1. Introduction
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), a typical metastatic cancer of the renal cortex, is predominantly characterized by globular masses of malignant clear renal cells originating in the cortex of the kidney. Occasionally, cells with eosinophilic granular cytoplasm are present. Its pathogenesis at the molecular level is not fully understood. In recent years, research and the acquisition of new knowledge have completely revolutionized the treatment of patients with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). The introduction of antiangiogenic drugs targeting tumor angiogenesis, in particular vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors (VEGFRs), has been a major change in the evolution of cancer therapy for RCC. Following the characterization of constitutive activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)/VEGF pathway in clear cell RCC, VEGF-targeted agents such as bevacizumab or VEGFR-targeted agents such as tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been developed to inhibit proangiogenic signaling [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Inhibition of proangiogenic factors reverses the “angiogenic switch” that drives the development of renal cancer. It inhibits endothelial cell proliferation and vascular hyperpermeability, leading to tumor proliferation, invasion of nearby tissues, and distant metastasis [
5]. One problem that arises when treating patients with angiogenesis inhibitors is that blocking angiogenesis is a reversible process that turns on and off when patients stop receiving the drug. Specifically, this leads to the production of IL-8, which induces a resumption of tumor growth through angiogenesis processes [
6]. To overcome this problem, immunotherapeutic agents have been approved in recent years for the treatment of renal cancer. The impact of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) on overall survival (OS) represents the second change in the management of patients with mRCC. The two major pathways targeted by this class include cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4) and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1. Regulatory authorities have approved the use of nivolumab after failure of antiangiogenic therapy in patients with mRCC. Importantly, the activity of VEGFR TKI and ICI monotherapies in mRCC has led to combination regimens that have marked a third paradigm shift in the management of patients with mRCC [
7].
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have approved pembrolizumab in combination with the VEGFR TKI axitinib and avelumab in combination with axitinib for the first-line treatment of mRCC. The increasing use of combination strategies (combining immunotherapies with traditional cancer treatments such as chemotherapy or combining two types of immunotherapies) may improve the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy. In some cases, for reasons not yet understood, it worsens patients’ condition and may even increase immune-related adverse events (irAEs). Until recently, sunitinib, a multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), was the standard first-line treatment for ccRCC, although many patients with ccRCC have developed resistance to this agent. In this scenario, it is crucial to adopt a multi-target strategy to circumvent these problems and drug resistance due to blockade of one or a few receptors, so new therapeutic strategies based on the use of non-toxic agents such as natural compounds or targeted agents have been proposed. Interesting results have shown that curcumin, a component of turmeric (Curcuma longa), and epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), found in Camelia sinensis, are able to synergistically inhibit cell survival, proliferation and angiogenesis of several types of cancer, including renal carcinoma, as shown in our results, by modulating different signaling pathways. Furthermore, pretreatment of mice with a diet containing 0.6% curcumin prior to ccRCC injection showed significant inhibition of tumor engraftment in 60% of mice compared to controls and other groups.
We also found that both polyphenols can induce identical or relevant biochemical actions and, consequently, synergistic effects. This suggests a new perspective regarding their full application in various therapeutic schemes, either alone or in combination with other drugs. It is proposed that the combination of these two natural polyphenols may produce a beneficial therapeutic outcome against ccRCC, similar to that observed so far in the treatment of ovarian [
8], breast [
9] and prostate [
10] cancers. Sunitinib has been the standard of care for the first-line treatment of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC), a disease with a very low patient survival rate [
1]. Sunitinib is a small molecule inhibitor of multiple receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), including vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3), platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGFR-α and PDGFR-β), fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), the receptor tyrosine kinase proto-oncogene (KIT), and the ret proto-oncogene (RET) [
2]. It should be noted that a high concentration of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which stimulates angiogenesis, is one of the poor predictors of this pathology [
3]. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are another important component of the tumor microenvironment and contribute to tumor progression through various effects, such as genetic instability that provides a niche for stem cells, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis [
11]. VEGFR-1 signaling promotes the recruitment of macrophage lineage cells from the bone marrow and induces solid tumor growth [
12]. TAMs are often classified into two major categories: M1 and M2. M2-polarized macrophages may contribute to tumor growth, angiogenesis, and tissue remodeling [
11]. VEGF-A exerts a chemo-attractive effect on macrophages but is not sufficient to induce M2 polarization of macrophages and requires the presence of IL-4 and IL-10 [
12]. Reports have provided evidence that sunitinib is able to inhibit angiogenesis and growth of ccRCC by targeting both the receptors of VEGF and PDGF, thus modulating the underlying molecular pathways [
4]. In addition, a number of antiangiogenic therapies targeting VEGF, which mediates angiogenesis, have demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of ccRCC [
5,
13]. The importance of VEGF signaling in ccRCC growth is also related to the high frequency of von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene mutations found in ccRCC. The VHL gene product regulates VEGF expression by suppressing the expression of the transcription factor HIF [
8]. Despite the proven efficacy of sunitinib in the treatment of ccRCC, the development of resistance in patients with ccRCC is a serious clinical limitation. Clinical reports showed that patients (40%) with advanced ccRCC had an initial positive response to sunitinib treatment, but eventually showed progressive disease recurrence, resulting in treatment failure [
9]. To reduce resistance to sunitinib and enhance its antiangiogenic and antitumor effects, new therapies based on the use of molecularly targeted agents [
10,
14,
15] and novel compounds such as nutraceuticals [
16] have been proposed. In particular, curcumin and EGCG, due to their spectacular antioxidant and antiproliferative properties, have been shown to inhibit the growth and angiogenesis of several types of cancer [
7,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21], including renal cancer [
22], although their effects on ccRCC have not yet been reported.
With our results, we can strongly support the hypothesis that the combination of curcumin and EGCG acts in a synergistic manner to inhibit the growth and angiogenesis of ccRCC, suggesting a possible implication for new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of patients with ccRCC.
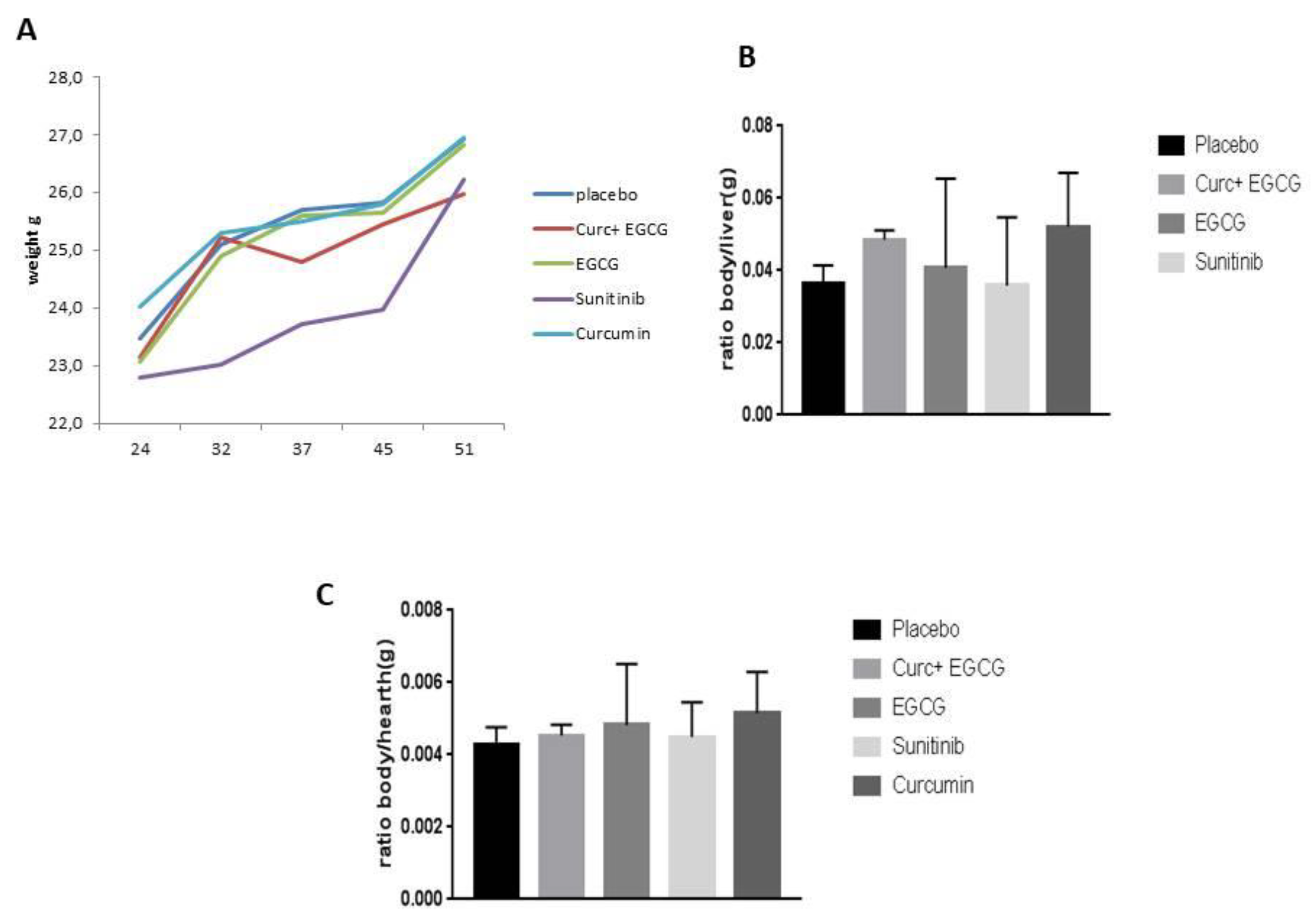
Given these premises, the objectives of our study were (1) to compare, for the first time to our knowledge, the antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of the combination of curcumin and EGCG compared to those obtained with sunitinib in a mouse model of ccRCC, (2) to demonstrate that curcumin and EGCG inhibited tumor growth in mice with ccRCC similarly to sunitinib, but with less body weight loss and liver toxicity, and (3) that mice treated with these natural compounds showed reduced angiogenesis and improved survival.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and reagents
Mice fed curcumin diet had free access to food and water ad libitum; the concentration of curcumin in the diet is 0.6%, purchased from Mucedola (Settimo Milanese, Italy). Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG, 99% purity) was purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Sunitinib was purchased from Selleckchem, Houston, TX,
https://www.selleckchem.com/h.
2.2. Cell line
Human renal cell carcinoma SN12C cells expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) were kindly provided by Dr. Stefania Scala (Istituto Nazionale per lo studio e la cura dei Tumori “Fondazione G. Pascale”, Naples). Cells were maintained in DMEM (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Invitrogen) and G418 1µg/µl (Invitrogen) in a humidified incubator containing 5% CO2 at 37°C.
2.3. Generation of xenograft mouse model of ccRCC and treatments
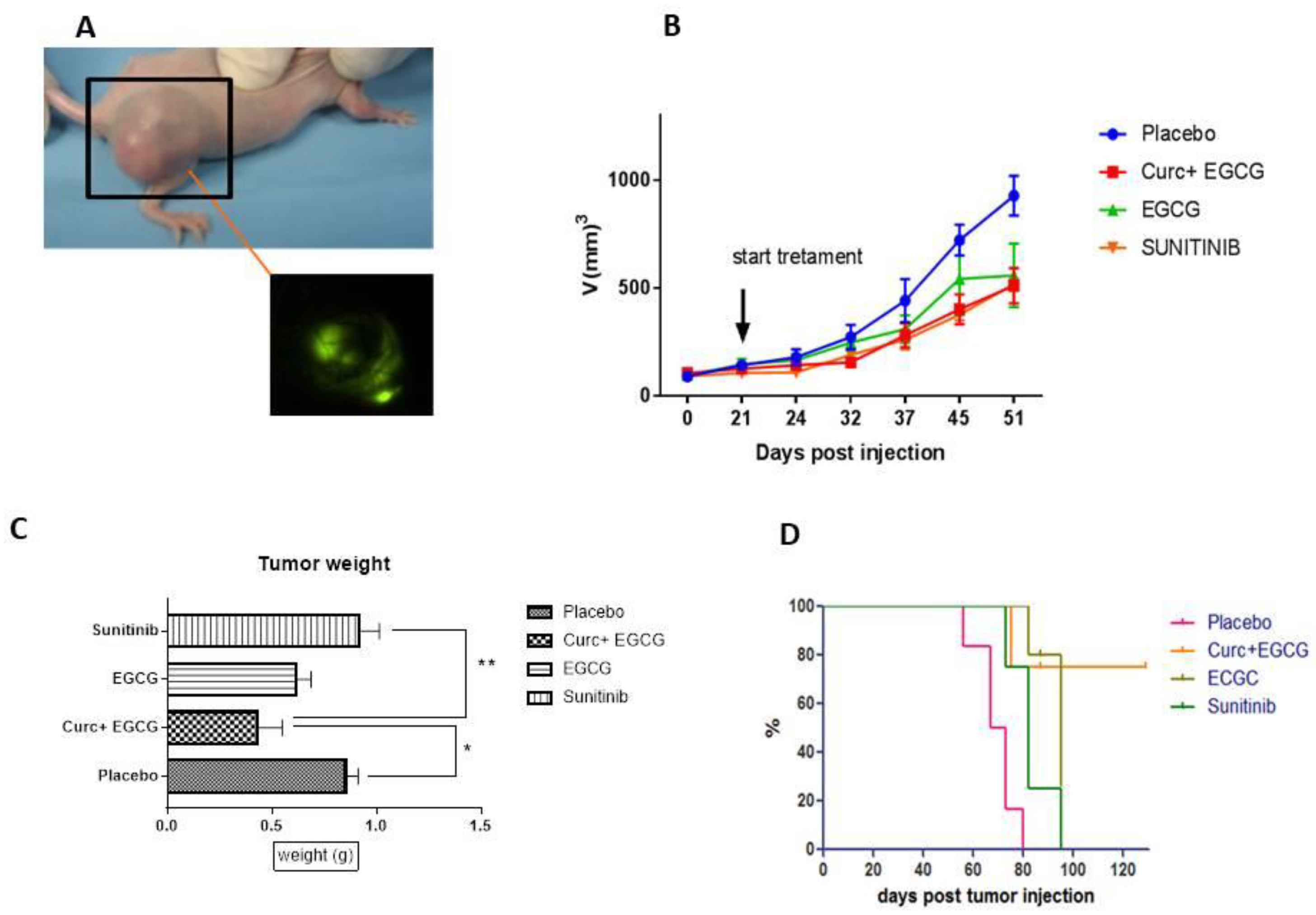
Fifty athymic naked Foxn1nu (6 to 8 weeks) were purchased from (Envigo, Udine, Italy). They were maintained at 21-24°C on a 12-hour light/dark cycle in a specially designed pathogen-free isolation facility and allowed to acclimate for 1 week prior to experiments. All mice were then inoculated with SN12C-eGFP (1 × 106/200 μL PBS) in the right flank until palpable tumors developed. Tumor volume was measured weekly using electronic calipers (B × W × H). When tumor volume reached 100 mm
3, mice (6 per group) were randomly assigned to specific treatment groups (except for the already pretreated curcumin-treated group). Mice in the curcumin-treated group were pre-treated with curcumin (diet supplemented with 0. 6% curcumin 200 mg/kg/day, po) one week before of tumor injection (to evaluate the antitumoral effect of curcumin respect to the standard treatment of mice after that the tumor is palpable ), while the other groups were treated when the tumor was palpable and measured from 30 ~100 mm
3 with EGCG (3 mg/KG/day, oral gavage), EGCG + curcumin and vehicle control, oral gavage 200 μl (PBS), sunitinib (oral gavage 50 mg/kg) for 5 weeks. All animal experiments were performed in accordance with the guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals of the National Cancer Institute - IRCCS - “Fondazione G. Pascale”. Furthermore, all experiments were performed in accordance with the European Directive [
23] and the Italian law [
24] approved by the Italian Ministry of Health. This study was conducted in accordance with the recommendations applicable to all scientific procedures involving the use of live animals.
2.4. Imaging techniques
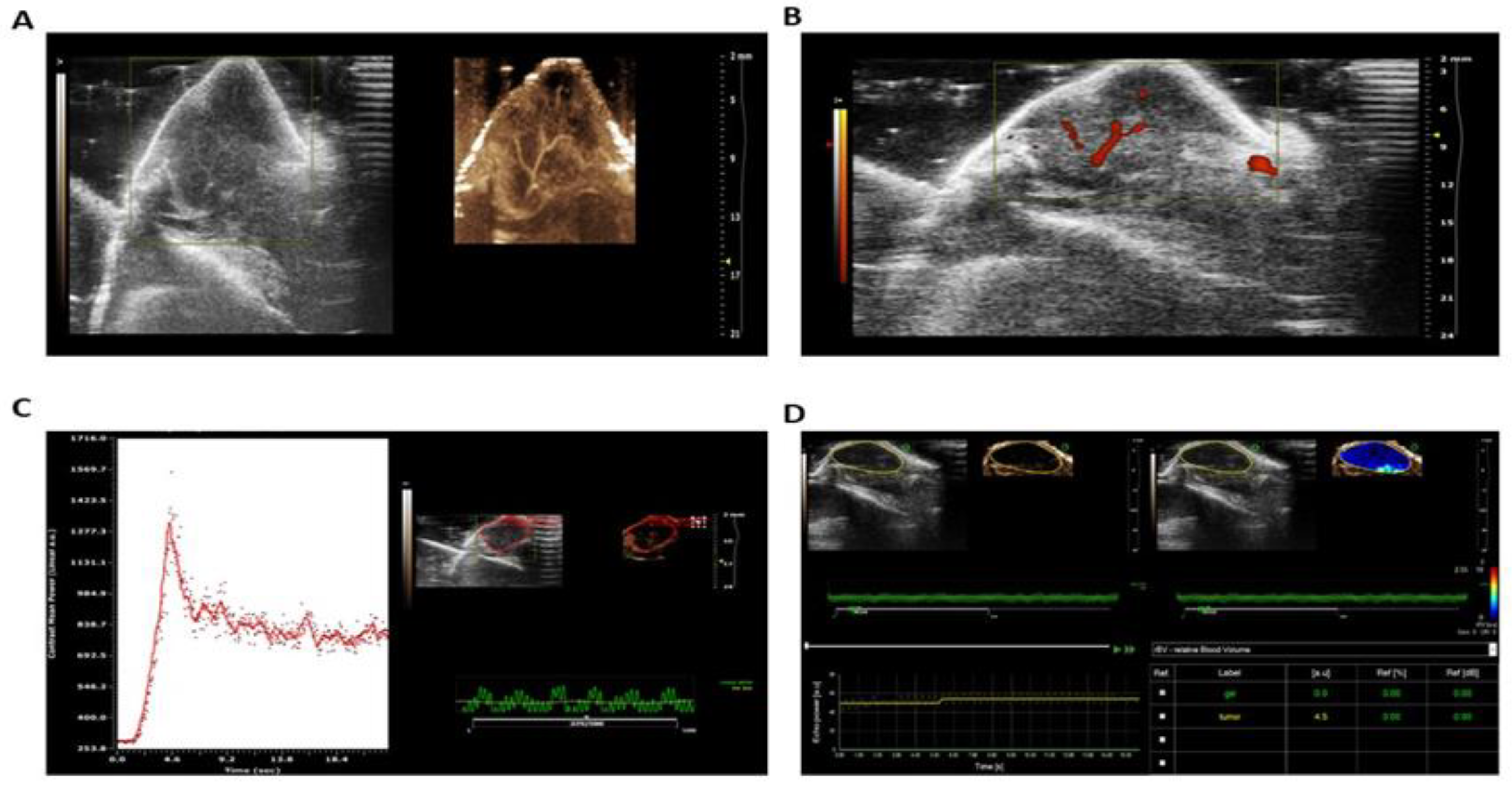
Ultrasound (US) imaging was performed in CEUS by a radiologist using a dedicated small-animal high-resolution imaging unit (Vevo 2100; VisualSonics, Toronto, Canada) and a 40-MHz high-frequency linear transducer (lateral resolution, 100 μm; transverse resolution, 40 μm; focal length, 6 mm; mechanical index, 0.14; transmit power, 50%; dynamic range, 52 dB). All imaging was performed in baseline brightness mode (B mode). The radiologist was aware of the tumor type and the type of microbubbles administered to the mice. Throughout the imaging session, the mice were anesthetized with 2% isoflurane in oxygen at 2 L/min on a heated platform with constant monitoring of their body temperature by using a rectal temperature probe. Prewarmed US gel was used as a coupling agent on the skin of the mice. Real-time imaging was performed at a frame rate of 20 Hz (corresponding to a temporal resolution of 50 msec). Two-dimensional B-mode image planes were acquired with optimized gain and time gain compensation settings, that were kept constant throughout the experiment. The acoustic focus was placed in the center of the tumor at the level of the largest transverse cross section and maintained throughout each experiment.
2.5. Fluorescent Imaging Macroscope
Leica Macrofluo Z6 APO (Wetzlar, Germany) with DFC 360 Fx camera is a microscope that uses fluorescence to evaluate the tumor and metastasis generated by injection of fluorescent tumor cells in oncology mouse models.
2.6. Contrast-enhanced US image protocol
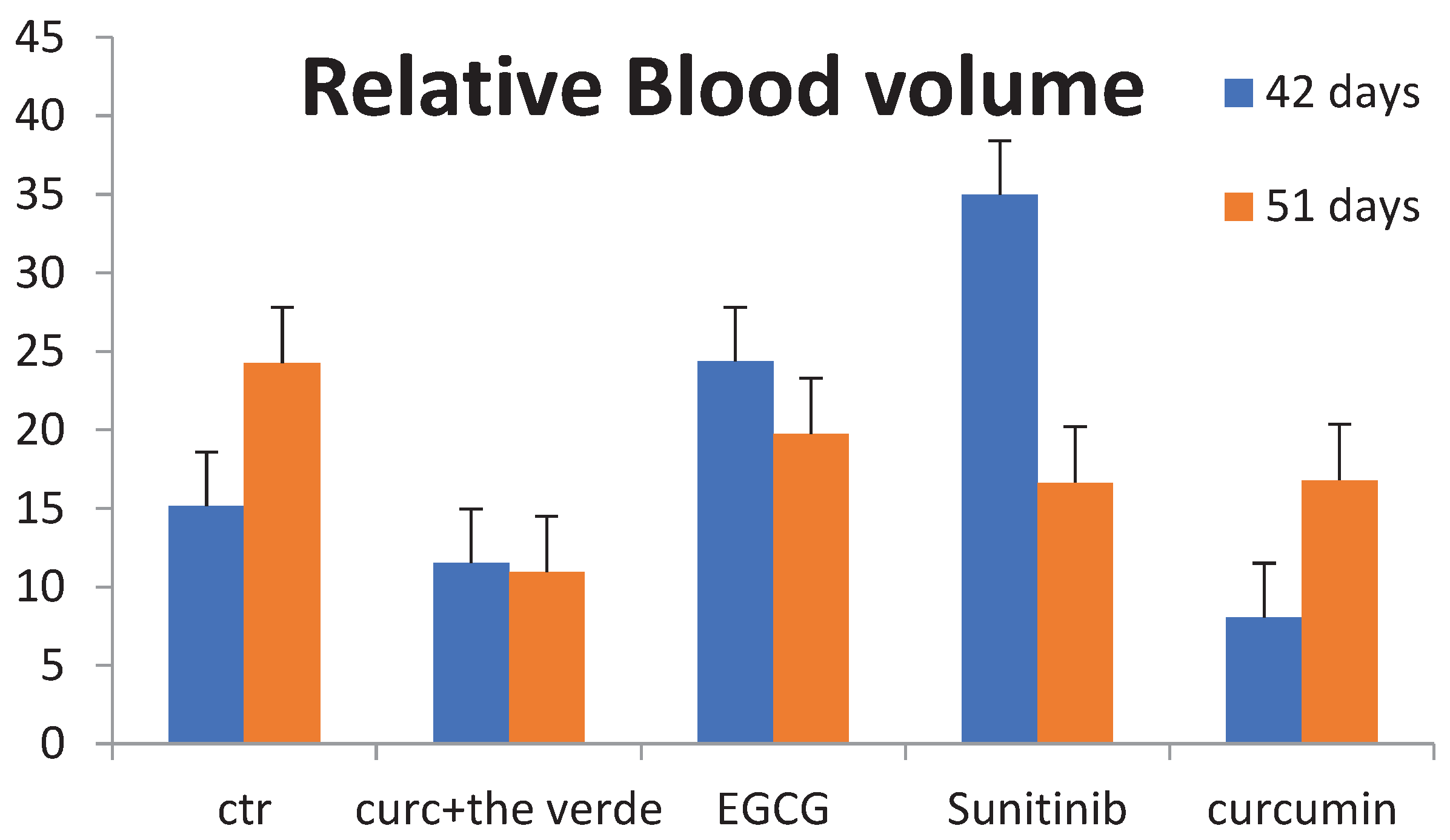
The goal of the US imaging protocol was to differentiate between the acoustic signal from adherent MBV and the signal from MBV still freely circulating in the bloodstream. After intravenous injection of 5 × 107 MBV (60 μL) into the tail vein of the mice (injection time, 3 seconds), imaging was paused for 4 minutes to allow retention of the microbubbles. One hundred twenty frames were then acquired over a 6-second period to obtain a signal from the tumor tissue as well as from the adherent and freely circulating microbubbles. A continuous 10-MHz high-power destructive pulse (mechanical index, ∼0.235; average power, ∼0.0676 W/cm2) was then applied for 3 seconds to destroy the microbubbles within the beam elevation. Nine seconds after destruction (to allow for replenishment of freely circulating microbubbles in tumor vessels within the beam elevation), 120 frames were acquired with the same US settings as before the pulse, containing signals from the tumor tissue and from freely circulating microbubbles. These signals were averaged and digitally subtracted from the initial pre-destruction frames to derive the signal attributable to adherent MBV only. Reproducibility of the targeted contrast-enhanced US imaging protocol was tested in five fibrosarcoma tumor-bearing mice. Mice were scanned according to the above protocol. After 24 hours, scanning was repeated using the same US settings as the first imaging session with a second injection of microbubbles and with the transducer as close as possible to the US imaging plane of the first imaging session by marking the position of the transducer on the skin of the mice at the first imaging session.
2.7. Image Analysis
Images were digitally recorded and analyzed offline using commercially available high-resolution micro-US imaging software (Vevo 2100; Visualsonics). Image analysis was performed in random order by a radiologist blinded to the type of microbubbles administered. Mean image brightness (video intensity, corresponding to the 8-bit log-compressed gray scale) was measured in regions of interest encompassing the entire tumor in the imaging plane (mean area, 20 mm2; range, 7-49 mm2). The difference in video intensity from the subtraction of the pre- and post-destruction image frames (see above) was automatically displayed by the software as a colored (green) overlay on the grayscale images. For assessment of contrast enhancement in hindlimb muscles, a region of interest was defined to include the adductor muscle (mean area, 10 mm2; range, 5-14 mm2). The central slice of the tumor, defined by the length of the 3D volume, was centered in the imaging plane and a baseline cineloop of 500-800 frames was acquired at 50% power. 100 µl of MicroMarker microbubble contrast agent (VisualSonics, Toronto, ON) was slowly injected over a 5-second period, followed by a 0.5 mL saline flush. Cineloops were collected from the bolus injection and from the circulating contrast after injection. After this procedure, mice were removed from the imaging setup and allowed to recover from anesthesia.
2.8. Histology and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
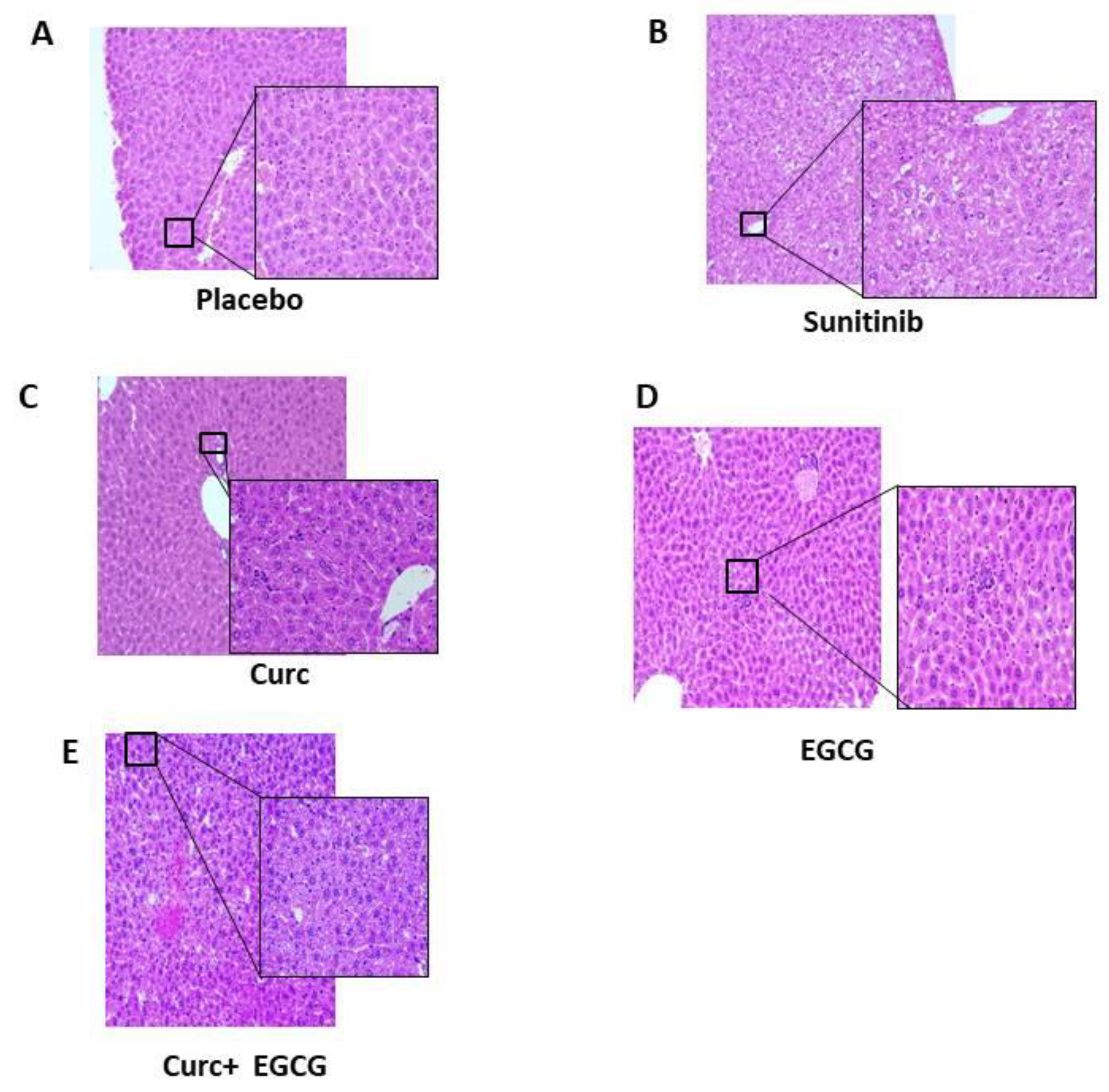
The expression of CD31 proteins in tumor specimen plugs was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. All sections were deparaffinized in xylene, rehydrated through a series of graded alcohols, and washed with PBS (pH 7.2). The sections were microwaved twice for 5 minutes in citrate buffer (pH 6.0) and then incubated overnight at 4°C with primary antibodies, followed by incubation with streptavidin/HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies. The conventional streptavidin/peroxidase method (Histostain™-Plus Kits, SP0023, Beijing Biosynthesis Biotechnology Co., LTD) was used to develop signals, and cells were counterstained with hematoxylin. Sections incubated with secondary antibodies in the absence of primary antibodies served as negative controls. Cells-stained brown represent positive immunoreactivity signals. For micro-vessel density (MVD) analysis, CD31 staining of tumors was performed and quantified. Briefly, 5-μm tissue sections of a representative tumor block were antigen retrieved in Tris/Borate/EDTA buffer (pH 8.0-8.5; Ventana, 950-124) at 95°C for 44 minutes. Immunohistochemistry for CD31 was performed on each of the above samples. The monoclonal anti-CD31 antibody (clone JC/70A, Dako-Agilent, Carpinteria, CA) recognizes a fixation-resistant epitope in endothelial cells.31 Slides were immersed in Reveal (Biocare Medical, Concord, CA) antigen retrieval solution in a decloaking chamber (Biocare) for 30 seconds at 125°C and 18 to 24 PSI. The primary antibody was diluted 1/100 with Da Vinci diluent (Biocare Medical) and incubated for 60 minutes.
2.9. Ethical Approval
This study was conducted in accordance with current guidelines and recommendations for all scientific procedures involving the use of live animals. The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Istituto Nazionale Tumori IRCCS Fondazione Pascale, Protocol No. 669/2011.
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SD (standard deviation). All statistical analyses were performed using JMP 10 software (SAS Institute, Inc.), GraphPad Prism8 (GraphPad Software, Inc.), or the R package (version 4.0.2; RStudio, Inc.). The significance of the differences between the two groups was assessed by unpaired Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney test. Significance of differences between three or more groups was assessed by one-way ANOVA with post hoc comparisons using Dunnett’s test or Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn’s post hoc test with Bonferroni correction. Survival curves were constructed using the Kaplan-Meier method, and differences between curves were assessed using the log-rank test.
4. Discussion
The increasing magnitude of cancer and the disappointing outcomes of traditional chemotherapy to significantly reduce mortality rates, demands always new approaches that could control cancer progression and mortality. The major weak point associated with cancer treatment with conventional chemotherapies are the nonspecific side effects along with the escape of cancer cells from the action of these drugs leading to recurrence. In this scenario the use of the phytochemicals as alternative therapeutic strategies for cancer is gaining the attention of scientific community due to a minimal side-effect associated with them. Here we have outlined the role of the common dietary polyphenolic natural plant compounds namely, curcumin, EGCG, in cancer progression and angiogenesis. These natural compounds can inhibit tumor growth, metastasis as well as overcome their drug-resistant behavior through the modulation of different signaling cascades due to their multitarget inhibition and the associated changes in gene expression profiles. In addition, they are capable of functioning independently and also exert synergism with other members in reducing cancer progression. Being components of regular dietary supplements accounts for their low side effects for which they can be used in combination with other members of the group or with conventional chemotherapeutics. The treatment with natural compounds results in long term tumor shrinkage with no side effects. The two other methods include targeting the cancer cells with a combination of the natural compounds and a conventional chemotherapeutic drug or in synergism with another natural compounds. In both cases, it can be observed that there is significant reduction in tumor volume and aggressiveness with increased sensitivity towards the therapeutics, with no side effects along with decreased recurrence as well as drug resistance. Sunitinib was until recently the standard of care for the treatment of advanced ccRCC. Pathological angiogenesis, a hallmark of tumorigenesis, involves development of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature and interplay of proangiogenic growth factors [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31]. Placental growth factor (PGF), VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D and their receptors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 (VEGFR-1), VEGFR-2, and VEGF-R3, are the major targets for anti-angiogenic agents [
32,
33,
34]. EGCG, an active catechin, is reportedly known for its inhibitory potential via binding to VEGF to its receptors which in turn block ERK/Akt phosphorylation [
33,
35]. This inhibition of ERK1/2 phosphorylation leads to reduced VEGFR1/2 phosphorylation [
36,
37]. Besides the VEGF and its receptors, EGCG has also been shown to inhibit hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) which, in turn halts VEGF/VEGFR axis activation [
38]. Moreover, as HIF-1 synthesis is regulated through PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK activation, blocking of ERK/Akt phosphorylation through EGCG inhibits HIF-1 [
39,
40]. However, the development of ccRCC resistance to Sunitinib therapy remains the main clinical problem. To study this problem, we have established ccRCC xenograft models which mimic the acquired Sunitinib resistance seen in the clinical setting. We show that the development of Sunitinib resistance was accompanied by evasion of Sunitinib’s antiangiogenic as observed by in vivo CEUS quantification and confirmed by immunohistochemistry analysis of CD31. These effects are due to an increased expression of tumor-derived IL-8 as proved by some authors [
41]. Furthermore, these authors showed that inhibition of IL-8 function with a neutralizing antibody attenuated Sunitinib resistance in ccRCC. These data are in line with our results and to show that the suspension of sunitinib led to a resumption of tumor growth due to pro-angiogenetic factors. Previous studies have suggested that IL-8 promoted malignant tumor growth and metastasis in an autocrine and paracrine manner [
42,
43]. In addition, tumor-derived IL-8 activated ECs in the tumor vasculature to promote angiogenesis [
44]. Moreover, other studies show that the silencing of IL-8 in HT-29 CM by IL-8-neutralizing antibody suppressed the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway and decreased the protein level of IL-8 in HT-29 CM-induced normal ECs. It has been known that the secreted IL-8 from tumor cells binding to two cell-surface G protein-coupled receptors, termed CXCR1 and CXCR2, promoted activation of JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway and nuclear translocation of STAT3 [
45]. Curcumin and EGCG have been reported acted as multitargeting agents in regulating JAK/STAT3 signaling in cancer [
11]. In addition, curcumin and EGCG have been used alone to demonstrate the anti-angiogenic effect [
46,
47]. However, the exact mechanism of their anti-angiogenic effect is still under controversy. Considering the poor absorption and low bioavailability of curcumin, and the synthesis anti-tumor effect of EGCG, the combination of curcumin and EGCG may produce a better antitumor effect as showed in our data [
48,
49]. More importantly, the combined inhibitory effect was stronger than either single agent. In summary, our results indicate that the combination of EGCG plus Curcumin show the same effects of tumor growth delay and angiogenesis reduction in an initial phase compared to Sunitinib treated mice. Interestingly, however natural compounds show a longer lasting effect due to their multitarget inhibition respect to monoclonal inhibition or of some receptors overexpressed in cancer cells. Although the problem of natural compounds is the low bioavailability the present study shows interesting effects that need of deeper investigations.
Only after the development of Sunitinib resistance did IL-8 inhibition have an effect on tumor growth. These findings suggest that ccRCC tumors initially rely primarily on VEGF/VEGFR proangiogenic signaling but could become reliant on IL-8–dependent angiogenesis after sustained VEGFR blockade. Notably, inhibition of IL-8 function alone was not sufficient to suppress the growth of tumors that had acquired Sunitinib resistance; continuing treatment with Sunitinib was also required. This suggests that Sunitinib-resistant ccRCCs may rapidly reactivate VEGFR-dependent angiogenesis upon discontinuation of Sunitinib treatment. This is consistent with clinical and preclinical observations that Sunitinib-inhibited tumors rapidly resume growth when Sunitinib treatment is halted. In this work we demonstrate antiproliferative, antiangiogenic and synergistic effects of some natural compounds as Curcumin and EGCG major active ingredient of green tea for the care of renal cancer. Growing body of evidence showed the importance of agents that have as target the angiogenesis for the care of renal cancer as report clinical studies but another important aspect that emerging by clinical and preclinical studies is the chemoresistance that occur in patient treated with drugs of new generation as monoclonal antibodies and target therapies due to the mechanism of escape that act the cell when we block one or more molecular pathways. Shao et al. reported that BDMC, a CUR derivative, in combination with the α-PD-L1 antibody, can inhibit the progression of Breast Cancer in vivo and prolong mouse survival. Such treatment significantly increased the intravascular infiltration of CD8 + T cells, expanded the level of IFN-γ, and decreased the number of intra-tumoral myeloid-derived suppressor cells [
50]. However, EGCG may increase the potency of doxorubicin, daunorubicin, cisplatin, rhodamine-123 and tamoxifen in a number of cancer cell lines. The inhibitory effect of EGCG on Multi Drug Resistance has been reported for cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells [
51,
52].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.B. and S.M.A.; methodology, A.L., M.L.B., C.P., M.B.; validation, G.S., C.S., F.S. and R.H.W.F.; formal analysis, A.B. and A.G.; investigation, T.A. and E.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.B., and A.P.; writing—review and editing, S.M.A.; visualization, A.L., M.L.B., C.P., M.B., G.S., C.S., T.A., F.S., E.C., M.C. and A.G.; supervision, R.H.W.F.; project administration, M.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.