Submitted:
30 November 2023
Posted:
01 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background
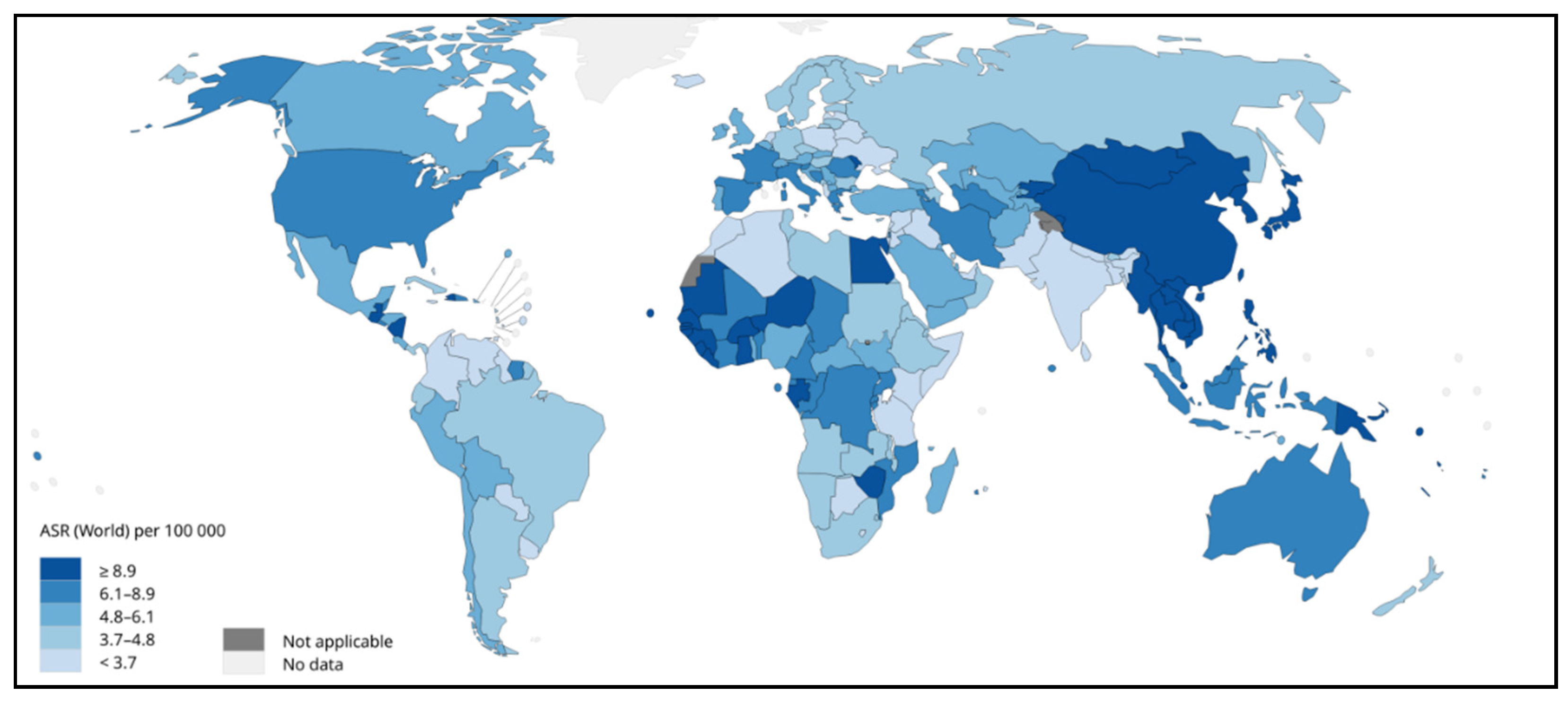
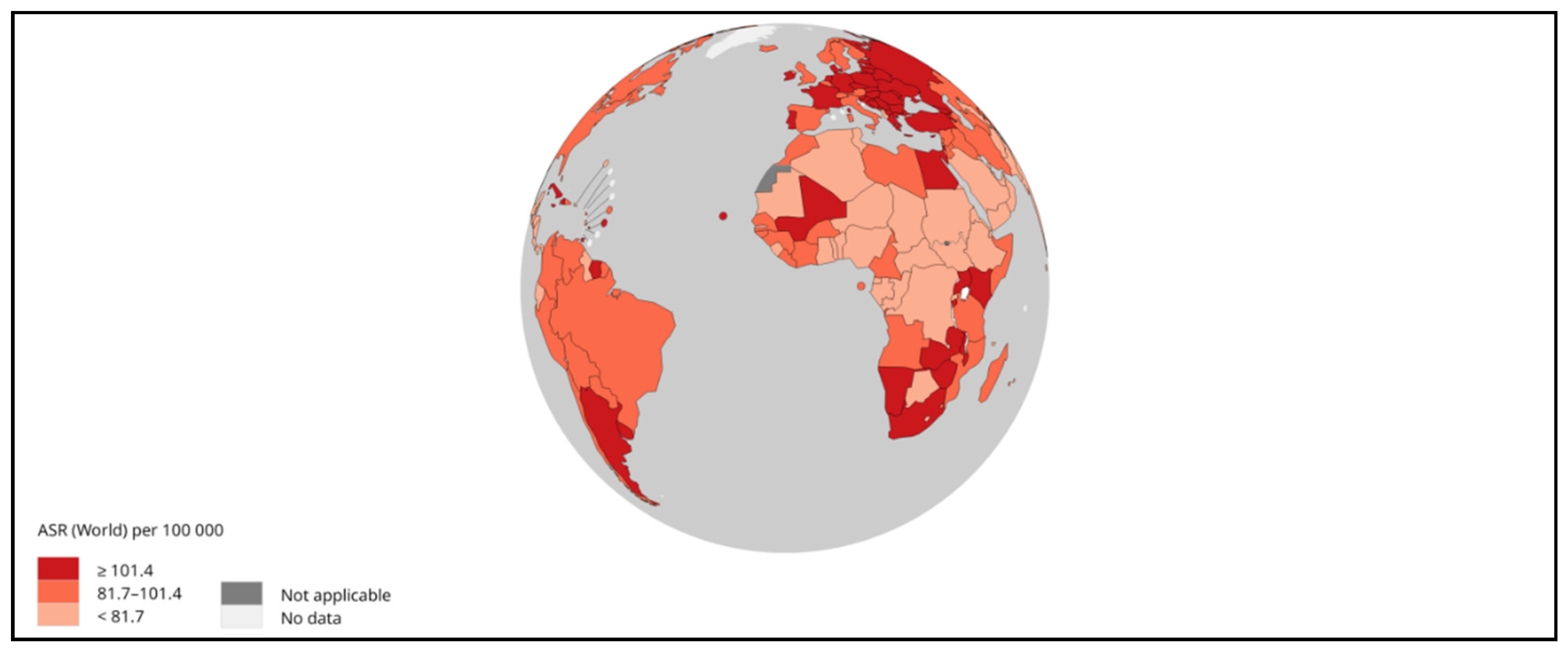
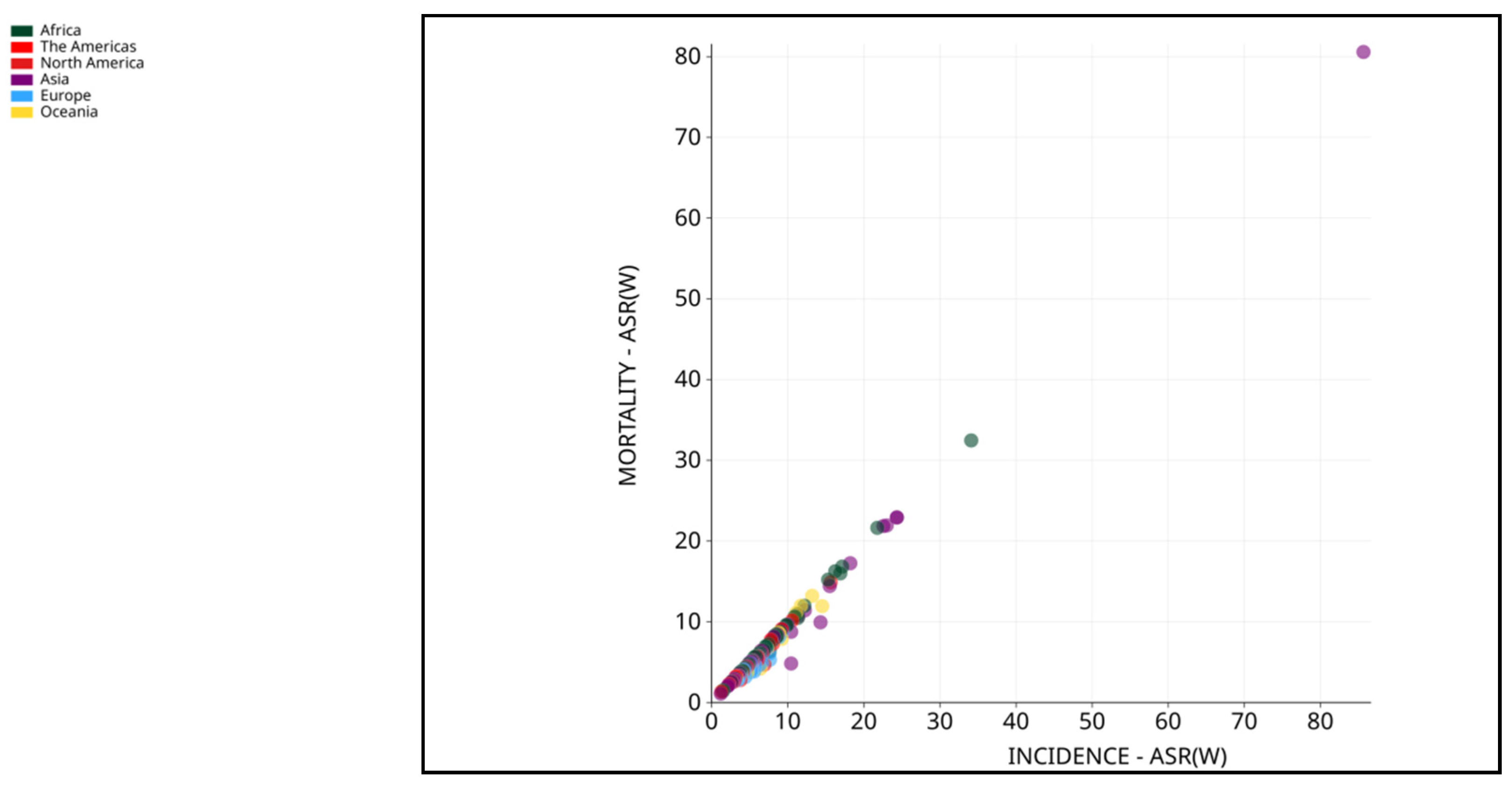
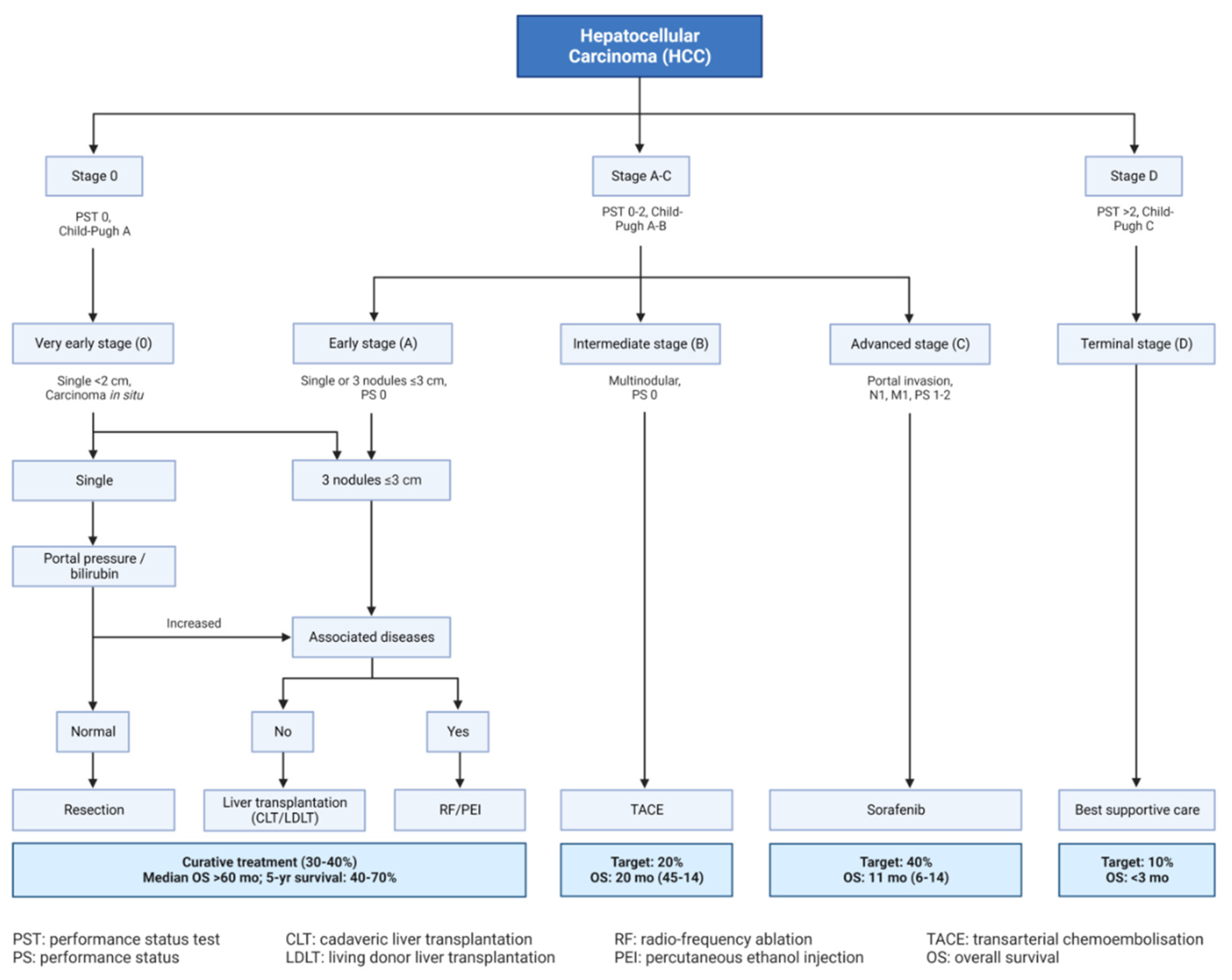
2. Pathophysiology of HCC
3. Molecular triggers of hepatocellular carcinoma
4. Checkpoint targets of hepatocellular carcinoma
4.1. Wnt–β-catenin signalling
CTNNB1
Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC)
AXIN1
4.2. Telomere maintenance
TERT
4.3. Cell cycle regulation
TP53
CDKN2A, CCND1, FGF3, FGF4 or FGF19
4.4. Oxidative stress
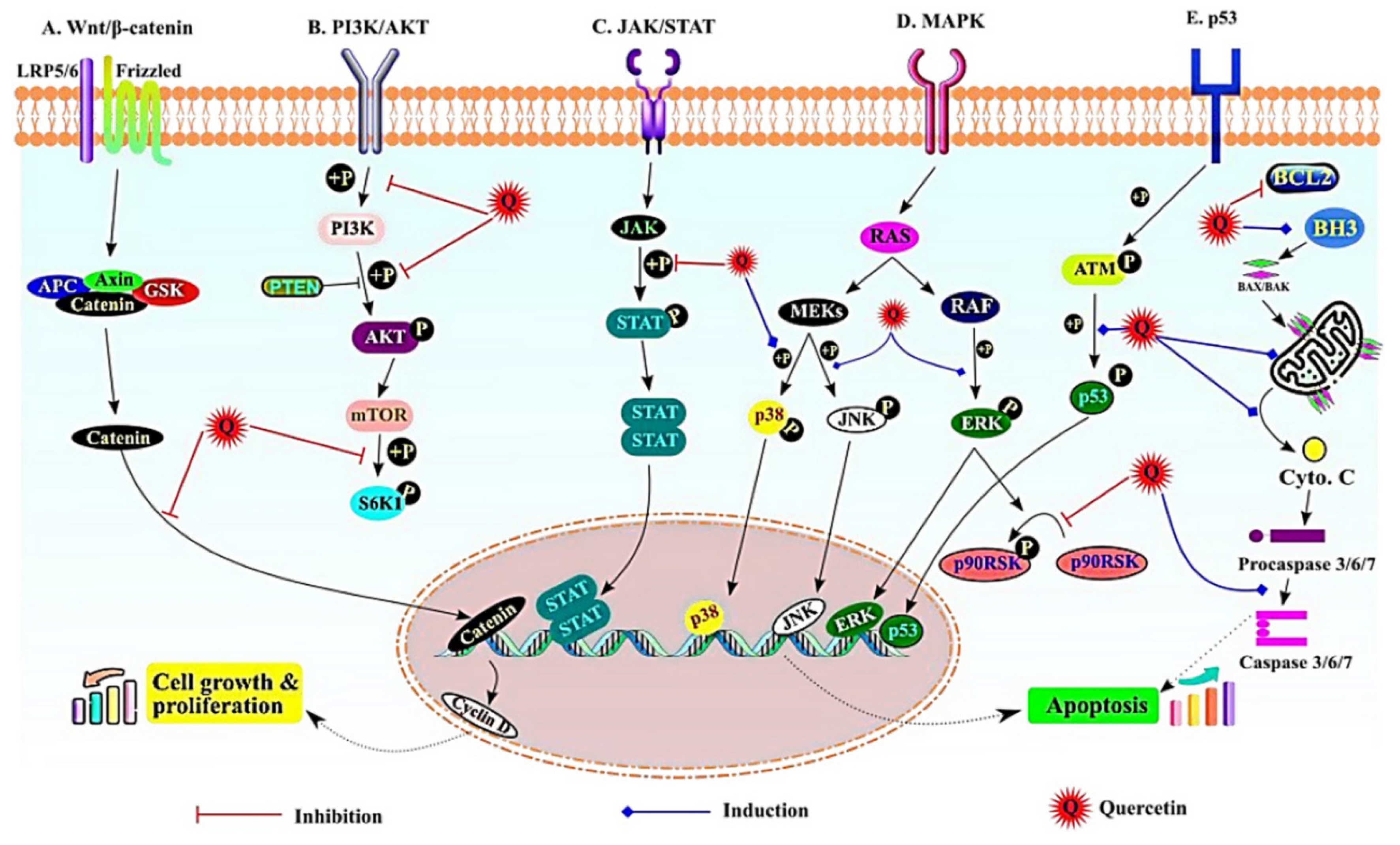
5. Potential anti-cancer mechanism of nano quercetin in HCC
5.1. Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
5.2. PI3K/AKT pathway
5.3. JAK/STAT signalling
5.4. The MAPK signalling
5.5. NF-ĸB, p53 and apoptotic signaling
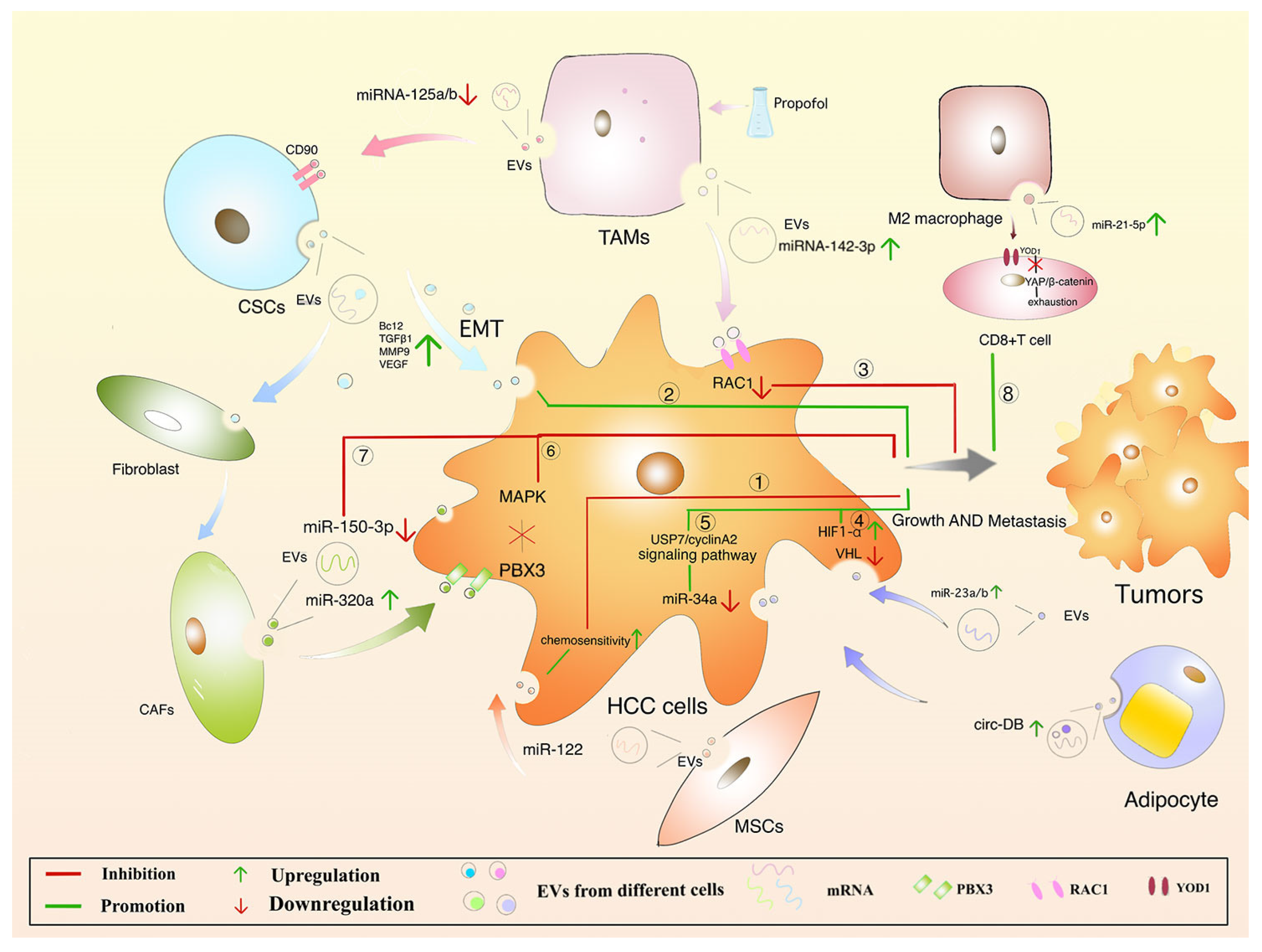
6. Protective mechanism of EVs in HCC
7. Challenges and perspectives of anti-cancer EVs biopharmaceuticals
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| UVR | Unrelenting virological response |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| AAPC | Average annual percent change |
| HKLC | Hong Kong Liver Cancer |
| CLIP | Cancer of the liver Italian program |
| BCLC | Barcelona clinic liver cancer |
| AASLD | American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases |
References
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration; Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, Dicker DJ, Chimed-Orchir O, Dandona R, Dandona L, Fleming T, Forouzanfar MH, Hancock J, Hay RJ, Hunter-Merrill R, Huynh C, Hosgood HD, Johnson CO, Jonas JB, Khubchandani J, Kumar GA, Kutz M, Lan Q, Larson HJ, Liang X, Lim SS, Lopez AD, MacIntyre MF, Marczak L, Marquez N, Mokdad AH, Pinho C, Pourmalek F, Salomon JA, Sanabria JR, Sandar L, Sartorius B, Schwartz SM, Shackelford KA, Shibuya K, Stanaway J, Steiner C, Sun J, Takahashi K, Vollset SE, Vos T, Wagner JA, Wang H, Westerman R, Zeeb H, Zoeckler L, Abd-Allah F, Ahmed MB, Alabed S, Alam NK, Aldhahri SF, Alem G, Alemayohu MA, Ali R, Al-Raddadi R, Amare A, Amoako Y, Artaman A, Asayesh H, Atnafu N, Awasthi A, Saleem HB, Barac A, Bedi N, Bensenor I, Berhane A, Bernabé E, Betsu B, Binagwaho A, Boneya D, Campos-Nonato I, Castañeda-Orjuela C, Catalá-López F, Chiang P, Chibueze C, Chitheer A, Choi JY, Cowie B, Damtew S, das Neves J, Dey S, Dharmaratne S, Dhillon P, Ding E, Driscoll T, Ekwueme D, Endries AY, Farvid M, Farzadfar F, Fernandes J, Fischer F, G/Hiwot TT, Gebru A, Gopalani S, Hailu A, Horino M, Horita N, Husseini A, Huybrechts I, Inoue M, Islami F, Jakovljevic M, James S, Javanbakht M, Jee SH, Kasaeian A, Kedir MS, Khader YS, Khang YH, Kim D, Leigh J, Linn S, Lunevicius R, El Razek HMA, Malekzadeh R, Malta DC, Marcenes W, Markos D, Melaku YA, Meles KG, Mendoza W, Mengiste DT, Meretoja TJ, Miller TR, Mohammad KA, Mohammadi A, Mohammed S, Moradi-Lakeh M, Nagel G, Nand D, Le Nguyen Q, Nolte S, Ogbo FA, Oladimeji KE, Oren E, Pa M, Park EK, Pereira DM, Plass D, Qorbani M, Radfar A, Rafay A, Rahman M, Rana SM, Søreide K, Satpathy M, Sawhney M, Sepanlou SG, Shaikh MA, She J, Shiue I, Shore HR, Shrime MG, So S, Soneji S, Stathopoulou V, Stroumpoulis K, Sufiyan MB, Sykes BL, Tabarés-Seisdedos R, Tadese F, Tedla BA, Tessema GA, Thakur JS, Tran BX, Ukwaja KN, Uzochukwu BSC, Vlassov VV, Weiderpass E, Wubshet Terefe M, Yebyo HG, Yimam HH, Yonemoto N, Younis MZ, Yu C, Zaidi Z, Zaki MES, Zenebe ZM, Murray CJL, Naghavi M. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017 Apr 1;3(4):524-548; Erratum in: JAMA Oncol. 2017 Mar 1;3(3):418. [CrossRef]
- Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, Lencioni R, Koike K, Zucman-Rossi J, Finn RS. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021 Jan 21;7(1):6. [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. GLOBOCAN 2018. IARC https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-map?v=2020&mode=population&mode_population=continents&population=900&populations=900&key=asr&sex=0&cancer=11&type=0&statistic=5&prevalence=0&population_groupearth&color_palette=default&map_scale=quantile&map_nb_colors=5&continent=0&rotate=%255B10%252C0%255D (Access on 03/03/2023).
- Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration; Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, Allen C, Al-Raddadi R, Alvis-Guzman N, Amoako Y, Artaman A, Ayele TA, Barac A, Bensenor I, Berhane A, Bhutta Z, Castillo-Rivas J, Chitheer A, Choi JY, Cowie B, Dandona L, Dandona R, Dey S, Dicker D, Phuc H, Ekwueme DU, Zaki MS, Fischer F, Fürst T, Hancock J, Hay SI, Hotez P, Jee SH, Kasaeian A, Khader Y, Khang YH, Kumar A, Kutz M, Larson H, Lopez A, Lunevicius R, Malekzadeh R, McAlinden C, Meier T, Mendoza W, Mokdad A, Moradi-Lakeh M, Nagel G, Nguyen Q, Nguyen G, Ogbo F, Patton G, Pereira DM, Pourmalek F, Qorbani M, Radfar A, Roshandel G, Salomon JA, Sanabria J, Sartorius B, Satpathy M, Sawhney M, Sepanlou S, Shackelford K, Shore H, Sun J, Mengistu DT, Topór-Mądry R, Tran B, Ukwaja KN, Vlassov V, Vollset SE, Vos T, Wakayo T, Weiderpass E, Werdecker A, Yonemoto N, Younis M, Yu C, Zaidi Z, Zhu L, Murray CJL, Naghavi M, Fitzmaurice C. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies From 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017 Dec 1;3(12):1683-1691. [CrossRef]
- Kanwal F, Kramer J, Asch SM, Chayanupatkul M, Cao Y, El-Serag HB. Risk of Hepatocellular Cancer in HCV Patients Treated With Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents. Gastroenterology. 2017 Oct;153(4):996-1005.e1. [CrossRef]
- Estes C, Razavi H, Loomba R, Younossi Z, Sanyal AJ. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology. 2018 Jan;67(1):123-133. [CrossRef]
- Nishida, N. Metabolic disease as a risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021 Jan;27(1):87-90. [CrossRef]
- Ascha MS, Hanouneh IA, Lopez R, Tamimi TA, Feldstein AF, Zein NN. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2010 Jun;51(6):1972-8.
- Zhao, L. The gut microbiota and obesity: from correlation to causality. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013 Sep;11(9):639-47. [CrossRef]
- WHO. Data Visualization Tools for Exploring the Global Cancer Burden in 2020. 2020. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/ (accessed on 03/03/2022).
- Kulik L, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2019 Jan;156(2):477-491.e1. [CrossRef]
- Petrick JL, Florio AA, Znaor A, Ruggieri D, Laversanne M, Alvarez CS, Ferlay J, Valery PC, Bray F, McGlynn KA. International trends in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, 1978-2012. Int J Cancer. 2020 Jul 15;147(2):317-330. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fan, J.; Gao, Q. Changing epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2029–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49.
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Parkin DM, Piñeros M, Znaor A, et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int J Cancer. 2021;149:778–89. [CrossRef]
- Tellapuri S, Sutphin PD, Beg MS, Singal AG, Kalva SP. Staging systems of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2018 Nov;37(6):481-491. [CrossRef]
- Liu L, Chen H, Wang M, Zhao Y, Cai G, Qi X, Han G. Combination therapy of sorafenib and TACE for unresectable HCC: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014 Mar 20;9(3):e91124. [CrossRef]
- Chidambaranathan-Reghupaty S, Fisher PB, Sarkar D. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology, etiology and molecular classification. Adv Cancer Res. 2021;149:1-61. [CrossRef]
- Lin S, Hoffmann K, Schemmer P. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Liver Cancer. 2012;1:144–58. [CrossRef]
- Li M, Zhang W, Wang B, Gao Y, Song Z, Zheng QC. Ligand-based targeted therapy: a novel strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Oct 31;11:5645-5669. [CrossRef]
- Llovet JM, Castet F, Heikenwalder M, Maini MK, Mazzaferro V, Pinato DJ, Pikarsky E, Zhu AX, Finn RS. Immunotherapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022 Mar;19(3):151-172. [CrossRef]
- Zucman-Rossi J, Villanueva A, Nault JC, Llovet JM. Genetic Landscape and Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2015 Oct;149(5):1226-1239.e4. [CrossRef]
- Sia D, Villanueva A, Friedman SL, Llovet JM. Liver Cancer Cell of Origin, Molecular Class, and Effects on Patient Prognosis. Gastroenterology. 2017 Mar;152(4):745-761. [CrossRef]
- Shafizadeh N, Kakar S. Diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular lesions: role of immunohistochemistry and other ancillary techniques. Adv Anat Pathol. 2011 Nov;18(6):438-45. [CrossRef]
- Michalopoulos, G. K. & Bhushan, B. Liver regeneration: biological and pathological mechanisms and implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18, 40–55 (2021).
- Bruno S, Herrera Sanchez MB, Chiabotto G, Fonsato V, Navarro-Tableros V, Pasquino C, Tapparo M, Camussi G. Human Liver Stem Cells: A Liver-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Like Population With Pro-regenerative Properties. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 26;9:644088. [CrossRef]
- Bayard Q, Meunier L, Peneau C, Renault V, Shinde J, Nault JC, Mami I, Couchy G, Amaddeo G, Tubacher E, Bacq D, Meyer V, La Bella T, Debaillon-Vesque A, Bioulac-Sage P, Seror O, Blanc JF, Calderaro J, Deleuze JF, Imbeaud S, Zucman-Rossi J, Letouzé E. Cyclin A2/E1 activation defines a hepatocellular carcinoma subclass with a rearrangement signature of replication stress. Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 7;9(1):5235. [CrossRef]
- Pfister D, Núñez NG, Pinyol R, Govaere O, Pinter M, Szydlowska M, Gupta R, Qiu M, Deczkowska A, Weiner A, Müller F, Sinha A, Friebel E, Engleitner T, Lenggenhager D, Moncsek A, Heide D, Stirm K, Kosla J, Kotsiliti E, Leone V, Dudek M, Yousuf S, Inverso D, Singh I, Teijeiro A, Castet F, Montironi C, Haber PK, Tiniakos D, Bedossa P, Cockell S, Younes R, Vacca M, Marra F, Schattenberg JM, Allison M, Bugianesi E, Ratziu V, Pressiani T, D'Alessio A, Personeni N, Rimassa L, Daly AK, Scheiner B, Pomej K, Kirstein MM, Vogel A, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Hucke F, Finkelmeier F, Waidmann O, Trojan J, Schulze K, Wege H, Koch S, Weinmann A, Bueter M, Rössler F, Siebenhüner A, De Dosso S, Mallm JP, Umansky V, Jugold M, Luedde T, Schietinger A, Schirmacher P, Emu B, Augustin HG, Billeter A, Müller-Stich B, Kikuchi H, Duda DG, Kütting F, Waldschmidt DT, Ebert MP, Rahbari N, Mei HE, Schulz AR, Ringelhan M, Malek N, Spahn S, Bitzer M, Ruiz de Galarreta M, Lujambio A, Dufour JF, Marron TU, Kaseb A, Kudo M, Huang YH, Djouder N, Wolter K, Zender L, Marche PN, Decaens T, Pinato DJ, Rad R, Mertens JC, Weber A, Unger K, Meissner F, Roth S, Jilkova ZM, Claassen M, Anstee QM, Amit I, Knolle P, Becher B, Llovet JM, Heikenwalder M. NASH limits anti-tumour surveillance in immunotherapy-treated HCC. Nature. 2021 Apr;592(7854):450-456. [CrossRef]
- Gellert-Kristensen H, Richardson TG, Davey Smith G, Nordestgaard BG, Tybjaerg-Hansen A, Stender S. Combined Effect of PNPLA3, TM6SF2, and HSD17B13 Variants on Risk of Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the General Population. Hepatology. 2020 Sep;72(3):845-856. [CrossRef]
- Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A, Plymoth A, Roberts LR. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Oct;16(10):589-604. [CrossRef]
- Nault JC, Letouzé E. Mutational Processes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Story of Aristolochic Acid. Semin Liver Dis. 2019 Jul;39(3):334-340. [CrossRef]
- Guichard C, Amaddeo G, Imbeaud S, Ladeiro Y, Pelletier L, Maad IB, Calderaro J, Bioulac-Sage P, Letexier M, Degos F, Clément B, Balabaud C, Chevet E, Laurent A, Couchy G, Letouzé E, Calvo F, Zucman-Rossi J. Integrated analysis of somatic mutations and focal copy-number changes identifies key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2012 May 6;44(6):694-8. [CrossRef]
- Takai A, Dang HT, Wang XW. Identification of drivers from cancer genome diversity in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Jun 20;15(6):11142-60. [CrossRef]
- Ahn SM, Jang SJ, Shim JH, Kim D, Hong SM, Sung CO, Baek D, Haq F, Ansari AA, Lee SY, Chun SM, Choi S, Choi HJ, Kim J, Kim S, Hwang S, Lee YJ, Lee JE, Jung WR, Jang HY, Yang E, Sung WK, Lee NP, Mao M, Lee C, Zucman-Rossi J, Yu E, Lee HC, Kong G. Genomic portrait of resectable hepatocellular carcinomas: implications of RB1 and FGF19 aberrations for patient stratification. Hepatology. 2014 Dec;60(6):1972-82. [CrossRef]
- Belinky F, Nativ N, Stelzer G, Zimmerman S, Iny Stein T, Safran M, Lancet D. PathCards: multi-source consolidation of human biological pathways. Database (Oxford). 2015;2015:bav006.
- Schulze K, Imbeaud S, Letouzé E, Alexandrov LB, Calderaro J, Rebouissou S, Couchy G, Meiller C, Shinde J, Soysouvanh F, Calatayud AL, Pinyol R, Pelletier L, Balabaud C, Laurent A, Blanc JF, Mazzaferro V, Calvo F, Villanueva A, Nault JC, Bioulac-Sage P, Stratton MR, Llovet JM, Zucman-Rossi J. Exome sequencing of hepatocellular carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Genet. 2015 May;47(5):505-511. [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. The Cancer Genome Atlas. Available online: http://cancergenome.nih.gov/ (accessed on 04 March 2023).
- Tao J, Xu E, Zhao Y, Singh S, Li X, Couchy G, Chen X, Zucman-Rossi J, Chikina M, Monga SP. Modeling a human hepatocellular carcinoma subset in mice through coexpression of met and point-mutant β-catenin. Hepatology. 2016 Nov;64(5):1587-1605. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Galarreta M, Bresnahan E, Molina-Sánchez P, Lindblad KE, Maier B, Sia D, Puigvehi M, Miguela V, Casanova-Acebes M, Dhainaut M, Villacorta-Martin C, Singhi AD, Moghe A, von Felden J, Tal Grinspan L, Wang S, Kamphorst AO, Monga SP, Brown BD, Villanueva A, Llovet JM, Merad M, Lujambio A. β-Catenin Activation Promotes Immune Escape and Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019 Aug;9(8):1124-1141. [CrossRef]
- Tao J, Krutsenko Y, Moghe A, Singh S, Poddar M, Bell A, Oertel M, Singhi AD, Geller D, Chen X, Lujambio A,Tan Liu S, Monga SP. Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and β-Catenin Coactivation in Hepatocellular Cancer: Biological and Therapeutic Implications. Hepatology. 2021 Aug;74(2):741-759. [CrossRef]
- Tan X, Behari J, Cieply B, Michalopoulos GK, Monga SP. Conditional deletion of beta-catenin reveals its role in liver growth and regeneration. Gastroenterology. 2006 Nov;131(5):1561-72. [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi Y, Nagase H, Ando H, Horii A, Ichii S, Nakatsuru S, Aoki T, Miki Y, Mori T, Nakamura Y. Somatic mutations of the APC gene in colorectal tumors: mutation cluster region in the APC gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1992 Jul;1(4):229-33. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Quan H, Liu Q, Si Z, He Z, Qi H. Alterations of axis inhibition protein 1 (AXIN1) in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and overexpression of AXIN1 induces apoptosis in hepatocellular cancer cells. Oncol Res. 2013;20(7):281-8. [CrossRef]
- Satoh S, Daigo Y, Furukawa Y, Kato T, Miwa N, Nishiwaki T, Kawasoe T, Ishiguro H, Fujita M, Tokino T, Sasaki Y, Imaoka S, Murata M, Shimano T, Yamaoka Y, Nakamura Y. AXIN1 mutations in hepatocellular carcinomas, and growth suppression in cancer cells by virus-mediated transfer of AXIN1. Nat Genet. 2000 Mar;24(3):245-50. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, Cheung A, Stegmeier F, Michaud GA, Charlat O, Wiellette E, Zhang Y, Wiessner S, Hild M, Shi X, Wilson CJ, Mickanin C, Myer V, Fazal A, Tomlinson R, Serluca F, Shao W, Cheng H, Shultz M, Rau C, Schirle M, Schlegl J, Ghidelli S, Fawell S, Lu C, Curtis D, Kirschner MW, Lengauer C, Finan PM, Tallarico JA, Bouwmeester T, Porter JA, Bauer A, Cong F. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature. 2009 Oct 1;461(7264):614-20. [CrossRef]
- Totoki Y, Tatsuno K, Covington KR, Ueda H, Creighton CJ, Kato M, Tsuji S, Donehower LA, Slagle BL, Nakamura H, Yamamoto S, Shinbrot E, Hama N, Lehmkuhl M, Hosoda F, Arai Y, Walker K, Dahdouli M, Gotoh K, Nagae G, Gingras MC, Muzny DM, Ojima H, Shimada K, Midorikawa Y, Goss JA, Cotton R, Hayashi A, Shibahara J, Ishikawa S, Guiteau J, Tanaka M, Urushidate T, Ohashi S, Okada N, Doddapaneni H, Wang M, Zhu Y, Dinh H, Okusaka T, Kokudo N, Kosuge T, Takayama T, Fukayama M, Gibbs RA, Wheeler DA, Aburatani H, Shibata T. Trans-ancestry mutational landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma genomes. Nat Genet. 2014 Dec;46(12):1267-73. [CrossRef]
- Pezzuto F, Izzo F, Buonaguro L, Annunziata C, Tatangelo F, Botti G, Buonaguro FM, Tornesello ML. Tumor specific mutations in TERT promoter and CTNNB1 gene in hepatitis B and hepatitis C related hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 23;7(34):54253-54262. [CrossRef]
- Huang FW, Hodis E, Xu MJ, Kryukov GV, Chin L, Garraway LA. Highly recurrent TERT promoter mutations in human melanoma. Science. 2013 Feb 22;339(6122):957-9. [CrossRef]
- Horn S, Figl A, Rachakonda PS, Fischer C, Sucker A, Gast A, Kadel S, Moll I, Nagore E, Hemminki K, Schadendorf D, Kumar R. TERT promoter mutations in familial and sporadic melanoma. Science. 2013 Feb 22;339(6122):959-61. [CrossRef]
- Borah S, Xi L, Zaug AJ, Powell NM, Dancik GM, Cohen SB, Costello JC, Theodorescu D, Cech TR. Cancer. TERT promoter mutations and telomerase reactivation in urothelial cancer. Science. 2015 Feb 27;347(6225):1006-10. [CrossRef]
- Lombardo D, Saitta C, Giosa D, Di Tocco FC, Musolino C, Caminiti G, Chines V, Franzè MS, Alibrandi A, Navarra G, Raimondo G, Pollicino T. Frequency of somatic mutations in TERT promoter, TP53 and CTNNB1 genes in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma from Southern Italy. Oncol Lett. 2020 Mar;19(3):2368-2374. [CrossRef]
- Sirma H, Kumar M, Meena JK, Witt B, Weise JM, Lechel A, Ande S, Sakk V, Guguen-Guillouzo C, Zender L, Rudolph KL, Günes C. The promoter of human telomerase reverse transcriptase is activated during liver regeneration and hepatocyte proliferation. Gastroenterology. 2011 Jul;141(1):326-37, 337.e1-3. [CrossRef]
- Liu T, Li W, Lu W, Chen M, Luo M, Zhang C, Li Y, Qin G, Shi D, Xiao B, Qiu H, Yu W, Kang L, Kang T, Huang W, Yu X, Wu X, Deng W. RBFOX3 Promotes Tumor Growth and Progression via hTERT Signaling and Predicts a Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Theranostics. 2017 Jul 22;7(12):3138-3154. [CrossRef]
- Esopi D, Graham MK, Brosnan-Cashman JA, Meyers J, Vaghasia A, Gupta A, Kumar B, Haffner MC, Heaphy CM, De Marzo AM, Meeker AK, Nelson WG, Wheelan SJ, Yegnasubramanian S. Pervasive promoter hypermethylation of silenced TERT alleles in human cancers. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Oct;43(5):847-861. [CrossRef]
- Montironi C, Castet F, Haber PK, Pinyol R, Torres-Martin M, Torrens L, Mesropian A, Wang H, Puigvehi M, Maeda M, Leow WQ, Harrod E, Taik P, Chinburen J, Taivanbaatar E, Chinbold E, Solé Arqués M, Donovan M, Thung S, Neely J, Mazzaferro V, Anderson J, Roayaie S, Schwartz M, Villanueva A, Friedman SL, Uzilov A, Sia D, Llovet JM. Inflamed and non-inflamed classes of HCC: a revised immunogenomic classification. Gut. 2023 Jan;72(1):129-140. [CrossRef]
- Villanueva A, Hoshida Y. Depicting the role of TP53 in hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J Hepatol. 2011 Sep;55(3):724-725. [CrossRef]
- Jeng YM, Hsu HC. Mutation of the DR5/TRAIL receptor 2 gene is infrequent in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2002 Jul 26;181(2):205-8. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. , Qiu, J., He, G. et al. TRAIL promotes hepatocellular carcinoma apoptosis and inhibits proliferation and migration via interacting with IER3. Cancer Cell Int 21, 63 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Salmena L, Lemmers B, Hakem A, Matysiak-Zablocki E, Murakami K, Au PY, Berry DM, Tamblyn L, Shehabeldin A, Migon E, Wakeham A, Bouchard D, Yeh WC, McGlade JC, Ohashi PS, Hakem R. Essential role for caspase 8 in T-cell homeostasis and T-cell-mediated immunity. Genes Dev. 2003 Apr 1;17(7):883-95. [CrossRef]
- Kim IK, Chung CW, Woo HN, Hong GS, Nagata S, Jung YK. Reconstitution of caspase-8 sensitizes JB6 cells to TRAIL. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Oct 22;277(2):311-6. [CrossRef]
- Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A, Schow P, Kim KJ, Ashkenazi A. Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity. 2000 Jun;12(6):611-20. [CrossRef]
- Lin Y, Devin A, Cook A, Keane MM, Kelliher M, Lipkowitz S, Liu ZG. The death domain kinase RIP is essential for TRAIL (Apo2L)-induced activation of IkappaB kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Sep;20(18):6638-45. [CrossRef]
- Schneider P, Thome M, Burns K, Bodmer JL, Hofmann K, Kataoka T, Holler N, Tschopp J. TRAIL receptors 1 (DR4) and 2 (DR5) signal FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate NF-kappaB. Immunity. 1997 Dec;7(6):831-6. [CrossRef]
- Belinky F, Nativ N, Stelzer G, Zimmerman S, Iny Stein T, Safran M, Lancet D. PathCards: multi-source consolidation of human biological pathways. Database (Oxford). 2015;2015:bav006.
- Knudsen ES, Gopal P, Singal AG. The changing landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma: etiology, genetics, and therapy. Am J Pathol. 2014 Mar;184(3):574-83. [CrossRef]
- Llovet JM, Villanueva A, Lachenmayer A, Finn RS. Advances in targeted therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma in the genomic era. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015 Aug;12(8):436. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Erratum for: Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015 Jul;12(7):408-24. [CrossRef]
- Sawey ET, Chanrion M, Cai C, Wu G, Zhang J, Zender L, Zhao A, Busuttil RW, Yee H, Stein L, French DM, Finn RS, Lowe SW, Powers S. Identification of a therapeutic strategy targeting amplified FGF19 in liver cancer by Oncogenomic screening. Cancer Cell. 2011 Mar 8;19(3):347-58. [CrossRef]
- Anstee QM, Reeves HL, Kotsiliti E, Govaere O, Heikenwalder M. From NASH to HCC: current concepts and future challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Jul;16(7):411-428. [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa H, Umemura A, Taniguchi K, Font-Burgada J, Dhar D, Ogata H, Zhong Z, Valasek MA, Seki E, Hidalgo J, Koike K, Kaufman RJ, Karin M. ER stress cooperates with hypernutrition to trigger TNF-dependent spontaneous HCC development. Cancer Cell. 2014 Sep 8;26(3):331-343. [CrossRef]
- Nishida N, Yada N, Hagiwara S, Sakurai T, Kitano M, Kudo M. Unique features associated with hepatic oxidative DNA damage and DNA methylation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Sep;31(9):1646-53. [CrossRef]
- Guri Y, Colombi M, Dazert E, Hindupur SK, Roszik J, Moes S, Jenoe P, Heim MH, Riezman I, Riezman H, Hall MN. mTORC2 Promotes Tumorigenesis via Lipid Synthesis. Cancer Cell. 2017 Dec 11;32(6):807-823.e12. [CrossRef]
- Liu D, Wong CC, Fu L, Chen H, Zhao L, Li C, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Xu W, Yang Y, Wu B, Cheng G, Lai PB, Wong N, Sung JJY, Yu J. Squalene epoxidase drives NAFLD-induced hepatocellular carcinoma and is a pharmaceutical target. Sci Transl Med. 2018 Apr 18;10(437):eaap9840. Erratum in: Sci Transl Med. 2018 Sep 26;10(460). [CrossRef]
- Estes C, Razavi H, Loomba R, Younossi Z, Sanyal AJ. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology. 2018 Jan;67(1):123-133. [CrossRef]
- Hsu CL, Yen GC. Phenolic compounds: evidence for inhibitory effects against obesity and their underlying molecular signaling mechanisms. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008 Jan;52(1):53-61. [CrossRef]
- Zhang HX, Jiang SS, Zhang XF, Zhou ZQ, Pan QZ, Chen CL, Zhao JJ, Tang Y, Xia JC, Weng DS. Protein kinase CK2α catalytic subunit is overexpressed and serves as an unfavorable prognostic marker in primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 27;6(33):34800-17. [CrossRef]
- Tawfic S, Yu S, Wang H, Faust R, Davis A, Ahmed K. Protein kinase CK2 signal in neoplasia. Histol Histopathol. 2001 Apr;16(2):573-82. [CrossRef]
- Yenice S, Davis AT, Goueli SA, Akdas A, Limas C, Ahmed K. Nuclear casein kinase 2 (CK-2) activity in human normal, benign hyperplastic, and cancerous prostate. Prostate. 1994;24(1):11-6. [CrossRef]
- Croquelois A, Blindenbacher A, Terracciano L, Wang X, Langer I, Radtke F, Heim MH. Inducible inactivation of Notch1 causes nodular regenerative hyperplasia in mice. Hepatology. 2005 Mar;41(3):487-96. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Wang X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Dec 4;13(1):165. [CrossRef]
- Mojsin M, Vicentic JM, Schwirtlich M, Topalovic V, Stevanovic M. Quercetin reduces pluripotency, migration and adhesion of human teratocarcinoma cell line NT2/D1 by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Food Funct. 2014 Oct;5(10):2564-73. [CrossRef]
- Kim H, Seo EM, Sharma AR, Ganbold B, Park J, Sharma G, Kang YH, Song DK, Lee SS, Nam JS. Regulation of Wnt signaling activity for growth suppression induced by quercetin in 4T1 murine mammary cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 2013 Oct;43(4):1319-25. [CrossRef]
- Osaki M, Oshimura M, Ito H. PI3K-Akt pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis. 2004 Nov;9(6):667-76. [CrossRef]
- Xiang T, Fang Y, Wang SX. Quercetin suppresses HeLa cells by blocking PI3K/Akt pathway. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2014 Oct;34(5):740-744. [CrossRef]
- Gulati N, Laudet B, Zohrabian VM, Murali R, Jhanwar-Uniyal M. The antiproliferative effect of Quercetin in cancer cells is mediated via inhibition of the PI3K-Akt/PKB pathway. Anticancer Res. 2006 Mar-Apr;26(2A):1177-81.
- Tan HK, Moad AI, Tan ML. The mTOR signalling pathway in cancer and the potential mTOR inhibitory activities of natural phytochemicals. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(16):6463-75. [CrossRef]
- Fyffe C, Falasca M. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 as an emerging target in the management of breast cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2013 Aug 23;5:271-80. [CrossRef]
- Maurya AK, Vinayak M. PI-103 and Quercetin Attenuate PI3K-AKT Signaling Pathway in T- Cell Lymphoma Exposed to Hydrogen Peroxide. PLoS One. 2016 Aug 5;11(8):e0160686. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Núñez L, Lozano ML, Martínez C, Vicente V, Rivera J. Effect of quercetin on platelet spreading on collagen and fibrinogen and on multiple platelet kinases. Fitoterapia. 2010 Mar;81(2):75-80. [CrossRef]
- O'Shea JJ, Schwartz DM, Villarino AV, Gadina M, McInnes IB, Laurence A. The JAK-STAT pathway: impact on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:311-28. [CrossRef]
- Qin Y, He LY, Chen Y, Wang WY, Zhao XH, Wu MY. Quercetin affects leptin and its receptor in human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells and JAK-STAT pathway. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Jan;28(1):12-6.
- Michaud-Levesque J, Bousquet-Gagnon N, Béliveau R. Quercetin abrogates IL-6/STAT3 signaling and inhibits glioblastoma cell line growth and migration. Exp Cell Res. 2012 May 1;318(8):925-35. [CrossRef]
- Seo HS, Ku JM, Choi HS, Choi YK, Woo JK, Kim M, Kim I, Na CH, Hur H, Jang BH, Shin YC, Ko SG. Quercetin induces caspase-dependent extrinsic apoptosis through inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling in HER2-overexpressing BT-474 breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):31-42. [CrossRef]
- Luo CL, Liu YQ, Wang P, Song CH, Wang KJ, Dai LP, Zhang JY, Ye H. The effect of quercetin nanoparticle on cervical cancer progression by inducing apoptosis, autophagy and anti-proliferation via JAK2 suppression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Aug;82:595-605. [CrossRef]
- Wu L, Li J, Liu T, Li S, Feng J, Yu Q, Zhang J, Chen J, Zhou Y, Ji J, Chen K, Mao Y, Wang F, Dai W, Fan X, Wu J, Guo C. Quercetin shows anti-tumor effect in hepatocellular carcinoma LM3 cells by abrogating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 2019 Aug;8(10):4806-4820. [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakopoulou M, Lendenmann T, Pramotton FM, Giampietro C, Stefopoulos G, Poulikakos D, Ferrari A. Cell cycle-dependent force transmission in cancer cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Oct 15;29(21):2528-2539. [CrossRef]
- Widmann C, Gibson S, Jarpe MB, Johnson GL. Mitogen-activated protein kinase: conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol Rev. 1999 Jan;79(1):143-80. [CrossRef]
- Xu D, Hu MJ, Wang YQ, Cui YL. Antioxidant Activities of Quercetin and Its Complexes for Medicinal Application. Molecules. 2019 Mar 21;24(6):1123. [CrossRef]
- Wang R, Zhang H, Wang Y, Song F, Yuan Y. Inhibitory effects of quercetin on the progression of liver fibrosis through the regulation of NF-кB/IкBα, p38 MAPK, and Bcl-2/Bax signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017 Jun;47:126-133. [CrossRef]
- Asgharian P, Tazekand AP, Hosseini K, Forouhandeh H, Ghasemnejad T, Ranjbar M, Hasan M, Kumar M, Beirami SM, Tarhriz V, Soofiyani SR, Kozhamzharova L, Sharifi-Rad J, Calina D, Cho WC. Potential mechanisms of quercetin in cancer prevention: focus on cellular and molecular targets. Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Aug 15;22(1):257. [CrossRef]
- Xavier CP, Lima CF, Rohde M, Pereira-Wilson C. Quercetin enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in MSI colorectal cancer cells through p53 modulation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011 Dec;68(6):1449-57. [CrossRef]
- Wang G, Zhang J, Liu L, Sharma S, Dong Q. Quercetin potentiates doxorubicin mediated antitumor effects against liver cancer through p53/Bcl-xl. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51764. [CrossRef]
- Bishayee K, Ghosh S, Mukherjee A, Sadhukhan R, Mondal J, Khuda-Bukhsh AR. Quercetin induces cytochrome-c release and ROS accumulation to promote apoptosis and arrest the cell cycle in G2/M, in cervical carcinoma: signal cascade and drug-DNA interaction. Cell Prolif. 2013 Apr;46(2):153-63. [CrossRef]
- Bishayee K, Khuda-Bukhsh AR, Huh SO. PLGA-Loaded Gold-Nanoparticles Precipitated with Quercetin Downregulate HDAC-Akt Activities Controlling Proliferation and Activate p53-ROS Crosstalk to Induce Apoptosis in Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Mol Cells. 2015 Jun;38(6):518-27. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen LT, Lee YH, Sharma AR, Park JB, Jagga S, Sharma G, Lee SS, Nam JS. Quercetin induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in triple-negative breast cancer cells through modulation of Foxo3a activity. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;21(2):205-213. [CrossRef]
- Wei JX, Lv LH, Wan YL, Cao Y, Li GL, Lin HM, Zhou R, Shang CZ, Cao J, He H, Han QF, Liu PQ, Zhou G, Min J. Vps4A functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating the secretion and uptake of exosomal microRNAs in human hepatoma cells. Hepatology. 2015 Apr;61(4):1284-94. [CrossRef]
- Giordano S, Columbano A. MicroRNAs: new tools for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma? Hepatology. 2013 Feb;57(2):840-7. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Pu J, Zhang Y, Yao T, Luo Z, Li W, Xu G, Liu J, Wei W, Deng Y. Exosome-transmitted long non-coding RNA SENP3-EIF4A1 suppresses the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jun 27;12(12):11550-11567. [CrossRef]
- Cao L, Xie B, Yang X, Liang H, Jiang X, Zhang D, Xue P, Chen D, Shao Z. MiR-324-5p Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Invasion by Counteracting ECM Degradation through Post-Transcriptionally Downregulating ETS1 and SP1. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0133074. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Z, Li X, Sun W, Yue S, Yang J, Li J, Ma B, Wang J, Yang X, Pu M, Ruan B, Zhao G, Huang Q, Wang L, Tao K, Dou K. Loss of exosomal miR-320a from cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to HCC proliferation and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2017 Jul 1;397:33-42. [CrossRef]
- Jiang W, Tan Y, Cai M, Zhao T, Mao F, Zhang X, Xu W, Yan Z, Qian H, Yan Y. Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl4-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018 Mar 4;2018:6079642. [CrossRef]
- Wang J, Wang X, Zhang X, Shao T, Luo Y, Wang W, Han Y. Extracellular Vesicles and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Opportunities and Challenges. Front Oncol. 2022 May 25;12:884369. [CrossRef]
- Yugawa K, Yoshizumi T, Mano Y, Itoh S, Harada N, Ikegami T, Kohashi K, Oda Y, Mori M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression through downregulation of exosomal miR-150-3p. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2021 Feb;47(2):384-393. [CrossRef]
- Xu T, Zhu Y, Xiong Y, Ge YY, Yun JP, Zhuang SM. MicroRNA-195 suppresses tumorigenicity and regulates G1/S transition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 2009 Jul;50(1):113-21. [CrossRef]
- Wang R, Zhao N, Li S, Fang JH, Chen MX, Yang J, Jia WH, Yuan Y, Zhuang SM. MicroRNA-195 suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting the expression of VEGF, VAV2, and CDC42. Hepatology. 2013 Aug;58(2):642-53. [CrossRef]
- Chen W, Quan Y, Fan S, Wang H, Liang J, Huang L, Chen L, Liu Q, He P, Ye Y. Exosome-transmitted circular RNA hsa_circ_0051443 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer Lett. 2020 Apr 10;475:119-128. [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry, PAT-A framework for innovative pharmaceutical development, manufacturing and quality assurance. http://www. fda. gov/cder/guidance/published.html. 2004. (Accessed on 08/03/2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




