Introduction
The term “information literacy” has evolved into “digital literacies” due to the shift from the information age to the digital age (Becker 2018). Digitization, which is the transition from print to on-screen reading-writing, has been responsible for this change (Dobson & Willinsky 2009). The digital revolution has had a significant impact on our daily lives, including those of people with disabilities (PwDs), who face challenges in accessing and using digital technology due to their physical limitations (Crammer 2021). PwDs also face discrimination and stigma in addition to these difficulties. PWDs encompass a wide range of types and variations, each with varying degrees or levels of impact. Some common types include physical, sensory, cognitive, psychiatric, developmental, and occasionally invisible disabilities (Venkatesan 2004). In an early study conducted by Harris, Harris, and Sally (1998), observations, interviews, and video recordings were used to examine how children with disabilities (CwDs) aged 4 to 11 years old utilized computers both at home and in school. Their computer usage was facilitated by simplifying and repeating tasks, minimizing distractions and irrelevant stimuli, providing models and demonstrations, offering ample practice opportunities, delivering instructions in manageable steps, and providing immediate or frequent reinforcement with feedback. The positive attitudes of parents and teachers played a crucial role in fostering computer literacy skills in their children.
Digital Divide
There exists a significant disparity in various aspects of life, such as physical access, employment opportunities, healthcare, social integration, and education, between individuals without disabilities and PWDs. The "digital gap" or "digital divide" is further exacerbating the challenges faced by disabled individuals. Many websites are inaccessible to those with visual impairments due to issues like text color, size, layout, and compatibility with screen readers. Others with impairments may struggle with using a mouse, keyboards, or extended periods of gadget usage. Unlike unaffected individuals who can visit cafes or libraries for internet access when their home Wi-Fi is down, PWDs have to consider factors like transportation, wheelchair accessibility, ramps, lifts, and restroom facilities when venturing outside their homes (Chiner et al., 2017; Kolotouchkina, Barroso, & Sánchez 2022; Scanlan 2022). Cho & Kim (2021) found that individuals without disabilities who possess higher education levels, household incomes, motivation for internet use, and stronger DL skills tend to experience more favorable outcomes compared to PWDs.
Critics of the digital divide concept argue that the gap between individuals with and without internet access will eventually diminish in the future. According to the Diffusion of Innovations Theory (Rogers 1986), the increasing use of technology, such as television, radio, and telephones, as a market force rather than relying solely on policies, will contribute to the elimination of this divide (Rogers 1962-2003). Indicators of the digital divide include the availability and affordability of internet connectivity, ownership of digital devices like computers, smartphones, or tablets, and proficiency in digital skills required to navigate and utilize digital technologies, online platforms, and services. However, it is important to note that PWDs are typically less likely to be online at any given time. They face inequities and barriers in accessing digital tools and content. Enhancing their DL skills is crucial to promote their inclusion through social participation, livelihood opportunities, and overall QOL (Compaine 2001).
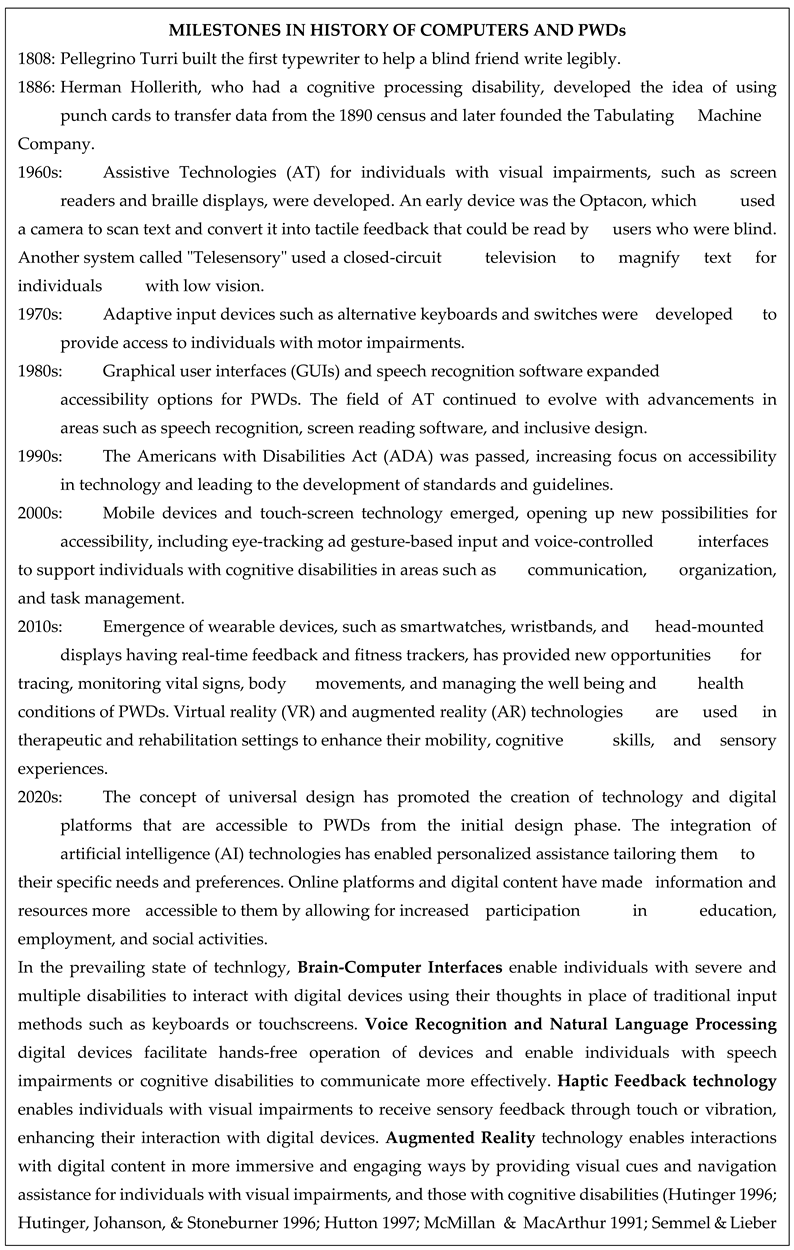 |
Digital Literacy
Digital Literacy (DL) refers to the ability and skills required to find, evaluate, use, share, and create content using ITs and the internet. DL is essential to live, learn, and work in a society where communication and access to information are increasingly through DTs such as social media, internet platforms, and mobile devices. Gilster (1997) first defined the concept of DL as "the ability to understand and use information in multiple formats from a wide range of sources when presented via computers." To use technology effectively, one must understand its uses and limitations as well as its risks and safety measures. DL involves the ability to locate, assess, produce, and communicate information using information communication technology (ICT). However, the meaning of DL has evolved over time (Berge 2017), and its usage varies depending on the background, whether it is for media, entertainment, education, or career (Treglia et al., 2019; McDougall, Readman & Wilkinson 2018; Hartley 2017; Chase & Laufenberg 2011). DL requires both cognitive and technical abilities and has a positive impact on one's QOL and self-esteem. However, accessibility for PWDs is not always guaranteed or consistent. For instance, smartphones may not be compatible with hearing aids required by the deaf, touch screens may be too sensitive for those with motor impairments, and web pages may lack the text labels needed by screen reading software used by the blind (Mengual-Andrés et al., 2020). Augmentative technologies can provide alternative communication methods for PWDs (Botelho 2021). Several sources have explained the basic conceptual similarities and differences of DL (Beliveau & Wiesnger 2023; Parker & Reddy 2019; Julien 2018; Wempen 2014).
Martin & Madigan (2006) advocate for using the term "Digital Literacies" instead of a singular form because it encompasses various components and cognitive-thinking strategies. This viewpoint is supported by other researchers (Knobel & Lankshear 2006). The definition of Digital Literacies has evolved significantly from solely covering computer programming skills in the 1960s. It now encompasses IT and ICT literacy, web literacy, online reading, media literacy, meta-literacy, visual literacy, communication literacy, information literacy, computer literacy, e-literacy, network literacy, and other lay terms like "basic skills," "Internet savvy," or "smart working." Multiple authors have explored the origins and concepts of Digital Literacies (Bawden 2001; 2008; Bawden & Robinson 2002; Kope 2006; Martin 2006a; 2006b; Williams & Minnian 2007). Examples of DL skills include operating gadgets, navigating the internet, managing files in various applications, conducting online searches, using smartphones for communication and other applications, understanding device components, practicing online safety, making online payments, efficient keyboard usage, creating/editing documents (word processing, spreadsheets, presentations), utilizing copy-paste functions, sharing files, formatting content, and utilizing digital tools such as podcasts, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, visual and graphic materials. DL also involve activities like commenting on blogs or forums, securing passwords, understanding basic programming languages and troubleshooting (Tinmaz et al. 2022; Bulger, Mayer, & Metzger 2014; Ba, Tally, & Tsikalas 2002). Alsalem (2016) examined how Digital Literacies benefit students with disabilities in terms of academic performance, collaborative learning, self-efficacy, self-motivation, positive learning environments, communication, engagement both inside and outside the classroom, independence, and technological skills.
On the other hand, digital illiteracy refers to the lack of information skills and understanding of how to use digital tools and technology. Several factors contribute to digital illiteracy, such as unaffordability or inaccessibility of digital devices, poor or no internet connectivity, socio-economic disparities, old age or illness, limited education, language or cultural barriers, fear or resistance to technology, and lack of awareness. DL is a significant contributor to the digital divide among vulnerable sections of society, such as the poor and elderly, who are likely to be excluded from mainstream society. It also affects employability and leads to a poor QOL (Datta et al. 2018; Fernando & Jain 2022). Are there people who lack digital skills entirely? Some individuals with chronic mental illnesses are reported to have no basic digital skills, such as changing passwords, connecting to Wi-Fi, purchasing goods, accessing healthcare online, or setting up an email account.
Spanakis et al. (2022) examined the digital skills of individuals with severe mental illness (SMI) and their ability to adapt to modern digitization trends. Using the Essential Digital Skills Framework, the study found that nearly half of the participants lacked foundational skills and internet access skills. These skills included tasks such as changing passwords, adjusting device settings for ease of use, connecting to secure Wi-Fi networks, and utilizing device controls. In another study, Camacho and Torous (2023) investigated the impact of DL and outreach program on self-reported functional skills and clinical outcomes among individuals with SMI. The study revealed statistically significant improvements in seven of these skills.
Venkatesan (2021) suggested the concept of a potential "digital skills disorder" as a future disability that encompasses the lack of proficiency in various technical and non-technical skills, such as use or operation of new-age gadgets, designing/ developing website, apps or software, not being a virtual netizen, tech-savvy, or were often being dubbed as computer illiterate (Combi 2016; Isin & Ruppert 2015; Selwyn & Facer 2013). The recognition of the economic impact of DL, now considered the fourth literacy, is growing among governments worldwide. There is a strong argument for implementing comprehensive strategies that start with early education and ensure that college graduates possess essential technology competencies when entering the modern workforce (Murray & Pérez 2014; Nelson, Courier, & Joseph 2011).
Levels of Digital Literacy
DL is not a binary concept, but rather a spectrum that varies in individuals and communities' ability to understand and utilize digital technologies in different life situations. The National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology (NIELIT), Ajmer, is implementing courses as part of the National Digital Literacy Mission (NDLM), aligning with the Prime Minister's vision of "Digital India." Through this initiative, eligible households in selected blocks across each state and union territory receive computer skills training. The goal is to provide trainees with basic ICT skills that are relevant to their needs, enabling them to effectively use IT and related applications, actively participate in the democratic process, and enhance their livelihood opportunities. The training aims to empower individuals to access information, knowledge, and skills through the use of digital devices. The course structure consists of two levels: (i) Appreciation of DL and (ii) Basics of DL.
In the first level (i) of the training, the objective is to develop IT literacy in the trainees. They are taught how to operate digital devices such as mobile phones or tablets, send and receive emails, and conduct internet searches for information. Moving on to the higher level (ii), the trainees learn how to effectively access various e-governance services provided to citizens. The syllabus covers topics such as digital device introduction and operation, internet usage, understanding digital technology safety and security, word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, and basic multimedia skills. To be eligible for level, 1, individuals can be illiterate or have completed up to 7th grade. For level, 2, a minimum qualification of 8th grade is required. The age range for participation is between 14 and 60 years. Eligible households nominate one person from their family to receive training at the nearest Training Centre/Common Service Center (CSC). The duration of the course is 20 hours for level, 1, with a minimum of 10 days and a maximum of 30 days. For level, 2, the course duration is 40 hours, with a minimum of 20 days and a maximum of 60 days. The training is conducted in any of the official languages of India. Evaluation is carried out by a national-level certifying agency such as NIELIT, NIOS, or IGNOU.
There are various frameworks that define the different levels of DL (DL). One common model includes five levels: (a) Apprentice; (b) Basic; (c) Intermediate; (d) Advanced; and (e) Expert. At the apprentice level, the goal is to develop IT literacy in individuals, enabling them to operate digital devices such as mobile phones, tablets, and others, send and receive emails, and conduct internet searches for information (Sung & Kim 2020). At the basic level, individuals are expected to identify and use digital devices for simple tasks such as browsing the internet, sending emails, and using basic software. This requires familiarity with various mainstream digital devices such as desktops, laptops, tablets, interactive whiteboards, personal mobile devices such as smartphones, iPods, cameras, gaming consoles, and communication applications like email, Skype, and Zoom. Specialist assistive technologies like Braille Notetaker, screen readers, Bluetooth, fitness trackers, smartwatches, virtual reality headsets, and others are also included. DL at the basic level is comparable to the cognitive-intellectual developmental maturity of adults with borderline-mild levels of intellectual disabilities or typical primary school children (Utaminingsih 2022; Koppel & Langer 2020; Uršej 2019).
At the intermediate level of DL, individuals are expected to have a more comprehensive understanding of digital tools and their application in complex tasks. This includes tasks such as document creation, data management, and the use of social media. At this level, proficiency in working with digital information, including communication, dissemination, creation, and management, is expected. Additionally, individuals should be able to utilize Internet-based tools such as web browsers, search engines, and email effectively. Clear presentation of information, including the use of spreadsheets, is also emphasized. Moving on to the advanced level, individuals are required to have skills in using digital tools for tasks like programming, data analysis, and multimedia production. The expert level demands a deep understanding of tools and the ability to innovate and create new digital solutions. Computational thinking or problem-solving at this level, involves cognitive processes such as data representation, algorithmic work, information analysis, and the ability to generalize solutions that can be applied across various domains of learning (Kimbell-Lopez, Cummins, & Manning 2016).
The levels of DL can be analyzed based on their basic usage, application, development, and transformation across three dimensions: cognitive, social, and technical aspects. PWDs have similar DL levels to their age-matched healthy peers, but they face additional challenges and considerations. A challenge is the use of accessible technology, such as screen readers or magnifiers for the blind. Barriers such as inaccessible websites, apps, and documents that are incompatible with AT must be eliminated. Further, there is a need for additional training and support to develop DL skills among PWDs, including accessible training materials, one-on-one support, and peer mentoring. For PIDs, teaching-learning materials should be presented in simplified language with visual aids. Tailor-made individualized interactive learner-paced training with peer tutoring and positive feedback can also be beneficial. In general, DL programs for PWDs must take into account their unique needs and challenges (Ayyildiz, Yilmaz, & Baltaci 2021). Park & Nam (2014) compared the DL of PWDs to unaffected controls in Korea based on data collected from the National Information Society Agency (NISA) regarding their internet and smart device usage. Among the 1500 individuals examined, 1190 (79.3%) were Internet users, and 535 (35.7%) were smart device users. Among PWDs 63.9% were Internet users, and 8.8% were smart device users. The results revealed significant effects of disability, gender, age, and education on internet use and production literacy. Tohara (2021) explored DL tools and strategies utilized by students with special needs in Malaysia from their perspective and those of their teachers.
Objectives
The topic of DL in relation to PWDs has received limited attention. There is a lack of research addressing the impact of digitization and digital technology on PWDs. The existing literature does not adequately cover the prevalence, challenges, and concerns associated with integrating the digital world into the lives of PWDs. Additionally, there is a need to explore the differences in accessibility, employment opportunities, social inclusion, and education options between PWDs and unaffected populations. The availability of evaluation instruments for measuring digital parameters in PWDs is also an area that requires further investigation. These questions highlight the importance of conducting a literature review on DL in PWDs and its implications for their QOL and digital training programs.
Method
This narrative review aimed to identify peer-reviewed research articles on DL in PWDs. Internet search engines such as Google and MSN were utilized to search databases including Google Scholar, JSTOR, PsycINFO, ERIC, ProQuest, CINAHL, Research Gate, Web of Science, Scopus, and PubMed. The review focused on books, chapters, and publications related to the meaning, characteristics, types, sources, dynamics, measurement, benefits, applications, and negative aspects of DL in PWDs. Only original research articles published in English ISSN journals and ISBN books were included, with specific keywords used for the search. Descriptive essays, newsletters, periodicals, unpublished dissertations, and incomplete or misleading cross-references were excluded. Inter-observer reliability checks undertaken by two mutually blinded independent coders for at least a quarter of the entries in the overall sample to minimize the risk of bias yielded a robust correlation coefficient (r: 0.94). Ethical considerations were prioritized to ensure the representation of diverse ethnic groups and their subjective experiences (Venkatesan 2009). Inter-observer reliability checks and statistical analysis using SPSS/PC were conducted (Pallant 2020). Effect sizes were analyzed using Cohen's guidelines (Cohen 1992). Efforts were made to adhere to PRISMA standards in the production of this publication.
Results
The aggregated data of references on DL vis-a-vis PWDs are classified into harvest plots by their format, timelines, topics or themes respectively (
Table 1).
As per the format of publications, most of the publications on DL in this review are Original Research Articles (N: 143 out of 196; 72.96%), followed by books (N: 26 out of 196; 13.27%), chapters (N: 12 out of 196; 6.12%), review articles (N: 9 out of 196; 4.59%), and proceedings of seminars (N: 3 out of 196; 1.53%). Going by the title of journals, Farias-Gaytan, Aguaded, & Ramirez-Montoya (2022) found the largest proportion of publications on DL originating from five continents were in the Journal of Adolescent and Adult Literacy with 14 articles and “Computers & Education,” and ”Nordic Journal of Digital Literacy” having 5 articles in each. Based on timelines, there is a six-fold increase in the number of publications on DL between the year 2000 (N: 10; 5.10%) to the 2020s (N: 55; 28.05%). Most of the topics or themes of research is focused on DL and PWDs in general (N: 22 out of 196; 11.22%) and fewer of them studied DL against sub types of disabilities (N: 42 out of 196; 21.43%). Among the sub types, most publications are on PIDs (N: 17 out of 196; 8.67%), followed by research on PH (N: 8 out of 196; 4.08%), and HoH/Deaf (N: 7 out of 196; 3.57%). Going by specific topics, training in DL (N: 25 out of 196; 12.76%), measures of DL (N: 16 out of 196; 8.16%) are studied. Areas such as theories, paradigms, or models of DL, digital rights or their violations, ethical issues are least prioritised.
There appears to be mismach between a search-engine extract on a list of journals dedicated to the publication of research articles on DL as against the list of journals as found in this studt (Table 2):
Disability-Specific Studies
Individuals with limited mobility or physical disabilities often require hardware adjustments, accommodations, and adaptations more than software changes. Examples of these adjustments include adaptive keyboards, foot pedals, mouth sticks, or input devices that utilize eye tracking to navigate the virtual world. Voice recognition software is also beneficial for individuals with limited mobility (Lowenthal et al. 2022). Arslantas and Gul (2022) conducted a study in Turkey to examine the DL skills of university students with visual impairment. They employed mixed methods, including an online survey, semi-structured interviews, and a DL Scale. The findings revealed that the participants had high levels of self-reported technical and cognitive DL skills, but low levels of social DL skills. While they possessed basic skills for accessing information and creating files, they lacked proficiency in information management, collaboration, communication, and digital content creation. To ensure accessibility for individuals with blindness, it is important to provide screen readers and other assistive devices that can read text aloud, as well as design websites and navigation aids for the virtual world. In a separate study by Mardiana, Suminar, and Sugiana (2019) involving 39 blind and low-vision students in an Indonesian Special School, it was observed that they were heavy internet users. They demonstrated good DL skills in terms of understanding responsible and polite behavior in digital communication. Around 40 percent of the students reported using the internet for more than four hours a day, with information search being the primary purpose, followed by social media usage. Some students were even able to utilize digital media for creating creative content, such as tutorials uploaded on YouTube.
The DL skills in people with intellectual disabilities (PIDs) have received research attention for the levels, extent, depth, form, types, and content. A particular form of functional DL is noted to be relevant for these people. Just as Functional Literacy has to do with writing or signing one's name, reading street signs, preparing a grocery list, filling out forms related to government schemes, and many other such things to lead a productive life and participate fully in society, functional DL is to with basics like sending and receiving email messages, scanning, photographing, uploading, and sharing documents. Functional DL for PWDs involves understanding how to advocate for their digital accessibility needs and rights in various contexts, such as in the workplace or in accessing online services. DL opened the door to possibilities for fostering social connections, pursuing personal interests, and organizing everyday life in PIDs (Barlott et al. 2020).
Research has examined the DL skills of PIDs in terms of their levels, extent, depth, form, types, and content. Functional DL, in particular, has been identified as relevant for this population. Similar to how Functional Literacy encompasses skills such as writing or signing one's name, reading street signs, creating a grocery list, and completing government forms to lead a productive life and actively participate in society, functional DL involves basic tasks like sending and receiving email messages, scanning documents, taking photographs, uploading files, and sharing documents. For PIDs, functional DL also includes understanding how to advocate for their digital accessibility needs and rights in various contexts, such as the workplace or when accessing online services. DL has provided opportunities for PIDs to establish social connections, pursue personal interests, and effectively organize their daily lives (Barlott et al., 2020).
Caton and Chapman (2016) conducted a systematic review of ten primary studies published in English between 2000-2014 to examine the use of social media by PIDs. The studies were identified through electronic database searches, communication with experts, and citation tracking. The findings revealed several barriers that impede the access of PIDs to social media, including concerns related to safeguarding, difficulties arising from poor literacy and communication skills, cyber-language and cyber-etiquette, and the accessibility and design of equipment. Borgström, Daneback, and Molin (2019) conducted a study that examined two peer-reviewed papers published between 2001-2017. They identified the studies through electronic database searches, Facebook, and communication with experts. The research focused on young PIDs and highlighted concerns related to online risks, vulnerability as victims of cyber-crime, and the need for support based on their levels of sociability, loneliness, anxiety, depression, poor insight and judgment, discrimination, ability to detect deception, reduced experience, and limited life opportunities (Chadwick 2019).
Social networks provide PIDs the opportunity to actively participate in society and enhance their self-determination. However, the question arises whether PIDs can effectively deal with unreliable information sources on the internet. According to an experiment, PIDs have a limited ability to evaluate recommendations in forums, which is attributed to atypical development rather than delayed development of these abilities (Salmerón, Gómez, & Fajardo 2016). An online research survey was conducted to examine the online experiences, challenges, and preferences of adults with ID who use Facebook. The study included 58 respondents who reported using Facebook as frequently as non-disabled users to connect with family and friends in the real world. However, the respondents also highlighted challenges such as privacy settings and literacy demands (Shpigelman & Gill 2014).
Observation and interviews of young adults aged 13-25 years with mild-moderate levels of intellectual disabilities revealed that they preferred using icons, pictures, voice-based strategies, and videos when accessing the internet through smartphones, desktop devices, and tablets (Alfredsson-Ågren, Kjellberg, & Hemmingsson 2020). Studies have also been conducted on the use of everyday technology such as digital stoves, cell phones, and elevators by PIDs. The studies recorded completion time from start to end of the task, number of errors, and help requests (Hällgren, Nygård, & Kottorp 2014). Additionally, the use of smartphones to assist people with Down syndrome over seven recorded sessions through task sequencing found that they learned and performed better or faster when using AssisT-Task than traditional methods (Gomez, Torrado, & Montoro 2017).
The digital participation of PIDs is than those of individuals with other disabilities due to factors like limited access to online content or technology abd inadequate DL skills. Additionally, social and economic barriers hinder the engagement of these individuals with digital technologies. Unfortunately, there are misconceptions that they are incapable of using digital technologies or that such technologies are irrelevant or unbeneficial for them. However, many PIDs can effectively use digital technologies with the right support and accommodations. Fortunately, there has been a steady increase in the digital skills of PIDs in recent years (Heitplatz, Bühler, & Hastall 2022; Heitplatz 2020). A study by Li-Tsang et al. (2005) found that only about 6% of respondents with ID knew how to use a keyboard, mouse, and access the internet, while approximately 33% were unable to operate a computer system at all. Despite 93% of them having a computer at home or in the workplace, they were not allowed to use it. The study also highlighted difficulties in training PIDs to use information technology due to insufficient knowledge of training techniques and a lack of suitable software for training. Furthermore, the views of parents and teachers played a significant role in shaping their use of social media, as demonstrated by a Swedish study (Molin, Sorbring, & Löfgren-Mårtenson 2015; Näslund & Gardelli 2013).
Khanlou et al. (2021) conducted a scoping review of 29 peer-reviewed journal articles to explore the barriers faced by young adults with developmental disabilities in accessing and utilizing digital technology, as well as their transition needs in education, daily living, community integration, and employment. The study identified barriers such as affordability, availability, infrastructure, design, lack of alignment with individual needs, limited access to community activities, low literacy levels, and the need for accommodations. McMohan et al. (2023; 2013) successfully trained individuals with developmental disabilities to use a mobile device with the Red Laser application to identify potential food allergens. The participants maintained their health, fitness, and wellness skills even six weeks later. In another study, McMohan et al. (2015) explored the use of location-based augmented reality navigation, comparing Google Maps and paper maps as aids for navigation in individuals with developmental disabilities. The results showed that participants were more successful in navigating to unknown business locations in a city using augmented reality compared to Google Maps and a paper map.
Several studies have focused on examining a modified or condensed version of functional digital literacy (DL) skills suitable for PIDs. These studies have specifically looked at basic skills such as sending and receiving email messages, organizing social bookmarking, accessing useful websites for downloading, revising, and uploading documents. The research has been conducted on various devices including Windows desktop computers, laptops, and iPad tablets (Cihak et al., 2015a; 2015b). In order to enhance the life skills and independence of students with moderate/severe ID and/or autism spectrum disorders, integrating mobile technology with instructional practices has been recommended. This involves providing direct support and customization to meet the specific needs of these students (Ayres, Mechling, & Sansosti 2013). It is crucial to incorporate DL skills into the curriculum for PIDs to equip them with the ability to navigate online risks and safely handle potential dangers encountered in virtual settings (Holzman & Thompson 2023).
DL can be a valuable tool for PIDs. It can support their skill development, enhance their communication and social interaction abilities. However, they face specific challenges when it comes to accessing and using digital technologies. They require appropriate support and training to ensure they have the necessary skills and knowledge to use technology effectively and safely as responsible digital citizens. Regarding the effects of serious games on PIDs or autism spectrum disorders (ASD), a review of 54 studies demonstrated that the majority of these games had a positive impact. They were found to be particularly effective in improving social and communication skills, rather than conceptual and cognitive skills (Tsikinas & Xinogalos 2019). Individuals with autism encounter difficulties with fine motor skills, making it challenging for them to use traditional keyboards or mice. They required adaptive input devices such as touch screens, alternative keyboards, visual aids, or other forms of assistive technology to support their learning and communication. Visual schedules or social stories can be beneficial in helping them understand and navigate digital tools and online environments. Overall, a personalized approach that considers the unique needs and strengths of each individual with autism is crucial for promoting DL and maximizing the benefits of technology (Lancioni & Singh 2014).
As inclusive post-secondary education for students with ID becomes more prevalent in colleges and universities, there is a growing emphasis on academic enrichment, socialization, independent living skills, integrated work experiences, and career skills. Consequently, there is an increasing need to integrate digital skills into their education to enable them to effectively use various technology devices such as computers, tablets, smartphones, and pads for various purposes (Baxter & Reeves 2022; Conley et al. 2019). In addition, Keeley & Bernasconi (2023) emphasized the importance of incorporating fun and practical content in DL training for individuals with multiple disabilities.
While there is confusion about the definition of learning disabilities (LD) between British and American versions, studies have focused on the television viewing habits and preferences of individuals with LD. The Talking Mats interview, which is a visual communication tool that uses symbols and pictures to help people with communication difficulties express their thoughts and feelings, has been used with individuals with aphasia, learning disabilities, dementia, and autism. Reviewing the video recordings of these interviews revealed areas of difficulty, such as the time duration of the interview, the tangibility of symbols, and the currency of vocabulary. This information helped to develop a tool that is fit for purpose (Bunning et al., 2017; Ryan 1988). However, little is known about the DL skills of individuals with LD. Research findings indicate that 74.5% of PWDs have very low to low DL levels, while 8.5% are on average and 17% are highly digitally literate. Adults with LD have lower mean DL scores than adults in the general population. The use of DL skills at home or work adds to the variance explained in DL skills. These findings have implications for adult educators and policymakers (Patterson 2022). In this age of increasing digitization, teachers can improve the attention and academic performance of all students with ADHD by incorporating targeted environmental, organizational, instructional techniques, and tech apps into their everyday instructional/classroom management practices (Barnett 2017).
The lives of individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing (DHH) have been significantly impacted by the digital revolution (Kritzer & Smith 2020). DHH individuals have embraced various forms of electronic communication in their social and professional lives. This includes using Short Message Services (SMS) for personal interactions, telephone typewriters (TTY) or voice/TTY relay services for longer communications, fax for business and social contacts, and engaging in activities such as email, web browsing, accessing chat rooms, word processing, games, and studying (Power, Power, & Horstmanshof 2006). While there are several DL resources available for educational purposes, none of them specifically cater to the needs of DHH learners. This highlights a gap in Deaf education where technology resources are not aligned to meet the requirements of DHH individuals.
Research indicates the importance of DL training for DHH students as well as their teachers. However, teachers of DHH students often rely on traditional methods when designing and delivering academic content-based learning activities. There is a lack of guidelines or frameworks for software developers or designers to create accessible resources. As a result, strategies need to be invented or adapted to effectively reach these learners. Consequently, the potential benefits that technology offers in terms of accessible communication solutions for DHH individuals are not fully realized (Flórez-Aristizábal et al., 2019). Various technological tools have proven useful for DHH individuals in terms of communication and access to information. These include electronic books, high-quality illustrated digital stories or websites with user-friendly closed captioning or subtitles for videos, text-based communication tools, and visual cues and alerts for notifications. These tools also serve as therapy aids for speech, language, and literacy development among DHH individuals (Alshawabkeh, Woolsey, & Kharbat 2021; DeForte et al., 2020; Harris 2015; Luft, Bonello, & Zirzow 2009).
Measures of Digital Literacy
DL is a significant obstacle to the adoption or use of digital devices and technologies by PWDs. As mentioned, DL of PWDs can expand opportunities, increase independence, or ameliorate their QOL. Even as DL in PWDs is being increasingly valued; there is a dearth of exclusively validated measurement tools for capturing the levels of DL in PWDss. Items at a basic level covering DL skills in connecting to a WiFi network, searching for a term or phrase on Google.com, opening a mobile browser, looking up information, opening a new tab in the browser, looking at a news headline on social media and finding information, bookmark a web page, clearing all cache and cookies from the browser, reply to a chat, delete and forward a message, record audio messages, report and block user are itself missing. The need, rationale, and justification for using measures of DL are evident if one proposes to undertake ICT literary initiatives or plans or plans a curriculum for PWDs (Chetty et al. 2018).
A few DL-related assessment tools or the theories on which they are based are available online through open source or published offline. Mostly, they target college students, teachers, employers, and employees by using simulated situations, multiple-choice items, or right/wrong answers. Note that measuring digital skills or competencies is different from measuring DL. The Digital Literacy Scale (DLS; Amin, Malik, & Akkaya 2021) based on Chen’s (2015) theory, Digital Literacy Assessment Test (DLAT; Bansal & Mishra 2021), Internet Literacy Scale (ILS; Ma et al. 2023), Digital Literacy Scale (DLS; Bayrakci & Narmanlioğlu 2021; Park 2022), and New-Digital Literacy Scale (N-DLS; Reddy et al. 2023) are among the few examples of DL measurement tools which are reported to be psychometrically sound, reliable, and valid. Greene, Seung, and Copeland (2014) measured the critical components of DL for college students. Sivrikaya (2020) examined the DL level of the students in sports science using a 17-item Digital Literacy Scale (DLS; Ng 2012). Baro, Obaro, & and Aduba (2019) attempted to assess DL skills in library and information professionals. A systematic review on the measurement of DL among older adults (Oh et al. 2021) and the eHealth Literacy Scale (eHEALS; Norman & Skinner 2006) is available for measuring DL among older adults. Other specialised measures include tools for measuring web-oriented DL (Hargittai 2005; Hargittai 2009) or another instrument that captures digital training experiences uses a novel data collection method in the form of a graphic questionnaire (Macevičiūtė, Wilson, & Manžuch, 2019). In sum, DL measurement tools with a focus exclusive to PWDs are found to be lacking (White, Pavlovic, & Poed 2020; Yustika & Iswati 2020; Covello & Lei 2010).
The need, rationale, and justification for the choice of a specific tool for the measurement of DL of PWDs has to be taken into account, whether it is for enabling individual or collective institutional decisions, at what level, or whether it is for framing a curriculum for learning. The validity, reliability, feasibility, context, utility, fairness, consistency, and precision of the instrument are important. The choice of targeted group viz.., children, teens, adults, or the aged, gender, socio-economic and health status, occupation (teachers, doctors, architects, sports persons, labor markets, or others) is also important (Bejaković & Mrnjavac 2020; Garcia-Martin & Garcia-Sanchez 2017). The measurement of DL as an essential life in research scholars of Law School is also available (Singh 2018; Pratap & Singh, 2018). Other populations addressed by studies include school students (Kulkarni & Ramesha 2021; Lazonder et al. 2020), and emergent literacy skills alongside conventional literacy skills in young children using e-books and digital games (Neumann, Finger, & Neumann 2017). The problems reported were delays in internet connectivity, difficulties in finding relevant information, high cost of access, irregular power supply, too long to view/download pages, and slow access speed. The reported purposes of for using the internet by the respondents were to gather information, prepare class notes, for entertainment, solve question papers, and generate online question bank
The theories of DL for PWDs often focus on concepts like Universal Design for Learning (UDL), where website developers incorporate features like alternative text for images and video captions to support users with visual or hearing impairments. UDL emphasizes the importance of providing multiple means of representation, expression, and engagement to support diverse learners. These theories align with the Social Model of Disability, that PWDs are not disabled by their impairments but by the disabling barriers they face in society. Therefore, the aim is to remove societal barriers for PWDs when they engage in the digital realm (Oliver 2013; Guo et al 2005). Additionally, they incorporate the Assistive Technology Model, which involves utilizing tools such as screen readers, Braille displays, and voice recognition software to assist individuals with visual or motor impairments. The compensation model (Cummings et al 2002) postulates that PWDs are isolated and have low levels of social interaction. Creating social interaction which is online can compensate to overcome 'limitations' in their body to improve their life chances. People who are socially inactive or dissatisfied with their social interactions in the physical non-ITC world tend to use the Internet more frequently, and hence benefit from it more.
The research on DL still lacks a well-established theoretical framework. A skills-based theoretical framework was first published by Eshet (2004). It covered a variety of complex cognitive, motor, sociological, and emotional skills needed to function effectively in digital environments. A holistic, refined conceptual framework for DL, which includes photo-visual literacy (understanding messages from graphical displays), reproduction literacy (utilizing digital reproduction to create new, meaningful materials from preexisting ones), branching literacy (constructing knowledge from non-linear, hypertextual navigation), information literacy (critically evaluating the quality and validity of information), and socio-emotional literacy (understanding the “rules” that prevail in the cyberspace and applying this understanding in virtual communication)(Eshet 2004). A sixth skill is the ability to think or process large volumes of stimuli at the same time, as in video games or online teaching was added later (Osterman 2012; Eshet 2012; Nawaz & Kundi 2010; Sefton-Green, Nixon, & Erstad 2009). The pedagogical usability, context of use, and implications of the framework for the design, evaluation, and training of DL skills using task analysis, shaping, modeling, guided practice, reinforcement, and prompting techniques is shown in school education (Hadjerrouit 2010).
Chen's theory of DL includes nine dimensions: communication, collaboration, critical thinking, creativity, citizenship, character, curation, copyright, and connectedness (Chen 2015). Ibraimkulov et al. (2022) developed a two-component model of DL viz., operational skills and informational and strategic skills to assess the level of development of DL in students with hearing impairment from special (correctional) schools in Kazakhstan. Later validation of tools for measuring DL (Peled, Kurtz & Avidov-Ungar 2021) based on archaic models (Gilster (1997) and the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM; Fred Davis 1980), The DL Skills Conceptual Model (Alkali & Amichai-Hamburger 2004), or the recent South Pacific Digital Literacy Framework (SPFLF) were developed (Reddy, Chaudhary, and Hussein 2023; Reddy, Chaudhary, & Sharma 2020; Reddy, Chaudhary, Sharma, & Chand 2022). In sum, there is still no model or theory of DL exclusive for PWDs (Ali, Raza, & Qazi 2023).
Digital Literacy Empowerment Programs (DLEPs)
DLEPs are initiatives that provide individuals with the skills and knowledge they need to navigate and use digital technologies effectively. These programs usually focus on teaching fundamental computer skills, internet use, online safety and digital communication. These programs aim to close the digital divide and allow people to fully participate in the digital space. DLEP programs, provided by educational institutions, NGOs, and government agencies, often include training workshops and online courses, as well as resources to help learners develop their digital skills. Vulnerable groups in society that have benefitted from DLEPs include seniors/older adults; low-income individuals; immigrants; women from low socio-economic backgrounds; the marginalized and refugees; PWDs; people with physical or mental disabilities; and people living in rural or remote areas who lack access to digital technologies because of infrastructure constraints (Njenga 2018; Bühler & Pelka 2014; Lee 2014). The National Digital Literacy Mission (NDLM) initiated by the Government of India and launched in August, 2014, targets key village-level workers into digitally literate person. Pallampara village, near Thiruvananthapuram city in Kerala is recorded as India's first fully digital literate panchayat (Gahlot & Gahlot 2020; Babu, Kalaivani, & Saileela 2019; Joseph, Kar, & Ilavarasan 2017; Rajeev et al. 2018).
COVID-19 has had a significant impact on the digital participation and inclusion of PWDs in society. The problems were exacerbated by their isolation and poor living conditions during the pandemic (Chadwick et al. 2022). Software developers needed training to incorporate the necessary design features, interface and structure in relation to special educational needs (Hobbs & Coiro 2019; Williams 2006). Their carers and parents needed training to foster DL skills in their wards (Promrub & Sranratana 2022). They needed navigation indicators and contextual aids, simplification of screen pages (graphically and textually) or game features, the predominant use of video based content, and the use of individual interviews (Sauve et al. 2023; Seok & DaCosta 2017) even during adverse times such as the Covid-19 pandemic (Karagul, Seker, & Aykut 2021; Saribanon et al. 2020).
There are various formal or standardized DL empowerment programs that are often initiated by non-profit organizations. Some examples include the Digital Literacy Corps (Clark & Visser 2011), Microsoft Digital Literacy (Kusumo, Subali, & Sunarto 2022), Google Digital Garage (Jaison 2020), Digital Promise, and TechSoup (Mallery 2013). These programs offer courses on basic computer skills, internet safety, digital citizenship, digital marketing, data analytics, and other digital skills. Additionally, Microsoft's Disability Answer Desk provides technical support to PWDs who use Microsoft products, WebAIM's Training offers online training courses on web accessibility for PWDs, and The National Federation of the Blind's Access Technology Institute Program provides training on assistive technology for people who are blind or visually impaired. The American Foundation for the Blind's eLearning Center Program is another program that offers training on assistive technology for PWDs (Darvishy, Eröcal, & Manning 2019).
There are several DL programs that focus on PIDs, including Project UNITE, The Arc's Tech Toolbox Program, The National Center on Disability and Access to Education Program, and The Digital Literacy Alliance Program. These programs typically cover topics like basic computer skills, internet safety, and social media. They use various technologies such as online courses, webinars, email, and social media to teach about accessing educational technology, AT, instructional materials, universal design for learning, and online communication. Several independent studies and projects have attempted to evaluate the impact of short or long-term DL initiatives on different segments of the population. Martin & Grudziecki (2006) undertook a DigEuLit Project to define and develop a framework and tools to measure DL in educational settings.
Literacy Enrichment and Technology Integration in Pre-Service Teacher Education examines the various strategies to resolve the challenges of technology integration for teachers while offering best practices for transforming education. Some key questions asked are: What is the needed set of best practices for teaching DL to teachers? Where should teachers begin? What are the essentials to be covered? K-12 contexts? How to optimally prepare teachers to achieve their agenda? (Keengwe, Onchwari, & Hucks 2013). What are the best practices in teaching DL to PWDs? This is done by integrating or incorporating technology tools and resources into lesson plans to enhance students' digital skills and literacy development, providing them with authentic real-world, hands-on activities or learning experiences that allow students to apply their DL skills in meaningful ways. Teach students how to critically evaluate digital information, including fact-checking, identifying bias, and assessing credibility. Encourage collaborative projects and online discussions to foster digital communication skills and teamwork. Promote responsible and ethical use of technology, including online safety, privacy, and respectful online behavior. Teach students how to create and interpret various forms of digital media, such as videos, podcasts, and presentations. Tailor instruction to meet individual students' needs and interests, allowing them to explore DL at their own pace. Provide continuous support and training for teachers to stay updated on the latest digital tools and pedagogues. In a widely acclaimed book, Hobbs (2011) demonstrated how to incorporate media literacy into the secondary classroom, providing the tools teachers need to: (i) Effectively foster students' critical thinking, collaboration, and communication skills; (ii) Integrate media literacy into every subject; (iii) Select meaningful media texts for use in the classroom; and (iv) Recognize the "teachable moment" in dialogue about popular culture. The book includes vignettes of Grade 6-12 teachers who are connecting their classroom subjects to media culture. A companion website offers video clips and discussion questions related to the sample lesson plans in each chapter. The book offers ideas to prepare students for college and the workforce. A preface, a bibliography, and an index are included. Individual DLEPs are shown to have positive impacts on performance through the use of digital tools like podcasts, blogs, and wikis (Mohammadyari & Singh 2015). Kaeophanuek, Na-Songkhla, and Nilsook (2018) used self-assessment and in-depth interviews to obtain information about their teaching environments, problems, and obstacles to deriving alternative methods for DL development among information sciences students.
Inclusive education for PWDs requires a reflection on their digital lives. Does disability limit their access to ICT? What factors affect their use and experience of ICT? What is the minimum ICT skills or abilities that need to be developed? How can PWDs remain secure in the digital space? Research on digital technologies vis-a-vis PWDs remains largely unexplored. If any accounts exist, they are based on the views of parents, caregivers, and teachers rather than the PWDs themselves. Annual Social Surveys have shown a continuous increase in ICT usage among PWDs in some countries, particularly after the turn-of-the-century. The dualism of ‘normal-disabled’ and ‘disabled-abled’ is to be rejected to strongly favour promoting DL for PWDs (Ozman 2019; Lissitsa & Madar 2018).
For PWDs, it has to be ensured that all digital materials used in teaching are accessible, such as screen readers, magnifiers, speech-to-text software, closed captions, and alt text for images. PWDs have different learning styles and abilities. Therefore, the use of a variety of teaching methods, such as visual aids, hands-on activities, and group work, to accommodate different learning needs is recommended. A supportive and inclusive learning environment that encourages participation and engagement from all learners by encouraging collaboration and peer support is suggested. Provision for assistive technology tools and software to help PWDs access and use digital resources. Encourage self-advocacy in learners with disabilities to advocate for themselves and their needs. Teach them how to communicate their needs effectively and seek out resources and support. Overall, teaching DL to PWDs requires a flexible and inclusive approach that takes into account the unique needs of each learner (Ortlieb, Cheek & Semingson 2018; Ortlieb & Cheek. 2013).
Based on six case studies, the authors advocate against dualism like “normal-deviant” or “disabled-abled.” by interpreting the cases from a social practice perspective before advocating fervently in favor of promoting DL for PWDs (Ozman 2019). Baek and Aguilar (2022) examined the learning analytics literature over the past ten years (2011-2020). Their results showed that only 33% of articles they retrieved focused on PWD and 67% of articles retrieved engaged with PWDs tangentially on several themes: detecting difficulties, early intervention, promoting learning, addressing accessibility issues and challenges, and discussing ethics and privacy concerns.
Ethical Issues of Digital Literacy In PWDs
The promotion of DL and AI for PWDs gives rise to ethical concerns regarding the cost and availability of AT, the responsibility of content creators and platform providers to ensure accessibility. PWDs are vulnerable to online threats such as cyberbullying, identity theft, and harassment, making it crucial to provide them with guidance on protecting their personal information and devices. They may also face challenges in understanding online activities, giving and obtaining informed consent, and adhering to the law (Joamets & Chochia 2021). PWDs have the same digital rights as everyone else, but they often encounter additional barriers that prevent them from accessing digital content and services without discrimination. It is essential to create avenues for them to exercise their right to privacy and data protection, participate in the digital economy on an equal basis, and express themselves freely. This can be achieved by making websites and apps accessible and promoting digital inclusion. As digitalization advances, new digital rights have emerged due to the development of Internet and Communication Technology (ICT), the Internet of Things (IoT), and innovative smart technologies, applications, and software. Unfortunately, there has also been an increase in cybercrimes and fraudulent activities, leading to terms like cyber-terrorism, cyber-bullying, cyber-stalking, hacking, phishing, and spamming. PWDs are particularly vulnerable to privacy invasions, surveillance, restrictions on digital access, and other forms of discrimination and harm in the digital realm (Peng & Yu 2022).
Future Directions
There is a need to strengthen the DL component in preparing future preschool educators in areas like interactive didactic games, basics of animation and programming, as well as network technologies, a growing need in the immediate future (Anisimova 2020). There is a need to introduce new learning models in the educational system based on the use of modern innovative technologies and DL methods (Liu et al. 2020). There are several potential directions in DL for PWDs for the future. Aspects such as inclusive design by incorporating considerations such as screen reader compatibility, smart boards, keyboard navigation, and alternative input methods are required. Advances in assistive technologies will continue to enhance DL for PWDs through innovations in speech recognition software, eye-tracking devices, and other tools that facilitate their access to digital content. DL programs will likely become more personalized to cater to the specific needs and abilities of PWDs. Adaptive learning platforms and individualized instruction to help them acquire digital skills at their own pace and in ways that suit their unique learning styles is the need of the times. Online platforms and communities will play a crucial role in fostering collaboration and peer support among PWDs in the times to come. They will provide opportunities for knowledge sharing, skill development, and networking, empowering PWDs to enhance their DL collectively. Above all, governments and organizations will continue to recognize the importance of digital inclusion for PWDs and implement policies to promote accessibility and equal opportunities in the digital realm (Buckingham 2015). Advocacy efforts will strive to raise awareness about the digital divide and work towards bridging it for PWDs. The future of DL for PWDs holds great potential for increased accessibility, inclusive, personalized learning, collaboration, and policy advancements (Sa et al. 2021). Addressing these limitations requires a comprehensive approach that considers accessibility, technology access, personalized learning, content diversity, and robust support systems. By addressing these challenges, DL programs can become more inclusive and effective for PWDs.
Abbreviations
ADA: Americans with Disability Act; ADD/ADHD: Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder; AR: Augmented Reality; ASD: Autism Spectrum Disorder; AT: Assistive Technology; CWDs: Children with Disabilities; DHH: Deaf or Hard of Hearing; DL-Digital Literacy; ICT: Information Communication Technology; ID: Intellectual Disabilities; IOT: Internet of Things;IT: Information Technology; LD: Learning Disabilities; NISA; National Information Society Agency; PWDs: People with Disabilities; QOL-Quality of Life; SMI: Severe Mental Illness; VR: Virtual Reality.
References
- Adebisi, R.O.; Liman, N.A.; Longpoe, P.K. Using Assistive Technology in Teaching Children with Learning Disabilities in the 21st Century. Journal of Education and Practice 2015, 6, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Alfredsson-Ågren, K.; Kjellberg, A.; Hemmingsson, H. Access to and use of the Internet among adolescents and young adults with intellectual disabilities in everyday settings. Journal of Intellectual & Developmental Disability 2020, 45, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Raza, A.A.; Qazi, I.A. Validated digital literacy measures for populations with low levels of internet experience. Development Engineering 2023, 8, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkali, Y.E.; Amichai-Hamburger, Y. Experiments in digital literacy. CyberPsychology & Behaviour 2004, 7, 421–429. [Google Scholar]
- Alsalem, M.A. Redefining literacy: The realities of digital literacy for students with disabilities in K-12. Journal of Education and Practice 2016, 7, 205–215. [Google Scholar]
- Alshawabkeh, A.A.; Woolsey, M.L.; Kharbat, F.F. Using on-line information technology for deaf students during COVID-19: A closer look from experience. Heliyon 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.; Malik, M.A.; Akkaya, B. Development and validation of digital literacy scale (DLS) and its implication for higher education. International Journal of Distance Education. E-Learn 2021, 7, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimova, E. Digital literacy of future preschool teachers. Journal of Social Studies Education Research 2020, 11, 230–253. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, P. Hope-in-the-Wall? A digital promise for free learning. British Journal of Educational Technology 2010, 41, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslantas, T.K.; Gul, A. Digital literacy skills of university students with visual impairment: A mixed-methods analysis. Education and Information Technologies 2022, 27, 5605–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayres, K.M.; Mechling, L.; Sansosti, F.J. The use of mobile technologies to assist with life skills/independence of students with moderate/severe intellectual disability and/or autism spectrum disorders: Considerations for the future of school psychology. Psychology in the Schools 2013, 50, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyildiz, P.; Yilmaz, A.; Baltaci, H.S. Exploring digital literacy levels and technology integration competence of Turkish academics. International Journal of Educational Methodology 2021, 7, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.; Tally, W.; Tsikalas, K. Investigating children’s emerging digital literacies. The Journal of Technology, Learning, and Assessment 2002, 1, 5–48. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, R.; Kalaivani, S.; Saileela, K. (2019). Empowering India Through Digital Literacy (Vol. 1). North Carolina; Lulu Press.
- Baek, C.; Aguilar, S.J. Past, present, and future directions of learning analytics research for students with disabilities. Journal of Research on Technology in Education 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, C.; Mishra, P.K. Digital literacy skills of secondary level students: An assessment. Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research 2021, 8, 430–436. [Google Scholar]
- Barlott, T.; Aplin, T.; Catchpole, E.; Kranz, R.; Le Goullon, D.; Toivanen, A.; Hutchens, S. Connectedness and ICT: Opening the door to possibilities for people with intellectual disabilities. Journal of Intellectual Disabilities 2020, 24, 503–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J.E.H. Helping students with ADHD in the age of digital distraction. Research, Advocacy, and Practice for Complex and Chronic Conditions 2017, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baro, E.E.; Obaro, O.G. & Aduba, E.D. (2019), An assessment of digital literacy skills and knowledge-based competencies among librarians working in university libraries in Africa, Digital Library Perspectives, 35, ¾, 172-92.
- Bawden, D. Information and digital literacies: A review of concepts. Journal of Documentation 2001, 57, 218–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawden, D. Origins and concepts of digital literacy. Digital literacies: Concepts, policies and practices 2008, 30, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bawden, D. & Robinson, L. (2002). Promoting literacy in a digital age: Approaches to training for information literacy, Learned Publishing 15, 297–301.
- Baxter, A.; Reeves, L.M. Inclusion of digital literacy skills in transition planning for students with intellectual disabilities. Journal of Special Education Technology 2022, 38, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakci, S.; Narmanlioğlu, H. Digital literacy as whole of digital competences: Scale development study. Thought and Society Social Sciences Journal 2021, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, B.W. Information literacy in the digital age: Myths and principles of digital literacy. School of Information Student Research Journal 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejaković, P.; Mrnjavac, Ž. The importance of digital literacy in the labour market. Employee Relations: The International Journal 2020, 42, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beliveau, R.; Wiesnger, S. (2023). Digital literacy: A primer on media, identity, and the evolution of technology, Second Edition. Bern, Switzerland: Peter Lang AG International Academic Publishers.
- Berge, O. Rethinking digital literacy in Nordic school curricula. Nordic Journal of digital literacy 2017, 12, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgström, Å.; Daneback, K.; Molin, M. Young people with intellectual disabilities and social media: A literature review and thematic analysis. Scandinavian Journal of Disability Research 2019, 21, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, D. Defining digital literacy-What do young people need to know about digital media? Nordic journal of digital literacy 2015, 10, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, C.; Pelka, B. (2014). Empowerment by digital media of people with disabilities: Three dimensions of support. In Computers Helping People with Special Needs: 14th International Conference, ICCHP, 2014, Paris, France, July 9-11, 2014, Proceedings, Part I 14 (pp. 17-24). New YorK: Springer International.
- Bulger, M.E.; Mayer, R.E.; Metzger, M.J. Knowledge and processes that predict proficiency in digital literacy. Reading and Writing 2014, 27, 1567–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunning, K.; Alder, R.; Proudman, L.; Wyborn, H. Co-production and pilot of a structured interview using Talking Mats® to survey the television viewing habits and preferences of adults and young people with learning disabilities. British Journal of Learning Disabilities 2017, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, E.; Torous, J. Impact of digital literacy training on outcomes for people with serious mental illness in community and inpatient settings. Psychiatric Services 2023, 74, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caton, S.; Chapman, M. The use of social media and people with intellectual disability: A systematic review and thematic analysis. Journal of Intellectual and Developmental Disability 2016, 41, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, D.D. Online risk for people with intellectual disabilities. Tizard Learning Disability Review 2019, 24, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, D.; Ågren, K.A.; Caton, S.; Chiner, E.; Danker, J.; Gómez-Puerta, M.; ... & Wallén, E.F. Digital inclusion and participation of people with intellectual disabilities during COVID-19: A rapid review and international bricolage. Journal of Policy and Practice in Intellectual Disabilities 2022, 19, 242–256.
- Chase, Z.; Laufenberg, D. Embracing the squishiness of digital literacy. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy 2011, 54, 535–537. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. (2022, July). Research on Comprehensive Management of Digital Literacy Education in the Era of Big Data. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Education and Multimedia Technology (pp. 421-427).
- Chetty, K.; Qigui, L.; Gcora, N.; Josie, J.; Wenwei, L.; Fang, C. Bridging the digital divide: Measuring digital literacy. Economics 2018, 12, 20180023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Kim, K.M. Exploring the disparity in tangible outcomes of internet use between persons with disabilities and persons without disabilities in South Korea. Disability and Health Journal 2021, 14, 101101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cihak, D.F.; McMahon, D.; Smith, C.C.; Wright, R.; Gibbons, M.M. Teaching individuals with intellectual disability to email across multiple device platforms. Research in Developmental Disabilities 2015, 36, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cihak, D.F.; Wright, R.; Smith, C.C.; McMahon, D.; Kraiss, K. Incorporating functional digital literacy skills as part of the curriculum for high school students with intellectual disability. Education and Training in Autism and Developmental Disabilities 2015, 50, 155–171. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.; Visser, M. Digital literacy takes center stage. Library Technology Reports 2011, 47, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J. Quantitative methods in psychology: A power primer. Psychological Bulletin 1992, 112, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combi, M. (2016) Cultures and technology: An analysis of some of the changes in progress—Digital, global and local culture. In: Borowiecki K.; Forbes N.; Fresa A. (eds). Cultural Heritage in a Changing World. New York: Springer.
- Compaine, B.M. (Ed.). (2001). The digital divide: Facing a crisis or creating a myth? London: The MIT Press.
- Conley, Q.; Scheufler, J.; Persichini, G.; Lowenthal, P.R.; Humphrey, M. (2019). Digital citizenship for all: Empowering young learners with disabilities to become digitally literate. Chapter 42. In: The Human Performance Technology: Concepts, Methodologies, Tools, and Applications, (Pp. 829-850). Hershey, PA.; IGI Global.
- Covello, S.; Lei, J. (2010). A review of digital literacy assessment instruments. Syracuse University 1: 31.
- Cranmer, S. (2021). Disabled children and digital technologies: Learning in the context of inclusive education. New York: Bloomsbury Academic.
- Cummings, J.N.; Sproull, L.; Kiesler, S.B. Beyond hearing: Where the real-world and online support meet. Group Dynamics: Theory, Research, and Practice 2002, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishy, A.; Eröcal, D.; Manning, J. (2019). Delivering together for inclusive development: Digital access to Information and knowledge for persons with disabilities. Paris, France: UNESCO Publishing.
- Datta, A.; Bhatia, V.; Noll, J.; Dixit, S. Bridging the digital divide: Challenges in opening the digital world to the elderly, poor, and digitally illiterate. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine 2018, 8, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeForte, S.; Sezgin, E.; Huefner, J.; Lucius, S.; Luna, J.; Satyapriya, A.A.; Malhotra, P. Usability of a Mobile App for Improving Literacy in Children With Hearing Impairment: Focus Group Study. JMIR Human Factors 2020, 7, e16310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, T.; Willinsky, J. Digital literacy. The Cambridge handbook of literacy 2009, 10, 286–312. [Google Scholar]
- Eshet, Y. Digital literacy: A conceptual framework for survival skills in the digital era. Journal of Educational Multimedia and Hypermedia 2004, 13, 93–106. [Google Scholar]
- Eshet, Y. Thinking in the digital era: A revised model for digital literacy. Issues in informing science and information technology 2012, 9, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias-Gaytan, S.; Aguaded, I.; Ramirez-Montoya, M.S. Transformation and digital literacy: Systematic literature mapping. Education and Information Technologies 2022, 27, 1417–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, J.G.; Jain, S.K. Digital illiteracy of teachers and its impact on online learning. Technoarete Transactions on Applications of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) in Education 2022, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez-Aristizábal, L.; Cano, S.; Collazos, C.A.; Benavides, F.; Moreira, F.; Fardoun, H.M. Digital transformation to support literacy teaching to deaf children: From storytelling to digital interactive storytelling. Telematics and Informatics 2019, 38, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, A.; Gahlot, S. Changing the state of literacy in the Digital Age in India. EPiC Series in Education Science 2020, 3, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Martin, J.; Garcia-Sanchez, J.N. Pre-service teachers' perceptions of the competence dimensions of digital literacy and of psychological and educational measures. Computers & Education 2017, 107, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Gilster, P. (1997). Digital Literacy. New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Goggin, G.; Ellis, K. Privacy and digital data of children with disabilities: Scenes from social media sharenting. Media and Communication 2020, 8, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.; Torrado, J.C.; Montoro, G. (2017). Using smartphones to assist people with Down syndrome in their labour training and integration: A case study. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, Article ID, 5062371, 15 pages. [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.A.; Seung, B.Y.; Copeland, D.Z. Measuring critical components of digital literacy and their relationships with learning. Computers & Education 2014, 76, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, B.; Bricout, J.C.; Huang, J. A common open space or a digital divide? A social model perspective on the online disability community in China. Disability & Society 2005, 20, 49–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hadjerrouit, S. (2010). A Theoretical Framework to Foster Digital Literacy: The Case of Digital Learning Resources. In: Reynolds, N.; Turcsányi-Szabó, M. (eds). Key Competencies in the Knowledge Society. KCKS 2010. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 324. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer.
- Hällgren, M.; Nygård, L.; Kottorp, A. Everyday technology use among people with mental retardation: Relevance, perceived difficulty, and influencing factors. Scandinavian Journal of Occupational Therapy 2014, 21, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargittai, E. Survey measures of web-oriented digital literacy. Social Science Computer Review 2005, 23, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargittai, E. An update on a survey measures of web-oriented digital literacy. Social Science Computer Review 2009, 27, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, D.; Harris, D.; Sally, B. (1998). A link to learning: The use of computers by children with disabilities. Wellington: New Zealand Council of Education Research.
- Harris, M. The impact of new technologies on the literacy attainment of deaf children. Topics in Language Disorders 2015, 35, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, J. (2017). The uses of digital literacy. Routledge.
- Heitplatz, V.N. Fostering digital participation for people with intellectual disabilities and their caregivers: Towards a guideline for designing education programs. Social Inclusion 2020, 8, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitplatz, V.N.; Bühler, C.; Hastall, M.R. Usage of digital media by people with intellectual disabilities: Contrasting individuals’ and formal caregivers’ perspectives. Journal of Intellectual Disabilities 2022, 26, 420–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, R. (2011). Digital and media literacy: Connecting culture and classroom. Thousand Oaks, California: Corwin Press.
- Hobbs, R.; Coiro, J. Design features of a professional development program in digital literacy. Journal of Adolescent & Adult Literacy 2019, 62, 401–409. [Google Scholar]
- Holzman, P.; Thompson, W. (2023). Digital literacy for students with intellectual disabilities. In Handbook of Research on Current Trends in Cybersecurity and Educational Technology (pp. 233-249). Hershey, Pennsylvania: IGI Global.
- Hutinger, P.L. Computer applications in programs for young children with disabilities: Recurring themes. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities 1996, 11, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutinger, P.; Johanson, J.; Stoneburner, R. Assistive technology applications in educational programs of children with multiple disabilities: A case study report on the state of the practice. Journal of Special Education Technology 1996, 13, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutton, R.S. Computers and the child with special learning needs: Salvation or sham? Computers in New Zealand 1997, 9, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ibraimkulov, A.; Khalikova, K.; Yerimbetova, A.; Gromaszek, K. Enhancement of digital literacy of students with disabilities. European Journal of Contemporary Education 2022, 11, 388–407. [Google Scholar]
- Irfan, T.; Salam, M.T. Kaarvan Crafts Foundation: Embracing digital literacy for women empowerment. Emerald Emerging Markets Case Studies 2020, 10, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isin, E.; Ruppert, E. (2015). Being digital citizens. London: RLI.
- Jaison, J. The impact of technology in 2020. XRDS: Crossroads, The ACM Magazine for Students 2020, 27, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joamets, K.; Chochia, A. Access to artificial intelligence for persons with disabilities: Legal and ethical questions concerning the application of trustworthy AI. Acta Baltica Historiae et Philosophiae Scientiarum 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N.; Kar, A.K.; Ilavarasan, P.V. (2017). A model for prioritization and rediction of impact of digital literacy training programmes and validation. In Conference on e-Business, e-Services and e-Society (pp. 227-238). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Julien, H. (2018). Digital literacy in theory and practice. In Encyclopedia of Information Science and Technology 4th Edition (pp. 2243-2252). IGI Global.
- Kaeophanuek, S.; Na-Songkhla, J.; Nilsook, P. How to enhance digital literacy skills among information sciences students. International Journal of Information and Education Technology 2018, 8, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagul, I.B.; Seker, M.; Aykut, C. Investigating students’ digital literacy levels during online education due to COVID-19 pandemic. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, C.; Bernasconi, T. Digital participation and digital education for people with profound and multiple disabilities and complex communication needs. Frontiers in Communication 2023, 8, 1229384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keengwe, J.; Onchwari, G.; Hucks, D. (2013). Literacy enrichment and technology integration in pre-service teacher education. Hershey: IGI Globa.
- Khanlou, N.; Khan, A.; Vazquez, L.M.; Zangeneh, M. Digital literacy, access to technology and inclusion for young adults with developmental disabilities. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities 2021, 33, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbell-Lopez, K.; Cummins, C.; Manning, E. Developing digital literacy in the middle school classroom. Computers in the Schools 2016, 33, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobel, M.; Lankshear, C. Digital literacy and digital literacies: Policy, pedagogy and research considerations for education. Nordic Journal of digital literacy 2006, 1, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolotouchkina, O.; Barroso, C.L.; Sánchez, J.L.M. Smart cities, the digital divide, and people with disabilities. Cities 2022, 123, 103613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kope, M. (Ed.). (2006). Understanding e-literacy. In A. Martin & D. Madigan (Eds.), Digital literacies for learning (pp. 68–79). London: Facet Publishing.
- Koppel, I.; Langer, S. Basic digital literacy–requirements and elements. Práxis Educacional 2020, 16, 326–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritzer, K.L.; Smith, C.E. (2020). Changing perspectives for the 21st century: Digital literacy and computational thinking for deaf/hard of hearing learners. Chapter 21. In The Oxford handbook of deaf studies in learning and cognition (Pp. 332-346). Oxf ord University Press, USA.
- Kulkarni, D.R.; Ramesha. An assessment of digital literacy skills among secondary school children: A study of Belgaum district, Karnataka. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Educational Research 2021, 10, 33–40.
- Kusumo, F.A.; Subali, B.; Sunarto, S. The Analysis of Student’s Digital Literacy with Microsoft E-Learning Media. Journal of Primary Education 2022, 11, 165–177. [Google Scholar]
- Lancioni, G.E.; Singh, N.N. (Eds.). (2014). Assistive technologies for people with diverse abilities. New York: Springer Science & Business Media.
- Lazonder, A.W.; Walraven, A.; Gijlers, H.; Janssen, N. Longitudinal assessment of digital literacy in children: Findings from a large Dutch single-school study. Computers & Education 2020, 143, 103681. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H. Digital literacy education for the development of digital literacy. International Journal of Digital Literacy and Digital Competence (IJDLDC) 2014, 5, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lev-On, A.; Steinfeld, N.; Abu-Kishk, H.; Pearl Naim, S. The long-term effects of digital literacy programs for disadvantaged populations: Analyzing participants’ perceptions. Journal of Information, Communication and Ethics in Society 2021, 19, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissitsa, S.; Madar, G. Do disabilities impede the use of information and communication technologies? Findings of a repeated cross-sectional study–2003-2015. Israel Journal of Health Policy Research 2018, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li-Tsang, C.; Yeung, S.; Chan, C.; Hui-Chan, C. Factors affecting people with intellectual disabilities in learning to use computer technology. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research 2005, 28, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.J.; Tretyakova, N.; Fedorov, V.; Kharakhordina, M. Digital literacy and digital didactics as the basis for new learning models development. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning (iJET) 2020, 15, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, S.; Third, A. Children and young people’s rights in the digital age: An emerging agenda. New Media & Society 2017, 19, 657–670. [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal, P.R.; Persichini, G.; Conley, Q.; Humphrey, M.; Scheufler, J. (2022). Digital literacy in special education: Preparing students for college and the workplace. In Research Anthology on Inclusive Practices for Educators and Administrators in Special Education (pp. 524-537). IGI Global.
- Luft, P.; Bonello, M.; Zirzow, N.K. Technology skills assessment for deaf and hard of hearing students in secondary school. American Annals of the Deaf 2009, 154, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Shu, Z.; Duan, Z.; Sun, L. Development and validation of internet literacy scale for high school students. Education and Information Technologies 2023, 28, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Macevičiūtė, E.; Wilson, T.D.; Manžuch, Z. Assessing the graphic questionnaire used in digital literacy training. Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology 2019, 16, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallery, M. Tech services on the web: TechSoup for nonprofits disaster planning and recovery Toolkit http://www. techsoup. org/toolkits/disasterplan. Technical Services Quarterly 2013, 30, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardiana, S.; Suminar, J.R.; Sugiana, D. Measuring digital literacy for students with visual impairments. library philosophy and practice digitalCommons@ University of Nebraska-Lincoln 2019, 43, 2–14. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, A.; Grudziecki, J. DigEuLit: Concepts and tools for digital literacy development. Innovation in Teaching and Learning in Information and Computer Sciences 2006, 5, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Madigan, D. (Eds.). (2006). Digital literacies for learning. London; Facet Publishing.
- McDougall, J.; Readman, M.; Wilkinson, P. The uses of (digital) literacy. Learning, Media and Technology 2018, 43, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.D.; Cihak, D.F.; Gibbons, M.M.; Fussell, L.; Mathison, S. Using a mobile app to teach individuals with intellectual disabilities to identify potential food allergens. Journal of Special Education Technology 2013, 28, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.D.; McMahon, A.K.; Anglin, M.; Abrams, K.; Wilds, K.; Aumel, A. Digital health, fitness, and wellness tools for students with disabilities. Journal of Special Education Technology 2023, 38, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.; Cihak, D.F.; Wright, R. Augmented reality as a navigation tool to employment opportunities for post secondary education students with intellectual disabilities and autism. Journal of Research on Technology in Education 2015, 47, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, F.; MacArthur, J. Computers and special needs at Forbury School. Computers in New Zealand Schools 1991, 3, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Meherali, S.; Rahim, K.A.; Campbell, S.; Lassi, Z.S. Does digital literacy empower adolescent girls in low-and middle-income countries: A systematic review. Frontiers in Public Health 2021, 9, 761394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengual-Andrés, S.; Chiner, E.; Gómez-Puerta, M. Internet and people with intellectual disability: A bibliometric analysis. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, S.J.; McCloskey, M.; Petri, G. (Eds.). (2023). The Routledge International Handbook of Disability Human Rights Hierarchies. Taylor & Francis.
- Mikołajczyk, B. Universal human rights instruments and digital literacy of older persons. The International Journal of Human Rights 2023, 27, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadyari, S.; Singh, H. Understanding the effect of e-learning on individual performance: The role of digital literacy. Computers & Education 2015, 82, 11–25. [Google Scholar]
- Molin, M.; Sorbring, E.; Löfgren-Mårtenson, L. Teachers’ and parents’ views on the Internet and social media usage by pupils with intellectual disabilities. Journal of Intellectual Disabilities 2015, 19, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, M.C.; Pérez, J. Unraveling the digital literacy paradox: How higher education fails at the fourth literacy. Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology 2014, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näslund, R.; Gardelli, Å. ‘I know, I can, I will try’: Youths and adults with intellectual disabilities in Sweden using information and communication technology in their everyday life. Disability & Society 2013, 28, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, A.; Kundi, G.M. Digital literacy: An analysis of the contemporary paradigms. Journal of Science and Technology Education Research 2010, 1, 19–29. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, K.; Courier, M.; Joseph, G.W. An investigation of digital literacy needs of students. Journal of Information Systems Education 2011, 22, 95–110. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, M.M.; Finger, G.; Neumann, D.L. A conceptual framework for emergent digital literacy. Early Childhood Education Journal 2017, 45, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W. Can we teach digital natives digital literacy? Computers & Education 2012, 59, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Njenga, J.K. Digital literacy: The quest of an inclusive definition. Reading & Writing-Journal of the Reading Association of South Africa 2018, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, C.D.; Skinner, H.A. eHEALS: The eHealth literacy scale. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2006, 8, e507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.S.; Kim, K.A.; Kim, M.; Oh, J.; Chu, S.H.; Choi, J. Measurement of digital literacy among older adults: Systematic review. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2021, 23, e26145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, M. The social model of disability: Thirty years on. Disability & Society 2013, 28, 1024–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Ortlieb, E.; Cheek Jr, E.H. (Eds.). (2013). Advanced literacy practices: From the clinic to the classroom. Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing.
- Ortlieb, E.; Cheek Jr, E.H.; Semingson, P. (Eds.). (2018). Best Practices in Teaching Digital Literacies. Literacy Research, Practice and Evaluation. Volume 9. Literacy Research, Practice and Evaluation. Emerald Publishing.
- Osterman, M.D. (2012). Digital literacy: Definition, theoretical framework, and competencies. In M. S. Plakhotnik, S.M. Nielsen, & D. M. Pane (Eds.), Proceedings of the 11th Annual College of Education & GSN Research Conference (pp. 135-141). Miami: Florida International University.
- Ozman, M. (2019). Digital platforms and disability in France. SSRN.
- Pallant, J. (2020). SPSS survival manual: A step-by-step guide to data analysis using IBM SPSS. Abingdon, Oxfordshire: Routledge.
- panchayath. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 119, 1943-1954.
- Paris, D.G.; Miller, K.R. (2018). Wearables and people with disabilities: Socio-cultural and vocational implications. In Wearable technologies: Concepts, methodologies, tools, and applications (pp. 833-849). IGI Global.
- Park, E.Y. Digital competence and internet use/behavior of persons with disabilities in PC and smart device use. Universal Access in the Information Society 2022, 21, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.Y.; Nam, S.J. An analysis of the digital literacy of people with disabilities in Korea: Verification of a moderating effect of gender, education and age. International Journal of Consumer Studies 2014, 38, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.; Reddy, K. (Eds.). (2019). Digital literacy unpacked. Chicago, Illinois: American Library Association.
- Patterson, M.B. Digital literacy skills and skill use of adults with learning disabilities. COABE Journal: The Resource for Adult Education 2022, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Peled, Y.; Kurtz, G.; Avidov-Ungar, O. Pathways to a knowledge society: A proposal for a hierarchical model for measuring digital literacy among Israeli pre-service teachers. Electronic Journal of e-Learning 2021, 19, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.; Yu, Z. (2022). A literature review of digital literacy over two decades. Education Research International, Article ID2533413, 8 pages. [CrossRef]
- Power, M.R.; Power, D.; Horstmanshof, L. Deaf People Communicating via SMS, TTY, Relay Service, Fax, and Computers in Australia. Journal of Deaf Studies and Deaf Education 2006, 12, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, R.V.; Singh, K. Digital literacy skills among students and research scholars of the law school, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India: A Study. International Journal of Next Generation Library and Technologies 2018, 4, 111. [Google Scholar]
- Promrub, S.; Sanrattana, W. Online program to empower teachers learning to develop students' digital literacy skills. Education Quarterly Reviews 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeev, V.R.; Pillai, N.M.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Bhavani, R.R. Evaluating digital India through national digital literacy mission in Kalliyoor panchayath. International Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics 2018, 119, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Hussein, S. A digital literacy model to narrow the digital literacy skills gap. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Sharma, B. Digital Literacy: A Review of Literature. International Journal of Techno-ethics (IJT) 2020, 11, 65–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Sharma, B.; Chand, R. Talismans of digital literacy: A statistical overview. Electronic Journal of e-Learning 2022, 20, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Sharma, B. & Hussein, S. Essaying the design, development and validation processes of a new digital literacy scale. Online Information Review 2023, 47, 371–397.
- Riga, A.; Ioannidi, V.; Papayiannis, N. Social stories and digital literacy practices for inclusive education. European Journal of Special Education Research 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. (1962-2003). Diffusion of innovations. 5th Edition. New York: Free Press.
- Rosen, D.J. Assessing and Teaching Adult Learners' Basic and Advanced 21st Century Digital Literacy Skills. Adult Literacy Education 2020, 2, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, G. (1988). Computer literacy instruction for learning disabled students with reading disabilities. Massachusetts, USA: Boston College.
- Sá, M.J.; Santos, A.I.; Serpa, S.; Ferreira, C.M. Digital Literacy in Digital Society 5.0. Academic Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies 2021, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmerón, L.; Gómez, M.; Fajardo, I. How students with intellectual disabilities evaluate recommendations from internet forums. Reading and Writing 2016, 29, 1653–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saribanon, N.; Siregar, M.A.P.; Joshi, L.K.; Zuhriansyah, Z.; Rubyawan, R. Digital Literacy And Access To Technology In The Empowerment Program For Persons With Disabilities During The Covid-19 Pandemic. Journal of Social Political Sciences 2020, 1, 129–143. [Google Scholar]
- Sauvé, L.; Plante, P.; Mendoza, G.A.A.; Brassard, C.; Desjardins, G. Developing the Digital Literacy of People with Cognitive Limitations in the Workplace. SN Computer Science 2023, 4, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, M. Reassessing the disability divide: Unequal access as the world is pushed online. Universal Access in the Information Society 2022, 21, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sefton-Green, J.; Nixon, H.; Erstad, O. Reviewing approaches and perspectives on “digital literacy”. Pedagogies: An international journal 2009, 4, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwyn, N.; Facer, K. (2013). The politics of education and technology: Conflicts, controversies, and connections. New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Semmel, M. I.; Lieber, J. Technology applications for infants and preschool children with handicaps: A review. International Journal of Special Education 1990, 5, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Seok, S.; DaCosta, B. Digital literacy of youth and young adults with intellectual disability predicted by support needs and social maturity. Assistive Technology 2017, 29, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpigelman, C.N.; Gill, C.J. How do adults with intellectual disabilities use Facebook? Disability & Society 2014, 29, 1601–1616. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M. Digital literacy: An essential life skill in the present era of growing and global educational Society. ournal of Advances and Scholarly Researches in Allied Education 2018, 15, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivrikaya, M.H. An analysis on digital literacy level of faculty of sports science students. Asian Journal of Education and Training 2020, 6, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanakis, P.; Wadman, R.; Walker, L.; Heron, P.; Mathers, A.; Baker, J.; ... & Peckham, E. (2022). Measuring the digital divide among people with severe mental ill health using the essential digital skills framework. Perspectives in Public Health. [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.; Kim, S. (2020, June). Can people with disabilities use the mobile Internet if they want to? In The 21st Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research (pp. 147-154).
- Tinmaz, H.; Lee, Y.T.; Fanea-Ivanovici, M.; Baber, H. A systematic review on digital literacy. Smart Learning Environments 2022, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohara, A.J.T. Exploring digital literacy strategies for students with special educational needs in the digital age. Turkish Journal of Computer and Mathematics Education (TURCOMAT) 2021, 12, 3345–3358. [Google Scholar]
- Treglia, E.; Magnanini, A.; Caione, G.; Lungu, M.A. Assistive Technologies, Digital Literacy and Didactic for Inclusion. International Journal of Digital Literacy and Digital Competence (IJDLDC) 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikinas, S.; Xinogalos, S. Studying the effects of computer serious games on people with intellectual disabilities or autism spectrum disorder: A systematic literature review. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning 2019, 35, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uršej, K. Digital literacy in the first three years of primary school: Case study in Slovenia. International Journal of Management, Knowledge and Learning 2019, 8, 61–77. [Google Scholar]
- Utaminingsih, S. Implementation of Digital Literacy in the Learning Module in Class VI Primary School. ANP Journal of Social Science and Humanities 2022, 3, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan, S. (2009). Ethical guidelines for bio-behavioral research involving human subjects. All India Institute of Speech and Hearing, Mysore.
- Venkatesan, S. (2004). Children with developmental disabilities: A training guide for parents, teachers and caregivers. Chapter 1. Introduction. (Pp. 19-48.). California/London/New Delhi: Sage.
- Venkatesan, S. (2021). Is it Specific Learning Disability or Teaching Inability? Revisiting the Basics of a Socio-Political Diagnostic Entity. Chapter 3. (Pp. 42-63). In: A. Pandey. (Ed.). Educational Developments-Volume 2. Bhopal, India: Innovare Academics Sciences.
- Viadero, D. (1997). Special assistance, technology is revolutionizing instruction for disabled students. Education Week, XVII (11), 14.
- Wempen, F. (2014). Digital literacy for dummies. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons.
- White, E.H.; Pavlovic, M.; Poed, S. (2020). Understanding and mapping digital literacy for students with disability. Understanding students with additional needs as learners, (Pp. 131-156). In: Griffin, P.; Woods, K. (eds) Understanding Students with Additional Needs as Learners. Cham: Springer.
- Willams, P.; Minnian, A. (2007). Exploring the challenges of developing digital literacy in the context of special educational needs communities. In S. Andretta (Ed.), Change and challenge: Information literacy for the 21st century (pp. 115–144). Adelaide: Auslib Press.
- Williams, P. Exploring the challenges of developing digital literacy in the context of special educational needs communities. Innovation in Teaching and Learning in Information and Computer Sciences 2006, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yustika, G.P.; Iswati, S. Digital literacy in formal online education: A short review. Dinamika Pendidikan 2020, 15, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Table 1.
Harvest plot showing the frequency distribution of compiled literature on DL in PWDs
Table 1.
Harvest plot showing the frequency distribution of compiled literature on DL in PWDs
| Variable |
N |
% |
| A. Format |
|
|
| ORA |
143 |
72.96 |
| Books |
26 |
13.27 |
| Chapters |
12 |
6.12 |
| Reviews |
10 |
5.10 |
| Proceedings of Seminars |
5 |
2.55 |
| Sub Total: 196 |
|
|
| Journals
|
153 |
78.06 |
| (i) Computers & Education |
5 |
2.55 |
| (ii) Nordic Journal of Digital Literacy |
5 |
2.55 |
| (iii) Issues in Informing Science & Information Technology |
4 |
2.04 |
| (iv) Journal of Special Education Technology |
4 |
2.04 |
| (v) Disability & Society |
3 |
1.53 |
| (vi) Education & Information Technologies |
3 |
1.53 |
| (vii) Journal of Intellectual Disabilities |
3 |
1.53 |
| Sub Total: 27 |
|
|
| B. Time-lines |
|
|
| <2000 |
10 |
5.10 |
| 2001-2010 |
27 |
13.78 |
| 2011-2015 |
36 |
18.37 |
| 2016-2020 |
68 |
34.69 |
| 2020> |
55 |
28.06 |
| Sub Total: 196 |
|
|
| C. Topics* |
|
|
| DL |
145 |
73.98 |
| PWDs |
22 |
11.22 |
| Disability-Specific; |
|
|
| (i) PIDs |
17 |
8.67 |
| (ii) PH |
8 |
4.08 |
| (iii) HoH/Deaf |
7 |
3.57 |
| (iv) SLD |
5 |
2.55 |
| (v) PVI/Blind |
2 |
1.02 |
| (vi) ADHD/ASD |
2 |
1.02 |
| (vii) PMI |
1 |
0.51 |
| Sub Total: 42 |
|
|
| Training |
25 |
12.76 |
| Measures |
16 |
8.16 |
| Gadgets (mobile, internet, email, computers, etc.) |
15 |
7.65 |
| COVID/Corona |
6 |
3.06 |
| Digital Divide |
3 |
1.53 |
| Inclusion |
3 |
1.53 |
| Training Teachers |
3 |
1.53 |
| Training Students |
3 |
1.53 |
| Grand Total |
196 |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).







