Submitted:
17 November 2023
Posted:
20 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Policosanol
2.2. Participants
| Groups | Age | BMI | Total Exercise | Strength Exercise | Aerobic Exercise | MET |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean ± SEM | mean ± SEM | min/week | min/week | min/week | Score | |
| Male (n=8) |
36.9 ± 1.9 | 31.0 ± 1.9 | 655.0 ± 97.4 | 285.7 ± 9.2 | 390.0 ± 102.7 | 7.0 ± 0.3 |
| Female (n=9) |
38.4 ± 2.7 | 29.0 ± 1.4 | 714.4 ± 94.5 | 194.4 ± 30.6 | 520.0 ± 84.3 | 7.4 ± 0.1 |
| Total (n=17) |
37.7 ± 1.6 | 30.1 ± 1.1 | 686.5 ± 66.1 | 234.4 ± 20.8 | 458.8 ± 65.7 | 7.2 ± 0.1 |
2.4. Exercise Program
2.5. Anthropometric Analysis
2.6. Blood Analysis
2.7. Quantification of Serum Coenzyme Q10
2.8. Isolation of Lipoproteins
2.9. Characterization of Lipoproteins
2.10. Electron Microscopy
2.11. Agarose Electrophoresis
2.12. Antioxidant Activities in the HDL
2.13. Zebrafish Maintenance
2.14. Microinjection of CML and HDL into Zebrafish Embryos
2.15. Imaging of Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis in Embryo
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Anthropometric Profiles
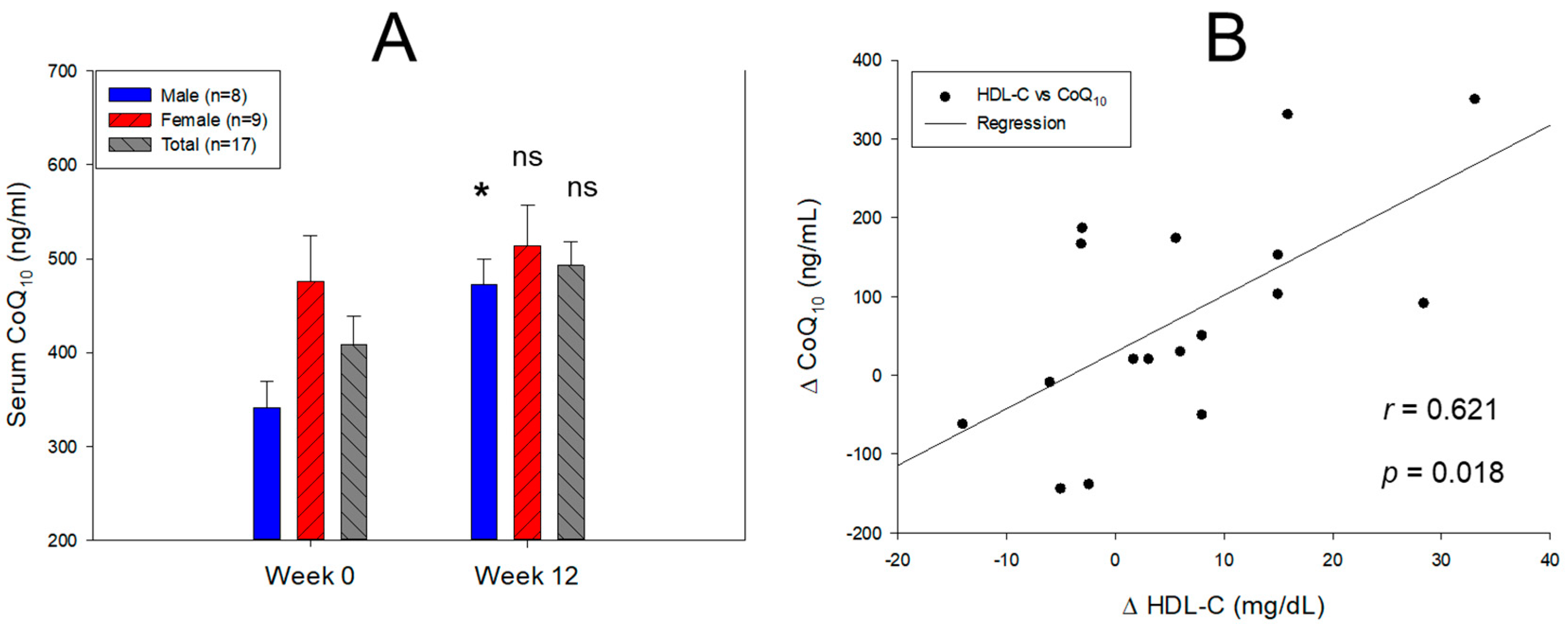
3.2. Change in Serum Coenzyme Q10 and Lipid Profiles
3.3. Change in the Serum Protein Parameters
3.4. Change of VLDL and LDL Properties and Compositions
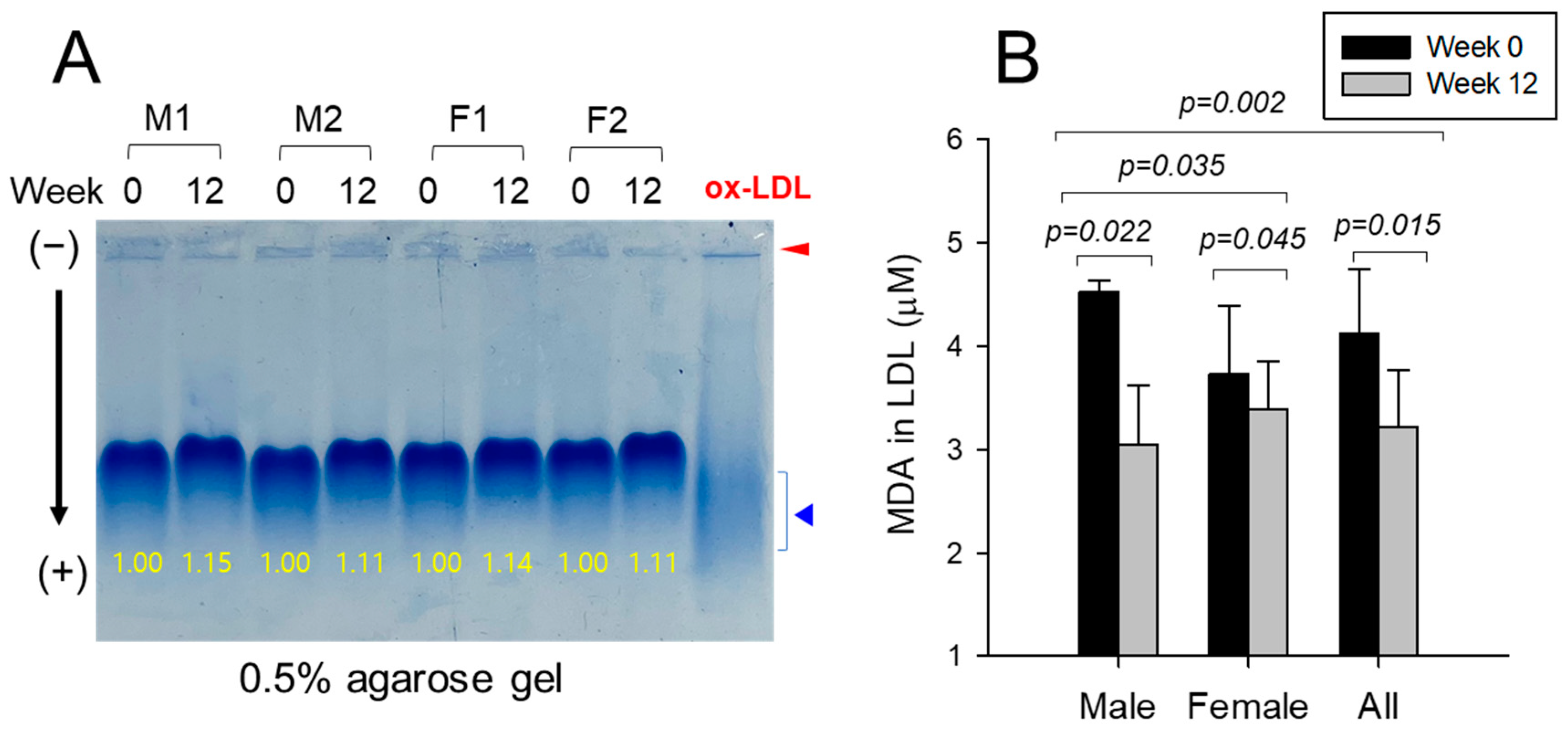
3.5. Electromobility of LDL and Extent of Oxidation
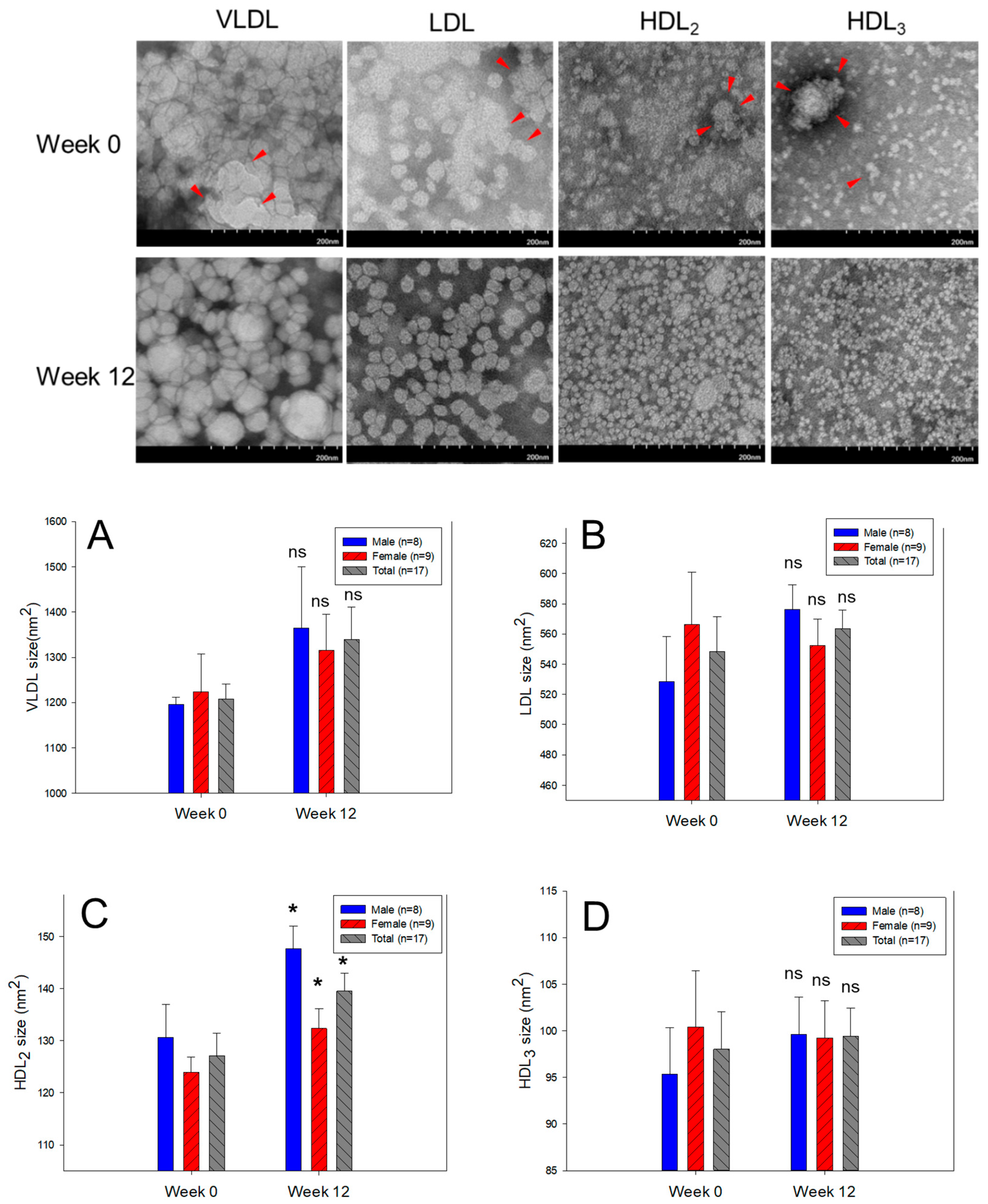
3.6. Electron Microscopic Observation of Lipoprotein Image
3.7. Change of HDL Quality during 12 Weeks
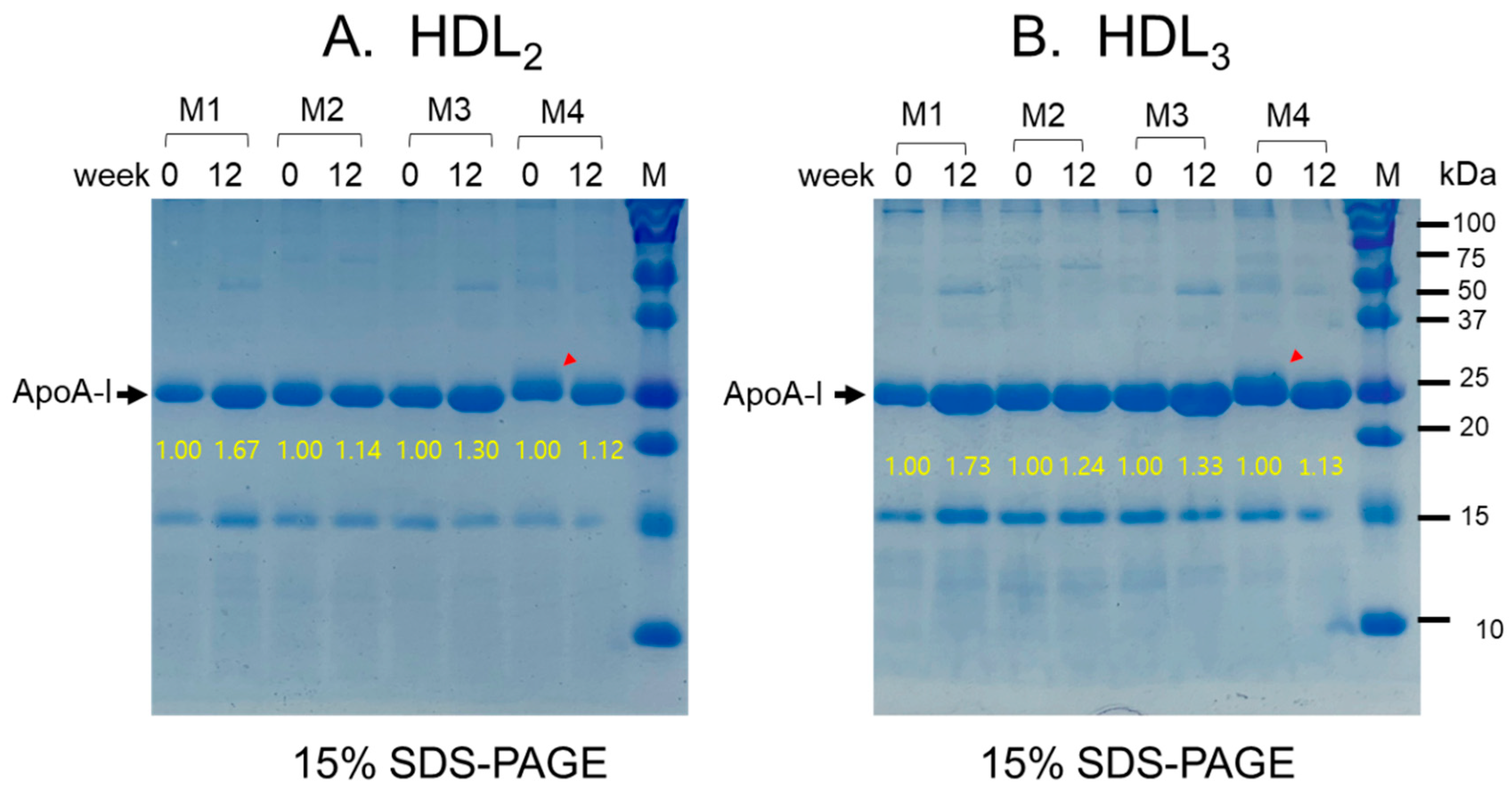
3.8. Change of apoA-I Expression in HDL
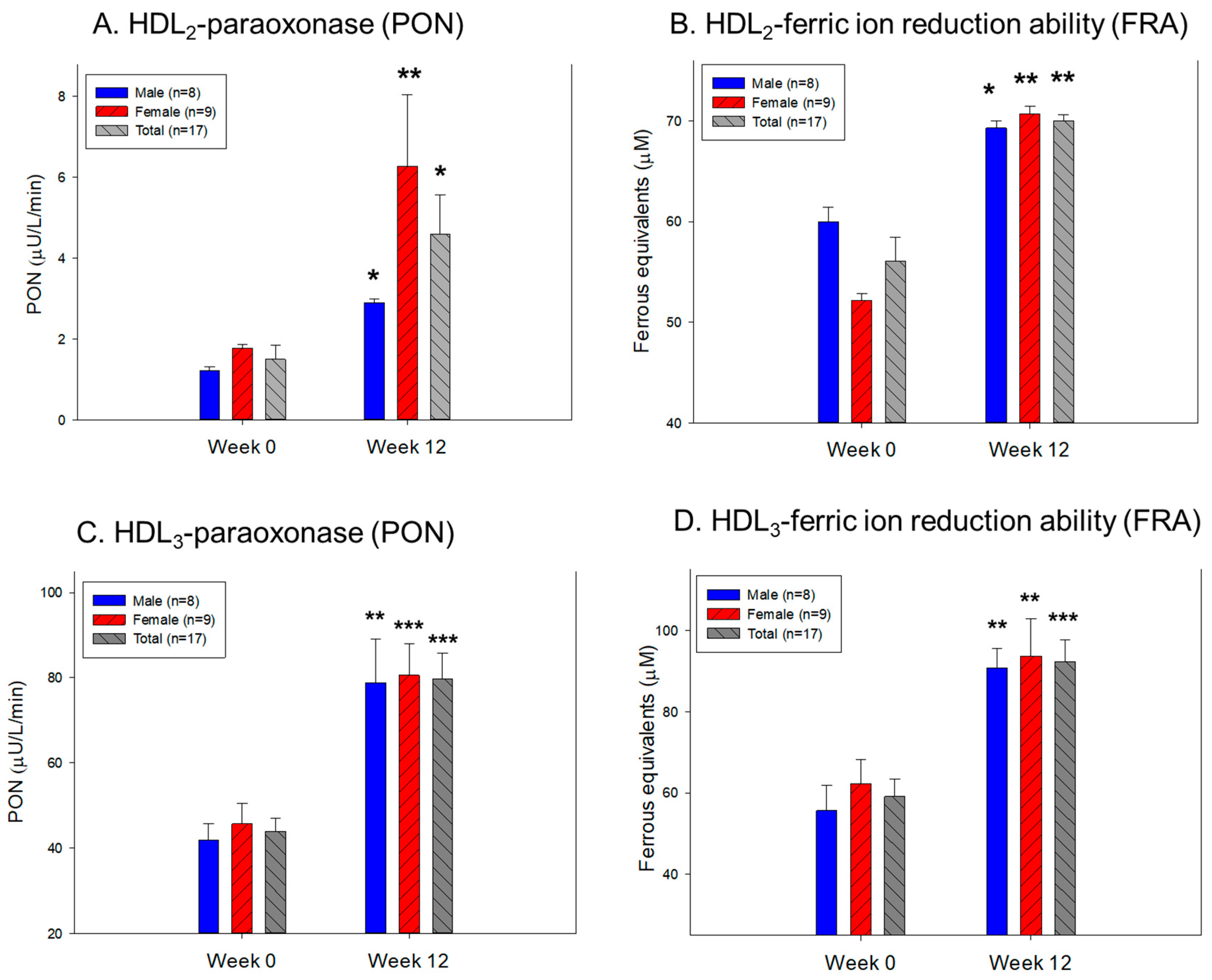
3.9. Change in the Antioxidant Ability in HDL2 and HDL3
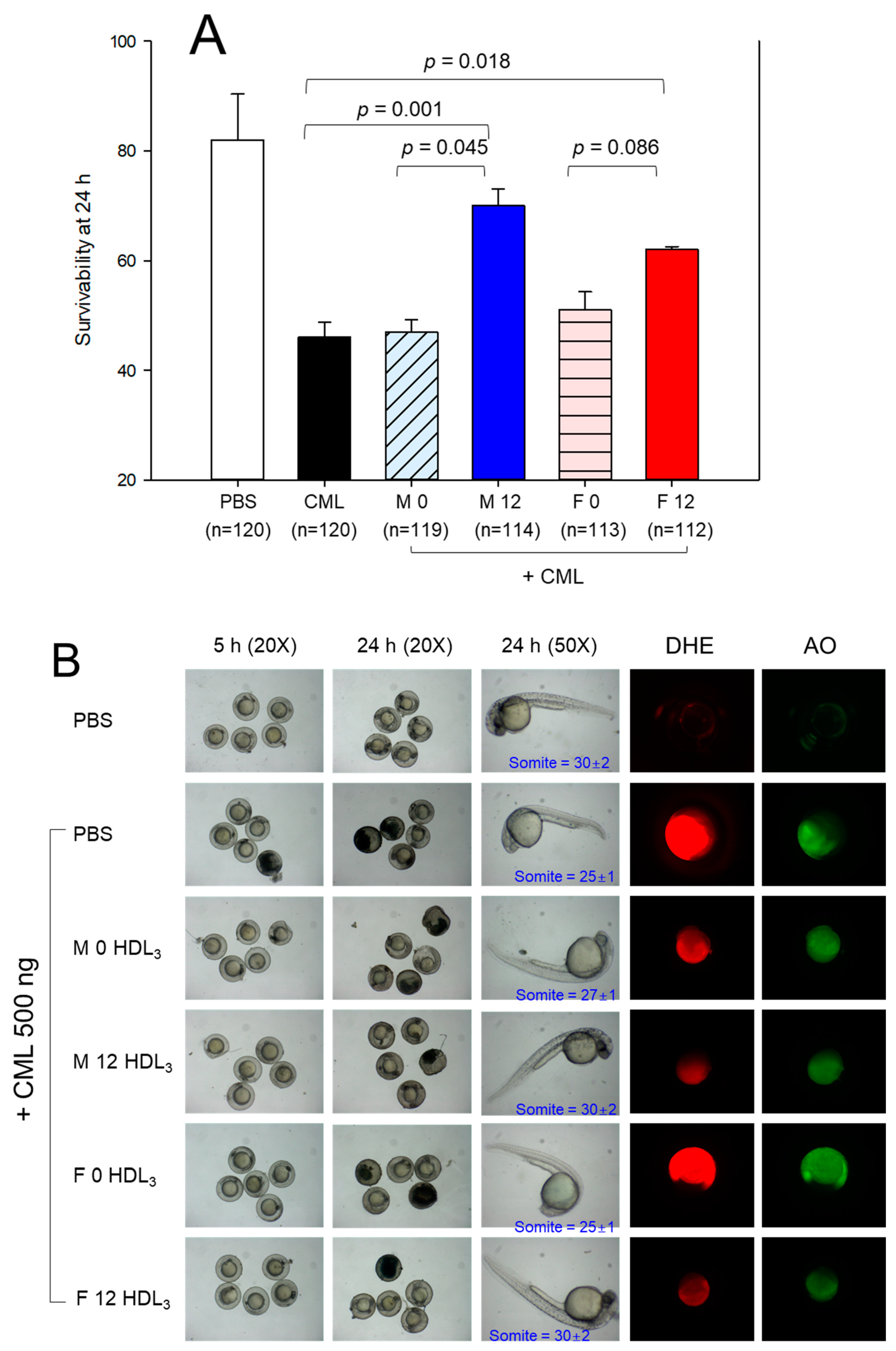
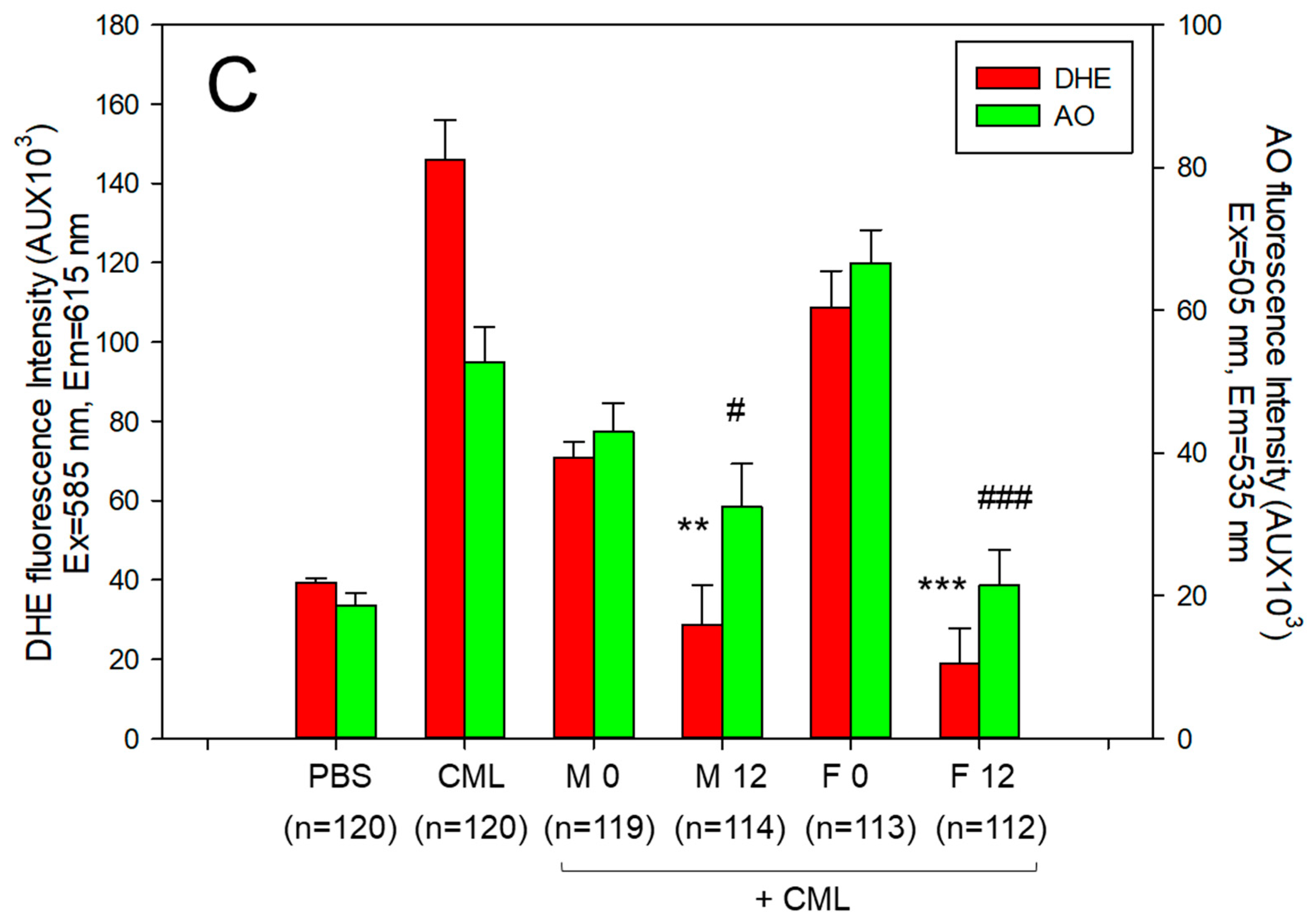
3.10. Embryo Survivability under the Presence of Carboxymethyllysine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chew NW, Ng CH, Tan DJH, Kong G, Lin C, Chin YH, et al. The global burden of metabolic disease: Data from 2000 to 2019. Cell. Metab. 2023;35(3):414-28. [CrossRef]
- Noubiap JJ, Nansseu JR, Lontchi Yimagou E, Nkeck JR, Nyaga UF, Ngouo AT, et al. Geographic distribution of metabolic syndrome and its components in the general adult population: A meta-analysis of global data from 28 million individuals. Diabetes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;188:109924. [CrossRef]
- Mainous III AG, Tanner RJ, Rahmanian KP, Jo A, Carek PJ. Effect of sedentary lifestyle on cardiovascular disease risk among healthy adults with body mass indexes 18.5 to 29.9 kg/m2. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019;123(5):764-8. [CrossRef]
- Paffenbarger Jr RS, Hyde RT, Wing AL, Lee IM, Jung DL, Kampert JB. The association of changes in physical-activity level and other lifestyle characteristics with mortality among men. New. Eng. J. Med. 1993;328(8):538-45. [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita K, Ozato N, Yamaguchi T, Sudo M, Yamashiro Y, Mori K, et al. Association of sedentary behaviour and physical activity with cardiometabolic health in Japanese adults. Sci. Rep. 2022;12(1):2262. [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen J, Hein HO, Suadicani P, Gyntelberg F. Relation of high TG–low HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol to the incidence of ischemic heart disease: An 8-year follow-up in the Copenhagen male study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1997;17(6):1114-20. [CrossRef]
- Paffenbarger Jr RS, Hyde R, Wing AL, Hsieh Cc. Physical activity, all-cause mortality, and longevity of college alumni. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986;314(10):605-13. [CrossRef]
- Blair SN, Kohl HW, Paffenbarger RS, Clark DG, Cooper KH, Gibbons LW. Physical fitness and all-cause mortality: a prospective study of healthy men and women. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1989;262(17):2395-401. [CrossRef]
- Couillard C, Després JP, Lamarche B, Bergeron J, Gagnon J, Leon AS, et al. Effects of endurance exercise training on plasma HDL cholesterol levels depend on levels of triglycerides: evidence from men of the Health, Risk Factors, Exercise Training and Genetics (HERITAGE) Family Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001;21(7):1226-3. [CrossRef]
- Palazón Bru A, Hernández Lozano D, Gil Guillén VF. Which physical exercise interventions increase HDL-cholesterol levels? A systematic review of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. Sports. Med. 2021;51:243-53. [CrossRef]
- Gao W, Lv M, Huang T. Effects of different types of exercise on hypertension in middle-aged and older adults: a network meta-analysis. Front. Public Health. 2023;11. [CrossRef]
- Lin M, Lin Y, Li Y, Lin X. Effect of exercise training on blood pressure variability in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PloS one. 2023;18(10):e0292020. [CrossRef]
- Toyama K, Sugiyama S, Oka H, Iwasaki Y, Sumida H, Tanaka T, et al. Combination treatment of rosuvastatin or atorvastatin, with regular exercise improves arterial wall stiffness in patients with coronary artery disease. PloS one. 2012;7(7):e41369. [CrossRef]
- Joy TR, Hegele RA. Narrative review: statin-related myopathy. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009;150(12):858-68. [CrossRef]
- Bonfim MR, Oliveira ASB, Amaral SLD, Monteiro HL. Treatment of dyslipidemia with statins and physical exercises: recent findings of skeletal muscle responses. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2015;104:324-31. [CrossRef]
- Meador BM, Huey KA. Statin-associated myopathy and its exacerbation with exercise. Muscle Nerve. 2010;42(4):469-79. [CrossRef]
- Vinci P, Panizon E, Tosoni LM, Cerrato C, Pellicori F, Mearelli F, Biasinutto C, Fiotti N, Di Girolamo FG, Biolo G. Statin-Associated Myopathy: Emphasis on Mechanisms and Targeted Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021 Oct 28;22(21):11687. [CrossRef]
- Opie, LH. Exercise-induced myalgia may limit the cardiovascular benefits of statins. Cardiovasc. Drugs. Ther. 2013;27:569-72. [CrossRef]
- Singh RB, Neki NS, Kartikey K, Pella D, Kumar A, Niaz MA, et al. Effect of coenzyme Q10 on risk of atherosclerosis in patients with recent myocardial infarction. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2003:75-82. [CrossRef]
- Cho KH, Kim SJ, Yadav D, Kim JY, Kim JR. Consumption of Cuban policosanol improves blood pressure and lipid profile via enhancement of HDL functionality in healthy women subjects: Randomized, double-blinded, and placebo-controlled study. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Park HJ, Yadav D, Jeong DJ, Kim SJ, Bae MA, Kim JR, et al. Short-term consumption of Cuban policosanol lowers aortic and peripheral blood pressure and ameliorates serum lipid parameters in healthy Korean participants: Randomized, double-blinded, and placebo-controlled study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019;16(5):809. [CrossRef]
- Kim SJ, Yadav D, Park HJ, Kim JR, Cho KH. Long-term consumption of Cuban policosanol lowers central and brachial blood pressure and improves lipid profile with enhancement of lipoprotein properties in healthy Korean participants. Front. physiol. 2018;9:412. [CrossRef]
- Kim HR, Han MA. Association between serum liver enzymes and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2018;15(8):1658. [CrossRef]
- Pettersson J, Hindorf U, Persson P, Bengtsson T, Malmqvist U, Werkström V, et al. Muscular exercise can cause highly pathological liver function tests in healthy men. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008;65(2):253-9. [CrossRef]
- Trede NS, Zapata A, Zon LI. Fishing for lymphoid genes. Trends. Immunol. 2001;22(6):302-7. [CrossRef]
- Novoa B, Bowman T, Zon L, Figueras A. LPS response and tolerance in the zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2009;26(2):326-31. [CrossRef]
- Canavaciolo VLG, Gómez CV. “Copycat-policosanols” versus genuine policosanol. Rev. CENIC Cienc. Quím. 2007;38(1):207-13.
- Haskell WL, Lee IM, Pate RR, Powell KE, Blair SN, Franklin BA, et al. Physical activity and public health: updated recommendation for adults from the American College of Sports Medicine and the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2007;116(9):1081. [CrossRef]
- Cho KH, Nam HS, Baek SH, Kang DJ, Na H, Komatsu T, et al. Beneficial Effect of Cuban Policosanol on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipoproteins Accompanied with Lowered Glycated Hemoglobin and Enhanced High-Density Lipoprotein Functionalities in a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, and Double-Blinded Trial with Healthy Japanese. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24(6):5185. [CrossRef]
- Havel RJ, Eder HA, Bragdon JH. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J. Clin. Investig. 1955;34(9):1345-53. [CrossRef]
- Markwell MAK, Haas SM, Bieber L, Tolbert N. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal. Biochem. 1978;87(1):206-10. [CrossRef]
- Blois, MS. Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature. 1958;181(4617):1199-200. [CrossRef]
- McPherson JD, Shilton BH, Walton DJ. Role of fructose in glycation and cross-linking of proteins. Biochem. 1988;27(6):1901-7. [CrossRef]
- Noble, RP. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J. Lipid Res. 1968;9(6):693-700. [CrossRef]
- Mackness M, Mackness B. Effect of dilution on high-density lipoprotein associated paraoxonase-1 activity. Clin. Biochem. 2011;44(14-15):1270-1. [CrossRef]
- Benzie IF, Strain JJ. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996;239(1):70-6. [CrossRef]
- Nusslein V, R Dahm. Zebrafish: A Practical Approach. Edited by C. Oxford University Press. 2002.
- National Research Council (US) Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th ed. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US). 2011. [CrossRef]
- Cho KH, Kim JE, Nam HS, Kang DJ, Na HJ. Anti-inflammatory activity of CIGB-258 against acute toxicity of carboxymethyl lysine in paralyzed zebrafish via enhancement of high-density lipoproteins stability and functionality. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23(17):10130. [CrossRef]
- Cho KH, Nam HS, Kim JE, Na HJ, del Carmen Dominguez-Horta M, Martinez-Donato G. CIGB-258 exerts potent anti-inflammatory activity against carboxymethyl lysine-induced acute inflammation in hyperlipidemic zebrafish via the protection of apolipoprotein A-I. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023;24(8):7044. [CrossRef]
- Owusu Ansah E, Yavari A, Mandal S, Banerjee U. Distinct mitochondrial retrograde signals control the G1-S cell cycle checkpoint. Nat. Genet. 2008;40(3):356-61. [CrossRef]
- Hayashi M, Sofuni T, Ishidate Jr M. An application of acridine orange fluorescent staining to the micronucleus test. Mutat. Res. Lett. 1983;120(4):241-7. [CrossRef]
- Park SH, Kim CG. What types of exercise are more effective in reducing obesity and blood pressure for middle-aged women? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2021;23(4):658-75. [CrossRef]
- Cho KH, Nam HS, Baek SH, Kang DJ, Na H, Komatsu T, Uehara Y. Beneficial Effect of Cuban Policosanol on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipoproteins Accompanied with Lowered Glycated Hemoglobin and Enhanced High-Density Lipoprotein Functionalities in a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, and Double-Blinded Trial with Healthy Japanese. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023 Mar 8;24(6):5185. [CrossRef]
- Askarpour M, Ghaedi E, Roshanravan N, Hadi A, Mohammadi H, Symonds ME, et al. Policosanol supplementation significantly improves blood pressure among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2019;45:89-97. [CrossRef]
- Swift DL, McGee JE, Earnest CP, Carlisle E, Nygard M, Johannsen NM. The effects of exercise and physical activity on weight loss and maintenance. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018;61(2):206-13. [CrossRef]
- Zmuda JM, Yurgalevitch SM, Flynn MM, Bausserman LL, Saratelli A, Spannaus-Martin DJ, Herbert PN, Thompson PD. Exercise training has little effect on HDL levels and metabolism in men with initially low HDL cholesterol. Atherosclerosis. 1998 Mar;137(1):215-21. [CrossRef]
- Kodama S, Tanaka S, Saito K, Shu M, Sone Y, Onitake F, et al. Effect of aerobic exercise training on serum levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol: a meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007;167(10):999-1008. [CrossRef]
- Ghirlanda G, Oradei A, Manto A, Lippa S, Uccioli L, Caputo S, et al. Evidence of plasma CoQ10-lowering effect by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1993;33(3):226-9. [CrossRef]
- Deichmann R, Lavie C, Andrews S. Coenzyme Q10 and statin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. Ochsner J. 2010;10(1):16-21.
- Pacanowski MA, Frye RF, Enogieru O, Schofield RS, Zineh I. Plasma Coenzyme Q10 Predicts Lipid-lowering Response to High-Dose Atorvastatin. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2008 Aug;2(4):289-97. [CrossRef]
- Tomasetti M, Alleva R, Solenghi MD, Littarru GP. Distribution of antioxidants among blood components and lipoproteins: significance of lipids/CoQ10 ratio as a possible marker of increased risk for atherosclerosis. Biofactors. 1999;9(2-4):231-40. [CrossRef]
- Kim J, Lee J, Kim S, Ryu HY, Cha KS, Sung DJ. Exercise-induced rhabdomyolysis mechanisms and prevention: A literature review. J. Sport. Health. Sci. 2016;5(3):324-33. 3. [CrossRef]
- Ho CM, Ho SL, Jeng YM, Lai YS, Chen YH, Lu SC, Chen HL, Chang PY, Hu RH, Lee PH. Accumulation of free cholesterol and oxidized low-density lipoprotein is associated with portal inflammation and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Inflamm. 2019 Apr 2;16:7. [CrossRef]
- Xiong DD, Zhang M, Li N, Gai JF, Mao L, Li M. Mediation of inflammation, obesity and fatty liver disease by advanced glycation endoproducts. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017;21(22). [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Pereira ENG, Paula DP, De Araujo BP, Da Fonseca MdJM, Diniz MdFHS, Daliry A, et al. Advanced glycation end product: A potential biomarker for risk stratification of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in ELSA-Brasil study. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2021;27(29):4913. [CrossRef]
- Cho KH, Kim JE, Komatsu T, Uehara Y. Protection of Liver Functions and Improvement of Kidney Functions by Twelve Weeks Consumption of Cuban Policosanol (Raydel®) with a Decrease of Glycated Hemoglobin and Blood Pressure from a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, and Double-Blinded Study with Healthy and Middle-Aged Japanese Participants. Life. 2023 Jun 4;13(6):1319. [CrossRef]
| Groups | Week 0 | Week 12 | Δ Change (%) |
p† | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SEM | Mean ± SEM | ||||
| SBP (mmHg) | Male (n=8) | 133.8 ± 6.8 | 119.1 ± 5.2 | –10.9 | 0.109 |
| Female (n=9) | 122.8 ± 2.8 | 117.2 ± 3.5 | –4.5 | 0.233 | |
| Total (n=17) | 127.9 ± 3.7 | 118.1 ± 3.0 | –7.7 | 0.046 | |
| DBP (mmHg) | Male (n=8) | 85.8 ± 5.2 | 69.1 ± 3.9 | –19.4 | 0.022 |
| Female (n=9) | 79.3 ± 2.1 | 74.2 ± 3.0 | –6.4 | 0.180 | |
| Total (n=17) | 82.4 ± 2.7 | 71.8 ± 2.4 | –12.8 | 0.007 | |
| BMI (kg/m²) | Male (n=8) | 31.0 ± 1.9 | 25.0 ± 2.7 | –19.3 | 0.092 |
| Female (n=9) | 29.0 ± 1.4 | 26.0 ± 1.4 | –10.5 | 0.146 | |
| Total (n=17) | 30.0 ± 1.1 | 25.5 ± 1.4 | –14.8 | 0.022 | |
| Weight (kg) | Male (n=8) | 99.9 ± 6.4 | 85.2 ± 5.5 | –14.7 | 0.104 |
| Female (n=9) | 79.0 ± 4.1 | 71.0 ± 4.2 | –10.2 | 0.190 | |
| Total (n=17) | 88.8 ± 4.4 | 77.7 ± 3.7 | –12.5 | 0.064 | |
| Waist circumference (cm) | Male (n=7) | 108.3 ± 3.8 | 89.7 ± 4.6 | –17.2 | 0.009 |
| Female (n=9) | 95.8 ± 3.7 | 87.4 ± 4.9 | –8.8 | 0.193 | |
| Total (n=16) | 101.2 ± 3.1 | 88.4 ± 3.3 | –12.7 | 0.008 | |
| Muscle mass (kg) | Male (n=8) | 65.3 ± 3.2 | 64.1 ± 2.8 | –1.8 | 0.786 |
| Female (n=9) | 45.2 ± 1.4 | 44.2 ± 1.4 | –2.2 | 0.625 | |
| Total (n=17) | 54.6 ± 3.0 | 53.6 ± 2.9 | –2.0 | 0.797 | |
| Total fat mass (kg) | Male (n=8) | 30.6 ± 3.4 | 17.1 ± 3.4 | –44.0 | 0.014 |
| Female (n=9) | 31.0 ± 3.4 | 24.0 ± 3.4 | –22.6 | 0.163 | |
| Total (n=17) | 30.8 ± 2.3 | 20.8 ± 2.5 | –32.6 | 0.006 | |
| Subcutaneous fat mass (kg) | Male (n=8) | 28.9 ± 3.4 | 15.8 ± 3.4 | –45.4 | 0.017 |
| Female (n=9) | 29.7 ± 3.3 | 22.9 ± 3.3 | –23.1 | 0.162 | |
| Total (n=17) | 29.3 ± 2.3 | 19.5 ± 2.5 | –33.4 | 0.007 | |
| Visceral fat mass (kg) | Male (n=8) | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.2 | –20.4 | 0.229 |
| Female (n=9) | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | –11.8 | 0.200 | |
| Total (n=17) | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | –16.4 | 0.109 | |
| Body fat percentage (%) |
Male (n=8) | 30.1 ± 1.6 | 19.2 ± 2.8 | –36.3 | 0.005 |
| Female (n=9) | 38.4 ± 2.8 | 32.7 ± 3.1 | –14.9 | 0.189 | |
| Total (n=17) | 34.5 ± 1.9 | 26.3 ± 2.7 | –23.7 | 0.018 | |
| Body water content (kg) |
Male (n=8) | 50.8 ± 2.5 | 50.0 ± 2.2 | –1.6– | 0.803 |
| Female (n=9) | 35.2 ± 1.1 | 34.4 ± 1.1 | –2.2 | 0.626 | |
| Total (n=17) | 42.5 ± 2.3 | 41.7 ± 2.2 | –1.9 | 0.806 |
| Groups | Week 0 | Week 12 | ΔChange (%) |
p† | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SEM | Mean ± SEM | ||||
| TC (mg/dL) | Male (n=8) | 267.7 ± 24.2 | 211.2 ± 12.5 | –21.1 | 0.056 |
| Female (n=9) | 221.4 ± 8.2 | 195.3 ± 15.3 | –11.8 | 0.152 | |
| Total (n=17) | 243.2 ± 13.1 | 202.8 ± 9.9 | –16.6 | 0.019 | |
| TG (mg/dL) | Male (n=8) | 191.4 ± 34.8 | 84.1 ± 17.4 | –56.1 | 0.015 |
| Female (n=9) | 102.2 ± 9.5 | 52.4 ± 6.5 | –48.7 | 0.001 | |
| Total (n=17) | 144.2 ± 19.9 | 67.3 ± 9.4 | –53.3 | 0.002 | |
| RC (mg/dL) | Male (n=8) | 36.2 ± 7.7 | 16.2 ± 3.4 | –55.4 | 0.032 |
| Female (n=9) | 20.5 ± 1.9 | 12.7 ± 2.2 | –38.0 | 0.017 | |
| Total (n=17) | 27.9 ± 4.1 | 14.3. ± 2.0 | –48.6 | 0.007 | |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | Male (n=8) | 43.8 ± 3.1 | 54.3 ± 4.7 | 23.9 | 0.084 |
| Female (n=9) | 56.3 ± 3.5 | 58.8 ± 5.9 | 4.4 | 0.721 | |
| Total (n=17) | 50.4 ± 2.8 | 56.6 ± 3.7 | 12.4 | 0.189 | |
| HDL-C/TC (%) | Male (n=8) | 17.1 ± 1.7 | 26.2 ± 2.4 | 53.2 | 0.008 |
| Female (n=9) | 25.7 ± 1.9 | 30.5 ± 2.3 | 18.6 | 0.126 | |
| Total (n=17) | 21.6 ± 1.6 | 28.5 ± 1.7 | 31.5 | 0.007 | |
| TG/HDL-C (ratio) |
Male (n=8) | 4.7 ± 0.9 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | –63.2 | 0.014 |
| Female (n=9) | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | –48.6 | 0.005 | |
| Total (n=17) | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | –58.6 | 0.005 | |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | Male (n=8) | 188.0 ± 18.7 | 140.8 ± 10.3 | –25.1 | 0.044 |
| Female (n=9) | 144.6 ± 8.3 | 123.7 ± 11.7 | –14.5 | 0.164 | |
| Total (n=17) | 165.0 ± 10.9 | 131.7 ± 7.9 | –20.2 | 0.019 | |
| LDL-C/HDL-C(ratio) | Male (n=8) | 4.5 ± 0.6 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | –38.2 | 0.029 |
| Female (n=9) | 2.7 ± 0.3 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | –17.9 | 0.198 | |
| Total (n=17) | 3.5 ± 0.4 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | –30.0 | 0.022 | |
| Serum CoQ10 (mol/L) |
Male (n=8) | 0.395 ± 0.032 | 0.547 ± 0.031 | 38.2 | 0.027 |
| Female (n=9) | 0.551 ± 0.056 | 0.595 ± 0.05 | 7.9 | 0.566 | |
| Total (n=17) | 0.473 ± 0.035 | 0.571 ± 0.029 | 20.6 | 0.090 | |
| CoQ10/TC (mol/mol) |
Male (n=8) | 59.4 ± 7.3 | 102.5 ± 11.1 | 72.6 | 0.007 |
| Female (n=9) | 99.5 ± 17.0 | 127.3 ± 20.9 | 27.9 | 0.323 | |
| Total (n=17) | 79.5 ± 10.5 | 114.9 ± 11.9 | 44.5 | 0.034 | |
| CoQ10/HDL-C (mol/mol) |
Male (n=8) | 369.7 ± 75.0 | 395.8 ± 39.7 | 7.1 | 0.764 |
| Female (n=9) | 400.5 ± 92.2 | 415.5 ± 75.3 | 3.7 | 0.902 | |
| Total (n=17) | 385.1 ± 57.3 | 405.6 ± 41.0 | 5.3 | 0.773 | |
| CoQ10/LDL-C (mol/mol) |
Male (n=8) | 85.9 ± 12.5 | 156.3 ± 19.4 | 82.0 | 0.010 |
| Female (n=9) | 155.1 ± 25.1 | 207.5 ± 34.2 | 33.8 | 0.240 | |
| Total (n=17) | 120.5 ± 16.6 | 181.9 ± 20.2 | 51.0 | 0.026 |
| Groups | Week 0 | Week 12 | Δ Change (%) |
p† | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SEM | Mean ± SEM | ||||
| AST (IU/L) | Male (n=8) | 33.5 ± 5.1 | 27.5 ± 2.2 | –17.9 | 0.306 |
| Female (n=9) | 23.7 ± 2.8 | 27.4 ± 2.8 | 16.0 | 0.352 | |
| Total (n=17) | 28.3 ± 3.0 | 27.5 ± 1.7 | –2.9 | 0.813 | |
| ALT (IU/L) | Male (n=8) | 37.8 ± 6.4 | 25.3 ± 2.8 | –33.1 | 0.103 |
| Female (n=9) | 29.2 ± 8.3 | 28.6 ± 7.0 | –2.3 | 0.952 | |
| Total (n=17) | 33.2 ± 5.3 | 27.0 ± 3.8 | –18.8 | 0.346 | |
| γ-GTP (IU/L) | Male (n=8) | 48.0 ± 11.6 | 19.9 ± 2.4 | –58.6 | 0.046 |
| Female (n=9) | 30.4 ± 6.9 | 15.6 ± 1.7 | –48.9 | 0.065 | |
| Total (n=17) | 38.7 ± 6.7 | 17.6 ± 1.5 | –54.6 | 0.007 | |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | Male (n=8) | 2.7 ± 1.1 | 3.4 ± 2.3 | 28.5 | 0.772 |
| Female (n=9) | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 2.0 ± 0.7 | –0.6 | 0.989 | |
| Total (n=17) | 2.3 ± 0.6 | 2.7 ± 1.1 | 15.2 | 0.781 | |
| apoA-I (mg/dL) | Male (n=8) | 144.5 ± 13.6 | 132.6 ± 8.7 | –8.2 | 0.473 |
| Female (n=9) | 140.9 ± 7.8 | 154.8 ± 10.4 | 9.9 | 0.303 | |
| Total (n=17) | 142.6 ± 7.4 | 144.4 ± 7.2 | 1.2 | 0.865 | |
| apo-B (mg/dL) | Male (n=8) | 140.8 ± 16.9 | 105.0 ± 7.2 | –25.4 | 0.072 |
| Female (n=9) | 89.9 ± 6.3 | 95.1 ± 7.3 | 5.8 | 0.596 | |
| Total (n=17) | 113.8 ± 10.5 | 99.8 ± 5.1 | –12.4 | 0.237 | |
| apo-B/apoA-I | Male (n=8) | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | –19.9 | 0.195 |
| Female (n=9) | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | –4.6 | 0.793 | |
| Total (n=17) | 0.8 ± 0.1 | 0.7 ± 0.0 | –13.4 | 0.277 | |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | Male (n=8) | 105.1 ± 5.7 | 97.3 ± 5.0 | –7.5 | 0.320 |
| Female (n=9) | 90.3 ± 3.7 | 89.2 ± 4.4 | –1.2 | 0.849 | |
| Total (n=17) | 97.3 ± 3.7 | 93.0 ± 3.4 | –4.4 | 0.398 | |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | Male (n=8) | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 1.1 ± 0.1 | –3.0 | 0.619 |
| Female (n=9) | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | –2.2 | 0.804 | |
| Total (n=17) | 1.1 ± 0.0 | 1.0 ± 0.0 | –2.6 | 0.627 | |
| e-GRF (mL/min/1.73m²) | Male (n=8) | 76.7 ± 2.9 | 80.0 ± 3.8 | 4.3 | 0.505 |
| Female (n=9) | 72.6 ± 4.2 | 70.1 ± 4.3 | –3.4 | 0.689 | |
| Total (n=17) | 74.4 ± 2.7 | 74.4 ± 3.1 | 0.1 | 0.988 |
| Groups | Week 0 | Week 12 | ΔChange (%) |
p† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SEM | Mean ± SEM | |||||
| VLDL | FI (Glycated) | Male (n=8) | 7131 ± 910 | 4431 ± 374 | –37.9 | 0.052 |
| Female (n=9) | 9311 ± 2943 | 5085 ± 782 | –45.4 | 0.214 | ||
| All (n=17) | 8221 ± 1484 | 4758 ± 420 | –42.1 | 0.041 | ||
| MDA (μM) | Male (n=8) | 27.1 ± 4.8 | 15.0 ± 1.9 | –44.6 | 0.080 | |
| Female (n=9) | 18.0 ± 6.5 | 10.4 ± 3.4 | –42.4 | 0.339 | ||
| All (n=17) | 22.6 ± 4.1 | 12.7 ± 2.0 | –43.7 | 0.050 | ||
| Diameter (nm) | Male (n=8) | 37.6 ± 0.4 | 39.4 ± 2.8 | 4.8 | 0.588 | |
| Female (n=9) | 38.8 ± 1.0 | 38.5 ± 2.6 | –0.8 | 0.918 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 38.1 ± 0.5 | 38.9 ± 1.7 | 2.2 | 0.659 | ||
| TC (μg/mg of protein) | Male (n=8) | 59.3 ± 10.1 | 53.1 ± 4.5 | –10.5 | 0.582 | |
| Female (n=9) | 66.6 ± 7.3 | 41.2 ± 3.4 | –38.2 | 0.009 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 63.2 ± 6.0 | 46.8 ± 3.1 | –26.0 | 0.023 | ||
| TG (μg/mg of protein) | Male (n=8) | 120.6 ± 19.4 | 74.0 ± 15.3 | –38.6 | 0.081 | |
| Female (n=9) | 131.4 ± 16.4 | 68.4 ± 10.8 | –47.9 | 0.006 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 126.3 ± 12.3 | 71.0 ± 8.9 | –43.7 | 0.001 | ||
| LDL | FI (Glycated) | Male (n=8) | 5009 ± 241 | 4358 ± 143 | –13.0 | 0.040 |
| Female (n=9) | 4907 ± 248 | 4138 ± 165 | –15.7 | 0.020 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 4955 ± 168 | 4242 ± 110 | –14.4 | 0.001 | ||
| MDA (μM) | Male (n=8) | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 3.0 ± 0.3 | –32.7 | 0.019 | |
| Female (n=9) | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.3 | –9.1 | 0.494 | ||
| All (n=17) | 4.1 ± 0.2 | 3.2 ± 0.2 | –22.0 | 0.012 | ||
| Diameter (nm) | Male (n=8) | 25.8 ± 0.7 | 27.4 ± 0.4 | 5.9 | 0.091 | |
| Female (n=9) | 26.7 ± 0.8 | 25.8 ± 0.6 | –3.5 | 0.367 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 26.3 ± 0.5 | 26.5 ± 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.740 | ||
| TC (μg/mg of protein) | Male (n=8) | 139.8 ± 14.6 | 103.2 ± 5.0 | –26.2 | 0.043 | |
| Female (n=9) | 150.1 ± 19.4 | 95.3 ± 4.7 | –36.5 | 0.023 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 145.3 ± 12.1 | 99.0 ± 3.5 | –31.8 | 0.002 | ||
| TG (μg/mg of protein) | Male (n=8) | 20.6 ± 2.1 | 12.2 ± 1.3 | –40.8 | 0.005 | |
| Female (n=9) | 19.7 ± 2.6 | 10.8 ± 1.7 | –45.2 | 0.010 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 20.1 ± 1.6 | 11.4 ± 1.1 | –43.1 | < 0.001 |
| Groups | Week 0 | Week 12 | Δ Change % |
p† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SEM | Mean ± SEM | |||||
| HDL₂ | FI (Glycated) | Male (n=8) | 2234 ± 213 | 1837 ± 180 | –17.8 | 0.175 |
| Female (n=9) | 1969 ± 166 | 1616 ± 153 | –17.9 | 0.138 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 2094 ± 133 | 1720 ± 117 | –17.9 | 0.043 | ||
| Diameter (nm) | Male (n=8) | 12.8 ± 0.4 | 13.5 ± 0.2 | 5.6 | 0.112 | |
| Female (n=9) | 12.5 ± 0.3 | 13.2 ± 0.4 | 6.0 | 0.180 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 12.6 ± 0.2 | 13.4 ± 0.2 | 5.8 | 0.038 | ||
| TC (μg/mg of protein) | Male (n=8) | 84.7 ± 12.5 | 67.2 ± 4.8 | –20.6 | 0.225 | |
| Female (n=9) | 68.7 ± 7.7 | 69.7 ± 3.6 | 1.4 | 0.910 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 76.2 ± 7.2 | 68.5 ± 2.9 | –10.1 | 0.332 | ||
| TG (μg/mg of protein) | Male (n=8) | 14.9 ± 2.8 | 7.5 ± 1.2 | –49.4 | 0.029 | |
| Female (n=9) | 9.8 ± 0.9 | 6.7 ± 1.0 | –32.2 | 0.033 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 12.2 ± 1.5 | 7.1 ± 0.8 | –42.1 | 0.004 | ||
| HDL₃ | FI (Glycated) | Male (n=8) | 1885 ± 208 | 1616 ± 159 | –14.3 | 0.322 |
| Female (n=9) | 1891 ± 241 | 1578 ± 136 | –16.6 | 0.278 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 1888 ± 156 | 1596 ± 101 | –15.5 | 0.126 | ||
| Diameter (nm) | Male (n=8) | 9.8 ± 0.3 | 11.2 ± 0.4 | 14.7 | 0.012 | |
| Female (n=9) | 9.5 ± 0.3 | 10.4 ± 0.4 | 9.5 | 0.070 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 9.6 ± 0.2 | 10.8 ± 0.3 | 12.0 | 0.002 | ||
| TC (μg/mg of protein) | Male (n=8) | 37.5 ± 1.3 | 50.0 ± 5.0 | 33.5 | 0.030 | |
| Female (n=9) | 40.5 ± 1.2 | 52.8 ± 6.7 | 30.5 | 0.107 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 39.1 ± 0.9 | 51.5 ± 4.2 | 31.8 | 0.009 | ||
| TG (μg/mg of protein) | Male (n=8) | 6.6 ± 1.2 | 5.6 ± 0.7 | –15.6 | 0.469 | |
| Female (n=9) | 4.8 ± 1.4 | 4.8 ± 0.7 | –0.2 | 1.000 | ||
| Total (n=17) | 5.7 ± 0.9 | 5.2 ± 0.5 | –8.7 | 0.643 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





