Submitted:
16 November 2023
Posted:
17 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Handwriting: acquisition and role
2. Handwriting deficits
3. Handwriting tools based on the product
4. Handwriting tools based on the process
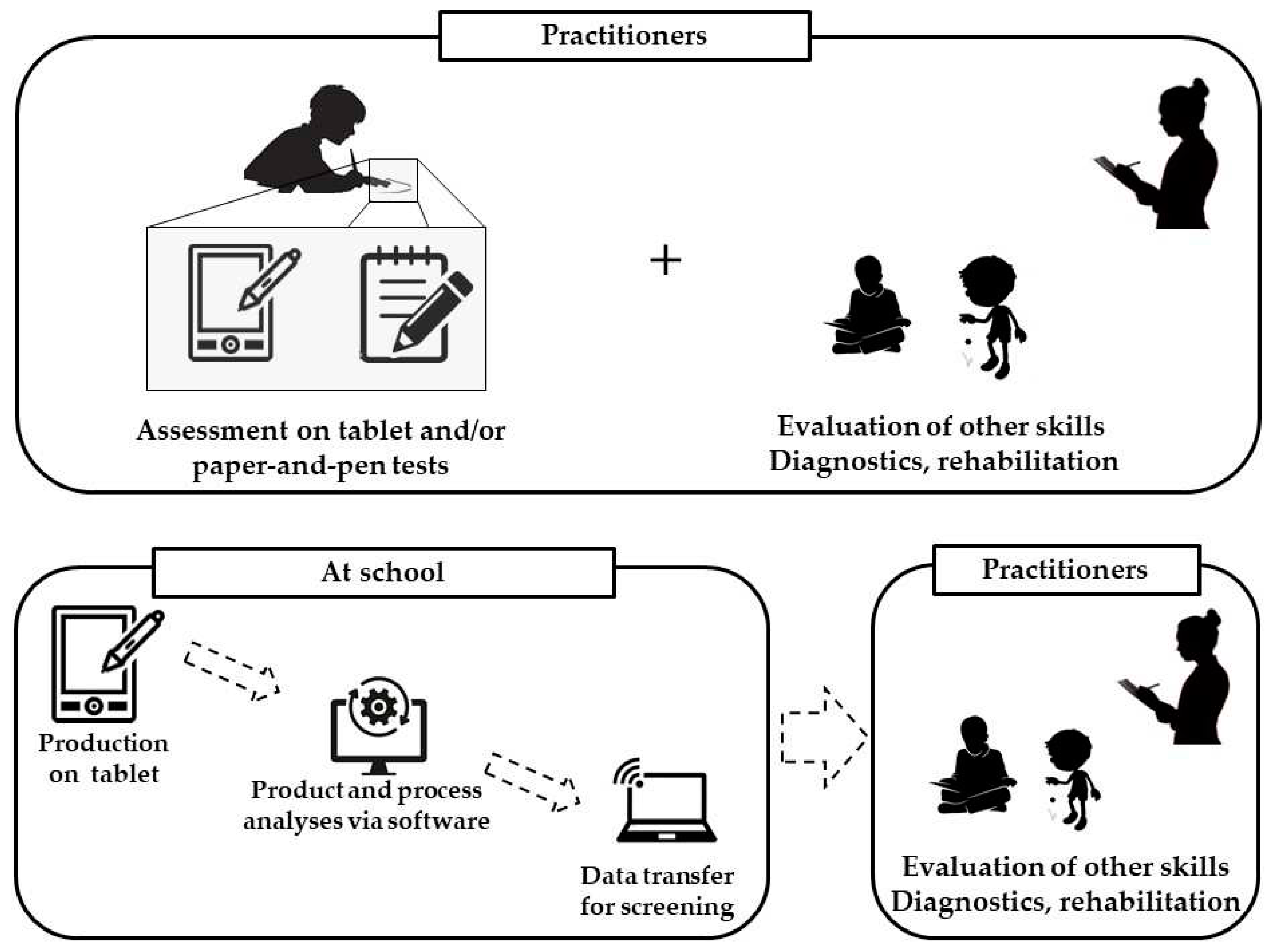
5. Perspectives: Towards a universal, standardized test of dysgraphia?
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berninger, V. W.; Abbott, R. D.; Abbott, S. P.; Graham, S.; Richards, T. Writing and reading: Connections between language by hand and language by eye. J. Learn. Disab. 2002, 35(1), 39-56. [CrossRef]
- McHale, K.; Cermak, S. A. Fine motor activities in elementary school: Preliminary findings and provisional implications for children with fine motor problems. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1992, 46(10), 898-903. [CrossRef]
- Mc Master, E.; Roberts, T. Handwriting in 2015: A main occupation for primary school–aged children in the classroom? J. Occup. Ther. Schools Early Interv. 2016, 9(1), 38. [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Christensen, C. A. Relationship between automaticity in handwriting and students' ability to generate written text. J. Educ. Psychol. 1999, 91(1), 44. [CrossRef]
- Danna, J.; Longcamp, M.; Nalborczyk, L.; Velay, J.-L.; Commengé, C.; Jover, M. Interaction between orthographic and graphomotor constraints in learning to write. Learn. Instruct. 2022, 80, 101622. [CrossRef]
- Olive, T.; Kellogg, R. T. Concurrent activation of high- and low-level production processes in written composition. Memory Cogn. 2002, 30, 594–600. [CrossRef]
- Marr, D.; Windsor, M. M.; Cermak, S. Handwriting readiness: Locatives and visuomotor skills in the kindergarten year. The Cambridge handbook of multimedia learning (2nd ed.). University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001.
- Karlsdottir, R.; Stefansson, T. Problems in developing functional handwriting. Percept. Mot. Skills 2002, 94(2), 623-662. [CrossRef]
- Palmis, S.; Danna, J.; Velay, J.-L.; Longcamp, M. Motor control of handwriting in the developing brain: A review. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2017, 34(3-4), 187-204. [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.J.; Patel, D.R.; Nizami, I. Disorder of written expression and dysgraphia: definition, diagnosis, and management. Transl. Pediatr. 2020, 9(Suppl.1), S46-S54. [CrossRef]
- Kalenjuk, E.; Laletas, S.; Subban, P.; Wilson, S. A scoping review to map research on children with dysgraphia, their carers, and educators. Austral. J. Learn. Difficult. 2022, 27(1), 19-63. [CrossRef]
- Aiswarya, G.S.; Ponniah, R.J. The modularity of dysgraphia. J. Psycholinguist. Res. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Hamstra-Bletz, L.; Blöte, A.W. A longitudinal study on dysgraphic handwriting in primary school. J. Learn. Disab. 1993, 26, 689-699. [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Pub: Washington DC, USA, 2013.
- Adi-Japha, E.; Landau, Y. E.; Frenkel, L.; Teicher, M.; Gross-Tsur, V.; Shalev, R. S. ADHD and dysgraphia: underlying mechanisms. Cortex 2007, 43, 700-709. [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.L.; Prunty, M. Handwriting Difficulties in Developmental Coordination Disorder (DCD). Curr. Dev. Disord. Rep. 2020, 8, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Biotteau, M.; Danna, J.; Baudou, E.; Puyjarinet, F.; Velay, J.-L.; Albaret, J.-M.; Chaix, Y. Developmental coordination disorder and dysgraphia: signs and symptoms, diagnosis, and rehabilitation. Neuropsy. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 1873-1885. [CrossRef]
- Capodieci, A.; Lachina, S.; Cornoldi, C. Handwriting difficulties in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Res. Dev. Disab. 2018, 74, 41-49. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.; Cohen-Kroitoru B.; Halevy, A.; Aharoni, S.; Aizenberg, I.; Shuper, A. Handwriting in children with Attention Deficient Hyperactive Disorder: role of graphology. BMC Pediatr. 2019, 19(1), 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Di Brina, C.; Caravale, B.; Mirante, N. Handwriting in children with developmental coordination disorder: Is legibility the only indicator of a poor performance? Occup. Ther. Health Care 2021, 36(4), 353-367. [CrossRef]
- Berninger, V.W.; May, M.O. Evidence-based diagnosis and treatment for specific learning disabilities involving impairments in written and/or oral language. J. Learn. Disab. 2011, 44, 167-183. [CrossRef]
- Afonso, O.; Suárez-Coalla, P.; Cuetos, F. Writing impairments in Spanish children with developmental dyslexia. J. Learn. Disab. 2020, 53, 109-119. [CrossRef]
- Alamargot, D.; Morin, M.-F.; Simard-Dupuis, E. Handwriting delay in dyslexia: children at the end of primary school still make numerous short pauses when producing letters. J. Learn. Disab., 2020, 53, 163-175. [CrossRef]
- Huau, A.; Velay, J.-L.; Jover, M. Graphomotor skills in children with developmental coordination disorder (DCD): Handwriting and learning a new letter. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2015, 42, 318-332. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B. P.; Papadopoulos, N.; Fielding, J.; Tonge, B.; Phillips, J. G.; Rinehart, N. J. Aquantitative comparison of handwriting in children with high-functioning autism andattention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Res. Autism Spectr. Dis. 2013, 7(12),1638–1646. [CrossRef]
- Jolly, C.; Jover, M.; Danna J. Dysgraphia differs between children with developmental coordination disorder and/or reading disorder. J. Learn. Disab. 2023 (in press).
- Sandler, A. D.; Watson, T. E.; Footo, M.; Levine, M. D.; Coleman, W. L.; Hooper, S. R. Neurodevelopmental study of writing disorders in middle childhood. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 1992, 13(1), 17–23. [CrossRef]
- Sumner, E.; Connelly, V.; Barnett, A.L. Children with dyslexia are slow writers because they pause more often and not because they are slow at handwriting execution. Read. Writ. 2013, 26(6), 991-1008. [CrossRef]
- Prunty, M.; Barnett, A.L. Accuracy and consistency of letter formation in children with developmental coordination disorder. J. Learn. Disab. 2020, 53(2), 120-130. [CrossRef]
- Richards, T.L.; Grabowski, T.J.; Boord, P.; Yagle, K.; Askren, M.; Mestre, Z.; Robinson, P.; Welker, O.; Gulliford, D.; Nagy, W.; Berninger, V. Contrasting brain patterns of writing-relatedDTI parameters, fMRI connectivity, and DTI–fMRI connectivity correlations in children with and without dysgraphia or dyslexia. NeuroImage: Clinical 2015, 8, 408–421. [CrossRef]
- Gosse, C.; Van Reybroeck, M. Do children with dyslexia present a handwriting deficit? Impact of word orthographic and graphic complexity on handwriting and spelling performance. Res. Dev. Disab. 2020, 97, 103553. [CrossRef]
- Berninger, V.; Abbott, R; Cook, C. R.; Nagy, W. Relationships of attention and executive functions to oral language, reading, and writing skills and systems in middle childhood and early adolescence. J. Learn. Disab. 2017, 50(4), 434-449. [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Harris, K. R. The role of self-regulation and transcription skills in writing and writing development. Educ. Psychol. 2000, 35(1), 3–12. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S. K.; Kelsch, K.; Miller, K. Occupational therapy interventions for children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review. Occup. Ther. Mental Health 2017, 33(1), 70–80. [CrossRef]
- Markham, L. R. Influences of handwriting quality on teacher evaluation of written work. Am. Educ. Res. J. 1976, 13(4), 277-283. [CrossRef]
- Engel-Yeger, B.; Nagauker-Yanuv, L.; Rosenblum, S. Handwriting performance, selfreports, and perceived self-efficacy among children with dysgraphia. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2009, 63(2), 182–192. [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Fishman, E. J.; Reid, R.; Hebert, M. Writing characteristics of students with attention deficit hyperactive disorder: A meta-analysis. Learn. Disab. Res. Pract. 2016 31(2), 75–89. [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, S.; Weiss, P. L.; Parush, S. Product and process evaluation of handwriting difficulties. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2003, 15, 41-81. [CrossRef]
- Asselborn, T.; Chapatte, M.; Dillenbourg, P. (2020). Extending the spectrum of dysgraphia: A data driven strategy to estimate handwriting quality. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3140. [CrossRef]
- Drotár, P.; Dobeš, M. Dysgraphia detection through machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21541. [CrossRef]
- Guilbert, J.; Alamargot, D.; Morin, M. F. Handwriting on a tablet screen: Role of visual and proprioceptive feedback in the control of movement by children and adults. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2019, 65, 30-41. [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, S.; Dror, G. Identifying developmental dysgraphia characteristics utilizing handwriting classification methods. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2017, 47(2), 293-298. [CrossRef]
- Hamstra-Bletz, E.; de Bie, J.; den Brinker, B.P.L.M. Beknopte beoordelingsmethode voor kinderhandschriften/ Concise evaluation scale for children’s handwriting. Swets & Zeitlinger: Lisse, Netherlands, 1987.
- Soppelsa, R.; Albaret, J.-M. BHK Ado. Editions du Centre de Psychologie Appliquée: Paris, France, 2013.
- Cornoldi, C.; Ferrara, R.; Re, A. M. BVSCO-3 Batteria per la Valutazione clinica della Scrittura e della Competenza Ortografica–3 [BVSCO-3, Battery for the assessment of writing and spelling accuracy]. Giunti Psychometrics: Italy, 2022.
- Phelps, J.; Stempel, L.; Speck, G. The Children’s Handwriting Scale: a new diagnostic tool. J. Educ. Res. 1985, 79, 46-50. [CrossRef]
- Phelps, J.; Stempel, L. The Children’s Handwriting Evaluation Scale for manuscript writing. Read. Improv. 1988, 25(4), 247-254.
- Barnett, A.; Henderson, S.; Scheib, B.; Schulz, J. Development and standardization of a new handwriting speed test: The Detailed Assessment of Speed of Handwriting. Teach. Learn. Writ. 2009, 1, 137-157.
- Scott, D.H.; Moyes, F.A.; Henderson, S.E. Diagnosis and remediation of handwriting problems. DRAKE Educational Associate: Fairwater, UK, 1985.
- Amundson, S.J. Evaluation Tool of Children’s Handwriting; OT KIDS: Homer, USA, 1995.
- Pouhet, A. L’évaluation de la vitesse d’écriture manuelle à l’aide d’une dictée de niveau progressif: l’EVEDP. A.N.A.E. 2005, 136-137, 354-363.
- Erez, N.; Parush, S. The Hebrew handwriting evaluation. School of Occupational Therapy. Faculty of Medicine. Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel; 1999.
- Barnett, A. L.; Prunty, M.; Rosenblum, S. Development of the handwriting legibility scale (HLS): A preliminary examination of reliability and validity. Res. Dev. Disab. 2018, 72, 240-247. [CrossRef]
- Pollock, N.; Lockhart, J.; Blowes, B.; Semple, K.; Webster, M.; Farhat, L.; Jacbson, J.; Bradley, J.; Brunetti, S. The McMAster Handwriting Assessment Protocol – 2nd ed. Hamilton: McMaster University, Canada, 2009.
- Reisman, J.E. Development and reliability of the research version of the Minnesota Handwriting Test. Phys. Occup. Ther. Pediatr. 1993, 13(2), 41-55. [CrossRef]
- Reisman, J.E. Minnesota Handwriting Assessment. Harcourt Assessment: San Antonio, USA, 1999.
- Mutti, M.; Martin, N.; Sterling, H.; Spalding, N. QNST-3R: Quick Neurological Screening Test (3rd ed.). Academic Therapy Publications: Novato, USA, 2017.
- Weil, M. J.; Cunningham Amundson, S. J. Relationship between visuomotor and handwriting skills of children in kindergarten. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1994, 48(11), 982-988. [CrossRef]
- Larsen, S.C.; Hammill, D.D. Test of legible handwriting: An ecological approach to holistic assessment. Pro-Ed: Austin, USA, 1989.
- Milone, M. THS-R: Test of Handwriting skills. Revised. Academic Therapy Publications: Novato, USA, 2007.
- Rosenblum, S. Development, reliability, and validity of the Handwriting Proficiency Screening Questionnaire (HPSQ). Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2008, 62(3), 298-307. [CrossRef]
- Santamaria, M.; Albaret, J.-M. Troubles graphomoteurs chez les enfants d’intelligence supérieure. Evolutions Psychomotrices 1996, 33(8), 113-120.
- Chartrel, E.; Vinter, A. The impact of spatio-temporal constraints on cursive letter handwriting in children. Learn. Instruct. 2008, 18(6), 537-547. [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, P.; Vander Hart, N.; Cortesa, C. The influence of instructional variables and task constraints on handwriting performance. J. Educ. Res. 2013, 106(3), 216-234. [CrossRef]
- Charles, M.; Soppelsa, R.; Albaret, J.-M. BHK – Echelle d’évaluation rapide de l’écriture chez l’enfant; Editions du Centre de Psychologie Appliquée: Paris, France, 2003.
- Di Brina, C.; Rossini, G. Test BHK-Scala sintetica per la valutazione della scrittura in età evolutiva. Erickson: Portland, USA, 2011; 242.
- Loizzo, A.; Zaccaria, V.; Caravale, B.; Di Brina, C. Validation of the concise assessment scale for children’s handwriting (BHK) in an Italian population. Children 2023, 10, 223. [CrossRef]
- Dimauro, G.; Bevilacqua, V.; Colizzi, L.; Di Pierro, D. TestGraphia, a software system for the early diagnosis of dysgraphia. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Isa, I. S.; Rahimi, W. N. S.; Ramlan, S. A.; Sulaiman, S. N. Automated detection of dyslexia symptom based on handwriting image for primary school children. Proced. Comp. Sci. 2019, 163, 440-449. [CrossRef]
- Skunda, J.; Nerusil, B.; Polec, J. Method for Dysgraphia Disorder Detection using Convolutional Neural Network. 30th Intl. Conf. Central Europe Comput. Graphics Visual Comput. Vision 2022.
- Asselborn, T.; Gargot, T.; Kidziński, Ł.; Johal, W.; Cohen, D.; Jolly, C.; Dillenbourg, P. Automated Human-Level Diagnosis of Dysgraphia Using a Consumer Tablet. Npj Dig. Med. 2018, 1, 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Dankovičová, Z.; Hurtuk, J.; Feciľak, P. Evaluation of Digitalized Handwriting for Dysgraphia Detection Using Random Forest Classification Method. In 2019 IEEE 17th Intl. Symp. Intell. Systems Inform. (SISY) 2019; pp. 000149-000154. [CrossRef]
- Devillaine, L.; Lambert, R.; Boutet, J.; Aloui, S.; Brault, V.; Jolly, C.; Labyt, E. Analysis of Graphomotor Tests with Machine learning Algorithms for an Early and Universal Pre-Diagnosis of Dysgraphia. Sensors 2021, 21(21), 7026. [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, L.; Devillaine, L.; Gaffet, C.; Lambert, R.; Aloui, S.; Boutet, J.; Brault, V.; Labyt, E.; Jolly, C. Development of a pre-diagnosis tool based on machine learning Algorithms on the BHK test to improve the diagnosis of dysgraphia. Adv. Artif. Intell. Mach. Learn. 2021, 1(2), 109-128. [CrossRef]
- Dui, L. G.; Lunardini, F.; Termine, C.; Matteucci, M.; Stucchi, N. A.; Borghese, N. A.; Ferrante, S. A tablet app for handwriting skill screening at the preliteracy stage: Instrument validation study. JMIR Serious Games 2020, 8(4), e20126. [CrossRef]
- Dui, L. G.; Calogero, E.; Malavolti, M.; Termine, C.; Matteucci, M.; Ferrante, S. Digital tools for handwriting proficiency evaluation in children. In 2021 IEEE EMBS Intl. Conf. Biomed. Health Inform. (BHI) 2021; pp. 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Dui, L. G.; Lomurno, E.; Lunardini, F.; Termine, C.; Campi, A.; Matteucci, M.; Ferrante, S. Identification and characterization of learning weakness from drawing analysis at the pre-literacy stage. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12(1), 21624. [CrossRef]
- Falk, T. H.; Tam, C.; Schellnus, H.; Chau, T. On the development of a computer-based handwriting assessment tool to objectively quantify handwriting proficiency in children. Comp. Meth. Progr. Biomed. 2011, 104(3), e102-e111. [CrossRef]
- Galaz, Z.; Mucha, J.; Zvoncak, V.; Mekyska, J.; Smekal, Z.; Safarova, K.; Ondrackova ; A.; Urbanke, T.; Havigerova, J. M.; Bednarova, J.; Faundez-Zanuy, M. Advanced parametrization of graphomotor difficulties in school-aged children. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 112883-112897. [CrossRef]
- Gargot, T.; Asselborn, T.; Pellerin, H.; Zammouri, I.; Anzalone, S.M.; Casteran, L.; Johal, W.; Dillenbourg, P.; Cohen, D.; Jolly, C. Acquisition of handwriting in children with and without dysgraphia: A computational approach, PLOS ONE 2020, 15(9), e0237575. [CrossRef]
- Herstic, A.Y.; Bansil, S.; Plotkin, M.; Zabel, T.A.; Mostofsky, S.H. Validity of an automated handwriting assessment in occupational therapy settings. J. Occup. Ther. Schools Early Interv. 2022, 16, 28-38. [CrossRef]
- Kedar, S. V. Identifying Learning Disability Through Digital Handwriting Analysis. Turk. J. Comp. Math. Educ. (TURCOMAT) 2021, 12(1S), 46-56. [CrossRef]
- Kunhoth, J.; Al Maadeed, S.; Saleh, M.; Akbari, Y. Exploration and analysis of On-Surface and In-Air handwriting attributes to improve dysgraphia disorder diagnosis in children based on machine learning methods. Biomed. Sign. Process. Control 2023, 83, 104715. [CrossRef]
- Mekyska, J.; Faundez-Zanuy, M.; Mzourek, Z.; Galaz, Z.; Smekal, Z.; Rosenblum, S. Identification and rating of developmental dysgraphia by handwriting analysis. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2016, 47(2), 235-248. [CrossRef]
- Mekyska, J.; Galaz, Z.; Safarova, K.; Zvoncak, V.; Mucha, J; Smekal, Z.; Ondrackova, A.; Urbanek, T.; Havigerova, J. M.; Bednarova, J.; Faundez-Zanuy, M. Computerised assessment of graphomotor difficulties in a cohort of school-aged children. In 2019 11th International Congress on Ultra Modern Telecommunications and Control Systems and Workshops (ICUMT) 2019 (pp. 1-6). [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, S.; Dvorkin, A.Y.; Weiss, P.L. Automatic segmentation as a tool for examining the handwriting process of children with dysgraphic and proficient handwriting. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2006, 25, 608-621. [CrossRef]
- Sihwi, S.W.; Fikri, K.; Aziz, A. Dysgraphia identification from handwriting with Support Vector Machine method. J. Physics Conf. Series 2019, 1201. [CrossRef]
- Zvoncak, V.; Mekyska, J.; Safarova, K.; Smekal, Z.; Brezany, P. New approach of dysgraphic handwriting analysis based on the tunable Q-factor wavelet transform. 42nd International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), 2019a, pp. 289-294.
- Zvoncak, V.; Mucha, J.; Galaz, Z.; Mekyska, J.; Safarova, K.; Faundez-Zanuy, M. Fractional order derivatives evaluation in computerized assessment of handwriting difficulties in school-aged children. 11th International Congress on Ultra Modern Telecommunications and Control Systems and Workshops (ICUMT), 2019b, pp. 1-6.
- Lopez, C.; Vaivre-Douret, L. Exploratory investigation of handwriting disorders in school-aged children from first to fifth grade. Children 2023a, 10, 1512. [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, L.; Gaffet, C.; Aloui, S.; Boutet, J.; Brault, V.; Labyt, E. Methodological issues in the creation of a diagnosis tool for dysgraphia. NPJ Dig. Med. 2019, 2(1), 36. [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.; Boutet, J.; Labyt, E.; Jolly, C. Analysis of Eye Movements in Children with Developmental Coordination Disorder During a Handwriting Copy Task. In International Graphonomics Conference, Evora, Portugal, October 2023. Cham: Springer Nature, Switzerland; (pp. 36-44).
- Lopez, C.; Cannafarina, A.; Vaivre-Douret, L. Validity of kinematics measures to assess handwriting development and disorders with a graphomotor task. Eur. Psych. 2021, 64.
- Bublin, M.; Werner, F.; Kerschbaumer, A.; Korak, G.; Geyer, S.; Rettinger, L.; Schönthaler, E.; Schmid-Kietreiber, M. Handwriting evaluation using deep-leraning with SensoGrip. Sensors 2023, 23¸ 5215. [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Vaivre-Douret, L. Concurrent and predictive validity of a cycloid loops copy task to assess handwriting disorders in children. Children 2023b, 10, 305. [CrossRef]
- Safarova, K.; Mekyska, J.; Zvoncak, V. Developmental dysgraphia: A new approach to diagnosis. Int. J. Assess. Eval. 2021, 28,143-160. [CrossRef]
| Test name | Reference | Ages / Classes | Duration of test | Language | Task(s) | Subdomains |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BHK: Brave Handwriting Kinder | [43] | 1st- to 5th-grade | 5 mn | Multi-language | Copy | Quality Speed |
| BHK Ado: Rapid writing evaluation scale for adolescents [Echelle d’évaluation rapide de l’écriture chez l’adolescent] | [44] | 6th- to 9th-grade | 5 mn | French | Copy | Quality Speed |
| BVSCO-3 – Test for the Evaluation of Writing and Orthographic Ability, 3rd ed. |
[45] | 6-14 y | Variable | Multi-language | Copy Dictation Spontaneous production |
Speed % of errors |
| CHES – Children's Handwriting Evaluation Scale | [46] | 3rd- to 8th-grade | 2 mn | English | Copy | Quality Fluency |
| CHES-M – Children's Handwriting Evaluation Scale - Manuscript Writing |
[47] | 1st- to 2nd-grade | 2 mn | English | Copy | Quality Fluency |
| DASH – Detailed Assessment of Speed of Handwriting | [48] | 9-16 y | 14 mn | English | Alphabet copy at normal and high speed Spontaneous production |
Speed |
| DRHP – Diagnosis and Remediation of Handwriting Problems | [49] | From 3rd-grade | Variable | English | Spontaneous production from images observation | Quality |
| ETCH-M – Evaluation Tool of Children's Handwriting - Manuscript |
[50] | 1st- to 2nd-grade | 15-20 mn | English | Copy Dictation Spontaneous production Handwriting from memory |
Quality Speed |
| EVEDP – Evaluation de la Vitesse d’Ecriture – Dictée Progressive | [51] | 2nd- to 5th-grade | Variable | French | Dictation | Speed |
| HHE - Hebrew Handwriting Evaluation | [52] | 6-18 y | 5 min | Hebrew | Alphabet Copy of a text |
Quality Speed |
| HLS – Handwriting Legibility Scale | [53] | 9-14 y | 10 mn | English | Spontaneous production | Quality |
| MMHAP – Mac Master Handwriting Assessment Protocol | [54] | Preschool to 6th-grade | Variable | English | Copy Dictation Spontaneous production Handwriting from memory |
Quality Speed |
| MHA – Minnesota Handwriting Assessment | [55,56] | 1st- to 2nd-grade | 2 mn ½ | English | Alphabet Copy |
Quality Speed |
| QNST-3 Revised – Quick Neurological Screening Test, 3rd ed. Revised | [57] | 5-80 y | 30 mn | English | Copy | Quality |
| SCRIPT– Scale of Children’s Readiness in PrinTing | [58] | N.A. | 3-8 mn | English | Copy | Quality |
| TOLH – Test Of Legible Handwriting | [59] | 2nd- to 12th-grade | Variable | English | Spontaneous production Text composition at school |
Quality |
| THS-R | [60] | 6-18 y | N.A. | English | Alphabet Copy |
Quality |
| HPSQ – Handwriting Proficiency Screening Questionnaire | [61] | 7-14 y | N.A. | Multi-language | Questionnaire | Quality |
| Questionnaire for children | [62] | 1st- to 5th-grade | 2-3 mn | French | Auto-questionnaire | Self-report on handwriting quality and difficulties |
| Test name [ref] | Number of participants | Country of validation | Inter-rater validity | Test-retest validity | Internal consistancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BHK [13,43] | 121 | Netherlands | .71 to .89 | .74 to .86 | N.A. |
| BHK - French adaptation [65] | 837 | France | .68 to .90 | .80 to .92 | N.A. |
| BHK Ado [44] | 471 | France | .24 to .66 | N.A. | N.A. |
| BHK - Italian adaptation [66,67] | 562 | Italy | .82 to .93 for speed .42 to .63 for quality |
N.A. | N.A. |
| CHES-M [47] | 643 | USA | .85 to .93 | N.A. | N.A. |
| DASH [48] | 1163 | Netherlands | .85 to .99 | .50 to .92 .81 | .88 to .94 |
| DRHP [49] | 300 | UK | .61 to .65 | N.A. | N.A. |
| ETCH-M [50] | N.A. | N.A. | .75 to .92 | .63 to .77 | N.A. |
| HHE [52] | N.A. | Israël | .75 to .79 | N.A. | N.A. |
| HPSQ [61] | 230 | Israël | .92 | .84 | .90 |
| MHA [55,56] | N.A. | USA | .87 to .98 | .58 to .94 | N.A. |
| THS-R [60] | N.A. | USA | N.A. | .82 | N.A. |
| TOLH [59] | 1723 | USA | .95 | .90 | .86 |
| Ref | Ages / Classes | Characteristics of participants | Task(s) | Language | Approach | Performances |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [68] | 7-10 y | Dysgraphic | BHK (5 lines) | Italian | Algorithms for document analysis | Sensitivity: 83 % Specificity: 98 % Precision: 96 % |
| [69] | 7-12 y | Dyslexic | Letters and digits writing | Malaysian | Machine Learning (ANN) | Sensitivity: 73 % |
| [70] | 8-15 y | Typically Developing and Dysgraphic |
Letters, syllables, words, pseudowords, and sentences |
Slovak | Machine Learning (CNN, RF, SVM, AdaBoost) | Precision: 79.7 % |
| Reference | Ages / Classes | n | Tasks | Langage / alphabet | Approach | Criteria analysed | Performances |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [71] | 6-10 y | 242 TD 56 DG |
Copy of a (BHK) | French | RF | Static Kinematic Pressure Pen tilt |
SE: 96,6 % SP: 99,2 % P: 97,98 % |
| [39] | 5-12 y |
390 TD 58 DG |
Letters, words, sentences | French | PCA + K-means clustering |
Static Kinematic |
SE: 91 % SP: 90 % |
| [72] | 10-13 y | 39 TD 39 DG |
Letters, words, sentences | Slovak | SVM | Kinematic | SE: 75,5 % |
| [73] | 7-11 y | 262 TD 63 DG |
Copy of graphic shapes | N.A. | SVM, RF, MLP, extra trees, AdaBoost, Gaussian Naive Bayes | Kinematic | SE: 75,1 % (RF) SP: 72,1 % (MLP) P: 73 % (extra trees), 73,4 % (RF) |
| [74] | 7-11 y | 458 TD 122 DG |
Copy of a text (BHK) | French | SVM | Kinematic Spatial | SE: 91 % SP: 81 % P: 86 % |
| [40] | 8-15 y | 63 TD 57 DG |
Letters, syllables, words, pseudowords, sentences with speed constraints | Slovak | AdaBoost, RF, SVM | Kinematic | SE: 79,7 % SP: 76,7 % P: 80 % |
| [75] | 5-8 y |
76 TD 28 DG |
Copy of words (8y), graphic shapes (5 and 8y) |
Italian | Statistical comparison between groups |
Kinematic Pressure |
N.A. |
| [76] | 7-8 y | 52 TD | Subtest of the BVSCO-2 (digits, sequence of small and large loops, words) | Italian | Statistical comparisons | Kinematic | N.A. |
| [77] | 5 y | 241 «at-risk of DG» | Copy of graphic shapes | N.A. | 1 dimension CNN | Kinematic | SE: 75 % SP: 77 % P: 76 % |
| [78] | 6-7 y |
26 TD 9 DG |
MHA | English | Statistical comparisons |
Static Kinematic |
N.A. |
| [79] | 8-12 y | 26 TD | Copy of graphic shapes | Czech | Q factor wavelet transform + statistical comparisons |
Static Kinematic |
P: 84 % |
| 27 DG | |||||||
| [80] | 7-10 y |
218 TD 62 DG |
Copy of a text (BHK) | French | Statistical comparisons between groups (linear regression), clustering |
Static Kinematic Pressure Pen tilt |
N.A. |
| [81] | 6-11 y |
5 TD 9 ADHD |
Dictation of letters and digits MHA |
English | Statistical correlations between manual and digital data |
Static Kinematic |
N.A. |
| [82] | 7-12 y | 60 | Copy of words, sentences and graphic shapes | Latin | RF, Decision tree, SVM | Kinematic | SE: 92,8 % P: 92,6 % |
| [83] | 8-15 y | 63 TD 57 DG |
Letters, words, sentences | Slovak | KNN, SVM, RF, AdaBoost | Kinematic (on-surface and in-air) | SE: 78,5 % P: 80,8 % |
| [84] | 8 y | 27 TD | Letters | Hebrew | RF, linear discriminant analysis | Kinematic | SE: 96 % |
| 27 DG | |||||||
| [85] | 8-9 y | 61 TD 15 DG |
Copy of patterns and figures | Czech | XG-Boost | Kinematic | SE: 90 % |
| [86] | 8-9 y |
14 TD 14 DG |
Copy of a text | Hebrew | Statistical comparisons between groups |
Static Kinematic |
N.A. |
| [42] | 8-9 y | 50 TD 49 DG |
Copy of letters and sentences | Hebrew | SVM | Static Kinematic |
SE: 90 % SP: 90 % P : 89,9 % |
| [87] | 8-11 y | 32 TD | Spontaneous writing (sentences), drawings | Indonesian | SVM & RBF Kernel | Kinematic | P : 82,5 % |
| [88] | 8-9 y | 33 TD 32 DG |
Copy of a text | Czech | Tunable Q-factor wavelet transfom, RF and SVM classifiers | Kinematic | SE: 88,7 % SP: 83 % P: 84,7 % |
| [89] | 8-9 y |
30 TD 25 DG |
Spontaneous writing of letters | Czech | Correlation between the kinematic features and the HPSQ-C | Kinematic | N.A. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





