Submitted:
09 October 2023
Posted:
17 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. METHODS
3. PATHOGENESIS OF ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN SELECTED INFLAMMATORY CONDITIONS
4. GENE EXPRESSION IN PSORIASIS, T2DM, AND RA PROMOTING ATHEROSCLEROSIS DEVELOPMENT
5. THE ROLE OF MICRORNAS IN ATHEROSCLEROSIS, PSORIASIS, T2DM AND RA
5.1. MiR-146a
5.2. MiR-210
5.3. MiR-143
5.4. MiR-223
5.5. MiR-155
5.6. MiR-145
5.7. MiR-200
5.8. MiR-133
5.9. MiR-135
5.10. MiR-221
5.11. MiR-424
5.12. Let-7
LONG NON-CODING RNA IN ATHEROSCLEROSIS, PSORIASIS, T2DM AND RA
6.1. LncRNA-H19
6.2. lncRNA-MEG3
6.3. lncRNA-UCA1
6.4. LncRNA-XIST
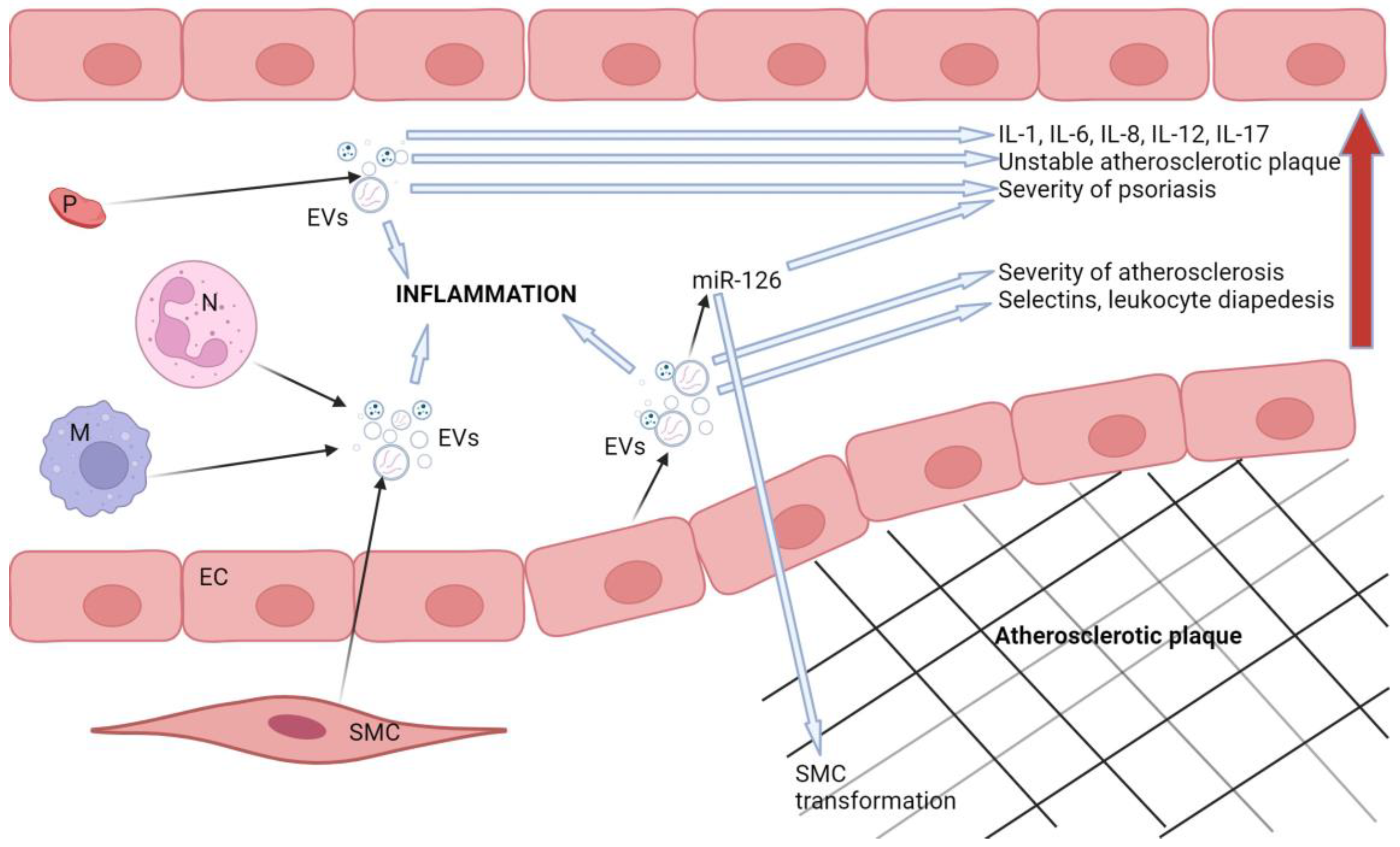
7. THE ROLE OF EXTRACELLULAR VESICLES IN ATHEROSCLEROSIS, PSORIASIS, T2DM, AND RA
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Libby, P. Inflammation during the life cycle of the atherosclerotic plaque. Cardiovasc Res. 2021;117(13):2525-2536. [CrossRef]
- Libby, P. The changing landscape of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2021;592(7855):524-533. [CrossRef]
- Henein MY, Vancheri S, Longo G, Vancheri F. The Role of Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(21):12906. Published 2022 Oct 26. [CrossRef]
- Lin YJ, Anzaghe M, Schülke S. Update on the Pathomechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. 2020;9(4):880. Published 2020 Apr 3. [CrossRef]
- Luc K, Schramm-Luc A, Guzik TJ, Mikolajczyk TP. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2019;70(6):10.26402/jpp.2019.6.01. [CrossRef]
- Tibaut M, Mankoč Ramuš S, Petrovič D. The C allele of the reactive oxygen species modulator 1 (ROMO1) polymorphism rs6060566 is a biomarker predicting coronary artery stenosis in Slovenian subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Med Genomics. 2020;13(1):184. Published 2020 Dec 10. [CrossRef]
- Borroni RG, Costanzo A. HLA-C*06 and psoriasis: susceptibility, phenotype, course and response to treatment. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178(4):825. [CrossRef]
- Chen L, Tsai TF. HLA-Cw6 and psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178(4):854-862. [CrossRef]
- Huang YW, Tsai TF. HLA-Cw1 and Psoriasis. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2021;22(3):339-347. [CrossRef]
- Caiazzo G, Fabbrocini G, Di Caprio R, et al. Psoriasis, Cardiovascular Events, and Biologics: Lights and Shadows. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1668. Published 2018 Aug 13. [CrossRef]
- Furue M, Tsuji G, Chiba T, Kadono T. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Comorbid with Psoriasis: Beyond the Skin. Intern Med. 2017;56(13):1613-1619. [CrossRef]
- Choudhary S, Patel R, Pradhan D, et al. Psoriasis and cardiovascular disorders: association or epiphenomenon? Meta-analysis of observational studies. 3 Biotech. 2020;10(3):104. [CrossRef]
- Reich, K. The concept of psoriasis as a systemic inflammation: implications for disease management. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2012;26 Suppl 2:3-11. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad E, Lim S, Lamptey R, Webb DR, Davies MJ. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2022;400(10365):1803-1820. [CrossRef]
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis [published correction appears in Lancet. 2016 Oct 22;388(10055):1984]. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2023-2038. [CrossRef]
- Finckh A, Gilbert B, Hodkinson B, et al. Global epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(10):591-602. [CrossRef]
- Praveenkumar U, Ganguly S, Ray L, Nanda SK, Kuruvila S. Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Psoriasis Patients and its Relation to Disease Duration: A Hospital Based Case-Control Study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(2):WC01-WC5. [CrossRef]
- Shibata S, Tada Y, Hau CS, et al. Adiponectin regulates psoriasiform skin inflammation by suppressing IL-17 production from γδ-T cells. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7687. Published 2015 Jul 15. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Cantero A, Gonzalez-Cantero J, Sanchez-Moya AI, et al. Subclinical atherosclerosis in psoriasis. Usefulness of femoral artery ultrasound for the diagnosis, and analysis of its relationship with insulin resistance. PLoS One. 2019;14(2):e0211808. Published 2019 Feb 8. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Morales JMG, Puig L, Daudén E, et al. Critical role of interleukin (IL)-17 in inflammatory and immune disorders: An updated review of the evidence focusing in controversies. Autoimmun Rev. 2020;19(1):102429. [CrossRef]
- Marder W, Khalatbari S, Myles JD, et al. Interleukin 17 as a novel predictor of vascular function in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(9):1550-1555. [CrossRef]
- Kaur R, Kaur M, Singh J. Endothelial dysfunction and platelet hyperactivity in type 2 diabetes mellitus: molecular insights and therapeutic strategies. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2018;17(1):121. Published 2018 Aug 31. [CrossRef]
- Kothiwala SK, Khanna N, Tandon N, et al. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular changes in patients with chronic plaque psoriasis and their correlation with disease severity: A hospital-based cross-sectional study. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2016;82(5):510-518. [CrossRef]
- Bordy R, Totoson P, Prati C, Marie C, Wendling D, Demougeot C. Microvascular endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14(7):404-420. [CrossRef]
- Ikeda N, Kogame N, Iijima R, Nakamura M, Sugi K. Carotid artery intima-media thickness and plaque score can predict the SYNTAX score. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(1):113-119. [CrossRef]
- Fang N, Jiang M, Fan Y. Association Between Psoriasis and Subclinical Atherosclerosis: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(20):e3576. [CrossRef]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration, Sarwar N, Gao P, et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies [published correction appears in Lancet. 2010 Sep 18;376(9745):958. Hillage, H L [corrected to Hillege, H L]]. Lancet. 2010;375(9733):2215-2222. [CrossRef]
- Brohall G, Odén A, Fagerberg B. Carotid artery intima-media thickness in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose tolerance: a systematic review. Diabet Med. 2006;23(6):609-616. [CrossRef]
- Wang P, Guan SY, Xu SZ, et al. Increased carotid intima-media thickness in rheumatoid arthritis: an update meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2016;35(2):315-323. [CrossRef]
- Que X, Hung MY, Yeang C, et al. Oxidized phospholipids are proinflammatory and proatherogenic in hypercholesterolaemic mice [published correction appears in Nature. 2018 Sep;561(7724):E43]. Nature. 2018;558(7709):301-306. [CrossRef]
- Kim TW, Febbraio M, Robinet P, et al. The critical role of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4-mediated NF-κB activation in modified low-density lipoprotein-induced inflammatory gene expression and atherosclerosis. J Immunol. 2011;186(5):2871-2880. [CrossRef]
- Mehta NN, Li R, Krishnamoorthy P, et al. Abnormal lipoprotein particles and cholesterol efflux capacity in patients with psoriasis. Atherosclerosis. 2012;224(1):218-221. [CrossRef]
- Bahiru E, Hsiao R, Phillipson D, Watson KE. Mechanisms and Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Diabetes. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021;23(4):26. Published 2021 Mar 2. [CrossRef]
- Venetsanopoulou AI, Pelechas E, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA. The lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis: the dark horse of the augmented cardiovascular risk. Rheumatol Int. 2020;40(8):1181-1191. [CrossRef]
- Chiu JJ, Chien S. Effects of disturbed flow on vascular endothelium: pathophysiological basis and clinical perspectives. Physiol Rev. 2011;91(1):327-387. [CrossRef]
- Popescu D, Rezus E, Badescu MC, et al. Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Accelerated Atherosclerosis, New Biomarkers, and the Effects of Biological Therapy. Life (Basel). 2023;13(2):319. Published 2023 Jan 23. [CrossRef]
- Su W, Zhao Y, Wei Y, Zhang X, Ji J, Yang S. Exploring the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis Complicated With Atherosclerosis via Microarray Data Analysis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:667690. Published 2021 May 27. [CrossRef]
- Zhang M, Cai ZR, Zhang B, et al. Functional polymorphisms in interleukin-23 receptor and susceptibility to coronary artery disease. DNA Cell Biol. 2014;33(12):891-897. [CrossRef]
- Eirís N, González-Lara L, Santos-Juanes J, Queiro R, Coto E, Coto-Segura P. Genetic variation at IL12B, IL23R and IL23A is associated with psoriasis severity, psoriatic arthritis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;75(3):167-172. [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Vázquez C, Posadas-Sánchez R, Pérez-Hernández N, et al. The rs2066808 Polymorphism Located Near the IL-23A Gene Is Associated with Premature Coronary Artery Disease in Mexican Population (GEA Study). DNA Cell Biol. 2019;38(8):880-886. [CrossRef]
- Eder L, Abji F, Rosen CF, Chandran V, Cook RJ, Gladman DD. The Association of HLA-class I Genes and the Extent of Atherosclerotic Plaques in Patients with Psoriatic Disease. J Rheumatol. 2016;43(10):1844-1851. [CrossRef]
- Harden JL, Lewis SM, Pierson KC, et al. CARD14 expression in dermal endothelial cells in psoriasis. PLoS One. 2014;9(11):e111255. Published 2014 Nov 4. [CrossRef]
- Fu Y, Xu L, Zhang H, et al. Identification and Validation of Immune-Related Genes Diagnostic for Progression of Atherosclerosis and Diabetes. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:505-521. Published 2023 Feb 10. [CrossRef]
- Xiao L, Yang Z, Lin S. Identification of hub genes and transcription factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis complicated with atherosclerosis. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):4677. Published 2022 Mar 18. [CrossRef]
- Tibaut M, Caprnda M, Kubatka P, et al. Markers of Atherosclerosis: Part 2 - Genetic and Imaging Markers. Heart Lung Circ. 2019;28(5):678-689. [CrossRef]
- Salvi V, Gianello V, Tiberio L, Sozzani S, Bosisio D. Cytokine Targeting by miRNAs in Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10:15. Published 2019 Jan 29. [CrossRef]
- Hermann H, Runnel T, Aab A, et al. miR-146b Probably Assists miRNA-146a in the Suppression of Keratinocyte Proliferation and Inflammatory Responses in Psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 2017;137(9):1945-1954. [CrossRef]
- Huang P, He XY, Xu M. The Role of miRNA-146a and Proinflammatory Cytokines in Carotid Atherosclerosis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6657734. Published 2020 Dec 9. [CrossRef]
- Xue L, Luo S, Ding H, et al. Upregulation of miR-146a-5p is associated with increased proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells in aortic dissection. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019;33(4):e22843. [CrossRef]
- Dong S, Xiong W, Yuan J, Li J, Liu J, Xu X. MiRNA-146a regulates the maturation and differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells by targeting NF-κB expression. Mol Med Rep. 2013;8(2):407-412. [CrossRef]
- Vaher H, Kivihall A, Runnel T, et al. SERPINB2 and miR-146a/b are coordinately regulated and act in the suppression of psoriasis-associated inflammatory responses in keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 2020;29(1):51-60. [CrossRef]
- Leal B, Carvalho C, Ferreira AM, et al. Serum Levels of miR-146a in Patients with Psoriasis. Mol Diagn Ther. 2021;25(4):475-485. [CrossRef]
- Ele-Refaei AM, El-Esawy FM. Effect of Narrow-Band Ultraviolet B Phototherapy and Methotrexate on MicroRNA (146a) Levels in Blood of Psoriatic Patients [published correction appears in Dermatol Res Pract. 2016;2016:7168587]. Dermatol Res Pract. 2015;2015:145769. [CrossRef]
- Raitoharju E, Lyytikäinen LP, Levula M, et al. miR-21, miR-210, miR-34a, and miR-146a/b are up-regulated in human atherosclerotic plaques in the Tampere Vascular Study. Atherosclerosis. 2011;219(1):211-217. [CrossRef]
- Zhelankin AV, Stonogina DA, Vasiliev SV, et al. Circulating Extracellular miRNA Analysis in Patients with Stable CAD and Acute Coronary Syndromes. Biomolecules. 2021;11(7):962. Published 2021 Jun 29. [CrossRef]
- Guo W, Li XN, Li J, et al. Increased plasma miR-146a levels are associated with subclinical atherosclerosis in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Complications. 2020;34(12):107725. [CrossRef]
- Gao W, Li R, Yu J, et al. LncRNA SCIRT is downregulated in atherosclerosis and suppresses the proliferation of human aortic smooth muscle cells (HAOSMCs) by sponging miR-146a in cytoplasm. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021;16(1):324. Published 2021 Nov 6. [CrossRef]
- Gong HB, Zhang SL, Wu XJ, Pu XM, Kang XJ. Association of rs2910164 polymorphism in MiR-146a gene with psoriasis susceptibility: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(6):e14401. [CrossRef]
- Bao Q, Li R, Wang C, et al. Association between microRNA-146a rs2910164 polymorphism and coronary heart disease: An updated meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(46):e31860. [CrossRef]
- Bao MH, Xiao Y, Zhang QS, et al. Meta-Analysis of miR-146a Polymorphisms Association with Coronary Artery Diseases and Ischemic Stroke. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(7):14305-14317. Published 2015 Jun 24. [CrossRef]
- Alipoor B, Ghaedi H, Meshkani R, et al. Association of MiR-146a Expression and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2017;6(3):156-163. [CrossRef]
- Zhu H, Leung SW. MicroRNA biomarkers of type 2 diabetes: evidence synthesis from meta-analyses and pathway modelling. Diabetologia. 2023;66(2):288-299. [CrossRef]
- Cheng L, Zhou M, Zhang D, Chen B. Association of miR-146a polymorphism rs2910164 and type 2 diabetes risk: a meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. 2020;48(8):300060520931313. [CrossRef]
- Shen J, Zhang M, Sun M, Tang K, Zhou B. The relationship of miR-146a gene polymorphism with carotid atherosclerosis in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Thromb Res. 2015;136(6):1149-1155. [CrossRef]
- Bae SC, Lee YH. MiR-146a levels in rheumatoid arthritis and their correlation with disease activity: a meta-analysis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21(7):1335-1342. [CrossRef]
- Liu F, Liang Y, Zhao Y, Chen L, Wang X, Zhang C. Meta-analysis of association of microRNAs genetic variants with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(17):e25689. [CrossRef]
- Tao J, Xia L, Cai Z, et al. Interaction Between microRNA and DNA Methylation in Atherosclerosis. DNA Cell Biol. 2021;40(1):101-115. [CrossRef]
- Ivan M, Harris AL, Martelli F, Kulshreshtha R. Hypoxia response and microRNAs: no longer two separate worlds. J Cell Mol Med. 2008;12(5A):1426-1431. [CrossRef]
- Signorelli SS, Volsi GL, Pitruzzella A, et al. Circulating miR-130a, miR-27b, and miR-210 in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease and Their Potential Relationship With Oxidative Stress. Angiology. 2016;67(10):945-950. [CrossRef]
- Eken SM, Jin H, Chernogubova E, et al. MicroRNA-210 Enhances Fibrous Cap Stability in Advanced Atherosclerotic Lesions. Circ Res. 2017;120(4):633-644. [CrossRef]
- Wu R, Zeng J, Yuan J, et al. MicroRNA-210 overexpression promotes psoriasis-like inflammation by inducing Th1 and Th17 cell differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(6):2551-2568. [CrossRef]
- Zhao M, Wang LT, Liang GP, et al. Up-regulation of microRNA-210 induces immune dysfunction via targeting FOXP3 in CD4(+) T cells of psoriasis vulgaris. Clin Immunol. 2014;150(1):22-30. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Jia Z, Zhao X, Xu M, Chen M. Expression of miR-210 in the peripheral blood of patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus and its effect on the number and function of endothelial progenitor cells. Microvasc Res. 2020;131:104032. [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Tian F, Sun Z, Zeng G, Tang P. Elevation of Circulating miR-210 Participates in the Occurrence and Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications. J Diabetes Res. 2022;2022:9611509. Published 2022 Nov 23. [CrossRef]
- Amr KS, Abdelmawgoud H, Ali ZY, Shehata S, Raslan HM. Potential value of circulating microRNA-126 and microRNA-210 as biomarkers for type 2 diabetes with coronary artery disease. Br J Biomed Sci. 2018;75(2):82-87. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Z, Collado A, Sun C, et al. Downregulation of Erythrocyte miR-210 Induces Endothelial Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes. 2022;71(2):285-297. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Zhang J, Qin Z, et al. Diagnostic and Predictive Values of Circulating Extracellular Vesicle-Carried microRNAs in Ischemic Heart Disease Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:813310. Published 2022 Feb 28. [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Maksoud RS, Sediq AM, Kattaia A, et al. Serum miR-210 and miR-155 expression levels as novel biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis. Br J Biomed Sci. 2017;74(4):209-213. [CrossRef]
- Huang Q, Chen SS, Li J, et al. miR-210 expression in PBMCs from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Ir J Med Sci. 2018;187(1):243-249. [CrossRef]
- Kumar S, Kim CW, Simmons RD, Jo H. Role of flow-sensitive microRNAs in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis: mechanosensitive athero-miRs. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014;34(10):2206-2216. [CrossRef]
- Vengrenyuk Y, Nishi H, Long X, et al. Cholesterol loading reprograms the microRNA-143/145-myocardin axis to convert aortic smooth muscle cells to a dysfunctional macrophage-like phenotype. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35(3):535-546. [CrossRef]
- Zhou C, Yang Y, Hu L, et al. Effects of miR-143 regulation on cardiomyocytes apoptosis in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Toxicol In Vitro. 2023;93:105662. [CrossRef]
- Meng L, Yu X, Han H, et al. Circulating miR-143 and miR-145 as promising biomarkers for evaluating severity of coronary artery stenosis in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Clin Biochem. 2023;111:32-40. [CrossRef]
- Løvendorf MB, Zibert JR, Gyldenløve M, Røpke MA, Skov L. MicroRNA-223 and miR-143 are important systemic biomarkers for disease activity in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;75(2):133-139. [CrossRef]
- Zheng YZ, Chen CF, Jia LY, Yu TG, Sun J, Wang XY. Correlation between microRNA-143 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and disease severity in patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Oncotarget. 2017;8(31):51288-51295. Published 2017 Apr 20. [CrossRef]
- Yue J, Lau TCK, Griffith JF, et al. Circulating miR-99b-5p as a novel predictor of erosion progression on high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography in early rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective cohort study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2019;22(9):1724-1733. [CrossRef]
- Shan Z, Qin S, Li W, et al. An Endocrine Genetic Signal Between Blood Cells and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: Role of MicroRNA-223 in Smooth Muscle Function and Atherogenesis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(23):2526-2537. [CrossRef]
- Vickers KC, Landstreet SR, Levin MG, et al. MicroRNA-223 coordinates cholesterol homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(40):14518-14523. [CrossRef]
- Ann SJ, Bang H, Lee CJ, et al. LncRNA HSPA7 in human atherosclerotic plaques sponges miR-223 and promotes the proinflammatory vascular smooth muscle cell transition. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(12):1842-1849. [CrossRef]
- Parrizas M, Mundet X, Castaño C, et al. miR-10b and miR-223-3p in serum microvesicles signal progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes. J Endocrinol Invest. 2020;43(4):451-459. [CrossRef]
- Singh S, de Ronde MWJ, Kok MGM, et al. MiR-223-3p and miR-122-5p as circulating biomarkers for plaque instability. Open Heart. 2020;7(1):e001223. [CrossRef]
- Guo JF, Zhang Y, Zheng QX, Zhang Y, Zhou HH, Cui LM. Association between elevated plasma microRNA-223 content and severity of coronary heart disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2018;78(5):373-378. [CrossRef]
- Zhu L, Wang Y, Qiao F. microRNA-223 and microRNA-126 are clinical indicators for predicting the plaque stability in carotid atherosclerosis patients [published online ahead of print, 2022 Oct 3]. J Hum Hypertens. 2022;10.1038/s41371-022-00760-3. [CrossRef]
- Wang R, Wang FF, Cao HW, Yang JY. MiR-223 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of IL-22-stimulated HaCat human keratinocyte cell lines via the PTEN/Akt pathway. Life Sci. 2019;230:28-34. [CrossRef]
- Pivarcsi A, Meisgen F, Xu N, Ståhle M, Sonkoly E. Changes in the level of serum microRNAs in patients with psoriasis after antitumour necrosis factor-α therapy. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169(3):563-570. [CrossRef]
- Alatas ET, Kara M, Dogan G, Akın Belli A. Blood microRNA expressions in patients with mild to moderate psoriasis and the relationship between microRNAs and psoriasis activity. An Bras Dermatol. 2020;95(6):702-707. [CrossRef]
- Ormseth MJ, Solus JF, Vickers KC, Oeser AM, Raggi P, Stein CM. Utility of Select Plasma MicroRNA for Disease and Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(10):1746-1751. [CrossRef]
- Fichtlscherer S, De Rosa S, Fox H, et al. Circulating microRNAs in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 2010;107(5):677-684. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Kong D, Chen H, et al. miR-155 acts as an anti-inflammatory factor in atherosclerosis-associated foam cell formation by repressing calcium-regulated heat stable protein 1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:21789. Published 2016 Feb 22. [CrossRef]
- Wang R, Dong LD, Meng XB, Shi Q, Sun WY. Unique MicroRNA signatures associated with early coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464(2):574-579. [CrossRef]
- García-Rodríguez S, Arias-Santiago S, Blasco-Morente G, et al. Increased expression of microRNA-155 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from psoriasis patients is related to disease activity. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31(2):312-322. [CrossRef]
- Xu L, Leng H, Shi X, Ji J, Fu J, Leng H. MiR-155 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis by PTEN signaling pathway in the psoriasis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;90:524-530. [CrossRef]
- Elmesmari A, Fraser AR, Wood C, et al. MicroRNA-155 regulates monocyte chemokine and chemokine receptor expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55(11):2056-2065. [CrossRef]
- Kadkhoda S, Ghafouri-Fard S. Function of miRNA-145-5p in the pathogenesis of human disorders. Pathol Res Pract. 2022;231:153780. [CrossRef]
- Chin DD, Poon C, Wang J, et al. miR-145 micelles mitigate atherosclerosis by modulating vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype. Biomaterials. 2021;273:120810. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Cao Y. miR-145-5p inhibits psoriasis progression by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(9):10439-10448. Published 2021 Sep 15.
- Yuan M, Zhang L, You F, et al. MiR-145-5p regulates hypoxia-induced inflammatory response and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by targeting CD40. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017;431(1-2):123-131. [CrossRef]
- Minin EOZ, Paim LR, Lopes ECP, et al. Association of Circulating miR-145-5p and miR-let7c and Atherosclerotic Plaques in Hypertensive Patients. Biomolecules. 2021;11(12):1840. Published 2021 Dec 7. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Zai L, Tao Z, Wu D, Lin M, Wan J. miR-145-5p affects autophagy by targeting CaMKIIδ in atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiol. 2022;360:68-75. [CrossRef]
- Lv Y, Yi Y, Jia S, Peng X, Yang H, Guo R. The miR-145 rs353291 C allele increases susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020;25(3):577-592. Published 2020 Jan 1. [CrossRef]
- Hall IF, Climent M, Viviani Anselmi C, et al. rs41291957 controls miR-143 and miR-145 expression and impacts coronary artery disease risk. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13(10):e14060. [CrossRef]
- Hong BK, You S, Yoo SA, et al. MicroRNA-143 and -145 modulate the phenotype of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(8):e363. Published 2017 Aug 4. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Tang K, Wang Y, et al. Elevated microRNA 145 5p increases matrix metalloproteinase 9 by activating the nuclear factor κB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(3):2703-2711. [CrossRef]
- Magenta A, D'Agostino M, Sileno S, et al. The Oxidative Stress-Induced miR-200c Is Upregulated in Psoriasis and Correlates with Disease Severity and Determinants of Cardiovascular Risk. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:8061901. Published 2019 Dec 19. [CrossRef]
- Magenta A, Sileno S, D'Agostino M, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque instability in carotid arteries: miR-200c as a promising biomarker. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018;132(22):2423-2436. Published 2018 Nov 21. [CrossRef]
- Wang XY, Chen XY, Li J, Zhang HY, Liu J, Sun LD. MiR-200a expression in CD4+ T cells correlates with the expression of Th17/Treg cells and relevant cytokines in psoriasis vulgaris: A case control study. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;93:1158-1164. [CrossRef]
- Kujawa M, O'Meara M, Li H, et al. MicroRNA-466 and microRNA-200 increase endothelial permeability in hyperglycemia by targeting Claudin-5. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022;29:259-271. Published 2022 Jul 6. [CrossRef]
- Ofori JK, Karagiannopoulos A, Nagao M, et al. Human Islet MicroRNA-200c Is Elevated in Type 2 Diabetes and Targets the Transcription Factor ETV5 to Reduce Insulin Secretion. Diabetes. 2022;71(2):275-284. [CrossRef]
- Lo WY, Yang WK, Peng CT, Pai WY, Wang HJ. MicroRNA-200a/200b Modulate High Glucose-Induced Endothelial Inflammation by Targeting O-linked N-Acetylglucosamine Transferase Expression [published correction appears in Front Physiol. 2018 Jun 19;9:786]. Front Physiol. 2018;9:355. Published 2018 Apr 18. [CrossRef]
- Balzano F, Deiana M, Dei Giudici S, et al. MicroRNA Expression Analysis of Centenarians and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Reveals a Common Expression Pattern. Int J Med Sci. 2017;14(7):622-628. Published 2017 Jun 14. [CrossRef]
- Gangwar RS, Rajagopalan S, Natarajan R, Deiuliis JA. Noncoding RNAs in Cardiovascular Disease: Pathological Relevance and Emerging Role as Biomarkers and Therapeutics. Am J Hypertens. 2018;31(2):150-165. [CrossRef]
- Jin X, Chen D, Zheng RH, Zhang H, Chen YP, Xiang Z. miRNA-133a-UCP2 pathway regulates inflammatory bowel disease progress by influencing inflammation, oxidative stress and energy metabolism. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(1):76-86. [CrossRef]
- Torella D, Iaconetti C, Catalucci D, et al. MicroRNA-133 controls vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch in vitro and vascular remodeling in vivo. Circ Res. 2011;109(8):880-893. [CrossRef]
- Liao XB, Zhang ZY, Yuan K, et al. MiR-133a modulates osteogenic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Endocrinology. 2013;154(9):3344-3352. [CrossRef]
- Navickas R, Gal D, Laucevičius A, Taparauskaitė A, Zdanytė M, Holvoet P. Identifying circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;111(4):322-337. [CrossRef]
- Šatrauskienė A, Navickas R, Laucevičius A, et al. Mir-1, miR-122, miR-132, and miR-133 Are Related to Subclinical Aortic Atherosclerosis Associated with Metabolic Syndrome. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(4):1483. Published 2021 Feb 4. [CrossRef]
- Wang F, Long G, Zhao C, et al. Plasma microRNA-133a is a new marker for both acute myocardial infarction and underlying coronary artery stenosis. J Transl Med. 2013;11:222. Published 2013 Sep 23. [CrossRef]
- Chicharro P, Rodríguez-Jiménez P, Llamas-Velasco M, et al. Expression of miR-135b in Psoriatic Skin and Its Association with Disease Improvement. Cells. 2020;9(7):1603. Published 2020 Jul 2. [CrossRef]
- de Gonzalo-Calvo D, van der Meer RW, Rijzewijk LJ, et al. Serum microRNA-1 and microRNA-133a levels reflect myocardial steatosis in uncomplicated type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):47. Published 2017 Mar 3. [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi H, Karimi J, Khodadadi I, Tavilani H. Correlation between miR-103 and miR-133a Expression and the Circulating ANGPTL8 in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Healthy Control Subjects. Clin Lab. 2019;65(11):10.7754/Clin.Lab.2019.190436. [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhtaresh HA, Salem AH, Al-Kafaji G. Upregulation of Circulating Cardiomyocyte-Enriched miR-1 and miR-133 Associate with the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Patients and Serve as Potential Biomarkers. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2019;12(4):347-357. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Lu J, Zhang Q, Luo Q, Liu B. CircRNA RSF1 regulated ox-LDL induced vascular endothelial cells proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation through modulating miR-135b-5p/HDAC1 axis in atherosclerosis. Biol Res. 2021;54(1):11. Published 2021 Mar 23. [CrossRef]
- Kadkhoda S, Eslami S, Mahmud Hussen B, Ghafouri-Fard S. A review on the importance of miRNA-135 in human diseases. Front Genet. 2022;13:973585. Published 2022 Sep 6. [CrossRef]
- Chicharro P, Rodríguez-Jiménez P, Llamas-Velasco M, et al. Expression of miR-135b in Psoriatic Skin and Its Association with Disease Improvement. Cells. 2020;9(7):1603. Published 2020 Jul 2. [CrossRef]
- Xu Z, Han Y, Liu J, et al. MiR-135b-5p and MiR-499a-3p Promote Cell Proliferation and Migration in Atherosclerosis by Directly Targeting MEF2C. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12276. Published 2015 Jul 17. [CrossRef]
- Li D, An Y. MiR-135a-5p inhibits vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and migration by inactivating FOXO1 and JAK2 signaling pathway. Pathol Res Pract. 2021;224:153091. [CrossRef]
- Joyce CE, Zhou X, Xia J, et al. Deep sequencing of small RNAs from human skin reveals major alterations in the psoriasis miRNAome. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20(20):4025-4040. [CrossRef]
- Sarookhani MR, Honardoost M, Foroughi F. Plasma miR-135a; a potential biomarker for diagnosis of new type 2 diabetes (T2DM). Bali Medical Journal. 2018; 7(2):296-301. [CrossRef]
- Monfared YK, Honardoost M, Sarookhani MR, Farzam SA. Circulating miR-135 May Serve as a Novel Co-biomarker of HbA1c in Type 2 Diabetes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2020;191(2):623-630. [CrossRef]
- Monfared YK, Mirzaii-Dizgah MR, Khodabandehloo E, Sarookhani MR, Hashemipour S, Mirzaii-Dizgah I. Salivary microRNA-126 and 135a: a potentially non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers of type- 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2021;20(2):1631-1638. Published 2021 Oct 28. [CrossRef]
- Liu J, Xue J, Xu B, et al. miR-135a-5p mediated down-regulation of STAT6 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(5):3092-3103. Published 2022 May 15.
- Xue Y, Wei Z, Ding H, et al. MicroRNA-19b/221/222 induces endothelial cell dysfunction via suppression of PGC-1α in the progression of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2015;241(2):671-681. [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov DA, Sobenin IA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV. Human miR-221/222 in Physiological and Atherosclerotic Vascular Remodeling. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:354517. [CrossRef]
- Minami Y, Satoh M, Maesawa C, et al. Effect of atorvastatin on microRNA 221 / 222 expression in endothelial progenitor cells obtained from patients with coronary artery disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 2009;39(5):359-367. [CrossRef]
- Zibert JR, Løvendorf MB, Litman T, Olsen J, Kaczkowski B, Skov L. MicroRNAs and potential target interactions in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci. 2010;58(3):177-185. [CrossRef]
- Meng Z, Qiu J, Zhang H. MiR-221-3p as a Potential Biomarker for Patients with Psoriasis and Its Role in Inflammatory Responses in Keratinocytes. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2021;34(5):300-306. [CrossRef]
- Wade SM, McGarry T, Wade SC, Fearon U, Veale DJ. Serum MicroRNA Signature as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Marker in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2020;47(12):1760-1767. [CrossRef]
- Abo ElAtta AS, Ali YBM, Bassyouni IH, Talaat RM. Upregulation of miR-221/222 expression in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients: correlation with disease activity. Clin Exp Med. 2019;19(1):47-53. [CrossRef]
- Cunningham CC, Wade S, Floudas A, et al. Serum miRNA Signature in Rheumatoid Arthritis and "At-Risk Individuals". Front Immunol. 2021;12:633201. Published 2021 Mar 3. [CrossRef]
- Cieśla M, Kolarz B, Majdan M, Darmochwał-Kolarz D. Plasma micro-RNA-22 is associated with disease activity in well-established rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40(5):945-951. [CrossRef]
- Wang H, He F, Liang B, et al. LincRNA-p21 alleviates atherosclerosis progression through regulating the miR-221/SIRT1/Pcsk9 axis. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(19):9141-9153. [CrossRef]
- Li C, Zhang M, Dai Y, Xu Z. MicroRNA-424-5p regulates aortic smooth muscle cell function in atherosclerosis by blocking APOC3-mediated nuclear factor-κB signalling pathway. Exp Physiol. 2020;105(6):1035-1049. [CrossRef]
- Ichihara A, Jinnin M, Yamane K, et al. microRNA-mediated keratinocyte hyperproliferation in psoriasis vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 2011;165(5):1003-1010. [CrossRef]
- Zhang ZZ, Chen JJ, Deng WY, Yu XH, Tan WH. CTRP1 decreases ABCA1 expression and promotes lipid accumulation through the miR-424-5p/FoxO1 pathway in THP-1 macrophage-derived foam cells. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(11):2226-2237. [CrossRef]
- Tsuru Y, Jinnin M, Ichihara A, et al. miR-424 levels in hair shaft are increased in psoriatic patients. J Dermatol. 2014;41(5):382-385. [CrossRef]
- Wang S, Xu J, Guo Y, et al. MicroRNA-497 Reduction and Increase of Its Family Member MicroRNA-424 Lead to Dysregulation of Multiple Inflammation Related Genes in Synovial Fibroblasts With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:619392. Published 2021 Mar 26. [CrossRef]
- Bao MH, Feng X, Zhang YW, Lou XY, Cheng Y, Zhou HH. Let-7 in cardiovascular diseases, heart development and cardiovascular differentiation from stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2013;14(11):23086-23102. Published 2013 Nov 21. [CrossRef]
- Zhu L, Li Q, Qi D, et al. Atherosclerosis-associated endothelial cell apoptosis by miRNA let7-b-mediated downregulation of HAS-2 [published online ahead of print, 2019 Nov 17]. J Cell Biochem. 2019;10.1002/jcb.29537. [CrossRef]
- Yu C, Wu B, Jiang J, Yang G, Weng C, Cai F. Overexpressed lncRNA ROR Promotes the Biological Characteristics of ox-LDL-Induced HUVECs via the let-7b-5p/HOXA1 Axis in Atherosclerosis. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:659769. Published 2021 Sep 13. [CrossRef]
- Long G, Wang F, Li H, et al. Circulating miR-30a, miR-126 and let-7b as biomarker for ischemic stroke in humans. BMC Neurol. 2013;13:178. Published 2013 Nov 16. [CrossRef]
- Huang YQ, Huang C, Chen JY, Li J, Feng YQ. Plasma expression level of miRNA let-7 is positively correlated with carotid intima-media thickness in patients with essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens. 2017;31(12):843-847. [CrossRef]
- Hu XP, Xie Q, Chen CF, Zhang W, Yu B. Let-7a Inhibits T-Cell Proliferation and IFN-γ Secretion by Down-Regulating STAT3 Expression in Patients with Psoriasis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(1):115-125. [CrossRef]
- Pasquali L, Svedbom A, Srivastava A, et al. Circulating microRNAs in extracellular vesicles as potential biomarkers for psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020;34(6):1248-1256. [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Zuñiga OA, Vals-Delgado C, Alcala-Diaz JF, et al. A set of miRNAs predicts T2DM remission in patients with coronary heart disease: from the CORDIOPREV study. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;23:255-263. Published 2020 Nov 11. [CrossRef]
- Brennan E, Wang B, McClelland A, et al. Protective Effect of let-7 miRNA Family in Regulating Inflammation in Diabetes-Associated Atherosclerosis. Diabetes. 2017;66(8):2266-2277. [CrossRef]
- Aljaibeji H, Elemam NM, Mohammed AK, et al. Let7b-5p is Upregulated in the Serum of Emirati Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Regulates Insulin Secretion in INS-1 Cells. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2022;130(1):22-29. [CrossRef]
- Tang J, Lin J, Yu Z, et al. Identification of circulating miR-22-3p and let-7a-5p as novel diagnostic biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40(1):69-77. [CrossRef]
- Ormseth MJ, Solus JF, Sheng Q, et al. Plasma miRNAs improve the prediction of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40(6):2211-2219. [CrossRef]
- Schmitz SU, Grote P, Herrmann BG. Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(13):2491-2509. [CrossRef]
- Hurst LD, Smith NG. Molecular evolutionary evidence that H19 mRNA is functional. Trends Genet. 1999;15(4):134-135. [CrossRef]
- Huang Y, Wang L, Mao Y, Nan G. Long Noncoding RNA-H19 Contributes to Atherosclerosis and Induces Ischemic Stroke via the Upregulation of Acid Phosphatase 5. Front Neurol. 2019;10:32. Published 2019 Feb 4. [CrossRef]
- Cao L, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhao P, Chen Y. LncRNA H19/miR-let-7 axis participates in the regulation of ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury via targeting periostin. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;72:496-503. [CrossRef]
- Zhu R, Liu X, He Z. Long non-coding RNA H19 and MALAT1 gene variants in patients with ischemic stroke in a northern Chinese Han population. Mol Brain. 2018;11(1):58. Published 2018 Oct 10. [CrossRef]
- Bitarafan S, Yari M, Broumand MA, et al. Association of Increased Levels of lncRNA H19 in PBMCs with Risk of Coronary Artery Disease. Cell J. 2019;20(4):564-568. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Cheng H, Yue Y, Li S, Zhang D, He R. H19 knockdown suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis by regulating miR-148b/WNT/β-catenin in ox-LDL -stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25(1):11. Published 2018 Feb 7. [CrossRef]
- Pan, JX. LncRNA H19 promotes atherosclerosis by regulating MAPK and NF-kB signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(2):322-328.
- Han Y, Ma J, Wang J, Wang L. Silencing of H19 inhibits the adipogenesis and inflammation response in ox-LDL-treated Raw264.7 cells by up-regulating miR-130b. Mol Immunol. 2018;93:107-114. [CrossRef]
- He Y, Yin X, Yan J, Li X, Sun Q. The lncRNA H19/miR-766-3p/S1PR3 Axis Contributes to the Hyperproliferation of Keratinocytes and Skin Inflammation in Psoriasis via the AKT/mTOR Pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:9991175. Published 2021 Dec 28. [CrossRef]
- Gupta R, Ahn R, Lai K, et al. Landscape of Long Noncoding RNAs in Psoriatic and Healthy Skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136(3):603-609. [CrossRef]
- Fawzy MS, Abdelghany AA, Toraih EA, Mohamed AM. Circulating long noncoding RNAs H19 and GAS5 are associated with type 2 diabetes but not with diabetic retinopathy: A preliminary study. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2020;20(3):365-371. Published 2020 Aug 3. [CrossRef]
- Cheng XW, Chen ZF, Wan YF, Zhou Q, Wang H, Zhu HQ. Long Non-coding RNA H19 Suppression Protects the Endothelium Against Hyperglycemic-Induced Inflammation via Inhibiting Expression of miR-29b Target Gene Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor a Through Activation of the Protein Kinase B/Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019;7:263. Published 2019 Nov 1. [CrossRef]
- Tello-Flores VA, Valladares-Salgado A, Ramírez-Vargas MA, et al. Altered levels of MALAT1 and H19 derived from serum or serum exosomes associated with type-2 diabetes. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020;5(2):71-76. Published 2020 Apr 11. [CrossRef]
- Alfaifi M, Verma AK, Alshahrani MY, et al. Assessment of Cell-Free Long Non-Coding RNA-H19 and miRNA-29a, miRNA-29b Expression and Severity of Diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:3727-3737. Published 2020 Oct 14. [CrossRef]
- Alrefai AA, Khader HF, Elbasuony HA, Elzorkany KM, Saleh AA. Evaluation of the expression levels of lncRNAs H19 and MEG3 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [published online ahead of print, 2023 Jun 9]. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;10.1007/s11033-023-08569-0. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi Z, Karamali N, Roghani SA, et al. Efficacy of DMARDs and methylprednisolone treatment on the gene expression levels of HSPA5, MMD, and non-coding RNAs MALAT1, H19, miR-199a-5p, and miR-1-3p, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;108:108878. [CrossRef]
- Lu Y, Qie D, Yang F, Wu J. LncRNA MEG3 aggravates adipocyte inflammation and insulin resistance by targeting IGF2BP2 to activate TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;121:110467. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110467. [CrossRef]
- Tang ZL, Zhang K, Lv SC, Xu GW, Zhang JF, Jia HY. LncRNA MEG3 suppresses PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway to enhance autophagy and inhibit inflammation in TNF-α-treated keratinocytes and psoriatic mice [published correction appears in Cytokine. 2022 May;153:155853]. Cytokine. 2021;148:155657. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Liu X, Bai X, et al. Melatonin prevents endothelial cell pyroptosis via regulation of long noncoding RNA MEG3/miR-223/NLRP3 axis. J Pineal Res. 2018;64(2):10.1111/jpi.12449. [CrossRef]
- Yu B, Wang S. Angio-LncRs: LncRNAs that regulate angiogenesis and vascular disease. Theranostics. 2018;8(13):3654-3675. Published 2018 Jun 8. [CrossRef]
- Jia HY, Zhang K, Lu WJ, Xu GW, Zhang JF, Tang ZL. LncRNA MEG3 influences the proliferation and apoptosis of psoriasis epidermal cells by targeting miR-21/caspase-8. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):46. Published 2019 Oct 28. [CrossRef]
- Bai Y, Zhang Q, Su Y, Pu Z, Li K. Modulation of the Proliferation/Apoptosis Balance of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Atherosclerosis by lncRNA-MEG3 via Regulation of miR-26a/Smad1 Axis. Int Heart J. 2019;60(2):444-450. [CrossRef]
- Wu Z, He Y, Li D, et al. Long noncoding RNA MEG3 suppressed endothelial cell proliferation and migration through regulating miR-21. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(7):3326-3335. Published 2017 Jul 15.
- Chang WW, Zhang L, Yao XM, et al. Upregulation of long non-coding RNA MEG3 in type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with vascular disease: a case-control study. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020;473(1-2):93-99. [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee S, Bhattcharjee D, Misra S, Saha A, Bhattacharyya NP, Ghosh A. Increase in MEG3, MALAT1, NEAT1 significantly predicts the clinical parameters in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Per Med. 2020;17(6):445-457. [CrossRef]
- Wahba AS, Ibrahim ME, Mesbah NM, Saleh SM, Abo-Elmatty DM, Mehanna ET. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 and its genetic variant rs941576 are associated with rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis in Egyptian patients. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(6):1571-1578. [CrossRef]
- Shefler A, Patrick MT, Wasikowski R, et al. Skin-Expressing lncRNAs in Inflammatory Responses. Front Genet. 2022;13:835740. Published 2022 Apr 26. [CrossRef]
- Ma XL, Wen GD, Yu C, Zhao Z, Gao N, Liu ZY. LncRNA UCA1 negatively regulates NF-kB activity in psoriatic keratinocytes through the miR125a-A20 axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2021;37(3):172-180. [CrossRef]
- Tian S, Yuan Y, Li Z, Gao M, Lu Y, Gao H. LncRNA UCA1 sponges miR-26a to regulate the migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Gene. 2018;673:159-166. [CrossRef]
- Yang JL, Han NH. LncRNA UCA1 stimulates the repair of hyperglycemic vascular smooth muscle cells through targeting miR-582-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(24):12859-12866. [CrossRef]
- Yan ZF, Zhao XY, Liu W, Liu XP. UCA1 impacts progress of rheumatoid arthritis by inducing the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocyte. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(4):914-920. [CrossRef]
- Raposo AC, Casanova M, Gendrel AV, da Rocha ST. The tandem repeat modules of Xist lncRNA: a swiss army knife for the control of X-chromosome inactivation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021;49(6):2549-2560. [CrossRef]
- Yang J, Qi M, Fei X, Wang X, Wang K. Long non-coding RNA XIST: a novel oncogene in multiple cancers. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):159. Published 2021 Dec 20. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Jiang F, Chen F, Zhang D, Wang J. LncRNA XIST Engages in Psoriasis via Sponging miR-338-5p to Regulate Keratinocyte Proliferation and Inflammation. Skin Pharmacol Physiol. 2022;35(4):196-205. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Tang Y, Yan J. LncRNA-XIST Promotes Proliferation and Migration in ox-LDL Stimulated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells through miR-539-5p/SPP1 Axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:9911982. Published 2022 Jan 4. [CrossRef]
- Yang K, Xue Y, Gao X. LncRNA XIST Promotes Atherosclerosis by Regulating miR-599/TLR4 Axis. Inflammation. 2021;44(3):965-973. [CrossRef]
- Mo L, Jiang HB, Tian GR, Lu GJ. The proliferation and migration of atherosclerosis-related HVSMCs were inhibited by downregulation of lncRNA XIST via regulation of the miR-761/BMP9 axis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2022;38(1):18-29. [CrossRef]
- Wang M, Hou Z, Li X, et al. Relationship of serum lncRNA XIST and miR-30d-5p levels with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(12):9001-9006. Published 2022 Dec 15.
- Liu BY, Li L, Bai LW, Xu CS. Long Non-coding RNA XIST Attenuates Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy by Inducing Autophagy Through MicroRNA-30d-5p/sirtuin1 Axis. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:655157. Published 2021 Apr 28. [CrossRef]
- Sohrabifar N, Ghaderian SMH, Alipour Parsa S, Ghaedi H, Jafari H. Variation in the expression level of MALAT1, MIAT and XIST lncRNAs in coronary artery disease patients with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2022;128(5):1308-1315. [CrossRef]
- Liu W, Song J, Feng X, Yang H, Zhong W. LncRNA XIST is involved in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes by sponging miR-126-3p via the NF-κB pathway. Autoimmunity. 2021;54(6):326-335. [CrossRef]
- Ferdin Jana and Lenassi Metka. Extracellular Vesicles and their Clinical Potential. Medicinski razgledi. 2016; 55 (1): 63–82.
- Konkoth A, Saraswat R, Dubrou C, et al. Multifaceted role of extracellular vesicles in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2021;319:121-131. [CrossRef]
- Thulin Å, Christersson C, Alfredsson J, Siegbahn A. Circulating cell-derived microparticles as biomarkers in cardiovascular disease. Biomark Med. 2016;10(9):1009-1022. [CrossRef]
- Amabile N, Rautou PE, Tedgui A, Boulanger CM. Microparticles: key protagonists in cardiovascular disorders. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2010;36(8):907-916. [CrossRef]
- Han WQ, Chang FJ, Wang QR, Pan JQ. Microparticles from Patients with the Acute Coronary Syndrome Impair Vasodilatation by Inhibiting the Akt/eNOS-Hsp90 Signaling Pathway. Cardiology. 2015;132(4):252-260. [CrossRef]
- Zu L, Ren C, Pan B, et al. Endothelial microparticles after antihypertensive and lipid-lowering therapy inhibit the adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells. Int J Cardiol. 2016;202:756-759. [CrossRef]
- Pelletier F, Garnache-Ottou F, Angelot F, et al. Increased Levels of Circulating Endothelial-Derived Microparticles and Small-Size Platelet-Derived Microparticles in Psoriasis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, Volume 131, Issue 7, 2011, Pages 1573-1576, ISSN 0022-202X. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, McGeoch SC, Johnstone AM, et al. Platelet-derived microparticle count and surface molecule expression differ between subjects with and without type 2 diabetes, independently of obesity status. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2014;37(4):455-463. [CrossRef]
- Zeiger F, Stephan S, Hoheisel G, Pfeiffer D, Ruehlmann C, Koksch M. P-Selectin expression, platelet aggregates, and platelet-derived microparticle formation are increased in peripheral arterial disease. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2000;11(8):723-728. [CrossRef]
- Papadavid E, Diamanti K, Spathis A, et al. Increased levels of circulating platelet-derived microparticles in psoriasis: Possible implications for the associated cardiovascular risk. World J Cardiol. 2016;8(11):667-675. [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa-Mineoka R, Katoh N, Kishimoto S. Platelet activation in patients with psoriasis: increased plasma levels of platelet-derived microparticles and soluble P-selectin. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2010;62(4):621-626. [CrossRef]
- Ho JC, Lee CH, Lin SH. No Significant Reduction of Circulating Endothelial-Derived and Platelet-Derived Microparticles in Patients with Psoriasis Successfully Treated with Anti-IL12/23. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3242143. [CrossRef]
- Pelletier F, Garnache-Ottou F, Biichlé S, et al. Effects of anti-TNF-α agents on circulating endothelial-derived and platelet-derived microparticles in psoriasis. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23(12):924-925. [CrossRef]
- Hu SC, Lan CE. Psoriasis and Cardiovascular Comorbidities: Focusing on Severe Vascular Events, Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Implications for Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2211. Published 2017 Oct 21. [CrossRef]
- Tan KT, Tayebjee MH, Lim HS, Lip GY. Clinically apparent atherosclerotic disease in diabetes is associated with an increase in platelet microparticle levels. Diabet Med. 2005;22(12):1657-1662. [CrossRef]
- Atehortúa L, Rojas M, Vásquez G, et al. Endothelial activation and injury by microparticles in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):34. Published 2019 Jan 23. [CrossRef]
- Michael BNR, Kommoju V, Kavadichanda Ganapathy C, Negi VS. Characterization of cell-derived microparticles in synovial fluid and plasma of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39(8):1377-1387. [CrossRef]
- Shao S, Fang H, Li Q, Wang G. Extracellular vesicles in Inflammatory Skin Disorders: from Pathophysiology to Treatment. Theranostics. 2020;10(22):9937-9955. Published 2020 Aug 7. [CrossRef]
- Hoyer FF, Giesen MK, Nunes França C, Lütjohann D, Nickenig G, Werner N. Monocytic microparticles promote atherogenesis by modulating inflammatory cells in mice. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16(11):2777-2788. [CrossRef]
- Murzina E, Dosenko V, Drevytska T, Litus O, Bardova K, Vozianova S. Relationship between mir-126 expression in children with psoriasis, disease progression and therapeutic response. J Med Life. 2021;14(5):667-675. [CrossRef]
- Feng S, Wang L, Liu W, Zhong Y, Xu S. MiR-126 correlates with increased disease severity and promotes keratinocytes proliferation and inflammation while suppresses cells' apoptosis in psoriasis. J Clin Lab Anal. 2018;32(9):e22588. [CrossRef]
- Pelosi A, Lunardi C, Fiore PF, et al. MicroRNA Expression Profiling in Psoriatic Arthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:7305380. Published 2018 Apr 23. [CrossRef]
- Duan Y, Zou J, Mao J, et al. Plasma miR-126 expression correlates with risk and severity of psoriasis and its high level at baseline predicts worse response to Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F in combination with acitretin. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;115:108761. [CrossRef]
- Takeshita J, Mohler ER, Krishnamoorthy P, et al. Endothelial cell-, platelet-, and monocyte/macrophage-derived microparticles are elevated in psoriasis beyond cardiometabolic risk factors. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014;3(1):e000507. Published 2014 Feb 28. [CrossRef]
- Chironi GN, Simon A, Boulanger CM, et al. Circulating microparticles may influence early carotid artery remodeling. J Hypertens. 2010;28(4):789-796. [CrossRef]
- Kandiyil N, MacSweeney ST, Heptinstall S, May J, Fox SC, Auer DP. Circulating Microparticles in Patients with Symptomatic Carotid Disease Are Related to Embolic Plaque Activity and Recent Cerebral Ischaemia. Cerebrovasc Dis Extra. 2019;9(1):9-18. [CrossRef]
- Ren S, Fan X, Peng L, et al. Expression of NF-κB, CD68 and CD105 in carotid atherosclerotic plaque. J Thorac Dis. 2013;5(6):771-776. [CrossRef]
- Li X, van der Meer JJ, van der Loos CM, et al. Microvascular endoglin (CD105) expression correlates with tissue markers for atherosclerotic plaque vulnerability in an ageing population with multivessel coronary artery disease. Histopathology. 2012;61(1):88-97. [CrossRef]
- Novikova OA, Nazarkina ZK, Cherepanova AV, et al. Isolation, culturing and gene expression profiling of inner mass cells from stable and vulnerable carotid atherosclerotic plaques. PLoS One. 2019;14(6):e0218892. Published 2019 Jun 26. [CrossRef]
- Marei I, Chidiac O, Thomas B, et al. Angiogenic content of microparticles in patients with diabetes and coronary artery disease predicts networks of endothelial dysfunction. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21(1):17. Published 2022 Feb 2. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carrio J, Alperi-López M, López P, et al. Altered profile of circulating microparticles in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Sci (Lond). 2015;128(7):437-448. [CrossRef]
- Georgescu A, Simionescu M. Extracellular Vesicles: Versatile Nanomediators, Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents in Atherosclerosis and COVID-19-Related Thrombosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(11):5967. Published 2021 May 31. [CrossRef]
- Mavropoulos A, Rigopoulou EI, Liaskos C, Bogdanos DP, Sakkas LI. The role of p38 MAPK in the aetiopathogenesis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:569751. [CrossRef]
- Diener C, Keller A, Meese E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: from cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022;38(6):613-626. [CrossRef]
| Type ofmicroRNA | Atherosclerosis | Psoriasis | Type 2 diabetes mellitus | Rheumatoid arthritis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Authors of the study | No. of patients/samples (Cases/controls) | Main findings | Authors of the study | No. of patient (Cases/controls) | Main findings | Authors of the study | No. of patients (Cases/controls) | Main findings | Authors of the study | No. of patients (Cases/controls) | Main findings | |
| miR-146a | Huang et al. | 180/90 | ↑ | Leal et al. | 99/78 | ↑ | Alipoor et al. | 344/316 | ↓ | Bae et al. | 683/477 | ↑ |
| Raitoharju et al. | 30/20 | ↑ | Ele-Refaei et al. | 40/20 | ↑ | Zhu and Leung | Adipose 24 | ↑ | ||||
| Zhelankin et al. | 50/30 | ↑ | Vaher et al. | 26/26 | ↑ | Zhu and Leung | PBMC 140 | ↓ | ||||
| Guo et al. | 42/58 | ↑ | ||||||||||
| Gao et al. | 56/56 | ↑ | ||||||||||
| miR-210 | Signorelli et al. | 27/27 | ↑ | Zhao et al. | 18/18 | ↑ | Li et al. | 32/32 | ↑ | Abdul-Maksoud et al. | 100/100 | ↓ |
| Raitoharju et al. | 30/20 | ↑ | Wu et al. | 30/30 | ↑ | Amr et al. | 100/20 | ↑ | Huang et al. | 38/45 | X | |
| Zhou et al. | 10/10 | ↓ | ||||||||||
| Zhang et al | 32/20 | ↓ | ||||||||||
| Zhu and Leung | 540 | ↑ | ||||||||||
| miR-143 | Meng et al. | 279/65 | ↓ | Løvendorf et al. | 55/33 | ↑ | Zhu and Leung | 112 | ↑ | Yue et al. | 117/6 | ↑ |
| Zheng et al. | 194/175 | ↓ | ||||||||||
| miR-223 | Singh et al. | 250/250 | ↑ | Løvendorf et al. | 55/33 | ↑ | Parrizas et al. | 1184/838 | ↓ | Ormseth et al. | 168/91 | ↑ |
| Guo et al. | 300/100 | ↑ | Pivarcsi et al. | 43/22 | x | Zhu and Leung | Plasma 309 | ↓ | ||||
| Zhu et al. | 52/25 | ↓ | Alatas et al. | 52/54 | ↓ | |||||||
| miR-155 | Fichtlscherer et al. | 31/14 | ↓ | García-Rodríguez et al. | 11/11 | ↑ | Zhu and Leung | Whole blood 120 | ↑ | Abdul-Maksoud et al. | 100/100 | ↑ |
| Li et al. | 70/55 | ↑ | Alatas et al. | 52/54 | ↑ | Zhu and Leung | PBMC 80 | ↓ | Elmesmari et al. | 24/22 | ↑ | |
| Wang et al. | 3/x | |||||||||||
| miR-145 | Meng et al. | 279/65 | ↓ | Wang et al. | 45/40 | ↓ | Zhu and Leung | 24 | ↑ | Yue et al. | 117/6 | ↑ |
| Minin et al. | 105/72 | ↑ | Hong et al. | 5/5 | ↑ | |||||||
| Lv et al. | 328/374 | ↓ | ||||||||||
| Li et al. | 70/55 | x | ||||||||||
| miR-200 | Magenta et al. | 24/19 | ↑ | Magenta et al. | 29/29 | ↑ | Kujawa et al. | 5/5 | ↑ | Balzano et al. | 28/20 | x |
| Wang et al. | 189/109 | ↑ | Ofori et al. | 9/27 | ↑ | |||||||
| Zhu and Leung | Plasma 242 | ↓ | ||||||||||
| miR-133 | Wang et al. | 154/92 | ↑ | Chicharro et al. | 44/5 | ↓ | De Gonzalo-Calvo et al. | 72/x | ↑ | - | - | - |
| Al-Muhtaresh et al. | 30/30 | ↑ | Ghasemi et al | 35/35 | ↑ | |||||||
| Al-Muhtaresh et al. | 30/30 | ↑ | ||||||||||
| Zhu and Leung | 169 | ↓ | ||||||||||
| miR-135 | Xu et al. | 77/45 | ↑ | Chicharro et al. | 44/5 | ↓ | Sarookhani et. al | 30/30 | ↑ | Liu et al. | 3/x | ↓ |
| Li et al. | 47/47 | ↓ | Joyce et al. | 26/26 | ↑ | Monfared et al. | 80/40 | ↑ | ||||
| miR-221 | Minami et al. | 44/22 | ↑ | Zibert et al. | 13/13 | ↑ | Zhu and Leung | Serum 793 | ↑ | Abo ElAtta et al. | 30/20 | ↑ |
| Meng et al. | 46/42 | ↑ | Cunningham et al. | 50/20 | ↑ | |||||||
| Wade et al. | 31/20 | ↑ | Ciesla et al. | 50/24 | x | |||||||
| Mir-424 | Li et al. | 75/60 | ↓ | Ichihara et al. | 15/15 | ↓ | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Alatas et al. | 52/54 | ↓ | ||||||||||
| Let-7 | Long et al. | 179/50 | ↑/↓ | Alatas et al. | 52/54 | ↑ | Aljaibeji et al. | 29/25 | ↑ | Cunningham et al. | 50/20 | ↑ |
| Huang et al. | 60/60 | ↑ | Hu et al. | 40/38 | ↓ | Zhu and Leung | Let-7-f Whole blood 89 | ↓ | Tang et al. | 76/36 | ↑ | |
| Minin et al. | 105/72 | ↑ | Zhu and Leung | Let-7-iserum 54 | ↓ | |||||||
| Yu et al. | 30/22 | ↓ | ||||||||||
| Type of lncRNA | Atherosclerosis | Psoriasis | Type 2 diabetes mellitus | Rheumatoid arthritis | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Authors of the study | No. of patients/samples (Cases/controls) | Main findings | Authors of the study | No. of patient (Cases/controls) | Main findings | Authors of the study | No. of patients (Cases/controls) | Main findings | Authors of the study | No. of patients (Cases/controls) | Main findings | |
| H19 | Cao et al. | 27/20 | ↑ | Gupta et al. | 18/16 | ↓ | Fawzy et al. | 119/110 | ↑ | Mahmoudi et al. | 25/25 | ↑ |
| Bitarafan et al. | 50/50 | ↑ | He et al. | 6/6 | ↓ | Cheng et al. | 30/30 | ↓ | ||||
| Zhang et al. | 40/40 | ↑ | Tello-Flores et al. | 60/60 | ↑ | |||||||
| Huang et al. | 80/85 | ↑ | Alfaifi et al. | 200/200 | ↓ | |||||||
| Pan et al. | 42/37 | ↑ | Alrefai et al. | 65/65 | ↓ | |||||||
| Han et al. | 30/30 | ↑ | ||||||||||
| MEG3 | Bai et al. | 40/35 | ↓ | Jia et al. | 19/19 | ↓ | Alrefai et al. | 65/65 | ↑ | Chatterjee et al. | 82/15 | ↑ |
| Wu et al. | 15/15 | ↓ | Chang et al. | 53/62 | ↑ | Wahba et al. | 100/100 | ↓ | ||||
| UCA1 | - | - | - | Ma et al. | 20/x | ↓ | Yang et al. | 40/40 | ↓ | - | - | - |
| XIST | Sohrabifar et al. | 25/25 | x | - | - | - | Wang et al. | 76/76 | ↓ | Liu et al. | 20/7 | ↑ |
| Sohrabifar et al. | 25/25 | ↑ | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





