Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Histology
2.2. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
3. Results
3.1. Histology
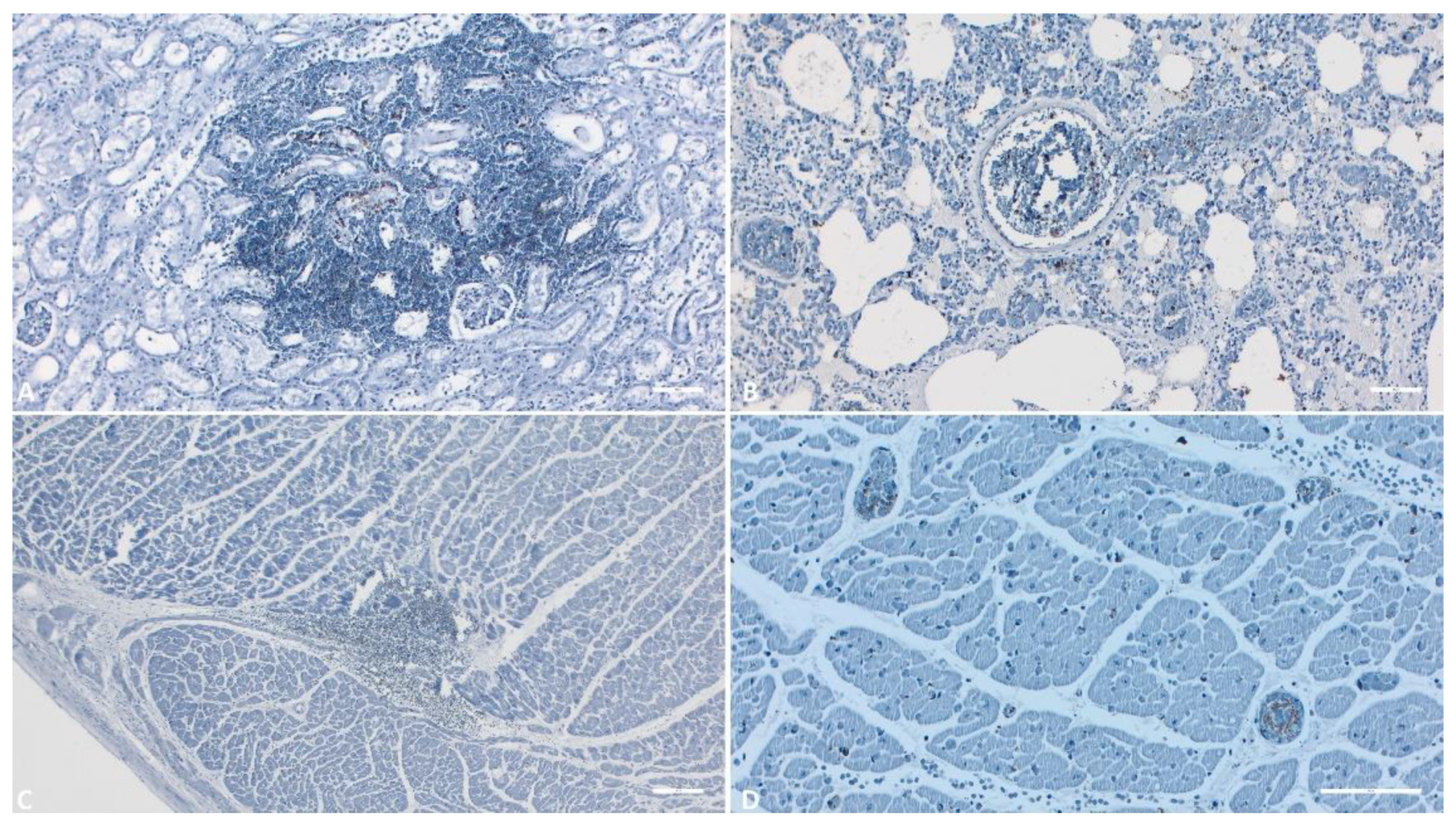
3.1.1. Kidney
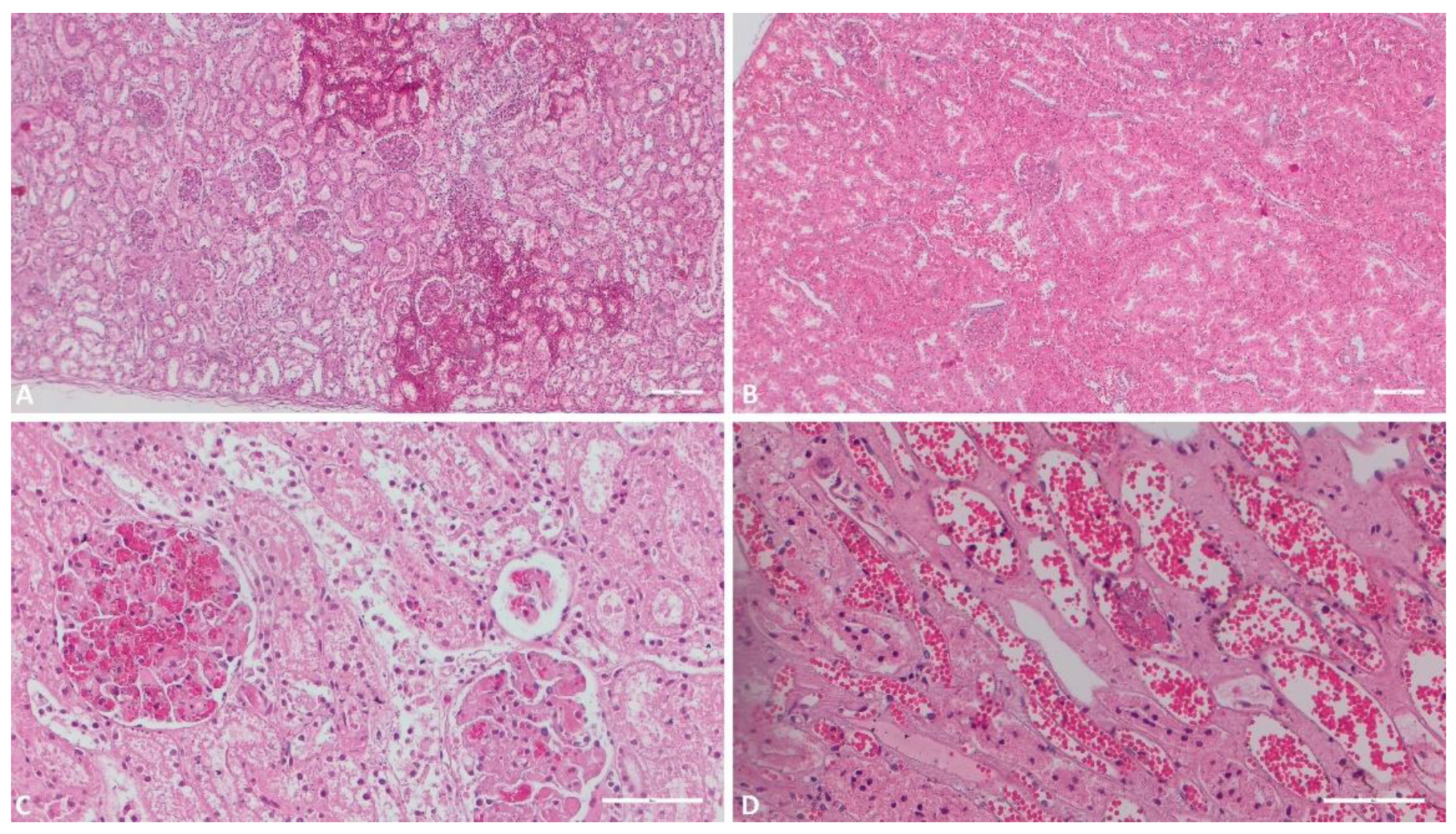
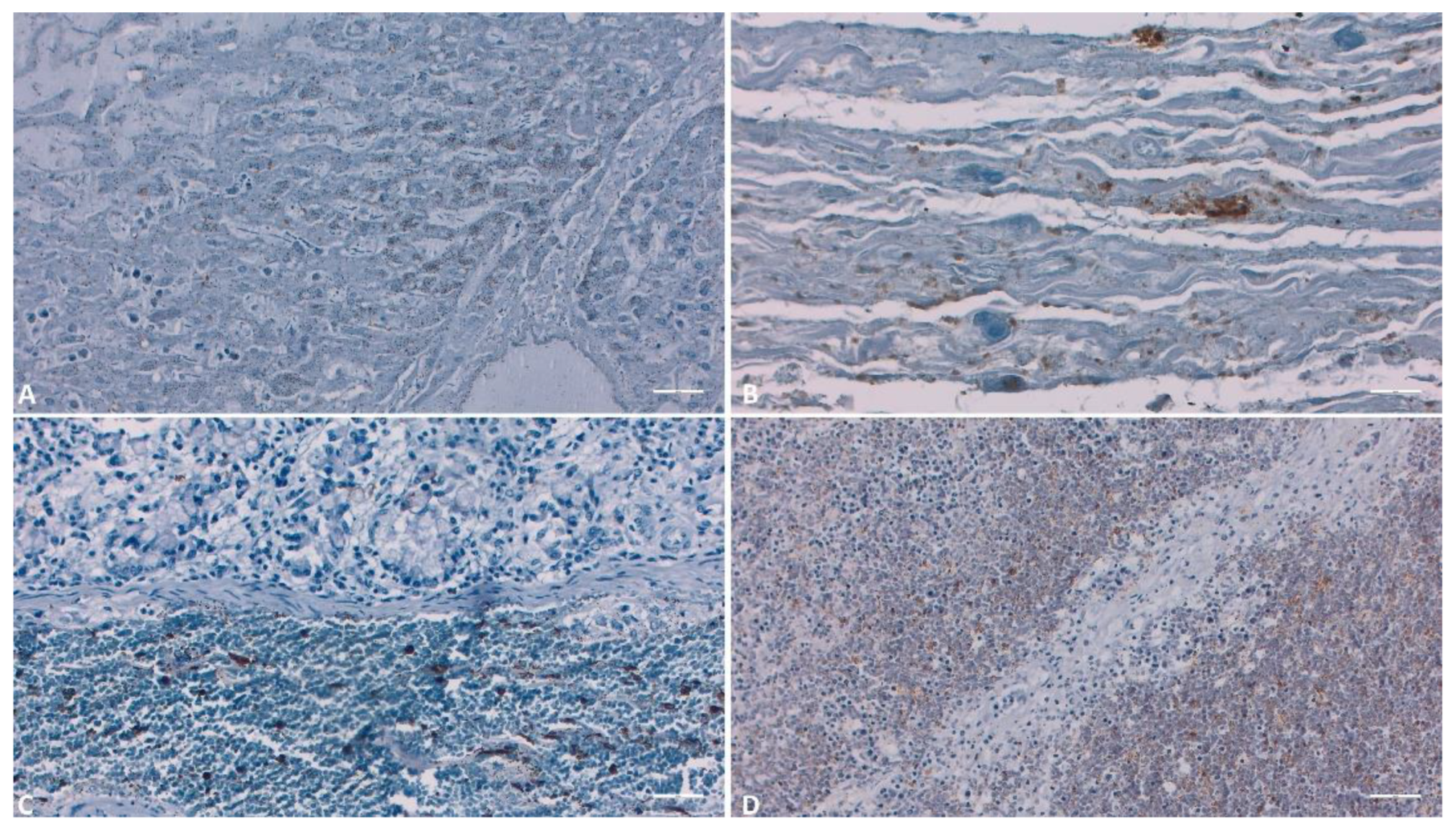
3.1.2. Liver
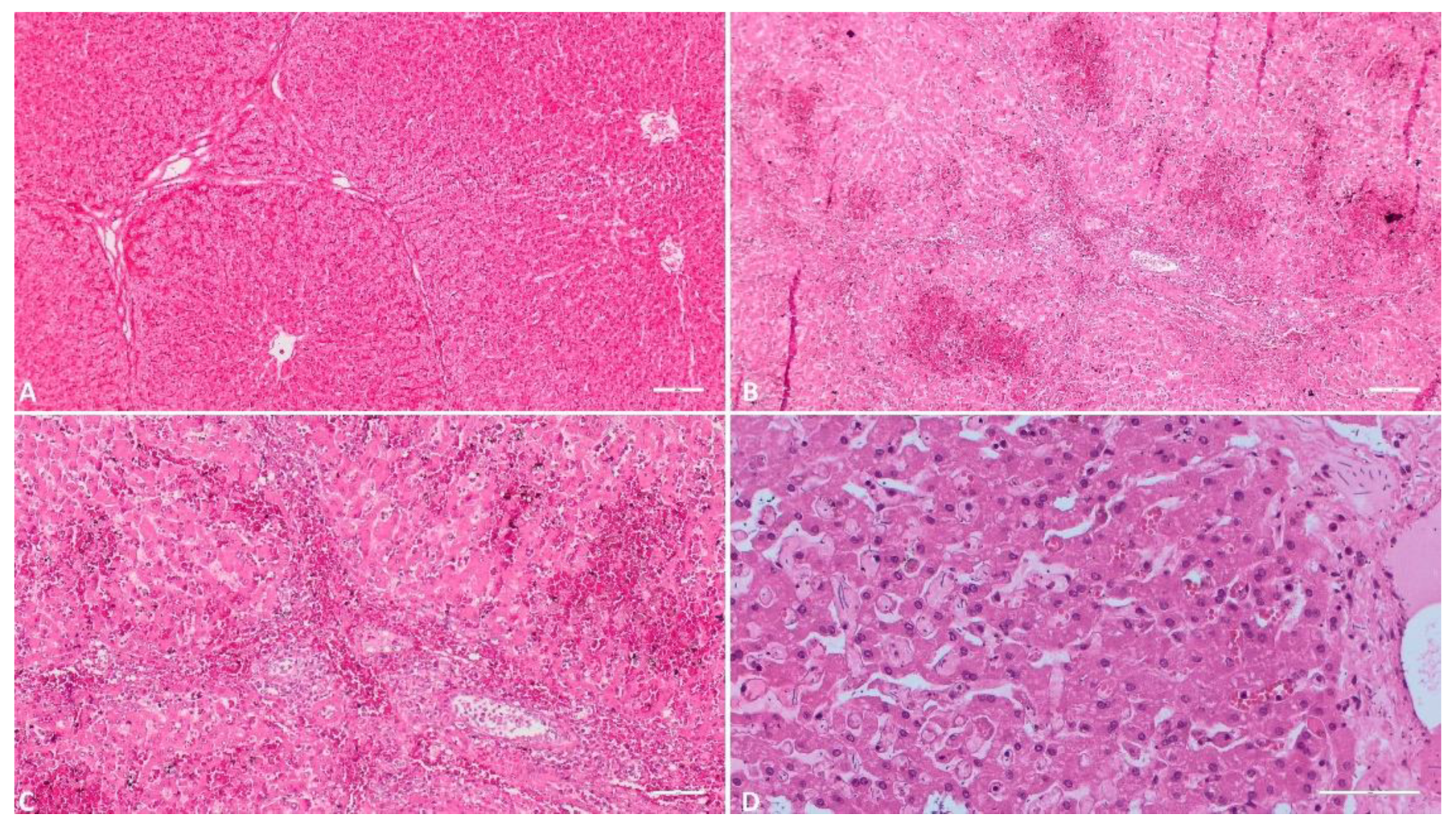
3.1.3. Gallbladder
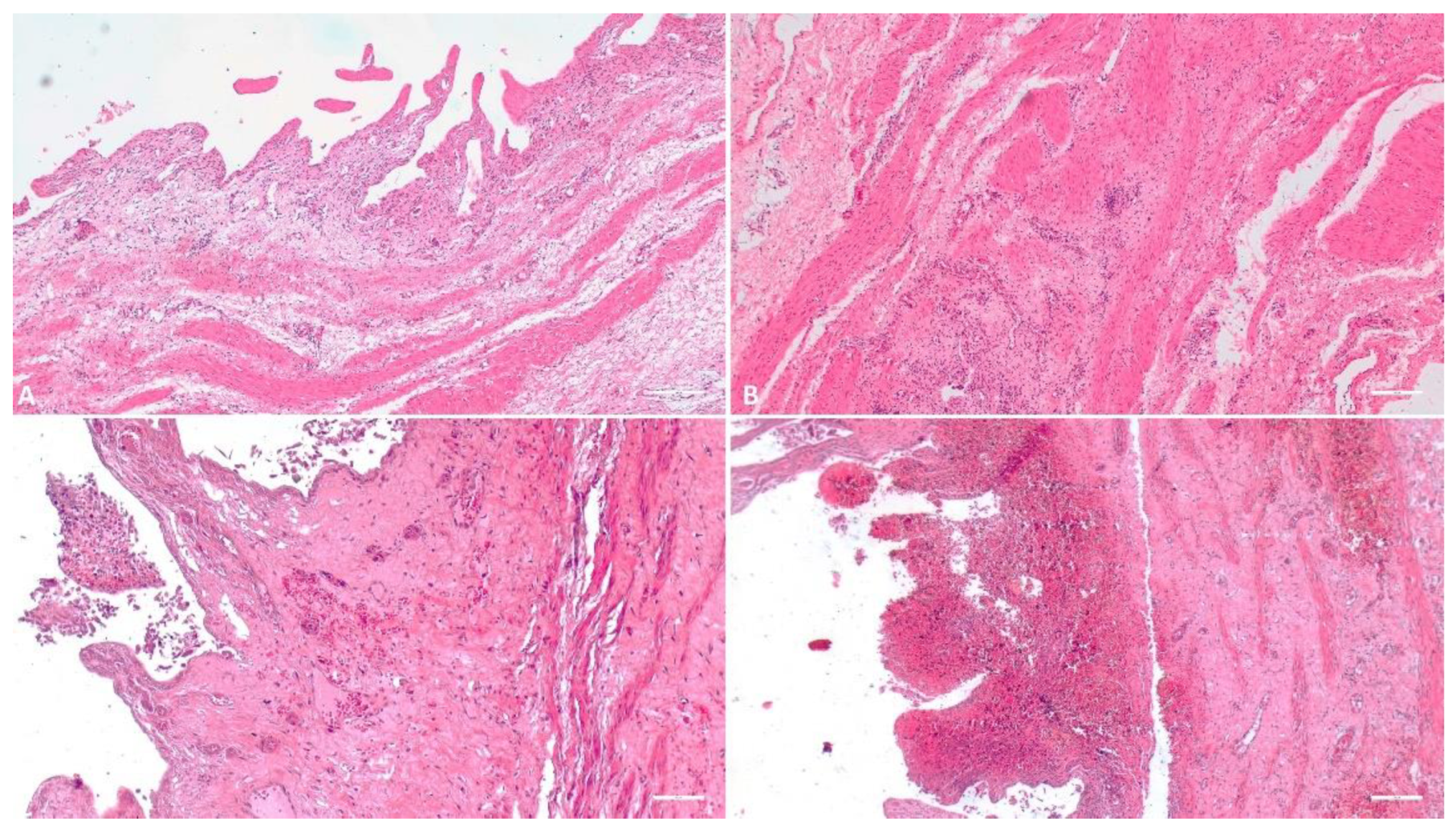
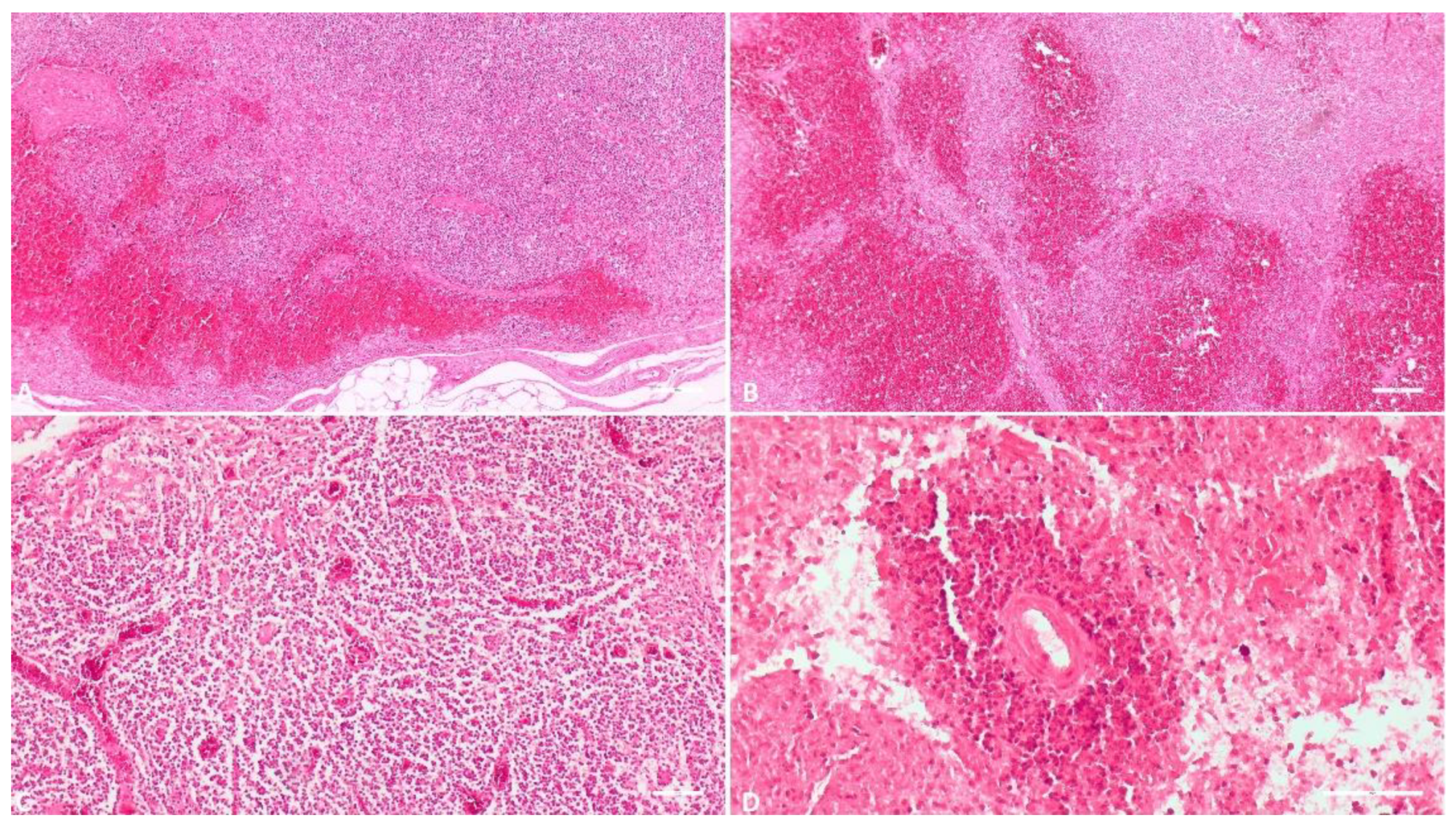
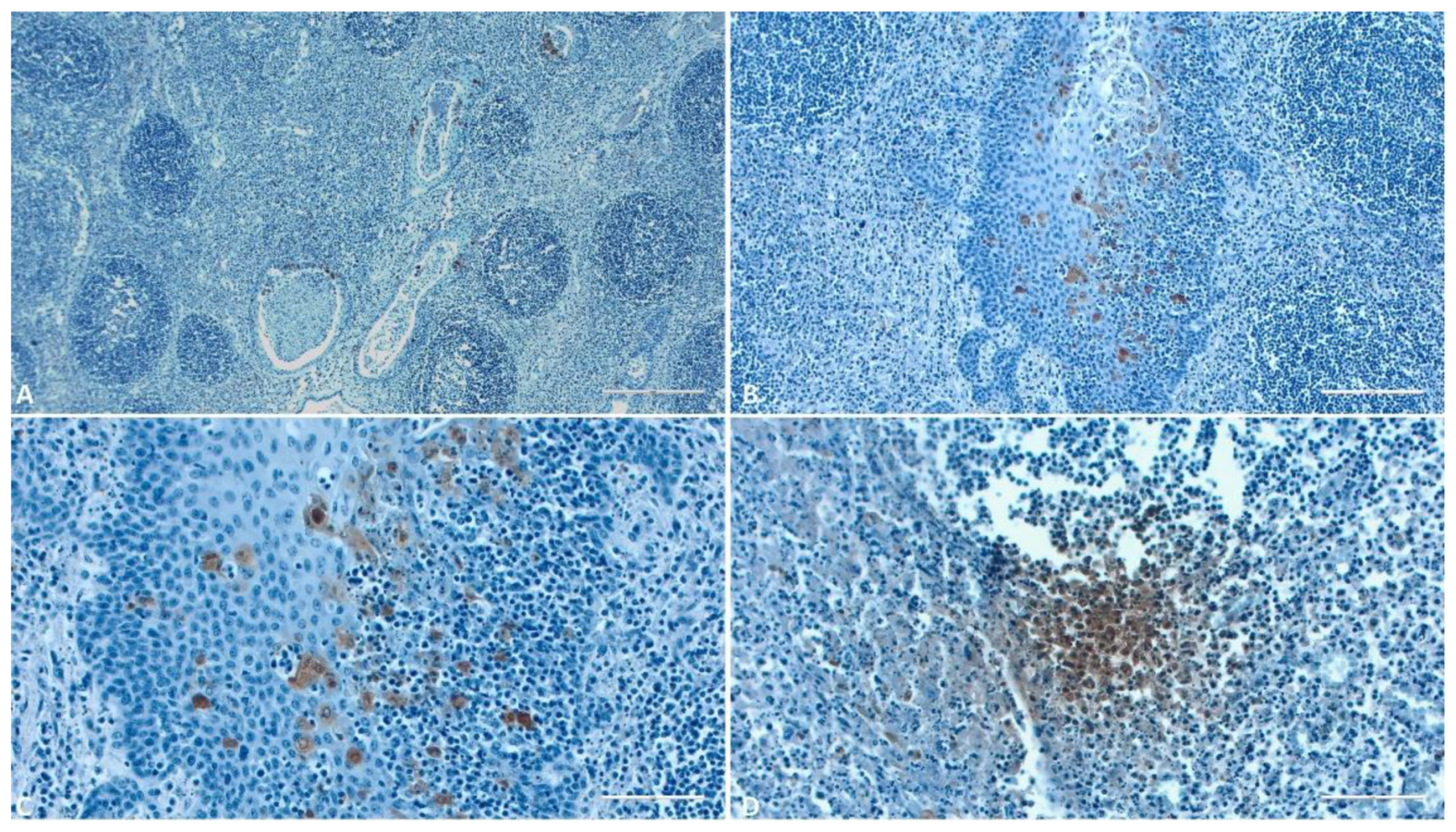
3.1.4. Spleen
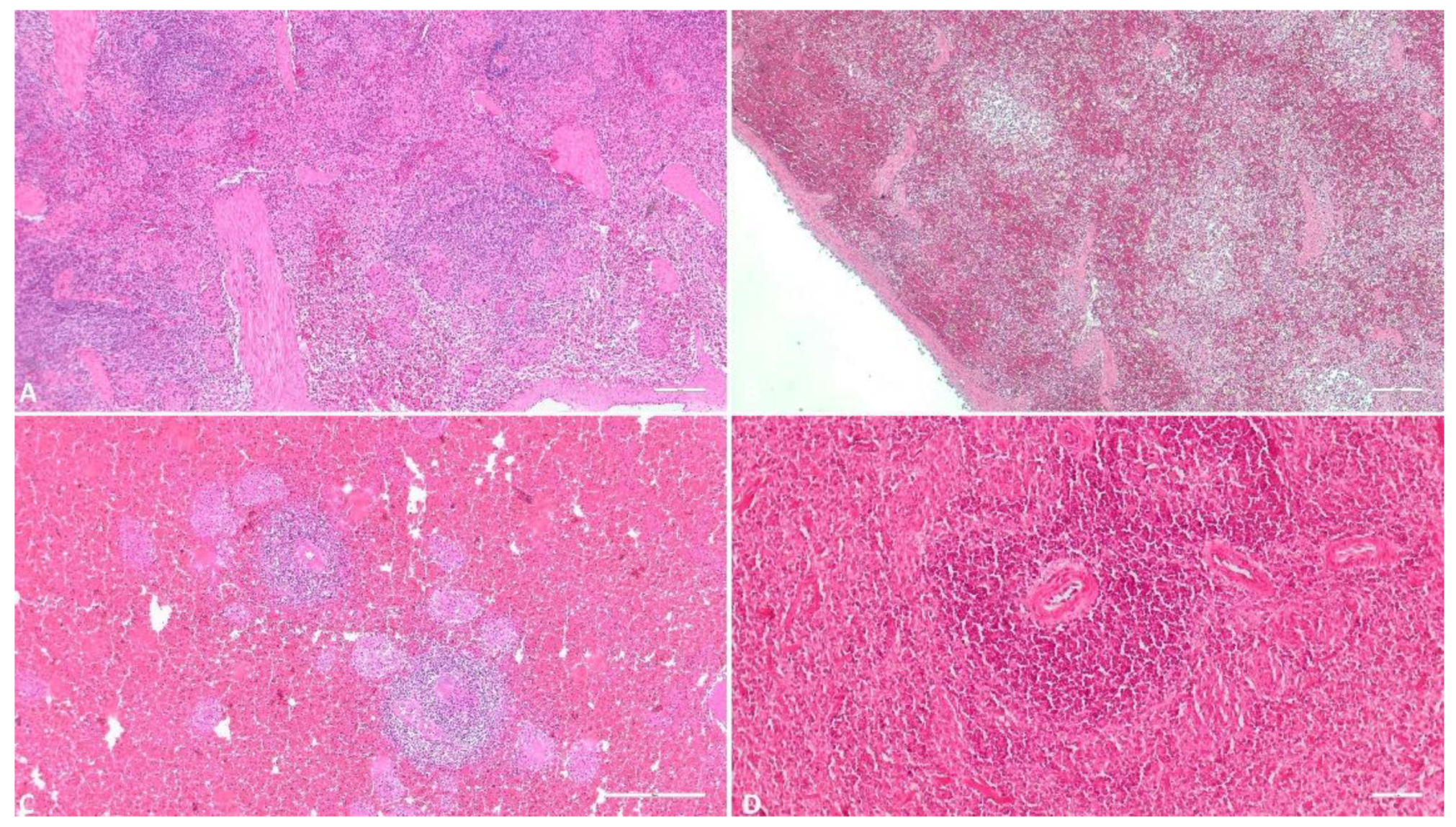
3.1.5. Lymph Node
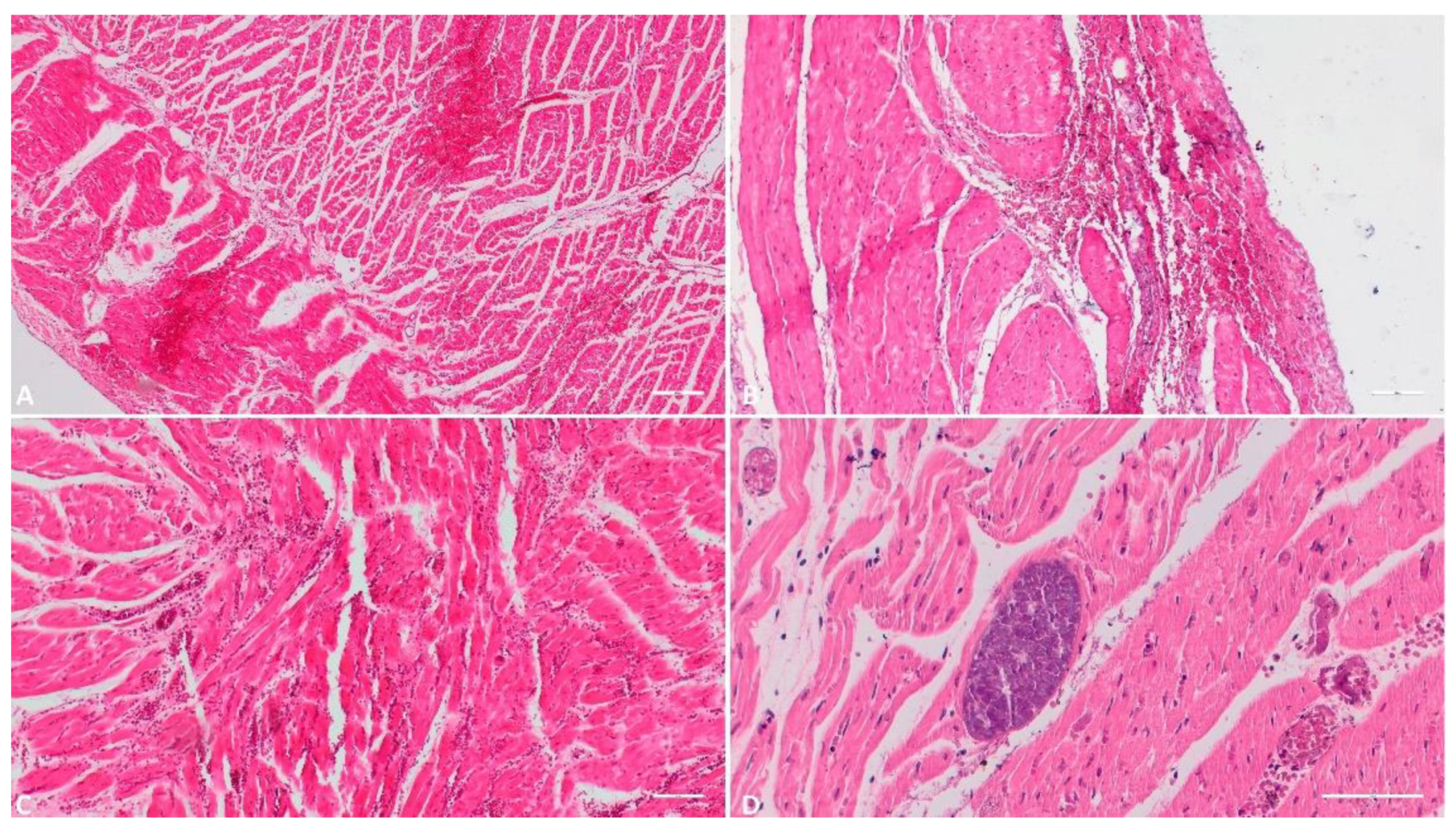
3.1.6. Heart
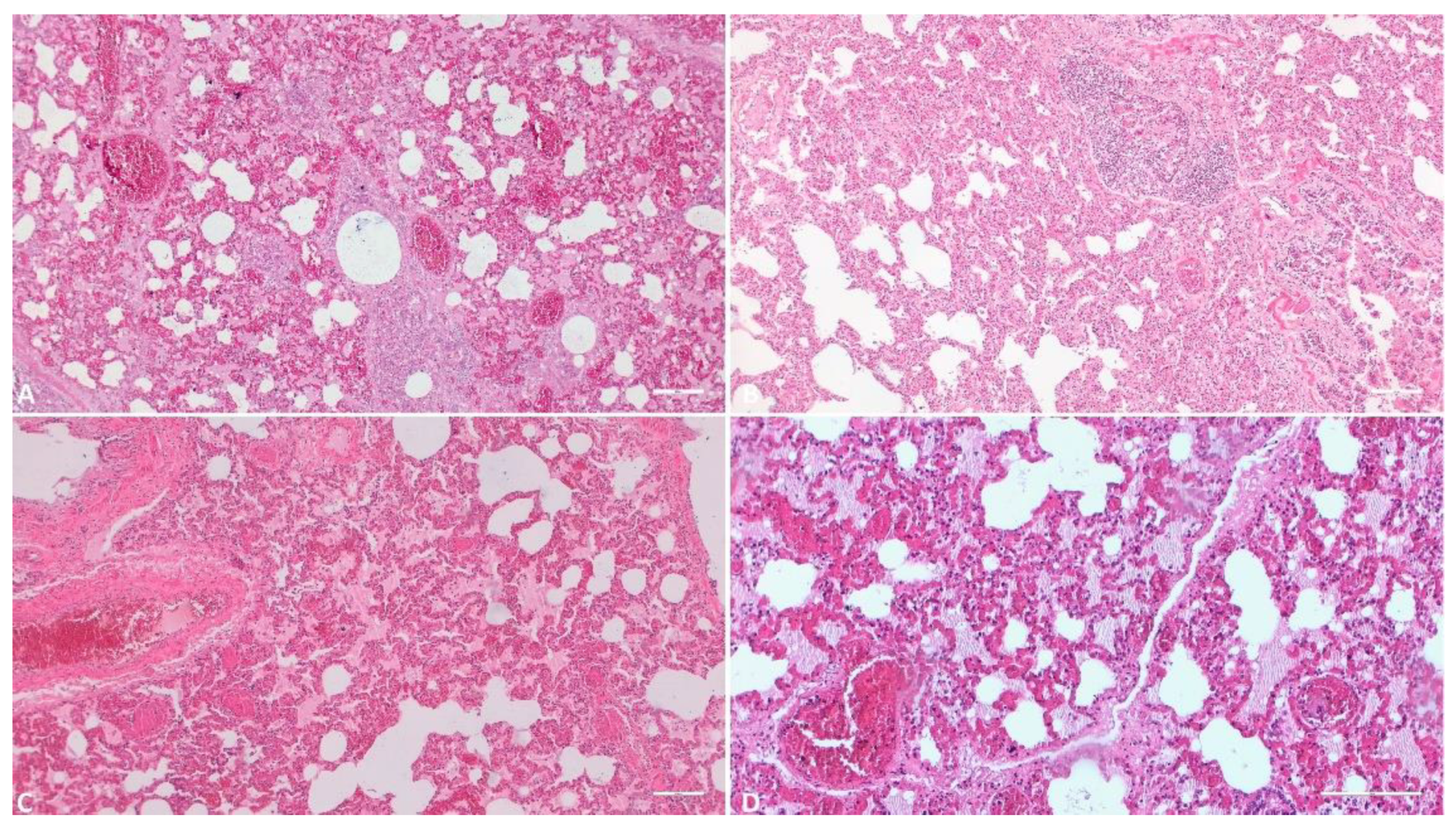
3.1.7. Lung
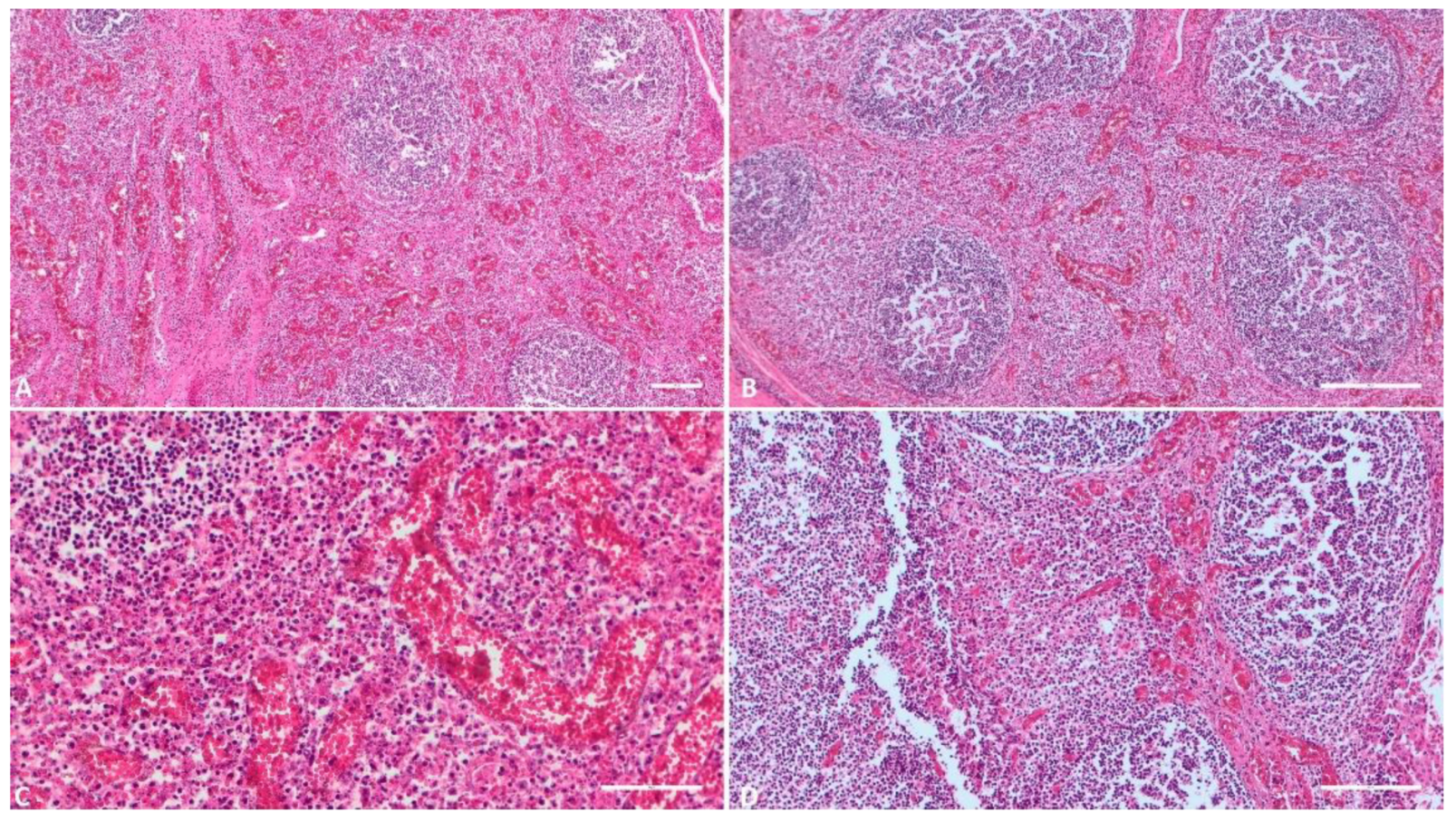
3.1.8. Tonsil
3.2. IHC
4. Discussion
4.1. Histology
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BERGMANN, H.; SCHULZ, K.; CONRATHS, F.J.; SAUTER-LOUIS, C., 2021. A Review of Environmental Risk Factors for African Swine Fever in European Wild Boar. Animals, 11, 2692. [CrossRef]
- MAZUR-PANASIUK, N., ŻMUDZKI, J., & WOŹNIAKOWSKI, G., 2019. African swine fever virus – persistence in different environmental conditions and the possibility of its indirect transmission. Journal of Veterinary Research, 63(3), 303-310. [CrossRef]
- BLOME, S., FRANZKE, K., & BEER, M., 2020. African swine fever – A review of current knowledge. Virus Research, 287, 198099. [CrossRef]
- FISCHER, M.; HÜHR, J.; BLOME, S.; CONRATHS, F.J.; PROBST, C., 2020. Stability of African Swine Fever Virus in Carcasses of Domestic Pigs and Wild Boar Experimentally Infected with the ASFV “Estonia 2014” Isolate. Viruses, 12, 1118. [CrossRef]
- BELLINI, S.; CASADEI, G.; DE LORENZI, G.; TAMBA, M., 2021. A Review of Risk Factors of African Swine Fever Incursion in Pig Farming within the European Union Scenario. Pathogens, 10, 84. [CrossRef]
- MONTGOMERY, R.E., 1921. On A Form of Swine Fever Occurring in British East Africa (Kenya Colony). J. Comp. Pathol. Ther., 34, 159–191. [CrossRef]
- SAUTER-LOUIS, C.; CONRATHS, F.J.; PROBST, C.; BLOHM, U.; SCHULZ, K.; SEHL, J.; FISCHER, M.; FORTH, J.H.; ZANI, L.; DEPNER, K.; ET AL., 2021. African Swine Fever in Wild Boar in Europe—A Review. Viruses, 13, 1717. [CrossRef]
- BOKLUND, A.; CAY, B.; DEPNER, K.; FÖLDI, Z.; GUBERTI, V.; MASIULIS, M.; MITEVA, A.; MORE, S.; OLSEVSKIS, E.; ŠATRÁN, P.; ET AL., 2018. Epidemiological analyses of African swine fever in the European Union (November 2017 until November 2018). EFSA J., 16, e05494. [CrossRef]
- Ungur, A.; Cazan, C.D.; Panait, L.C.; Taulescu, M.; Balmoș, O.M.; Mihaiu, M.; Bărbuceanu, F.; Mihalca, A.D.; Cătoi, C. Genotyping of African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV) Isolates in Romania with the First Report of Genotype II in Symptomatic Pigs. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 290. [CrossRef]
- SALMAN, M., 2009. The role of veterinary epidemiology in combating infectious animal diseases on a global scale: The impact of training and outreach programs. Prev. Vet. Med., 92, 284–287. [CrossRef]
- VILTROP, A.; REIMUS, K.; NIINE, T.; MÕTUS, K., 2021. Biosecurity Levels and Farm Characteristics of African Swine Fever Outbreak and Unaffected Farms in Estonia—What Can Be Learned from Them? Animals, 12, 68. [CrossRef]
- Ungur, A.; Cazan, C.D.; Panait, L.-C.; Coroian, M.; Cătoi, C. What Is the Real Influence of Climatic and Environmental Factors in the Outbreaks of African Swine Fever? Animals 2022, 12, 781. [CrossRef]
- GALLARDO, M.C., REOYO, A.D.L.T., FERNÁNDEZ-PINERO, J. ET AL., 2015. African swine fever: a global view of the current challenge. Porc Health Manag 1, 21. [CrossRef]
- OURA C.A.L., L. EDWARDS, C.A. BATTEN., 2013. Virological diagnosis of African swine fever—Comparative study of available tests, Virus Research 1., 173., 150-158. [CrossRef]
- GALLARDO, C., FERNÁNDEZ-PINERO, J., & ARIAS, M., 2019. African swine fever (ASF) diagnosis, an essential tool in the epidemiological investigation. Virus Research, 271, 197676. [CrossRef]
- OURA CA, POWELL PP, PARKHOUSE RM., 1998. African swine fever: a disease characterized by apoptosis. J Gen Virol. 79 (Pt 6):1427–38. [CrossRef]
- PÉREZ, J., RODRÍGUEZ, F., FERNÁNDEZ, A., DE LAS MULAS, J.M., GÓMEZ-VILLAMANDOS, J.C., SIERRA, M.A., 1994. Detection of African swine fever virus protein VP73 in tissues of experimentally and naturally infected pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 6, 360–365. [CrossRef]
- MOULTON J. E., PAN I. C., HESS W. R., DEBOER C. J., TESSLER J., 1975. Pathologic features of chronic pneumonia in pigs with experimentally induced African swine fever. American Journal of Veterinary Research 36(1):27-32.
- RUIZ-GONZALVO F., CARNERO M.E., BRUYEL V., 1981. Immunological responses of pigs to partially attenuated African swine fever virus and their resistance to virulent homologous and heterologous viruses. Wilkinson P.J., pp. 206–216.
- CARRASCO L, DE LARA FC, MARTIN DE LAS MULAS J, GOMEZ-VILLAMANDOS JC, PEREZ J, WILKINSON PJ, ET AL. 1996. Apoptosis in lymph nodes in acute African swine fever. J Comp Pathol. 115:415–28. [CrossRef]
- CARRASCO L, BAUTISTA MJ, GOMEZ-VILLAMANDOS JC, MARTIN DE LAS MULAS J, CHACON LF, WILKINSON PJ, ET AL., 1997. Development of microscopic lesions in splenic cords of pigs infected with African swine fever virus. Vet Res., 28:93–9.
- CARRASCO L, CHACON LF, MARTIN DE LAS MULAS J, GOMEZ-VILLAMANDOS JC, SIERRA MA, VILLEDA CJ, ET AL., 1997. Ultrastructural changes related to the lymph node haemorrhages in acute African swine fever. Res Vet Sci. 62:199–204. [CrossRef]
- SALGUERO FJ, SANCHEZ-CORDON PJ, NUNEZ A, FERNANDEZ DE MARCO M, GOMEZ-VILLAMANDOS JC., 2005. Proinflammatory cytokines induce lymphocyte apoptosis in acute African swine fever infection. J Comp Pathol. 132:289–302. [CrossRef]
- Horter, D.C., Yoon, K.J., Zimmerman, J.J., 2003. A review of porcine tonsils in immunity and disease. Animal Health Research Reviews 4, 143–155. [CrossRef]
- IZZATI UZ, INANAGA M, HOA NT, NUEANGPHUET P, MYINT O, TRUONG QL, ET AL., 2021. Pathological investigation and viral antigen distribution of emerging African swine fever in Vietnam. Transbound Emerg Dis. 68:2039–50. [CrossRef]
- SALGUERO FJ, RUIZ-VILLAMOR E, BAUTISTA MJ, SANCHEZ-CORDON PJ, CARRASCO L, GOMEZ-VILLAMANDOS JC., 2002. Changes in macrophages in spleen and lymph nodes during acute African swine fever: expression of cytokines. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 90:11–22. [CrossRef]
- GOMEZ-VILLAMANDOS JC, CARRASCO L, BAUTISTA MJ, SIERRA MA, QUEZADA M, HERVAS J, ET AL. 2003. African swine fever and classical swine fever: a review of the pathogenesis. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 110:165–9.
- FERNANDEZ DE MARCO M, SALGUERO FJ, BAUTISTA MJ, NUNEZ A, SANCHEZ-CORDON PJ, GOMEZ-VILLAMANDOS JC., 2007. An immunehistochemical study of the tonsils in pigs with acute African swine fever virus infection. Res Vet Sci. 83:198–203. [CrossRef]
- JAMBALANG, A. R., OGO, N. I., AGADA, G., OWOLODUN, O., & KUMBISH, P., 2016. Detection of African Swine Fever Virus by Histopathology and Transmission Electron Microscopy. Nigerian Veterinary Journal, 35(4).
- LINDEN, A.; LICOPPE, A.; VOLPE, R.; PATERNOSTRE, J.; LESENFANT, S.C.; CASSART, D.; GARIGLIANY, M.; TIGNON, M.; VAN DEN BERG, T.; DESMECHT, D.; ET AL., 2019. African swine fever virus hits north-western Europe. Transbound. Emerg. Dis., 66, 54–55.
- PIKALO J., ZANI L., HÜHR J., BEER M., BLOME S., 2019. Pathogenesis of African swine fever in domestic pigs and European wild boar – Lessons learned from recent animal trials. Virus Research 271:197614, 8 p. [CrossRef]
- NGA BT, TRAN ANH DAO B, NGUYEN THI L, OSAKI M, KAWASHIMA K, SONG D, SALGUERO FJ, LE VP., 2020. Clinical and pathological study of the first outbreak cases of African swine fever in Vietnam, 2019. Frontiers in Veterinary Science. Jul 8; 7:392. [CrossRef]
- TIZHE EV, LUKA PD, ADEDEJI AJ, TANKO P, GURUMYEN GY, BUBA DM, TIZHE UD, BITRUS AA, ORAGWA AO, SHAIBU SJ, UNANAM ES., 2021. Laboratory diagnosis of a new outbreak of acute African swine fever in smallholder pig farms in Jos, Nigeria. Veterinary Medicine and Science. May;7(3):705-13. [CrossRef]
- SÁNCHEZ-CORDÓN PJ, FLOYD T, HICKS D, CROOKE HR, MCCLEARY S, MCCARTHY RR, STRONG R, DIXON LK, NEIMANIS A, WIKSTRÖM-LASSA E, GAVIER-WIDÉN D., 2021. Evaluation of lesions and viral antigen distribution in domestic pigs inoculated intranasally with African swine fever virus Ken05/Tk1 (genotype X). Pathogens. Jun 18;10(6):768. [CrossRef]
- FERNÁNDEZ, A., PEREZ, J., CARRASCO, L., SIERRA, M.A., SANCHEZ-VIZCAINO, M., JOVER, A., 1992. Detection of African swine fever viral antigens in paraffin-embedded tissues by use of immunohistologic methods and polyclonal antibodies. Am. J. Vet. Res. 53, 1462–1467. [CrossRef]
- PÉREZ, J., FERNÁNDEZ, I., SIERRA, M.A., HERRÁEZ, P., FERNÁNDEZ, A., DE LAS MULAS, J.M., 1998. Serological and immunohistochemical study of African swine fever in wild boar in Spain. Vet. Rec. 143, 136–139. [CrossRef]
- SZEREDI L, BAKCSA E, ZÁDORI Z, MÉSZÁROS I, OLASZ F, BÁLINT Á, LOCSMÁNDI G, ERDÉLYI K., 2020. Detection of African swine fever virus in cell culture and wild boar tissues using a commercially available monoclonal antibody. Journal of Virological Methods. Aug 1; 282:113886. [CrossRef]
- GREGG, D.A., MEBUS, C.A., SCHLAFER, D.H., 1995. A comparison of three avidin-biotin complex immunoenzyme systems for detection of African swine fever virus antigen in paraffin-embedded tissues. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 7, 17–22. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




