Submitted:
22 November 2023
Posted:
23 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Creation
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Definitions
2.4. Article Screening Process
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Article Quality Grading
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
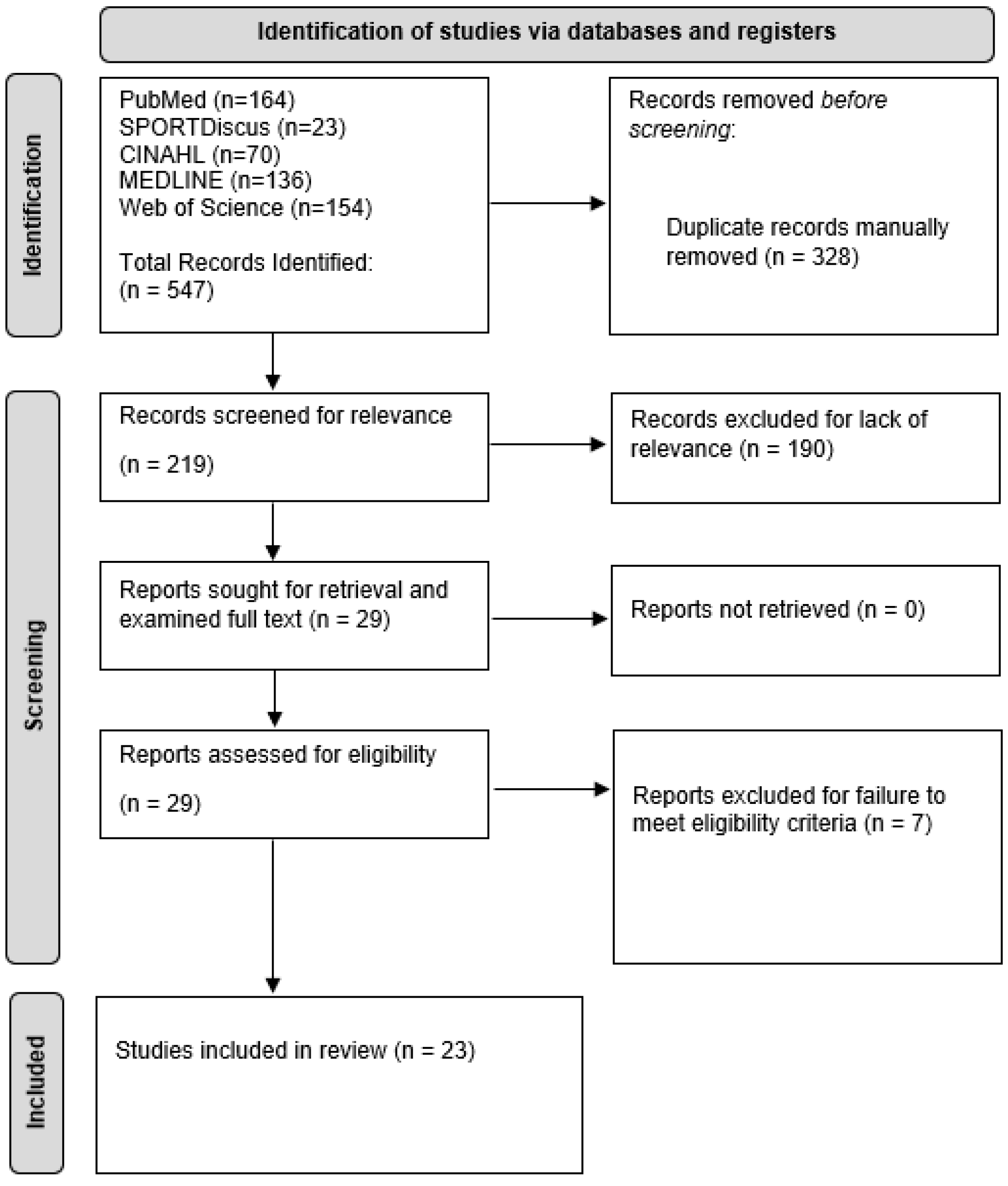
3.1. Initial Study Results
3.2. Article Quality Results
3.3. General Patient Demographics
3.4. Severity of Hallux Valgus by Imaging
3.5. Midfoot Instability via Intermetatarsal Angle
3.6. Midfoot Instability via Tarsometatarsal angle
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MANN, R.A. and M.J. COUGHLIN, Hallux valgus—etiology, anatomy, treatment and surgical considerations. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research®, 1981. 157: p. 31-41.
- Coughlin, M., Juvenile hallux valgus. Surgery of the Foot and Ankle, 1999.
- Perera, A., L. Mason, and M. Stephens, The pathogenesis of hallux valgus. JBJS, 2011. 93(17): p. 1650-1661. [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, M.J., Instructional course lectures, The American academy of orthopaedic surgeons-hallux valgus. JBJS, 1996. 78(6): p. 932-66.
- Coughlin, M.J., Hallux valgus: causes, evaluation, and treatment. Postgraduate medicine, 1984. 75(5): p. 174-187.
- Hardy, R. and J. Clapham, Hallux valgus predisposing anatomical causes. The Lancet, 1952. 259(6720): p. 1180-1183. [CrossRef]
- Hardy, R. and J. Clapham, Observations on hallux valgus. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery British Volume, 1951. 33(3): p. 376-391.
- Hawkins, F., C.L. Mitchell, and D.W. Hedrick, Correction of hallux valgus by metatarsal osteotomy. JBJS, 1945. 27(3): p. 387-394.
- Jones, C.P., et al., The validity and reliability of the Klaue device. Foot & ankle international, 2005. 26(11): p. 951-956. [CrossRef]
- Hansen Jr, S., Hallux valgus surgery. Morton and Lapidus were right! Clinics in podiatric medicine and surgery, 1996. 13(3): p. 347-354.
- Hofbauer, M. and J. Grossman, The Lapidus procedure. Clinics in podiatric medicine and surgery, 1996. 13(3): p. 485-496.
- Johnson, K. and T. Kile, Hallux valgus due to cuneiform-metatarsal instability. Journal of the Southern Orthopaedic Association, 1994. 3(4): p. 273-282.
- Myerson, M., Metatarsocuneiform arthrodesis for treatment of hallux valgus and metatarsus primus varus. 1990, SLACK Incorporated Thorofare, NJ. p. 1025-1031. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y., et al., Multiplanar instability of the first tarsometatarsal joint in hallux valgus and hallux rigidus patients: a case–control study. International Orthopaedics, 2022. 46(2): p. 255-263. [CrossRef]
- Brage, M.E., J.R. Holmes, and B.J. Sangeorzan, The influence of x-ray orientation on the first metatarsocuneiform joint angle. Foot & ankle international, 1994. 15(9): p. 495-497. [CrossRef]
- Nix, S., M. Smith, and B. Vicenzino, Prevalence of hallux valgus in the general population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of foot and ankle research, 2010. 3: p. 1-9. [CrossRef]
- MANN, R.A., M.J. COUGHLIN, and H.L. DUVRIES, Hallux rigidus: a review of the literature and a method of treatment. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research®, 1979(142): p. 57-63.
- Barg, A., et al., Unfavorable outcomes following surgical treatment of hallux valgus deformity: a systematic literature review. The Journal of Bone and Joint surgery. American Volume, 2018. 100(18): p. 1563.
- Page, M.J., et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. International journal of surgery, 2021. 88: p. 105906.
- Ouzzani, M., et al., Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Systematic reviews, 2016. 5: p. 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Slim, K., et al., Methodological index for non-randomized studies (MINORS): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ journal of surgery, 2003. 73(9): p. 712-716. [CrossRef]
- Javed, A., et al., PREVALENCE OF HALLUX VALGUX DEFORMITY IN ADULTS.
- Conti, M.S., et al., Association of first metatarsal pronation correction with patient-reported outcomes and recurrence rates in hallux valgus. Foot & Ankle International, 2022. 43(3): p. 309-320. [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.S., et al., Effect of the modified Lapidus procedure on pronation of the first ray in hallux valgus. Foot & Ankle International, 2020. 41(2): p. 125-132. [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, M.J. and C.P. Jones, Hallux valgus: demographics, etiology, and radiographic assessment. Foot & ankle international, 2007. 28(7): p. 759-777. [CrossRef]
- Faber, F.W., et al., Mobility of the first tarsometatarsal joint in hallux valgus patients: a radiographic analysis. Foot & ankle international, 2001. 22(12): p. 965-969. [CrossRef]
- Greeff, W., et al., Radiographic assessment of relative first metatarsal length following modified lapidus procedure. Foot & Ankle International, 2020. 41(8): p. 972-977. [CrossRef]
- Ji, L., et al., The role of first tarsometatarsal joint morphology and instability in the etiology of hallux valgus: a case-control study. Foot & Ankle International, 2023. 44(8): p. 778-787. [CrossRef]
- Kernozek, T.W. and S.A. Sterriker, Chevron (Austin) distal metatarsal osteotomy for hallux valgus: comparison of pre-and post-surgical characteristics. Foot & ankle international, 2002. 23(6): p. 503-508. [CrossRef]
- King, D.M. and B.C. Toolan, Associated deformities and hypermobility in hallux valgus: an investigation with weightbearing radiographs. Foot & ankle international, 2004. 25(4): p. 251-255. [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.J., et al., The modified Lapidus procedure for hallux valgus: a clinical and radiographic analysis. Foot & ankle international, 2005. 26(11): p. 913-917. [CrossRef]
- Lalevée, M., et al., Coronal Plane Rotation of the Medial Column in Hallux Valgus: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Foot & Ankle International, 2022. 43(8): p. 1041-1048. [CrossRef]
- Ahuero, J.S., J.S. Kirchner, and P.M. Ryan, Medial Cuneiform Opening-Wedge Osteotomy for the Treatment of Hallux Valgus. Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics, 2019. 4(1): p. 2473011418813318. [CrossRef]
- Shelton, T.J., et al., The influence of percentage weight-bearing on foot radiographs. Foot & Ankle Specialist, 2019. 12(4): p. 363-369. [CrossRef]
- Ferreyra, M., et al., Can we correct first metatarsal rotation and sesamoid position with the 3D Lapidus procedure? Foot and Ankle Surgery, 2022. 28(3): p. 313-318.
- Ozturk, A.M., et al., Three-dimensional printed anatomical models help in correcting foot alignment in hallux valgus deformities. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics, 2020. 54: p. 199-209. [CrossRef]
- Manceron, A., et al., Correlation between first tarsometatarsal joint mobility and hallux valgus severity. International Orthopaedics, 2022. 46(4): p. 855-859. [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T., et al., Evaluation of first-ray mobility in patients with hallux valgus using weight-bearing CT and a 3-D analysis system: a comparison with normal feet. JBJS, 2017. 99(3): p. 247-255.
- Dayton, P., et al., Comparison of radiographic measurements before and after triplane tarsometatarsal arthrodesis for hallux valgus. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 2020. 59(2): p. 291-297. [CrossRef]
- Naguib, S., B. Derner, and A.J. Meyr, Evaluation of the mechanical axis of the first ray before and after first metatarsal-phalangeal joint reconstructive surgery. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 2018. 57(6): p. 1140-1142. [CrossRef]
- Oravakangas, R., et al., Proximal opening wedge osteotomy provides satisfactory midterm results with a low complication rate. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 2016. 55(3): p. 456-460. [CrossRef]
- Randich, J.R., et al., Frontal plane rotation of the first Ray in hallux valgus using standing computerized tomography (CT). The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 2021. 60(3): p. 489-493. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.M. and C.F. Hyer, Maintenance of Correction of the Modified Lapidus Procedure With a First Metatarsal to Second Metatarsal Screw With “Spot Weld” Technique: A Retrospective and Radiographic Analysis. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Klemola, T., et al., First Tarsometatarsal Joint Derotational Arthrodesis for Flexible Hallux Valgus: Results from Follow-Up of 3–8 Years. Scandinavian Journal of Surgery, 2017. 106(4): p. 325-331. [CrossRef]
- Karasick, D. and K.L. Wapner, Hallux valgus deformity: preoperative radiologic assessment. AJR Am j Roentgenol, 1990. 155(1): p. 119-23. [CrossRef]
- Faber, F.W., et al., Mobility of the first tarsometatarsal joint in relation to hallux valgus deformity: anatomical and biomechanical aspects. Foot & ankle international, 1999. 20(10): p. 651-656. [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho, K.A.M., et al., Comparison between Weightbearing-CT semiautomatic and manual measurements in Hallux Valgus. Foot and Ankle Surgery, 2022. 28(4): p. 518-525.
- Mahmoud, K., et al., The role of weightbearing computed tomography scan in hallux valgus. Foot & Ankle International, 2021. 42(3): p. 287-293. [CrossRef]
- Najefi, A.-A., et al., Imaging findings and first metatarsal rotation in hallux valgus. Foot & Ankle International, 2022. 43(5): p. 665-675. [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, M.J. and E. Freund, The reliability of angular measurements in hallux valgus deformities. Foot & ankle international, 2001. 22(5): p. 369-379. [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y., et al., A new measure of tibial sesamoid position in hallux valgus in relation to the coronal rotation of the first metatarsal in CT scans. Foot & ankle international, 2015. 36(8): p. 944-952. [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, N., et al., Factors associated with early loss of hallux valgus correction. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 2018. 57(2): p. 236-240. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, P., et al., Validity and reliability of a new radiological method to estimate medial column internal rotation in hallux valgus using foot weight-bearing x-ray. Foot & Ankle Specialist, 2021: p. 19386400211029162. [CrossRef]
- Lintz, F., et al., Three-Dimensional Weightbearing Assessment of the First Ray in Hallux Valgus: A Case-Control Study. Foot & Ankle Orthopaedics, 2019. 4(4): p. 2473011419S00050. [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.J., et al., Multicenter early radiographic outcomes of triplanar tarsometatarsal arthrodesis with early weightbearing. Foot & ankle international, 2019. 40(8): p. 955-960. [CrossRef]
- Dayton, P., M. Kauwe, and M. Feilmeier, Is our current paradigm for evaluation and management of the bunion deformity flawed? A discussion of procedure philosophy relative to anatomy. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 2015. 54(1): p. 102-111. [CrossRef]
- Mashima, N., et al., Correction of hallux valgus deformity using the center of rotation of angulation method. Journal of Orthopaedic Science, 2009. 14(4): p. 377-384. [CrossRef]
- Mortier, J.-P., J.-L. Bernard, and M. Maestro, Axial rotation of the first metatarsal head in a normal population and hallux valgus patients. Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research, 2012. 98(6): p. 677-683. [CrossRef]
- Paley, D., et al., Deformity planning for frontal and sagittal plane corrective osteotomies. Orthopedic Clinics of North America, 1994. 25(3): p. 425-466. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y., et al., Radiographic analysis of hallux valgus. A two-dimensional coordinate system. JBJS, 1995. 77(2): p. 205-213. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E., C. Ortiz, and P. Wagner, Using the center of rotation of angulation concept in hallux valgus correction: why do we choose the proximal oblique sliding closing wedge osteotomy? Foot and Ankle Clinics, 2018. 23(2): p. 247-256.
- Watanabe, K., et al., Three-dimensional analysis of tarsal bone response to axial loading in patients with hallux valgus and normal feet. Clinical Biomechanics, 2017. 42: p. 65-69. [CrossRef]
| Author (Year) | Study Type | Total MINORS Score | Clearly stated aim | Inclusion of consecutive patients | Prospective collection of data | End points appropriate to study aim | Unbiased assessment of study end point | Follow-up period appropriate to study aim | Less than 5% lost to follow up | Prospective calculation of the study size | Adequate control group | Contemporary groups | Baseline equivalence of groups | Adequate statistical analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conti (2020) | Non-comparative | 10 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| King (2004) | Comparative | 15 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Ferreyra (2022) | Non-comparative | 8 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Kernozek (2002) | Non-comparative | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Dayton (2020) | Non-comparative | 9 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Lalevée (2022) | Comparative | 16 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Manceron (2022) | Non-comparative | 8 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Conti (2022) | Non-comparative | 12 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | - | - | - | - |
| Kimura (2017) | Comparative | 20 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Naguib (2018) | Non-comparative | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Klemola (2017) | Non-comparative | 7 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Randich (2021) | Comparative | 16 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Coughlin (2007) | Non-comparative | 10 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Thompson (2023) | Non-comparative | 9 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Ahuero (2019) | Non-comparative | 12 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Faber (2001) | Non-comparative | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Lee (2022) | Comparative | 14 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| Oravakangas (2016) | Non-comparative | 8 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Greeff (2020) | Non-comparative | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Almaawi (2021) | Non-comparative | 9 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Kopp (2005) | Non-comparative | 8 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Ji (2023) | Comparative | 16 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Ozturk (2020) | Non-comparative | 8 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| Author (year) | Study type | Treatment group | Patients (n) | Feet (n) | Mean age (standard deviation) (range) | Imaging Modality | HVA (AP) | HVA (lateral) | HVA (axial) | HVA (sagittal) | HVA (frontal) | DMAA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conti (2020) | Retrospective | HV | 31 | 31 | 51.2 (29–67) | WBCT | - | - | - | 29.9 (17–47) | - | - |
| Lalevée (2022) | Retrospective | Healthy | 20 | 20 | 37.3 (16.5) | WBCT | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| HV | 22 | 22 | 40.1 (17.4) | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Kimura (2017) | Retrospective | Healthy | 10 | 10 | 56 (5) (50–66) | WBCT | - | - | - | 14.1 (2.8) | - | - |
| HV | 10 | 10 | 58 (14.2) (33–74) | - | - | - | 43.2 (10.1) | - | - | |||
| Randich (2021) | Retrospective | Healthy | 36 | 36 | 49.31 (12.71) | WBCT | - | - | - | - | 11.03 (6.56) | - |
| HV | 10 | 10 | 53.00 (19.35) | - | - | - | - | 28.66 (10.99) | - | |||
| Lee (2022) | Retrospective | Healthy | 30 | 30 | 42.97 (17.52) | WBCT | - | - | 7.52 (4.49) | - | - | - |
| HV | 27 | 30 | 54.20 (14.01) | - | - | 33.50 (9.47) | - | - | - | |||
| Ji (2023) | Retrospective | Healthy | - | 79 | 42 (32–51) | WBCT | - | - | 11.6 (10.1–14.0) | - | - | - |
| HV | - | 82 | 46 (37–55) | - | - | 30.4 (22.4–38.6) | - | - | - | |||
| Conti (2022) | Retrospective | HV | 39 | - | 51.5 (24.1–64.3) | WBRG | 33.2 (10.7) | - | - | - | - | - |
| WBCT | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||
| King (2004) | Prospective | Healthy | 15 | - | 36 (15) (18–62) | WBRG | 5 (3) | - | - | - | - | - |
| HV | 25 | - | 48 (17) (14–81) | 13 (7) | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Ferreyra (2022) | Retrospective | HV | 30 | 37 | 45.68 (15–76) | WBRG | 32.12 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Kernozek (2002) | Retrospective | HV | 25 | - | 43 (40–60) | WBRG | 31.7 (4.7) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Naguib (2018) | Retrospective | HV | - | 59 | - | WBRG | 11.59 (3.79) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Klemola (2017) | Retrospective | HV | 66 | 84 | 47.9 (10.2) | WBRG | 30.1 (7.0) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Coughlin (2007) | Retrospective | HV | 103 | 122 | 50 (22–78) | WBRG | 30 (20–53) | - | - | - | - | 10 (0–20) |
| Thompson (2023) | Retrospective | HV | 77 | 90 | 48.8 (16.2) | WBRG | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ahuero (2019) | Retrospective | HV | 13 | 14 | 56 (22–75) | WBRG | 32 (26.5–41) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Faber (2001) | Prospective | HV | 94 | 109 | 41.4 (15–63) | WBRG | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Oravakangas (2016) | Retrospective | HV | 20 | 23 | 50 (22–69) | WBRG | 38 (5) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Greeff (2020) | Retrospective | HV | 23 | 32 | 43 (20–68) | WBRG | 33 (16–46) | - | - | - | - | 16 (4–26) |
| Almaawi (2021) | Retrospective | HV | 89 | 100 | 40.7 | WBRG | 33.2 (8.0) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Kopp (2005) | Retrospective | HV | 29 | 34 | 54.2 (27–84) | WBRG | 33.6 (17–61) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ozturk (2020) | Prospective | HV | 10 | 10 | 59.3 (15.8)(25–72) | WBRG | 38.4 (6.5) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Manceron (2022) | Retrospective | HV | - | 20 | - | WBRG | 32 | - | - | - | - | - |
| HV | - | 20 | - | 34.2 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| HV | - | 9 | - | 37.9 | - | - | - | - | - | |||
| Dayton (2020) | Retrospective | HV | 108 | 109 | 33.9 (14.1) | WBRG | 22.9 (7.6) | - | - | - | - | 19.6 (9.2) |
| Author (Year) | Treatment Group | Patients | # Feet | IMT Angle (AP) | IMT Angle (Lateral) | IMT Angle (Axial) | IMT Angle (Sagittal) | IMT Angle (Frontal) | TMTAngle (AP) | TMTAngle (Lateral) | TMTAngle (Axial) | TMTAngle(Sagittal) | TMTAngle (Frontal) | Sagittal Lift (mm) | Meary’s Angle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conti (2020) | HV | 31 | 31 | - | - | - | 16.7 (10–25) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lalevée (2022) | Healthy | 20 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| HV | 22 | 22 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Kimura (2017) | Healthy | 10 | 10 | - | - | - | 9.3 (1.3) | - | - | - | - | 3.2 (1.3) | - | - | - |
| HV | 10 | 10 | - | - | - | 22.1 (4.1) | - | - | - | - | 6.5 (2.6) | - | - | - | |
| Randich (2021) | Healthy | 36 | 36 | - | - | - | - | 8.77 (2.45) | - | - | - | - | -1.28 (6.33) | - | - |
| HV | 10 | 10 | - | - | - | - | 16.45 (4.47) | - | - | - | - | -5.36 (6.28) | - | - | |
| Lee (2022) | Healthy | 30 | 30 | - | - | 9.46 (2.58) | - | - | - | - | - | 0.23 (0.42) | - | - | - |
| HV | 27 | 30 | - | - | 16.98 (5.27) | - | - | - | - | - | 1.15 (1.23) | - | - | - | |
| Ji (2023) | Healthy | - | 79 | - | - | 8.3 (7.8–8.7) | - | - | - | - | - | 0.9 (0.8–1.0) | - | - | - |
| HV | - | 82 | - | - | 14.8 (11.8–16.7) | - | - | - | - | - | 1.6 (1.6–2.1) | - | - | - | |
| Conti (2022) | HV | 39 | - | 15.6 (3.2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||
| King (2004) | Healthy | 15 | - | 8 (2) | - | 0.0001 | - | - | 8 (4) | 4 (8) | - | - | - | 0.3 (0.5) | - |
| HV | 25 | - | 15 (3) | - | - | - | 11 (7) | 13 (8) | - | - | - | 2 (2) | - | ||
| Ferreyra (2022) | HV | 30 | 37 | 16.42 | - | - | - | - | 27.2 (7.3) | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Kernozek (2002) | HV | 25 | - | 14.5 (1.7) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Naguib (2018) | HV | - | 59 | 23.86 (7.76) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Klemola (2017) | HV | 66 | 84 | 13.3 (2.7) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -3.7 (6.8) |
| Coughlin (2007) | HV | 103 | 122 | 14.5 (7–23) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Thompson (2023) | HV | 77 | 90 | 14.9 (3.1) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ahuero (2019) | HV | 13 | 14 | 16 (9.5–21) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Faber (2001) | HV | 94 | 109 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 12.9 (4.8) | - | - | - | - | - |
| Oravakangas (2016) | HV | 20 | 23 | 17 (2) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | -5 (8) |
| Greeff (2020) | HV | 23 | 32 | 15 (11–20) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Almaawi (2021) | HV | 89 | 100 | 14.4 (3.3) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 5.5 (4.1) |
| Kopp (2005) | HV | 29 | 34 | 15.9 (10–22) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ozturk (2020) | HV | 10 | 10 | 13.8 (0.5) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Manceron (2022) | HV | - | 20 | 13.3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| HV | - | 20 | 14.8 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| HV | - | 9 | 16.9 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Dayton (2020) | HV | 108 | 109 | 13.3 (2.4) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





