (2023) 687. [CrossRef]
- S. Amir, A. Arathi, S. Reshma, P. V Mohanan, Microfluidic devices for the detection of disease-specific proteins and other macromolecules, disease modelling and drug development: A review, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. (2023) 123784. [CrossRef]
- E.M. Tottoli, R. Dorati, I. Genta, E. Chiesa, S. Pisani, B. Conti, Skin wound healing process and new emerging technologies for skin wound care and regeneration, Pharmaceutics. 12 (2020) 735. [CrossRef]
- S.P. Stawicki, R. Jeanmonod, A.C. Miller, L. Paladino, D.F. Gaieski, A.Q. Yaffee, A. De Wulf, J. Grover, T.J. Papadimos, C. Bloem, The 2019–2020 novel coronavirus (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2) pandemic: A joint american college of academic international medicine-world academic council of emergency medicine multidisciplinary COVID-19 working group consensus paper, J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 12 (2020) 47. [CrossRef]
- T. Yuan, L. Meijia, C. Xinyao, C. Xinyue, H. Lijun, Exosome derived from human adipose-derived stem cell improve wound healing quality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical animal studies, Int. Wound J. (2023). [CrossRef]
- Z. Weiliang, G. Lili, Research advances in the application of adipose-derived stem cells derived exosomes in cutaneous wound healing, Ann. Dermatol. 33 (2021) 309. [CrossRef]
- A. Joorabloo, T. Liu, Engineering exosome-based biomimetic nanovehicles for wound healing, J. Control. Release. 356 (2023) 463–480. [CrossRef]
- L. Hou, X. Zhang, H. Du, Advances in mesenchymal stromal cells and nanomaterials for diabetic wound healing, Diabetes. Metab. Res. Rev. (2023) e3638. [CrossRef]
- H. Wang, Y. Li, Z. Yue, Y. Liu, Q. Chen, D. Hu, J. Han, Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes Inhibit Hypertrophic Scaring Formation by Regulating Th17/Treg Cell Balance, Biomed Res. Int. 2022 (2022). [CrossRef]
- T.-H. Chang, C.-S. Wu, S.-H. Chiou, C.-H. Chang, H.-J. Liao, Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes as a Novel Anti-Inflammatory Agent and the Current Therapeutic Targets for Rheumatoid Arthritis, Biomedicines. 10 (2022) 1725. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang, Y. Pan, Y. Liu, X. Li, L. Tang, M. Duan, J. Li, G. Zhang, Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells stimulate regenerative wound healing via transforming growth factor-β receptor inhibition, Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12 (2021) 1–14. [CrossRef]
- L.T. Nguyen, N.T. Tran, U.T.T. Than, M.Q. Nguyen, A.M. Tran, P.T.X. Do, T.T. Chu, T.D. Nguyen, A.V. Bui, T.A. Ngo, Optimization of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cell isolation and culture methods in serum-and xeno-free conditions, Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13 (2022) 1–19. [CrossRef]
- M. Maqsood, M. Kang, X. Wu, J. Chen, L. Teng, L. Qiu, Adult mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes: Sources, characteristics, and application in regenerative medicine, Life Sci. 256 (2020) 118002. [CrossRef]
- T. Jiang, Z. Wang, J. Sun, Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulate cutaneous wound healing mediates through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway, Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11 (2020) 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Y.-J. Kim, D.H. Seo, S.H. Lee, S.-H. Lee, G.-H. An, H.-J. Ahn, D. Kwon, K.-W. Seo, K.-S. Kang, Conditioned media from human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells stimulate rejuvenation function in human skin, Biochem. Biophys. Reports. 16 (2018) 96–102. [CrossRef]
- W.E. Putri, A. Endaryanto, F.A. Rantam, C.R.S. Prakoeswa, Mesenchymal Stem cell-Conditioned Medium (secretome) in skin aging A systematic review, Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 15 (2021) 613–635.
- J. Hu, J. Hao, Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Derivatives for Skin Rejuvenation, (2023).
- J.-Y. Wu, S.-N. Wu, L.-P. Zhang, X.-S. Zhao, Y. Li, Q.-Y. Yang, R.-Y. Yuan, J.-L. Liu, H.-J. Mao, N.-W. Zhu, Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A New Method for Reversing Skin Aging, Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 19 (2022) 961–968. [CrossRef]
- D.R. Cooper, C. Wang, R. Patel, A. Trujillo, N.A. Patel, J. Prather, L.J. Gould, M.H. Wu, Human adipose-derived stem cell conditioned media and exosomes containing MALAT1 promote human dermal fibroblast migration and ischemic wound healing, Adv. wound care. 7 (2018) 299–308. [CrossRef]
- M. Salamito, B. Gillet, D. Syx, E. Vaganay, M. Malbouyres, C. Cerutti, N. Tissot, C. Exbrayat-Heritier, P. Perez, C. Jones, NRF2 shortage in human skin fibroblasts dysregulates matrisome gene expression and affects collagen fibrillogenesis, J. Invest. Dermatol. 143 (2023) 386–397. [CrossRef]
- S. Hu, Z. Li, J. Cores, K. Huang, T. Su, P.-U. Dinh, K. Cheng, Needle-free injection of exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblast spheroids ameliorates skin photoaging, ACS Nano. 13 (2019) 11273–11282. [CrossRef]
- H. Merzendorfer, E. Cohen, Chitin/chitosan: versatile ecological, industrial, and biomedical applications, Extracell. Sugar-Based Biopolym. Matrices. (2019) 541–624. [CrossRef]
- I.A. Ahmed, M.A. Mikail, N.H. Zamakshshari, M.R. Mustafa, N.M. Hashim, R. Othman, Trends and challenges in phytotherapy and phytocosmetics for skin aging, Saudi J. Biol. Sci. (2022) 103363. [CrossRef]
- F.A. Alzahrani, M.I. Khan, N. Kameli, E. Alsahafi, Y.M. Riza, Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Exciting Potential as the Future of Next-Generation Drug Delivery, Biomolecules. 13 (2023) 839. [CrossRef]
- K.S. Vyas, J. Kaufman, G.S. Munavalli, K. Robertson, A. Behfar, S.P. Wyles, Exosomes: the latest in regenerative aesthetics, Regen. Med. 18 (2023) 181–194. [CrossRef]
- T. Frazier, A. Alarcon, X. Wu, O.A. Mohiuddin, J.M. Motherwell, A.H. Carlsson, R.J. Christy, J. V Edwards, R.T. Mackin, N. Prevost, Clinical translational potential in skin wound regeneration for adipose-derived, blood-derived, and cellulose materials: cells, exosomes, and hydrogels, Biomolecules. 10 (2020) 1373. [CrossRef]
- P.L. Gupta, M. Rajput, T. Oza, U. Trivedi, G. Sanghvi, Eminence of microbial products in cosmetic industry, Nat. Products Bioprospect. 9 (2019) 267–278. [CrossRef]
- N. Bharadvaja, S. Gautam, H. Singh, Natural polyphenols: a promising bioactive compounds for skin care and cosmetics, Mol. Biol. Rep. 50 (2023) 1817–1828. [CrossRef]
- N. Srinivasan, R. Murali, Niosomes: A promising novel drug delivery systems for phytoconstituents, Ann. Phytomedicine. 12 (2023) 1–7. [CrossRef]
- W.S. Alharbi, F.A. Almughem, A.M. Almehmady, S.J. Jarallah, W.K. Alsharif, N.M. Alzahrani, A.A. Alshehri, Phytosomes as an emerging nanotechnology platform for the topical delivery of bioactive phytochemicals, Pharmaceutics. 13 (2021) 1475. [CrossRef]
- L.N. Borgheti-Cardoso, J.S.R. Viegas, A.V.P. Silvestrini, A.L. Caron, F.G. Praca, M. Kravicz, M.V.L.B. Bentley, Nanotechnology approaches in the current therapy of skin cancer, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 153 (2020) 109–136. [CrossRef]
- R. Lee, H.J. Ko, K. Kim, Y. Sohn, S.Y. Min, J.A. Kim, D. Na, J.H. Yeon, Anti-melanogenic effects of extracellular vesicles derived from plant leaves and stems in mouse melanoma cells and human healthy skin, J. Extracell. Vesicles. 9 (2020) 1703480. [CrossRef]
- L.M. Fonseca, F.T. da Silva, G.P. Bruni, C.D. Borges, E. da Rosa Zavareze, A.R.G. Dias, Aerogels based on corn starch as carriers for pinhão coat extract (Araucaria angustifolia) rich in phenolic compounds for active packaging, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 169 (2021) 362–370. [CrossRef]
- N.S. Sadick, M.P. Lupo, Z.D. Draelos, Cosmeceutical Science in Clinical Practice, CRC Press, 2023.
- K. Tan, T. Chang, X. Lin, Secretomes as an emerging class of bioactive ingredients for enhanced cosmeceutical applications, Exp. Dermatol. 31 (2022) 674–688. [CrossRef]
- S. Shafei, M. Khanmohammadi, R. Heidari, H. Ghanbari, V. Taghdiri Nooshabadi, S. Farzamfar, M. Akbariqomi, N.S. Sanikhani, M. Absalan, G. Tavoosidana, Exosome loaded alginate hydrogel promotes tissue regeneration in full-thickness skin wounds: An in vivo study, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A. 108 (2020) 545–556. [CrossRef]
- C. Wang, M. Wang, T. Xu, X. Zhang, C. Lin, W. Gao, H. Xu, B. Lei, C. Mao, Engineering bioactive self-healing antibacterial exosomes hydrogel for promoting chronic diabetic wound healing and complete skin regeneration, Theranostics. 9 (2019) 65. [CrossRef]
- Q. Shi, Z. Qian, D. Liu, J. Sun, X. Wang, H. Liu, J. Xu, X. Guo, GMSC-derived exosomes combined with a chitosan/silk hydrogel sponge accelerates wound healing in a diabetic rat skin defect model, Front. Physiol. 8 (2017) 904. [CrossRef]
- D. Zhao, Z. Yu, Y. Li, Y. Wang, Q. Li, D. Han, GelMA combined with sustained release of HUVECs derived exosomes for promoting cutaneous wound healing and facilitating skin regeneration, J. Mol. Histol. 51 (2020) 251–263. [CrossRef]
- M. Jiang, H. Fang, S. Shao, E. Dang, J. Zhang, P. Qiao, A. Yang, G. Wang, Keratinocyte exosomes activate neutrophils and enhance skin inflammation in psoriasis, FASEB J. 33 (2019) 13241–13253. [CrossRef]


| Primer | Sequence and Size |
| Collagen I | forward 5′- ATCAGCCCAAACCCCAAGGAGA -3′ reverse 5′- CGCAGGAAGGTCAGCTGGATAG -3′, 233bp |
| Collagen III | forward 5'- TGATGGGATCCAATGAGGGAGA -3' reverse 5'- GAGTCTCATGGCCTTGCGTGTTT -3', |
| Elastin | forward 5’- CTTCCTGGTGGAGTTCCCGGTGGA -3 reverse 3’- CCGATGCCACCAATACCACCGACA -5’, |
| PH1 | Forward 5’- CGGGATCCTCGGACACCCTGTAAATG Reverse 5´ GGAATTCCAAGCAGTCCTCAGCTGT 3´, |
| GAPDH | Forward 5’-CCATTCTTCCACCTTTGATGCT-3 Reverse 5´ TGTTGCTGTAGCCATATTCATTGT 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




