Introduction
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) has become increasingly
prevalent in the construction industry due to its affordability, structural reliability0,
and sustainable qualities2. However, despite its widespread application3,
OSB is a flammable material which produces toxic fire effluent upon
decomposition4. However, as smoke toxicity is unregulated outside of
the mass transport industry, there is no set methodology for assessing smoke
toxicity of construction products, like OSB, on a large-scale. The ISO 9705
room corner test5 primarily assesses the flammability of materials6
and as the materials are mounted to the walls during a test and is not suited
for smoke toxicity assessment. Additionally, little research is published
surrounding how to force under-ventilated fire conditions when conducting
large-scale tests. Smoke toxicity is typically most dangerous during
post-flashover under-ventilated fires, and so the need for a methodology to
assess the most toxic scenario is needed to determine the best, and worst case
scenarios construction products may be exposed to.
This research aims to assess the novel design of a
modified ISO 9705 room corner test designed for smoke toxicity quantification.
Additionally, three tests conditions will be assessed to determine the best
methodology for testing in well-ventilated, and under-ventilated fire
conditions. This research seeks to determine if restriction of ventilation is
enough to force a fire to transition to under-ventilated flaming, or if the
fuel loading is much more important in affecting the fire severity and fire condition.
The research also aims to assess if the proposed configuration and
modifications to the ISO 9705 room are suitable for providing a methodology for
large-scale assessment of smoke toxicity. The test designs used are novel and
have not been based on any previous testing conducted in literature.
Method
The methodology used is identical to that of other
published large-scale work by the author(s). The tests were all conducted in a
series over a short time-period.
Gas Analysis and Fire Condition Measurements
Three stainless steel tubes with an internal
diameter of 6 mm were secured near the top of the doorway. One was used as a
sampling line for a phi meter that was specifically designed and created to
monitor the equivalence ratio7. The two remaining sampling lines
went to a specially made portable gas analyser, designed and created for this
work (containing an NDIR, and O2 electrochemical cells). The three
tubes were placed approximately 0.1 m from the ceiling pointing upwards and
were approximately 0.3 m across the doorway.
Silicone tubing was connected to the stainless
steel tubing at the bottom. The stainless steel tubes were approximately 1 m in
length. This allowed the effluent to cool slightly before using silicone tubing
connections to the analysers and prevented the tubing from melting during
testing. The silicone tubing was connected to a glass tube filled with glass
wool to filter the soot from the sample gas to prevent blockages inside the
analysers. The analyser sampled O2, CO and CO2
continuously at a flow rate of 1 L min-1.
The phi meter sampling line was connected to the
third stainless steel tube in the doorway. Silicone tubing was attached to the
stainless steel tube. A glass tube filled with glass wool to act as a filter
was attached to the silicone tubing. The filter was attached to an Omega 3100
series 0-5 L min-1 flow meter set to a regulated flow of 1.5 L min-1,
followed by a Charles Austen d5 SE air pump. The gas was then split into two
lines using a glass T-piece. One line was connected directly to an exhaust, the
other was connected to the sample inlet of the phi meter. This minimised
sampling time delays due to the very low flow rates used in the phi meter for
analysis. The sampling was continuous throughout the tests.
As silicone tubing was used, there is likely to be
losses occurring during sampling. Use of a heated line would have eliminated
any potential losses; however a heated line was unavailable for this work and
so while preferable, one was not used.
Monitoring Air Flow and Temperature
The airflow in the doorway was monitored to enable
gas yields to be calculated (alongside using the mass loss) for reaction
products produced and measured during the test. Air velocity in and out of the
door was monitored using bi-directional McCaffrey probes (McC)
89 with a differential pressure
transducer at the end. The pressure transducers were obtained from Farnell
components. A Sensirion CMOSens SPD1000-LO25 pressure transducer was attached
to the end of silicone tubing attached to the McCaffrey probe. The
pressure transducer was connected to a 5 V power supply, and the signal wires
were connected to a data logger to log the voltage output of the pressure
transducer. The probes were placed in the doorway at set heights. The heights
have been summarised in
Table 1. The
probes were placed approximately 0.2 m into the doorway for each test.
The gas velocity profile in the test doorway was
calculated by using the measurements obtained by the probes alongside the
temperature profile data obtained from the thermocouple tree10
located in the centre of the doorway.
Standard Measurements
All standard room corner measurements were taken
throughout the experiments as described in ISO 9705. Oxygen was monitored using
a paramagnetic analyser, and CO/CO2 was monitored using an infrared
spectrophotometer within the analysis system. Additional measurements also
included duct flow, temperature, smoke obscuration, air pressure, humidity and
temperature. Heat release is calculated by the test room software. Systems were
logged by a VeeCan DAQ system.
All standard room corner measurements were logged
every 3 seconds. The additional gas analysis systems used for the experiments
were logged every 1 second. Consequentially, the two time scales were required
to be matched afterwards.
Test Layout and Fuel Loading
OSB sheets were attached to a singular single
burning item (SBI) rig11 with a 4 mm air gap between the material
and the calcium silicate boards. The board was approximately 12 mm thick and
slightly raised above the burner, as in the SBI test. Three separate tests were
carried out: 1xSBI (no door), 1xSBI (door), and 2xSBI no door. The 1xSBI (no
door) test was used to replicate well-ventilated flaming conditions. The 1xSBI
(door) test was performed to see if restriction of the ventilation would force
under-ventilated flaming conditions. The 2xSBI (no door) test was performed to
see if doubling the fuel loading would result in under-ventilated flaming
conditions.
One SBI rig was set up for both 1xSBI tests. A
total mass of 14.72 kg and 14.59 kg of OSB was used for the 1xSBI (door) and
1xSBI (no door) tests respectively. The SBI rig was placed on the load cell in
the centre of the ISO room. Gas analysers were calibrated and set up for
testing. Heptane was measured out and poured into the burner(s) inside the
room. The ISO room measurements were started alongside the gas analysers and
phi meter 2 minutes before ignition. The heptane burner was ignited manually. In
the 1xSBI (door) test, a 1.3 m door was placed over the bottom part of the door
of the ISO room after ignition to restrict the ventilation into the room. The
2xSBI (no door) test was performed identically, however the two SBI rigs were
set up (facing one another) and the total mass of OSB used was 30.65kg.
The airflow was monitored using McCaffrey probes
throughout the test. In this test, the lower McCaffrey probe was altered so
that the inlet to the probe was facing outwards to record the airflow into the
test room. The data was recorded for future use for calculations of the volume
flow of gas in the doorway to be used for yield calculations. The yield
calculations are beyond the scope of this paper.
Results
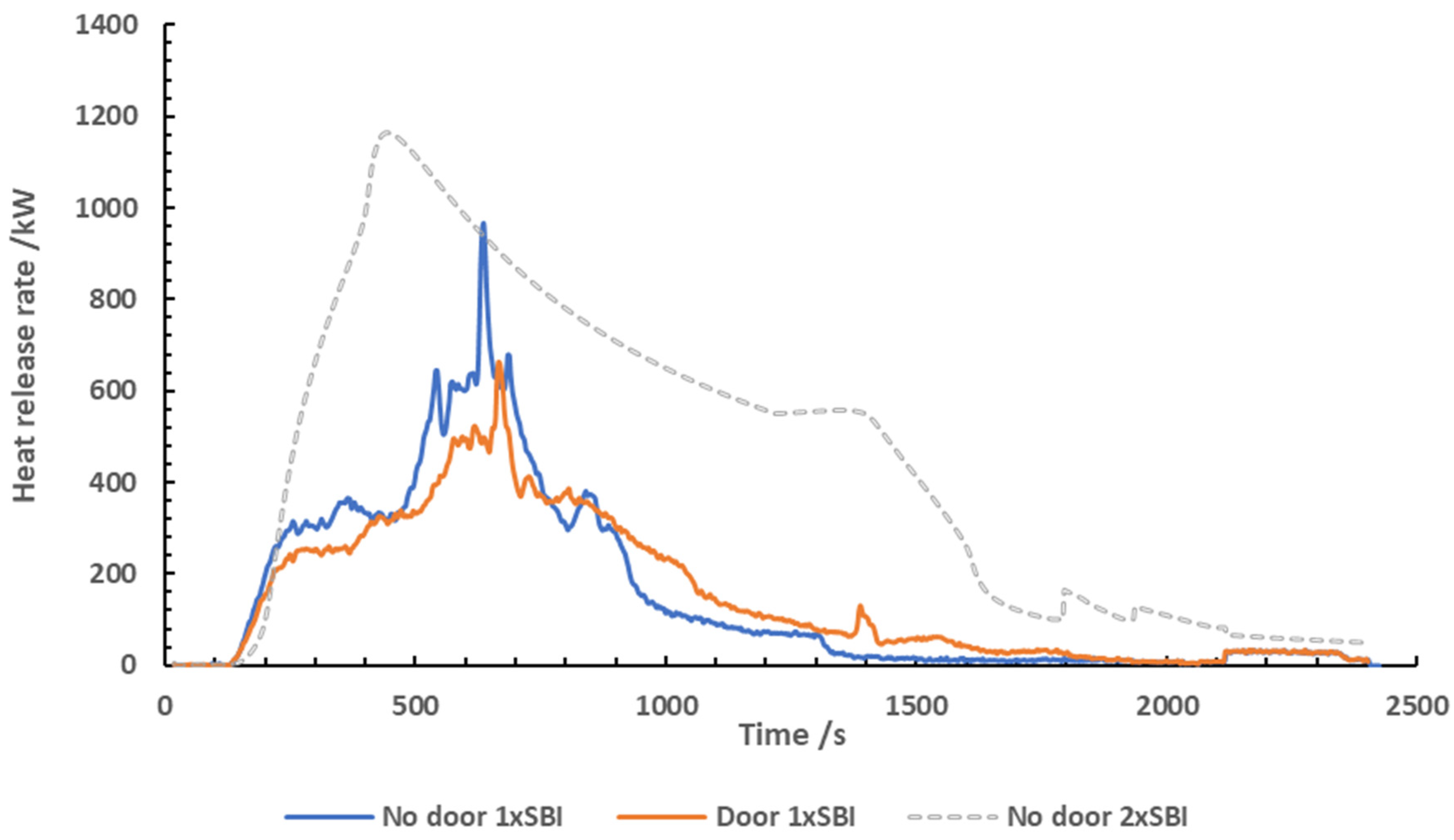
Heat Release
The heat release data from the tests are shown in
Figure 1. The heat release data is shown with
the inclusion of the heat released from the ignition source.
In the test using 1x SBI with no door, the heat
release rose to 300 kW rapidly after ignition, which is likely a result of the
heat release from the heptane burner and the ignition of the OSB sheet. From
250 to 450 seconds, the heat release was relatively steady. At 500 seconds, the
heat release rose rapidly again, reaching its peak heat release of 990 kW at
approximately 700 seconds into the test. At this point, the entire OSB sheet
was burning. After reaching its peak, the heat release dropped rapidly. This
was likely a result of the OSB becoming burnt through, meaning there was no
fuel left to facilitate the fire.
In the test using 1x SBI with a door, the heat
release rose rapidly after ignition and reached the peak heat release of 670 kW
at 720 seconds into the test. At 725 seconds, the heat release dropped rapidly
before gradually declining as the fuel began to run out. The heat release with
the restricted ventilation was much lower.
In the test using 2x SBI with no door, the peak
heat release of 1180 kW was reached at 420 seconds into the test. The sharp
rise was thought to be due to a radiant effect from the two SBI rigs facing
each other after both were fully flaming, or a result of both sides of the OSB
flaming at once. The rigs facing each other forced the fire to be much more
severe than using 1x SBI.
The HRR curves for 1 x SBI where the doorway was
fully open and shut off show remarkable similarity, including a similar peak
occurring at 640 seconds. This was presumably when both sides of the OSB were
burning at the same time. However, the peak HR for the partially blocked
doorway is around 670 kW, rather than 990 kW for the open doorway. This
demonstrates the effect of partially blocking the door to the ISO room is
slowing the rate of burning, rather than forcing under-ventilated flaming. The
peak heat release measured decreased with the addition of the door on the test
room. This was likely a result of the calcium silicate board used as the door
absorbing a portion of the heat from the fire, resulting in a lower heat
measurement.
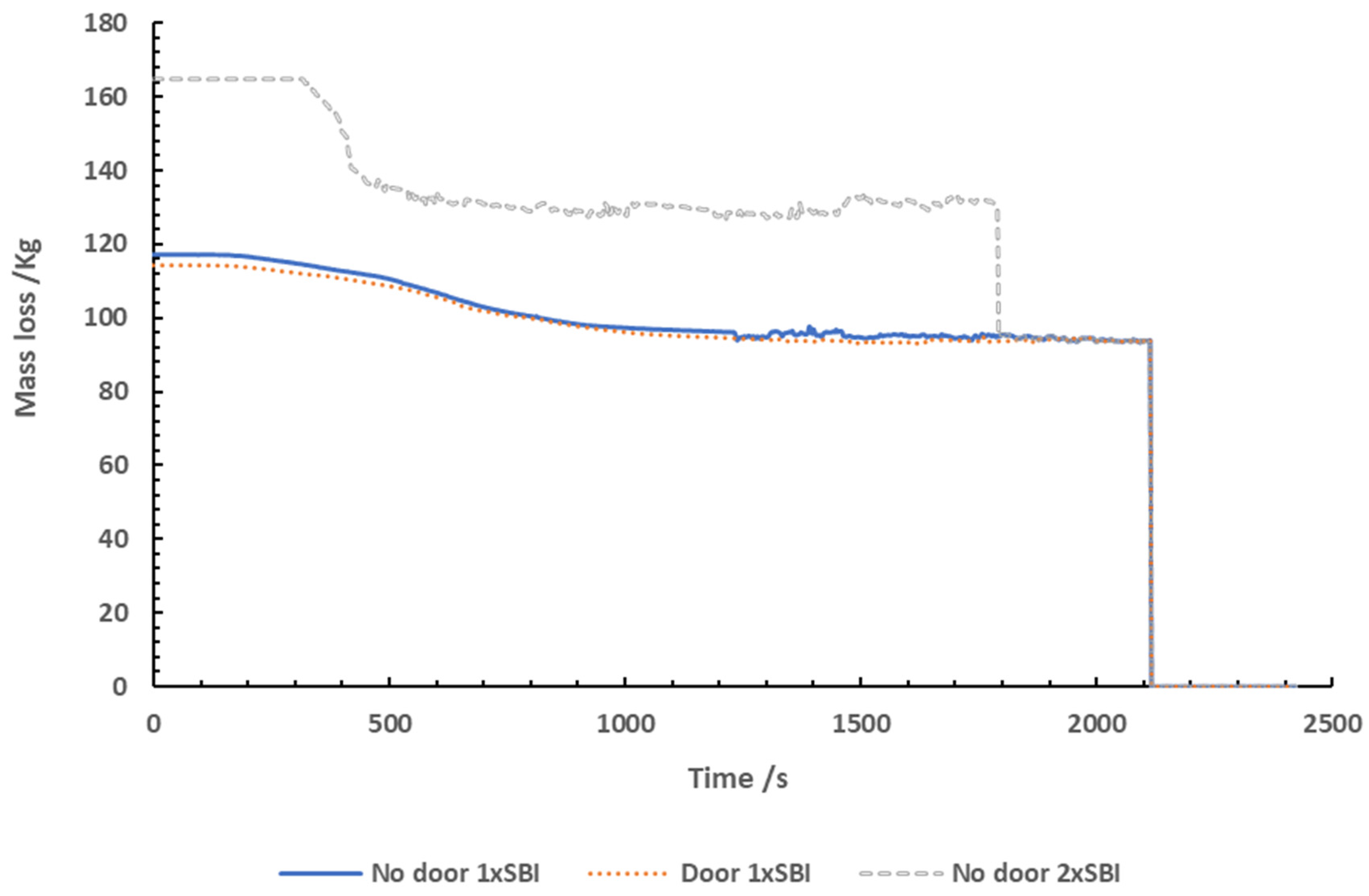
Mass Loss
The mass loss measured using the scale in the test
room for each test is shown in
Figure 2.
As the test using 1x SBI with no door only used one
rig, the test rig's total mass was within the range's limits. The mass loss
measurements showed a steady decline over the course of the entire test, with
the mass reducing to approximately from 118 kg to 100 Kg by 800 seconds.
The data obtained when testing 1x SBI with a door
has been presented, however it is thought that the scale did not appear to
provide an accurate mass loss measurement as the mass appears to only change by
approximately 15 Kg. As the majority of the weight was from the steel frame, it
is difficult to see the actual mass loss that occurred during the test,
although the mass was seen to steadily decline over the course of the test. The
mass of the residue at the end of the test was unfortunately not recorded.
The initial measurement of the test using 2x SBI
with no door was not recorded due to the test rig exceeding the maximum
measurement of the scale (165 kg). The mass had reduced enough by 420 seconds
to measure the actual mass loss occurring. The largest mass loss was observed
at 320 seconds to 420 seconds. The plateau observed from 400 onwards is a
result of a slow smouldering fire occurring after the test had finished.
Temperature
Temperature measurements were taken in the doorway
of the ISO room throughout the tests. The temperature profile recorded can be
used in the future to identify the neutral plane within the doorway to
calculate air velocity in and out of the room with the addition of air velocity
measurements. Within the temperature data, a clear distinction between the
upper and lower plane in the doorway was seen. The upper plane can be seen from
40 cm from the ceiling down to 80 cm from the ceiling. The lower plane is seen
from 100 cm to the bottom of the room. The thermocouple at 80 cm sits in the
middle of the two planes. This was taken as the neutral plane point and can be used
to calculate gas yields measured in the doorway for future work.
The temperatures measured when testing 1x SBI with
no door increased rapidly upon ignition, reaching a maximum temperature of 590
°C approximately 650 seconds into the test. After reaching its peak, the
temperature began to slowly decline as the fire began to decrease. The peak
temperature measured corresponds to the same point the peak heat release was
measured during the test.
The temperatures measured when testing 1x SBI with
a door show a rapid increase upon ignition, reaching a maximum temperature of
580 °C before slowly declining as the fire begins to decrease. The temperature
profile was used to identify the neutral plane to calculate air velocity in and
out of the room. As the door covered the bottom third of the door, the
measurements taken more than 80 cm from the ceiling are negligible.
When testing 2x SBI with no door, the peak
temperature was 900 °C, measured 40 cm below the ceiling. The excess heat
produced from the fire was likely a result of radiant effects occurring as the
two burning test rigs faced each other, causing an increase in the overall heat
measured inside the room.
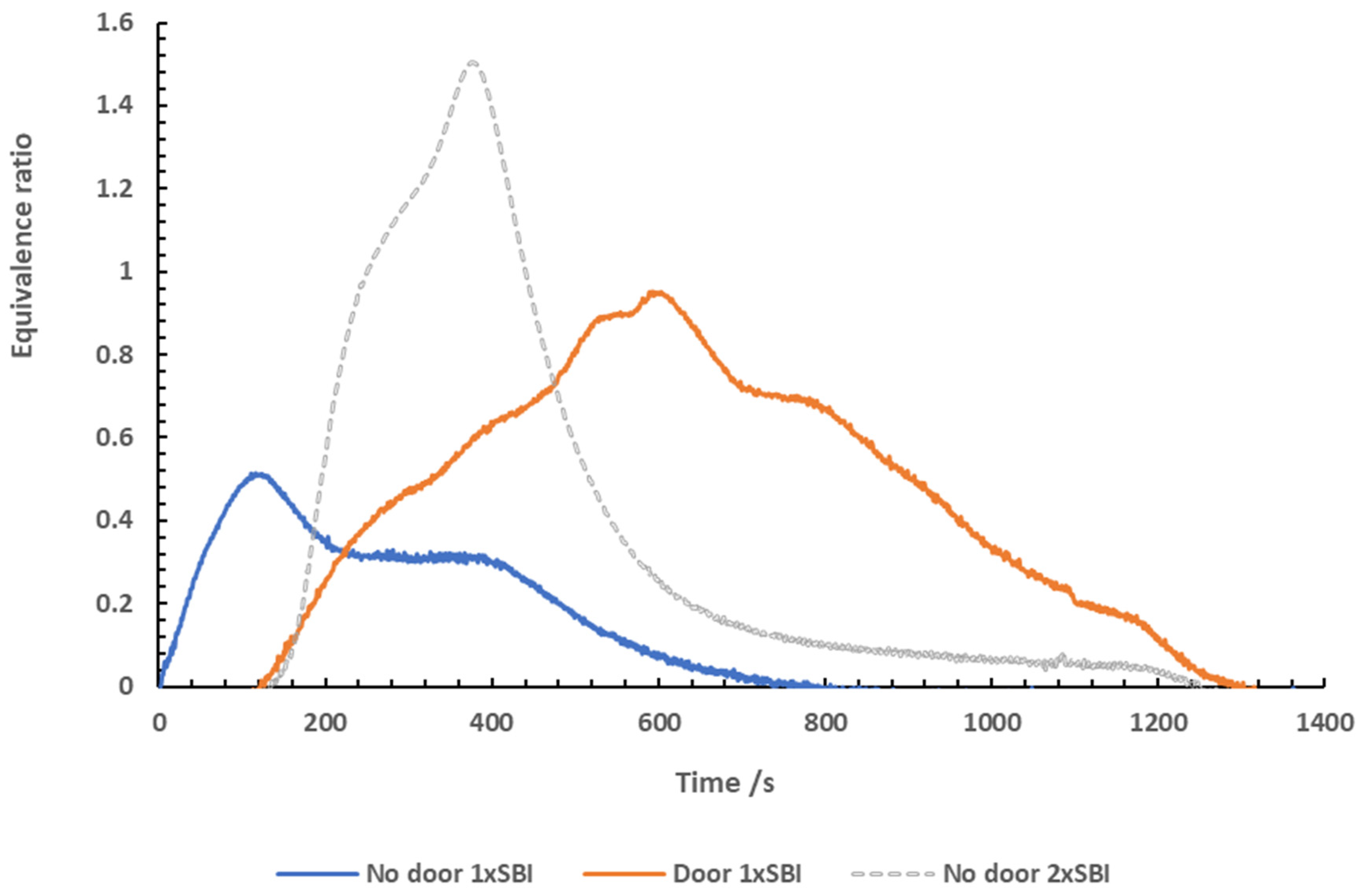
Fire Condition
The equivalence ratio was logged throughout the
tests using a phi meter [7]. The results
obtained are shown in
Figure 3.
After ignition, the equivalence ratio measured
using 1x SBI with no door grew steadily, reaching a peak value of 0.71
approximately 650 seconds into the test, corresponding to the same time the
peak heat release was reached. The equivalence ratio remained below 1
throughout the test, showing that the fire remained well-ventilated for the
test duration. For most of the test, the equivalence ratio remained between 0.3
and 0.7, which is representative of early well-ventilated flaming. This was
likely a result of the open door, as fresh air could enter the fire allowing
for more complete combustion to occur throughout. After 650 seconds, the
equivalence ratio begins to decline as a result of the lack of fuel. While the
HRR data shows a sharp peak at 680 seconds, the phi meter peak is much softer.
This is a result of the slower response time of the phi meter, resulting in a
softer peak being measured.
The peak equivalence ratio measured when testing 1x
SBI with a door was 0.95 and was reached 610 seconds into the test. The
equivalence ratio rose steadily upon ignition, however the fire did not
transition into under-ventilated flaming despite the door restricting the
ventilation of the test room.
Upon ignition, the equivalence ratio grew rapidly
when testing 2x SBI with no door, reaching a peak value of 1.50 at 400 seconds
into the test. The fire was able to transition fully into under-ventilated
flaming due to the significant amount of fuel present in the test room and the
high heat release. Under-ventilated flaming was sustained between 300 to 420
seconds. After this point, the fuel became limited, and the fire began to
decrease in size, seen by a decrease in equivalence ratio.
When the maximum equivalence ratio was reached,
flaming combustion occurred in the doorway due to the severity of the test, and
so the stainless steel sampling lines were sampling from the flame zone within
the doorway. This means that while the fire was clearly under-ventilated, the
measurements taken may not be truly representative of the actual burning
conditions occurring inside of the room.
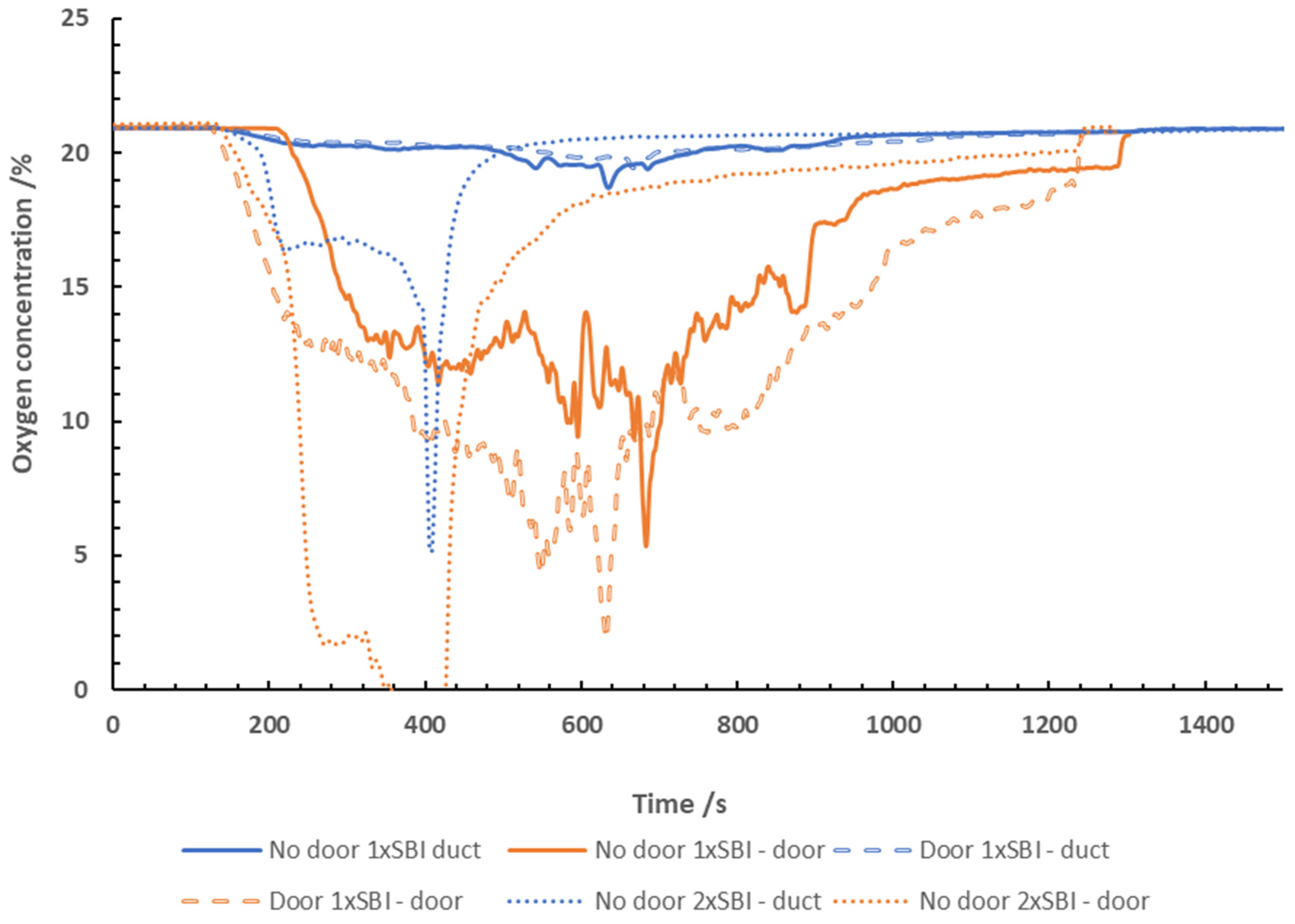
Oxygen Measurements
The oxygen measured in the door and exhaust duct
throughout the tests is shown in
Figure 4.
After ignition, the oxygen levels in the door began
to decline rapidly before settling between 12 to 13 % for around 200 seconds
when testing 1x SBI with no door. As the fire progressed, a significant drop in
oxygen was observed, reaching 5.5 % in the door at 650 seconds. This
corresponded with the time at which the equivalence ratio and the heat release
was at its highest. The oxygen did not stay below 10 % for longer than 50
seconds. For the duration of the test, the oxygen predominantly settled between
10 to 15 %, indicating the fire was well-ventilated. The oxygen concentration
measured in the exhaust duct did not significantly change from its baseline
value. This was likely due to the excess dilution occurring from the large flow
rate used in the extraction hood causing significant dilution to the
measurements taken.
When testing 1x SBI with a door, the oxygen
concentrations measured in the door dropped rapidly upon ignition, gradually
lowering to 2.5 % at 620 seconds. The oxygen concentrations remained below 15 %
throughout the middle of the test. In the duct, the oxygen concentration did
not deviate significantly from baseline values.
After ignition of the 2x SBI (no door) test, the
oxygen levels in the door begin to decline rapidly. The oxygen in the exhaust
duct dropped to 16.5 % approximately 200 seconds into the test, with the door
measurements dropping to 2 % comparatively. At 350 seconds into the test, the
oxygen measurements in the doorway dropped to 0 %, and remaining that low for
200 seconds. The sampling at this point was occurring within the flame zone as
the flames from the fire were seen to be exiting the doorway during this time.
The oxygen concentrations in the exhaust duct fell to 5 % at approximately 400
seconds into the test. The concentration was higher than that measured in the
door from a combination of the excess air flow being drawn into the exhaust
duct, as well as the sampling not occurring within the flame zone. The concentrations
measured in the exhaust duct and the doorway were representative of
under-ventilated flaming. After 400 seconds, the fire began to run out of fuel,
resulting in less flaming combustion occurring. This allowed more oxygen to
enter the room and the oxygen concentrations were observed to rise gradually
until baseline values were reached.
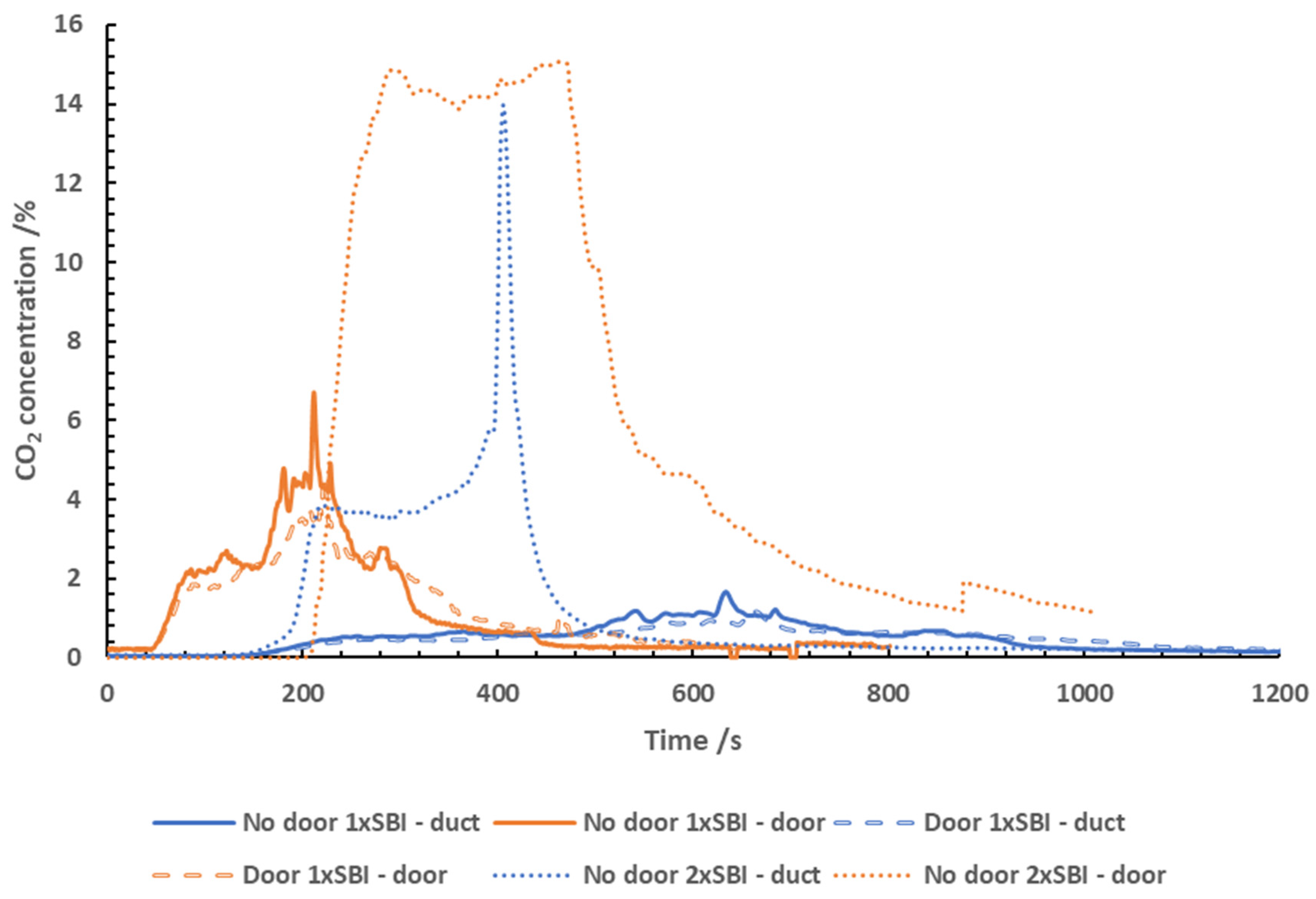
CO2 Measurements
The CO
2 concentrations logged in the
exhaust duct throughout the test is shown in
Figure 5.
When testing 1x SBI, the measurement of CO2 in
the doorway were not logged for this test due to an error in the test
equipment, and so the CO2 concentration in the doorway was
calculated by multiplying the duct measurement by 4 (the approximate dilution
factor). The CO2 increased after ignition occurred, rising to a
predicted peak concentration of 7 % in the doorway, and a peak concentration of
1.7 % in the exhaust duct. The peak concentrations were reached approximately
650 seconds into the test. The dilution resulted in concentrations in the
doorway being approximately 2.5 times more concentrated than those measured in
the exhaust duct. The CO2 concentrations reached in the doorway are
representative of well-ventilated flaming.
The concentration measured became relatively stable
from 400 seconds to around 700 seconds. The decline in CO2 at 700
seconds occurs rapidly, and concentrations decline to baseline values. This was
the point at which the fire began to slow down due to a lack of fuel.
When testing 1x SBI, due to a measurement issue in
the doorway, the CO2 concentrations were not logged. The doorway
measurement was calculated using the exhaust duct data multiplied by the
dilution factor (4). The CO2 measured in the exhaust duct remained
relatively low, reaching its peak concentration of 1.2 % at approximately 620
seconds into the test. Overall, the CO2 measured was relatively
stable and steady. The CO2 measured in the door reached a calculated
peak concentration of 4.45 % 620 seconds into the test.
When testing 2x SBI with no door, the CO2
concentrations measured in the exhaust rose rapidly upon ignition, reaching a
concentration of 5.8 % in the exhaust duct at 200 seconds. The concentration
plateaued, until another sharp rise in concentration was observed at 400
seconds, reaching 14 %. Similarly, the CO2 in the doorway rose
rapidly upon ignition, reaching a concentration of 14.8 % and plateauing for
approximately 40 seconds before rising again, recording a peak concentration of
16.8%. This is towards the upper limit of the measurable range of the NDIR used
in the analysis system. However, it is also indicative of more CO2
being formed after it passed the doorway.
The CO2 concentration declined rapidly
after reaching the peak concentration as a result of the fire running out of
fuel. The CO2 concentrations measured in the door were indicative of
under-ventilated flaming occurring. The point at which the CO2
concentrations were at their highest coincides with the point at which the
equivalence ratio was at its highest, and the oxygen concentration was at its
lowest.
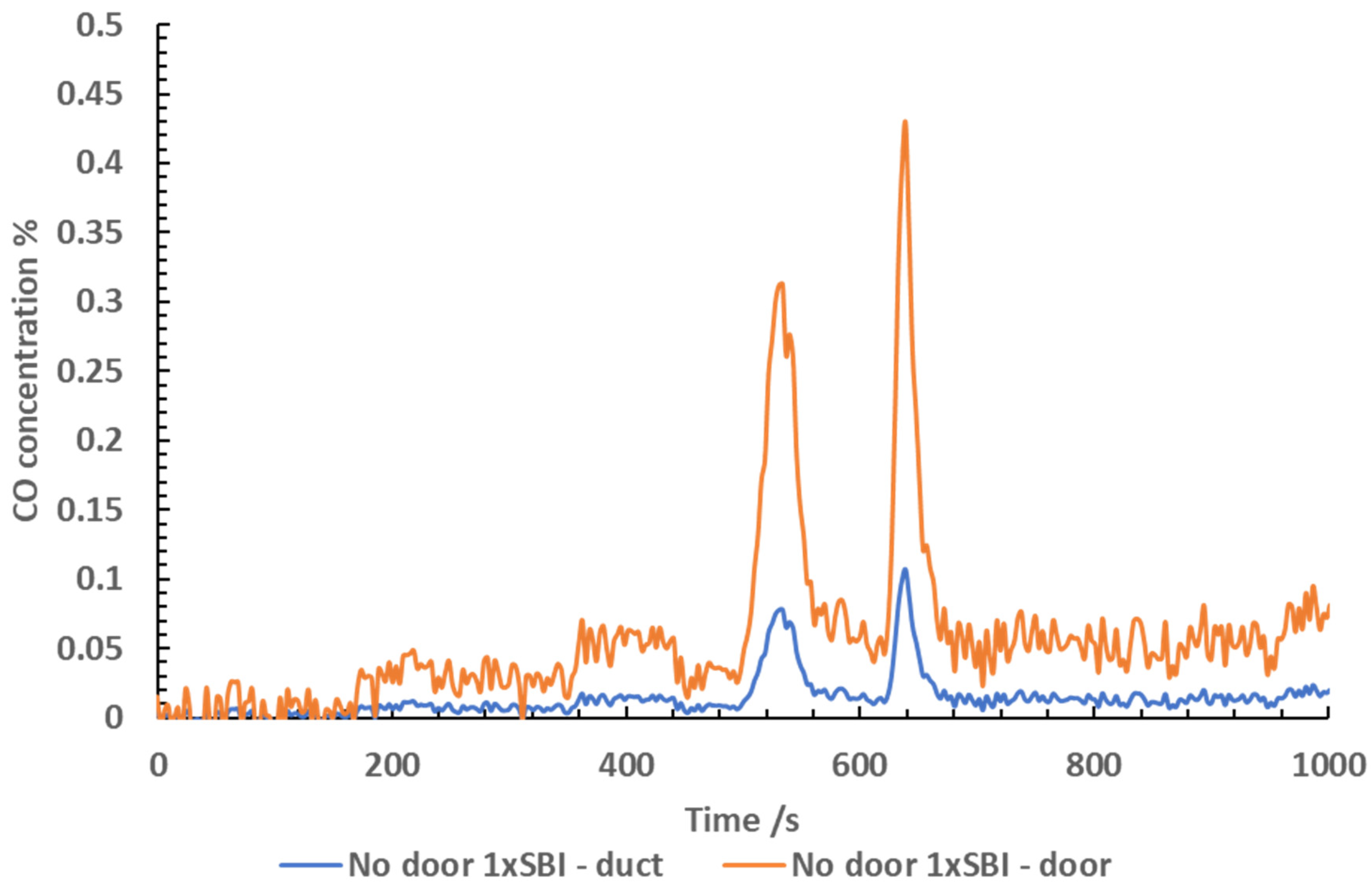
CO Measurements
The CO concentrations measured throughout the test
are shown in
Figure 6. Due to a
measurement issue, the CO was not logged in the doorway during the test conducted
using 1x SBI with no door. The CO measurement of the doorway was calculated
using the exhaust duct values multiplied by 4 (the approximate dilution
factor). Overall, the CO measured in the exhaust duct was substantially lower
than that measured in the door. The CO concentrations remained low for the
first 500 seconds of the test. The CO concentration in both the doorway (calculated)
and exhaust duct peaked at 580 seconds, and again at 680 seconds. In the first
initial peak, the CO concentrations reached 0.1 % in the exhaust duct, and 0.4
% in the doorway (calculated). In the second peak that occurred at 580 seconds,
the CO reached 0.12 % in the exhaust duct, and 0.48 % in the doorway.
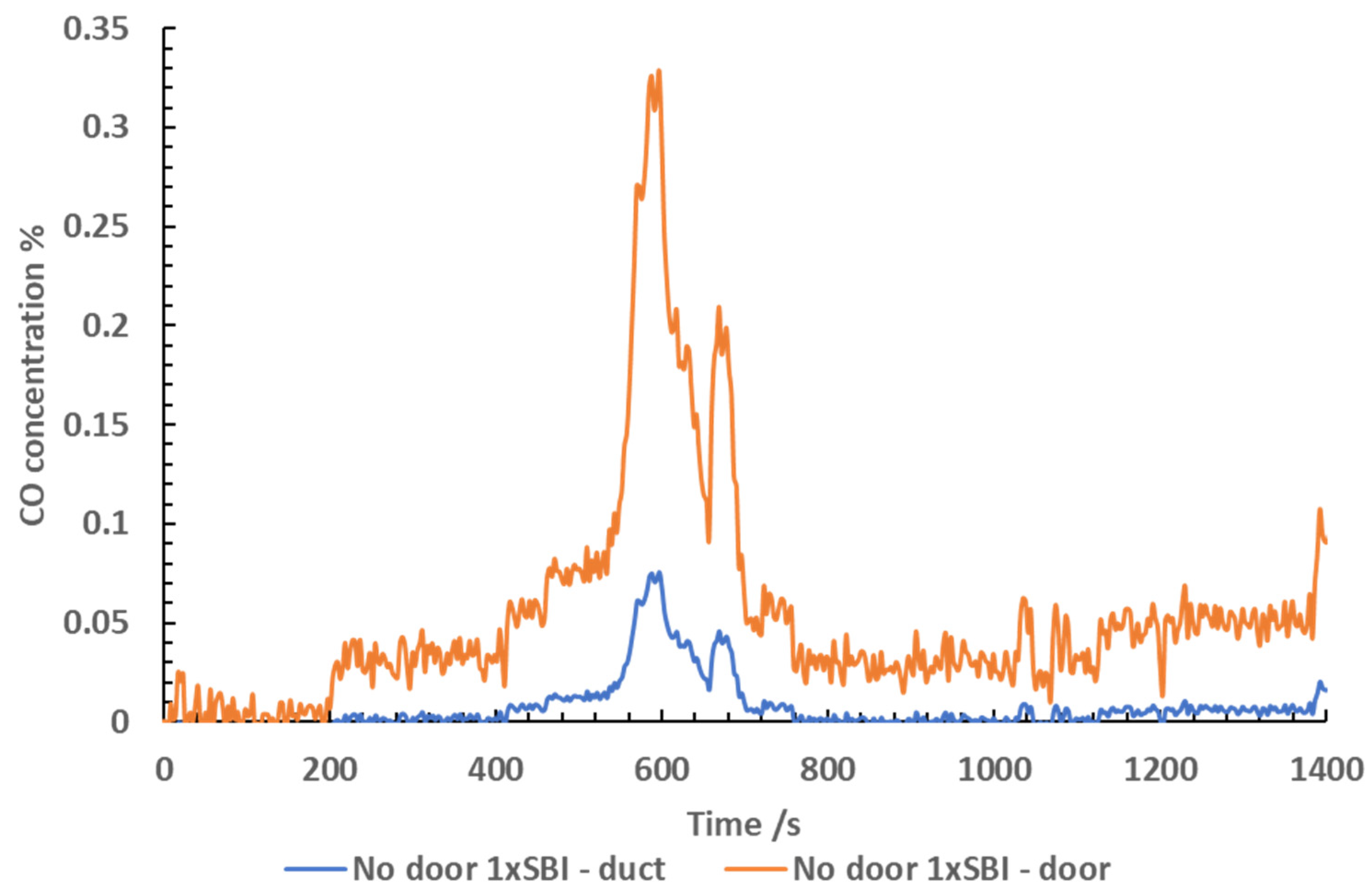
The CO measurements taken when testing 1x SBI with
a door in the door and exhaust duct are shown in
Figure 7. Due to a measurement issue in the
doorway, the concentrations of CO were not logged. The CO presented is a
calculated value using the exhaust duct data multiplied by the dilution factor
of 4. The CO in the exhaust duct was similar to the concentrations measured in
the door. The door measured slightly higher concentrations of CO, with a peak
concentration of 0.09 % at 600 seconds into the test, shortly after ignition.
At this point it was calculated that the concentration in the doorway was 0.34
%. A peak concentration of 0.075% was reached in the exhaust duct at 700
seconds into the test, and 0.3 % in the doorway.
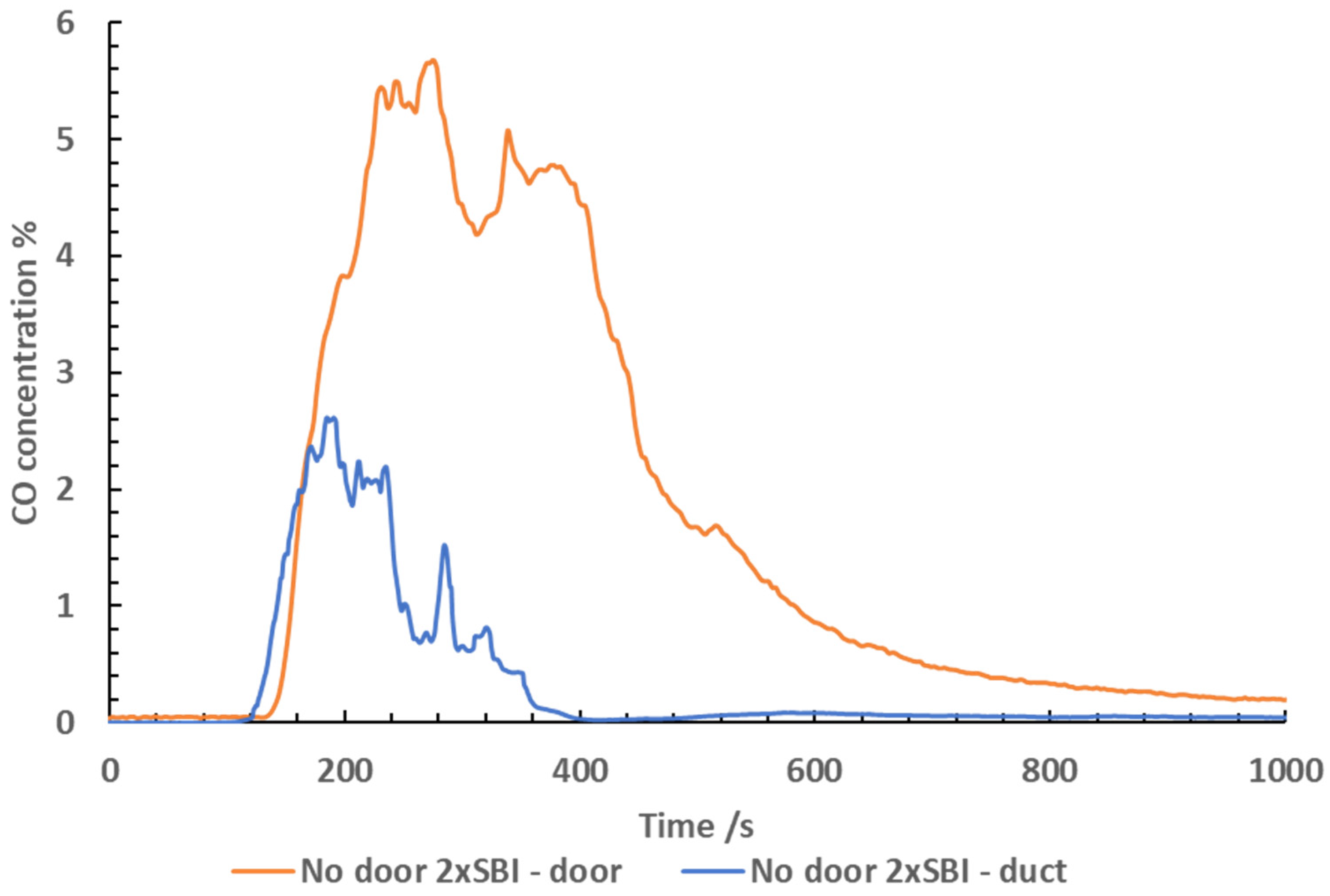
The CO concentrations logged when testing 2x SBI no
door are shown in
Figure 8. The CO concentrations
measured rose rapidly upon ignition, reaching a concentration of 5.8 % in the doorway
at 200 seconds. Similarly, the CO in the duct rose rapidly upon ignition,
reaching a concentration of 2.6 %.
The CO concentration declined rapidly
after reaching the peak concentration as a result of the fire running out of
fuel. The CO concentrations calculated for the door were indicative of
under-ventilated flaming occurring. The point at which the CO concentrations
were at their highest coincides with the point at which the equivalence ratio
was at its highest, and the oxygen concentration was at its lowest.
Summary
The data obtained from the three tests has been
summarised in
Table 2.
During both tests conducted using 1x SBI, the fire effluent slowly rose to the ceiling and a smoke layer developed in the test room. As the fire progressed, the effluent became diluted with plenty of fresh air entering the room and mixed with the fire effluent. As the test continued, the hot smoke layer grew and was observed to leave the room in a plume 40 to 70 cm down from the ceiling. When no door was used, the fuel loading in the test was limited and so the fire did not transition to under-ventilated flaming. Using the door to restrict the ventilation resulted in the door absorbing some of the heat from the fire. Combined with the low fuel loading, the test did not reach under-ventilated flaming. Therefore the use of a door (1/3 of the opening restricted) to restrict ventilation is not sufficient to force a fire to transition to under-ventilated flaming. As the smoke was extracted from the room, the fire could continue growing until all the available fuel ran out due to the availability of oxygen from the open and partially open doorway. The smoke produced was relatively clean with only small amounts of sooty smoke being observed. For both tests, the oxygen, CO and CO2 data were all representative of well-ventilated flaming conditions, which were in agreement with the equivalence ratio measurements taken throughout the test.
When using 2x SBI (doubling the fuel loading), the fire started off well-ventilated. As the fire continued to grow, the upper smoke layer grew and descended in the room. As the fire progressed, the smoke layer started to pour out of the doorway. As the equivalence ratio surpasses 1, the fire visibly transitioned to under-ventilated flaming where the flames were seen to reach the room's ceiling. The concentration of air entering the fire began to decrease. This continued as the equivalence ratio increased.
During the test, the flames descended below the smoke layer. This is typical in fires where the size of the room is the limiting factor. At this point, the smoke layer began to descend until it reached a steady burning period. During this point, oxygen concentrations in the door dropped below 1%, reaching 0% at their lowest. At this point of the test, the flames were pouring out of the door, passing over the stainless steel sampling lines. The measurements were taken in the flame zone, so it is likely that the effluent sampled underwent further chemistry later in the exhaust duct.
The peak equivalence ratio reached was 1.5. The peak aligns with the point at which CO concentrations measured at the door are at their highest, and where the oxygen concentration in the door dropped to its lowest.
Conclusions
Conducting three different test scenarios on the same material has allowed for the identification of test conditions to be made in regards to controlling the ventilation of the test. In large-scale testing, particularly when using the ISO room, fuel loading and test geometry has more significant impact on the fire condition than restricting the ventilation. While imposing restrictions on the test rooms ventilation did increase the equivalence ratio, it was not sufficient enough to force the transition into under-ventilated flaming. Using three different test configurations allowed for different experimental set-ups to be assessed to identify what is needed to achieve specific burning conditions in the ISO room corner test. The use of 1x SBI rig with no door meant that the fire had enough ventilation and fuel to burn well-ventilated. This was evidenced by the equivalence ratio of 0.7. The heat release from the test was relatively high, with a peak heat release of 990 kW being measured. The CO yield obtained were representative of well-ventilated flaming. The measurements taken in the exhaust duct were very dilute. This was the case for most of the gas measurements taken in the duct when compared to the door measurements.
Comparatively, the addition of a door to the test room did not force the fire to transition to under-ventilated flaming. Despite the restriction on the ventilation, the maximum equivalence ratio reached was only 0.95.
When using 2x SBI rigs with no door, there was sufficient fuel for the fire to transition to under-ventilated flaming. The equivalence ratio was measured to be 1.5 at its peak, which is representative of under-ventilated conditions. However, the sampling did take place inside of the flame as the fire became so vigorous that the flames poured out of the test room for a significant portion of the test. This means that the equivalence ratio was 1.5 within the flame zone, and is less indicative of the actual fire condition in the room.
This research has provided the experimental methodologies to assess smoke toxicity at a range of ventilation conditions in an ISO 9705 test room. The equivalence ratios obtained were representative of well-ventilated and under-ventilated flaming and the transition point between the ventilation conditions (ϕ = 0.95).
Acknowledgments
The author (GP) would like to thank Rockwool, Denmark, for use of their test facilities and supplying the materials for testing. The author (GP) would also like to thank FSEU for providing funding for this research, and Richard Hull for obtaining funding for this project. This work has was completed as part of the authors (GP) doctoral thesis.
References
- Caffarello. F. M., Mascia. N. T., Et al. Structural analysis of timber gridshell covered by OSB panels considering the effect of wind (2022), Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture (16), pp. 277-293. [CrossRef]
- Ferro. F. S., Silva. D. A., Lahr. F. A. Et al. Environmental aspects of oriented strand boards production. A Brazilian case study (2018), Journal of Cleaner Production (183), pp. 710-719. [CrossRef]
- Ding. Y., Pang. Z., Lan. K., Et al. Emerging engineered wood for building applications (2023), Chemical Reviews (123) 5, pp. 1843-1888. [CrossRef]
- Peck. G. Bench and Large-scale assessment of smoke toxicity (2023), University of Central Lancashire, Doctoral Thesis.
- ISO 9705-1:2016 Reaction to fire tests: Room corner test for wall and ceiling lining products- Part 1: Test method for a small room configuration.
- Wade. C., Baker. G. 5- Fire hazard assessment of wall and ceiling fire spread in rooms (2022), Flammability Testing of Materials Used in Construction, Transport and Mining (second edition), Woodhead Publishing series in civil and structural engineering, pp. 127-156. [CrossRef]
- Peck. G., Hull. T. R. Design, construction and validation of a simple, low-cost phi meter (2023) Fire Safety Journal (14), pp. 141-144). [CrossRef]
- Smolka. J., Kempna. K. Et al. Setup of 3D printed wind tunnel: Application for calibrating bi-directional velocity probes used in fire engineering applications (2023), HardwareX (15). [CrossRef]
- Schneider. M. E., Kent. L. A. The design and application of bi-directional velocity probes for measurements in large-scale pool fires (1987) Instrument Society of America (26) 4, pp. 2-9.
- Nadjai. A., Naveed. A., Charlier. M., Et al. Large scale fire test: The development of a travelling fire in open ventilation conditions and its influence on the surrounding steel structure (2022), Fire Safety Journal (130). [CrossRef]
- EN/ISO 13823:2020 Reaction to fire tests for building products - Building products excluding floorings exposed to the thermal attack by a single burning item.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).