Submitted:
28 November 2023
Posted:
29 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
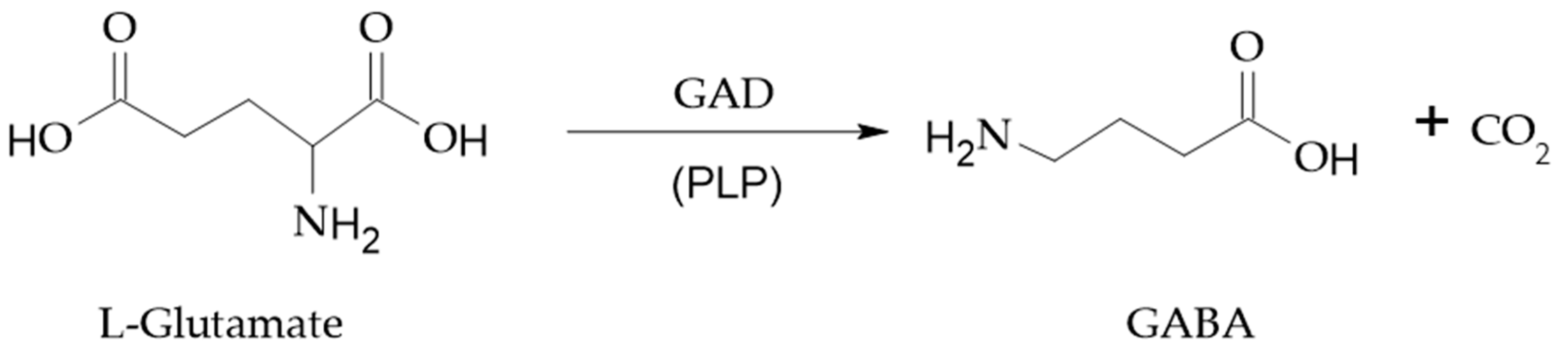
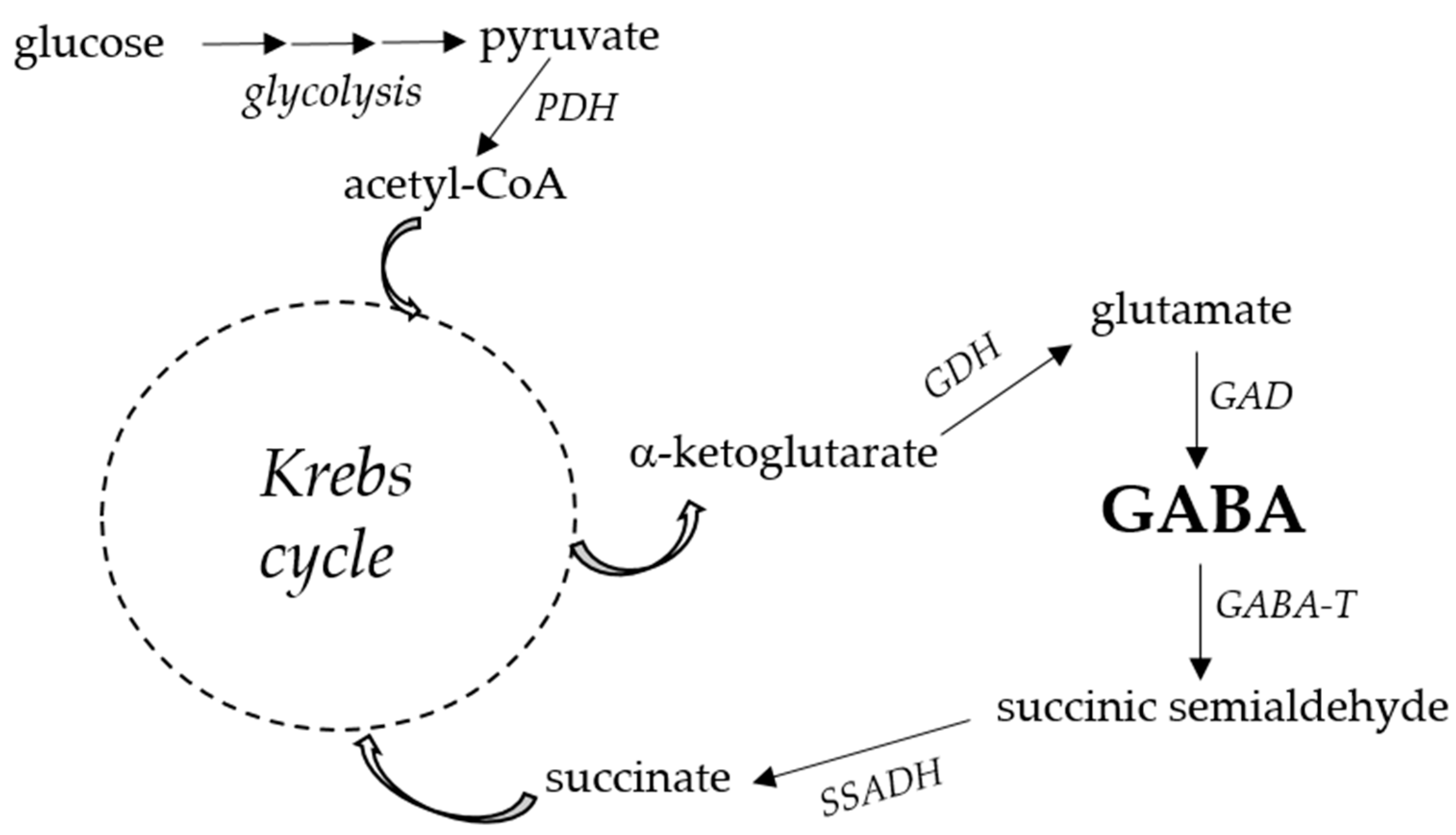
2. GABA biosynthesis
3. GABA, an ancestral molecule
4. Production of GABA by Microorganism
5. Production of GABA by Fungi
6. Production of GABA by bacteria
7. Production of GABA by L. plantarum
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.; Dou, N.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C. The versatile GABA in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillakaratne, N.J.K.; Medina-Kauwe, L.; Gibsons, K.M.; Courtwright, K.H.; Summers, J.W. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) metabolism in mammalian neural and nonneural tissues Introduction Functions of GABA. Comp. Biochem. Physiol 1995, 112, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakal, R.; Bajpai, V.K.; Baek, K.H. Production of GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid) by microorganisms: A review. Brazilian J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 1230–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Cui, J.; Zhao, Y.; Han, B.; Li, T.; Zhao, P.; Xu, J.W.; Yu, X. Enhancing Haematococcus pluvialis biomass and γ-aminobutyric acid accumulation by two-step cultivation and salt supplementation. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiels, K.; Murray, P.; Saha, S.K. Marine cyanobacteria as potential alternative source for GABA production. Bioresour. Technol. Reports 2019, 8, 100342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonburapong, B.; Laloknam, S.; Incharoensakdi, A. Accumulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid in the halotolerant cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica under salt and acid stress. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantaro, S.; Kanwal, S. Low-molecular-weight nitrogenous compounds (GABA and Polyamines) in Blue–Green Algae. In Algal Green Chemistry; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 149–169.
- Diez-Gutiérrez, L.; San Vicente, L.; Luis, L.J.; Villarán, M. del C.; Chávarri, M. Gamma-aminobutyric acid and probiotics: Multiple health benefits and their future in the global functional food and nutraceuticals market. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heli, Z.; Hongyu, C.; Dapeng, B.; Yee Shin, T.; Yejun, Z.; Xi, Z.; Yingying, W. Recent advances of γ-aminobutyric acid: Physiological and immunity function, enrichment, and metabolic pathway. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, D.H.; Vo, T.S. An updated review on pharmaceutical properties of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Molecules 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, E.; de Kleijn, R.; Colzato, L.S.; Alkemade, A.; Forstmann, B.U.; Nieuwenhuis, S. Neurotransmitters as food supplements: The effects of GABA on brain and behavior. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, S.; Winter, M.K.; McCarson, K.E.; Tamminga, C.A.; Enna, S.J. The GABA B receptor as a target for antidepressant drug action. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdou, A.M.; Higashiguchi, S.; Horie, K.; Kim, M.; Hatta, H.; Yokogoshi, H. Relaxation and immunity enhancement effects of γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) administration in humans. BioFactors 2006, 26, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.J.; Seok, H.; Ha, E.M. GABA-producing Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits metastatic properties and induces apoptosis of 5-FU-resistant colorectal cancer cells via GABAB receptor signaling. J. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini Dastgerdi, A.; Sharifi, M.; Soltani, N. GABA administration improves liver function and insulin resistance in offspring of type 2 diabetic rats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Nikmaram, N.; Dar, B.; Roohinejad, S.; Koubaa, M.; Barba, F.J.; Greiner, R.; Johnson, S.K. Recent advances in γ -aminobutyric acid (GABA) properties in pulses: an overview. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 2681–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Ruiz, R.; Poirot, E.; Flores-Mosquera, M. GABA, a non-protein amino acid ubiquitous in food matrices. Cogent Food Agric. 2018, 4, 1–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Mehmood, A.; Battino, M.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X. Enrichment of gamma-aminobutyric acid in foods: From conventional methods to innovative technologies. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahab, N.R.M.; Subroto, E.; Balia, R.L.; Utama, G.L. γ-Aminobutyric acid found in fermented foods and beverages: current trends. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, N.; Wang, T.; Ge, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bao, H. γ -Amino Butyric Acid (GABA) synthesis enabled by copper-catalyzed carboamination of alkenes. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4718–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Yang, R.; Zhang, L.; Gu, Z. Salt stress induces accumulation of γ–aminobutyric acid in germinated foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). Cereal Chem. 2013, 90, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, M.; Quílez, J.; Rafecas, M. Gamma-aminobutyric acid as a bioactive compound in foods: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liu, Z.; Xie, F.; Bilal, M.; Liu, L.; Yang, R.; Wang, Z. Microbial production of gamma-aminobutyric acid: applications, state-of-the-art achievements, and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Lv, M.; Shao, Z.; Hungwe, M.; Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, W. Metabolism characteristics of lactic acid bacteria and the expanding applications in food industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-M.; Fehér, C.; Cao, M.; Lu, F.; Jensen, P.R. Editorial: Lactic acid bacteria: microbial metabolism and expanding applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Miao, K.; Niyaphorn, S.; Qu, X. Production of gamma-aminobutyric acid from lactic acid bacteria: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.; Di Benedetto, G.; Bird, J.K.; Dabene, V.; Vadakumchery, L.; May, A.; Schyns, G.; Sybesma, W.; Mak, T.N. Development of a workflow for the selection, identification and optimization of lactic acid bacteria with high γ-aminobutyric acid production. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogeswara, I.B.A.; Maneerat, S.; Haltrich, D. Glutamate decarboxylase from lactic acid bacteria—a key enzyme in GABA synthesis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siezen, R.J.; van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T. Genomic diversity and versatility of Lactobacillus plantarum, a natural metabolic engineer. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filannino, P.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Gozzi, G.; Riciputi, Y.; Gobbetti, M. How Lactobacillus plantarum shapes its transcriptome in response to contrasting habitats. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 3700–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, B.; Lombardi, S.J.; Tremonte, P.; Succi, M.; Tipaldi, L.; Pannella, G.; Sorrentino, E.; Iorizzo, M.; Coppola, R. Biodiversity of Lactobacillus plantarum from traditional Italian wines. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 2299–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorizzo, M.; Lombardi, S.J.; Macciola, V.; Testa, B.; Lustrato, G.; Lopez, F.; De Leonardis, A. Technological potential of Lactobacillus strains isolated from fermented green olives: In vitro studies with emphasis on oleuropein-degrading capability. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorizzo, M.; Testa, B.; Ganassi, S.; Lombardi, S.J.; Ianiro, M.; Letizia, F.; Succi, M.; Tremonte, P.; Vergalito, F.; Cozzolino, A.; et al. Probiotic properties and potentiality of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains for the biological control of chalkbrood disease. J. Fungi 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorizzo, M.; Testa, B.; Lombardi, S.J.; Ganassi, S.; Ianiro, M.; Letizia, F.; Succi, M.; Tremonte, P.; Vergalito, F.; Cozzolino, A.; et al. Antimicrobial activity against Paenibacillus larvae and functional properties of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains: Potential benefits for honeybee health. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letizia, F.; Albanese, G.; Testa, B.; Vergalito, F.; Bagnoli, D.; Di Martino, C.; Carillo, P.; Verrillo, L.; Succi, M.; Sorrentino, E.; et al. In vitro assessment of bio-functional properties from Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 2321–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorizzo, M.; Albanese, G.; Letizia, F.; Testa, B.; Tremonte, P.; Vergalito, F.; Lombardi, S.J.; Succi, M.; Coppola, R.; Sorrentino, E. Probiotic potentiality from versatile Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains as resource to enhance freshwater fish health. Microorganisms 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fidanza, M.; Panigrahi, P.; Kollmann, T.R. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum–nomad and ideal probiotic. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.S.; Ray, R.C.; Zdolec, N. Lactobacillus plantarum with functional properties: an approach to increase safety and shelf-life of fermented foods. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Bangar, S.P.; Echegaray, N.; Suri, S.; Tomasevic, I.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Melekoglu, E.; Rocha, J.M.; Ozogul, F. The impacts of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the functional properties of fermented foods: A Review of Current Knowledge. Microorganisms 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leonardis, A.; Testa, B.; Macciola, V.; Lombardi, S.J.; Iorizzo, M. Exploring enzyme and microbial technology for the preparation of green table olives. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, S.J.; Pannella, G.; Iorizzo, M.; Testa, B.; Succi, M.; Tremonte, P.; Sorrentino, E.; Di Renzo, M.; Strollo, D.; Coppola, R. Inoculum strategies and performances of malolactic starter Lactobacillus plantarum M10: Impact on chemical and sensorial characteristics of fiano wine. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Succi, M.; Pannella, G.; Tremonte, P.; Tipaldi, L.; Coppola, R.; Iorizzo, M.; Lombardi, S.J.; Sorrentino, E. Sub-optimal pH preadaptation improves the survival of Lactobacillus plantarum strains and the malic acid consumption in wine-like medium. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddik, H.A.; Bendali, F.; Gancel, F.; Fliss, I.; Spano, G.; Drider, D. Lactobacillus plantarum and Its Probiotic and Food Potentialities. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenalti, G.; Law, R.H.P.; Buckle, A.M.; Langendorf, C.; Tuck, K.; Rosado, C.J.; Faux, N.G.; Mahmood, K.; Hampe, C.S.; Banga, J.P.; et al. GABA production by glutamic acid decarboxylase is regulated by a dynamic catalytic loop. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Shen, Y. Regulation of γ-aminobutyric acid on plant growth and development and stress resistance Plant Physiol. J. 2020, 56, 600–612. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Wu, X.; Gong, B.; Huo, R.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Lü, G.; Gao, H. GABA Metabolism, Transport and Their Roles and Mechanisms in the Regulation of Abiotic Stress (Hypoxia, Salt, Drought) Resistance in Plants. Metabolites 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.A.; Tyerman, S.D.; Gilliham, M.; Xu, B. γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) signalling in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1577–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Lu, P.; Yan, C.; Fan, C.; Yin, P.; Wang, J.; Shi, Y. Structure and mechanism of a glutamate-GABA antiporter. Nature 2012, 483, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feehily, C.; Karatzas, K.A.G. Role of glutamate metabolism in bacterial responses towards acid and other stresses. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quillin, S.J.; Tran, P.; Prindle, A. Potential roles for gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling in bacterial communities. Bioelectricity 2021, 3, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouché, N.; Lacombe, B.; Fromm, H. GABA signaling: A conserved and ubiquitous mechanism. Trends Cell Biol. 2003, 13, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dover, S.; Halpern, Y.S. Genetic analysis of the γ aminobutyrate utilization pathway in Escherichia coli K 12. J. Bacteriol. 1974, 117, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Punekar, N.S. The metabolism of 4-aminobutyrate (GABA) in fungi. Mycol. Res. 1997, 101, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, S.T.; Fang, T.K.; Rovinsky, S.A.; Turano, F.J.; Moye-Rowley, W.S. Expression of a glutamate decarboxylase homologue is required for normal oxidative stress tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steward, F.C.; Thompson, J.F.; Dent, C.E. γ-aminobutyric acid: A constituent of the potato tuber? Science (80-. ). 1949, 110, 439–440. [Google Scholar]
- Bouché, N.; Fromm, H. GABA in plants: Just a metabolite? Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunt, G.G. GABA and GABA receptors in invertebrates. Semin. Neurosci. 1991, 3, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Rocheleau, T.A.; Steichen, J.C.; Chalmers, A.E. A point mutation in a Drosophila GABA receptor confers insecticide resistance. Nature 1993, 363, 449–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usherwood, P.N.; Grundfest, H. Peripheral inhibition in skeletal muscle of insects. J. Neurophysiol. 1965, 28, 497–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, D.E.; Hooker, N.; Duncan, H.; Jensen, L. γ-Aminobutyric acid, a neurotransmitter, induces planktonic abalone larvae to settle and begin metamorphosis. Science (80). 1979, 204, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, P.S.; Oliver, R.P. The nitrogen content of the tomato leaf apoplast increases during infection by Cladosporium fulvum. Planta 2001, 213, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bown, A.W.; MacGregor, K.B.; Shelp, B.J. Gamma-aminobutyrate: defense against invertebrate pests? Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevrot, R.; Rosen, R.; Haudecoeur, E.; Cirou, A.; Shelp, B.J.; Ron, E.; Faure, D. GABA controls the level of quorum-sensing signal in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2006, 103, 7460–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, H.; Yokooji, Y.; Ishibashi, T.; Imanaka, T.; Atomia, H. An archaeal glutamate decarboxylase homolog functions as an aspartate decarboxylase and is involved in β-Alanine and coenzyme a biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Wei, L.; Liu, J. Biotechnological advances and perspectives of gamma-aminobutyric acid production. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Tang, J.; Feng, Q.; Niu, Z.; Shen, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhou, S. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA): a comprehensive review of dietary sources, enrichment technologies, processing effects, health benefits, and its applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudec, J.; Kobida, L.; Čanigová, M.; Lacko-Bartošová, M.; Ložek, O.; Chlebo, P.; Mrázová, J.; Ducsay, L.; Bystrická, J. Production of γ-aminobutyric acid by microorganisms from different food sources. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, H.; Uda, I.; Tagami, K.; Furuya, Y.; Endo, Y.; Fujimoto, K. The production of a new tempeh-like fermented soybean containing a high level of γ-aminobutyric acid by anaerobic incubation with Rhizopus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Ali, N.; Mohd Yusof, H.; Long, K.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y.; Beh, B.K.; Koh, S.P.; Abdullah, M.P.; Alitheen, N.B. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of aqueous extract of germinated and fermented mung bean on ethanol-mediated liver damage. Biomed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, S. P. , Jamaluddin, A., Alitheen, Mohd-Ali, N. B., Mohd-Yusof, N., H., Yeap, S. K., & Long, K. Nutritive value between fermented and germinated soybean: γ-aminobutyric acid, amino acids content and antioxidant properties. Borneo Sci. 2012; 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, K.; Guo, X.-F.; Uryu, N.; Hagiwara, T.; Watabe, S. Isolation of marine yeasts collected from the pacific ocean showing a high production of γ-aminobutyric acid. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 3265–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.-F.; Aoki, H.; Hagiwara, T.; Masuda, K.; Watabe, S. Identification of high γ-aminobutyric acid producing marine yeast strains by physiological and biochemical characteristics and gene sequence analyses. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, L.; Wang, J.; Li, L. Effects of processing and NaCl on Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme inhibitory activity and γ-aminobutyric acid content during sufu manufacturing. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1782–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Tan, X.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, L.; Tang, J.; Xiang, W. Characterization of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae and coculture with Lactobacillus plantarum for mulberry beverage brewing. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yue, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, W.; Piao, C.; Yu, H. Optimization of fermentation for γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production by yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus C21 in okara (soybean residue). Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 45, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perpetuini, G.; Tittarelli, F.; Battistelli, N.; Suzzi, G.; Tofalo, R. γ-aminobutyric acid production by Kluyveromyces marxianus strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.-M.; Jeon, S.-J.; Lee, H.-B.; Lee, J.-S. Screening of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing wild yeasts and their microbiological characteristics. Korean J. Mycol. 2016, 44, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ab Kadir, S.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Mohammad, R.; Abdul Halim Lim, S.; Sabo Mohammed, A.; Saari, N. Evaluation of commercial soy sauce koji strains of Aspergillus oryzae for γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 43, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajar-Azhari, S.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ab Kadir, S.; Rahim, M.H.A.; Saari, N. Evaluation of a Malaysian soy sauce koji strain Aspergillus oryzae NSK for γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production using different native sugars. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Ab Kadir, S.; Halim-Lim, S.A.; Ilham, Z.; Hajar-Azhari, S.; Saari, N. Vital parameters for high gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production by an industrial soy sauce koji Aspergillus oryzae NSK in submerged-liquid fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin Yee, C.; Sohedein, M.N.A.; Poh Suan, O.; Weng Loen, A.W.; Abd Rahim, M.H.; Soumaya, S.; Ilham, Z.; Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I. The production of functional γ-aminobutyric acid Malaysian soy sauce koji and moromi using the trio of Aspergillus oryzae NSK, Bacillus cereus KBC, and the newly identified Tetragenococcus halophilus KBC in liquid-state fermentation. Futur. Foods 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareian, M.; Oskoueian, E.; Majdinasab, M.; Forghani, B. Production of GABA-enriched: Idli with ACE inhibitory and antioxidant properties using Aspergillus oryzae: The antihypertensive effects in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 4304–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Gao, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, O.; Wu, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, F.; Ji, B. Evaluation of γ- aminobutyric acid, phytate and antioxidant activity of tempeh-like fermented oats (Avena sativa L.) prepared with different filamentous fungi. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2544–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kono, I.; Himeno, K. Changes in γ-aminobutyric acid content during beni-koji making. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 617–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.-C.; Wang, J.-J.; Lin, T.-T.; Pan, T.-M. Production of the secondary metabolites γ-aminobutyric acid and monacolin K by Monascus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feehily, C.; Karatzas, K.A.G. Role of glutamate metabolism in bacterial responses towards acid and other stresses. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwanmanon, K.; Hsieh, P.-C. Isolating Bacillus subtilis and optimizing its fermentative medium for GABA and nattokinase production. CYTA - J. Food 2014, 12, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan-Mohtar, W.A.A.Q.I.; Sohedein, M.N.A.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Kadir, S.A.; Suan, O.P.; Loen, A.W.W.; Sassi, S.; Ilham, Z. Isolation, identification, and optimization of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing Bacillus cereus strain KBC from a commercial soy Sauce moromi in submerged-liquid fermentation. Processes 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Li, Y. Synthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid by expressing Lactobacillus brevis-derived glutamate decarboxylase in the Corynebacterium glutamicum strain ATCC 13032. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 2469–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeng, K.-C.; Chen, C.-S.; Fang, Y.-P.; Hou, R.C.-W.; Chen, Y.-S. Effect of microbial fermentation on content of statin, GABA, and polyphenols in Pu-erh tea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8787–8792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otaru, N.; Ye, K.; Mujezinovic, D.; Berchtold, L.; Constancias, F.; Cornejo, F.A.; Krzystek, A.; de Wouters, T.; Braegger, C.; Lacroix, C.; et al. GABA production by human intestinal Bacteroides spp.: prevalence, regulation, and role in acid stress tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, S.; Ruiz, L.; Lugli, G.A.; Tames, H.; Milani, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Mancino, W.; Longhi, G.; Carnevali, L.; Sgoifo, A.; et al. Bifidobacterium adolescentis as a key member of the human gut microbiota in the production of GABA. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, E.; Ross, R.P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Stanton, C. γ-Aminobutyric acid production by culturable bacteria from the human intestine. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cao, Y. Lactic acid bacterial cell factories for gamma-aminobutyric acid. Amino Acids 2010, 39, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, P.B.; Rajapuram, D.R.; Jayamanohar, J.; Verma, M.; Kavitake, D.; Meenachi Avany, B.A.; Rani, P.U.; Ravi, R.; Shetty, P.H. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production by potential probiotic strains of indigenous fermented foods origin and RSM based production optimization. LWT 2023, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannerchelvan, S.; Rios-Solis, L.; Faizal Wong, F.W.; Zaidan, U.H.; Wasoh, H.; Mohamed, M.S.; Tan, J.S.; Mohamad, R.; Halim, M. Strategies for improvement of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) biosynthesis via lactic acid bacteria (LAB) fermentation. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 3929–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siragusa, S.; De Angelis, M.; Di Cagno, R.; Rizzello, C.G.; Coda, R.; Gobbetti, M. Synthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid by lactic acid bacteria isolated from a variety of Italian cheeses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7283–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanlari, Z.; Moayedi, A.; Ebrahimi, P.; Khomeiri, M.; Sadeghi, A. Enhancement of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) content in fermented milk by using Enterococcus faecium and Weissella confusa isolated from sourdough. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franciosi, E.; Carafa, I.; Nardin, T.; Schiavon, S.; Poznanski, E.; Cavazza, A.; Larcher, R.; Tuohy, K.M. Biodiversity and γ -aminobutyric acid production by lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional alpine raw cow’s milk cheeses. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteagudo-Mera, A.; Fanti, V.; Rodriguez-Sobstel, C.; Gibson, G.; Wijeyesekera, A.; Karatzas, K.-A.; Chakrabarti, B. Gamma aminobutyric acid production by commercially available probiotic strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xiang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Z. Characterization of two novel pentose-fermenting and GABA-producing species: Levilactobacillus tujiorum sp. nov. and Secundilactobacillus angelensis sp. nov. Isolated from a solid-state fermented zha-chili. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 45, 126344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amatachaya, A.; Siramolpiwat, S.; Kraisorn, M.; Yasiri, A. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) producing probiotic Lactiplantibacillus pentosus isolated from fermented spider plant (pak sian dong) in Thailand. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 17, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavand, F.; Daly, D.F.M.; G. Gómez-Mascaraque, L. Biofunctional, structural, and tribological attributes of GABA-enriched probiotic yoghurts containing Lacticaseibacillus paracasei alone or in combination with prebiotics. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 129, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Gutiérrez, L.; Vicente, L.S.; Sáenz, J.; Esquivel, A.; Barron, L.J.R.; Chávarri, M. Biosynthesis of gamma-aminobutyric acid by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum K16 as an alternative to revalue agri-food by-products. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, G.-H.; Yoon, S.-S. Probiotic properties and optimization of gamma-aminobutyric acid production by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum FBT215. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 32, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siezen, R.J.; Tzeneva, V.A.; Castioni, A.; Wels, M.; Phan, H.T.K.; Rademaker, J.L.W.; Starrenburg, M.J.C.; Kleerebezem, M.; Molenaar, D.; Van Hylckama Vlieg, J.E.T. Phenotypic and genomic diversity of Lactobacillus plantarum strains isolated from various environmental niches. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 758–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, M.E.; Bayjanov, J.R.; Caffrey, B.E.; Wels, M.; Joncour, P.; Hughes, S.; Gillet, B.; Kleerebezem, M.; van Hijum, S.A.F.T.; Leulier, F. Nomadic lifestyle of Lactobacillus plantarum revealed by comparative genomics of 54 strains isolated from different habitats. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4974–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorizzo, M.; Pannella, G.; Lombardi, S.J.; Ganassi, S.; Testa, B.; Succi, M.; Sorrentino, E.; Petrarca, S.; De Cristofaro, A.; Coppola, R.; et al. Inter-and intra-species diversity of lactic acid bacteria in apis mellifera ligustica colonies. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorizzo, M.; Albanese, G.; Testa, B.; Ianiro, M.; Letizia, F.; Succi, M.; Tremonte, P.; D’andrea, M.; Iaffaldano, N.; Coppola, R. Presence of lactic acid bacteria in the intestinal tract of the mediterranean trout (Salmo macrostigma) in its natural environment. Life 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-Y.; Lim, S.-D. Probiotic characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum FH185 isolated from human feces. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2015, 35, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutsoumanis, K.; Allende, A.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Hilbert, F.; Lindqvist, R.; et al. Update of the list of QPS-recommended biological agents intentionally added to food or feed as notified to EFSA 12: suitability of taxonomic units notified to EFSA until March 2020. EFSA J. 2020, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Echegaray, N.; Yilmaz, B.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, M.; Pateiro, M.; Ozogul, F.; Lorenzo, J.M. A novel approach to Lactiplantibacillus plantarum: From probiotic properties to the omics insights. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 268, 127289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, C.; Zhao, W.; Peng, C.; Hu, S.; Fang, H.; Hua, Y.; Yao, S.; Huang, J.; Mei, L. Exploring the contributions of two glutamate decarboxylase isozymes in Lactobacillus brevis to acid resistance and γ-aminobutyric acid production. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Tun, H.M.; Law, Y.-S.; Khafipour, E.; Shah, N.P. Common distribution of gad operon in Lactobacillus brevis and its GadA contributes to efficient GABA synthesis toward cytosolic near-neutral pH. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezgin, E.; Tekin, B. Molecular evolution and population genetics of glutamate decarboxylase acid resistance pathway in lactic acid bacteria. Front. Genet. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, Y.; Fukao, M.; Fukaya, T. Genome sequence of Lactobacillus plantarum KB1253, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) producer used in GABA-enriched tomato juice production. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, J.A.; Flórez, A.B.; Vázquez, L.; Vasek, O.M.; Mayo, B. Production of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by lactic acid bacteria strains isolated from traditional, starter-free dairy products made of raw milk. Benef. Microbes 2019, 10, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surachat, K.; Deachamag, P.; Kantachote, D.; Wonglapsuwan, M.; Jeenkeawpiam, K.; Chukamnerd, A. In silico comparative genomics analysis of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DW12, a potential gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing strain. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 251, 126833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kang, H.J.; Shin, M.; Yang, S.Y.; Yang, J.; Jung, Y.H. Enhanced production of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) using Lactobacillus plantarum EJ2014 with simple medium composition. Lwt 2021, 137, 110443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Goyal, A. Antioxidant activity and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) producing ability of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum DM5 isolated from Marcha of Sikkim. Lwt 2015, 61, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Ra, C.H. Evaluation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) production by Lactobacillus plantarum using two-step fermentation. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Lee, S.P. Novel bioconversion of sodium glutamate to γ-amino butyric acid by co-culture of Lactobacillus plantarum K154 in Ceriporia lacerata culture broth. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.W.; Lim, S.D. The probiotic characteristics and GABA production of Lactobacillus plantarum K154 isolated from kimchi. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajabadi, N.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Baradaran, A.; Rahim, R.A.; Mahyudin, N.A.; Manap, M.Y.A.; Bakar, F.A.; Saari, N. Optimization of γ-aminobutyric acid production by Lactobacillus plantarum Taj-Apis362 from honeybees. Molecules 2015, 20, 6654–6669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, D.; Mayrhofer, S.; Yogeswara, I.B.A.; Nguyen, T.H.; Domig, K.J. Identification, classification and screening for γ-amino-butyric acid production in lactic acid bacteria from cambodian fermented foods. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yogeswara, I.B.A.; Kittibunchakul, S.; Rahayu, E.S.; Domig, K.J.; Haltrich, D.; Nguyen, T.H. Microbial production and enzymatic biosynthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) using Lactobacillus plantarum FNCC 260 isolated from indonesian fermented foods. Processes 2021, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zeng, L.; Tan, X.; Tang, J.; Xiang, W. An efficient γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) producing and nitrite reducing ability of Lactobacillus plantarum BC114 isolated from Chinese paocai. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2017, 23, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuengjayaem, S.; Booncharoen, A.; Tanasupawat, S. Characterization and comparative genomic analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-producing lactic acid bacteria from Thai fermented foods. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021, 43, 1637–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zareian, M.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Sabo Mohamed, A.K.; Saari, N. Modeling of glutamic acid production by Lactobacillus plantarum MNZ. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, M.K.; Lim, S.D. Physiological characteristics and GABA production of Lactobacillus plantarum K255 isolated from kimchi. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2013, 33, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Son, J.-Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, B.-J.; Choi, I.-S.; Sohn, J.H. Production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum B-134 isolated from Makgeolli, traditional korean rice wine. J. Life Sci. 2017, 27, 567–574. [Google Scholar]
- Krongkeha, W. Isolation and identification of GABA-producing lactic acid bacteria from fermented foods. RMUTSB J. 2022, 10, 66–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.-W.; Kim, M.-S.; Lee, M.-H.; Kim, G.-A.; Bae, K.; Yoon, S.-S. Gamma-aminobutyric acid fermentation in MRS-based medium by the fructophilic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Y7. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 31, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanamool, V.; Hongsachart, P.; Soemphol, W. Screening and characterisation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) producing lactic acid bacteria isolated from Thai fermented fish (Plaa-som) in Nong Khai and its application in Thai fermented vegetables (Som-pak). Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 40, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Liu, W.; Han, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, P.; Meng, K. Optimization of gamma-aminobutyric acid production by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum FRT7 from chinese Paocai. Foods 2023, 12, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Lan, H.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Z. Enhanced production of γ-aminobutyric acid in litchi juice fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum HU-C2W. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, D. De man, rogosa and sharpe (MRS) agar. Prog. Ind. Microbiol. 1995, 34, 362–363. [Google Scholar]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Enhancement of γ-amminobutyric acid production by co-culturing of two Lactobacilli strains. Asian J. Biotechnol. 2015, 7, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Man, C.X.; Han, X.; Li, L.; Guo, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.W.; Jiang, Y.J. Evaluation of improved γ-aminobutyric acid production in yogurt using Lactobacillus plantarum NDC75017. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Li, D.; Qin, H. Molecular cloning, expression, and immobilization of glutamate decarboxylase from Lactobacillus fermentum YS2. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, H.; Joo, Y.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, D. Characterization of glutamate decarboxylase from Lactobacillus plantarum and its C-terminal function for the pH dependence of activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12186–12193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; He, J.; Pan, D.; Wu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zeng, X.; Lian, L. Metabolomics analysis of Lactobacillus plantarum ATCC 14917 adhesion activity under initial acid and alkali stress. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0196231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogeswara, I.B.A.; Kusumawati, I.G.A.W.; Nursini, N.W.; Mariyatun, M.; Rahayu, E.S.; Haltrich, D. Health-Promoting role of fermented pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan L (Mill)) milk enriched with γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) using probiotic Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Dad-13. Fermentation 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Rao, Z.; Kimani, B.G.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.T. Two-step production of gamma-aminobutyric acid from cassava powder using Corynebacterium glutamicum and Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.-H.; Moon, Y.-J.; Oh, C.-H. γ -aminobutyric acid (GABA) content of selected uncooked foods. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2003, 8, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coda, R.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M. Use of sourdough fermentation and pseudo-cereals and leguminous flours for the making of a functional bread enriched of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 137, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cagno, R.; Mazzacane, F.; Rizzello, C.G.; De Angelis, M.; Giuliani, G.; Meloni, M.; De Servi, B.; Gobbetti, M. Synthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) by Lactobacillus plantarum DSM19463: Functional grape must beverage and dermatological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 86, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatani, Y.; Fukaya, T.; Kishino, S.; Ogawa, J. Production of GABA-enriched tomato juice by Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KB1253. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2022, 134, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.B.; Oh, S.H. Production of yogurt with enhanced levels of gamma-aminobutyric acid and valuable nutrients using lactic acid bacteria and germinated soybean extract. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, Y.T.; Lee, B.H.; Liu, C.F.; Pan, T.M. Optimization of Culture condition for ACEI and GABA Production by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzello, C.G.; Cassone, A.; Di Cagno, R.; Gobbetti, M. Synthesis of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptides and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) during sourdough fermentation by selected lactic acid bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6936–6943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharbi, H.F.; Algonaiman, R.; Barakat, H. Ameliorative and antioxidative potential of Lactobacillus plantarum-fermented oat (Avena sativa) and fermented oat supplemented with sidr honey against streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes in rats. Antioxidants 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algonaiman, R.; Alharbi, H.F.; Barakat, H. Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic efficiency of Lactobacillus plantarum fermented oat (Avena sativa) extract in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Fermentation 2022, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanaburee, A.; Kantachote, D.; Charernjiratrakul, W.; Penjamras, P.; Chaiyasut, C. Enhancement of γ-aminobutyric acid in a fermented red seaweed beverage by starter culture Lactobacillus plantarum DW12. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Hayisama-ae, W.; Kantachote, D.; Bhongsuwan, D.; Nokkaew, U.; Chaiyasut, C. A potential synbiotic beverage from fermented red seaweed (Gracilaria fisheri) using Lactobacillus plantarum DW12. Int. Food Res. J. 2014, 21, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar]
- Kantachote, D.; Ratanaburee, A.; Hayisama-ae, W.; Sukhoom, A.; Nunkaew, T. The use of potential probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum DW12 for producing a novel functional beverage from mature coconut water. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, E.S.; Yogeswara, A.; Mariyatun; Windiarti, L. ; Utami, T.; Watanabe, K. Molecular characteristics of indigenous probiotic strains from Indonesia. Int. J. Probiotics Prebiotics 2016, 11, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, D.Q.; Murphy, C.; Kingwell-Banham, E.; Castillo, C.C.; Naik, S. Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. origins and domestication: the South and Southeast Asian archaeobotanical evidence. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2019, 66, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Gao, Y.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Farag, M.A.; Chen, W.; Yao, D.; Delmas, D.; Chen, Z.; Liu, K.; Hu, H.; et al. Litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.): a comprehensive review of phytochemistry, medicinal properties, and product development. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 9527–9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewmanomont, K.; Chirapart, A. Biodiversity, cultivation and utilization of seaweeds in Thailand: an overview. In Sustainable Global Resources Of Seaweeds Volume 1; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 91–107. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo Prado, F.; De Dea Lindner, J.; Inaba, J.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Kaur Brar, S.; Soccol, C.R. Development and evaluation of a fermented coconut water beverage with potential health benefits. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 12, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, F.; Nateghi, L.; Eshaghi, M.R.; Abadi, M.E.T. Production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in whey protein drink during fermentation by Lactobacillus plantarum. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Food Sci. 2020, 9, 1087–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, F.; Nateghi, L.; Eshaghi, M.R.; Taj Abadi, M.E. Optimization of Gamma-aminobutyric acid production in probiotics extracted from local dairy products in West Region of Iran using MRS broth and whey protein media. Appl. Food Biotechnol. 2018, 5, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan Phong, H.; Quoc Viet, L.; Minh Chau, L.; Dang Long, B.H.; Thanh, N.N.; Tan Phat, D.; Truong, L.D. Isolation and selection of lactic acid bacteria with the capacity of producing γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and antimicrobial activity: its application in fermented meat product. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 19, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Ghasemi, Y.; Sharifan, A.; Bakhoda, H. Producing and analyzing gamma-aminobutyric acid containing probiotic black grape juice using Lactobacillus plantarum plantarum IBRC(10817) and Lactobacillus brevis IBRC(10818). Meas. Food 2022, 8, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Gutiérrez, L.; San Vicente, L.; Sáenz, J.; Barron, L.J.R.; Chávarri, M. Characterisation of the probiotic potential of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum K16 and its ability to produce the postbiotic metabolite γ-aminobutyric acid. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 97, 105230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, F.S.; Chay, S.Y.; Hussin, A.S.M.; Wan Ibadullah, W.Z.; Muhialdin, B.J.; Abd Ghani, M.S.; Saari, N. GABA enhancement by simple carbohydrates in yoghurt fermented using novel, self-cloned Lactobacillus plantarum Taj-Apis362 and metabolomics profiling. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajabadi, N.; Baradaran, A.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Rahim, R.A.; Bakar, F.A.; Manap, M.Y.A.; Mohammed, A.S.; Saari, N. Overexpression and optimization of glutamate decarboxylase in Lactobacillus plantarum Taj-Apis362 for high gamma-aminobutyric acid production. Microb. Biotechnol. 2015, 8, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussin, F.S.; Chay, S.Y.; Zarei, M.; Meor Hussin, A.S.; Ibadullah, W.Z.W.; Zaharuddin, N.D.; Wazir, H.; Saari, N. Potentiality of self-cloned Lactobacillus plantarum Taj-Apis362 for enhancing GABA production in yogurt under glucose induction: optimization and its cardiovascular effect on spontaneous hypertensive rats. Foods 2020, 9, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, Y.; Hayakawa, K.; Ueno, H. Effects of co-culturing lab on GABA production. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 11, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.-J.; Garcia, C. V.; Youn, S.-J.; Park, C.-D.; Lee, S.-P. Fortification of γ-aminobutyric acid and bioactive compounds in Cucurbita moschata by novel two-step fermentation using Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus plantarum. LWT 2019, 102, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-S.; Garcia, C. V.; Lee, S.-P. Optimized Production of GABA and γ-PGA in a Turmeric and roasted soybean mixture co-fermented by Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus plantarum. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2016, 22, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.S.; Song, Y.C.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.P. Novel bioconversion of sodium glutamate to γ-poly-glutamic acid and γ-amino butyric acid in a mixed fermentation using Bacillus subtilis HA and Lactobacillus plantarum K154. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1551–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-Y.; Garcia, C. V.; Song, Y.-C.; Lee, S.-P. GABA-enriched water dropwort produced by co-fermentation with Leuconostoc mesenteroides SM and Lactobacillus plantarum K154. LWT 2016, 73, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woraratphoka, J.; Innok, S.; Soisungnoen, P.; Tanamool, V.; Soemphol, W. γ-Aminobutyric acid production and antioxidant activities in fresh cheese by Lactobacillus plantarum L10-11. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Niu, H.; Xin, X.; Chen, J.; Yi, H.; Liu, D. The impact of Levilactobacillus brevis YSJ3 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum JLSC2-6 co-culture on gamma-aminobutyric acid yield, volatile and non-volatile metabolites, antioxidant activity, and bacterial community in fermented cauliflower byproducts. Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimian, E.; Moayedi, A.; Khomeiri, M.; Aalami, M.; Mahoonak, A.S. Application of high-GABA producing Lactobacillus plantarum isolated from traditional cabbage pickle in the production of functional fermented whey-based formulate. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 3408–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servili, M.; Rizzello, C.G.; Taticchi, A.; Esposto, S.; Urbani, S.; Mazzacane, F.; Di Maio, I.; Selvaggini, R.; Gobbetti, M.; Di Cagno, R. Functional milk beverage fortified with phenolic compounds extracted from olive vegetation water, and fermented with functional lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 147, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.Y.; Lee, S.P. Enrichment of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in old antler extract fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 50, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.-T.; Yang, T.; Zhang, S.; Xia, H.; Rao, Z. Screening, identification and primary optimizing of a strain producing γ-aminobutyric acid from L-glutamic acid. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2010, 29, 742–747. [Google Scholar]
| Microorganism | Isolation Source |
Culture medium | GABA production |
Comments | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. plantarum C48 | cheese | MRS | 16.0 mg/kg | Survival and GABA production in simulated GI conditions | [97] |
|
L. plantarum CCARM 0067 |
CCARM | CDM | ≈700 mM (48h) | Anti-proliferative and anti-metastatic activity in HT-29/5FUR cell line | [14] |
| L. plantarum DM5 | Marcha of Sikkim | MRS + 100 mM MSG |
not quantified | GABA production has been qualitatively identified by the TLC | [120] |
| L. plantarum KCTC 3103 | Unknown | MRS modified | 0.67 g/L | Two-stage fermentation: cell grown (stage 1); GABA production (stage 2) | [121] |
| L. plantarum K154 | kimchi | broth fortified with skim milk and 2% MSG | 15.53 mg/mL | Co-culture with Ceriporia lacerata | [122] |
| L. plantarum EJ2014 | Rice bran | SM | 19.8 g/L | Optimization of production by the addition of yeast extract | [119] |
| L. plantarum K154 | kimchi | MRS + 30 g/L MSG | 0.2 g/L | Potential probiotic: good resistance to vancomycin and polymyxin B, tolerance to bile juice and low pH | [123] |
| L. plantarum Taj-Apis362 | honeycomb and stomach of honeybee | MRS + 50 mM MSG | 7.15 mM | culture temperature of 36 °C, initial pH of 5.31 and incubation time of 60 h | [124] |
| L. plantarum 45a | cambodian fermented foods | MRS + 2% MSG | 20.34 mM | Two other strains of L. plantarum capable of synthesizing GABA have been identified: 44d (16.47 mM GABA) and 37e (5.63 mM GABA) | [125] |
| L. plantarum FNCC 260 | indonesian fermented foods | MRS + 25-100 mM MSG | 809.2 mg/L | MSG, PLP, and pyridoxine were shown to positively affect GABA production |
[126] |
| L. plantarum BC114 | Sichuan paocai (fermented vegetable) | MRS + 20 g/L MSG | 3.45 g/L |
L. plantarum BC114 highlighted the ability to produce GABA and reduce nitrates |
[127] |
| L. plantarum LSI2- 1 | Thailand fermented food | GYP + 3% MSG | 22.94 g/L | Only the gadA as glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) was found in the genome |
[128] |
| L. plantarum MNZ | fermented soybean | MRS | 3.96 mM | 6% glucose, 0.7% ammonium nitrate, pH 4.5 and temperature 37ºC. | [129] |
| Strain K255 | kimchi | MRS+3% MSG | 821.2 µg/mL | the K255 strain was incubated at 37° C for 18 h. | [130] |
| L. plantarum FBT215 | kimchi | MRS modified (1%fructose; 2% tryptone, 50 mM MSG) | 103.7 μg/mL | PLP is a major factor influencing GABA production |
[105] |
| L. plantarum B-134 | Makgeolli | MRS + 3% MSG | 25 mM | optimum culture condition: 37℃, pH 5.7 without NaCl | [131] |
|
L. plantarum N1-2 |
Nham | MRS + 5% MSG | 0.13 mg/10g |
pH of 5.7, without NaCl |
[132] |
| L. plantarum Y7 | kimchi | MRS modified (2% fructose, 2% peptone and 175 mM MSG) | 4.9 μg/mL | culture conditions: 37 °C, pH 6.5, and 48 h. |
[133] |
| L. plantarum L10-11 | Plaa-som | MRS + 4% MSG | 15.74 g/L | addition of NaCl by up to 7% (w/v) did not suppress GABA production |
[134] |
|
L. plantarum FRT7 |
Paocai | MRS 3% MSG and 2 mmol/L of PLP | 1158.6 mg/L | 40 ◦C; pH of 7.0 for 48 h |
[135] |
| L. plantarum HUC2W | MRS + 4% MSG | 3.92 g/L | at 37 ◦C for 24 h | [136] |
| Microorganism | Isolation Source |
Fermented food | GABA production |
Comments | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. plantarum C48 | cheese | buckwheat, amaranth, chickpea and quinoa flours | 504 mg/kg in bread | Good organoleptic properties of bread enriched of GABA | [146] |
| L. plantarum DSM19463 | cheese | grape must | 8.9 g/kg in fermented grape must | In vitro potential anti-hypertensive effect and dermatological protection. | [147] |
| L. plantarum KB1253 | pickles | tomato juice | 41 mM | GABA-enriched fermented tomato juice | [148] |
| L. plantarum KCTC 3105 | Unknown | soya milk | 424.67 µg/g DW | Soya yogurt with high levels of GABA, produced using a co-culture of L. acidophilus, L. plantarum and L. brevis strains | [149] |
| L. plantarum NDC75017 | fermented milk | 12% skim milk + 80 mM MSG | 314.56 mg/100 g | Good flavor and texture of fermented milk-based product | [139] |
| L. plantarum NTU102 | cabbage pickles | 8% skim milk + 1% (w/v) MSG | 629 mg/L | together with GABA, production of ACEI was also found, suggesting a possible use of fermented products as potential functional food (hypertension regulation) | [150] |
| L. plantarum C48 | cheese | wholemeal wheat flour | 100 mg/K | low ACE inhibitory activity (15%) due to synthesis of ACEI | [151] |
| L. plantarum GB01-21 | cassava powder | 80.5 g/L 2.68 g/L h (productivity) |
two-step production with Corynebacterium glutamicum G01 (to produce glutamate) and L. plantarum GB01-21 |
[144] | |
| L. plantarum Dad-13 | FNCC | pigeon pea milk | 5.6 g/L | The supplementation of sucrose, MSG, and whey isolate significantly increased GABA levels in fermented pigeon pea | [143] |
| L. plantarum NRRL B-59151 | FOE and HFOE (oat) |
GABA content: 7.35 mg/100 g in FOE and 8.49 mg/100 g in HFOE | Fermented oat demonstrated antidiabetic effects |
[152] [153] |
|
| Lactobacillus plantarum HU-C2W | litchi juice | 134 mg/100 mL | Fermentation condition: 37 °C for 40 h | [136] | |
| L. plantarum DW12 | fermented red seaweed | red seaweed+ 1% MSG | 4 g/L | Fermentation at 30°C after 60 days. Substrate composition: red seaweed, cane sugar and potable water in a ratio of 3:1:10, pH 6 | [154] |
| L. plantarum DW12 | fermented red seaweed | red seaweed + 0.5% MSG | 1284 mg/L | Fermentation at 30°C after 60 days. Substrate composition: red seaweed, cane sugar and potable water in a ratio of 3:1:10, pH 6 |
[155] |
| L. plantarum DW12 | fermented red seaweed | MCW + 0.5% MSG | 12.8 mg/100 mL | MCW supplemented with 0.5% MSG and 1% sugarcane, pH 6 after 72 h of fermentation | [156] |
| L. plantarum strains | cooperative species/strain | Food or culture medium |
GABA production |
Notes | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L. plantarum EJ2014 | B. subtilis HA | pumpkin | 1.47% | Two-step fermentation | [171] |
| L. plantarum K154 | B. subtilis HA | turmeric (Curcuma longa) / roasted soybean meal mixture + 5% MSG | 1.78 % | Two-step fermentation | [172] |
| L. plantarum K154 | B. subtilis HA | defined medium fortified with glutamate and skim milk | 4800 µg/mL | Two-step fermentation | [173] |
| L. plantarum K154 | Leuconostoc mesenteroides SM | Water dropwort | 100 mM | Two-step fermentation | [174] |
| L. plantarum BC114 | S. cerevisiae SC125 | mulberry beverage brewing | 2.42 g/L | Co-fermentation | [74] |
| L. plantarum GB01-21 | C. glutamicum G01 | cassava powder | 80.5 g/L | Two-step fermentation | [144] |
| L. plantarum Taj-Apis362 | S. thermophilus and L. delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus | Skim milk + 2% glucose and 11.5 mM MSG | 59.0 mg/100 g | Co-fermentation | [169] |
| L. plantarum K154 | Ceriporia lacerata | broth fortified with skim milk and 2% MSG | 15.53 mg/mL | Two-step fermentation | [122] |
| L. plantarum (KCTC 3105) |
Lactobacillus brevis OPY-1 L. acidophilus KCCM 40265 |
Soya milk | 424.67 µg/g | Co-fermentation | [149] |
| L. plantarum L10-11 | Lactococcus lactis spp. lactis and Lactococcus lactis spp. cremonis | milk | 11.3 mg/100 mL | Co-fermentation | [175] |
| L. plantarum JLSC2-6 | Levilactobacillus brevis YSJ3 | cauliflower stems | 35.00 mg/L | Co-fermentation | [176] |
| L. plantarum MCM4 | Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis | whey-based formulate | 365.6 mg/100 mL | Co-fermentation | [177] |
| L. plantarum DSM749 |
L. brevis NM101-1 |
PM | 224.69 mM | Co-fermentation | [138] |
| L. plantarum C48 |
Lactobacillus paracasei 15N, Streptococcus thermophilus DPPMAST1, Lactobacillus delbruecki subsp. bulgarigus DPPMALDb5 |
Milk + 100 or mg/L of olive vegetation water phenolic extract | 67 mg/L | Co-fermentation | [178] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





