Submitted:
27 November 2023
Posted:
28 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We present a comprehensive hierarchical cognitive framework for autonomous driving, addressing the challenge of responding to novel observations in dynamic environments. This framework marks a fundamental shift from rule-based learning models to cognitive entities capable of AV navigating unseen terrains.
- The proposed framework firmly grounded the principles of Bayesian learning, enabling ADS to adapt its probabilistic models continually. This adaptation is essential for the continuous improvement of the cognitive model through experiences. Consequently, an AV can consistently update its beliefs regarding the surroundings.
- We expand upon a global dictionary to incrementally develop a dynamic world model during the learning process. This world model efficiently structures newly acquired environmental knowledge, enhancing AV perception and decision-making.
- Through active inference, the proposed approach equipped the AV with a sense of self-awareness by continually comparing sensory observations with internal beliefs and aiming to minimize free energy. This self-awareness enables them to make informed decisions about seeking additional information through exploratory actions and when to rely on existing knowledge.
- The dynamic interaction between the ego AV and its environment, as facilitated by active inference, forms the basis for adaptive learning. This adaptability augments AV’s decision-making capabilities, positioning it as a cognitive entity capable of navigating confidently and effectively in uncertain and complex environments.
2. Related Works
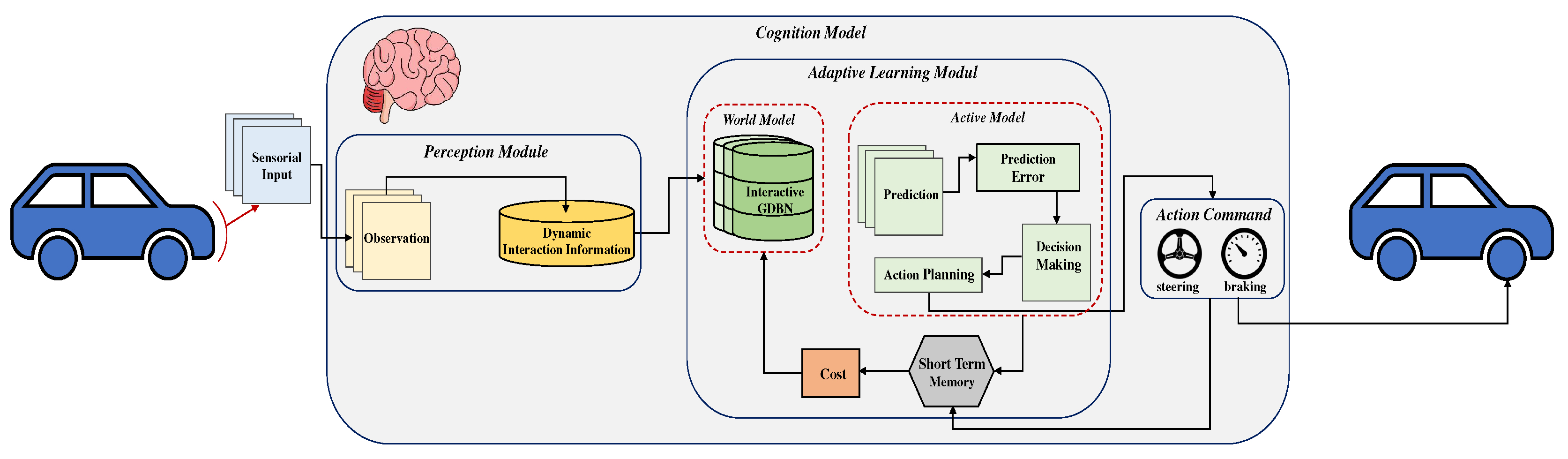
3. Proposed Framework
3.1. Perception Module
3.2. Adaptive Learning Module
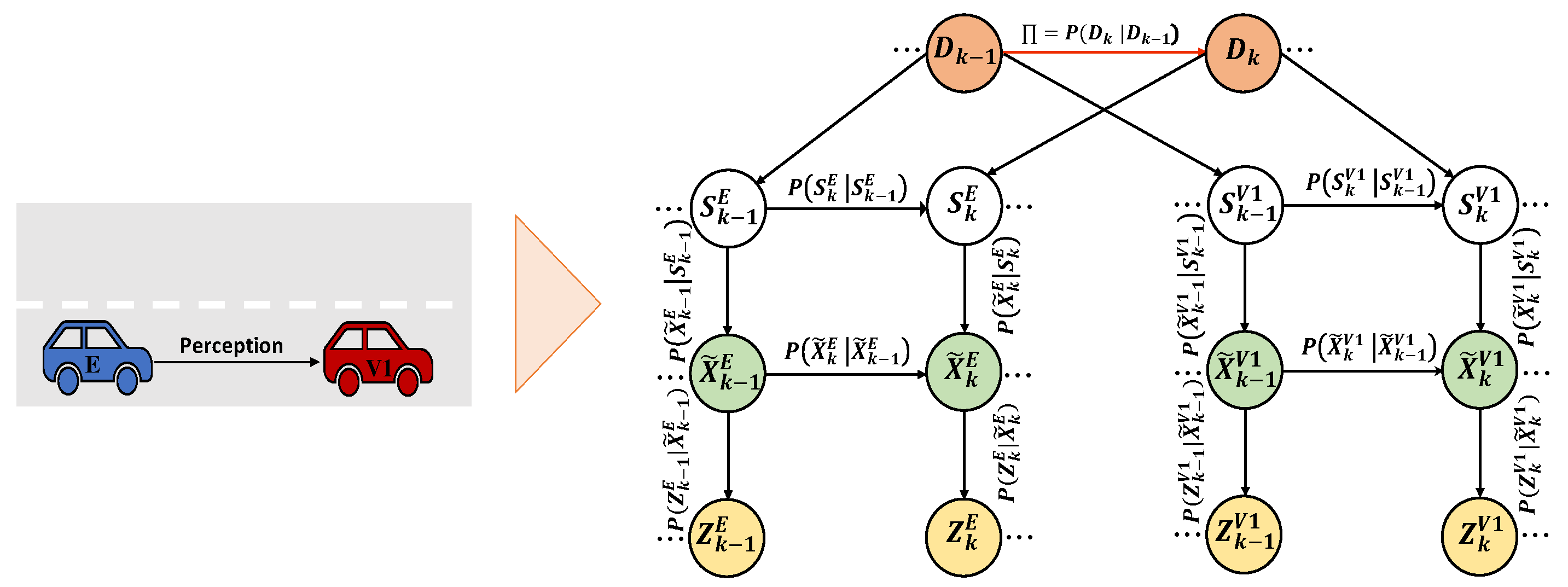
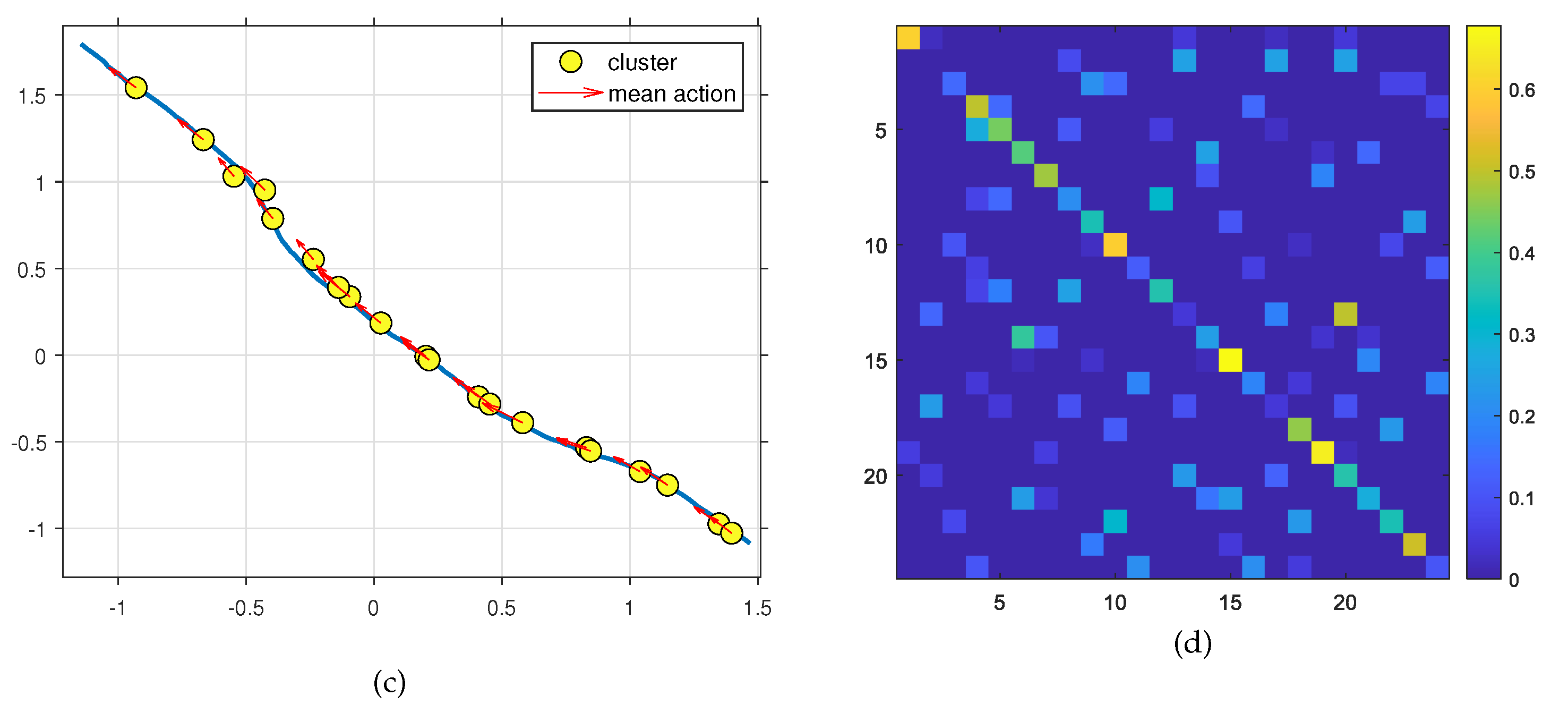
3.2.1. World Model
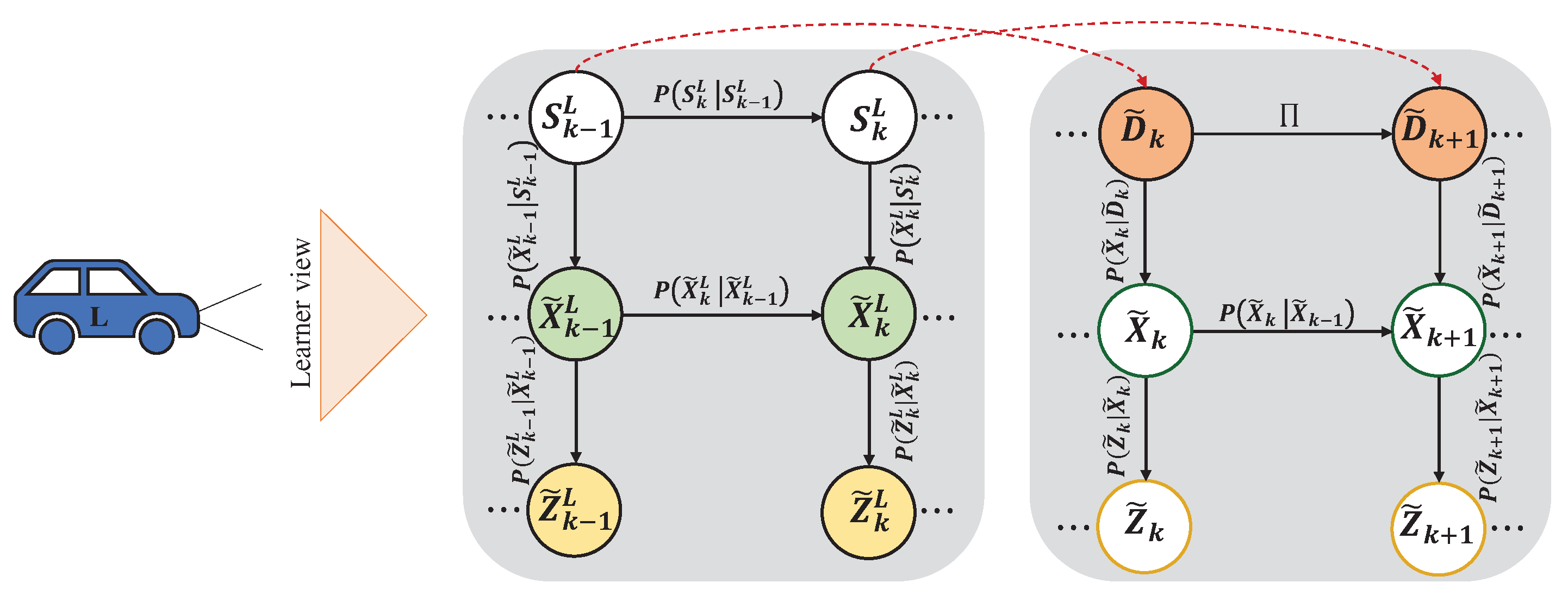
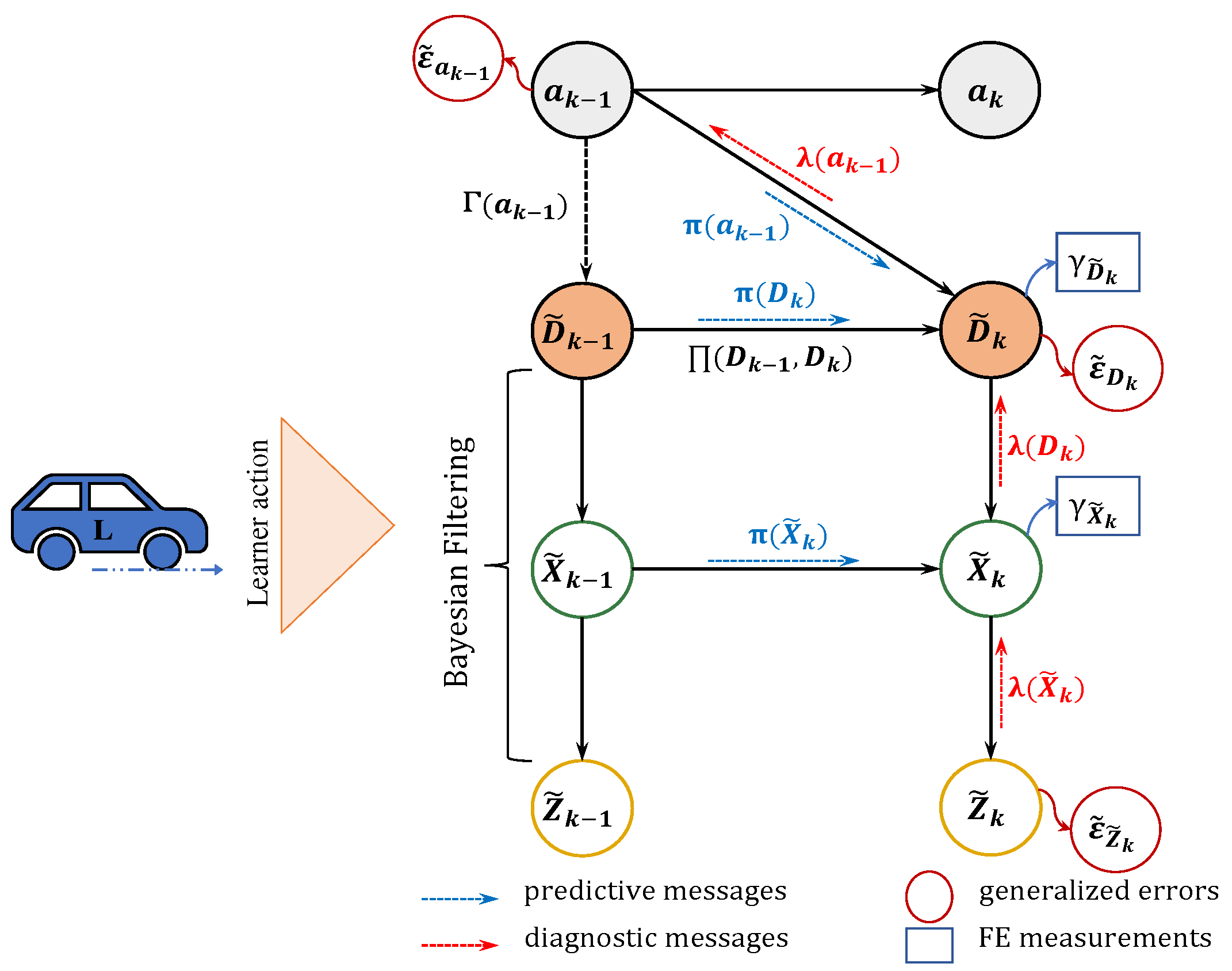
3.2.2. Active Model
- often relies on observations, formulated as , to deduce actual environmental states that are not directly perceived.
- forms beliefs about the hidden environmental states, represented as (,). These beliefs evolve according to and .
- engages with its surroundings by choosing actions that minimize the abnormalities and prediction errors.
- Joint Prediction and Perception:
- Action Selection:
- Free Energy Measurements and GEs
- Incremental Active Learning
- Action Update:
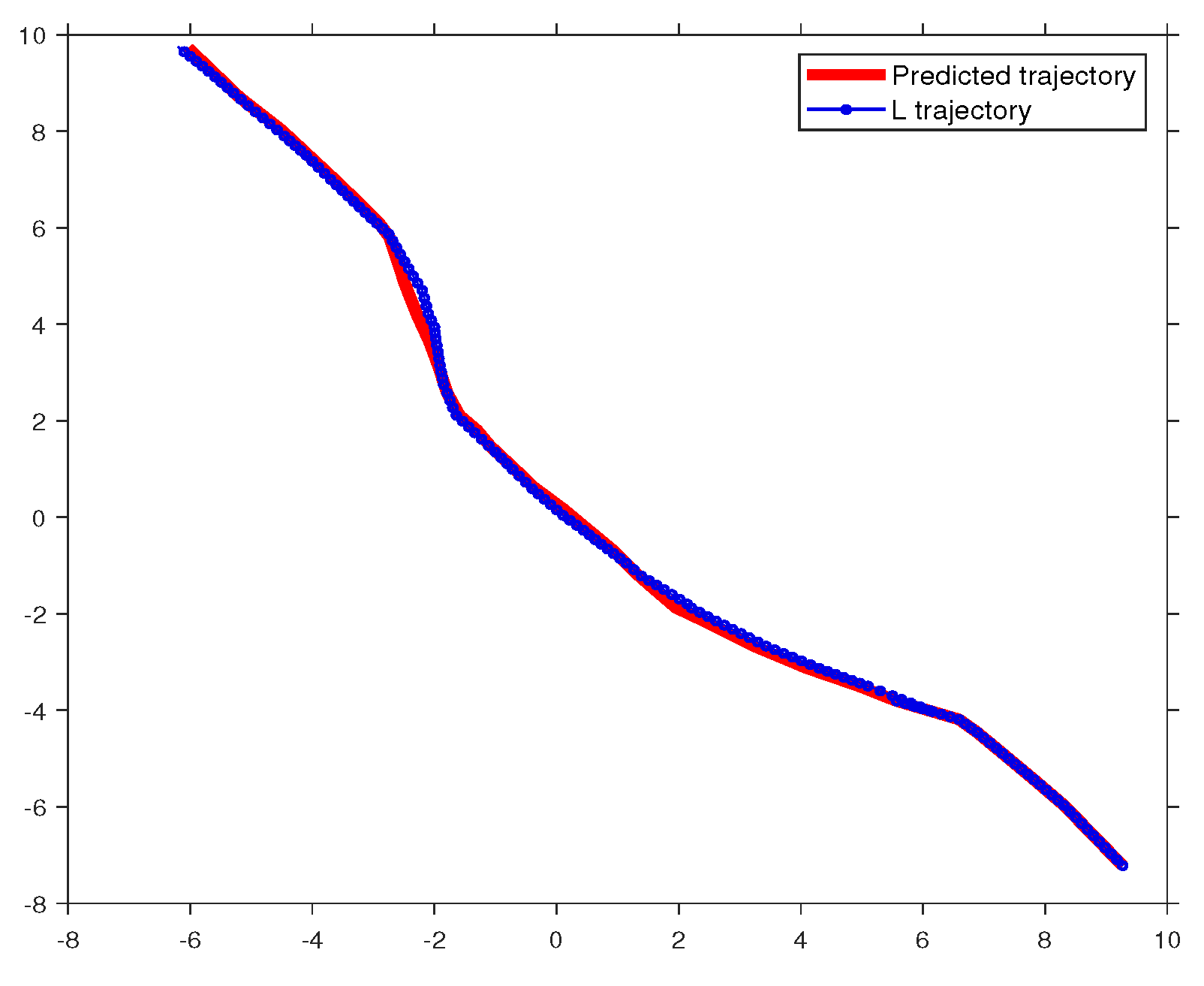
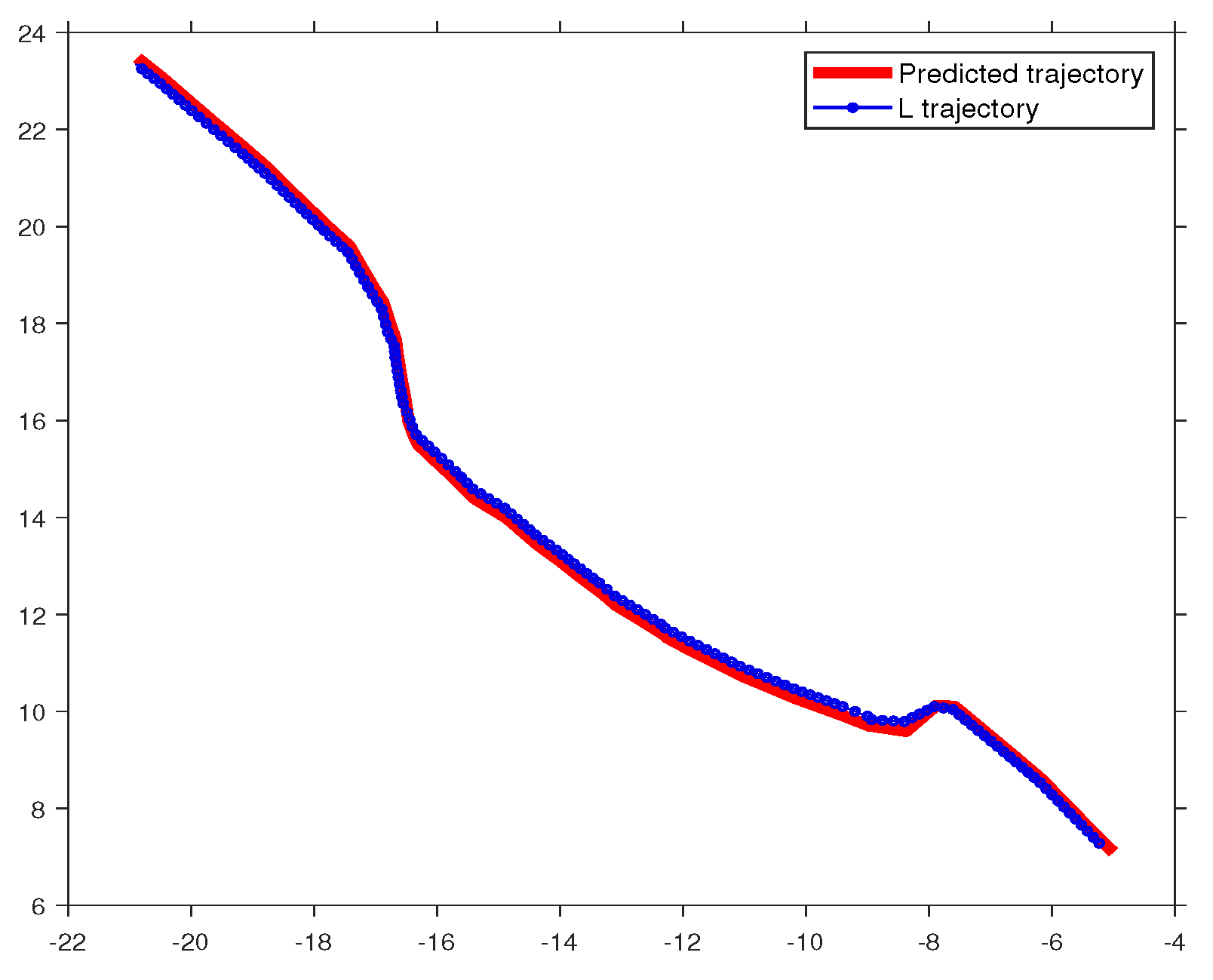
4. Resuts
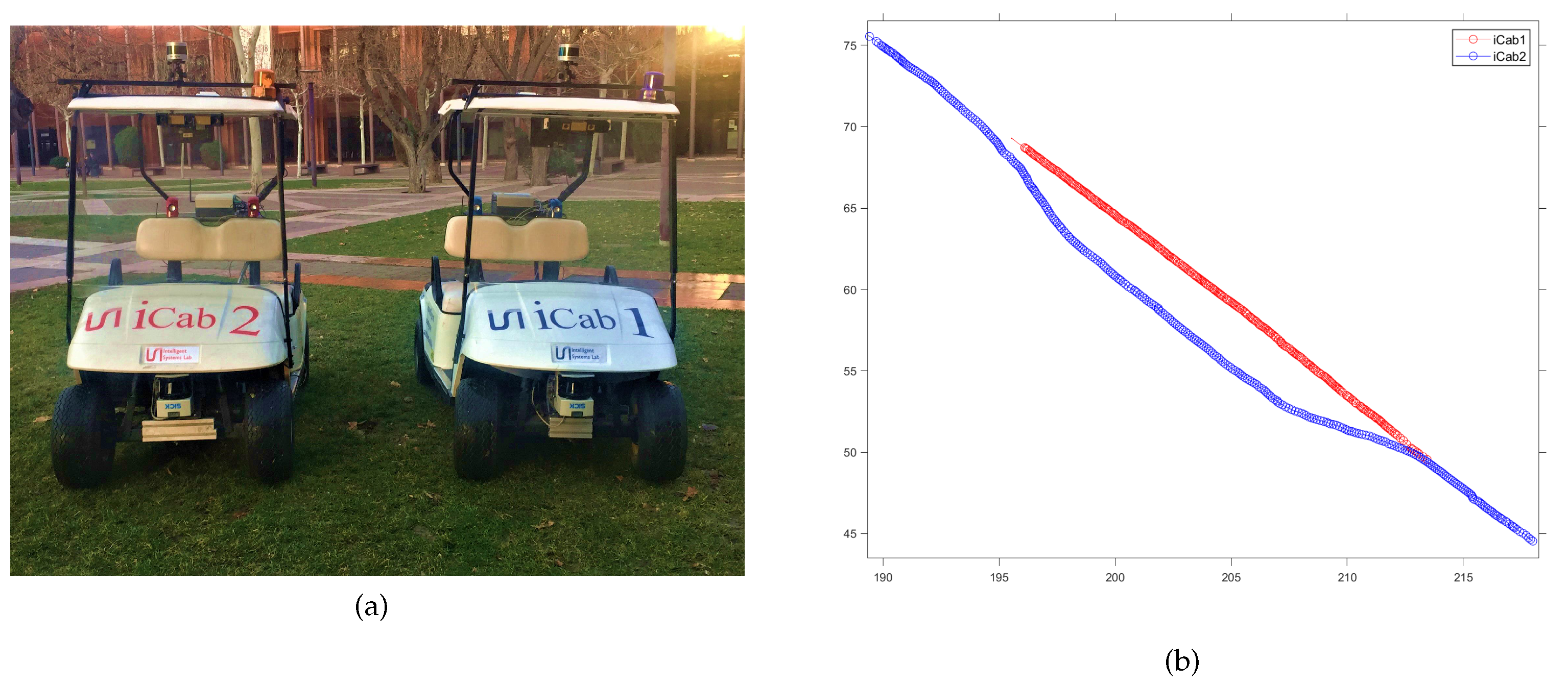
4.1. Experimental Dataset
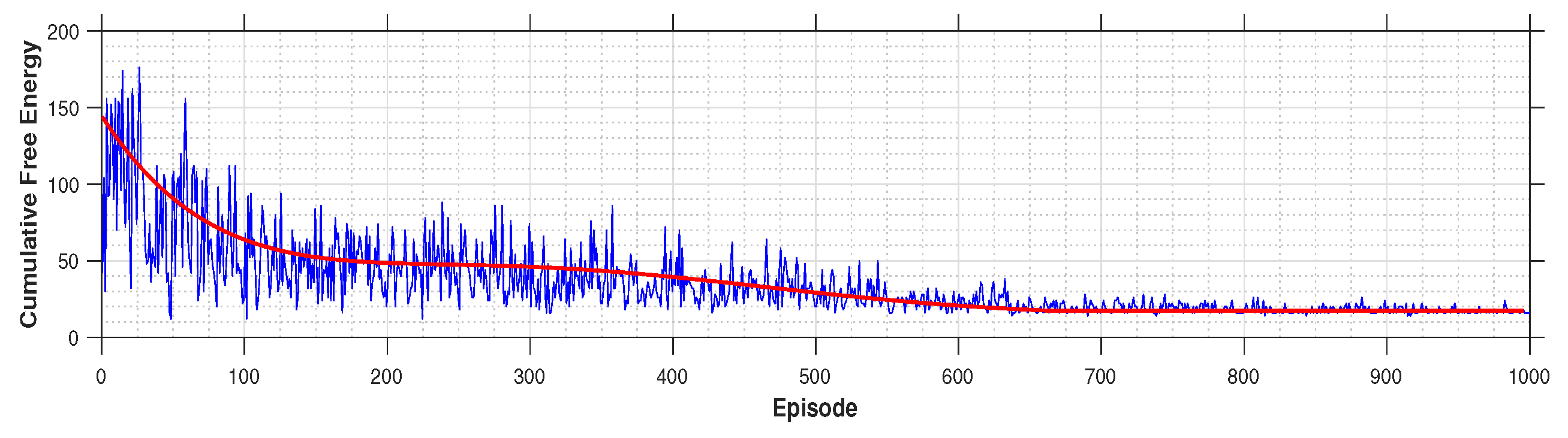
4.2. Offline Learning Phase
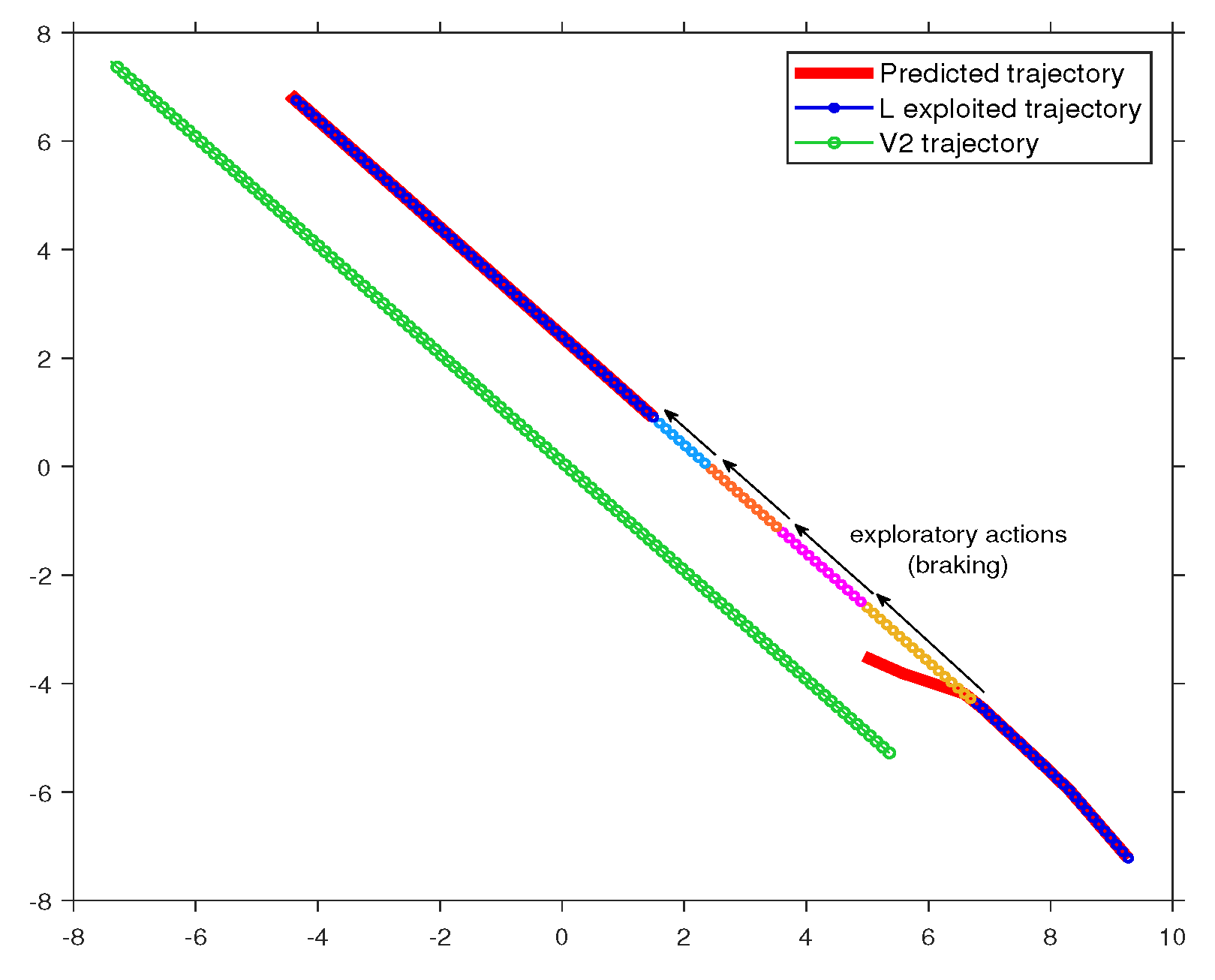
4.3. Online Learning Phase
4.3.1. Action-Oriented Model
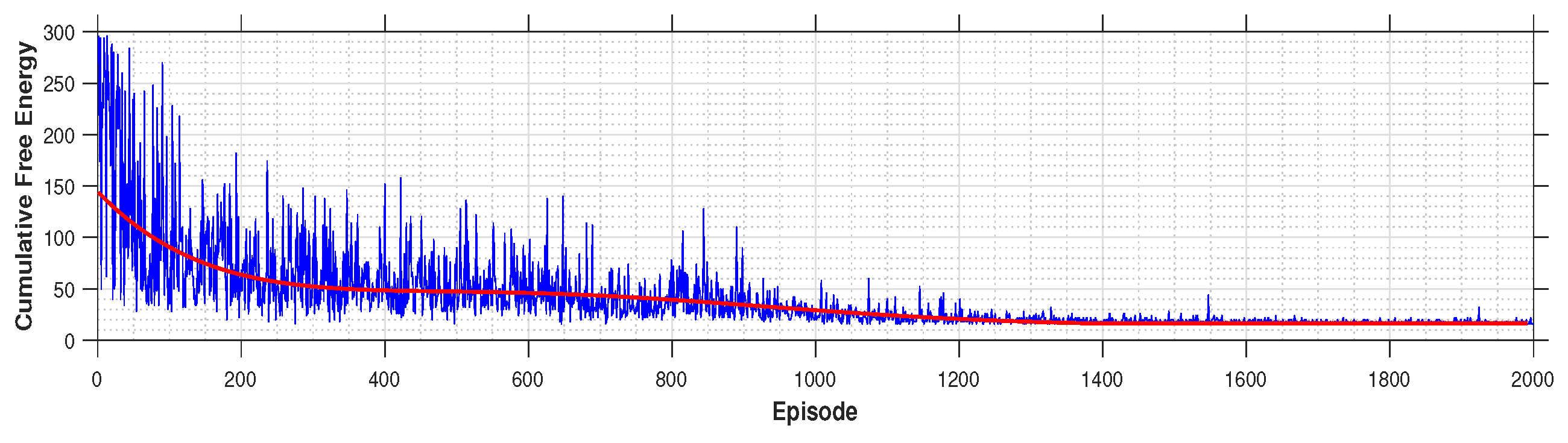
4.3.2. Cost of Learning
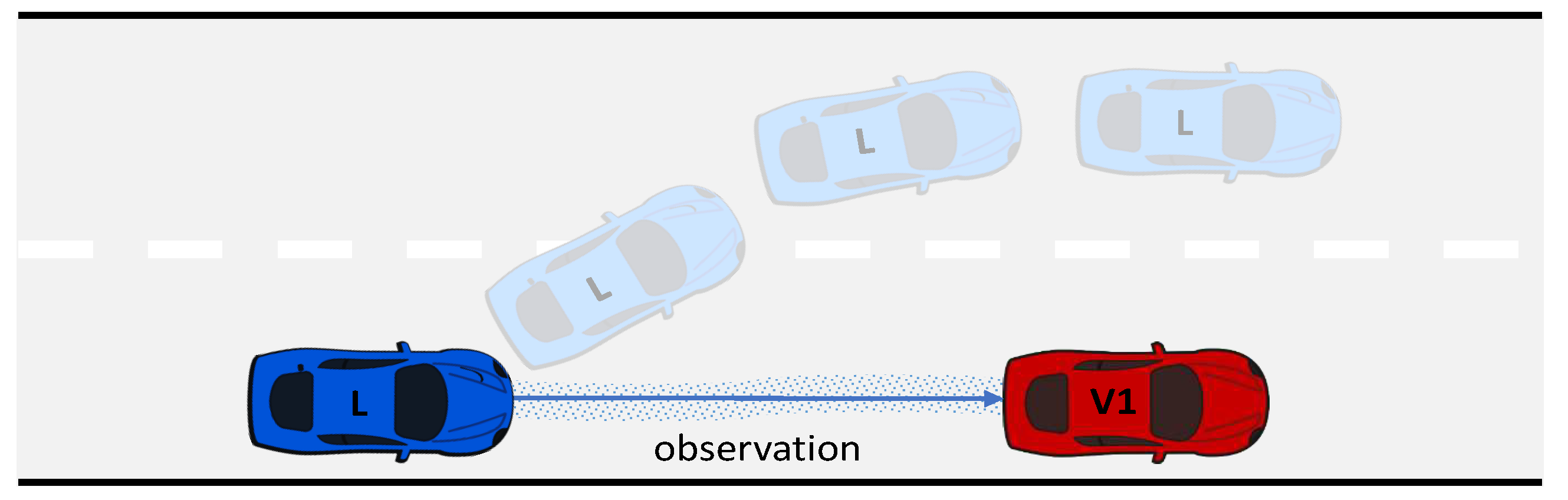
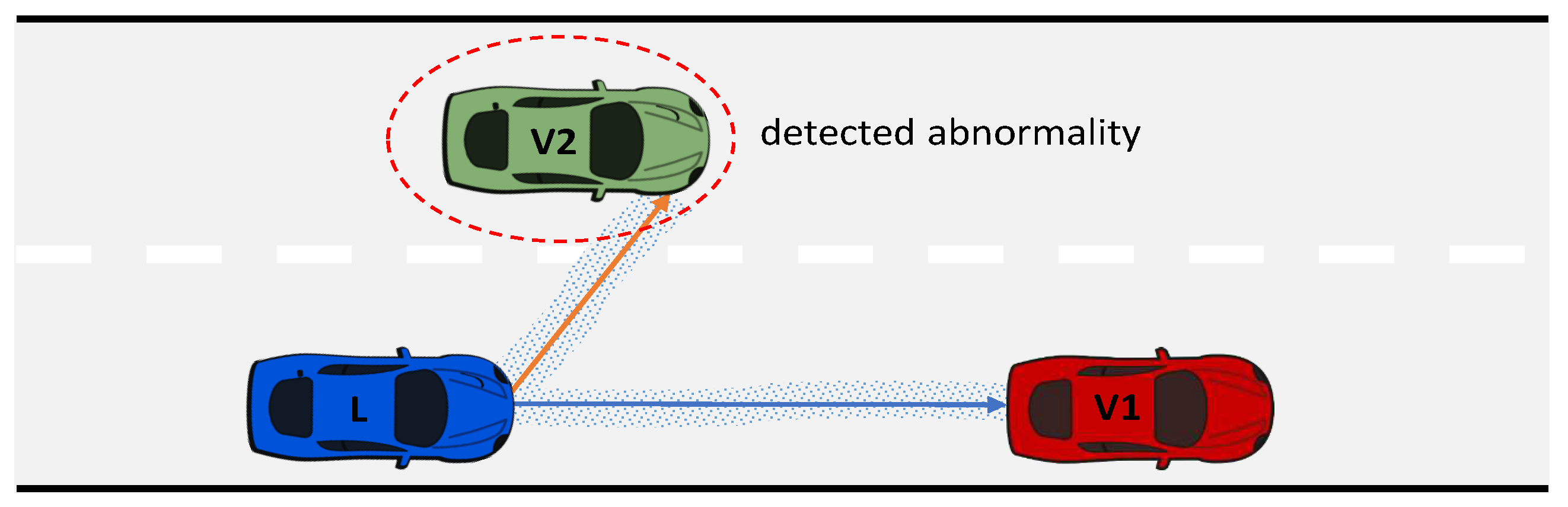
- Model A, developed in a normal situation during the online learning phase, where can overtake .
- Model B, formulated in an abnormal situation during the online learning phase, where is temporarily unable to overtake due to traffic in the adjacent lane.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | autonomous driving |
| ADS | autonomous driving systems |
| AFP-M | Active First-Person model |
| AV | autonomous vehicle |
| E | expert agent |
| FE | free energy |
| FP-M | First-Person model |
| GDBN | Generative Dynamic Bayesian Network |
| GE | Generalized error |
| GM | Generative model |
| GS | Generalized state |
| IL | imitation learning |
| KF | Kalman filter |
| L | learning agent |
| MJPF | Markov Jump Particle Filter |
| PF | particle filter |
| POMDP | partially observed Markov decision process |
| RL | reinforcement learning |
| SM | Situation model |
| WM | World mode |
References
- Bezai, N.E.; Medjdoub, B.; Al-Habaibeh, A.; Chalal, M.L.; Fadli, F. Future cities and autonomous vehicles: analysis of the barriers to full adoption. Energy and Built Environment 2021, 2, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, D.; Poddar, N.; Rajpurkar, A.; Chahal, M.; Kumar, N.; Joshi, G.P.; Cho, W. A review on autonomous vehicles: Progress, methods and challenges. Electronics 2022, 11, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürnkranz, J.; Gamberger, D.; Lavrač, N. Foundations of rule learning; Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, M.H.; Waterfall, H.R.; Lotem, A.; Halpern, J.Y.; Schwade, J.A.; Onnis, L.; Edelman, S. General cognitive principles for learning structure in time and space. Trends in cognitive sciences 2010, 14, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knill, D.C.; Pouget, A. The Bayesian brain: the role of uncertainty in neural coding and computation. TRENDS in Neurosciences 2004, 27, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Duan, L.M. A quantum machine learning algorithm based on generative models. Science advances 2018, 4, eaat9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayani, A.; Khan, K.; Marcenaro, L.; Marchese, M.; Regazzoni, C. A Goal-Directed Trajectory Planning Using Active Inference in UAV-Assisted Wireless Networks. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friston, K.; FitzGerald, T.; Rigoli, F.; Schwartenbeck, P.; Pezzulo, G. Active inference: a process theory. Neural computation 2017, 29, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friston, K. The free-energy principle: a unified brain theory? Nature reviews neuroscience 2010, 11, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regazzoni, C.S.; Marcenaro, L.; Campo, D.; Rinner, B. Multisensorial generative and descriptive self-awareness models for autonomous systems. Proceedings of the IEEE 2020, 108, 987–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondruš, J.; Kolla, E.; Vertal’, P.; Šarić, Ž. How do autonomous cars work? Transportation Research Procedia 2020, 44, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paden, B.; Čáp, M.; Yong, S.Z.; Yershov, D.; Frazzoli, E. A survey of motion planning and control techniques for self-driving urban vehicles. IEEE Transactions on intelligent vehicles 2016, 1, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, D.; Pérez, J.; Milanés, V.; Nashashibi, F. A review of motion planning techniques for automated vehicles. IEEE Transactions on intelligent transportation systems 2015, 17, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakdamanian, E.; Sheng, S.; Baee, S.; Heo, S.; Kraus, S.; Feng, L. Deeptake: Prediction of driver takeover behavior using multimodal data. In Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems; 2021; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Luo, X. Trajectory planning and safety assessment of autonomous vehicles based on motion prediction and model predictive control. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2019, 68, 8546–8556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkeson, C.G.; Schaal, S. Robot learning from demonstration. ICML, 1997, Vol. 97, pp. 12–20.
- Schaal, S. Is imitation learning the route to humanoid robots? Trends in cognitive sciences 1999, 3, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billard, A.; Calinon, S.; Dillmann, R.; Schaal, S. Robot programming by demonstration. In Springer handbook of robotics; Springer, 2008; pp. 1371–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, S.; Haider, S.; Williams, M.A. Teaching coordinated strategies to soccer robots via imitation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO); IEEE, 2012; pp. 1434–1439. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, A.; Gaber, M.M.; Elyan, E.; Jayne, C. Imitation learning: A survey of learning methods. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 2017, 50, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, T.; Motoyoshi, T.; Suga, Y.; Mori, H.; Ogata, T. End-to-end learning method for self-driving cars with trajectory recovery using a path-following function. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN); IEEE, 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Huang, X. End-to-end learning for lane keeping of self-driving cars. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV); IEEE, 2017; pp. 1856–1860. [Google Scholar]
- Bojarski, M.; Del Testa, D.; Dworakowski, D.; Firner, B.; Flepp, B.; Goyal, P.; Jackel, L.D.; Monfort, M.; Muller, U.; Zhang, J.; et al. End to end learning for self-driving cars. arXiv preprint 2016, arXiv:1604.07316. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, A.; Savinov, N.; Geiger, A. Conditional affordance learning for driving in urban environments. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning. PMLR; 2018; pp. 237–252. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, D.; Ben Amor, H.; Berger, E.; Jung, B. Learning two-person interaction models for responsive synthetic humanoids. Journal of Virtual Reality and Broadcastings 2014, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Droniou, A.; Ivaldi, S.; Sigaud, O. Learning a repertoire of actions with deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Development and Learning and on Epigenetic Robotics; IEEE, 2014; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Buntine, W.; Haffari, G. Learning how to actively learn: A deep imitation learning approach. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); 2018; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Argall, B.D.; Chernova, S.; Veloso, M.; Browning, B. A survey of robot learning from demonstration. Robotics and autonomous systems 2009, 57, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.; Bagnell, D. Efficient reductions for imitation learning. In Proceedings of the thirteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics; JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings. 2010; pp. 661–668. [Google Scholar]
- Gangwani, T.; Peng, J. State-only imitation with transition dynamics mismatch. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2002.11879. [Google Scholar]
- Ogishima, R.; Karino, I.; Kuniyoshi, Y. Combining imitation and reinforcement learning with free energy principle 2020.
- Kuefler, A.; Morton, J.; Wheeler, T.; Kochenderfer, M. Imitating driver behavior with generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV); IEEE, 2017; pp. 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Schroecker, Y.; Vecerik, M.; Scholz, J. Generative predecessor models for sample-efficient imitation learning. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1904.01139. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Gu, Y.; Wu, D. Survey of incremental learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 chinese control and decision conference (ccdc); IEEE, 2019; pp. 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Chalup, S.K. Incremental learning in biological and machine learning systems. International Journal of Neural Systems 2002, 12, 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Laschi, C.; Trimmer, B. Soft robotics: a bioinspired evolution in robotics. Trends in biotechnology 2013, 31, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozari, S.; Krayani, A.; Marin, P.; Marcenaro, L.; Martin, D.; Regazzoni, C. Adapting Exploratory Behaviour in Active Inference for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023-2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP); IEEE, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nozari, S.; Krayani, A.; Marin-Plaza, P.; Marcenaro, L.; Gomez, D.M.; Regazzoni, C. Active Inference Integrated With Imitation Learning for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 49738–49756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayani, A.; Alam, A.S.; Marcenaro, L.; Nallanathan, A.; Regazzoni, C. Automatic Jamming Signal Classification in Cognitive UAV Radios. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2022, 71, 12972–12988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, L. Statistical inference based on divergence measures; CRC press, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Marín-Plaza, P.; et al. Stereo Vision-based Local Occupancy Grid Map for Autonomous Navigation in ROS. In Proceedings of the 11th Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications - Volume 3: VISAPP, (VISIGRAPP 2016). INSTICC; SciTePress, 2016; pp. 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




