1. Introduction
China has 98% of the worldwide jujube resources that are widely distributed in Heilongjiang, Jilin, Tibet, and Xinjiang [
1]. Because of its rich nutritional and high economic value, jujube is the main economic crop planted in China. The development of jujube leaves is affected when the water supply is insufficient in the early stages of development [
2]. Water and fertilizer integration is an agricultural technology combining irrigation and fertilization in which the fertilizer and water mixture is applied to the rhizosphere soil layer [
3]. Compared with traditional agricultural irrigation technology, water and fertilizer integration technology can accurately control the amount of irrigation and fertilization and improve the utilization rate of water and fertilizer [
4]. Water and fertilizer integration technology is quick, efficient, accurate, controllable, labor-saving, and non-destructive, and water and fertilizer are supplied simultaneously [
5] while also increasing production [
6].
Owing to the large demand for water and fertilizer in the production process of fruit trees, traditional agricultural irrigation methods can easily cause excessive water and fertilizer use, leading to a low utilization rate of water and fertilizer and causing environmental pollution [
7]. The integration of water and fertilizer can effectively improve the current situation of insufficient water and fertilizer use and improve fruit tree growth and soil fertility [
8]. An experimental study on integrating water and fertilizer in Red Fuji apples found that this method can effectively improve fruit hardness, soluble solids, and single-fruit weight [
9]. Furthermore, compared with the control, the number of green leaves, leaf length, and plant height of pineapples cultivated using integrated water and fertilizer increased by 12.90%, 12.10%, and 8.77%, respectively. Soluble sugar and vitamin C in the fruit were significantly improved compared to those in the control [
10]. Furthermore, integrated water and fertilizer management with no-tillage and grass planting improved avocado growth and the soil microenvironment of orchards, increased soil organic matter content, loosened the soil, and reduced soil moisture loss during high-temperature seasons [
11].
However, few studies have been conducted on the effects of water and fertilizer integration on the growth and fruit quality of fruit-bearing jujube trees in orchards. Therefore, this study aimed to elucidate the effects of different amounts of water and fertilizer on the quality of jujube fruits to determine the optimal amount of water and fertilizer to ensure quality and reduce costs and to provide theoretical support for studying water and fertilizer integration for jujube trees.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Site Characteristics
The experiment was conducted at the sixth new company of the ninth regiment of Alar City, the first division of the Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps. The experimental area belongs to the Tarim Basin, and receives sufficient sunshine, an annual rainfall of 40–82 mm, and an evaporation of 1876–2558 mm. Seven-year-old jujube trees (gray jujube variety, sour jujube rootstock) were used. The plant row spacing was 1 × 6 m, the size of the test site was 0.2 hm
2, and the soil type was sandy loam.
Table 1 lists the basic physical and chemical properties of soil samples from the experimental area.
2.2. Test Schemes
This experiment was conducted between 2021 and 2022. Experiments 1 and 2 were three-factor randomized block experiments using water (W), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) as influencing factors, and each factor was set at five levels. A total of 15 treatments were tested and each treatment was repeated three times for a total of 45 plots; experiment 2 consisted of eight treatments and each treatment was repeated three times for a total of 24 plots. There were five trees in each plot, and the area of each tree was 6 m
2. The amounts of N and P were expressed as the amount of pure nutrient. The first levels of N, P, and W were 300.0 kg·hm
-2, 270.0 kg·hm
-2, and 4400.0 m
3·hm
-2; the second levels were 397.5 kg·hm
-2, 352.5 kg·hm
-2, and 5600.0 m
3·hm
-2; the third levels were 495.0 kg·hm
-2, 435.0 kg·hm
-2, and 6800.0 m
3·hm
-2; the fourth levels were 592.5 kg·hm
-2, 517.5 kg·hm
-2, and 8000.0 m
3·hm
-2; and the fifth levels were 690.0 kg·hm
-2, 600.0 kg·hm
-2, and 9200.0 m
3·hm
-2, respectively. The treatment number and the amount of nitrogen, phosphorus, and water in each treatment are shown in
Table 2.
The fertilizer types were urea (N: 46%), diammonium phosphate (N-P2O5: 18-46-0), and potassium sulfate (K2O: 50%). The fertilizer was dissolved in a fertilization tank and dripped into the soil using water pressure to control the amount of irrigation in each plot.
The trees were fertilized five times throughout the growth period. A germination fertilizer was applied in early April and during the late-May flowering period. A strong fruit fertilizer was applied from the end of June to the beginning of July and applied once during the fruit expansion period in mid-late July. The last fertilization was applied in early and middle August. The trees were irrigated eight times throughout the growing period. The first irrigation was in the middle of April for germination. The trees were then watered once at the beginning and in late May during flowering. The trees were watered once in mid-June during the flowering period, and once in early July during the fruit-promoting period. Trees were watered once during fruit expansion in mid-July, once in late July at the white ripe stage, and, lastly, watered once in early August.
2.3. Test Indicators and Methods
Fruits with no pests or diseases and of similar sizes were randomly collected from each tree at the fruit maturity stage 2 m above the ground to determine soluble sugar, reducing vitamin C (Vc), titratable acid, and other indicators.
Soluble sugar was measured using anthrone colorimetry, and the molybdenum blue colorimetric method was used to determine the Vc content. The titratable acid content was determined using standard sodium hydroxide titration [
12]. The sugar-to-acid ratio was calculated as the soluble sugar-to-titratable acid ratio. The yield was calculated by dividing the location of each plot, and the jujube fruit in each plot area was weighed.
2.4. Data Analysis
Excel and SPSS 26.0 were used to process the data and analyze the conclusions. The soluble sugar (X1), titratable acid (X2), Vc (X3), sugar-to-acid ratio (X4), and yield (X5) of jujube fruit were used as the evaluation indices. The eigenvectors and eigenvalues of each index were obtained using principal component analysis using the SPSS 26.0 data processing system.
3. Results
3.1. Different Water and Fertilizer Treatments Improve Fruit Quality and Yield
By analyzing and comparing the fruit quality and yield of ‘Huizao’ in 2021 and 2022, there were no significant differences in the vitamin C content and sugar–acid ratio while there were significant differences in the soluble sugar content, titratable acid content, and yield in the fruits of each treatment in 2021 (
Table 3). In 2022, there were significant differences in the vitamin C content and sugar–acid ratio in the fruits, but the difference in yield changed from significant to insignificant.
The treatment with the highest soluble sugar content in the first year of fruiting was N1P1W1 (197.56 g·kg-1), which was 48.4 % higher than that of the lowest treatment N3P1W1. The treatment with the highest titratable acid content was N3P1W1 (2.00 g·kg-1), which was 60.0 % higher than that of the lowest treatment N3P3W1. The treatment with the highest yield was N4P3W1 (8060 kg·hm-2), which was 200.0 % higher than that of the lowest treatment N3P1W1.
The treatment with the highest vitamin C content in the second year was N4P3W2 (3.75 g·kg-1), which was 29.0 % higher than that of the lowest treatment N3P3W2. The treatment with the highest soluble sugar content was N4P3W3 (210.17 g·kg-1), which was 44.1 % higher than that of the lowest treatment N3P3W2. The treatment with the highest titratable acid content was N3P4W3 (1.83 g·kg-1), which was 100.0 % higher than that of the lowest treatment N4P3W2. The treatment with the highest sugar–acid ratio was N4P3W2 (224.42); compared with the lowest treatment N3P3W2, it increased by 167.7 %.
The results showed that increasing the amount of N, P, and W could increase the soluble sugar content and yield while reducing the titratable acid content, but excessive N, P, and W would reduce the soluble sugar content and yield while increasing the titratable acid content. Via the interactions of N, P, and W, the quality, content, and yield of fruits can be further improved.
3.2. Principal Component Analysis Based on Yield and Fruit Quality
The results of the principal component analysis are shown in
Table 4 and
Table 5. The cumulative contribution rate of the first two principal component variances was 82.4160% (because the eigenvalues of the first two principal components were >1, the principal components F3–F5 include 17.5840% of the original data variation, and the principal component eigenvalues were <1; therefore, the data are not listed in
Table 5), which contains most of the variation information in the original data. Therefore, the first two principal components were selected to evaluate the effects of irrigation and fertilization on the yield and fruit quality of the main fruit type. The variance contribution rate of the principal component F1 was 62.345 %, and the load on the yield index was large. The principal component F1 could be defined as the yield factor. The variance contribution rate of the principal component F2 was 20.071 %, and the load on the quality index was large. The principal component F2 could be defined as the quality factor. According to
Table 4, the equations can be established as follows:
3.3. Comprehensive Evaluation Based on Fruit Yield and Quality
The corresponding positions of leaf nutrients, yield, and fruit quality of jujube under different water and fertilizer treatments can be obtained using the factor scores of each principal component in
Table 4 and
Table 5 to select the combination of water and fertilizer with a positive effect on the growth and development of jujube trees and fruit quality.
Table 6 shows that the nutrient and quality factor scores of jujubes under the different treatments varied. The order of comprehensive evaluation of the principal component analysis of each treatment was N4P3W2>N4P3W3>N4P4W3>N4P4W2>N3P3W3>N3P4W3>N3P4W2>N3P3W2.
3.4. The Establishment of the Yield and Economic Models
3.4.1. Establishment of the Yield Model
The regression model of yield with N, P, and W dosages was obtained using ternary quadratic regression fitting between yield and N, P, and W dosages in each experimental treatment. The significance test of Equation (4):
found that R
2=0.849, indicating that the degree of fit between the predicted and true values was good. The primary item coefficients were -27.6450, -10.7630, and 2.8700, respectively, indicating that the influence of each factor on yield was W>P>N. The interaction coefficients were 0.1160, -0.0020, and 0.0040, respectively, indicating that the interaction between each factor and yield was N*P>P*W>N*W.
To explore the influence of coupling various factors on the yield, the factors in Equation 4 were set at the lowest level and the following equations were obtained:
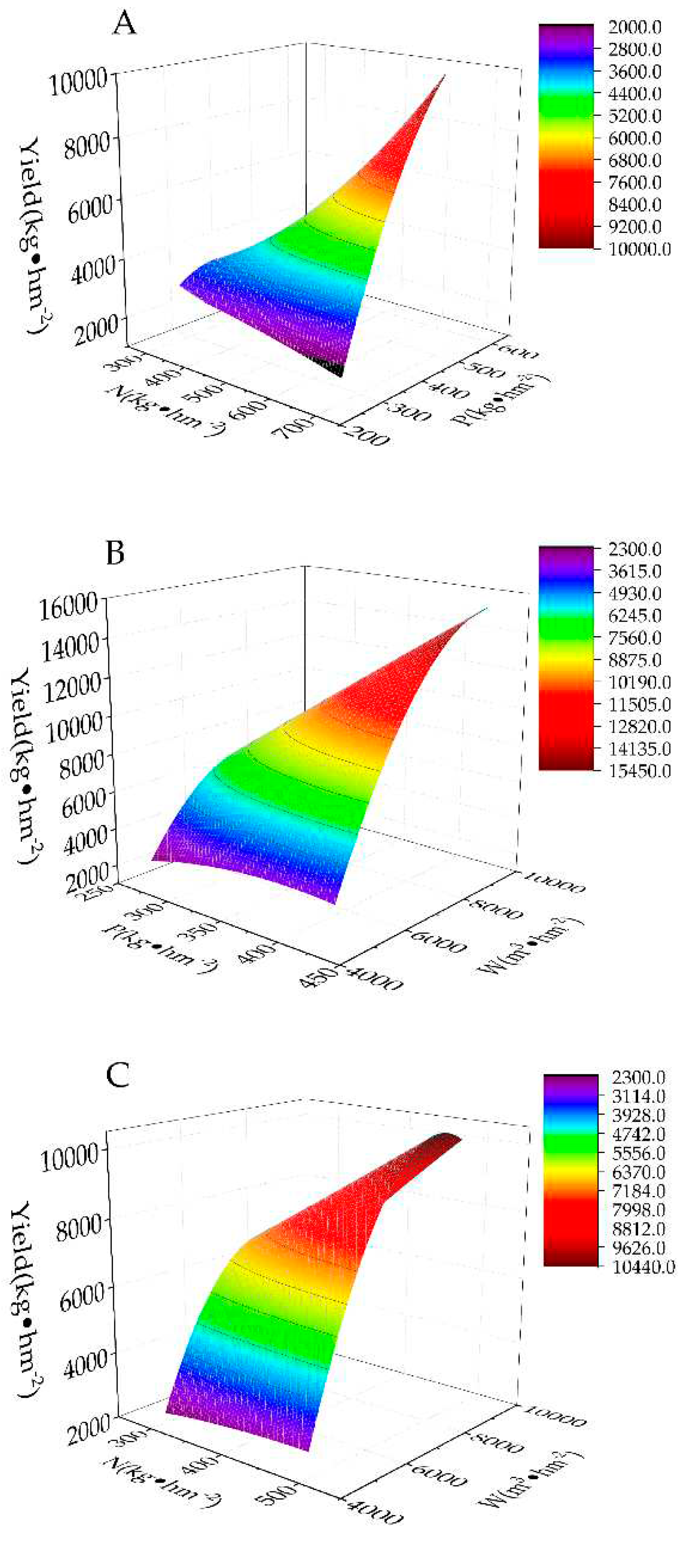
The response surface of yield to nitrogen and phosphorus interaction was a non-linear surface with a downward opening. When the nitrogen fertilizer was at the third level (495.0 kg·hm
-2) and the phosphorus fertilizer was at the fourth level (517.5 kg·hm
-2), the yield reached a maximum. At this time, the yield decreased with an increase in nitrogen fertilizer (
Figure 1A). The response surface of the interaction effect of water and phosphorus on yield was a non-linear surface with a downward opening. When the irrigation amount reached the highest level (9200 m
3·hm
-2), the yield reached a maximum value. At this time, the amount of phosphate fertilizer was low, and a continued increase in the amount of phosphate fertilizer led to a decrease in yield (
Figure 1B). The response surface of yield to water and nitrogen interaction was a non-linear surface with a downward opening. When the nitrogen fertilizer was at the third level (495.0 kg·hm
-2), an increase in the irrigation amount increased the yield. When the irrigation amount was 9200 m
3·hm
-2, the yield reached a maximum (
Figure 1C).
3.4.2. Establishment of the Economic Model
The economic benefit of each treatment was calculated using the yield, W, fertilizer, and labor costs obtained in the experiment. The regression models of economic benefit (Eb), N (C
N), P (C
P), and W (C
W) were obtained using ternary quadratic regression fitting of the economic benefits and N, P, and W costs:
A significance test of Equation (8) found that R
2=0.975, indicating that the degree of fit between the predicted and true values was good. The following three equations can be obtained from the partial differential derivation of Equation (8):
Let dEb/dCN=0, dEb/dCP=0, and dEb/dCW=0; the optimal solution of Equation 8 is CN=247.15, CP=889.26, and CW=7278.19. According to the relationship between the amounts of N and P and the pure nutrients of N and P, it can be concluded that the amounts of N (pure nutrients), P (pure nutrients), and water under the optimal solution are 275.56 kg·hm-2, 413.66 kg·hm-2, and 7278.19 m3·hm-2, respectively. Bringing these values into Equation 4, it is concluded that the theoretical yield under this condition is 8622.00 kg·hm-2.
4. Discussion
Nitrogen plays different roles throughout the crop growing period. During fruit growth, N affects the sugar content in the fruit by affecting the acid invertase, neutral invertase, sucrose synthase-cleavage, sucrose synthase-synthesis, and sucrose phosphate synthase content. Nitrogen also affects malic acid, citric acid, and pyruvate production in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, and gluconeogenesis cycles to change the total acid content. Simultaneously, the sucrose content in fruit decreased under high-temperature stress (28–35 °C) in another study; however, an increase in the N application rate offset the negative effect of high-temperature stress, and this phenomenon reduced hexose metabolism and led to hexose accumulation by inhibiting hexose kinase activity [
13]. Our study found that, with an increase in N fertilizer, the content of soluble sugar in fruit increased, whereas an excessive increase in P fertilizer reduced the content of soluble sugar in fruit, similar to the conclusion of Zhou et al. [
14]. Similarly, an increase in N fertilizer directly affected the total soluble solids (TSS) content in grape juice [
15]. The utilization rate of N fertilizer in apple trees decreased under the influence of distribution merchandising price promotion (DMPP); however, the soluble sugar content in the fruit increased with an increase in the amount of N fertilizer within a certain range [
16].
Furthermore, our study showed a significant difference in the titratable acid content of fruits in each treatment. The amount of N fertilizer was negatively correlated with the titratable acid content of the fruit. Increasing the amount of N fertilizer within a certain range reduced the titratable acid content in the fruit, similar to the findings of other studies [
17,
18,
19]. In contrast, the amount of P fertilizer was positively correlated with the titratable acid content of the fruit, similar to the results of other studies [
20]. In another study, the titratable acid content in red-fleshed navel orange pulp decreased significantly when the amount of P fertilizer was increased compared to the treatment without phosphate fertilizer; however, the decrease in titratable acid content decreased gradually with an increase in P fertilizer [
21]. The change in the irrigation amount had little effect on the titratable acid content of the fruit.
In this study, increasing the amount of N fertilizer significantly increased the Vc content in jujube fruit, and the effect of increasing the irrigation amount on the Vc content was less than that of N fertilizer change on Vc content. When the P fertilizer was increased, the Vc content in the fruit decreased significantly, similar to the conclusions of previous studies [
22,
23]. The Vc content of pepper fruit is typically used as an indicator for evaluating fruit quality. Appropriate N fertilizer application increased the activity of dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR) in green-ripe fruit and monodehydroascorbate reductase (MDHAR) in red-ripe fruit [
24]. DHAR generally maintains the AsA (the main biologically active form of Vc) pool and its redox state. DHA-to-AsA recycling in the green and MDHA-to-AsA recycling in the red ripe period increases with increasing N fertilizer application. Therefore, increasing the amount of N fertilizer or reducing the amount of P fertilizer can increase the Vc content in different fruits [
20,
25,
26,
27,
28].
Changes in W and fertilizer application rates significantly affected jujube fruit yield. When the amount of N fertilizer and irrigation increased, the jujube fruit yield increased significantly; however, the effect of the N fertilizer application rate on yield was greater than that of the irrigation amount, similar to the results of previous research [
29]. In another study, an increase in N and P fertilizer significantly increased maize yield. This yield increase was attributed to increased yield components, such as grain number per spike, grain weight per spike, and 1000-grain weight [
30]. Another study on rice found that the yield was also significantly increased when the amount of N fertilizer, N content in rice grains, and straw were increased [
31]. The irrigation mode is also a factor affecting yield. Under low N and potassium conditions, the drip irrigation mode significantly increased the yield compared to that of the non-drip irrigation mode; however, when the N and potassium fertilizers were increased, the effect of the irrigation mode change on yield was weakened [
32].
5. Conclusions
The increase in N fertilizer affected the nutritional quality of fruits, effectively increasing the content of soluble sugar, Vc, and the sugar–acid ratio in fruits and reducing the content of titratable acid, thus increasing the flavor and taste. Phosphorus fertilizer can also increase the content of soluble sugars and Vc in the fruit but is less effective than increasing the amount of N fertilizer. Simultaneously, an increase in P fertilizer also leads to an increase in the titratable acid content in the fruit and affects the taste of jujube fruit. An increase in irrigation slightly increased the soluble sugar and Vc content but significantly increased the titratable acid content in the fruit, which reduced its flavor and taste.
The comprehensive score of the N4P3W2 treatment was the highest, and that of the N3P3W2 treatment was the lowest. Therefore, coupling W, N, and P under water and fertilizer integration effectively improves the fruit quality of trunk fruit-shaped gray jujubes. The fruit quality and yield improvement effect of the N4P3W2 treatment was the most significant.
When the N, P, and W dosages are 275.56 kg·hm-2, 413.66 kg·hm-2, and 7278.19 m3·hm-2, respectively, the theoretical economic benefit is the best, and the theoretical yield is 8622.00 kg·hm-2. In conclusion, the N4P3W2 treatment was the best.
Author Contributions
X.Z. completed the experimental work and model analysis, drafted the manuscript, and designed the experiment. J.Z. supervised the study and reviewed the manuscript. X.B. and J.W. presented and discussed the study. S.A. conducted the investigation. Q.Z. and Z.T. participated in the mechanism discussion and provided language editing. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Bintuan Science and Technology Program (2021AA005) and the President’s Fund Innovation Team Project of Tarim University (TDZKCX202301).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
References
- Wan, S.; Liu, W.F.; Yu, T.; Sun, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, F.M.; Yang, Z.P.; Wang, L.N.; Wang, S.J.; et al. Multivariate analysis and optimization of soil nutrients and fruit quality of Huizao in Xinjiang. Econ. Forest Res. 2021, 39, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Q.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Hu, J.S.; He, X.L.; Li, C.Y. Effects of water and fertilizer coupling on photosynthetic characteristics and yield of drip-irrigated jujube in sandy area of southern Xinjiang. Northwest. Agric. J. 2018, 27, 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Fan, J.H.; Cheng, N.N.; Lin, D. Effects of integrated water and fertilizer reduction fertilization on yield, quality and fertilizer consumption of mango. China Soil Fert. 2019, 2, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Shen, M.X.; Jiang, X.P.; Jiang, K.S.; Feng, Q. Structure optimization and performance test of fertilizer absorber for water and fertilizer integrated irrigation and fertilization machine. J. Agric. Mach. 2015, 4, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.P. The characteristics and application of simple water and fertilizer integration technology in orchard. Jiangxi Agric. 2020, 41, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.C.; Lu, X.P.; Pan, B.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, Z.M.; Tang, C.L.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.H.; Xie, S.X. Research progress on integrated water and fertilizer technology of fruit trees. Fruit Trees in Southern China 2018, 47, 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.Y.; Tang, S.; Wang, H. China’s organic fertilizer resources and industrial development status. China Soil Fert. 2020, 3, 210–219. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Song, Y.P.; Lv, G.L. Research progress and development trend of orchard water and fertilizer integration equipment at home and abroad. Chin. J. Agric. Mach. Chem. 2020, 41, 191–195. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.H. Study on the effect of boutique management technology of red Fuji apple in Penglai City. Deciduous Fruit Trees 2016, 48, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Li, J.H. Effects of water and fertilizer integration on the growth and quality of mountain cultivated pineapple. J. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 36, 102–106. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, X.P.; Jing, T.; Zhu, J.W.; Wang, J.S.; Ge, Y.; Lin, X.E.; Ma, W.H. Integrated technology and application of water and fertilizer under no-tillage and drip irrigation in avocado orchard in Hainan. China Trop. Agric. 2018, 5, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis. ed. 3 [M]; China Agriculture Press, 2000.
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Khattak, W.A. Transcriptome analysis of sugar and acid metabolism in young tomato fruits under high temperature and nitrogen fertilizer influence. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1197553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.M.; Zhang, F.C.; Kjelgren, R.; Wu, L.F.; Fan, J.L.; Xiang, Y.Z. Effects of water and fertilizer coupling on yield, fruit quality and water and fertilizer use efficiency of young apple tree. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon, W.S.; Gill, P.P.S.; Singh, N.P. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilization on growth, yield and quality of pomegranate ‘Kandhari’. Acta Hortic. 2011, 890, 45. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Ge, S.F.; Lyu, M.X.; Liu, J.Q.; Li, M.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.X.; Xing, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. DMPP reduces nitrogen fertilizer application rate, improves fruit quality, and reduces environmental cost of intensive apple production in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.G.; Zhang, R.H.; Xia, S.J.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, R.Q.; Fan, Z.H.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y. Interactions between N, P and K fertilizers affect the environment and the yield and quality of satsumas. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 19, e00663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spironello, A.; Quaggio, J.A.; Teixeira, L.A.J.; Furlani, P.R.; Sigrist, J.M.M. Pineapple yield and fruit quality effected by NPK fertilization in a tropical soil. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2004, 26, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.P.; Duan, M.; Yan, S.; Liu, Z.F.; Wang, Q.; Fu, J.; Tong, Y.A. Effects of different fertilizations on fruit quality, yield and soil fertility in field-grown kiwifruit orchard. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Hu, C.X.; Liu, H.W.; Wei, G.S.; Zhuang, M.L.; Li, X.S. Effects of reduced application of nitrogen and phosphorus on yield and quality of Guanxi pomelo for 5 consecutive years. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci. 2022, 28, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.W.; Li, M.; Zhang, C.M.; Tan, Q.L.; Yang, X.Z.; Sun, X.C.; Pan, Z.Y.; Deng, X.X.; Hu, C.X. Effects of phosphorus on fruit soluble sugar and citric acid accumulations in citrus. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.D.; Li, J.; Cheng, M.H.; Zhang, F.C.; Wang, X.K.; Fan, J.L.; Wu, L.F.; Fang, D.P.; Zou, H.Y.; Xiang, Y.Z. . Optimal drip fertigation management improves yield, quality, water and nitrogen use efficiency of greenhouse cucumber. Scientia Horticulturae 2019, 243, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Xu, F.S.; Chen, G.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.P.; Du, L.; Ding, G.D. Evaluation of the effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium applications on the growth, yield, and quality of lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Shen, Y.P.; Wang, X.Z.; Yang, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Lakshmanan, P.; P. ; et al. Physiological and metabolomic analysis reveals maturity stage-dependent nitrogen regulation of vitamin C content in pepper fruit. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1049785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.H.; Yang, N.; Wang, K.A. Effect of chemical fertilizer dose on yield, quality and nutrient utilization rate of sweet pepper in organic substrate. Acta Hortic. 2013, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Bai, Y.G.; Chai, Z.P.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, H.B.; Zheng, M.; Ding, P.; Jiang, Z. Effects of water and fertilizer synergy on grape berry growth, yield and quality. J. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 7, 041. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.B.; Tian, J.C.; Li, W.C.; Shen, H. Photosynthesis-yield-quality experiment and comprehensive evaluation of broccoli under drip irrigation based on water and fertilizer coupling. Soil Water Conserv. J. 2021, 35, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Aminifard, M.H.; Bayat, H. Influence of different rates of nitrogen fertilizer on growth, yield and fruit quality of sweet pepper (Capsicum annum L. var. California Wander). J. Hortic. Postharvest Res. 2018, 1, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, B.; Dawar, K.; Abbas, A. Growth and yield response of maize to nitrogen and phosphorus rates with varying irrigation timings. Environ. Pl. Syst 2015, 1, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhtar, T.; Arif, M.; Hussain, S.; Tariq, M.; Mehmood, K. Effect of different rates of nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers on growth and yield of maize. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 49, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Hu, F.; Zhu, D.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Effect of N fertilization pattern on rice yield, N use efficiency and fertilizer–N fate in the Yangtze River Basin, China. PLOS ONE 2016, 11, e0166002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaggio, J.A.; Souza, T.R.; Zambrosi, F.C.B.; Mattos, D.; Boaretto, R.M.; Silva, G. Citrus fruit yield response to nitrogen and potassium fertilization depends on nutrient-water management system. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 249, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).