Submitted:
29 November 2023
Posted:
29 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Basic Information of PP2C Genes in Quinoa
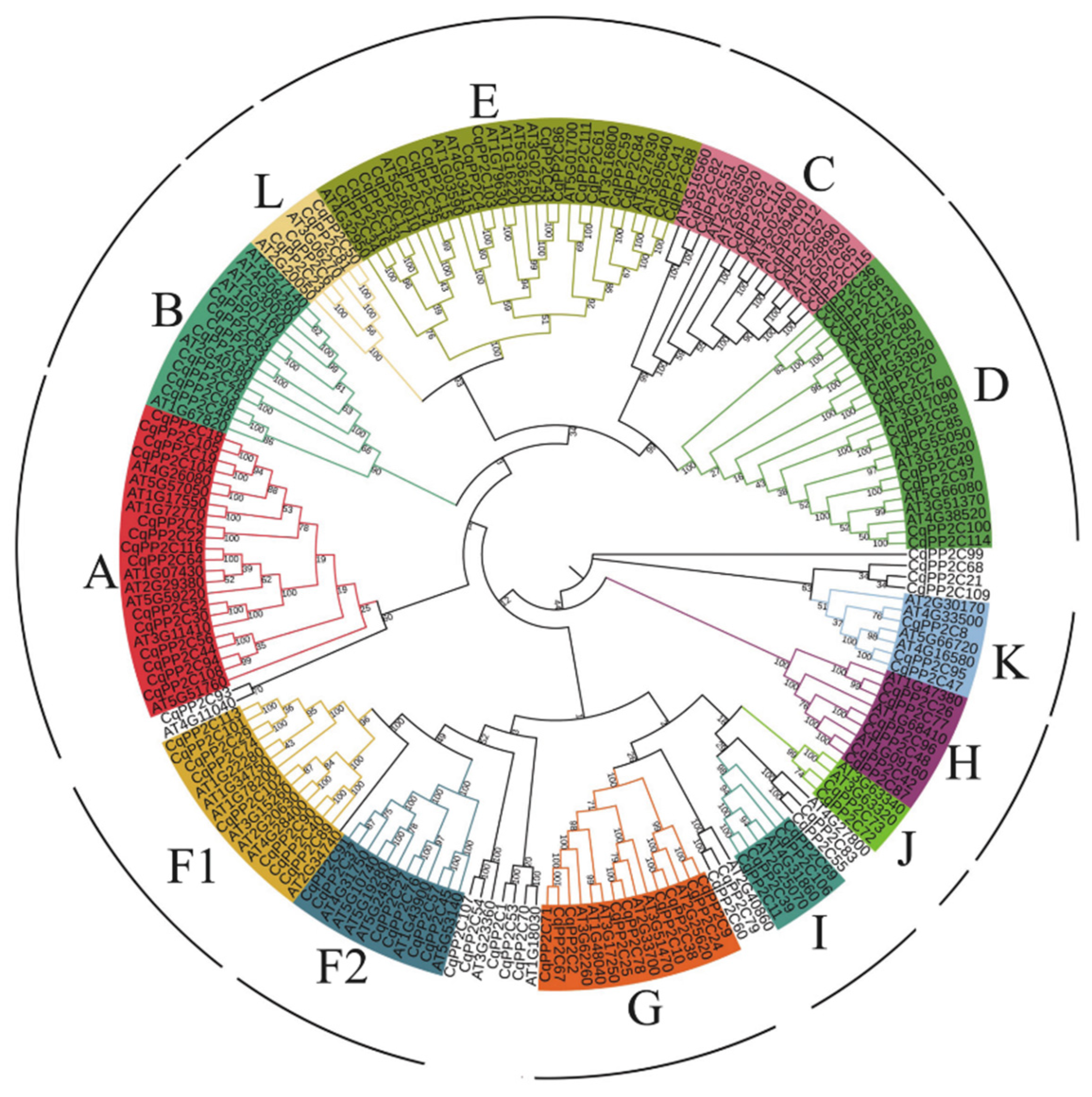
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of CqPP2C Genes
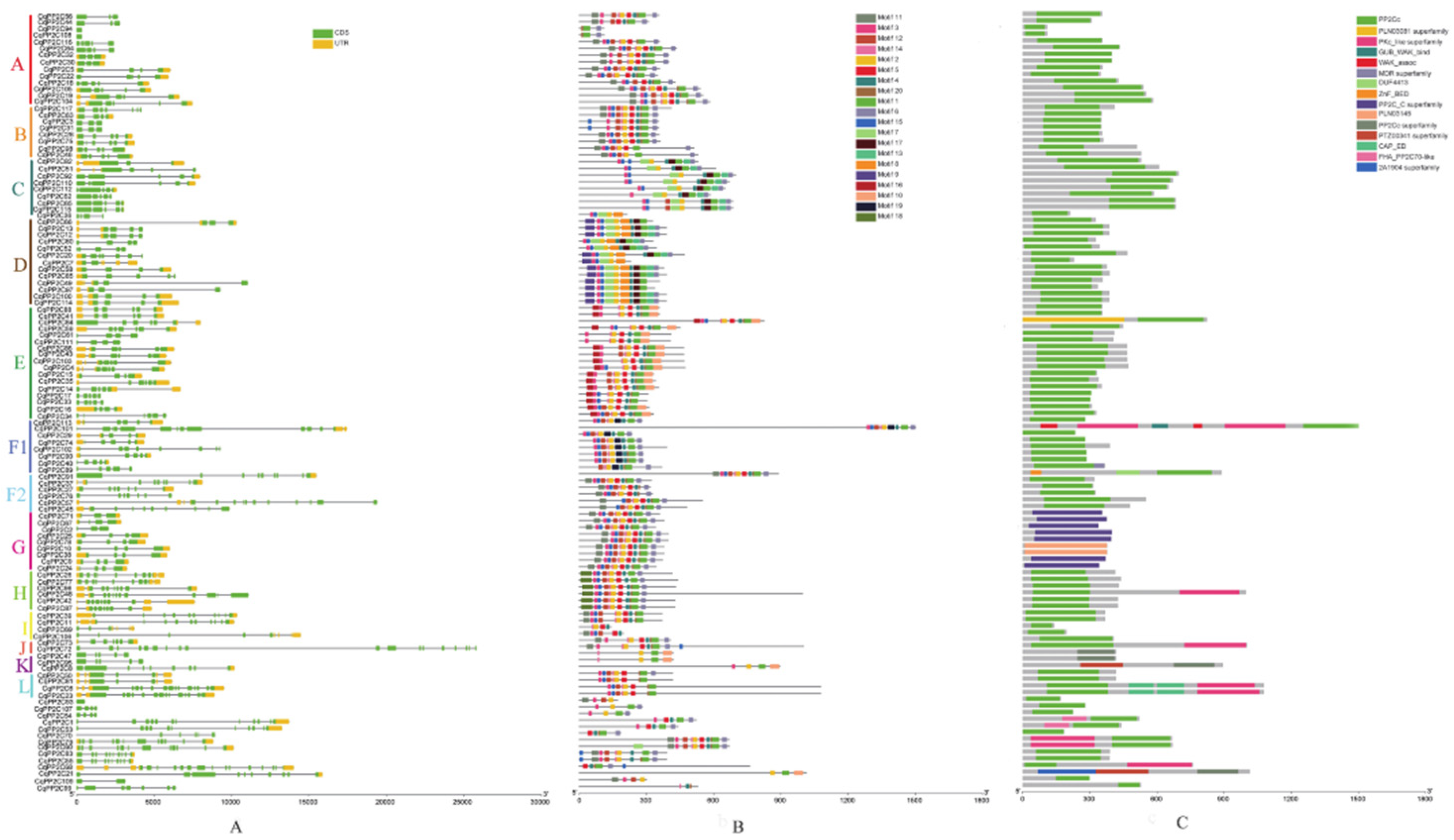
2.3. Gene Structural and Conserved Domain Analyses of CqPP2Cs
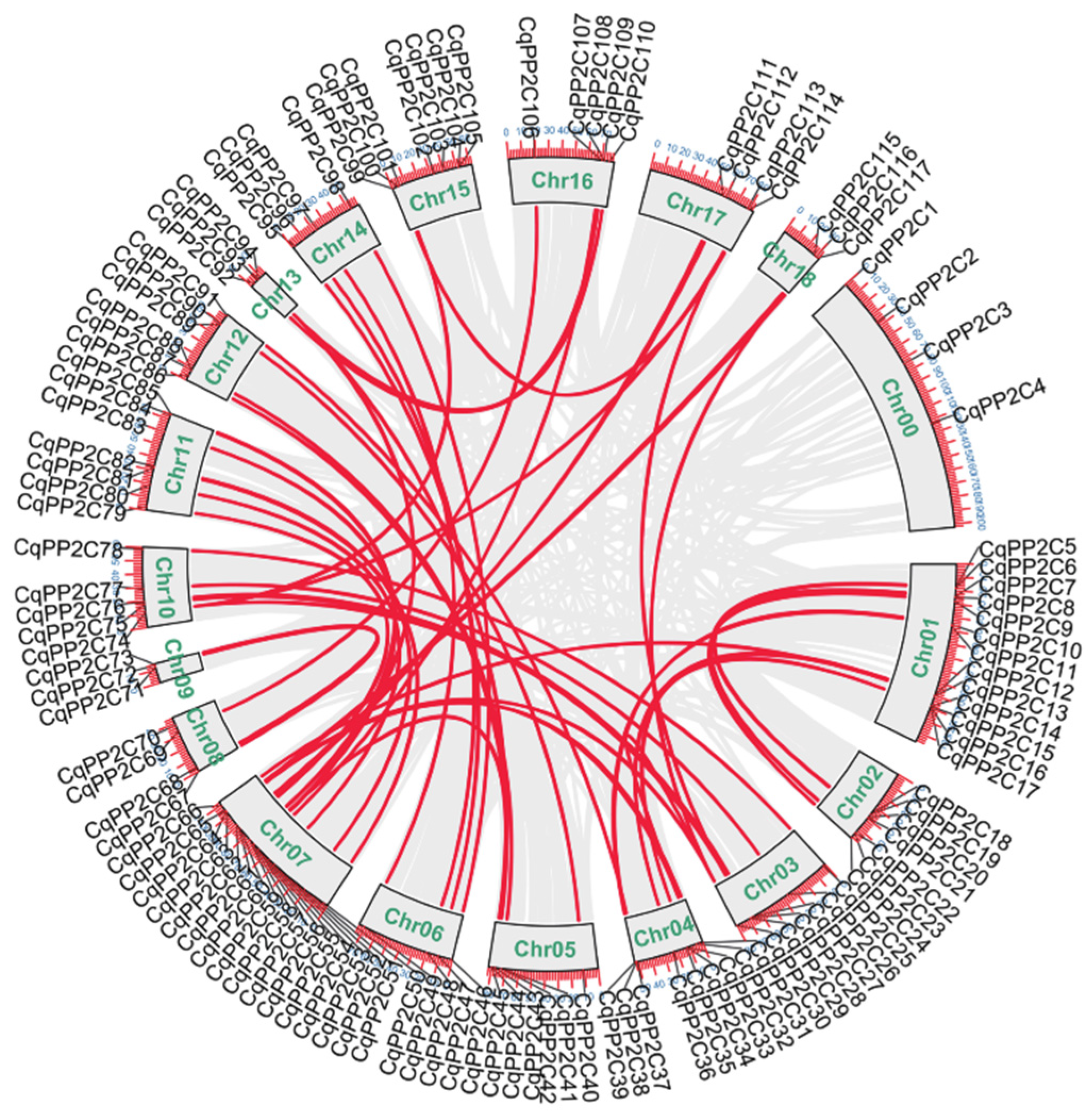
2.4. Chromosomal Location and Duplication of CqPP2C Genes
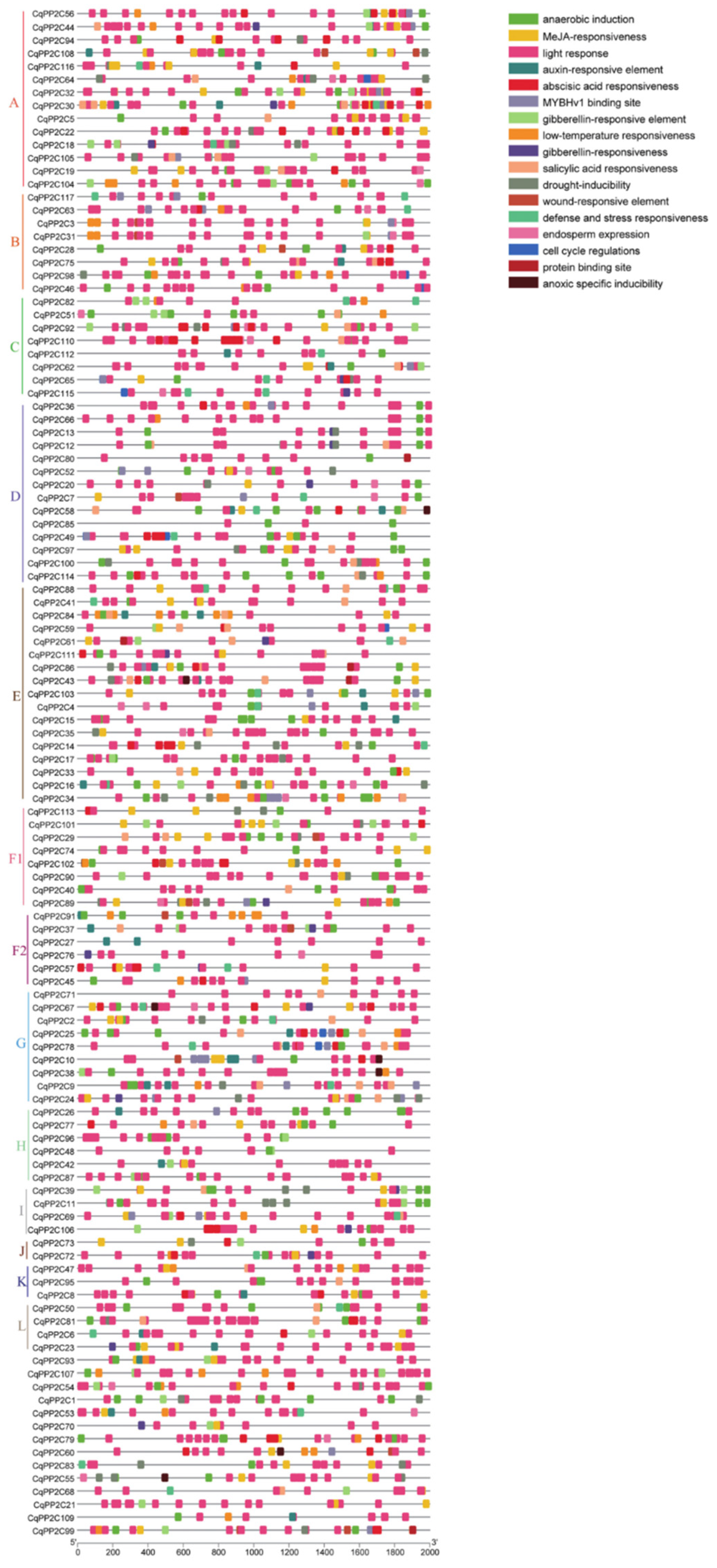
2.5. Cis-acting Elements Analysis
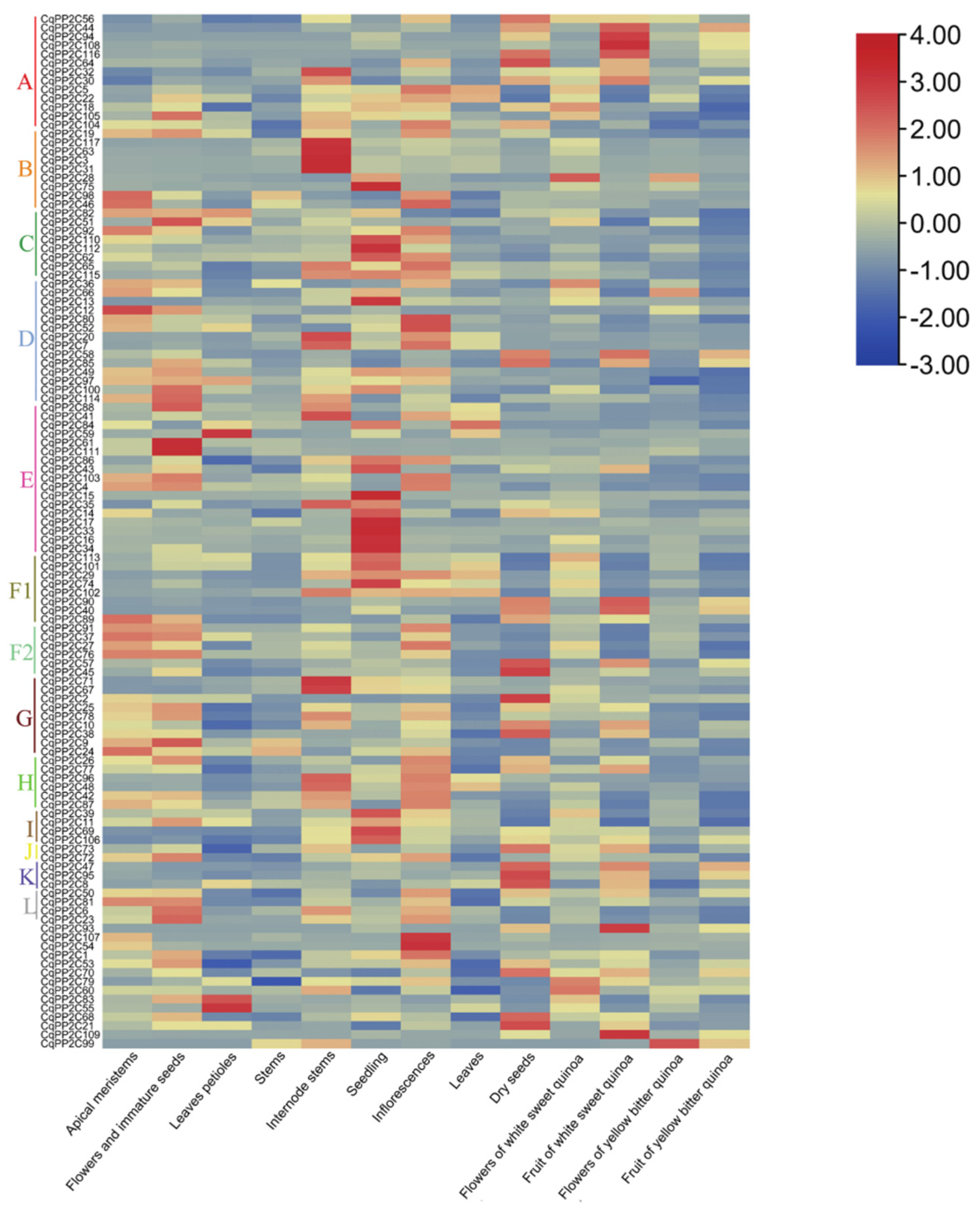
2.6. Expression of CqPP2C Genes in Different Quinoa Tissues
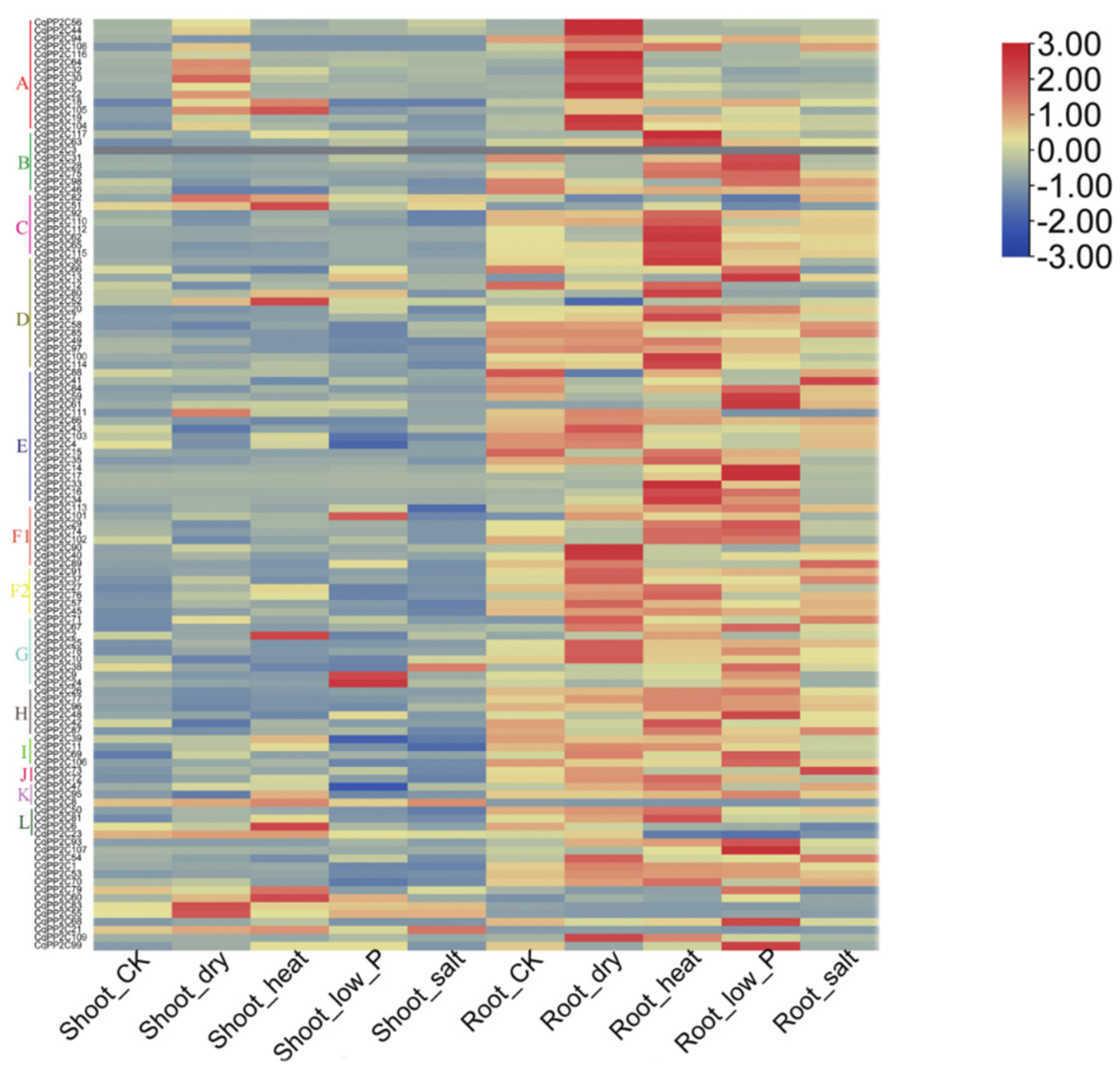
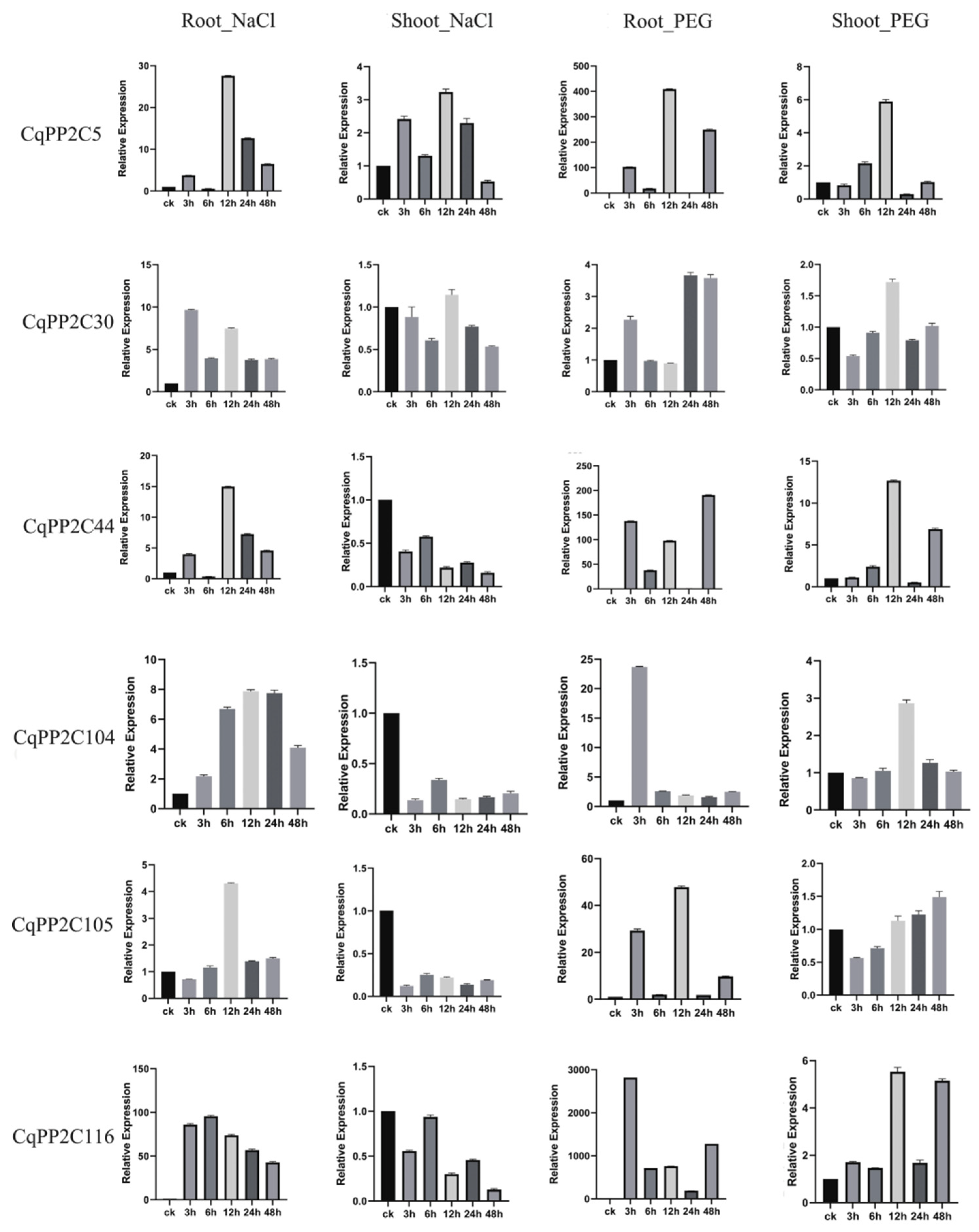
2.7. Expression Patterns of CqPP2C Genes under Stress Conditions
2.8. Protein Interaction between Subfamily A CqPP2Cs and CqSnRK2s
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of the PP2C Gene Family in Quinoa
4.2. Evolutionary Relationship of the PP2C Gene Family
4.3. Gene Structure and Protein Conserved Motif Analysis
4.4. Chromosomal Location and Gene Duplication Analysis
4.5. Analysis of Cis-acting Elements in the Promoter Regions
4.6. Analysis of CqPP2C Gene Expression Patterns
4.7. Quinoa Treatment and RNA Extraction
4.9. Yeast Two-hybrid Assays
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter, T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell 1995, 80, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerk, D.; Templeton, G.; Moorhead, G.B. Evolutionary radiation pattern of novel protein phosphatases revealed by analysis of protein data from the completely sequenced genomes of humans, green algae, and higher plants. Plant physiology 2008, 146, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, I.; Dombradi, V.; Miskei, M.; Szabados, L.; Koncz, C. Arabidopsis PPP family of serine/threonine phosphatases. Trends Plant Sci 2007, 12, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Máthé, C.; Freytag, C.; Kelemen, A.; M, M.H.; Garda, T., “B” Regulatory Subunits of PP2A: Their Roles in Plant Development and Stress Reactions. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24, 5147. [CrossRef]
- Barford, D.; Das, A.K.; Egloff, M.P. The structure and mechanism of protein phosphatases: insights into catalysis and regulation. Annual review of biophysics and biomolecular structure 1998, 27, 133–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Jiang, M.; Li, P.; Chu, Z. Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analyses of the PP2C gene family with their expression profiling in response to multiple stresses in Brachypodium distachyon. BMC genomics 2016, 17, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweighofer, A.; Hirt, H.; Meskiene, I. Plant PP2C phosphatases: emerging functions in stress signaling. Trends Plant Sci 2004, 9, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, D.T.; Bardwell, A.J.; Abdollahi, M.; Bardwell, L. A docking site in MKK4 mediates high affinity binding to JNK MAPKs and competes with similar docking sites in JNK substrates. The Journal of biological chemistry 2003, 278, 32662–32672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiozaki, K.; Russell, P. Counteractive roles of protein phosphatase 2C (PP2C) and a MAP kinase kinase homolog in the osmoregulation of fission yeast. The EMBO journal 1995, 14, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatebayashi, K.; Saito, H. Two activating phosphorylation sites of Pbs2 MAP2K in the yeast HOG pathway are differentially dephosphorylated by four PP2C phosphatases Ptc1-Ptc4. The Journal of biological chemistry 2023, 299, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takekawa, M.; Maeda, T.; Saito, H. Protein phosphatase 2Calpha inhibits the human stress-responsive p38 and JNK MAPK pathways. The EMBO journal 1998, 17, 4744–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, M.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Komaki, K.; Ohnishi, M.; Katsura, K.; Kanamaru, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Tamura, S. Regulation of the TAK1 signaling pathway by protein phosphatase 2C. The Journal of biological chemistry 2001, 276, 5753–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.G.; Katsura, K.; Nomiyama, H.; Komaki, K.; Ninomiya-Tsuji, J.; Matsumoto, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Tamura, S. Regulation of the interleukin-1-induced signaling pathways by a novel member of the protein phosphatase 2C family (PP2Cepsilon). The Journal of biological chemistry 2003, 278, 12013–12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, K.; Suzuki, N.; Kuwamura, M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Nakatani, M.; Ohtawa, H.; Takezawa, D.; Seki, M.; Tanaka, M.; Taji, T.; Hayashi, T.; Sakata, Y. Group A PP2Cs evolved in land plants as key regulators of intrinsic desiccation tolerance. Nature communications 2013, 4, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, T.; Umezawa, T. The PP2C-SnRK2 complex: the central regulator of an abscisic acid signaling pathway. Plant signaling & behavior 2010, 5, 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Schweighofer, A.; Kazanaviciute, V.; Scheikl, E.; Teige, M.; Doczi, R.; Hirt, H.; Schwanninger, M.; Kant, M.; Schuurink, R.; Mauch, F.; Buchala, A.; Cardinale, F.; Meskiene, I. The PP2C-type phosphatase AP2C1, which negatively regulates MPK4 and MPK6, modulates innate immunity, jasmonic acid, and ethylene levels in Arabidopsis. The Plant cell 2007, 19, 2213–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidonskaya, E.; Schweighofer, A.; Shubchynskyy, V.; Kammerhofer, N.; Hofmann, J.; Wieczorek, K.; Meskiene, I. Plant resistance against the parasitic nematode Heterodera schachtii is mediated by MPK3 and MPK6 kinases, which are controlled by the MAPK phosphatase AP2C1 in Arabidopsis. Journal of experimental botany 2016, 67, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shubchynskyy, V.; Boniecka, J.; Schweighofer, A.; Simulis, J.; Kvederaviciute, K.; Stumpe, M.; Mauch, F.; Balazadeh, S.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Boutrot, F.; Zipfel, C.; Meskiene, I. Protein phosphatase AP2C1 negatively regulates basal resistance and defense responses to Pseudomonas syringae. Journal of experimental botany 2017, 68, 1169–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.K.; Hofhuis, H.; Lee, M.M.; Clark, S.E. Key divisions in the early Arabidopsis embryo require POL and PLL1 phosphatases to establish the root stem cell organizer and vascular axis. Developmental cell 2008, 15, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.K.; Yun, Y.B.; Lee, M.M. POLTERGEIST and POLTERGEIST-LIKE1 are essential for the maintenance of post-embryonic shoot and root apical meristems as revealed by a partial loss-of-function mutant allele of pll1 in Arabidopsis. Genes & genomics 2020, 42, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Yu, Y.; Ding, X.; Liu, B.; Duanmu, H.; Zhu, D.; Sun, X.; Cao, L.; Zaib Un, N.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Y. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of PP2C clade D under saline and alkali stresses in wild soybean and Arabidopsis. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servet, C.; Benhamed, M.; Latrasse, D.; Kim, W.; Delarue, M.; Zhou, D.X. Characterization of a phosphatase 2C protein as an interacting partner of the histone acetyltransferase GCN5 in Arabidopsis. Biochimica et biophysica acta 2008, 1779, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.W.; Jelenska, J.; Greenberg, J.T. Arabidopsis proteins important for modulating defense responses to Pseudomonas syringae that secrete HopW1-1. The Plant journal: for cell and molecular biology 2008, 54, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiguzov, A.; Ingelsson, B.; Samol, I.; Andres, C.; Kessler, F.; Rochaix, J.D.; Vener, A.V.; Goldschmidt-Clermont, M. The PPH1 phosphatase is specifically involved in LHCII dephosphorylation and state transitions in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2010, 107, 4782–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Park, S.I.; Kwon, H.; Cho, M.H.; Kim, B.G.; Chung, J.H.; Nam, M.H.; Song, J.S.; Kim, K.H.; Yoon, I.S. The Rice Abscisic Acid-Responsive RING Finger E3 Ligase OsRF1 Targets OsPP2C09 for Degradation and Confers Drought and Salinity Tolerance in Rice. Frontiers in plant science 2021, 12, 797940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Liu, S.; Gao, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Kinoshita, T.; Huang, C.F. PP2C.D phosphatase SAL1 positively regulates aluminum resistance via restriction of aluminum uptake in rice. Plant physiology 2023, 192, 1498–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Qi, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Z. The clade F PP2C phosphatase ZmPP84 negatively regulates drought tolerance by repressing stomatal closure in maize. The New phytologist 2023, 237, 1728–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Cao, Y.; Qu, J.; Sun, F.; Yang, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, L.; Fu, F.; Yu, H. ZmPP2C26 Alternative Splicing Variants Negatively Regulate Drought Tolerance in Maize. Frontiers in plant science 2022, 13, 851531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, S.C.; Luciani, A.; Eddy, S.R.; Park, Y.; Lopez, R.; Finn, R.D. HMMER web server: 2018 update. Nucleic acids research 2018, 46, W200–W204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A.; Yang, M.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, C.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Marchler-Bauer, A. CDD/SPARCLE: the conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic acids research 2020, (D1), D265–d268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Han, J.; Wang, E.; Xiao, J.; Hu, R.; Yang, G.; He, G. Genome-Wide Identification and Homoeologous Expression Analysis of PP2C Genes in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front Genet 2019, 10, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvaud, S.; Gabella, C.; Lisacek, F.; Stockinger, H.; Ioannidis, V.; Durinx, C. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic acids research 2021, 49, W216–W227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, E.; Zheng, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, W.J.P.M.B.R. Protein Subcellular Location: The Gap Between Prediction and Experimentation. 2015, 34, 52–61. [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Wang, D.; Zhang, S.; Ehlting, J.; Ni, F.; Jakab, S.; Zheng, C.; Zhong, Y. Genome-wide and expression analysis of protein phosphatase 2C in rice and Arabidopsis. BMC Genomics 2008, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, S.; Li, X.; Lyu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wan, Z.; Yu, J. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the cucumber PP2C gene family. BMC Genomics 2022, 23, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic acids research 2009, (Web Server issue), W202–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; Kissinger, J.C.; Paterson, A.H. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic acids research 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Molecular plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic acids research 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, F.F.; Ng, L.M.; Zhou, X.E.; West, G.M.; Kovach, A.; Tan, M.H.; Suino-Powell, K.M.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chalmers, M.J.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Yong, E.L.; Cutler, S.; Zhu, J.K.; Griffin, P.R.; Melcher, K.; Xu, H.E. Molecular mimicry regulates ABA signaling by SnRK2 kinases and PP2C phosphatases. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2012, 335, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, N.; Sarkeshik, A.; Nito, K.; Park, S.Y.; Wang, A.; Carvalho, P.C.; Lee, S.; Caddell, D.F.; Cutler, S.R.; Chory, J.; Yates, J.R.; Schroeder, J.I. PYR/PYL/RCAR family members are major in-vivo ABI1 protein phosphatase 2C-interacting proteins in Arabidopsis. The Plant journal: for cell and molecular biology 2010, 61, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC plant biology 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Chang, X.; Zhi, Y.; Wang, L.; Xing, G.; Song, W.; Nie, X., Evolution and Identification of the WRKY Gene Family in Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa). Genes 2019, 10, (2). [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Nguyen, N.H.; Cheong, J.J., Transcriptional Regulation of Protein Phosphatase 2C Genes to Modulate Abscisic Acid Signaling. International journal of molecular sciences 2020, 21, (24). [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.W.; Baek, W.; Jung, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.C. Function of ABA in Stomatal Defense against Biotic and Drought Stresses. International journal of molecular sciences 2015, 16, 15251–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, M.; Chen, P.; Meng, S.; Xu, P.; Lan, W. The Arabidopsis phosphatase PP2C49 negatively regulates salt tolerance through inhibition of AtHKT1;1. Journal of integrative plant biology 2021, 63, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, K.; Niu, X.; Wang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R. Genome-wide Identification of PP2C Genes and Their Expression Profiling in Response to Drought and Cold Stresses in Medicago truncatula. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Ni, L.; Xia, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lang, M.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Protein Phosphatase 2C Genes in Tomato. Genes 2022, 13, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Pan, S. Maize protein phosphatase gene family: identification and molecular characterization. BMC genomics 2014, 15, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, S.; Grill, E.; Meskiene, I.; Schweighofer, A. Type 2C protein phosphatases in plants. The FEBS journal 2013, 280, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosti, F.; Beaudoin, N.; Serizet, C.; Webb, A.A.; Vartanian, N.; Giraudat, J. ABI1 protein phosphatase 2C is a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling. The Plant cell 1999, 11, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlot, S.; Gosti, F.; Guerrier, D.; Vavasseur, A.; Giraudat, J. The ABI1 and ABI2 protein phosphatases 2C act in a negative feedback regulatory loop of the abscisic acid signalling pathway. The Plant journal: for cell and molecular biology 2001, 25, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, H.; Kondo, S.; Tanaka, T.; Imamura, C.; Muramoto, N.; Hattori, E.; Ogawa, K.; Mitsukawa, N.; Ohto, C. Overexpression of a novel Arabidopsis PP2C isoform, AtPP2CF1, enhances plant biomass production by increasing inflorescence stem growth. Journal of experimental botany 2014, 65, 5385–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Lu, S.; Liu, T.; Nai, G.; Ren, J.; Gou, H.; Chen, B.; Mao, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Abiotic Stress Response Analysis of PP2C Gene Family in Woodland and Pineapple Strawberries. International journal of molecular sciences 2023, 24, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Morris, E.R.; Gallazzi, F.; Pandit, S.; Skolnick, J.; Walker, J.C.; Van Doren, S.R. Phosphoprotein and phosphopeptide interactions with the FHA domain from Arabidopsis kinase-associated protein phosphatase. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 2684–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Kesawat, M.S.; Ali, A.; Lee, S.C.; Gill, S.S.; Kim, A.H.U., Integration of Abscisic Acid Signaling with Other Signaling Pathways in Plant Stress Responses and Development. Plants (Basel, Switzerland) 2019, 8, (12). [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Pandey, A.; Srivastava, A.K.; Tran, L.S.; Pandey, G.K. Plant protein phosphatases 2C: from genomic diversity to functional multiplicity and importance in stress management. Critical reviews in biotechnology 2016, 36, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskara, G.B.; Nguyen, T.T.; Verslues, P.E. Unique drought resistance functions of the highly ABA-induced clade A protein phosphatase 2Cs. Plant physiology 2012, 160, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, C.; Xia, X.; Yin, W.; Tian, Q. A Putative PP2C-Encoding Gene Negatively Regulates ABA Signaling in Populus euphratica. PloS one 2015, 10, e0139466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Fujita, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. ABA-mediated transcriptional regulation in response to osmotic stress in plants. Journal of plant research 2011, 124, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umezawa, T.; Sugiyama, N.; Mizoguchi, M.; Hayashi, S.; Myouga, F.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Ishihama, Y.; Hirayama, T.; Shinozaki, K. Type 2C protein phosphatases directly regulate abscisic acid-activated protein kinases in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2009, 106, 17588–17593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, T.; Nakashima, K.; Miyakawa, T.; Kuromori, T.; Tanokura, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Molecular basis of the core regulatory network in ABA responses: sensing, signaling and transport. Plant & cell physiology 2010, 51, 1821–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.C.; Lan, W.; Buchanan, B.B.; Luan, S. A protein kinase-phosphatase pair interacts with an ion channel to regulate ABA signaling in plant guard cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2009, 106, 21419–21424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hwang, H.; Hong, J.W.; Lee, Y.N.; Ahn, I.P.; Yoon, I.S.; Yoo, S.D.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, B.G. A rice orthologue of the ABA receptor, OsPYL/RCAR5, is a positive regulator of the ABA signal transduction pathway in seed germination and early seedling growth. Journal of experimental botany 2012, 63, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, W.; Sun, J.; Liang, X.; Yang, X.; Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Yang, G.; He, G. Genome-wide analysis of SnRK gene family in Brachypodium distachyon and functional characterization of BdSnRK2.9. Plant science: an international journal of experimental plant biology 2015, 237, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




