1. Introduction
In the U.S., lymphoma has a significant impact on public health. It's estimated that 89,380 new cases will be diagnosed in 2023, ranking it among the top ten most frequently diagnosed cancers worldwide [
1]. Tragically, the 5-year mortality rate for lymphoma exceeds 25% [
1], and the disease is anticipated to claim over 21,080 lives within 2023 [
1], highlighting the urgent need for innovative treatments. Phase 1 clinical trials play a crucial role in this arena, representing the first phase of human testing for investigational agents and turning years of lab research into actionable clinical solutions [
2]. These trials form the foundation for later stages that emphasize efficacy and wider patient benefits. Their significance is clear: without these initial insights, the progression of novel treatments would be halted.
In this study, we aim to develop a binary predictive model to determine if trials will align with the average duration derived from our dataset sourced from clinicaltrials.gov. Recognizing this benchmark is pivotal for several reasons:
Resource and Strategic Planning: Predicting trial durations helps ensure optimal distribution of personnel and funds, minimizing inefficiencies. Furthermore, this foresight enables organizations to make informed decisions about trial prioritization, resource allocation, and initiation timelines [
3,
4].
Patient Involvement & Safety: Estimating trial durations provides patients with clarity on their commitment, which safeguards their well-being and promotes informed participation [
5].
Transparent Relations with Regulators: Providing predictions on trial durations, whether below or above the average, fosters open communication with regulatory authorities. This strengthens compliance, builds trust, and establishes transparent relationships among all stakeholders [
6].
2. Background
As lymphoma diagnoses increase, the precision in predicting Phase 1 lymphoma clinical trial durations has become crucial. Accurate predictions allow for efficient resource distribution, strategic foresight, enhanced patient participation and safety, and open dialogue with regulatory authorities. A report in
Nature has shown that various factors, from strategic challenges and commercial barriers to operational setbacks, often lead to unanticipated delays in clinical trials [
7]. Multiple industry studies further emphasize this, noting that nearly 85% of trials experience setbacks [
8], highlighting the pressing need for reliable prediction tools. Given the unpredictable nature of continuous outcomes in clinical research [
9,
10,
11], our technique leans towards binary prediction. Instead of estimating exact durations, our model evaluates whether a trial will be shorter or longer than the average duration derived from clinicaltrials.gov dataset. This approach aligns with recent trends in oncology predictions [
12,
13,
14], presenting several benefits. Notably, the binary framework is less influenced by outliers, reducing distortions from extreme values [
15,
16,
17,
18]. By categorizing results into distinct, actionable groups, our model brings clarity and ensures a balance between practicality and prediction reliability.
Machine learning has shown immense promise in clinical trials for aspects like trial design, patient recruitment, outcome predictions, and regulatory adherence. A deeper dive into existing literature, however, reveals a distinct lack of research on using machine learning to predict clinical trial durations, especially regarding Phase 1 lymphoma trials. There are noteworthy machine learning applications in various trial phases, such as using ML to optimize trial design for ARDS patients in ICUs [
19], forecasting early trial terminations [
20], and refining trial design to improve success rates [
21]. In patient recruitment, ML combined with EHR data and NLP have been employed for patient eligibility [
22] and participant identification [
23]. A wealth of studies also exists on outcome predictions using ML, from predicting treatment responses [
24] to forecasting outcomes based on patient profiles [
25], to predicting negative outcomes, with an emphasis on mortality events [
26]. In regulatory compliance, ML has been used to automate clinical research classification [
27] and recommend regulatory strategies for ML-based trials [
6].
However, in this vast landscape, the specific application of machine learning for clinical trial duration prediction remains largely untapped. One pertinent study did use a gradient-boosted tree-based model on Roche's dataset to gauge trial efficiency, albeit not concentrating on duration prediction [
4]. Currently, a significant gap exists in applying ML models for clinical trial duration predictions—a void our research intends to fill. We are at the forefront of this domain, showcasing how machine learning can predict clinical trial timeframes. Our study not only addresses a significant gap in the literature but also stresses the importance of duration prediction in clinical trial planning and resource allocation.
Key Contributions:
Pioneering Work in Duration Prediction: Our model stands as a trailblazing effort in the domain, bridging the existing gap in duration prediction applications and establishing benchmarks for future research.
Diverse Modeling: We extensively reviewed eight machine learning models, highlighting the Random Forest model for its unparalleled efficiency in predicting durations.
Comprehensive Variable Exploration: Our model incorporates varied variables, from enrollment metrics to study patterns, enhancing its predictive capabilities.
Insight into Data Volume: Beyond mere predictions, we delve into determining the optimal data volume required for precise forecasting.
In-Depth Model Probability: Apart from binary predictions, our model associates higher probabilities with longer average durations, along with a 95% CI. This precision offers a comprehensive range of potential trial durations, aiding informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Broad Applicability: With proven efficacy in lung cancer trials, our model showcases its potential use across various oncology areas.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset
We sourced our dataset from clinicaltrials.gov [
28], a prominent global registry for clinical research studies. Our research focused exclusively on Phase 1 trials related to 'Lymphoma' that had started before 2023 and were marked as 'Completed'. This approach resulted in a collection of 1,231 studies. The decision to exclude trials conducted in 2023 was primarily driven by concerns related to seasonality. Given that we are only halfway through the year, data from 2023 may not provide a comprehensive understanding of the seasonal factors affecting trial durations.
For external validation, we gathered data on 907 completed Phase 1 trials related to 'Lung Cancer' up to the same reference date.
Table 1 provides an overview of the dataset's columns using an example trial. The 'Duration' variable was computed by calculating the time interval between the 'Start Date' and the 'Completion Date'. The average duration of Phase 1 lymphoma trials was found to be 1,788 days, roughly equivalent to 5 years.
Subsequently, we established a binary prediction target based on this 5-year benchmark. The remaining variables in our dataset were utilized as predictors for our model. In the dataset, approximately 40% of trials exceeded this benchmark, while around 60% fell below it.
3.2. Data Preprocessing
To build an appropriate predictive model for Phase 1 lymphoma clinical trial durations, we conducted data preprocessing. We first removed trials with missing start or completion dates, reducing the lymphoma dataset from 1,231 to 1,089 studies. We split this data into 80% for training and 20% for testing and used 5-fold cross-validation for hyperparameter tuning and model selection. We addressed missing values by imputing the mean for numerical variables like enrollment in the lymphoma data. Categorical variables with missing values were treated as a separate category. For the lung cancer dataset, which served as external validation, we followed a similar process, reducing the dataset from 907 to 840 studies. We imputed missing values in the enrollment variable with the mean and treated missing values in categorical variables as a separate category.
3.3. Data Exploration and Feature Engineering
Upon analyzing the lymphoma clinical trials dataset, we pinpointed several columns significantly influencing the clinical trial duration. These include:
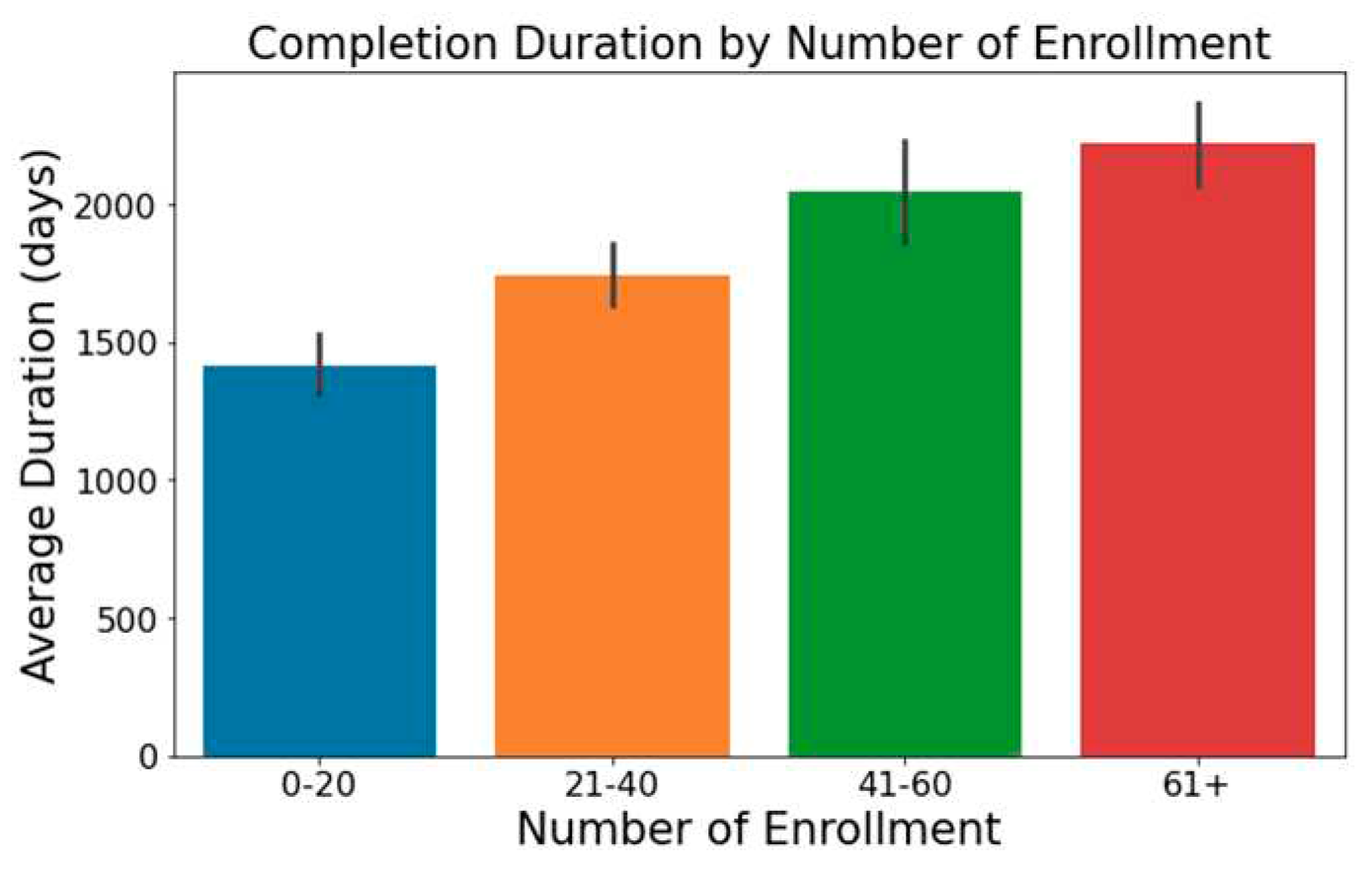
Trials with increased enrollment often exhibit longer durations, as illustrated in
Figure 1.
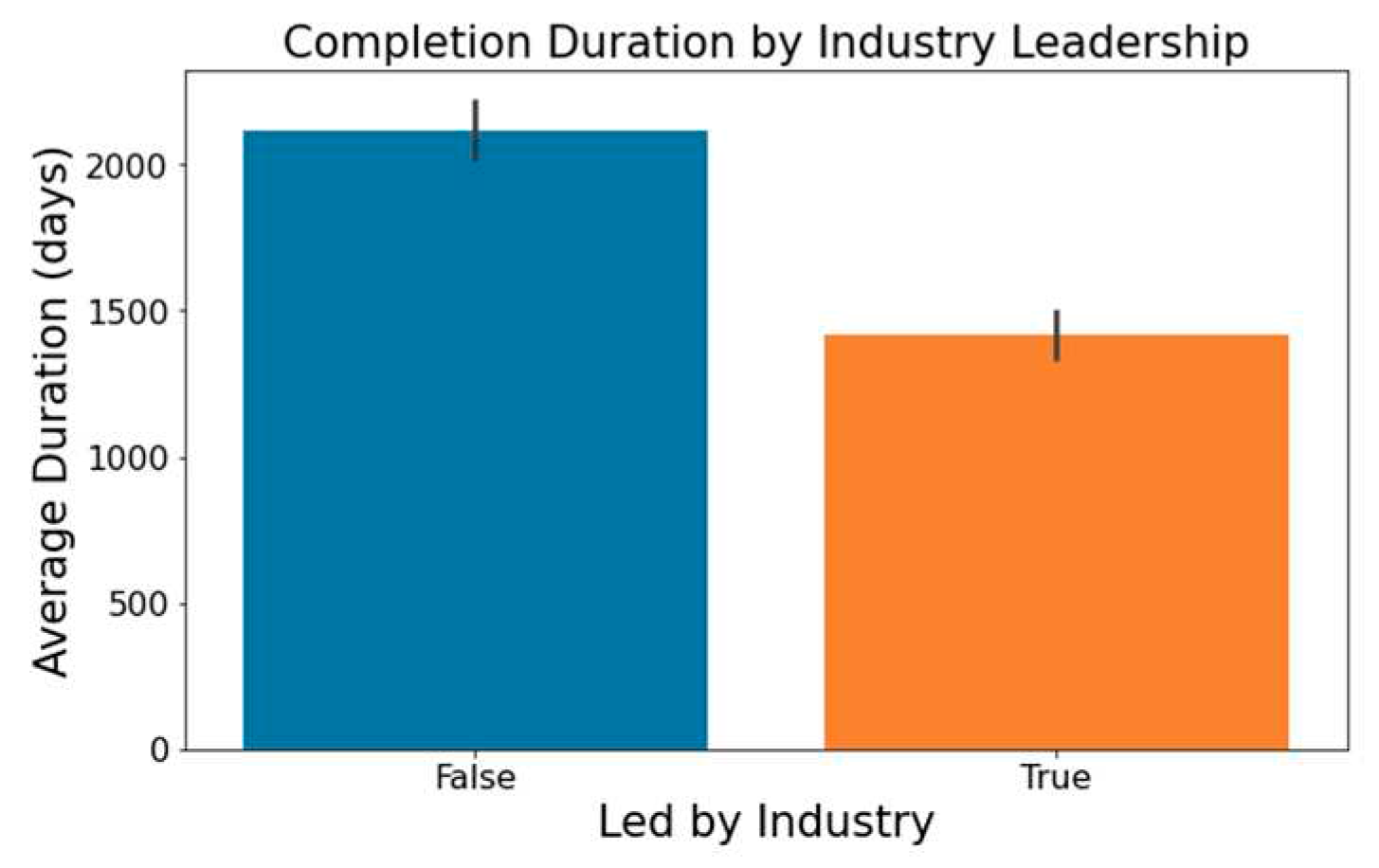
Figure 2 highlights that industry-led trials tend to wrap up more swiftly than non-industry-led ones.
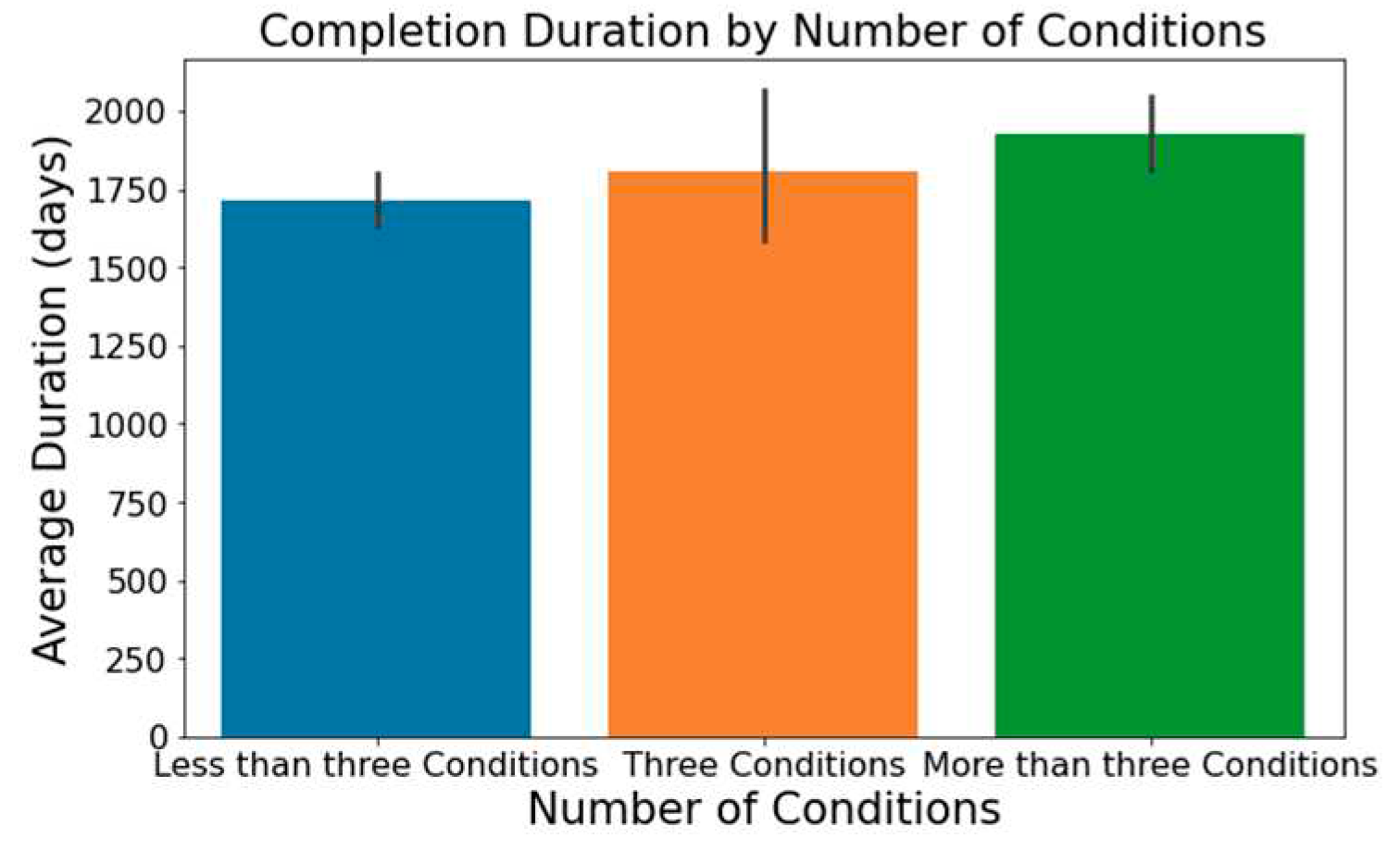
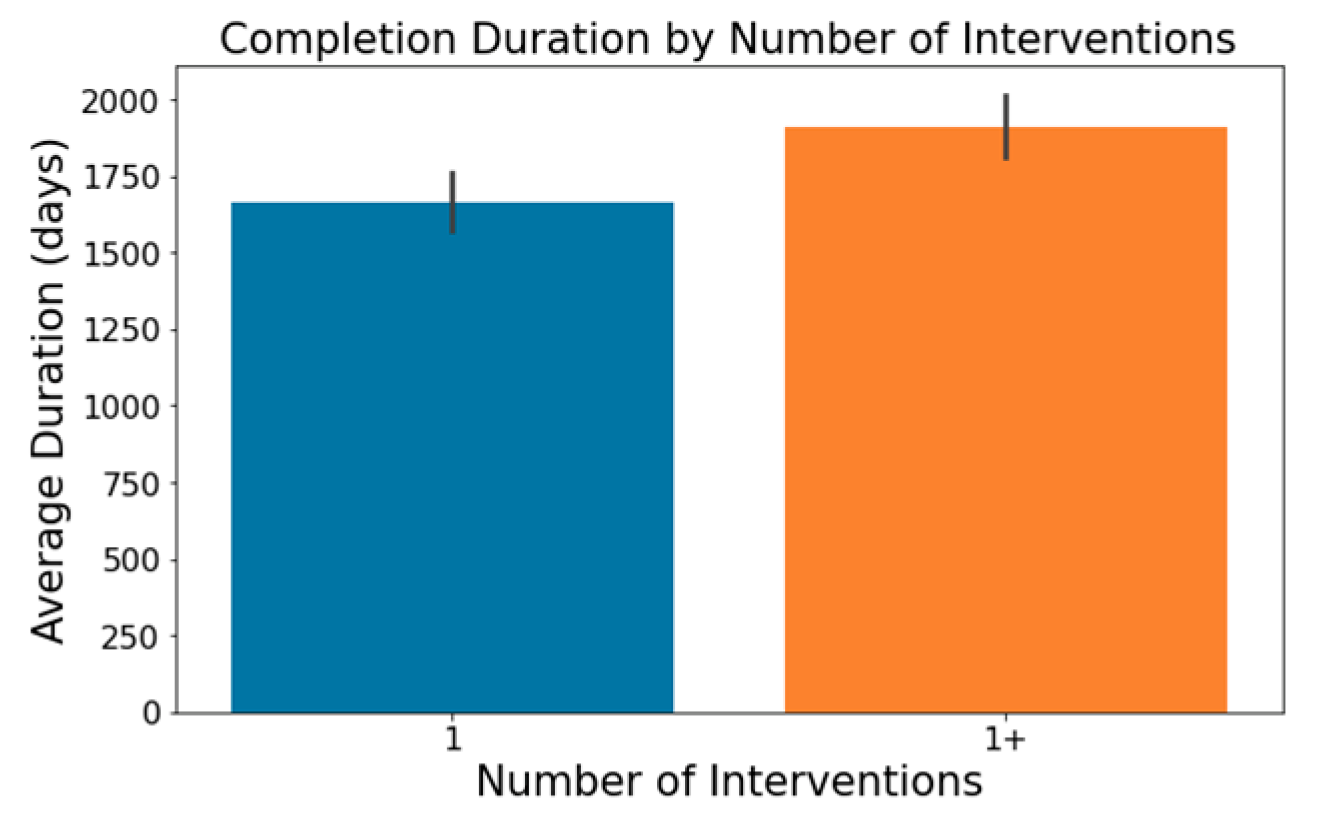
The number of conditions or interventions in a trial can affect its length, with a broader scope often correlating with extended durations; this is depicted in
Figure 3 and
Figure 4.
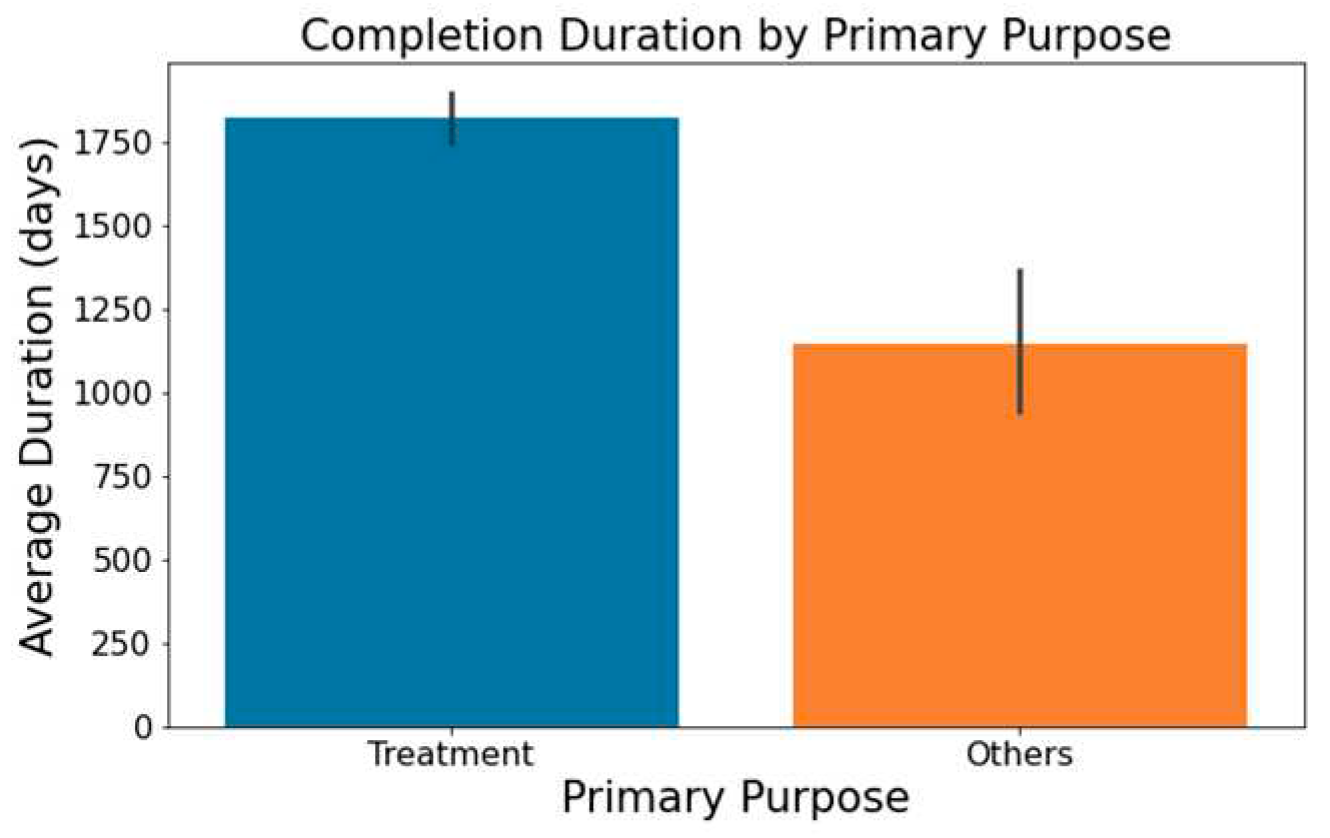
As showcased in
Figure 5, trials with a primary emphasis on 'Treatment' typically have longer durations than those aimed at 'Supportive Care,' 'Diagnostics,' 'Prevention,' or other areas.
In columns with substantial textual data, such as 'Outcome Measures' and 'Sponsor/Collaborators', we employed spaCy library [
29] to determine semantic resemblance between terms. Words with a similarity score surpassing 0.8 were grouped using a Disjoint Set Union (DSU) approach [
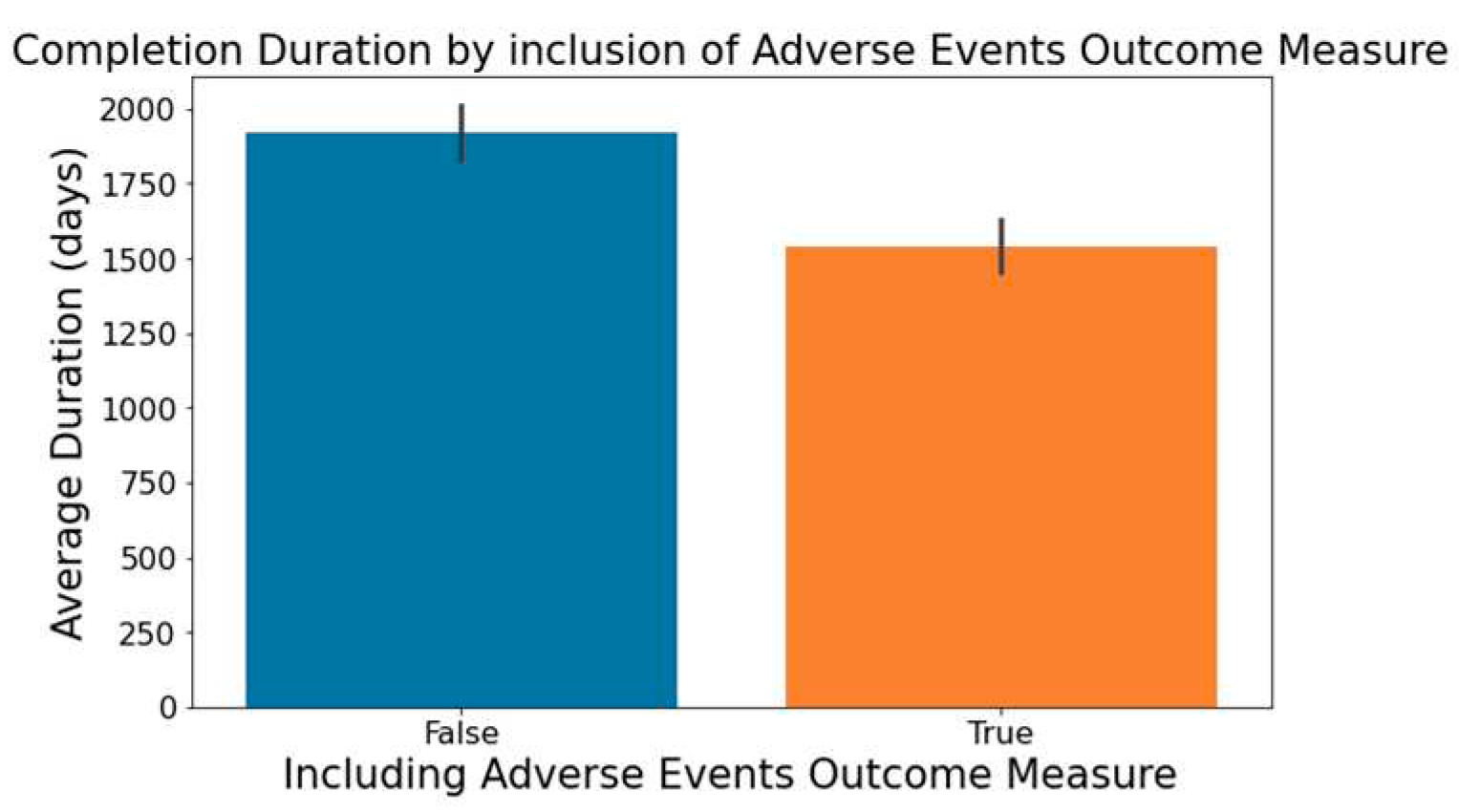
30], enhancing the categorization beyond mere string matching. For example, terms such as ‘adverse events’, ‘adverse reactions’, and ’aes’ all relate to the 'Outcome Measures' category for adverse events. Notable findings from this analysis segment include:
Figure 6 demonstrates that trials focusing on the measurement of adverse events within the 'Outcome Measures' column tend to be completed faster.
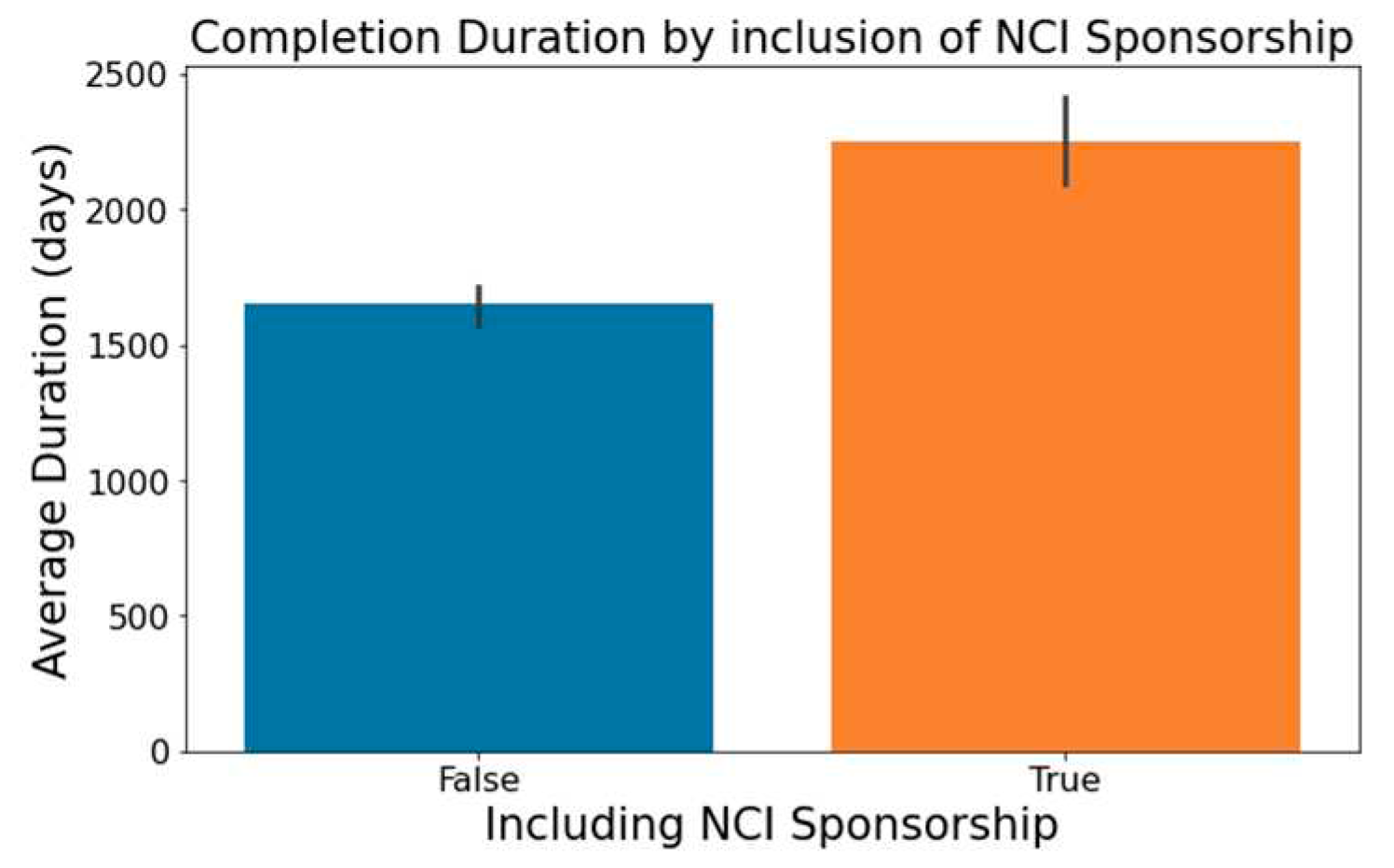
Trials indicating 'National Cancer Institute (NCI)' in the 'Sponsor/Collaborators' column are observed to have lengthier durations, a trend captured in
Figure 7.
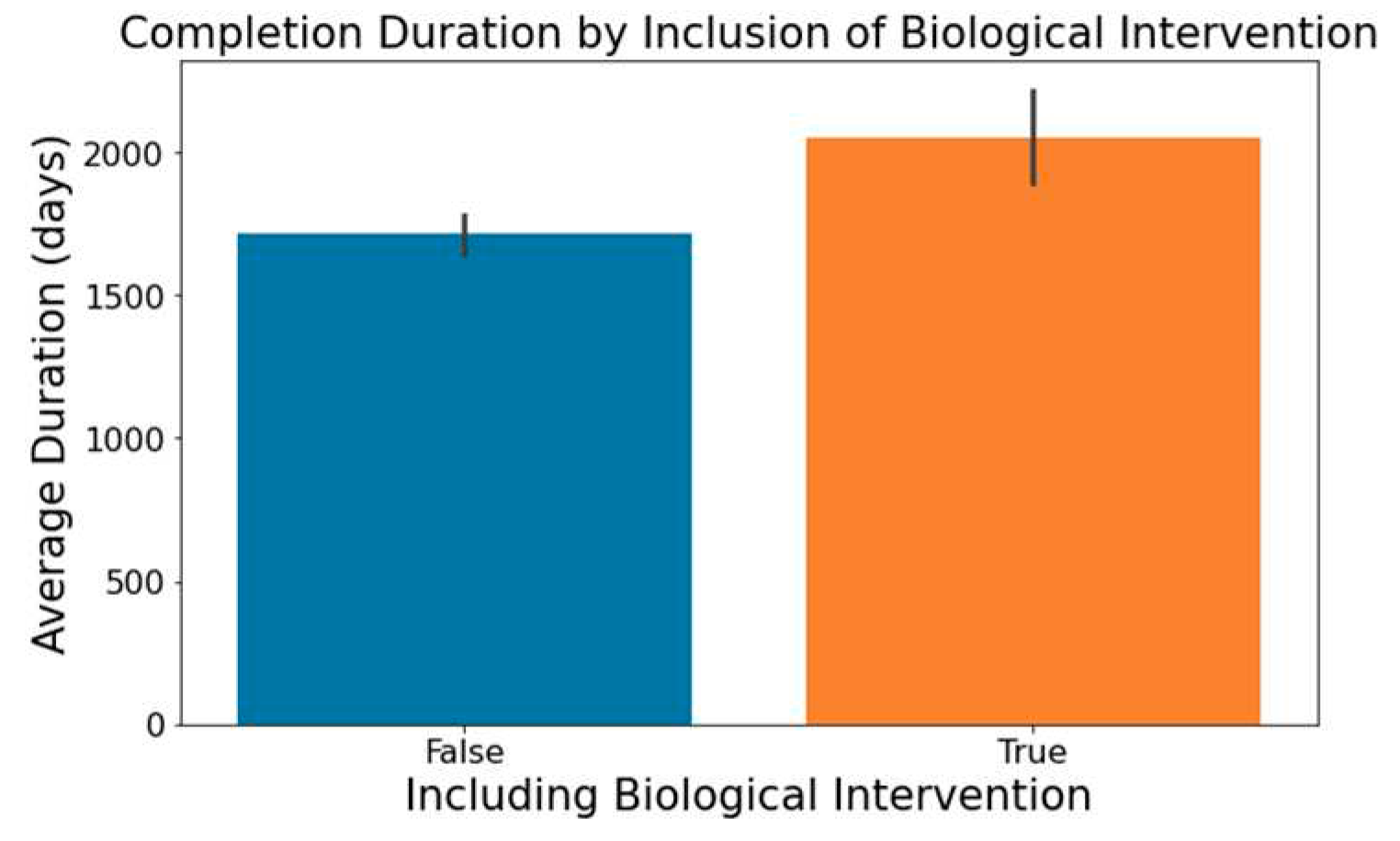
The involvement of biological interventions in trials, represented in the ‘Interventions’ column, often results in extended durations, as seen in
Figure 8.
These insights from our exploratory data analysis informed our feature creation for modeling. Following iterative selection, we incorporated 30 features into our models. The
Table 2 below enumerates these features, ranked by descending order of importance, as determined by Gini Gain [
31].
3.4. Machine Learning Models and Evaluation Metrics
Using Python 3.9.7, we selected eight distinct machine learning models/classifiers to predict the duration of Lymphoma clinical trials. Our choices were informed by previous research in oncology clinical trial predictions [
4,
6,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27] and the inherent strengths of each model. These models are: Logistic Regression (LR), K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN), Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest (RF), XGBoost (XGB), Linear Discriminative Analysis (LDA), Gaussian Naïve Bayes (Gaussian NB), and Multi-Layer Perceptron Classifier (MLP).
Each model underwent thorough evaluation on the Lymphoma dataset. To refine the models and achieve optimal results, we used the GridSearchCV (GSCV) technique from the Scikit-Learn library [
32]. GSCV effectively helps in hyperparameter tuning by cross validating the classifier's predictions, pinpointing the best parameter combination for peak performance.
3.4.1. Logistic Regression (LR)
We started with Logistic Regression for its simplicity and clarity. We utilized the LogisticRegression() function from Scikit-Learn's linear_model library [
32]. However, its linear decision boundary might fall short in capturing complex data relationships.
3.4.2. K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
To address the limitations of linearity, we next looked to KNN, an instance-based learning method that classifies based on data similarity. We implemented KNN using the KNeighborsClassifier() from Scikit-Learn's neighbors library [
32]. Given its computational intensity, especially with a relatively higher number of features, we sought more computationally efficient models, leading us to tree-based options, starting with the Decision Tree (DT).
3.4.3. Decision Tree (DT)
Decision Trees offer a more expressive way of modeling. We implemented the model using the DecisionTreeClassifier() function from Scikit-Learn's tree library [
32]. However, their susceptibility to overfitting led us to consider ensemble techniques such as Random Forest and XGBoost.
3.4.4. Random Forest (RF) & 3.4.5. XGBoost (XGB)
Random Forests and XGBoost leverage the collective strength of multiple trees. Specifically, Random Forest aggregates trees using bagging, while XGBoost refines predictions sequentially through a boosting mechanism. We implemented Random Forest using the RandomForestClassifier() from Scikit-Learn's ensemble library [
32] and XGBoost using the XGBClassifier() function from the xgboost library [
33].
3.4.6. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) & 3.4.7. Gaussian Naïve Bayes (Gaussian NB)
Transitioning from discriminative models like Logistic Regression, KNN, and tree-based methods, we integrated Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) and Gaussian Naïve Bayes (Gaussian NB) to explore a probabilistic approach.
LDA seeks to maximize class separation by identifying the linear combination of features that best distinguish between classes. This method presupposes that features within each class are normally distributed with identical covariance matrices. On the other hand, Gaussian NB is grounded in Bayes' theorem, operating under the assumption of feature independence.
We employed the LinearDiscriminantAnalysis() function for LDA and the GaussianNB() function for Gaussian NB, both sourced from Scikit-Learn [
31]. Recognizing the stringent assumptions of these methods, we turned our attention to models renowned for their flexibility and potential for high accuracy, specifically neural networks.
3.4.8. Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP)
Concluding our model selection, we turned to the Multi-Layer Perceptron, a neural network renowned for its ability to model complex relationships without being bound by strict data assumptions. However, MLP's "black box" nature makes it less transparent compared to models like Logistic Regression and Decision Trees. This can hinder its interpretability in critical scenarios. We implemented MLP using Scikit-Learn's MLPClassifier() from the neural_network library [
32].
To assess the effectiveness of our classifiers, we employed established metrics, specifically accuracy, Area Under the Curve (AUC) of the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC), precision, recall and F1-score. These metrics are grounded in values of true positives (TP), false positives (FP), false negatives (FN), and true negatives (TN):
Accuracy measures the fraction of correct predictions (See Equation (1)).
ROC visually represents classifier performance by plotting recall against the false positive rate ((See Equation (2)) across diverse thresholds. This visual representation is condensed into a metric via the AUC; a value between 0 and 1, where 1 signifies flawless classification
Precision gauges the reliability of positive classifications, shedding light on the inverse of the false positive rate (See Equation (3)).
Recall (or sensitivity) denotes the fraction of actual positives correctly identified, emphasizing the influence of false negatives (See Equation (4)).
F1-score provides a balance between precision and recall, acting as their harmonic mean (See Equation (5)).
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Sample Characteristics
In our model for predicting the duration of Phase I clinical trials for lymphoma, we partitioned our data such that 80% was used for training and validation, employing a 5-fold cross-validation technique. The remaining 20% was reserved for testing.
Table 3 provides a detailed breakdown of the main attributes of our datasets, spotlighting the 12 most salient features identified in
Section 3 – Data Exploration, for both the training/cross-validation and testing set.
The table illustrates the similarities between our training/cross-validation and testing datasets across various attributes. Notably, both sets have an equivalent distribution of the target variable, with 40% of trials taking over 5 years to complete. Metrics like Average Enrollment of Trial Participants and Percentage of Trials Led by Industry show only slight variations. This uniformity across key characteristics supports the appropriateness of the data split for model training and testing.
4.2 Machine Learning Classification
Table 4 assesses the prediction capabilities of eight machine learning classifiers using a 5-fold cross-validation approach. Results were presented as average values within a standard deviation. While all these metrics hold significance in gauging a model's forecasting ability, we primarily focused on accuracy followed by the ROC-AUC metric.
Both XGBoost (XGB) and Random Forest (RF) demonstrated strong performance metrics. XGB achieved an accuracy of 74.42%, a ROC-AUC score of 78.54% and a precision of 70.09%, and RF followed closely with an accuracy of 73.71% and an ROC-AUC of 77.55%, emphasizing its notable predictive prowess. Although their average metrics were similar, RF exhibited more variability in parameters like recall (62.86%±9.69%). Logistic Regression (LR) and Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) provided comparable results, with accuracies of 71.18% and 70.72%, and respective ROC-AUC scores of 77.60% and 75.67%. Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) registered an accuracy of 67.17% and a ROC-AUC of 70.71%. However, its recall's higher standard deviation (49.14%±9.84%) hinted at potential inconsistencies across runs. Gaussian Naïve Bayes notably achieved a high recall of 90.86%, but its accuracy is compromised given its score of 52.93%. K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) and Decision Tree (DT) lagged in performance, indicating potential areas for improvement.
In the cross-validation sets, both XGBoost and Random Forest surpassed other models. Yet, on the testing set, RF held a discernible advantage. As detailed in
Table 5, RF recorded an accuracy of 0.7248, superior to XGBoost's 0.6881. Additionally, RF also outperformed in ROC-AUC, precision, recall, and F1-Score.
Interestingly, XGBoost, while excelling consistently during cross-validation, did not mirror the same dominance on the testing set. This difference might be due to overfitting, with XGBoost possibly aligning too closely to the cross-validation data, affecting its generalization on new data. In contrast, Random Forest's stable performance across datasets might arise from its bagging ensemble strategy, which leverages multiple decision trees.
In conclusion, the Random Forest model consistently outperformed in accuracy, ROC-AUC, and other key metrics on both cross-validation and out-of-sample testing datasets. Thus, we advocate for its adoption as the most reliable model to predict the duration of phase I lymphoma clinical trials.
Table 6 delves into the parameter tuning for this model. In our grid search for RF, we experimented with tree counts ranging from 50 to 500, max depths of None, 10, 20, 30, min sample splits of 2, 5, 10, and explored both bootstrap options. The best-performing configuration utilized a max depth of 20, a min samples split of 10, 100 trees, and no bootstrap.
With the final trained Random Forest model, we forecasted the probability of a phase 1 trial exceeding a duration of five years on the lymphoma testing set.
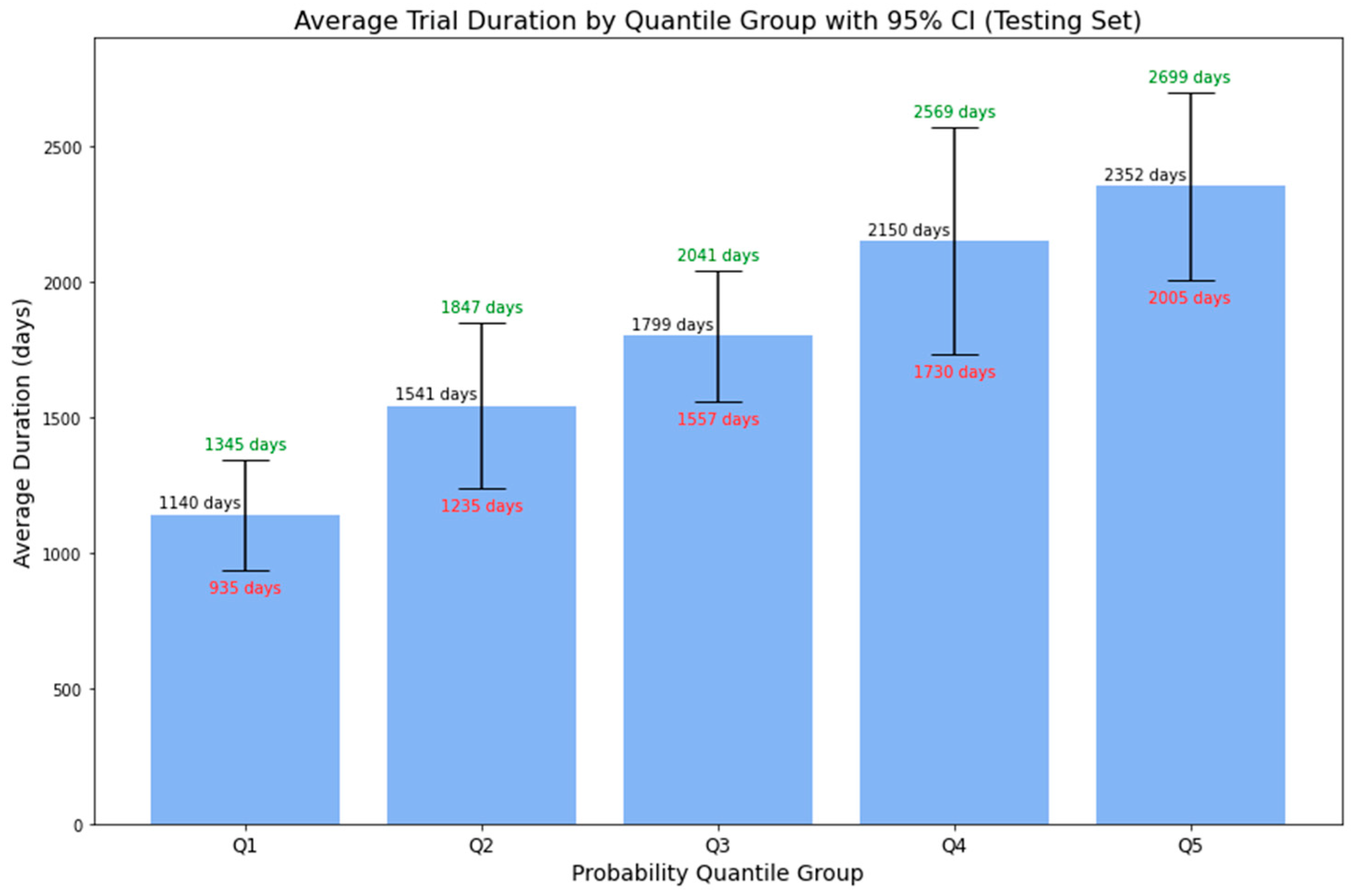
Figure 9 displays the average duration of phase 1 lymphoma trials across 5-quantile probability groups, with associated 95% confidence intervals. The data shows an increasing trend: the average duration rises with higher predicted probabilities. Specifically, the average duration is around 3.12 years (or 1140 days) for the first quantile group and approximately 6.44 years (or 2352 days) for the fifth quantile group. Furthermore, for all probability groups, the upper bounds of the 95% CI correlate with higher predicted probabilities, while the lower bounds follow the inverse pattern. This enhanced representation provides more than just a binary outcome, offering stakeholders a detailed range of potential trial durations complete with confidence intervals. Such precision aids in better decision-making and strategic planning, turning uncertainties into clear, actionable insights for efficient clinical trial management.
Table 7 delineates the corresponding probability range by quantile groups based on the results from the lymphoma testing set.
4.3. Random Forest Model Validation
4.3.1. Impact of Varying Training Data Sizes on Model Performance
In
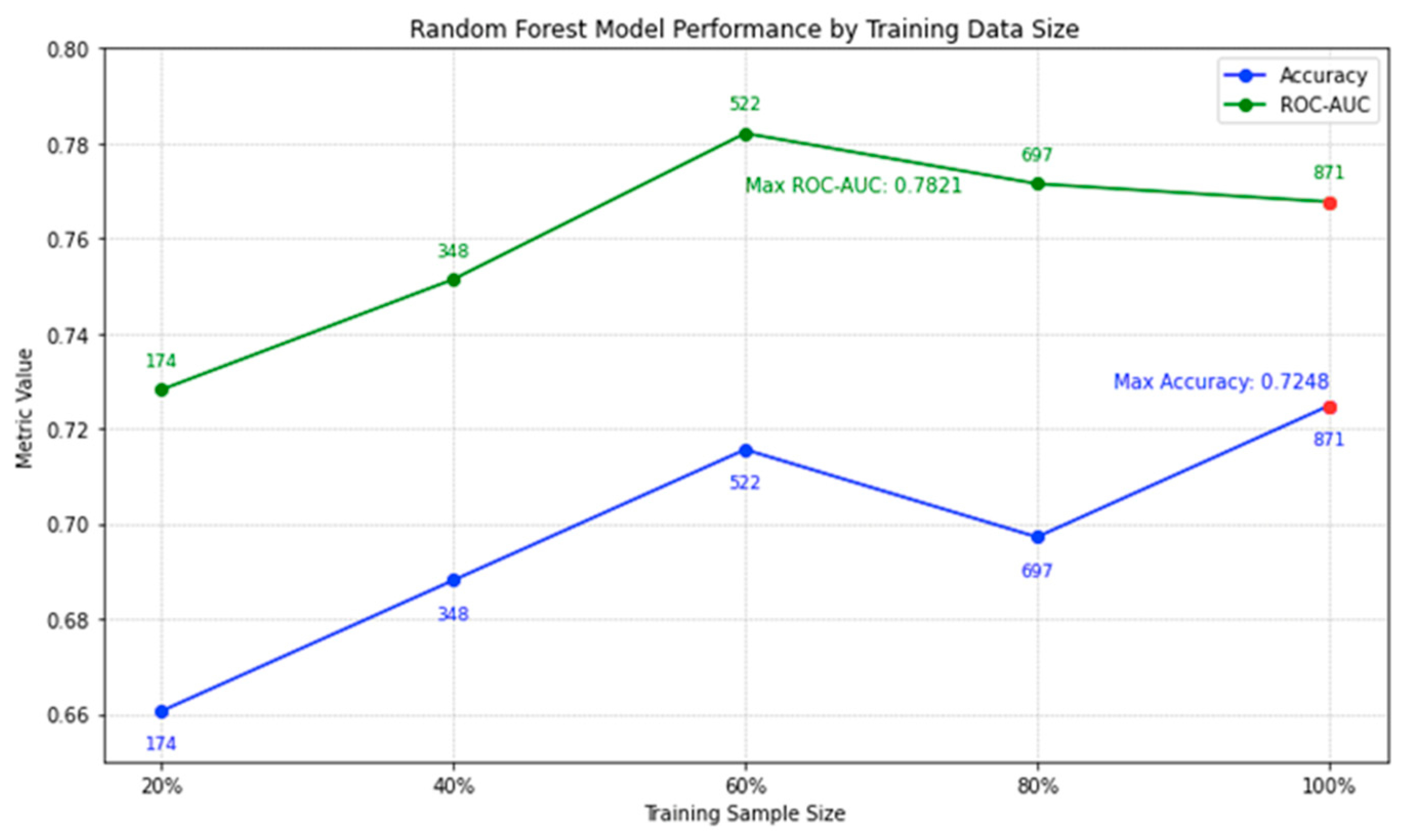
Figure 10, we illustrate the performance trajectory of our random forest model on lymphoma testing data with increasing training sizes. An interesting trend emerges: while there is a positive correlation between training size and accuracy, the incremental gains in accuracy diminish as the dataset size increases. For instance, the leap in accuracy from 20% to 60% training size is notable, but post the 60% mark, the growth rate tapers. By the time we reach our full set of 871 trials, the model achieves an accuracy peak of 0.7248. It's noteworthy that even though the highest ROC-AUC is recorded at 60% data usage, the difference in comparison to the full dataset is slim. This subtle increase in accuracy, coupled with the broadened data spectrum when using all 871 trials, assures us of a well-generalized model. The current analysis underscores our confidence in the 871-trial dataset; additional data from clinicaltrials.gov might refine the model further, but the likelihood of a significant boost in efficiency is marginal.
4.3.2. External Validation using Phase 1 Lung Cancer Trial Data
In the external validation process, we evaluated the efficacy of eight machine learning models on Phase 1 lung cancer trial data.
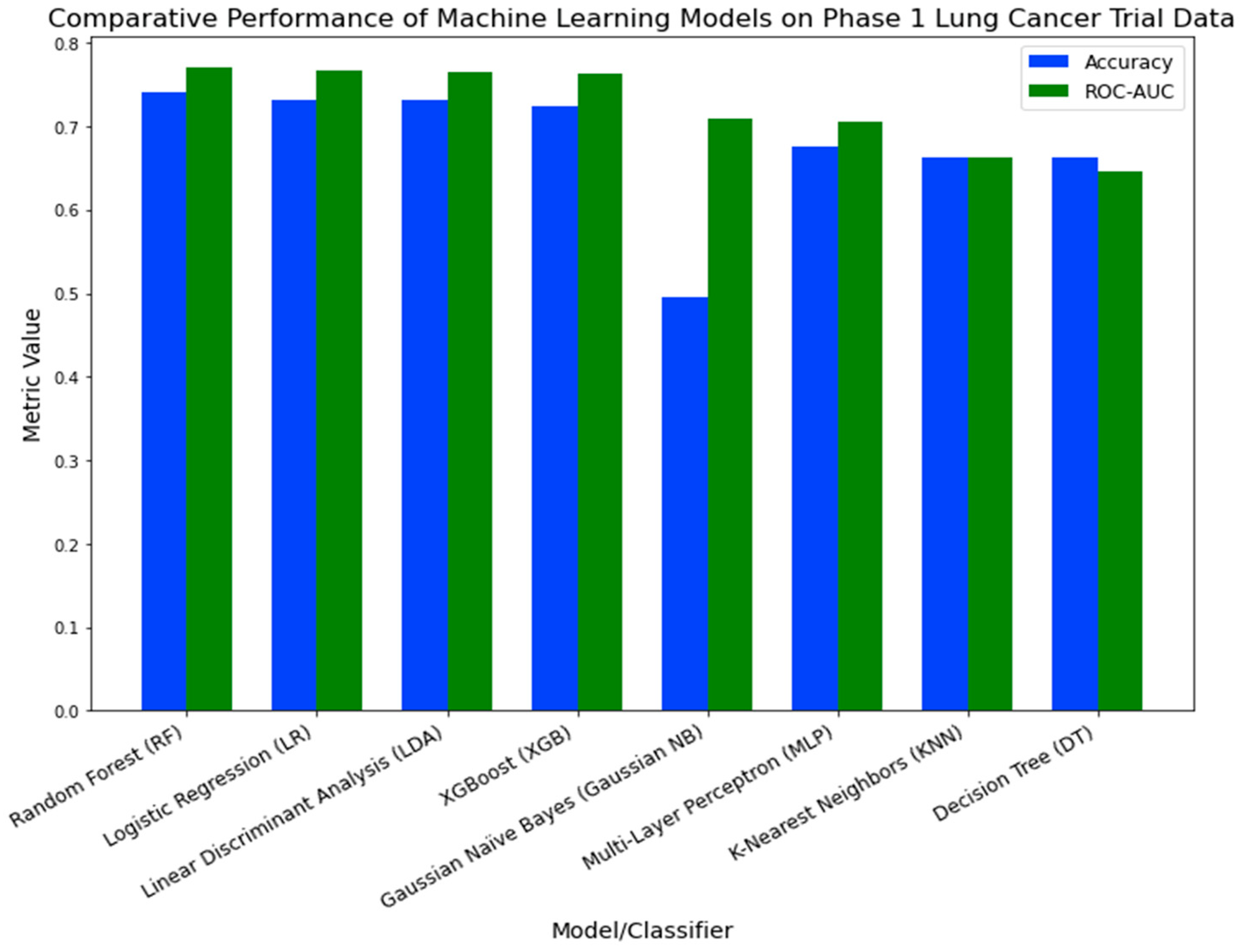
Figure 11 illustrates the performance metrics for each model. The Random Forest (RF) classifier demonstrated the highest performance, with an accuracy of 0.7405 and a ROC-AUC of 0.7701. Logistic Regression (LR) and Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) followed, registering accuracy rates of 0.7321 and 0.7310, and ROC-AUC values of 0.7671 and 0.7647, respectively. Despite its recognized robustness in a variety of healthcare applications [
34,
35,
36,
37], XGBoost (XGB) was ranked fourth, with an accuracy of 0.725 and a ROC-AUC of 0.7632. The other models displayed relatively lower performance metrics.
Utilizing the final trained Random Forest model, similarly to our approach with the lymphoma dataset, we predicted the probability of a Phase 1 lung cancer trial extending beyond five years.
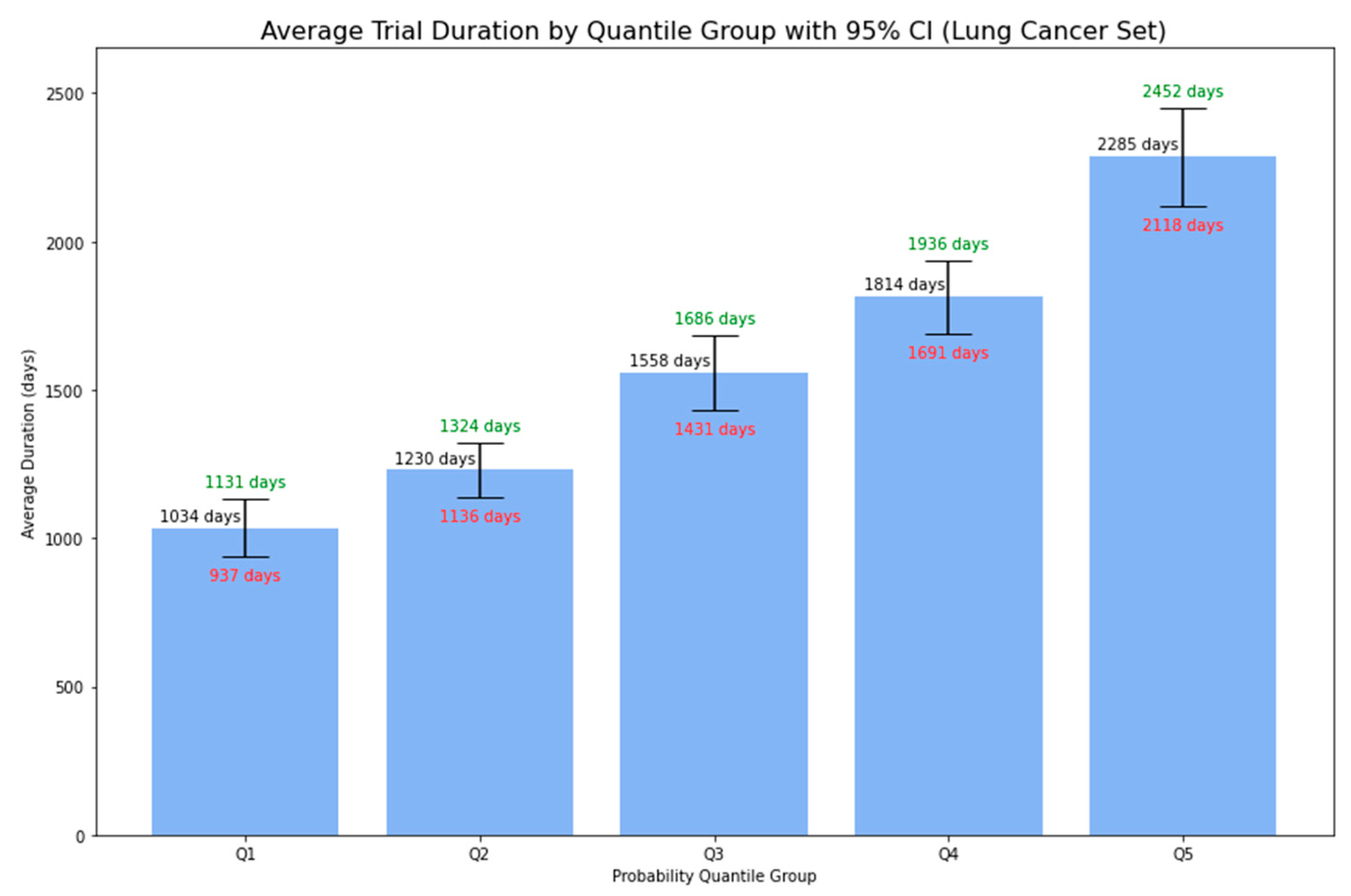
Figure 12 presents the average duration of Phase 1 lymphoma trials, grouped by 5-quantile probability, accompanied by 95% confidence intervals. There was a clear trend: trials with higher predicted probabilities tended to have longer average durations. This trend, observed in both lymphoma and lung cancer trials, not only supplements the simple binary output regarding whether the trial is likely to be below or beyond 5 years but also provides essential insights for stakeholders in planning and resource allocation for clinical trial research.
Considering the cross-validation and testing results from the lymphoma dataset, the consistent performance of the Random Forest model was evident. These outcomes further justify our selection of RF as the optimal model for forecasting Phase 1 lymphoma clinical trials. The RF classifier's consistency across both datasets suggests its potential general applicability for Phase 1 clinical trial predictions.
Limitations:
This study, while providing valuable insights, comes with certain limitations that merit consideration. Primarily, our dataset was exclusively extracted from clinicaltrials.gov, which, although a comprehensive platform, doesn't cover all Phase 1 lymphoma trials worldwide. This may introduce biases or omit nuances evident in trials recorded in other databases or those from different regions. Furthermore, the decision to eliminate trials with missing start or completion dates, while methodologically sound, could inadvertently exclude particular patterns or outliers that are relevant [
38]. Employing mean imputation as a method to address missing values, while a common practice, has its limitations as it can reduce the variance and might influence the predictive power of our models [
39]. The external validation with the lung cancer data strengthens our findings, but it also emphasizes the need for further validations across various cancer types to understand the comprehensive applicability of our model. Finally, while the Random Forest model demonstrated consistency across the datasets, the inherent variability and intricacies of clinical trials, even within the same phase or disease type, could impact its generalizability. Enhancing the model's general applicability might be achieved by incorporating more diverse datasets, adding domain-specific features, or refining preprocessing strategies to account for these complexities.
5. Conclusion
In our analysis of Phase 1 lymphoma clinical trials from clinicaltrials.gov, we pinpointed 30 significant factors affecting trial durations. For instance, trials with larger enrollments usually had extended durations, while industry-led efforts concluded more promptly. Trials linked to the 'National Cancer Institute (NCI)' or those examining a more extensive range of conditions or interventions generally took longer. Conversely, trials concentrating on adverse event measurements ended more rapidly.
Of the 8 machine learning models we evaluated, the Random Forest classifier stood out as the most effective. It achieved an accuracy of 0.7248 and a ROC-AUC score of 0.7677 on the lymphoma trials testing dataset. Adjusting the training data size revealed that accuracy gains began to level off after using 60% of the data. This indicates that our chosen dataset size is close to optimal for this analysis. Notably, when tested on Phase 1 lung cancer trial data, the classifier achieved an accuracy of 0.7405 and a ROC-AUC of 0.7701, underscoring its adaptability beyond just lymphoma trials. This points to its potential in predicting durations for a broader set of Phase 1 clinical trials.
Going deeper, we carried out a thorough analysis of average durations by predicted probability groups. This additional exploration provided stakeholders with more precise duration estimates, accompanied by a 95% confidence interval for each group. This information is invaluable for strategic planning, resource allocation, and risk mitigation.
Together, these insights pave the way for refining clinical research methods and enhancing patient outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L., S.L. and J.W.; methodology, B.L. and S.L.; software, B.L. and S.L.; validation, J.W, S.L. and S.B.; formal analysis, J.W.; investigation, S.B.; resources, B.L., S.L. and J.W.; data curation, J.W. and S.B.; writing—original draft preparation, B.L.; writing—review and editing, J.W., S.B., S.L. and B.L.; visualization, B.L. and S.L.; supervision, S.B.; project administration, S.B. and J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. These data can be found here:
https://clinicaltrials.gov (Accessed: July 25, 2023).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Fangya Tan for her valuable domain knowledge in clinical research and for the insightful discussions that contributed to the creation of features. Her ResearchGate profile is available at:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Fangya-Tan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- R. L. Siegel, K. D. Miller, N. S. Wagle, and A. Jemal, “Cancer statistics, 2023,” Ca Cancer J Clin, vol. 73, no. 1, pp. 17–48, 2023.
- T. G. Roberts et al., “Trends in the risks and benefits to patients with cancer participating in phase 1 clinical trials,” Jama, vol. 292, no. 17, pp. 2130–2140, 2004. [CrossRef]
- E. H. Weissler et al., “The role of machine learning in clinical research: transforming the future of evidence generation,” Trials, vol. 22, no. 1, p. 537, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. Wu et al., “Machine Learning Prediction of Clinical Trial Operational Efficiency,” AAPS J., vol. 24, no. 3, p. 57, May 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. L. Beauchamp and J. F. Childress, Principles of biomedical ethics. Oxford University Press, USA, 2001. Accessed: Oct. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=_14H7MOw1o4C&oi=fnd&pg=PR9&dq=Beauchamp,+T.+L.,+%26+Childress,+J.+F.+(2013).+Principles+of+biomedical+ethics+(7th+ed.).+New+York:+Oxford+University+Press.&ots=1x_n4OBqWq&sig=pCzR4XfW0iDFmXEFsOajo6dGdU4.
- D. A. Dri, M. Massella, D. Gramaglia, C. Marianecci, and S. Petraglia, “Clinical Trials and Machine Learning: Regulatory Approach Review,” Rev. Recent Clin. Trials, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 341–350, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. K. Harrison, “Phase II and phase III failures: 2013–2015,” Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., vol. 15, no. 12, Art. no. 12, Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Uniform, “How to avoid costly Clinical Research delays | Blog,” MESM. Accessed: Oct. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.mesm.com/blog/tips-to-help-you-avoid-costly-clinical-research-delays/.
- E. W. Steyerberg, Clinical Prediction Models: A Practical Approach to Development, Validation, and Updating. in Statistics for Biology and Health. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. J. Sargent, B. A. Conley, C. Allegra, and L. Collette, “Clinical trial designs for predictive marker validation in cancer treatment trials,” J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol., vol. 23, no. 9, pp. 2020–2027, Mar. 2005. [CrossRef]
- I. Kola and J. Landis, “Can the pharmaceutical industry reduce attrition rates?,” Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., vol. 3, no. 8, Art. no. 8, Aug. 2004. [CrossRef]
- E. W. Steyerberg and Y. Vergouwe, “Towards better clinical prediction models: seven steps for development and an ABCD for validation,” Eur. Heart J., vol. 35, no. 29, pp. 1925–1931, Aug. 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Mandrekar and D. Sargent, “Clinical Trial Designs for Predictive Biomarker Validation: One Size Does Not Fit All,” J. Biopharm. Stat., vol. 19, pp. 530–42, Feb. 2009. [CrossRef]
- P. Blanche, J.-F. Dartigues, and H. Jacqmin-Gadda, “Estimating and comparing time-dependent areas under receiver operating characteristic curves for censored event times with competing risks,” Stat. Med., vol. 32, no. 30, pp. 5381–5397, Dec. 2013. [CrossRef]
- P. J. Rousseeuw and A. M. Leroy, Robust regression and outlier detection. John wiley & sons, 2005. Accessed: Oct. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=woaH_73s-MwC&oi=fnd&pg=PR13&dq=Rousseeuw,+P.J.,+Leroy,+A.M.+(1987).+Robust+Regression+and+Outlier+Detection.+John+Wiley+%26+Sons.&ots=TCuOR_zkjR&sig=pwLEHKv7QboOplfEIV0LO6POvdY.
- T. Hastie, J. Friedman, and R. Tibshirani, The Elements of Statistical Learning. in Springer Series in Statistics. New York, NY: Springer New York, 2001. [CrossRef]
- C. M. Bishop and N. M. Nasrabadi, Pattern recognition and machine learning, vol. 4. Springer, 2006. Accessed: Oct. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://link.springer.com/book/9780387310732.
- J. Fox, Applied regression analysis and generalized linear models, 2nd ed. in Applied regression analysis and generalized linear models, 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications, Inc, 2008, pp. xxi, 665.
- E. Schwager et al., “Utilizing machine learning to improve clinical trial design for acute respiratory distress syndrome,” Npj Digit. Med., vol. 4, no. 1, Art. no. 1, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Kavalci and A. Hartshorn, “Improving clinical trial design using interpretable machine learning based prediction of early trial termination,” Sci. Rep., vol. 13, no. 1, Art. no. 1, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Harrer, P. Shah, B. Antony, and J. Hu, “Artificial Intelligence for Clinical Trial Design,” Trends Pharmacol. Sci., vol. 40, no. 8, pp. 577–591, Aug. 2019. [CrossRef]
- T. Cai et al., “Improving the Efficiency of Clinical Trial Recruitment Using an Ensemble Machine Learning to Assist With Eligibility Screening,” ACR Open Rheumatol., vol. 3, no. 9, pp. 593–600, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Vazquez, S. Abdelrahman, L. M. Byrne, M. Russell, P. Harris, and J. C. Facelli, “Using supervised machine learning classifiers to estimate likelihood of participating in clinical trials of a de-identified version of ResearchMatch,” J. Clin. Transl. Sci., vol. 5, no. 1, p. e42, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. M. Chekroud et al., “Cross-trial prediction of treatment outcome in depression: a machine learning approach,” Lancet Psychiatry, vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 243–250, Mar. 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. V. Schperberg, A. Boichard, I. F. Tsigelny, S. B. Richard, and R. Kurzrock, “Machine learning model to predict oncologic outcomes for drugs in randomized clinical trials,” Int. J. Cancer, vol. 147, no. 9, pp. 2537–2549, 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Tong, J. Luo, R. Cisler, and M. Cantor, “Machine Learning-Based Modeling of Big Clinical Trials Data for Adverse Outcome Prediction: A Case Study of Death Events,” in 2019 IEEE 43rd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Jul. 2019, pp. 269–274. [CrossRef]
- E. Batanova, I. Birmpa, and G. Meisser, “Use of Machine Learning to classify clinical research to identify applicable compliance requirements,” Inform. Med. Unlocked, vol. 39, p. 101255, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- "ClinicalTrials.gov," National Library of Medicine, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://clinicaltrials.gov/. [Accessed: July 25, 2023].
- M. Honnibal and I. Montani, “spaCy 2: Natural language understanding with Bloom embeddings, convolutional neural networks and incremental parsing,” 2017.
- A. Yadav, H. Shokeen, and J. Yadav, “Disjoint Set Union for Trees,” in 2021 12th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–6. Accessed: Oct. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9580066/.
- L. Breiman, J. Friedman, R. Olshen, and C. Stone, “Classification and regression trees–crc press,” Boca Raton Fla., 1984.
- F. Pedregosa et al., “Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python,” J. Mach. Learn. Res., vol. 12, no. Oct, pp. 2825–2830, 2011.
- T. Chen and C. Guestrin, “XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System,” in Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, in KDD ’16. New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2016, pp. 785–794. [CrossRef]
- M. K. Hasan, M. A. Alam, S. Roy, A. Dutta, M. T. Jawad, and S. Das, “Missing value imputation affects the performance of machine learning: A review and analysis of the literature (2010–2021),” Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, vol. 27, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wu, Q. Zhang, Y. Hu, K. Sun-Woo, X. Zhang, H. Zhu, L. jie, and S. Li, “Novel binary logistic regression model based on feature transformation of XGBoost for type 2 Diabetes Mellitus prediction in healthcare systems,” Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 129, pp. 1-12, 2022. [CrossRef]
- N. S. Rajliwall, R. Davey, and G. Chetty, “Cardiovascular Risk Prediction Based on XGBoost,” in 2018 5th Asia-Pacific World Congress on Computer Science and Engineering (APWC on CSE), Nadi, Fiji, 2018, pp. 246-252. [CrossRef]
- B. Long, F. Tan, and M. Newman, “Ensemble DeBERTa Models on USMLE Patient Notes Automatic Scoring using Note-based and Character-based approaches,” Advances in Engineering Technology Research, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 107-107, 2023. [CrossRef]
- V. Barnett and T. Lewis, Outliers in statistical data, vol. 3. Wiley New York, 1994. Accessed: Oct. 30, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://scholar.archive.org/work/l4rvge57snh7fjjzpc5idiyxj4/access/wayback/http://tocs.ulb.tu-darmstadt.de:80/214880745.pdf.
- K. Maheswari, P. Packia Amutha Priya, S. Ramkumar, and M. Arun, “Missing Data Handling by Mean Imputation Method and Statistical Analysis of Classification Algorithm,” in EAI International Conference on Big Data Innovation for Sustainable Cognitive Computing, A. Haldorai, A. Ramu, S. Mohanram, and C. C. Onn, Eds., in EAI/Springer Innovations in Communication and Computing. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 137–149. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Impact of Enrollment Numbers on Trial Duration.
Figure 1.
Impact of Enrollment Numbers on Trial Duration.
Figure 2.
Impact of Industry Leadership on Trial Duration.
Figure 2.
Impact of Industry Leadership on Trial Duration.
Figure 3.
Impact of Condition Count on Trial Duration.
Figure 3.
Impact of Condition Count on Trial Duration.
Figure 4.
Impact of Intervention Count on Trial Duration
Figure 4.
Impact of Intervention Count on Trial Duration
Figure 5.
Impact of Trial Focus on Trial Duration
Figure 5.
Impact of Trial Focus on Trial Duration
Figure 6.
Impact of Adverse Events Outcome Measure on Trial Duration.
Figure 6.
Impact of Adverse Events Outcome Measure on Trial Duration.
Figure 7.
Impact of NCI Sponsorship on Trial Duration.
Figure 7.
Impact of NCI Sponsorship on Trial Duration.
Figure 8.
Impact of Biological Intervention on Trial Duration.
Figure 8.
Impact of Biological Intervention on Trial Duration.
Figure 9.
Average Duration of Phase 1 Lymphoma Trials by Probability Quantile Group.
Figure 9.
Average Duration of Phase 1 Lymphoma Trials by Probability Quantile Group.
Figure 10.
Random Forest Model Performance by Training Data Size
Figure 10.
Random Forest Model Performance by Training Data Size
Figure 11.
Comparative Performance of Machine Learning Models on Phase 1 Lung Cancer Trial Data.
Figure 11.
Comparative Performance of Machine Learning Models on Phase 1 Lung Cancer Trial Data.
Figure 12.
Average Duration of Phase 1 Lung Cancer Trials by Probability Quantile Group.
Figure 12.
Average Duration of Phase 1 Lung Cancer Trials by Probability Quantile Group.
Table 1.
Overview of Columns in the Phase 1 Lymphoma Trial Dataset using an Example Trial.
Table 1.
Overview of Columns in the Phase 1 Lymphoma Trial Dataset using an Example Trial.
| Rank |
47 |
| NCT Number |
NCT02220842 |
| Title |
A Safety and Pharmacology Study of Atezolizumab (MPDL3280A) Administered With Obinutuzumab or Tazemetostat in Participants With Relapsed/Refractory Follicular Lymphoma and Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma |
| Acronym |
|
| Status |
Completed |
| Study Results |
No Results Available |
| Conditions |
Lymphoma |
| Interventions |
Drug: Atezolizumab|Drug: Obinutuzumab|Drug: Tazemetostat |
| Outcome Measures |
Percentage of Participants With Dose Limiting Toxicities (DLTs)|Recommended Phase 2 Dose (RP2D) of Atezolizumab|Obinutuzumab Minimum Serum Concentration (Cmin)|Percentage of Participants With Adverse Events (AEs) Graded According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0 (CTCAE v4.0)... |
| Sponsor/Collaborators |
Hoffmann-La Roche |
| Gender |
All |
| Age |
18 Years and older   (Adult, Older Adult) |
| Phases |
Phase 1 |
| Enrollment |
96 |
| Funded Bys |
Industry |
| Study Type |
Interventional |
| Study Designs |
Allocation: Non-Randomized|Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment|Masking: None (Open Label)|Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Other IDs |
GO29383|2014-001812-21 |
| Start Date |
18-Dec-14 |
| Primary Completion Date |
21-Jan-20 |
| Completion Date |
21-Jan-20 |
| First Posted |
20-Aug-14 |
| Results First Posted |
|
| Last Update Posted |
27-Jan-20 |
| Locations |
City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, California, United States|Fort Wayne Neurological Center, Fort Wayne, Indiana, United States|Hackensack University Medical Center, Hackensack, New Jersey, United States… |
| Study Documents |
|
| URL |
https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT02220842 |
Table 2.
Features Ranked by Importance Based on Gini Gain.
Table 2.
Features Ranked by Importance Based on Gini Gain.
| Feature Name |
Explanation |
| Enrollment |
Number of trial participants |
| Industry-led |
Trial led by the industry (True/False) |
| Location Count |
Number of trial locations |
| Measures Count |
Number of outcome measures |
| Condition Count |
Number of medical conditions |
| Intervention Count |
Number of interventions |
| NCI Sponsorship |
Sponsorship includes NCI (True/False) |
| AES Outcome Measure |
Outcome measure includes adverse events (True/False) |
| Open Masking Label |
Trial uses open masking label (True/False) |
| Biological Intervention |
Intervention type includes biological (True/False) |
| Efficacy Keywords |
Title includes efficacy-related keywords (True/False) |
| Random Allocation |
Patient allocation is random (True/False) |
| US-led |
Trial primarily in the US (True/False) |
| Procedure Intervention |
Intervention type includes procedure (True/False) |
| Overall Survival Outcome Measure |
Outcome measure includes overall survival rate (True/False) |
| Drug Intervention |
Intervention type includes drugs (True/False) |
| MTD Outcome Measure |
Outcome measure includes maximally tolerated dose (True/False) |
| US-included |
Trial location includes the US (True/False) |
| DOR Outcome Measure |
Outcome measure includes duration of response (True/False) |
| Prevention Purpose |
Primary purpose is prevention (True/False) |
| AES Outcome Measure (Lead) |
Leading outcome measure is adverse events (True/False) |
| DLT Outcome Measure |
Outcome measure includes dose-limiting toxicity (True/False) |
| Treatment Purpose |
Primary purpose is treatment (True/False) |
| DLT Outcome Measure (Lead) |
Leading outcome measure is dose-limiting toxicity (True/False) |
| MTD Outcome Measure (Lead) |
Leading outcome measure is maximally tolerated dose (True/False) |
| Radiation Intervention |
Intervention type includes radiation (True/False) |
| Tmax Outcome Measure |
Outcome measure includes time of Cmax (True/False) |
| Cmax Outcome Measure |
Outcome measure includes maximum measured concentration (True/False) |
| Non-Open Masking Label |
Trial use non-open masking label (True/False) |
| Crossover Assignment |
Patient assignment is crossover (True/False) |
Table 3.
Key Characteristics of Training/Cross-Validation and Testing Datasets for Lymphoma Clinical Trials.
Table 3.
Key Characteristics of Training/Cross-Validation and Testing Datasets for Lymphoma Clinical Trials.
| Characteristics |
Training/Cross-Validation Sets (n=871) |
Testing Set (n=218) |
| Percentage of Trials Exceeding 5-Year Completion Time (Target) |
40% |
40% |
| Mean Trial Participant Enrollment |
49 |
50 |
| Percentage of Industry-led Trials |
46% |
48% |
| Average Number of Trial Locations |
6 |
6 |
| Average Outcome Measures Count |
6 |
6 |
| Average Medical Conditions Addressed |
4 |
4 |
| Average Interventions per Trial |
3 |
2 |
| Percentage of NCI-Sponsored Trials |
23% |
24% |
| Percentage of Trials with AES Outcome Measure |
34% |
34% |
| Percentage of Trials with Open Label Masking |
91% |
92% |
| Percentage of Titles Suggesting Efficacy |
50% |
51% |
| Percentage of Trials Involving Biological Interventions |
23% |
20% |
| Percentage of Randomly Allocated Patient Trials |
24% |
27% |
Table 4.
Performance Metrics of Machine Learning Classifiers Using 5-Fold Cross-Validation.
Table 4.
Performance Metrics of Machine Learning Classifiers Using 5-Fold Cross-Validation.
| Models/Classifier |
Accuracy |
ROC-AUC |
Precision |
Recall |
F1-Score |
| XGBoost (XGB) |
0.7442±0.0384 |
0.7854±0.0389 |
0.7009±0.0439 |
0.6286±0.0828 |
0.6614±0.0633 |
| Random Forest (RF) |
0.7371±0.0389 |
0.7755±0.0418 |
0.6877±0.0403 |
0.6286±0.0969 |
0.6544±0.0667 |
| Logistic Regression (LR) |
0.7118±0.0324 |
0.7760±0.0282 |
0.6525±0.0487 |
0.6171±0.0506 |
0.6323±0.0367 |
| Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) |
0.7072±0.0393 |
0.7567±0.0365 |
0.6457±0.0545 |
0.6114±0.0388 |
0.6272±0.0412 |
| Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) |
0.6717±0.0302 |
0.7071±0.0593 |
0.6133±0.0423 |
0.4914±0.0984 |
0.5414±0.0684 |
| Gaussian Naïve Bayes (Gaussian NB) |
0.5293±0.0169 |
0.6980±0.0274 |
0.4571±0.0096 |
0.9086±0.0194 |
0.6081±0.0097 |
| K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) |
0.6223±0.0475 |
0.6487±0.0445 |
0.5385±0.0762 |
0.4286±0.0619 |
0.4786±0.0661 |
| Decision Tree (DT) |
0.6464±0.0252 |
0.6363±0.0317 |
0.5567±0.0295 |
0.5771±0.0780 |
0.5651±0.0502 |
Table 5.
Comparative Performance of Random Forest and XGBoost on Lymphoma Testing Data.
Table 5.
Comparative Performance of Random Forest and XGBoost on Lymphoma Testing Data.
| Model/Classifier |
Accuracy |
ROC-AUC |
Precision |
Recall |
F1-Score |
| Random Forest (RF) |
0.7248 |
0.7677 |
0.675 |
0.6136 |
0.6429 |
| XGBoost (XGB) |
0.6881 |
0.7574 |
0.6282 |
0.5568 |
0.5904 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Table 6.
Parameter Tuning Results for the Optimal Random Forest Model.
Table 6.
Parameter Tuning Results for the Optimal Random Forest Model.
| Model/Classifier |
Parameter Adjustment |
| Random Forest (RF) |
maxDepth: 20; minSamplesSplit: 10; numTress: 100; bootstrap: False; seed: 42 |
Table 7.
Probability Quantile Groups with Corresponding Average Duration and 95% Confidence Intervals.
Table 7.
Probability Quantile Groups with Corresponding Average Duration and 95% Confidence Intervals.
| Probability Quantile Group |
Probability Range |
Average Duration |
Lower Bound (95% CI) |
Upper Bound (95% CI) |
| Q1 |
0 to 0.1624 |
1140 days |
935 days |
1345 days |
| Q2 |
0.1624 to 0.3039 |
1541 days |
1235 days |
1847 days |
| Q3 |
0.3039 to 0.4697 |
1799 days |
1557 days |
2041 days |
| Q4 |
0.4697 to 0.6291 |
2150 days |
1730 days |
2569 days |
| Q5 |
0.6291 to 1 |
2352 days |
2005 days |
2699 days |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).